Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Using D-Q Simplified Model and Parity Equations †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Motivation
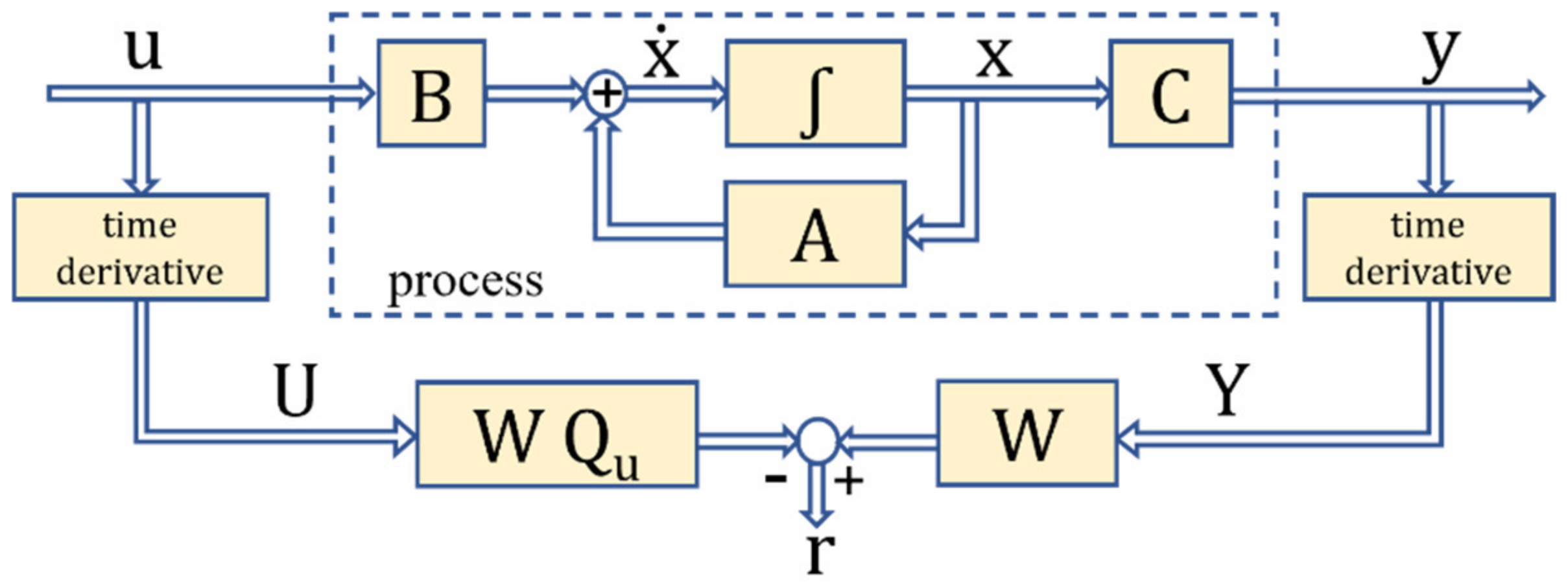
2.1. Parity Equation Method for Fault Detection
- is a vector
- is a vector
- is a matrix
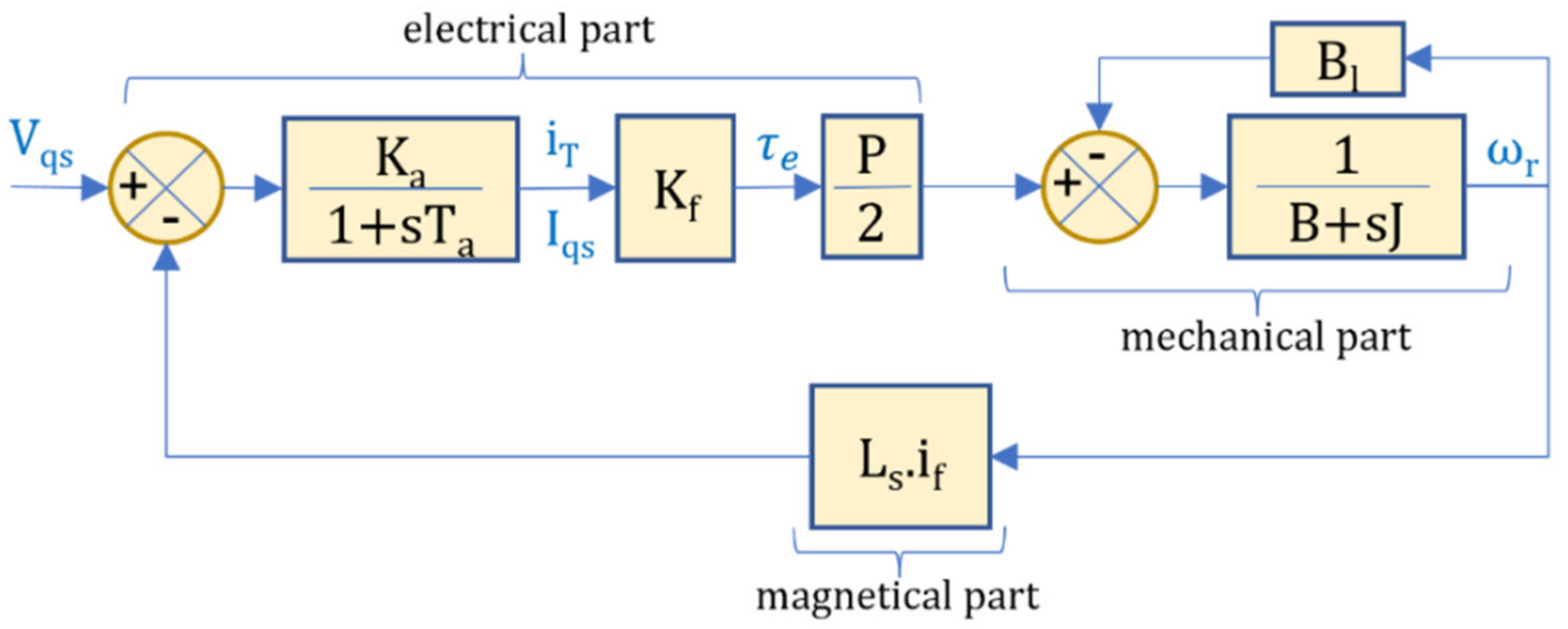
2.2. Linearized 3-Phase Induction Motor Model
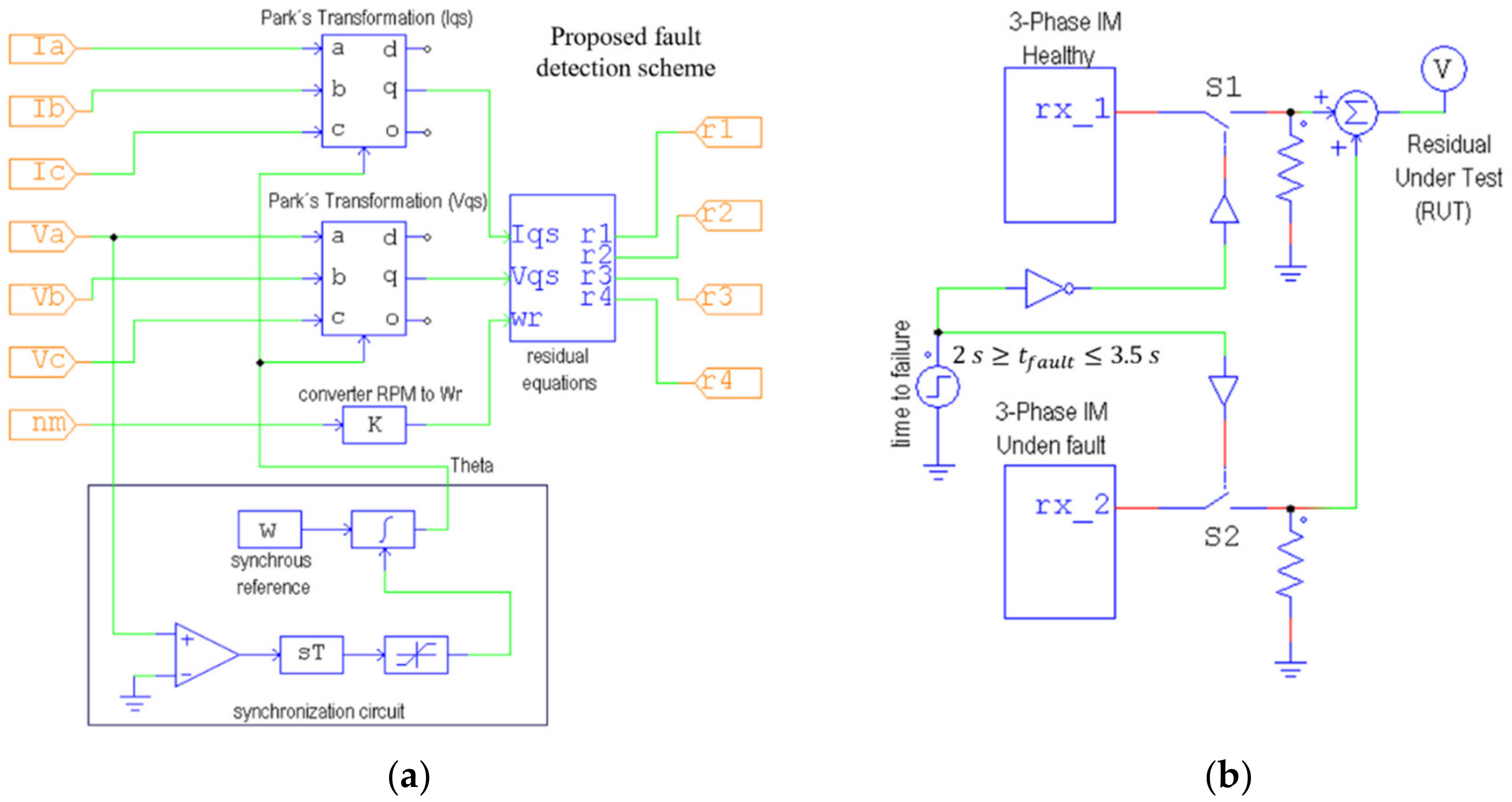
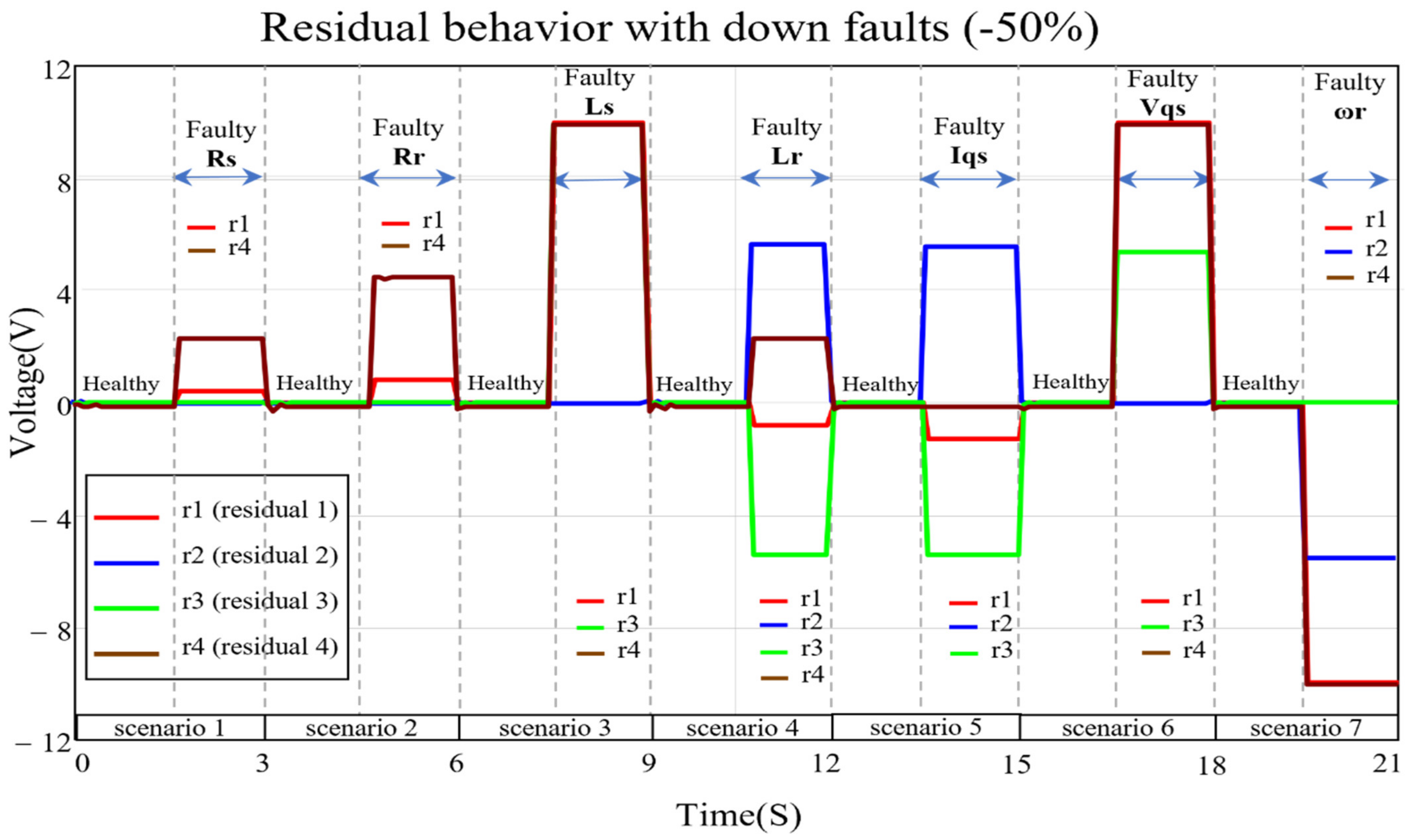
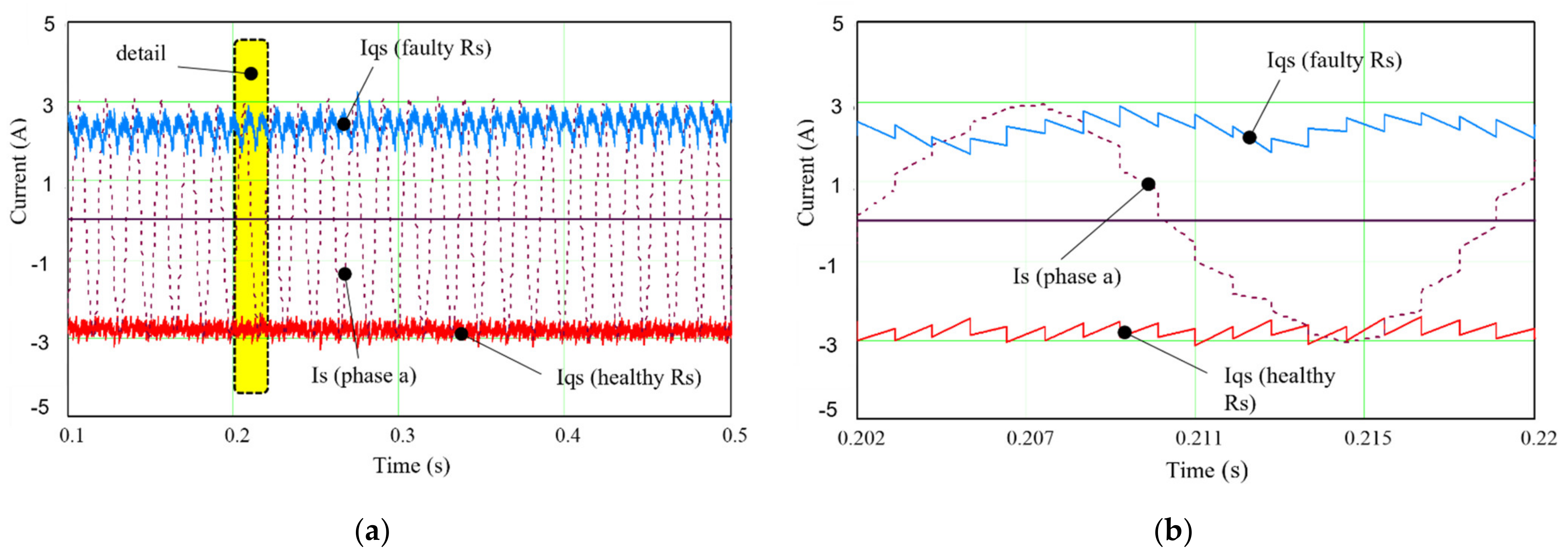
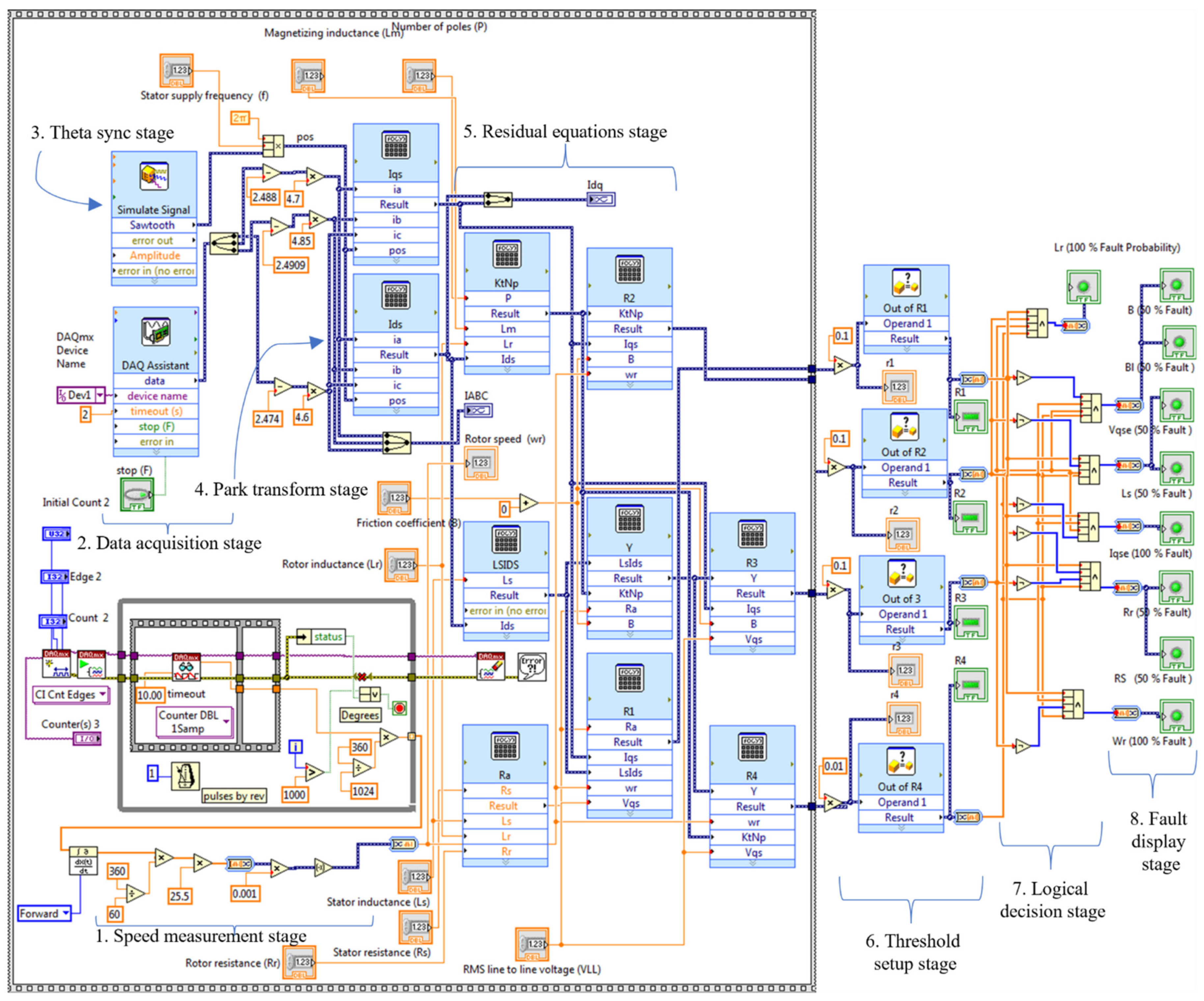
3. Fault Detection for 3-Phase Induction Motor Using Parity Equation
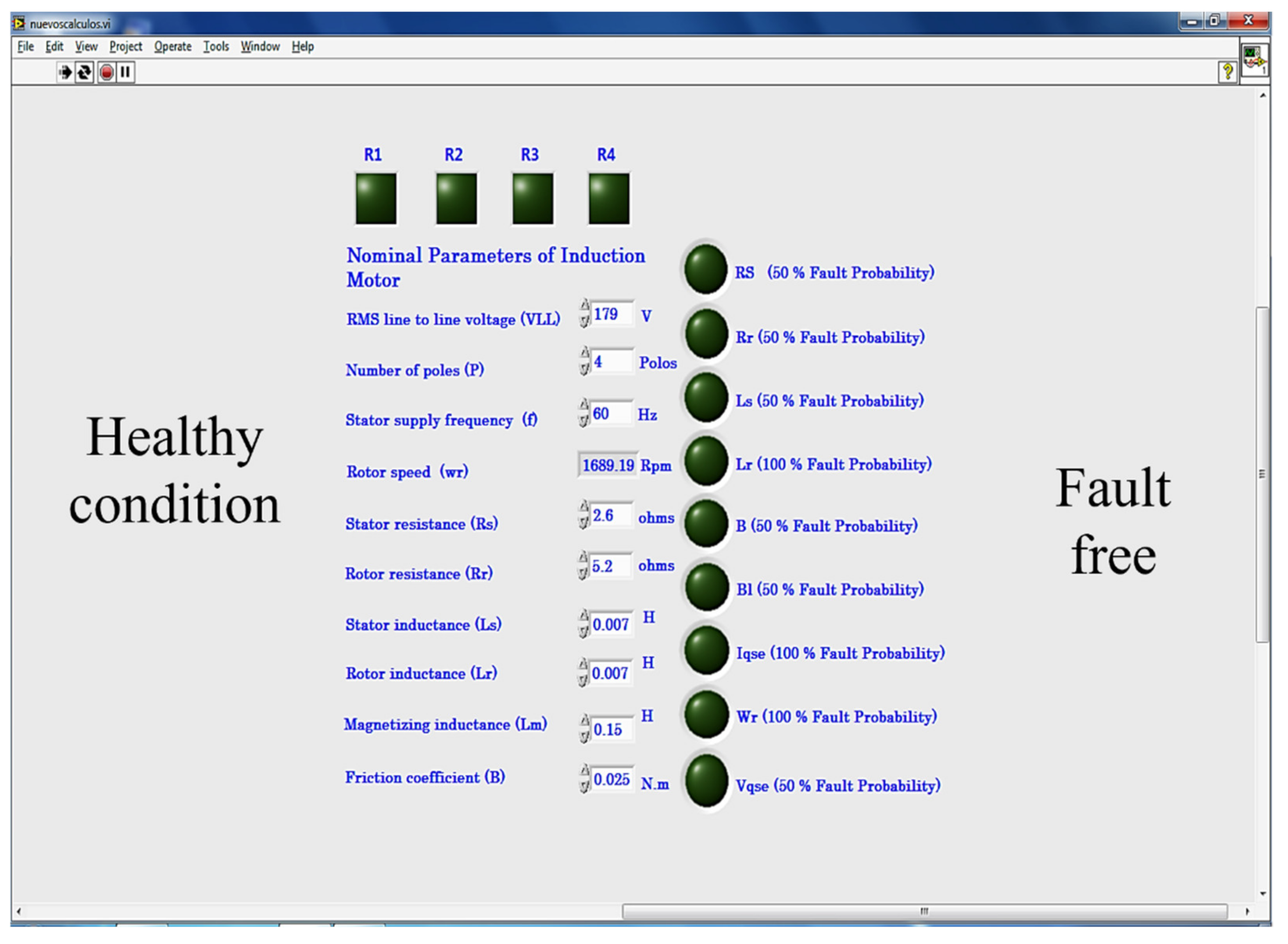
4. Simulation and Experimental Development
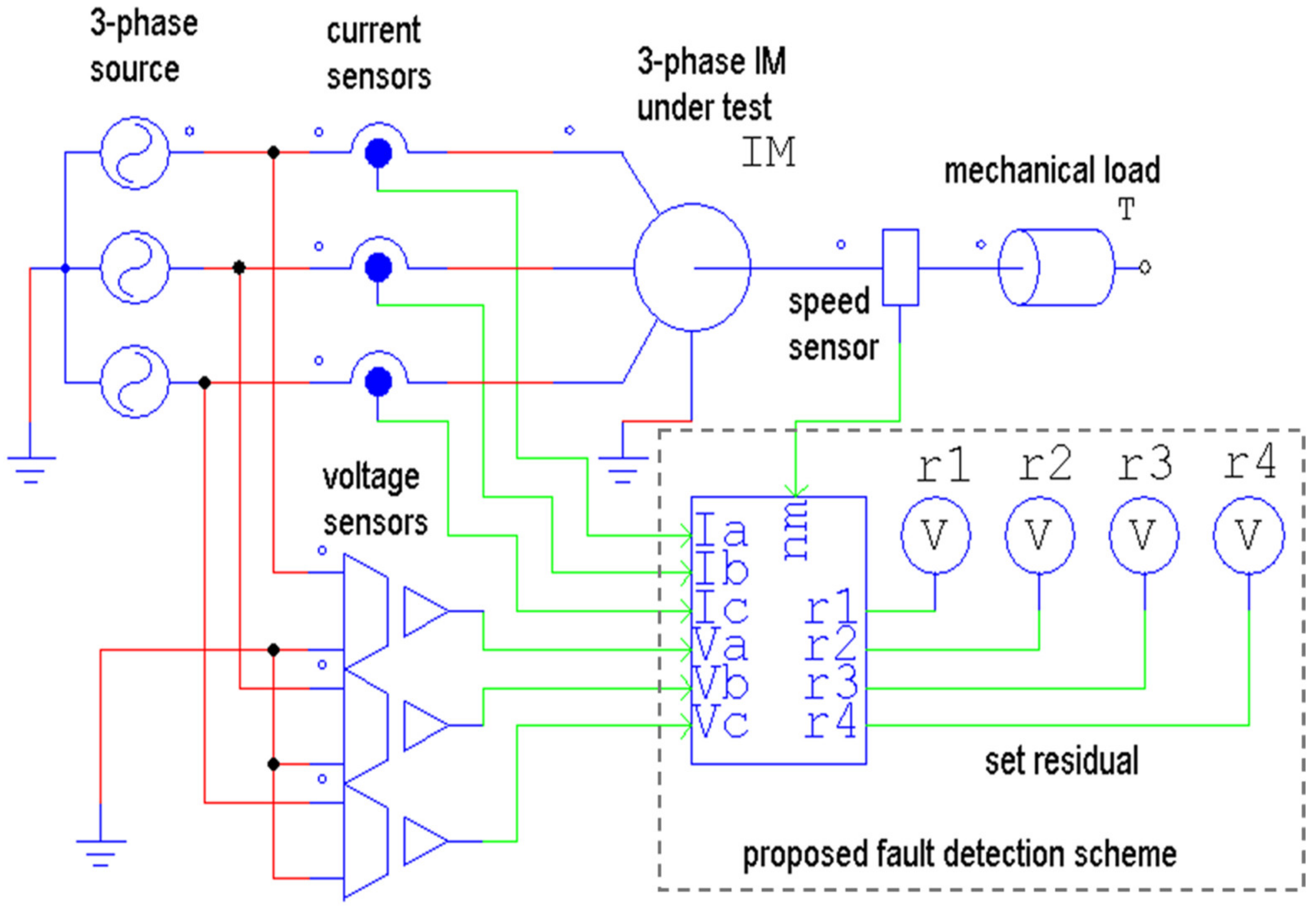
4.1. Simulation Setup
4.2. Experimental Setup
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| stator d-axis voltage in synchronous reference frame (V) | |
| stator q-axis voltage in synchronous reference frame (V) | |
| rotor d-axis current in synchronous reference frame (A) | |
| stator d-axis current in synchronous reference frame (A) | |
| rotor q-axis current in synchronous reference frame (A) | |
| stator q-axis current in synchronous reference frame (A) | |
| load friction coefficient | |
| magnetizing inductance (H) | |
| rotor inductance matrix (H) | |
| stator inductance matrix (H) | |
| number of poles | |
| rotor resistance matrix (Ω) | |
| stator resistance matrix (Ω) | |
| stator d-axis voltage (V) | |
| stator q-axis voltage (V) | |
| stator current torque-production component (A) | |
| stator d-axis current (A) | |
| stator current flux-producing component (A) | |
| rotor q-axis current (A) | |
| stator d-axis current (A) | |
| rotor flux linkage (Wb) | |
| load torque (N) | |
| electromagnetic torque (A) | |
| mechanical speed (radians/sec) | |
| rotor electrical speed (radians/sec) | |
| stator speed (radians/sec) | |
| slip speed (radians/sec) | |
| friction coefficient | |
| moment of inertia (Kg.m2) | |
| pair of poles | |
| derivative operator | |
| leakage coefficient |
References
- Report of Large Motor Reliability Survey of Industrial and Commercial Installations, Part II. IEEE Trans. Ind. Applicat. 1985, IA-21, 865–872. [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Arredondo, P.A.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Avina-Cervantes, J.G.; Rostro-Gonzalez, H.; Romero-Troncoso, R.d.J. Methodology for Fault Detection in Induction Motors via Sound and Vibration Signals. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 83, 568–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoletti, M.A.; Donolo, P.D.; Pezzani, C.M.; Oliveira, M.O.; Bossio, G.R.; De Angelo, C.H. Stator Faults Detection on Induction Motors Using Harmonic Sequence Current Components Analysis. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2021, 19, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Goyal, D.; Shimi, S.L.; Akula, A. Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motors: A Review. Arch. Computat. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.-J.; Kim, K.-M. Inter-Turn Short Circuit Diagnosis Using New D-Q Synchronous Min–Max Coordinate System and Linear Discriminant Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.-J.; Kim, O. Linear Method for Diagnosis of Inter-Turn Short Circuits in 3-Phase Induction Motors. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallesoe, C.S.; Izadi-Zamanabadi, R.; Vadstrup, P.; Rasmussen, H. Observer-Based Estimation of Stator-Winding Faults in Delta-Connected Induction Motors: A Linear Matrix Inequality Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2007, 43, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.; Sathyanarayana Rao, M.G. Detection of Stator Winding Inter-Turn Short Circuit Fault in Induction Motor Using Vibration Signals by MEMS Accelerometer. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2017, 45, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia-Barron, A.; Tapia-Tinoco, G.; Razo-Hernandez, J.R.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Granados-Lieberman, D. A Neural Network-Based Model for MCSA of Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Faults in Induction Motors and Its Power Hardware in the Loop Simulation. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowron, M.; Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Wolkiewicz, M.; Kowalski, C.T. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Stator Current Data-Driven Incipient Stator Fault Diagnosis of Inverter-Fed Induction Motor. Energies 2020, 13, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, O.E.; Amer, M.; Abdelsalam, A.K.; Williams, B.W. Induction Motor Broken Rotor Bar Fault Detection Techniques Based on Fault Signature Analysis—A Review. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, B.; Vaimann, T.; Rassõlkin, A.; Kallaste, A.; Belahcen, A. A Survey of Broken Rotor Bar Fault Diagnostic Methods of Induction Motor. Electr. Control Commun. Eng. 2018, 14, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, A.; Drozdowski, P. Induction Motor Fault Diagnosis Based on Zero-Sequence Current Analysis. Energies 2020, 13, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esam El-Dine Atta, M.; Ibrahim, D.K.; Gilany, M.I. Broken Bar Faults Detection Under Induction Motor Starting Conditions Using the Optimized Stockwell Transform and Adaptive Time–Frequency Filter. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3518110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defdaf, M.; Berrabah, F.; Chebabhi, A.; Cherif, B.D.E. A New Transform Discrete Wavelet Technique Based on Artificial Neural Network for Induction Motor Broken Rotor Bar Faults Diagnosis. Int. Trans. Electr. Energ. Syst 2021, 31, e12807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshorman, O.; Alshorman, A. A Review of Intelligent Methods for Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Stator and Rotor Faults of Induction Machines. IJECE 2021, 11, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liang, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Gao, L. Thermal Equivalent Network Method for Calculating Stator Temperature of a Shielding Induction Motor. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 147, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areias, I.A.d.S.; Borges da Silva, L.E.; Bonaldi, E.L.; de Lacerda de Oliveira, L.E.; Lambert-Torres, G.; Bernardes, V.A. Evaluation of Current Signature in Bearing Defects by Envelope Analysis of the Vibration in Induction Motors. Energies 2019, 12, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuejun, A.; Zhiheng, Z.; Ming, L.; Guangyu, W.; Xiangling, K.; Zaihang, L. Influence of Asymmetrical Stator Axes on the Electromagnetic Field and Driving Characteristics of Canned Induction Motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertler, J.J. Fault Detection and Diagnosis in Engineering Systems, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-203-75612-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.W.; Hua, S.; Hong-Yue, Z. Application of Fully Decoupled Parity Equation in Fault Detection and Identification of DC Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouattour, J. Diagnosing Parametric Faults in Induction Motors with Nonlinear Parity Relations. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2000, 33, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isermann, R. Supervision, Fault-Detection and Fault-Diagnosis Methods—An Introduction. Control Eng. Pract. 1997, 5, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-C.; Jheng, Y.-M.; Kuo, C.-C.; Hsueh, Y.-M. Induction Motors Condition Monitoring System with Fault Diagnosis Using a Hybrid Approach. Energies 2019, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojet El Khil, S.; Jlassi, I.; Estima, J.O.; Mrabet-Bellaaj, N.; Marques Cardoso, A.J. Current Sensor Fault Detection and Isolation Method for PMSM Drives, Using Average Normalised Currents. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 1434–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, C.S. Online Fault Detection of Induction Motors Using Frequency Domain Independent Components Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Gdansk, Poland, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, T.W.; Tan, W.W.; Wang, Z.-X.; Chang, C.S. Hybrid Time-Frequency Domain Analysis for Inverter-Fed Induction Motor Fault Detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Bari, Italy, 4–7 July 2010; pp. 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Pen, H.; Wang, Z.; Chang, C.S. Feature Knowledge Based Fault Detection of Induction Motors Through the Analysis of Stator Current Data. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseler, O.; Isermann, R. Application of Model-Based Fault Detection to a Brushless DC Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2000, 47, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Mid, E.; Dua, V. Model-Based Parameter Estimation for Fault Detection Using Multiparametric Programming. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 8000–8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, S.; Stoss, J.; Liske, A.; Brodatzki, M.; Kolb, J.; Braun, M. Online Parameter Identification of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines with Nonlinear Magnetics Based on the Inverter Induced Current Slopes and the Dq-System Equations. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE ’19 ECCE Europe), Genova, Italy, 3–5 September 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.A.; Hernandez, M.; Mendez, F.; Sibaja, P.; Hernandez, L. A Simple Fault Detection of Induction Motor by Using Parity Equations. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics & Drives, Bologna, Italy, 5–8 September 2011; pp. 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulines, E.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Duran, I.; Sánchez, R. Simplified Model of a Three-Phase Induction Motor for Fault Diagnostic Using the Synchronous Reference Frame DQ and Parity Equations. IFAC-Pap. 2018, 51, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isermann, R. Fault-Diagnosis Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; ISBN 978-3-540-24112-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertler, J.; Singer, D. A New Structural Framework for Parity Equation-Based Failure Detection and Isolation. Automatica 1990, 26, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Toliyat, H.A.; Li, X. Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Electrical Motors—A Review. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Wasynczuk, O.; Sudhoff, S.; Pekarek, S. (Eds.) Analysis of Electric Machinery and Drive Systems; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-118-52433-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierkowski, M.P. Electric Motor Drives: Modeling, Analysis and Control, R. Krishan, Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2001, Xxviii + 626 Pp. ISBN 0-13-0910147: BOOK REVIEW. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2004, 14, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfling, T.; Isermann, R. Fault Detection Based on Adaptive Parity Equations and Single-Parameter Tracking. Control Eng. Pract. 1996, 4, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Blanco, M.A.; Golikov, V.; Vazquez-Avila, J.L.; Samovarov, O.; Sanchez-Lara, R.; Osorio-Sánchez, R.; Pérez-Ramírez, A. Comprehensive and Simplified Fault Diagnosis for Three-Phase Induction Motor Using Parity Equation Approach in Stator Current Reference Frame. Machines 2022, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhri, S.; Ertugrul, N. A Negative Sequence Current Phasor Compensation Technique for the Accurate Detection of Stator Shorted Turn Faults in Induction Motors. Energies 2022, 15, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



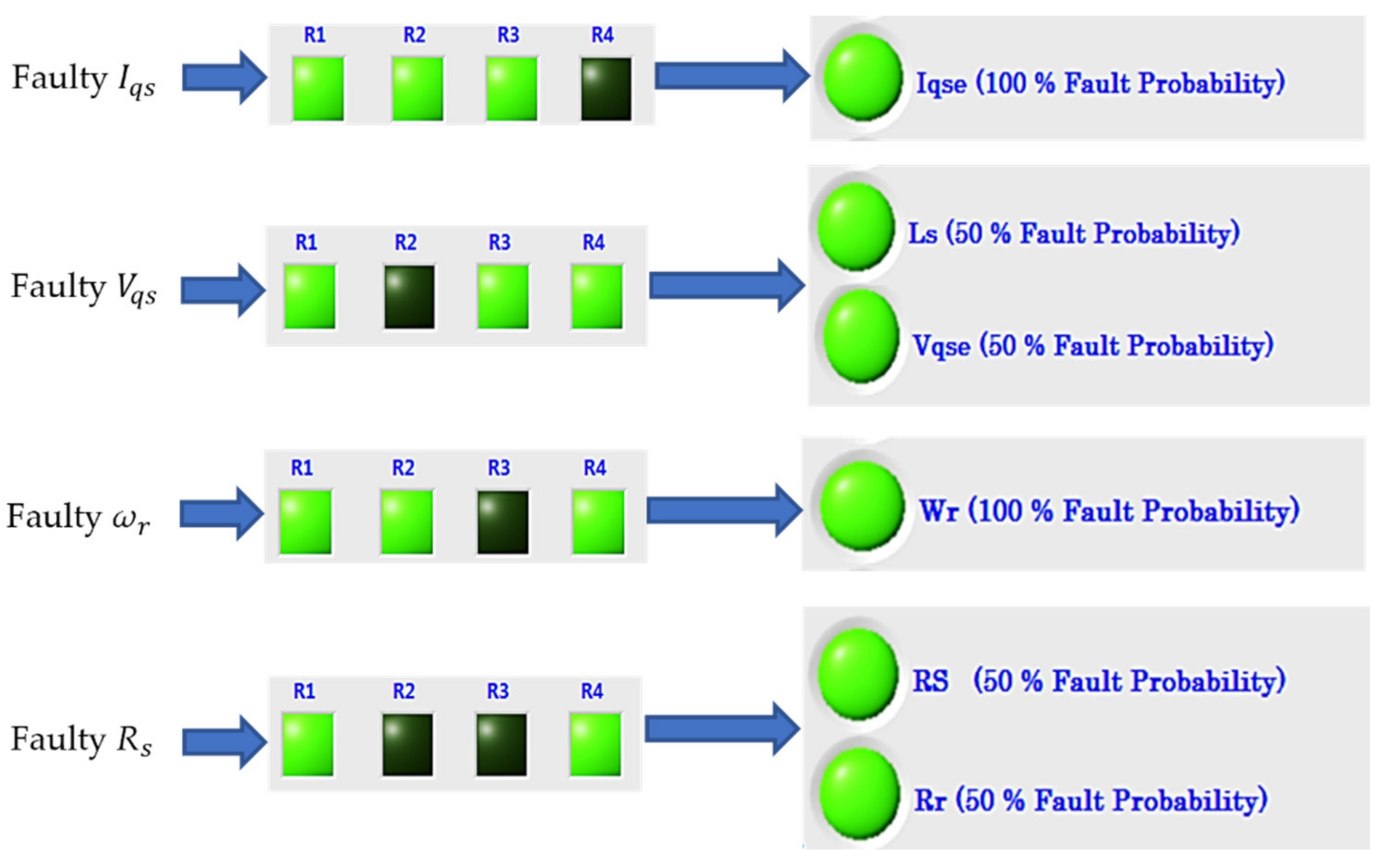
| Faults | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parametric | I | 0 | 0 | I | |
| I | 0 | 0 | I | ||
| I | 0 | I | I | ||
| I | I | I | I | ||
| 0 | I | I | I | ||
| 0 | I | I | I | ||
| Additive | I | I | I | 0 | |
| I | 0 | I | I | ||
| I | I | 0 | I | ||
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| 3-phase power supply | Manufacturer Delorenzo (Rozzano, Milan, Italy), model DL1013M3 |
| 3-phase induction motor | Manufacturer Delorenzo (Rozzano, Milan, Italy), model DL10115A1, 300 W, star configuration and access to neutral terminal |
| 3-phase measurement module | Manufacturer K-oz Soluciones integrales (Merida, Yucatan Mexico), model MOD.MEW-3P-180V15A-MIX |
| Encoder speed sensor | Manufacturer Yumo Electric Co. (Yueqing city, China), model E6B2-CWZ3E, resolution 1024 pulses/rev |
| DAQ board | Manufacturer National Instruments (Austin, TX, USA), model PCI-SCB-100 |
| PC Intel Pentium | Manufacture Lanix (Hermosillo, Mexico), model Titan. |
| PC Screen | Manufacturer Lanix (Hermosillo, Mexico), model 900W, screen 24 inch |
| Test resistors | Manufacturer Delorenzo (Rozzano, Milan, Italy), model DL2643, 3-phase 1 Ω |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez-Blanco, M.A.; Golikov, V.; Osorio-Sánchez, R.; Samovarov, O.; Ortiz-Torres, G.; Sanchez-Lara, R.; Vazquez-Avila, J.L. Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Using D-Q Simplified Model and Parity Equations. Energies 2022, 15, 8372. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228372
Rodriguez-Blanco MA, Golikov V, Osorio-Sánchez R, Samovarov O, Ortiz-Torres G, Sanchez-Lara R, Vazquez-Avila JL. Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Using D-Q Simplified Model and Parity Equations. Energies. 2022; 15(22):8372. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228372
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez-Blanco, Marco Antonio, Victor Golikov, René Osorio-Sánchez, Oleg Samovarov, Gerardo Ortiz-Torres, Rafael Sanchez-Lara, and Jose Luis Vazquez-Avila. 2022. "Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Using D-Q Simplified Model and Parity Equations" Energies 15, no. 22: 8372. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228372
APA StyleRodriguez-Blanco, M. A., Golikov, V., Osorio-Sánchez, R., Samovarov, O., Ortiz-Torres, G., Sanchez-Lara, R., & Vazquez-Avila, J. L. (2022). Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Using D-Q Simplified Model and Parity Equations. Energies, 15(22), 8372. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228372










