Abstract
Multi-tube multi-fin heat exchangers are extensively used in various industries. In the current work, detailed experimental investigations were carried out to establish the flow/heat transfer characteristics in three distinct heat exchanger geometries. A novel perforated plain fin design was developed, and its performance was evaluated against standard plain and louvred fins designs. Experimental setups were designed, and the tests were carefully carried out which enabled quantification of the heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics. In the experiments the average velocity of air was varied in the range of 0.7 m/s to 4 m/s corresponding to Reynolds numbers of 600 to 2650. The water side flow rates in the tubes were kept at 0.12, 0.18, 0.24, 0.3, and 0.36 m3/h corresponding to Reynolds numbers between 6000 and 30,000. It was found that the louvred fins produced the highest heat transfer rate due to the availability of higher surface area, but it also produced the highest pressure drops. Conversely, while the new perforated design produced a slightly higher pressure drop than the plain fin design, it gave a higher value of heat transfer rate than the plain fin especially at the lower liquid flow rates. Specifically, the louvred fin gave consistently high pressure drops, up to 3 to 4 times more than the plain and perforated models at 4 m/s air flow, however, the heat transfer enhancement was only about 11% and 13% over the perforated and plain fin models, respectively. The mean heat transfer rate and pressure drops were used to calculate the Colburn and Fanning friction factors. Two novel semiempirical relationships were derived for the heat exchanger’s Fanning and Colburn factors as functions of the non-dimensional fin surface area and the Reynolds number. It was demonstrated that the Colburn and Fanning factors were predicted by the new correlations to within ±15% of the experiments.
1. Introduction
Heat exchanging devices are used to transfer thermal energy between two or more mediums, which could be fluid–fluid or fluid–gas systems. The heat transfer process is carefully considered in the design of heat exchangers, which may involve various modes of heat transfer. Heat exchangers are used widely in a wide range of industries where there may be a need for controlled heating or cooling of flow streams, controlled evaporation, or controlled condensation, such as ventilation and air conditioning systems (HVAC), power generation industries, process industries, and manufacturing plants [1,2].
There are specific guidelines and procedures for designing and predicting performance of the heat exchangers. Knowledge and adherence to these during a design process are of great importance for maintaining proper and efficient operation. The performance of heat exchangers depends on geometric, flow, and fluid variables. Thus, appropriate selection of these variables is very important for the optimum performance of the heat exchanger unit for a given duty. The heat exchanger geometry (flow paths and fins geometry) is often optimised to provide best heat transfer performance for minimum operational and capital costs.
Heat exchanger analysis and design processes have seen considerable improvement over the years because of extensive research in this area and currently significant focus is directed towards optimising such systems. The main aim of these investigations is directed towards improving the heat transfer rate and minimise pumping costs as well as reduce costs associated with size and weight of the heat exchanger. In general, optimisation approaches can be classified under either active or passive categories. In the first category, an external force is used to drive heat transfer performance. Conversely, inserts and other additional geometrical protrusions are used to modify the flow in the second category. In practice however, a combination of the two may be used to optimise the performance of a heat exchanger [3,4].
Wilson [5] developed an experimental technique to measure the effectiveness of various heat transfer processes. The process performance was quantified through the calculated convection coefficients. The overall thermal resistance was divided into three major categories: two convections (internal and external) and tube wall. The method has been extensively used and even adapted for use in modified systems i.e., for helical tubes and for pipe annuli. It assumes that the outside coefficient and the fouling resistance are constant and that the coefficients , , and of the correlation devised are known:
Wilson method was modified by different investigators such as Sieder-Tate [6], Colburn [7] and Dittus-Boelter [8]. The nature of parametric intercedence relating the Nusselt, Reynolds and Prandtl numbers in Equation (1) was the subject of most modifications.
Wang et al. [9] experimentally studied 15 plate, fin and tube heat exchangers having a 9.52 mm tube diameter with different geometries. The evaluated effects of parameters corresponding to fins (thickness, spacing) and tube (number of rows) on the typical flow and heat transfer characteristics. They found that the fin thickness and spacing have limited effect on the flow and heat transfer characteristics. Wang et al. [9] also found that the number of tube rows has a negligible influence on a friction factor behaviour.
Abu Madi et al. [10] assessed the performance behaviour of finned plate and tube heat exchangers. They correlated geometry of flat and corrugated fins with Colburn and friction factors. They found that the fin type had an effect on heat transfer and friction factor. However, the number of tube rows was found to be of much less significance. Furthermore, they found that the effect of the number of tube rows was influenced by the fin and tube geometries and the Reynolds number. It has been established by Webb et al. [11] and Wang et al. [12], that the most effective methods of enhancing the heat transfer performance is to extend the fin surface. Additionally, the plain fin is the most widely used due to its ease of manufacture, simplicity of assembly and has low pressure drop characteristics.
Wang et al. [13] analysed experimentally compact slit fins exchangers with plain and louvred fins. Similar to previous studies, it was seen that the frictional performance had been affected only minimally by the number of rows, whereas louvred fins had been found to increase the heat transfer. Fernández-Seara et al. [14] designed an experimental setup to measure the heat transfer coefficients in the processes of vapour generation and its condensation in heat exchanger tubes. They extended the use of underlying method to a number of convection heat transfer cases which they noted would be useful to design engineers handling thermal problems.
An experimental study was carried out by Wang et al. [15] and in this study the airside performance characteristics of plain, semi-dimpled vortex generator (VG) and louvred fin-and-tube heat exchangers were comparatively evaluated. They investigated the effect of the number of tube rows and the effect of different fins on the heat transfer coefficient. Their results showed that number of tubes in a row had a negligible effect on the heat transfer coefficients for the louvred and semi-dimpled VG fin geometry. Moreover, the heat transfer coefficients for the louvred fin geometry were found to be higher (in the range of 2–15%) than in the case of the semi-dimpled VG geometry. It is however noted that these findings are valid for heat exchangers with number of tubes rows of between 2 and 4.
Liu et al. [16] conducted CFD investigations on the effect of perforation size, fin spacing, and number of perforations, on the Colburn factor corresponding to the air side. The thermal characteristics of finned-tube heat exchangers were also studied. The thermal performance of perforated heat exchanger was compared with that of the plain fin heat exchanger, and they found that the Colburn factor (air side) increased by more than 3 and 8% for constant fin spacing, respectively when the Reynolds number (air side) increases from 750 to 2350. Conversely, it was found that the Colburn factor (air side) was lower for plain fin heat exchanger in comparison to perforated fins heat exchanger.
Kalantari et al. [17] carried out a parametric study to cover a wide range of design configurations, geometrical and operating parameters. They investigated Reynolds numbers of up to 12,000 and found that longer fins, fin pitch and smaller tube diameter result in higher heat transfer coefficients. A correlation for the conjugate heat transfer coefficient was developed that applies to gas–liquid finned tube heat exchangers. In the correlation, the Nusselt number was expressed in terms of the Prandtl number and non-dimensional geometrical parameters.
Altwieb et al. [18] assessed the thermal performance of a multi-tube heat exchanger with plain fins and having different geometrical modification using three-dimensional CFD simulations. Three enhancements were analysed. These include fin spacing and longitudinal as well as transverse pitch. This was done to determine their influence on the Colburn and Fanning factors. Validation experiments were carried out and compared with the CFD; and were in turn utilised to calculate the Fanning and Colburn factors; and the local fin efficiency for each of the geometrical modifications. Two empirical correlations were developed for the Fanning and Colburn friction factors and the authors demonstrated predictions within 10% the experimental data. Similarly, Altwieb & Mishra [19] reported an experimental and numerical study on the thermal response of multi tube and fin heat exchanger with plain, louvred and semi-dimple vortex generator. The heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics were extensively investigated in this work. Two new design equations were developed for the heat transfer rate and the pressure drop behaviour.
The scope of the work summarised above is quite limited since most investigations are focussed only on the simple arrangement of perforations in the plain fins and only limited information is available on complex perforations in plain fins. Also limited information is available on louvered fins. Perforations are used to provide passive heat transfer enhancements in the heat exchanger. The effect of fin perforation on local and global performance indicators is a key and ongoing area of research that requires deeper understanding. Furthermore, the majority of design equations proposed have very limited range and do not include varied geometric parameters such as fin pitch, spacing and the presence of perforations.
The aim of this paper is to experimentally investigate the steady state heat transfer and thermal performance of a wide range of fin configurations (plain, louvred and perforated fin) heat exchanger. Using the experimental data, new mechanistic prediction models for the Colburn factor (j) and the Fanning friction factor (f) as a function of Reynolds number and heat exchanger geometry were developed and their prediction error margins analysed. It is envisaged that these equations will contribute to improved design and operation of such heat exchanger configurations.
2. Materials and Methods
An experimental setup was designed and developed to study the thermal behaviour of a multi-tube multi-fin heat exchanger. Details of the setup, equipment, instrumentation and uncertainties are given in the following sections.
2.1. Experimental Rig
The experimental setup is composed of the following parts: a 5-litre water tank (wrapped with a reflector foil to minimise heat loss), a heater, circulation pump integrated with a 0.9 kW heater unit, flow meter (Flowmax 44i with measuring range of 0.3–21 L/min or 0.018–1.26 m3/h), the heat exchanger testing unit, pressure transducers (IMP, with 0–10 V analogue output signal and range 0–4 bars), T-type thermocouples (with accuracy of ±0.15 °C), thermocouples data logger, RTD sensors (PT100, with range of −75–250 °C) and data acquisition system. Figure 1a–f includes various details including a schematic representation of the experimental setup and photos of the various test rig components. These have been use d for numerous previous experimental campaigns [20,21,22,23] with a high degree of consistency and reliability.
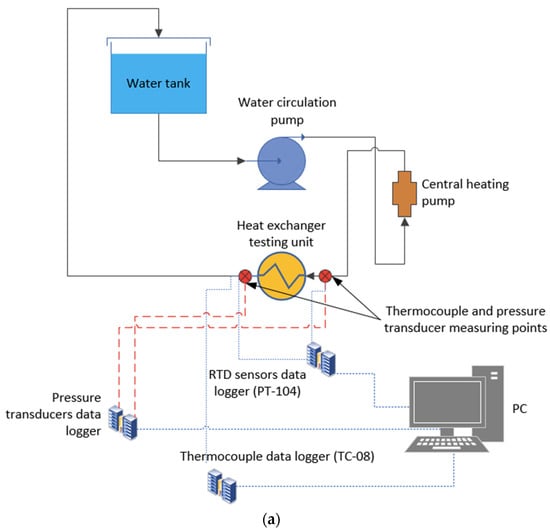
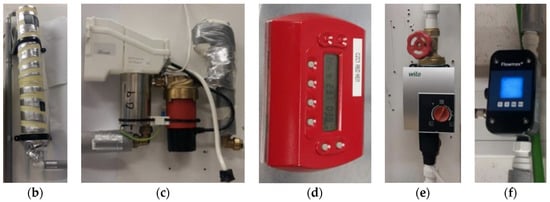
Figure 1.
Schematic of the experimental setup: (a) overall schematic of a heater flow loop, (b) insulated 5 litre water tank, (c) water heater, (d) heater controller unit, (e) water pump, (f) water flow meter.
2.1.1. Heat Exchanger Testing Unit
Figure 2a illustrates a schematic diagram of the heat exchanger testing unit. The testing unit was made from a 2-mm thick galvanised steel sheet. The dimensions of the unit include a length of 0.650 m; and corresponding width of 0.165 m and a height of 0.175 m. Airflow is supplied to the testing unit using a single-sided centrifugal fan which has an incorporated electric motor. The fan has a power rating of 119 W and is able to deliver a maximum of 610 m3/h airflow rate. The speed of the fan’s electric motor was controlled using a potentiometer.
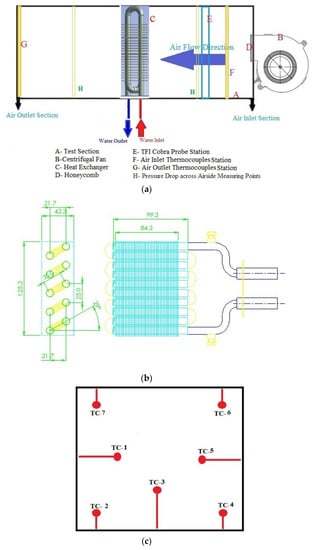
Figure 2.
(a) Schematic representation of the heat exchanger testing unit (b) dimensions of the plain fin heat exchanger (c) Arrangement of thermocouples at the specific measurement location.
The incoming flow was conditioned by using a honeycomb structure and various velocity components associated with incoming flow were measure by TFI cobra probe [24] at the entry to the test section. A typical cobra probe has four pressure sensing ports, and these pressure values are used to find the three flow velocity components. At the inlet the flow velocity was measured at 25 points to obtain the average velocity using the ASHRAE standard 41.2 [15,25].
The upstream and downstream air temperatures within the test section were measured at two specific locations. At each of the specific locations seven T-type thermocouples were used. The thermocouples have exposed welded copper/constantan tips to minimise it thermal inertia [15]. There are benefits of using multiple thermocouples at each location. Due to this the accuracy is improved since more samples are available for averaging and automatic averaging can be carried out simultaneously. The arrangement of these thermocouples at each specific location is shown in Figure 2c. During the experimentation, the thermocouples repeatability was ensured by taking multiple measurements and individual thermocouples were calibrated using a laboratory grade thermometer. All temperatures measured were recorded using a data acquisition system [Pico Technology (PicoTech)]. The data from the thermocouples were logged were then averaged.
The inlet and outlet water temperatures in the tubes were measured by PicoTech temperature probes (RTD-PT100). The accuracy of these probes is ±0.03 °C during the testing and the repeatability in the measurements was ensured by having multiple measurements. Also, the probes were calibrated using a standard thermometer. The water flow rate was measured by using the Flowmax 44i water flowmeter which is an ultrasonic-based volumetric flow meter with a ±2% maximum error of measurement and its repeatability is within ±0.5%.
The heat exchanger’s airside pressure drop was measured using a DPM TT550 micro-manometer. It has the ability of measuring the static pressure within the range: 0.4–5000 Pa. The heat exchanger’s water side pressure drop was measured using two pressure transducers. They were respectively placed at the water inlet and outlet tubes and were in turn connected to a PC via a USB-1616HS Series Data Acquisition interface. The voltage readings were then recorded. Using the calibration equations these voltage values were converted to corresponding pressure values.
2.1.2. Fin Geometries
Three main fin geometries were used to carry out this study. They are:
- Plain fin
- Perforated plain fin
- Louvred fin
The plain fin heat exchanger used in the present investigation is a multi-tube multi-fin type. There are two tube rows provided, and each tube has a diameter of 9.52 mm. Each of the rows included five 0.26-mm thick copper tubes and the overall length of each tube is 0.130 m. The bend of each tube has a diameter of 16 mm. The heat exchanger has 21 staggered 0.12 mm aluminium plain fins which have a width of 43.3 mm and a height 125.3 mm. Along the heat exchanger, the fins are placed at a distance of 4.23 mm from each other. The dimensions of the heat exchangers are shown in Figure 2b.
The novel heat exchanger model (perforated plain fins) was manufactured by arranging twelve equal diameter holes (3 mm) in each plain fin material. This is shown in Figure 3a,b with the inclined distribution of the 3-mm perforated holes. Finally, the louvred fins heat exchanger used has the same dimensions as the plain and perforated plain fin models. It is shown in Figure 3c and is identical to the louvred fins used in Wang et al. [15].
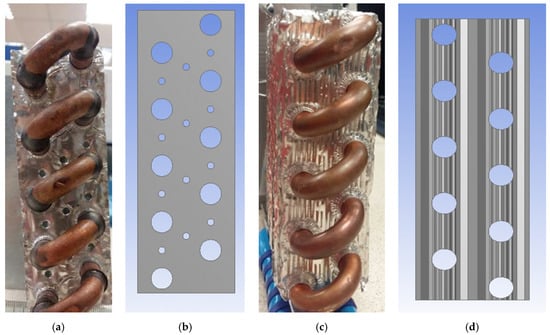
Figure 3.
(a) Picture of perforated plain fin type heat exchanger, (b) perforated holes’ arrangement, (c) louvred fins heat exchanger, (d) louvred fin shape.
2.1.3. Experimental Procedure
Steady-state tests provide thermal performances of the heat exchanger that are time independent. The test process involved drawing an airflow within the heat exchanger on the fin-side and allowing hot water to circulate through the tubes within the heat exchanger. Both the average air velocity (from 0.7 m/s to 4 m/s) and water flow rates (0.12 to 0.36 m3/h) were varied. The above indicates that the flow within the tubes is fully turbulent. The test matrix for the experiments carried out in this study are presented in Table 1. It shows that a total of 25 tests were carried out for up to 0.36 m3/h water flow rate with 0.7–4 m/s air velocities for each water flow rate.

Table 1.
Test matrix for the comparative steady-state tests conducted.
Each test point was run for about 2100 s (35 min) for the system to first attain steady conditions and overcome the initial high thermal inertia (as shown in Figure 4) before any readings were taken. The tests were further repeated twice to obtain representative measurements. An acceptable level of repeatability was obtained as measurements showed less than ±3% of deviation between each test condition.
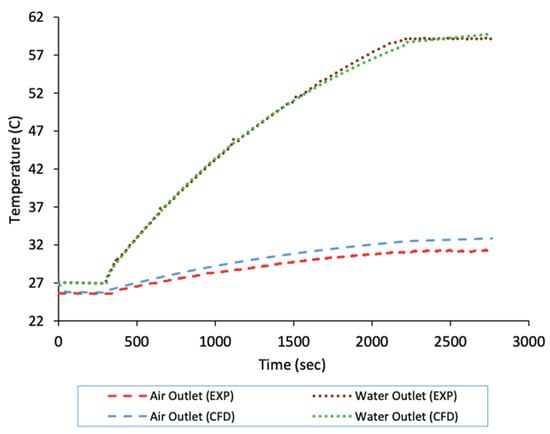
Figure 4.
Starting up test showing experimental and transient CFD temperatures for air and water outlets.
2.2. Data Analysis
To compute heat transfer rates, first the temperatures of the flowing streams (air and hot water) were measured at both the entry and exit locations. Also, the respective pressure drops were also measured. The heat transfer rates then can be computed using the following equation both for water and air, respectively.
where the subscripts and indicate air and water; and indicate inlet and outlet, respectively. The average value of the heat transfer rate can be computed as follows:
Furthermore, in order to carry out an assessment of heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics, the Colburn factor (j) and Fanning friction factor (f) were calculated and used for this purpose. The f-factor symbolises the pressure drop characteristics while the j-factor symbolises the heat transfer process and the j/f ratio is termed as the efficiency index. The Colburn factor and the friction factor are respectively calculated using:
where is the minimum free flow area of the air side; Ao is the total surface area of the air side; the variables and are the entrance and exit pressure loss coefficients. Equation (6) was developed by Kays and London [21] using the data from Figures 14–26 in McQuiston et al. [2]. Additionally, the Stanton and the Prandtl numbers used to define the Colburn j-factor in Equation (5) are, respectively, given as:
where is the heat transfer coefficient calculated using the total surface area of the air side; is the density of air, is the maximum air velocity; is the specific heat capacity of air; is the air dynamic viscosity and is its thermal conductivity. Since the - and -factors are most commonly used by researchers to assess the performance of heat exchanger fin strips, they will be used here for assessing the performance of the three geometries used in this study.
3. Results
In this section, the trend of the measured pressure drops, and heat transfer rates are studied and discussed in detail. These values were used to calculate the j- and f-factors, and the efficiency index for characterising the performance of the three fin and tube heat exchanger models.
3.1. Performance Comparison of Fin Geometry
The plots in Figure 5 show the trend of the mean heat transfer rate variation with respect to the average air velocity corresponding to the three heat exchangers (i.e., for perforated plain fins, ordinary plain fins and louvred fins) over a range of water flow rates namely 0.12, 0.18, 0.24, 0.3 and 0.36 m3/h. The error bars represent the combined uncertainty of the thermocouples and deviation between repeated measurements. The uncertainties were determined to be ±5%.
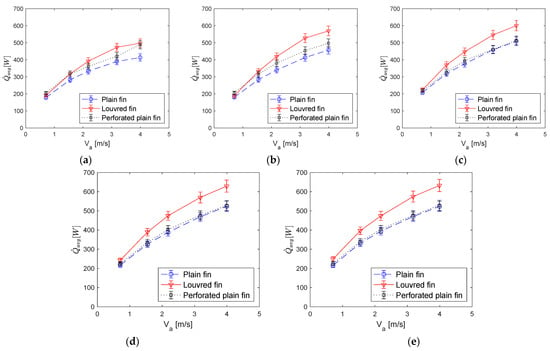
Figure 5.
Variation of against Va for various heat exchangers; (a) for water flow rate 0.12 m3/h, (b) for water flow rate 0.18 m3/h, (c) for water flow rate 0.24 m3/h, (d) for water flow rate 0.3 m3/h and (e) for water flow rate 0.36 m3/h.
Figure 5a shows the variation of average heat transfer rate against the average air velocity for water flow rate of 0.12 m3/h for different heat exchanger geometries. It can be seen from the figure that the louvred fins heat exchanger exhibited a higher mean heat transfer rate when compared with the perforated plain, and plain fin heat exchangers. For all cases, the average heat transfer rate increases as the water flow rate increases, first at a faster rate at lower air velocities and the rate of increase starts to decrease, more noticeably beyond 3 m/s. Figure 5b shows a similar trend but the rate of heat transfer increase beyond 3 m/s is now higher than the previous case and this is maintained for water flow rates of 0.24, 0.3 and 0.36 m3/h as shown in Figure 5c–e, respectively. The louvred fin geometry produced correspondingly higher increase in the average heat transfer rates especially at 0.3 and 0.36 m3/h water flow rates than at the lower water flow rates.
Figure 6a shows the variation of pressure gradient on air side with average air velocity at a given water flow rate. It can be seen that for louvered fins heat exchanger pressured drop increases almost linearly with air velocity. The louvred fin geometry exhibits much higher pressure drops than the other geometries. It is seen from the figure that the louvered fin produces up to 380% more pressure drop than the plain fin geometry at = 4 m/s while the perforated plain fin geometry produced a maximum of 65% difference when compared with the plain fin geometry. The large pressure drop in the louvred fin heat exchanger is due to the uneven surface of the louvred fins which result in higher pressure losses. As expected, the pressure drop behaviour remains constant with changing water flow rates giving only marginal differences (which are within experimental uncertainties) as seen in Figure 6b–e.
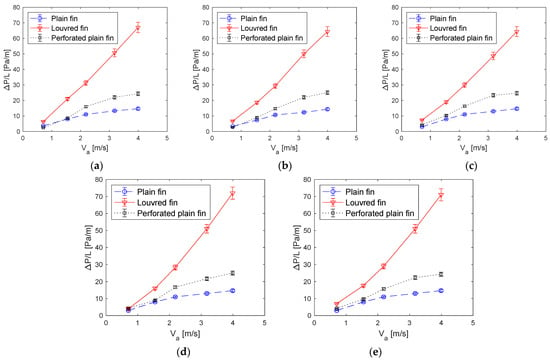
Figure 6.
Variation of against for various heat exchanger; (a) at water flow rate of 0.12 m3/h, (b) at water flow rate of 0.18 m3/h, (c) at water flow rate of 0.24 m3/h, (d) at water flow rate of 0.3 m3/h and (e) at water flow rate of 0.36 m3/h.
Looking at the heat transfer characteristics and corresponding pressure drops associated with different geometries (Figure 6 and Figure 7), it can be seen that quantitatively, at the lowest water flow rates of 0.12 m3/h, an increase in heat transfer rate was noticed for the louvred fins as compared to plain fins (about 13% lower) and plain perforated fins (2.7% lower). These values change to about 15% for plan fins and 6% for the perforated plain fin model at a water flow rate of 0.18 m3/h. At flow rate of 0.24 m3/h again the corresponding values were 13% and 11%. However, such significant increase of the heat transfer was made at the expense of a significant air pressure drop (Figure 6). It is assumed that the perforated fins increased the flow vorticity. At 0.3 m3/h almost similar levels of change in heat transfer rate was noticed. In general, there is an increasing trend in heat transfer as the water flow rate increases for all types of heat exchangers. This is evidenced by an increase in the rate of heat transfer from about 500 to 600 W for louvered fins heat exchanger, 400 W to 523 W for plain fin heat exchanger, and 488 to 528 W for perforated plain fin heat exchanger at = 4 m/s. Nevertheless, the perforated plain fin model appears to be least affected by an increase in water flow rate. Its heat transfer rate has only marginally increased at higher water flow rates. This may be because the perforations have reduced the heat transfer area below a certain threshold where the fluid flow rates can have a significant effect. As a result, in certain situations this aspect should be kept in view whilst designing a perforated plain heat exchanger.
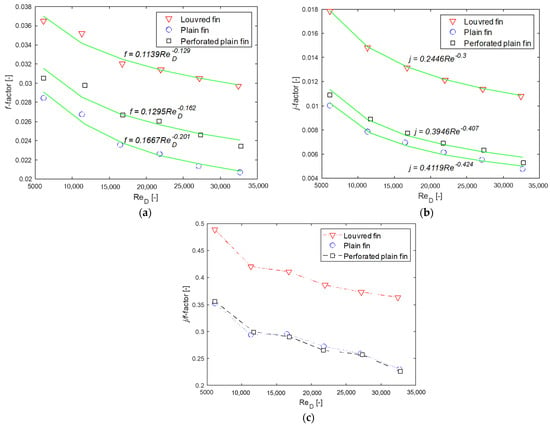
Figure 7.
Variations of (a) friction f-factor (b) Colburn j-factor and (c) efficiency index j/f for different fin arrangements as a function of Reynolds number.
Figure 7a shows the variation of friction factor (f) for the heat exchangers as a function of Reynolds number. It shows that the friction factor decreases with increasing Reynolds number and is consistent with previous observations including those in the Moody chart for pipe flows. For each of heat exchanger, there is a steep decreasing slope in the curve between Re = 11,000 and 17,000 before slope of the curve becomes flatter. As is seen in the plots, power law curves were fitted to the three sets of data (louvred, plain and perforated fins). This was done to develop a prediction model for f as a function of . It can be seen that all the heat exchangers show slightly different slopes (power of Reynolds number are −0.129, −0.162 and −0.201). For the j-factor the corresponding values of indices are −0.300, −0.407 and −0.424 for the louvred, plain and perforated plain fin geometries, respectively.
Figure 7b shows the variation of the Colburn j-factor of the three heat exchangers as a function of Reynolds number. It shows that the Colburn j-factor decreases with increasing Reynolds number indicating a higher heat transfer rate at lower Reynolds numbers. The louvred fin heat exchanger gave the highest j values within the range 0.011–0.02 compared to 0.005–0.011 and 0.004–0.010 for the perforated and plain fin heat exchangers respectively. The fitted power law curves to the three sets of data give prediction models for j as a function of . Similar to the f-factor, for the j-factor, there is a slight decrease in slope from plain to perforated fin to louvred with the coefficients and indices of the equations being 0.2446, 0.3946, 0.4119 and −0.3, −0.407 and −0.424, respectively. Figure 7c depicts efficiency index (j/f) variations corresponding to three different heat exchangers as a function of Reynolds number with an inverse relationship existing between the efficiency index and . The plain and perforated models exhibited similar behaviour in j/f magnitudes of 0.022–0.036 across the entire range studied. However, the louvred fin gave much larger values of the efficiency index of between 0.37 and 0.49. While the louvred fin exhibits a far more superior efficiency than the other two geometries, the plain and perforated plain fin models gave near identical behaviour throughout the experimental range of investigated–with both geometries exhibiting a similar efficiency index across the experimental range. The nature of the curves in Figure 7a–c clearly establish that the friction, Colburn factors and the efficiency index asymptotically decrease with the Reynolds number for all the three different heat exchanger models. It can be seen that the Colburn and friction factor values are significantly higher for the louvred fins heat exchanger as compared to the plain and perforated plain fin geometries. This observation can be explained based on the higher surface area available for the louvred fin heat exchanger as compared to the plain and perforated plain fin heat exchangers. Due to this the heat transfer coefficient for louvered heat exchanger is higher which in turn leads to high Colburn j-factor values.
Based on the heat transfer measurements it can be shown that there is an improvement in the average heat transfer rate of nearly 10% and 20% for the perforated plain fin and louvred fin heat exchangers, respectively, when compared to the plain fin geometry. However, this improvement was accompanied by large increases in the corresponding pressure drop on the airside respectively as earlier highlighted. The data collected during the current experiments and after processing were used for the development of the two new design correlations for predicting the Fanning f- and Colburn j-factors as functions of the flow velocity and area available. To represent these in non-dimensional form, Reynolds number and an area ratio term (the ratio of the heat exchanger’s fin surface area divided by the total surface area) have been used in the correlations.
3.2. Development of New Empirical Relations for Fanning f and Colburn j-Factor
For the complex geometries used in the present investigation, the experimental data obtained in the present investigation were used for developing a set of novel design equations for the prediction of Fanning f- and the Colburn j-factors. As previously stated, the f- and j-factors quantify the pressure drop and heat transfer characteristics of the heat exchanger units. Therefore, it is imperative to develop correlations that relate them with the flow, fluid, and geometrical parameters. The correlation was developed using multivariate regression analysis using the curve fitting tools in Microsoft Excel’s Solver® which are based on the least squares’ method. The dimensionless parameters used to develop the predictive correlation are, as mentioned earlier, the Reynolds number, and the ratio between total fin surface area to the total heat transfer surface area of the heat exchanger which is a design parameter used by Palmer et al. [26] that can be used for estimating heat transfer areas needed for a given amount of heat to be transmitted. Other authors have used similar dimensionless groupings to correlate the heat transfer properties of fin and tube heat exchangers [13,17,18]. The newly derived equations are as follows:
where is the Reynolds number calculated using the hydraulic diameter of the heat exchanger face’s cross-section; Dc is the outside diameter of the fin’s collar (m): is the total surface area of the fins (m2); is the heat exchanger’s overall heat transfer surface area (m2). The Equations (9) and (10) show that the Colburn and Fanning factors are inversely proportional to the Reynolds numbers which are consistent with experimental observations (in Figure 7a,b). Additionally, the relatively large indices (29.218 and 12.811) for the parameter reflects the small magnitude of the ratio. It is advised that the equations are valid within the Reynolds number range: and for the heating cycle in forced convection heat transfer.
In order to estimate the accuracy of predictions from the developed equations Figure 8a,b have been prepared to depict the relationship between the experimentally evaluated values and the predicted values of Colburn factor (j) and Fanning friction factor (f), respectively. From the Figure 7a,b, it can be concluded that there is a good match between the experimental and the computed values and almost 100% of the data lie within ±15% error band. Furthermore, the correlation coefficients which compare the goodness of fit between the experimentally evaluated and predicted data for Equations (9) and (10) are 0.853 and 0.811, respectively. As such, the newly developed correlations can be used with confidence.
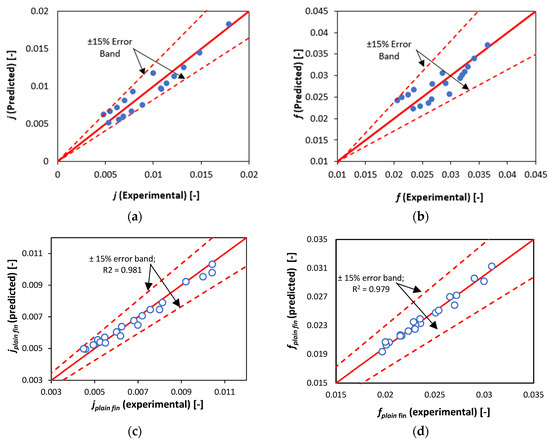
Figure 8.
Comparisons of predicted (by Equations (9) and (10)) and experimental values of (a) Colburn j-factor and (b) Fanning f-factor (c) plain fin Colburn factor (d) plain fin Fanning factor.
In order to account for geometric variations of the fins (their spacing , longitudinal pitch and transverse pitch ), validated CFD data (previously reported in ref. [18]) was combined with the experimental data obtained in this study to generate new empirical correlations for j and f for the plain fin model using nonlinear least squares regression. The longitudinal pitches considered were 20, 22 and 24 mm; transverse pitches were 23.5, 25 and 26.5 mm; while the fin spacings investigated were 3.7, 4.2 and 4.7 mm at air Reynolds numbers of 6000 to 32,000. There were a combined total of 21 points (15 CFD and 6 experimental). Figure 7c,d show that the correlations have very high goodness of fit R2 values of 0.931 and 0.979 for the j and f factors, respectively, and the predictions of the new correlations are well within ±15% of the underlying CFD and experimental data. The two new correlations are given below as follows:
To summarise, it can be concluded that the developed equations are very much capable of predicting the Fanning f- and Colburn j-factors of these heat exchangers having the stated fin geometries with sufficient accuracy. Consequently, the equations can be used during the design and evaluation of existing multi-tube multi-fin heat exchanger with plain, perforated or louvred fins.
4. Conclusions
This study has presented novel geometric configurations for multi-tube multi-fin heat exchanger. The configurations were designed in order to conduct a robust experimental investigation with three heat exchanger geometries namely plain, perforated plain and louvred fin heat exchangers. Some important observations were made during the experiments and analysis of the pressure drop and heat transfer data. It was found that for all inlet air and water flow rates and hence velocities, the louvred fins produced the highest heat transfer rate. This was attributed to increased surface area available for heat transfer. Conversely, it also produced the highest pressure losses when compared to the other two designs. Also, while the new perforated design produced a slightly higher pressure drop than the plain fin design, due to the vortices generated by the perforations, an enhancement in its heat transfer characteristics was observed when comparing with the plain and louvred fin models. This enhancement is relatively high at a small water flow rate. The experimental results were subsequently used to generate a set of novel empirical equations for design optimisation which can be used to predict the heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of the heat exchangers represented by the Colburn and Fanning factors. The empirical equations were developed as functions of the heat exchangers’ geometrical parameters, and we have shown that the performance of the equations are well within acceptable ±15% error margins in relation to the experimental data.
Author Contributions
M.A.: Experimentation, Data curation, formal analysis, Investigation, methodology, validation, visualization, writing—original draft; R.M.: Conceptualisation, supervision, writing—review and editing; A.M.A.: Writing—review & editing, formal analysis; K.J.K.: supervision, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shah, R.K.; Sekulic, D.P. Fundamentals of Heat Exchanger Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mcquiston, F.C.; Parker, J.D.; Spilter, J.K. Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning: Analysis and Design; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Naphon, P.; Wongwises, S. A review of flow and heat transfer characteristics in curved tubes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2006, 10, 463–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulukkanam, K. Heat Exchanger Design Handbook, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, E.E. A basis for rational design of heat transfer apparatus. J. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1915, 37, 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Sieder, E.N.; Corporation, G.E.T.A.T.E.F.W.; York, N. Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop of Liquids in Tubes O Oil A, Heating Oil B, Heating Oil A, Cooling Oil C, Cooling; American Chemical Society: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Colburn, A.P. A method of correlating forced convection heat-transfer data and a comparison with fluid friction. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1964, 7, 1359–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittus, F.W.; Boelter, L.M.K. Heat transfer in automobile radiators of the tubular type. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 1985, 12, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-J.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-T. Sensible heat and friction characteristics of plate fin-and-tube heat exchangers having plane fins. Int. J. Refrig. 1996, 19, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Madi, M.; Johns, R.; Heikal, M. Performance characteristics correlation for round tube and plate finned heat exchangers. Int. J. Refrig. 1998, 21, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.; Kim, N.-H. Advances in Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger Technology. J. Enhanc. Heat Transf. 2007, 14, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C. A survey of recent patents of fin-and-tube heat exchangers from 2001 to 2009. Int. J. Air-Cond. Refrig. 2010, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Lee, W.-S.; Sheu, W.-J. A comparative study of compact enhanced fin-and-tube heat exchangers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2001, 44, 3565–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Seara, J.; Uhía, F.J.; Sieres, J.; Campo, A. A general review of the Wilson plot method and its modifications to determine convection coefficients in heat exchange devices. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.-C.; Chen, K.-Y.; Liaw, J.-S.; Tseng, C.-Y. An experimental study of the air-side performance of fin-and-tube heat exchangers having plain, louver, and semi-dimple vortex generator configuration. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 80, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Yan, G. A numerical study on the air-side heat transfer of perforated finned-tube heat exchangers with large fin pitches. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 100, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, H.; Ghoreishi-Madiseh, S.A.; Kurnia, J.C.; Sasmito, A.P. An analytical correlation for conjugate heat transfer in fin and tube heat exchangers. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 164, 106915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altwieb, M.; Kubiak, K.J.; Aliyu, A.M.; Mishra, R. A new three-dimensional CFD model for efficiency optimisation of fluid-to-air multi-fin heat exchanger. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 19, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altwieb, M.O.; Mishra, R. Experimental and Numerical Investigations on the Response of a Multi Tubes and Fins Heat Exchanger under Steady State Operating Conditions. In Proceedings of the 6th International and 43rd National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power, Allahabad, India, 15–17 December 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Aliyu, A.; Charlton, M.; Mishra, R.; Asim, T.; Oliveira, A. Local multiphase flow characteristics of a severe-service control valve. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 195, 107557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Charlton, M.; Asim, T.; Mishra, R.; Townsend, A.; Blunt, L. Quantification of additive manufacturing induced variations in the global and local performance characteristics of a complex multi-stage control valve trim. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 190, 107053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, T.; Mishra, R.; Oliveira, A.; Charlton, M. Effects of the geometrical features of flow paths on the flow capacity of a control valve trim. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 172, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asim, T.; Charlton, M.; Mishra, R. CFD based investigations for the design of severe service control valves used in energy systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 153, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- TFI. Cobra Probe. 2021. Available online: https://www.turbulentflow.com.au/Products/CobraProbe/CobraProbe.php (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- ASHRAE. HVAC Design Manual for Hospitals and Clinics; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, E.; Mishra, R.; Fieldhouse, J. An optimization study of a multiple-row pin-vented brake disc to promote brake cooling using computational fluid dynamics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2009, 223, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).