Steam Gasification of Refuse-Derived Fuel with CaO Modification for Hydrogen-Rich Syngas Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Simulation Methods
2.1. RDF Characterization
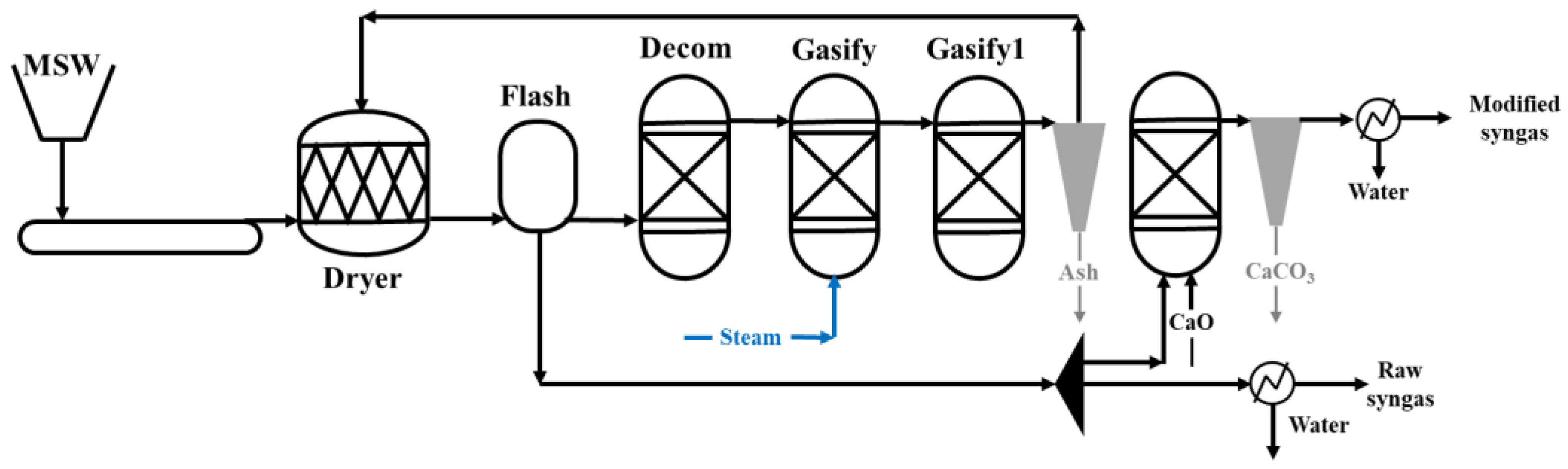
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Data Evaluation
2.4. Model Developing
2.4.1. Drying Block
2.4.2. Decomposing Block
2.4.3. Gasifying Block
2.4.4. Modifying Block
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Results
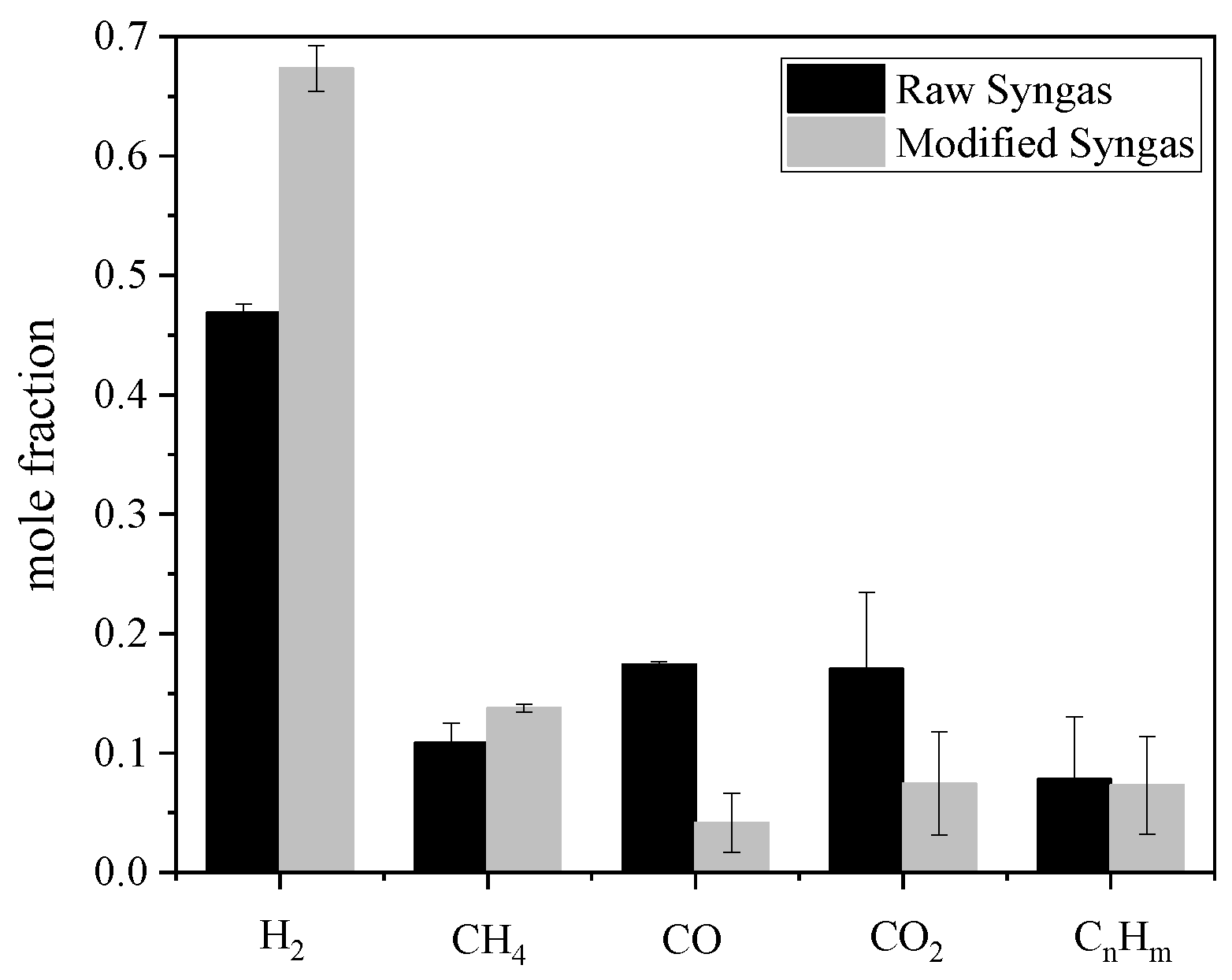
3.1.1. Basic Scenario Results
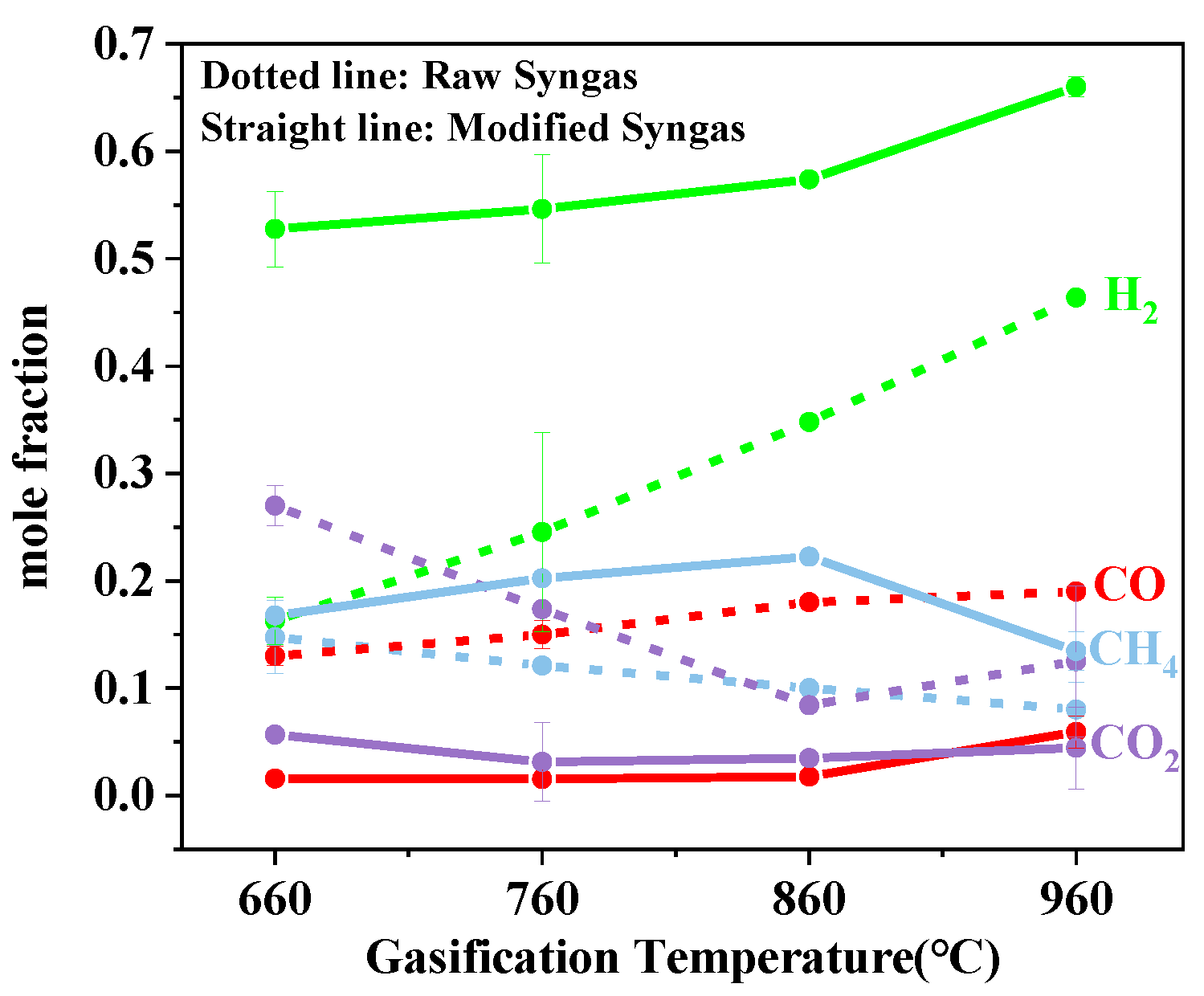
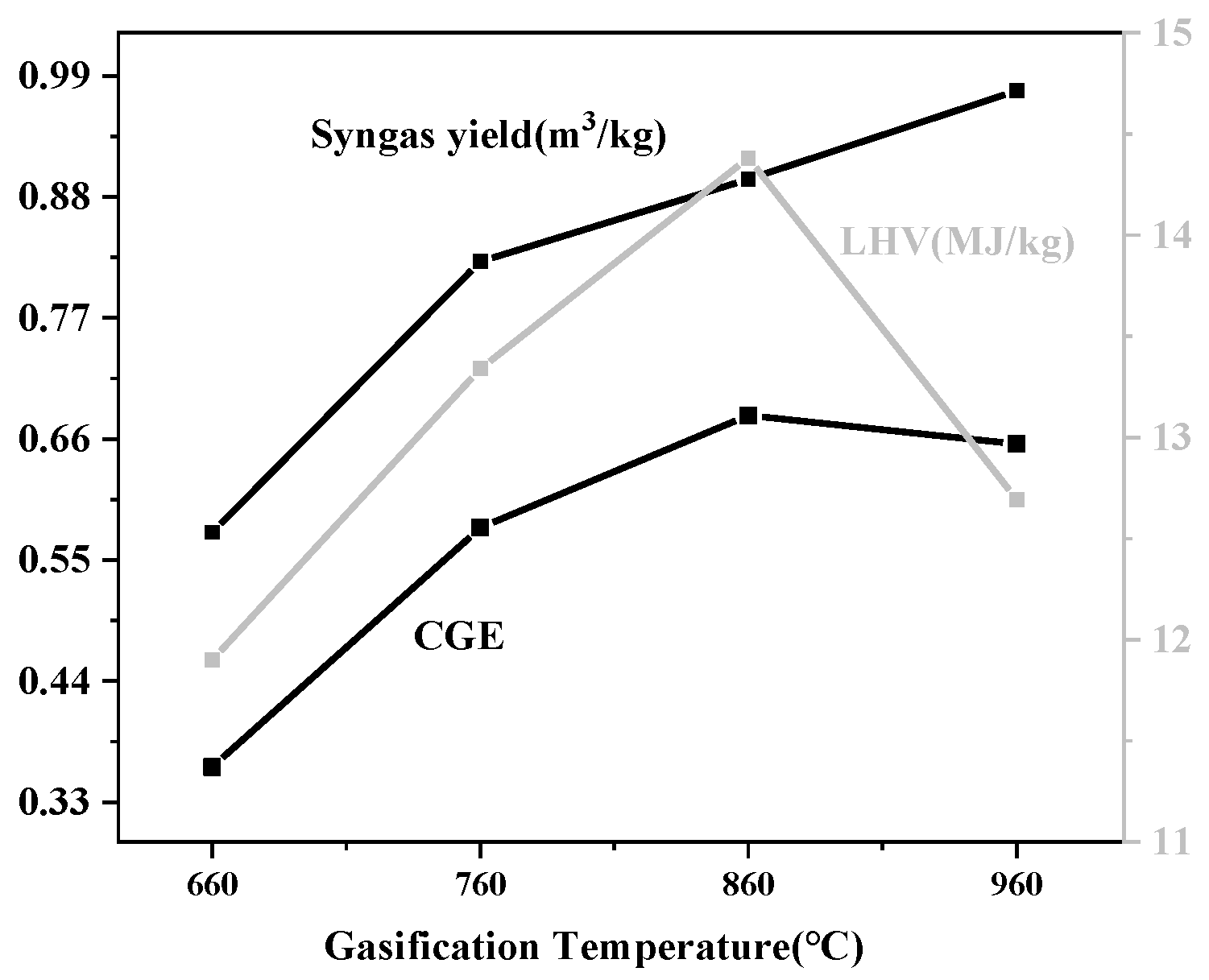
3.1.2. Effect of Gasification Temperature
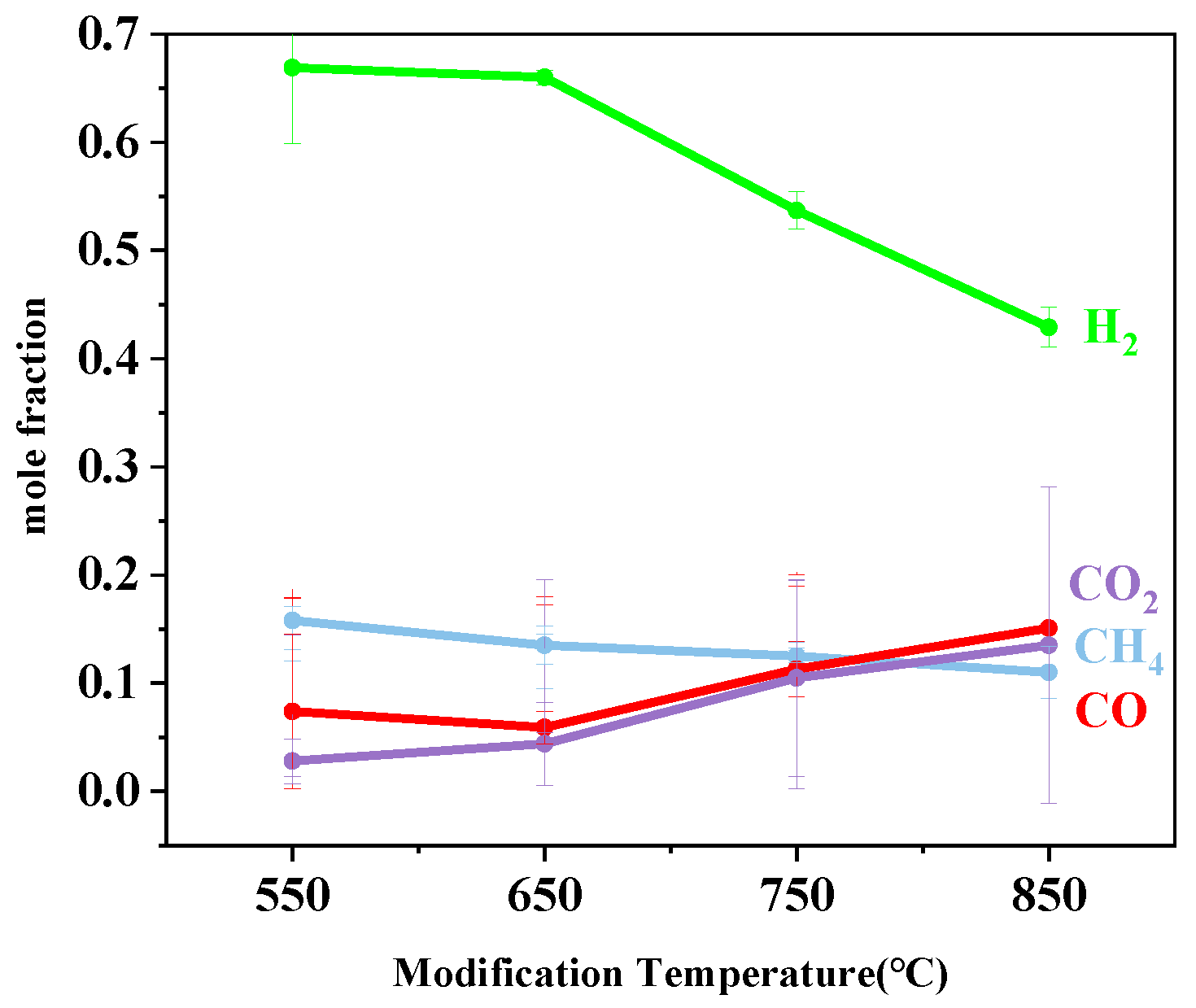
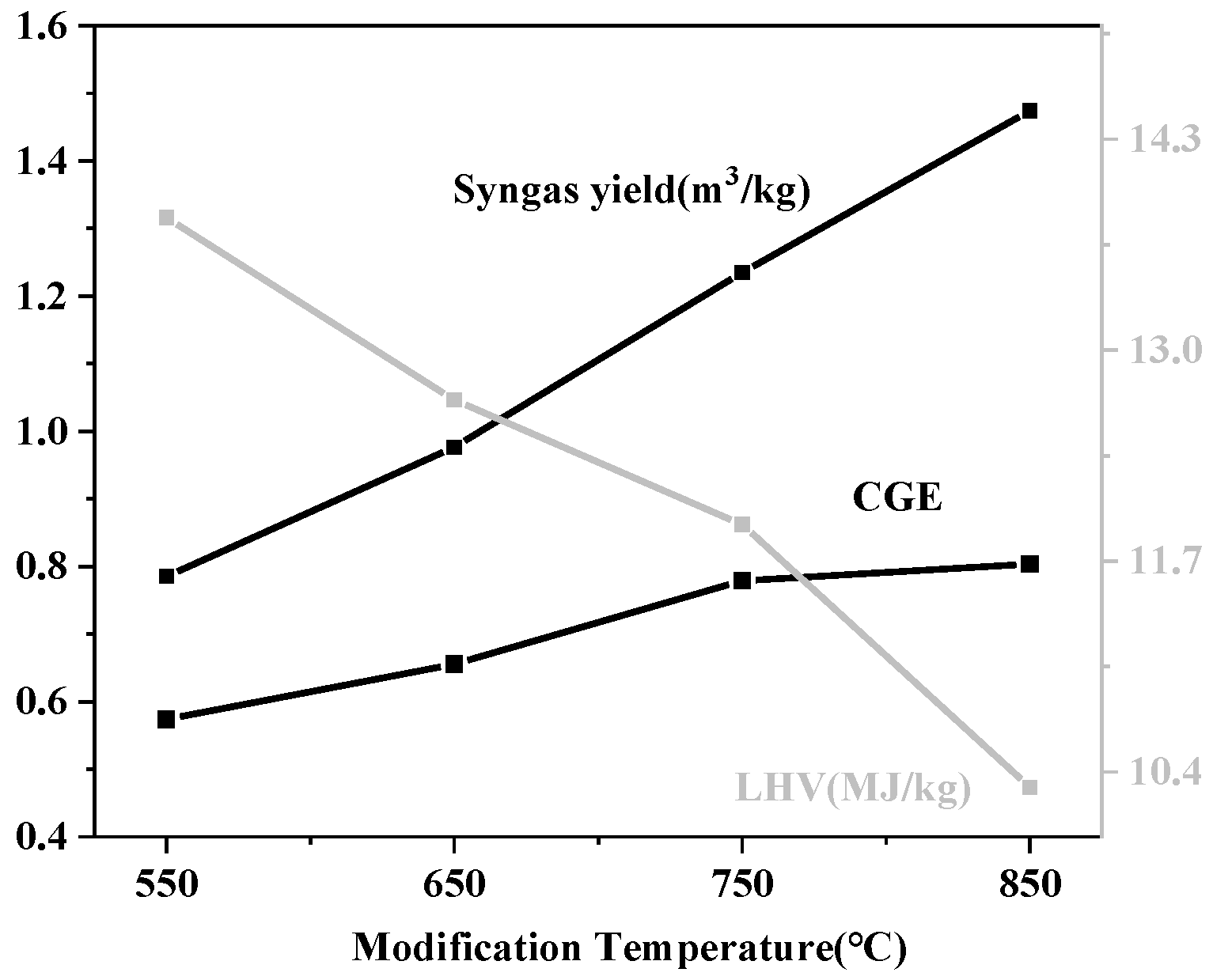
3.1.3. Effect of Modification Temperature
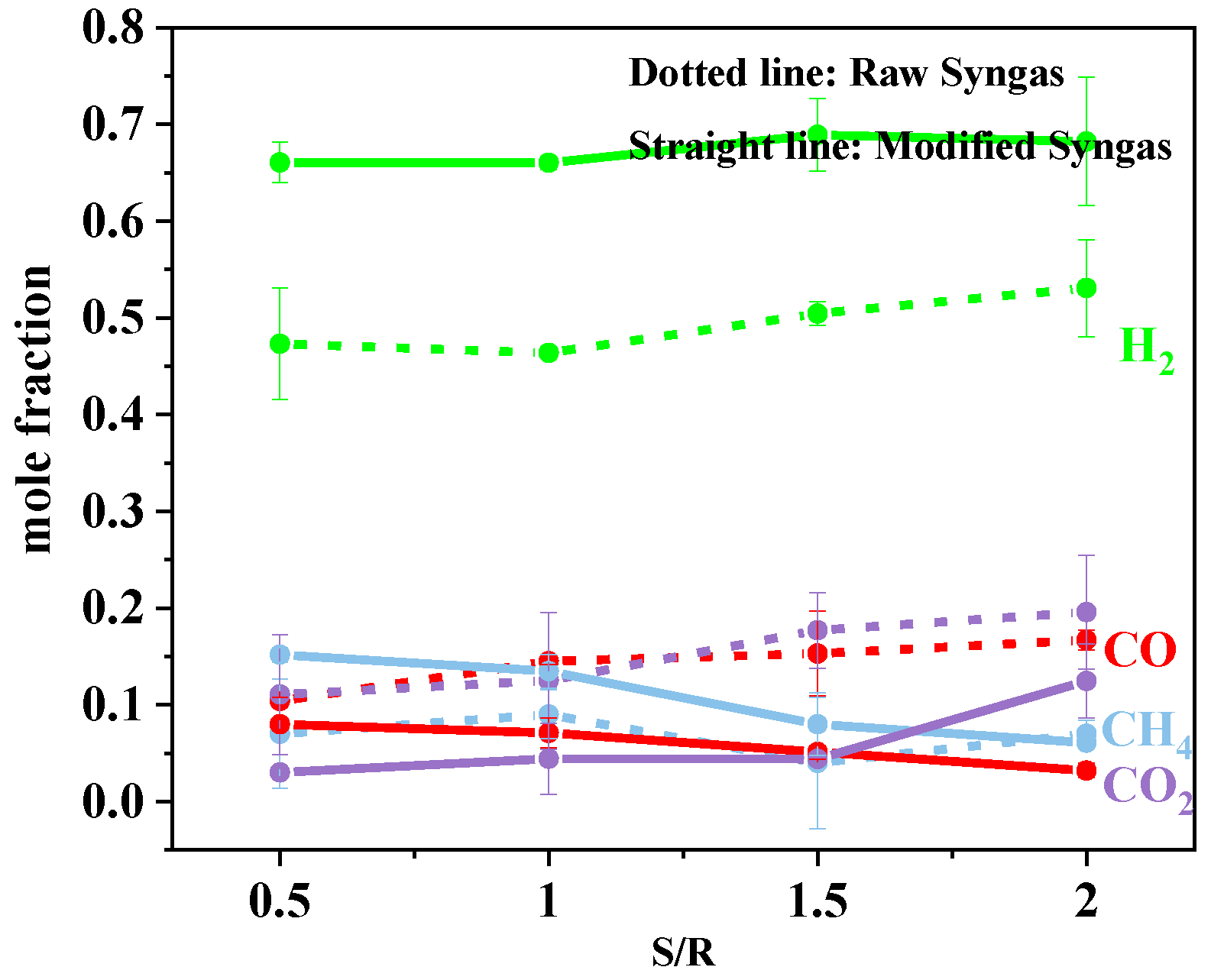
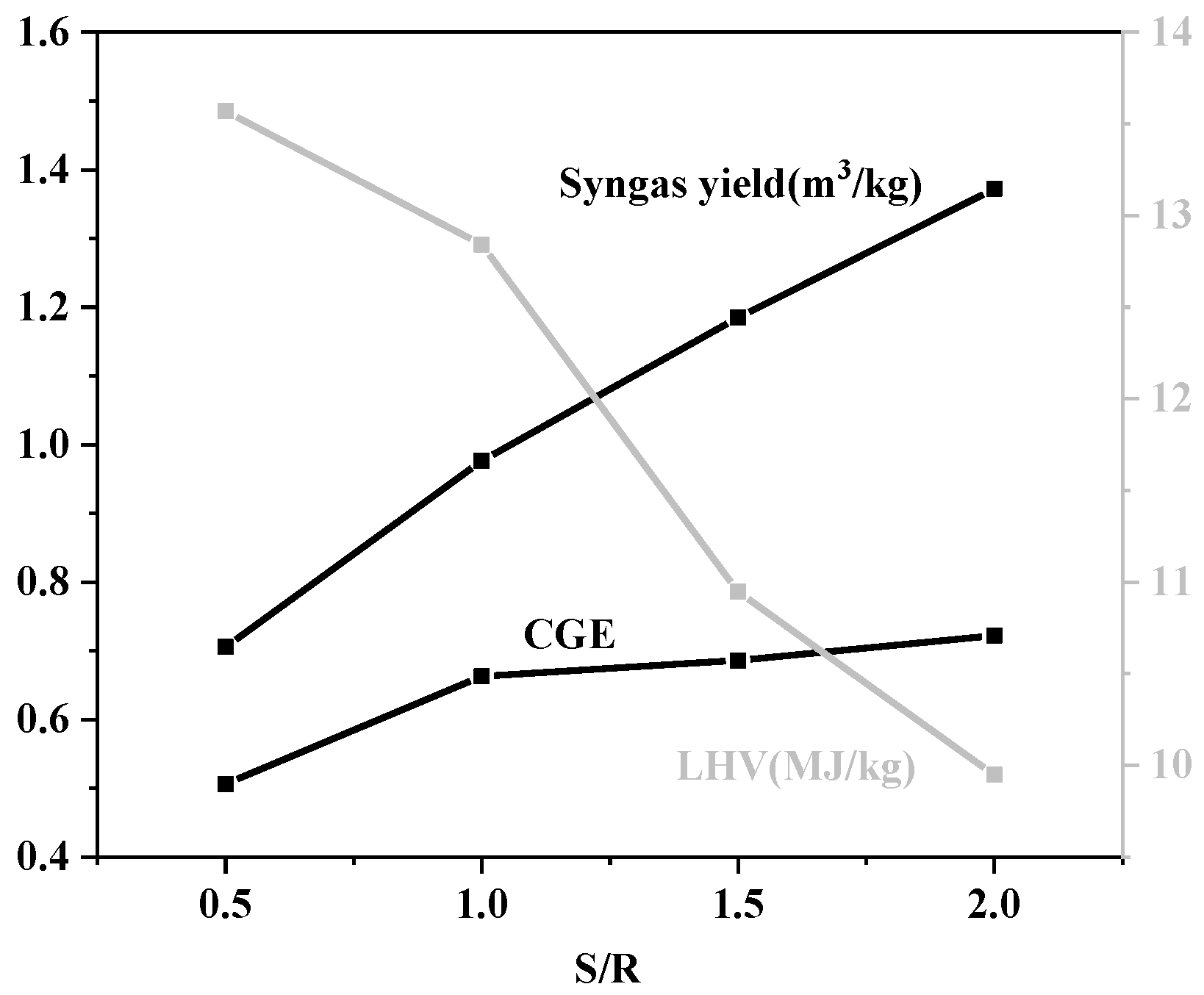
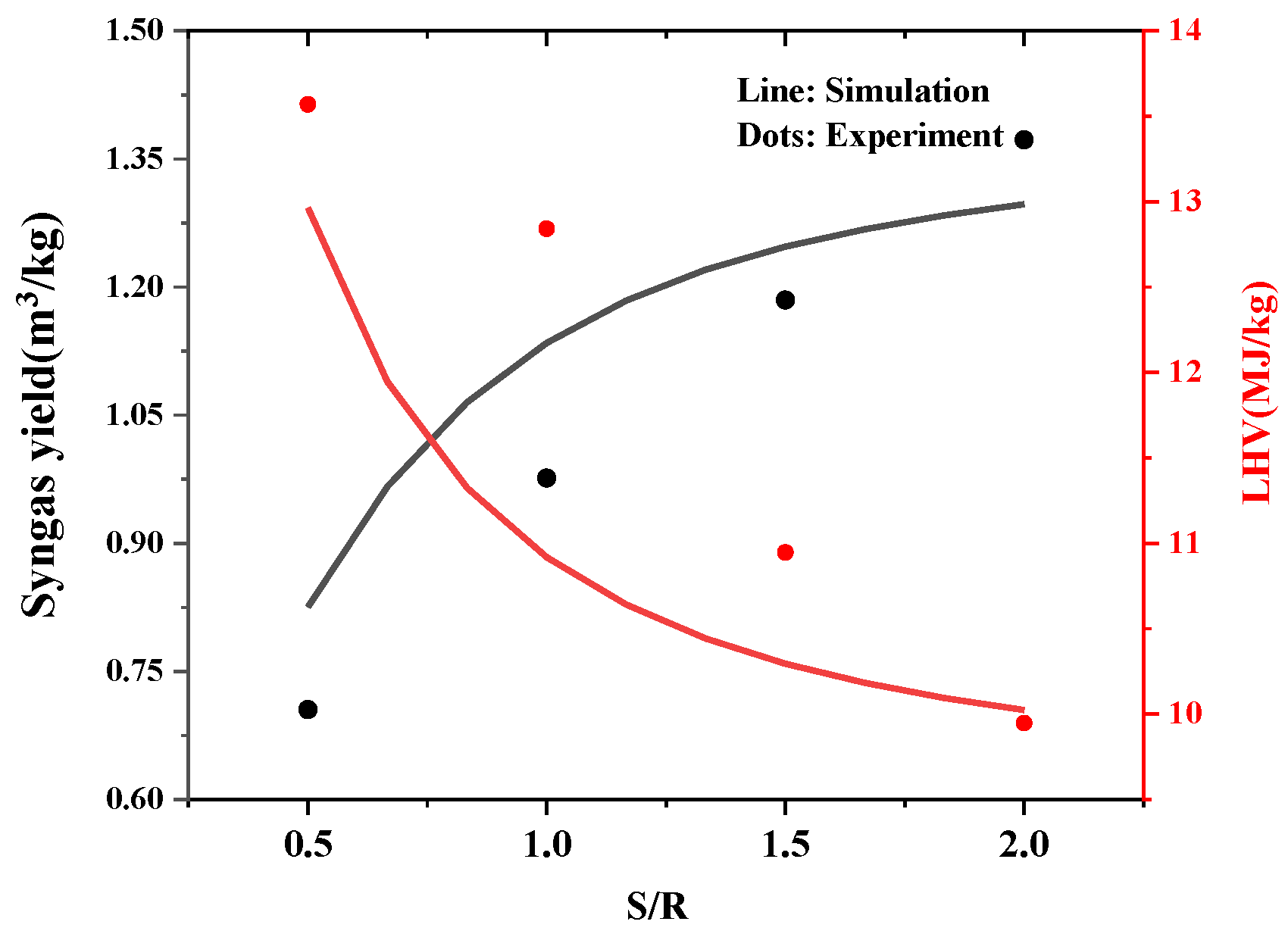
3.1.4. Effect of S/R
3.2. Simulation Results
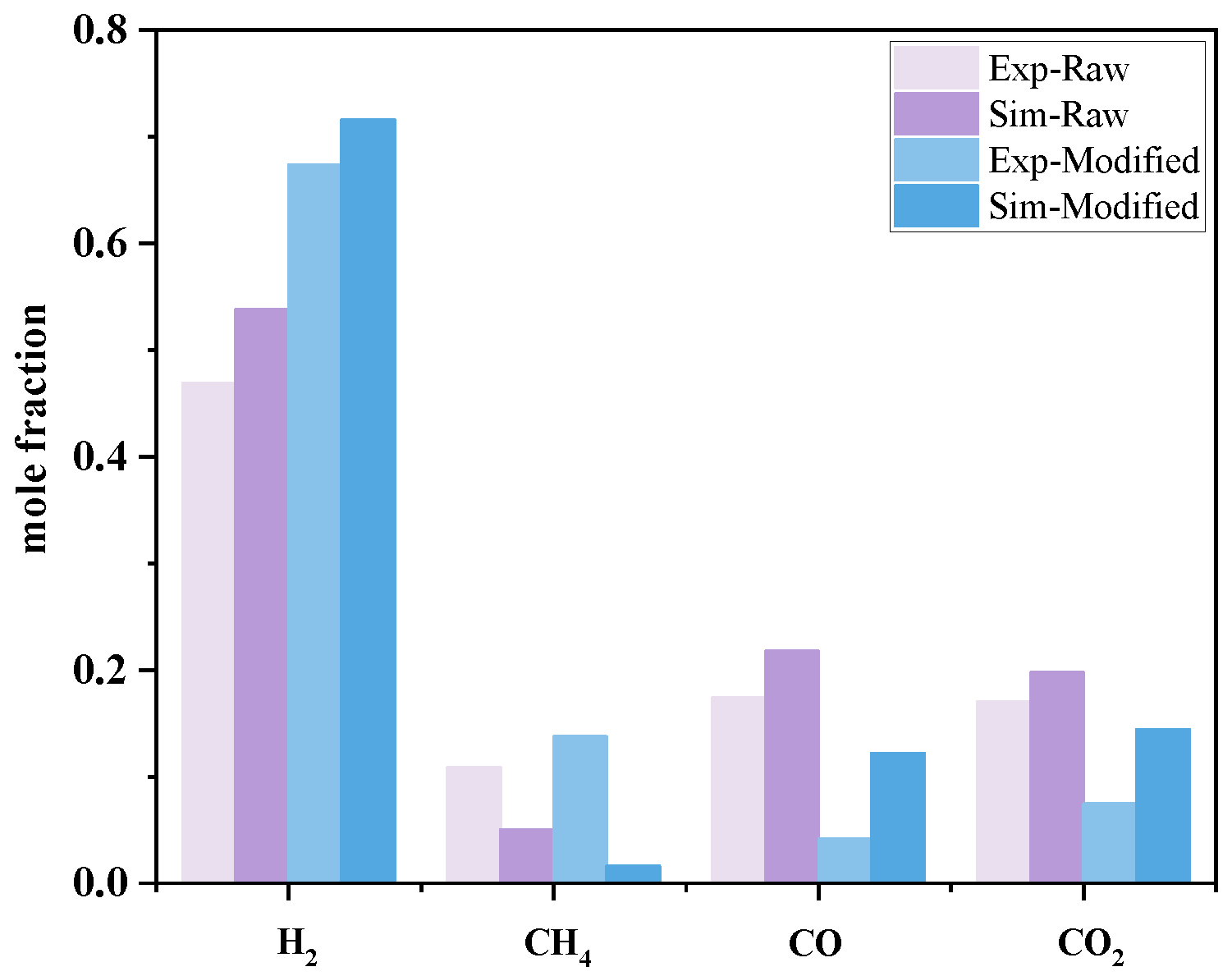
3.2.1. Basic Scenario Simulation Results
3.2.2. Effect of Gasification Temperature
3.2.3. Effect of the Modification Temperature
3.2.4. Effect of S/R
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA Global Hydrogen Review. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-hydrogen-review-2022 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Hossain, H.M.Z.; Hasna, Q.H.; Monir, M.M.U.; Ahmed, M.T. Municipal solid waste (MSW) as a source of renewable energy in Bangladesh: Revisited. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, D.; Aldás, C.; López, G.; Kaparaju, P. Municipal solid waste as a valuable renewable energy resource: A worldwide opportunity of energy recovery by using Waste-To-Energy Technologies. Energy Procedia 2017, 134, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Woerden, V.F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; Urban Development Series; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/what-a-waste/ (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Lu, J.W.; Zhang, S.; Hai, J.; Lei, M. Status and perspectives of municipal solid waste incineration in China: A comparison with developed regions. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.W.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, J.; Shao, Z.; Iris, C.; Pan, B.; Li, X.; et al. A review of China’s municipal solid waste (MSW) and comparison with international regions: Management and technologies in treatment and resource utilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 10, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.Z.; Wu, W.X.; Lu, S.Y.; Chen, T.; Huang, H.L.; Chen, Y.X.; Yan, J.H. Effect of MSW source-classified collection on the emission of PCDDs/Fs and heavy metals from incineration in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Cheng, Y.; He, D.; Yang, E.H. Review of leaching behavior of municipal solid waste incineration (MSW) ash. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Meng, A.; Long, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. An overview of characteristics of municipal solid waste fuel in China: Physical, chemical composition and heating value. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 36, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liew, R.K.; Tamothran, A.M.; Foong, S.Y.; Yek PN, Y.; Chia, P.W.; Van Tran, T.; Peng, W.; Lam, S.S. Gasification of refuse-derived fuel from municipal solid waste for energy production: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djlab, C. Gasification of municipal solid waste (MSW) as a cleaner final disposal route: A mini-review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 344, 126217. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Tang, Y.; Nzihou, A.; Chi, Y.; Weiss-Hortala, E.; Ni, M.; Zhou, Z. Comparison of waste-to-energy technologies of gasification and incineration using life cycle assessment: Case studies in Finland, France and China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryem, D.; Kaouther, G.; Walid, H.; Ahmed, G.; Lioua, K.; Mohamed, N.B. Simulation of Biomass Air Gasification in a Bubbling Fluidized Bed Using Aspen Plus: A Comprehensive Model Including Tar Production. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 33518–33529. [Google Scholar]
- Alouani, Y.; Saifaoui, D.; Alouani, A.; Alouani, M.A. Municipal solid waste gasification to produce hydrogen: Integrated simulation model and performance analysis. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 20068–20078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Mohanty, P. Utilization of paper mill sludge as a sustainable source of hydrogen production. Biofuels 2022, 13, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, X. Torrefaction/carbonization-enhanced gasification-steam reforming of biomass for promoting hydrogen-enriched syngas production and tar elimination over gasification biochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, M.K.; Xu, S.P.; Wang, C. Catalytic biomass gasification in decoupled dual loop gasification system over alkali-feldspar for hydrogen rich-gas production. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 161, 106472. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Cichonski, W. Ultrahigh Temperature Steam Gasification of Biomass and Solid Wastes. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 24, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aayush, R.; Sanjeev, Y. Hydrogen rich syngas production from food waste via an integrated two-stage process of in-situ steam gasification after fast pyrolysis. Energy Sources 2022, 44, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Mahishi, M.R.; Goswami, D.Y. An experimental study of hydrogen production by gasification of biomass in the presence of a CO2 sorbent. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 2803–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Christian, F.M.M.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S. A review of CaO based catalysts for tar removal during biomass gasification. Energy 2022, 244, 123172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Liu, G.C.; Zhao, Y.N.; Boon Veksha, A.; Giannis, A.; Lim, T.T.; Grzegorz, L. Dual-functional witherite in improving chemical looping performance of iron ore and simultaneous adsorption of HCl in syngas at high temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.C.; Wang, H.M.; Veksha, A.; Giannis, A.; Lim, T.T.; Lisak, G. Chemical looping combustion-adsorption of HCl-containing syngas using alkaline-earth coated iron ore composites for simultaneous purification and combustion enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Liu, G.C.; Veksha, A.; Giannis, A.; Lim, T.T.; Lisak, G. Effective H2S control during chemical looping combustion by iron ore modified with alkaline earth metal oxides. Energy 2021, 218, 119548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaba, I.F.; Wu, C.F.; Williams, P.T. Hydrogen production from the pyrolysis gasification of waste tyres with a nickel/cerium catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 6628–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, H.Y. Physical Composition and Characteristics Analysis of The Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) In Beijing. Environ. Eng. 2018, 36, 132–136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.I.; Tsai, J.; Wu, K.H. Mathematical model for carbon dioxide evolution from the thermophilic composting of synthetic food wastes made of dog food. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavando JA, M.; Silva, V.B.; Tarelho, L.A.; Cardoso, J.S.; Eusébio, D. Snapshot review of refuse-derived fuels. Util. Policy 2022, 74, 10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DPio, D.T.; Tarelho LA, C.; Tavares AM, A.; Matos MA, A.; Silva, V. Co-gasification of refused derived fuel and biomass in a pilot-scale bubbling fluidized bed reactor. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 206, 112476. [Google Scholar]
- Henrietta, E.W.; Khaled, L.; Sary, A.; Mohand, T. Pyrolytic oil production by catalytic pyrolysis of refuse-derived fuels: Investigation of low cost catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 140, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Trirat, K.; Ratchaphon, S. Effect of Equivalence Ratio on an Efficiency of Single Throat Downdraft Gasifier Using RDF from Municipal solid waste. Energy Procedia 2017, 138, 784–788. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Chen, M. By-products recycling for syngas cleanup in biomass pyrolysis–An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 1246–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Ren, R.R.; Liu, B.J.; You, C.F. Hydrogen production with an auto-thermal MSW steam gasification and direct melting system: A process modeling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 10, 6508–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarian, S.; Unnthornorsson, R.; Richter, C. A review of biomass gasification modelling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 110, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, N.; Ashraf, A.; Naveed, S.; Malik, A. Simulation of hybrid biomass gasification using Aspen plus: A comparative performance analysis for food, municipal solid and poultry waste. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 359, 3962–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Fan, J.M.; Jiang, P.; Li, L.L. MSW to synthetic natural gas: System modeling and thermodynamics assessment. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, L.P.R.; Wang, Q.; Kolb, G.; Hessel, V. Steam gasification of biomass with subsequent syngas adjustment using shift reaction for syngas production: An Aspen Plus model. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Qin, Z.; Tang, Y.T.; Huang, T.; Ding, S.C.; Ma, X.Q. Techno-environmental-economic evaluation on municipal solid waste (MSW) to power/fuel by gasification-based and incineration-based routes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Hong, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Jin, H. Thermodynamic performance of SNG and power coproduction from MSW with recovery of chemical unreacted gas. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopaul, S.G.; Dutta, A.; Clemmer, R. Chemical looping gasification for hydrogen production: A comparison of two unique processes simulated using Aspen Plus. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5804–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigaki, N.; Manako, K.; Osada, M. Co-gasification of municipal solid waste and material recovery in a large-scale gasification and melting system. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lopez, M.; Pedroche, J.; Valverde, J.L.; Sanchez-Silva, L. Simulation of the gasification of animal wastes in a dual gasifier using Aspen Plus. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 140, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, F.; Florin, N.H.; Anthony, E.J.; Fennell, P.S. Influence of High-Temperature Steam on the Reactivity of CaO Sorbent for CO2 Capture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.M.; Yi, C.J. Syngas production by catalytic steam gasification of municipal solid waste in fixed-bed reactor. Energy 2012, 44, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
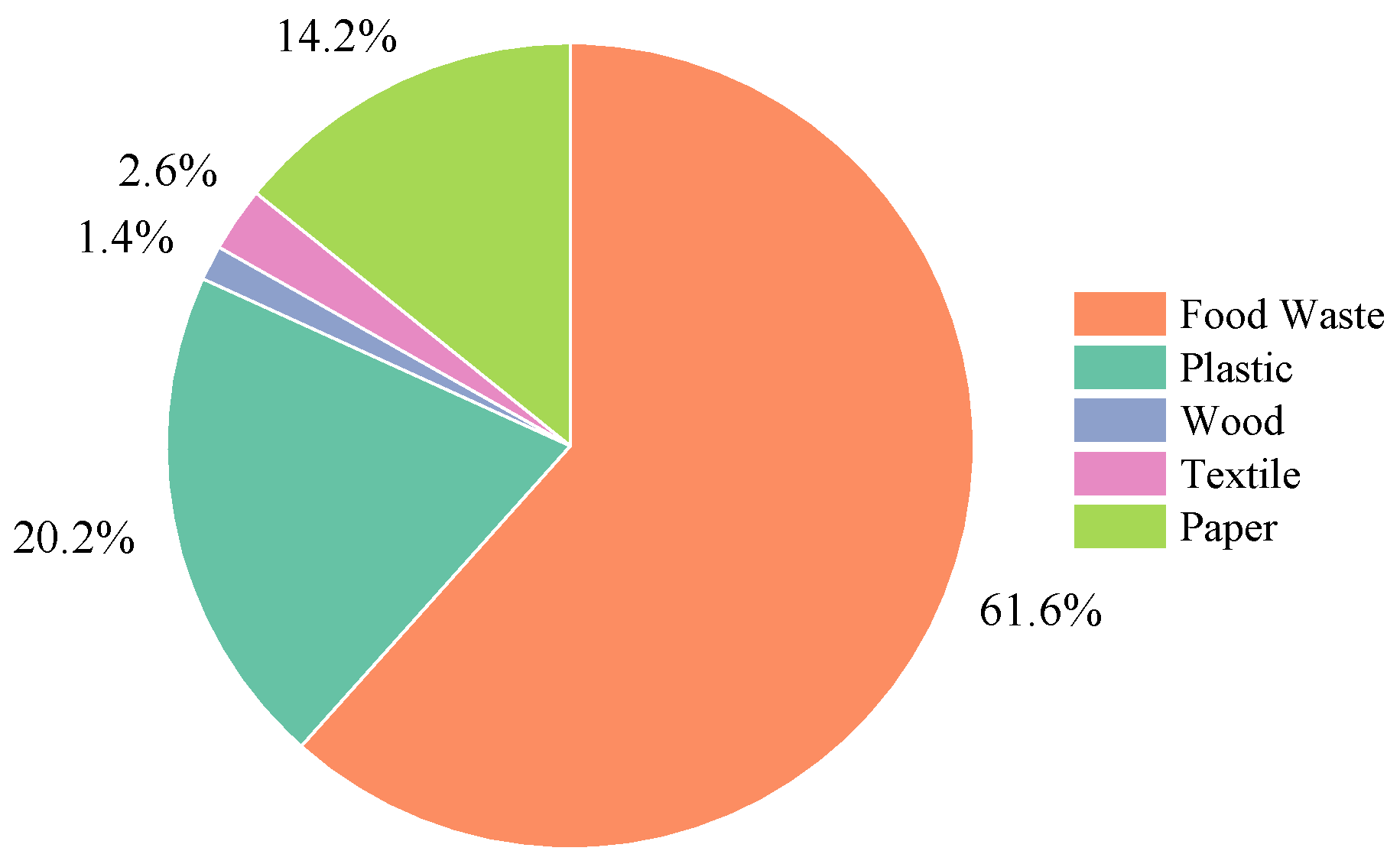







| Ultimate Analysis/wt% | |
|---|---|
| C | 41.03 |
| H | 5.86 |
| O | 38.22 |
| N | 0.14 |
| S | 1.42 |
| Proximate Analysis/wt% | |
| Moisture | 6.37 |
| Ash | 13.33 |
| Volatile | 76.34 |
| Fixed carbon | 10.33 |
| LHV (MJ/kg) | 18.91 |
| Number | Reaction | Reaction Heat (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | C + 1/2O2→CO | −111 |
| (2) | CO + 1/2O2→CO2 | −283 |
| (3) | C + O2→CO2 | −394 |
| (4) | H2 + 1/2O2→H2O | −242 |
| (5) | C + H2O↔CO + H2 | +131 |
| (6) | CO + H2O↔CO2 + H2 | −41 |
| (7) | CH4 + H2O↔CO + 3H2 | +206 |
| (8) | CH4 + CO2↔2CO + 2H2 | +259 |
| (9) | CO + 3H2↔CH4 + H2O | −227 |
| (10) | C + CO2↔2CO | +172 |
| (11) | CaO + CO2↔CaCO3 | −166 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| RDF feeding rate | 0.25 kg/h |
| Steam injection rate | 0.25 kg/h |
| S/R | 1 |
| Gasification Temperature | 960 °C |
| CaO Modification Temperature | 650 °C |
| Temperature (°C) | H2 (%) | CO | CO2 | CH4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Experiment [44] | ||||
| 700 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.38 | 0.10 |
| 750 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 0.3676 | 0.05 |
| 800 | 0.47 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.02 |
| 850 | 0.51 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.02 |
| 900 | 0.54 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.01 |
| This Study (Raw Syngas) | ||||
| 660 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.14 |
| 760 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
| 860 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 0.10 |
| 960 | 0.46 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.08 |
| This Study (Modified Syngas) | ||||
| 660 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| 760 | 0.55 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| 860 | 0.57 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| 960 | 0.66 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| S/C | H2 | CO | CO2 | CH4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Experiment [44] | ||||
| 0 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.12 |
| 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.48 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
| 0.84 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.13 | 0.02 |
| 1.52 | 0.53 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.02 |
| 1.88 | 0.54 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.01 |
| 2.41 | 0.54 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.01 |
| This Study (Raw Syngas) | ||||
| S/M | H2 | CO | CO2 | CH4 |
| 0.5 | 0.47 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.07 |
| 1 | 0.46 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.09 |
| 1.5 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.04 |
| 2 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.07 |
| This Study (Modified Syngas) | ||||
| 0.5 | 0.66 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.15 |
| 1 | 0.66 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.13 |
| 1.5 | 0.69 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.08 |
| 2 | 0.68 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, R.; Wang, H.; You, C. Steam Gasification of Refuse-Derived Fuel with CaO Modification for Hydrogen-Rich Syngas Production. Energies 2022, 15, 8279. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15218279
Ren R, Wang H, You C. Steam Gasification of Refuse-Derived Fuel with CaO Modification for Hydrogen-Rich Syngas Production. Energies. 2022; 15(21):8279. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15218279
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Ranwei, Haiming Wang, and Changfu You. 2022. "Steam Gasification of Refuse-Derived Fuel with CaO Modification for Hydrogen-Rich Syngas Production" Energies 15, no. 21: 8279. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15218279
APA StyleRen, R., Wang, H., & You, C. (2022). Steam Gasification of Refuse-Derived Fuel with CaO Modification for Hydrogen-Rich Syngas Production. Energies, 15(21), 8279. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15218279






