The Applicability of Biogeography-Based Optimization and Earthworm Optimization Algorithm Hybridized with ANFIS as Reliable Solutions in Estimation of Cooling Load in Buildings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Established Database
3. Methodology
3.1. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Interface System (ANFIS)
3.2. Biogeography-Based Optimization (BBO)
3.3. Earthworm Optimization Algorithm (EWA)
- (1).
- Reproduction 1
- (2).
- Reproduction 2
- (3).
- Weighted Summation
- (4).
- Cauchy mutation
- (5).
- Steps for EWA algorithm as applied to OPF in brief
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Accuracy Indicators
4.2. Incorporated FIS with Optimizers
4.3. Error Analysis
4.4. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Z.; Haghighat, F.; Fung, B.C.; Yoshino, H. A decision tree method for building energy demand modeling. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanas, A.; Xifara, A. Accurate quantitative estimation of energy performance of residential buildings using statistical machine learning tools. Energy Build. 2012, 49, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zhang, C.; Bibi, T.; Zhu, L.; Cao, L.; Li, C.; Hsiao, P.-C. Investigation of five different low-cost locally available isolation layer materials used in sliding base isolation systems. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 154, 107127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Lombard, L.; Ortiz, J.; Pout, C. A review on buildings energy consumption information. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Ren, H. China building energy consumption: Situation, challenges and corresponding measures. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Terzija, V. Review on deep learning applications in frequency analysis and control of modern power system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 136, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, G.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Poulton, G.; James, G.; Wall, J. Adaptive HVAC zone modeling for sustainable buildings. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Li, B.; Steemers, K. Energy policy and standard for built environment in China. Renew. Energy 2005, 30, 1973–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, M.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S. Experimental study of predamaged columns strengthened by HPFL and BSP under combined load cases. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 17, 1210–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yezioro, A.; Dong, B.; Leite, F. An applied artificial intelligence approach towards assessing building performance simulation tools. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, D.B.; Hand, J.W.; Kummert, M.; Griffith, B.T. Contrasting the capabilities of building energy performance simulation programs. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hou, K.; Xu, X.; Jia, H.; Zhu, L.; Mu, Y. Probabilistic energy flow calculation for regional integrated energy system considering cross-system failures. Appl. Energy 2022, 308, 118326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedzadeh, S.; Rahimian, F.P.; Rastogi, P.; Glesk, I. Tuning machine learning models for prediction of building energy loads. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Sun, Y. A piecewise probabilistic harmonic power flow approach in unbalanced residential distribution systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 141, 108114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, W.; Li, M.; Huang, K. Building a series of consistent night-time light data (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia by integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.-x.; Magoulès, F. A review on the prediction of building energy consumption. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Foong, L.K. Predicting Electrical Power Output of Combined Cycle Power Plants Using a Novel Artificial Neural Network Optimized by Electrostatic Discharge Algorithm. Measurement 2022, 198, 111405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, L.K.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, C.; Xu, C. Efficient metaheuristic-retrofitted techniques for concrete slump simulation. Smart Struct. Syst. Int. J. 2021, 27, 745–759. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Ban, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Yin, L.; Liu, S.; Zheng, W. Adaptive control of time delay teleoperation system with uncertain dynamics. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 928863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Ma, T.; Li, M.; Huang, K. Mapping urban dynamics (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia using consistent nighttime light data from DMSP and VIIRS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, D.B.; Lawrie, L.K.; Winkelmann, F.C.; Buhl, W.F.; Huang, Y.J.; Pedersen, C.O.; Strand, R.K.; Liesen, R.J.; Fisher, D.E.; Witte, M.J. EnergyPlus: Creating a new-generation building energy simulation program. Energy Build. 2001, 33, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citherlet, S. Towards the Holistic Assessment of Building Performance Based on an Integrated Simulation Approach. 2001. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Towards-the-holistic-assessment-of-building-based-Citherlet/e4d8bbb0ad26827f539df78bc32749bf0e402d88 (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Duanmu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, Z.J.; Li, X. A simplified method to predict hourly building cooling load for urban energy planning. Energy Build. 2013, 58, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husaunndee, A.; Lahrech, R.; Vaezi-Nejad, H.; Visier, J. SIMBAD: A simulation toolbox for the design and test of HVAC control systems. In Proceedings of the 5th International IBPSA Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 8–10 September 1997; pp. 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, M.C.; Finlayson, N.; Kummert, M.; Macbeth, J. Live Energy TRNSYS–TRNSYS Simulation within Google SketchUp. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International IBPSA Conference, Glasgow, Scotland, 27–30 July 2009; pp. 1389–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, B.; Plettner, J.; Wemhöner, C.; Wenzel, T. CARNOT Blockset-User’s Guide; Solar-Institut Jülich der FH Aachen: Aachen, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Ma, C.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, N.; Guo, L. Geometrically Enabled Soft Electroactuators via Laser Cutting. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1900664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, L.; Mou, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, X.; Zheng, W.; Yin, L. Improved Four-channel PBTDPA control strategy using force feedback bilateral teleoperation system. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2022, 20, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, S.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Control of Time Delay Force Feedback Teleoperation System with Finite Time Convergence. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 877069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.A.; Neocleous, C.; Schizas, C. Building heating load estimation using artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 November 1997; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Chen, D. Data-driven dynamic harmonic model for modern household appliances. Appl. Energy 2022, 312, 118759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalina, T.; Virgone, J.; Blanco, E. Development and validation of regression models to predict monthly heating demand for residential buildings. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Cao, C.; Lee, S.E. Applying support vector machines to predict building energy consumption in tropical region. Energy Build. 2005, 37, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Haghighat, F. Development of Artificial Neural Network based heat convection algorithm for thermal simulation of large rectangular cross-sectional area Earth-to-Air Heat Exchangers. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, C.; Eang, L.S.; Yang, J.; Santamouris, M. Forecasting diurnal cooling energy load for institutional buildings using Artificial Neural Networks. Energy Build. 2016, 121, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, R.; Rodríguez, F.; Castilla, M.; Arahal, M.R. A prediction model based on neural networks for the energy consumption of a bioclimatic building. Energy Build. 2014, 82, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platon, R.; Dehkordi, V.R.; Martel, J. Hourly prediction of a building’s electricity consumption using case-based reasoning, artificial neural networks and principal component analysis. Energy Build. 2015, 92, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Moayedi, H.; Bahiraei, M.; Foong, L.K. Employing TLBO and SCE for optimal prediction of the compressive strength of concrete. Smart Struct. Syst. 2020, 26, 753–763. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Hu, C.; Liu, G.; Xue, W. Building’s electricity consumption prediction using optimized artificial neural networks and principal component analysis. Energy Build. 2015, 108, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-M.; Paterson, G.; Mumovic, D.; Steadman, P. Improved benchmarking comparability for energy consumption in schools. Build. Res. Inf. 2014, 42, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayatian, F.; Sarto, L. Application of neural networks for evaluating energy performance certificates of residential buildings. Energy Build. 2016, 125, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Joseph, A.J.J.M.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, C.; Gul, D.; Schellenberg, A.; Hu, N. Deterministic snap-through buckling and energy trapping in axially-loaded notched strips for compliant building blocks. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 02LT03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samui, P.; Kim, D.; Viswanathan, R. Spatial variability of rock depth using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and multivariate adaptive regression spline (MARS). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4265–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-S. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z. Subset simulation with adaptable intermediate failure probability for robust reliability analysis: An unsupervised learning-based approach. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2022, 65, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, S.; Sadegh, S.S. Forecasting energy consumption using ensemble ARIMA–ANFIS hybrid algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 82, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, H.; Bai, L.; Tang, M.; Chen, H.; Su, D. Fragility analyses of bridge structures using the logarithmic piecewise function-based probabilistic seismic demand model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Biogeography-based optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2008, 12, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.K. Biogeography-based optimization for different economic load dispatch problems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 25, 1064–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-G.; Deb, S.; Coelho, L.D.S. Earthworm optimisation algorithm: A bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimisation problems. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 2018, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samui, P.; Kumar, R.; Yadav, U.; Kumari, S.; Bui, D.T. Reliability analysis of slope safety factor by using GPR and GP. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Kumar, D.; Samui, P.; Roy, L.B.; Goh, A.; Zhang, W. Application of soft computing techniques for shallow foundation reliability in geotechnical engineering. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Samui, P. Reliability analysis of pile foundation using ELM and MARS. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 3447–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardani, M.N.; Baghban, A.; Hamzehie, M.E.; Baghban, M. Phase behavior modeling of asphaltene precipitation utilizing RBF-ANN approach. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Jahed Armaghani, D.; Tahir, M.; Pham, B.T.; Huynh, V.V. A combination of feature selection and random forest techniques to solve a problem related to blast-induced ground vibration. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhong, X.; Foong, L.K. Predicting the splitting tensile strength of concrete using an equilibrium optimization model. Steel Compos. Struct. Int. J. 2021, 39, 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, H.; Song, C.; Wang, Z. Predicting compressive strength of manufactured-sand concrete using conventional and metaheuristic-tuned artificial neural network. Measurement 2022, 194, 110993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X.; Jia, B. A novel artificial bee colony algorithm for structural damage detection. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 6, 3743089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
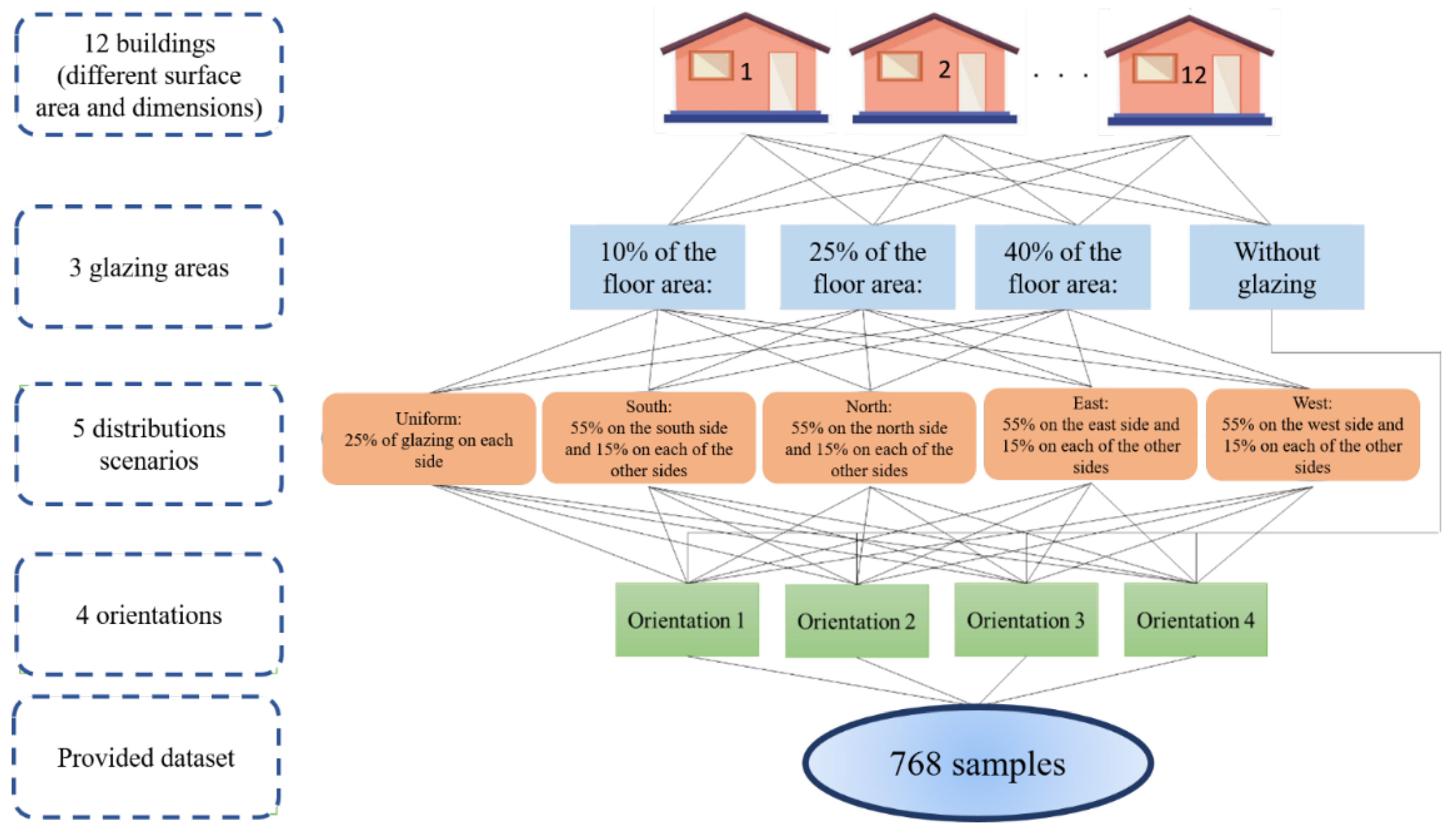

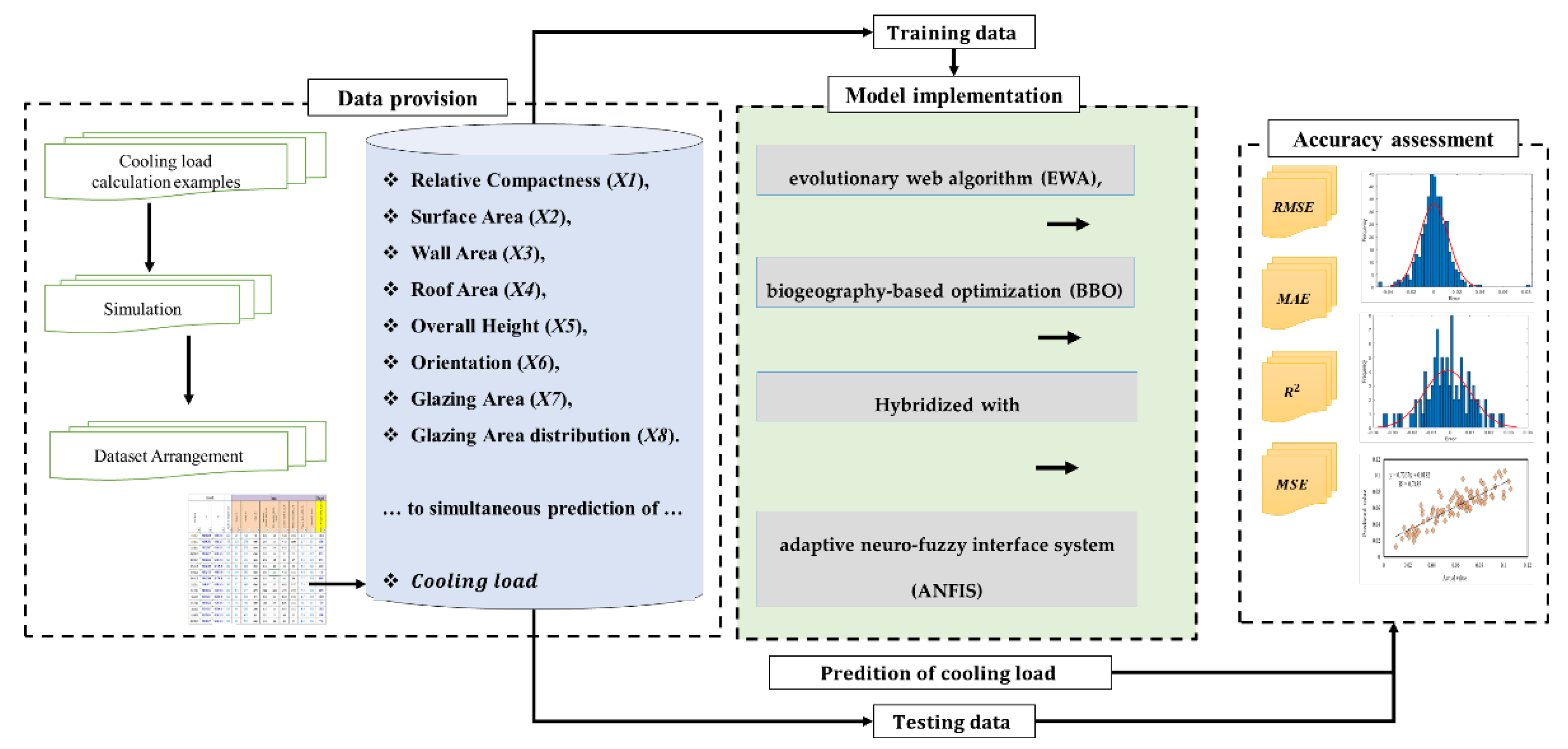
| Input Variables | Count | Mean | Min | Max | Std. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative Compactness (-) | 768 | 0.764 | 0.62 | 0.98 | 0.105 |
| Surface Area (m2) | 768 | 671.7 | 514.5 | 808.5 | 88.08 |
| Wall Area (m2) | 768 | 318.5 | 245 | 416.5 | 43.62 |
| Roof Area (m2) | 768 | 176.6 | 110.25 | 220.5 | 45.16 |
| Overall Height (m) | 768 | 5.25 | 3.5 | 7 | 1.751 |
| Orientation (-) | 768 | 3.5 | 2 | 5 | 1.118 |
| Glazing Area (m2) | 768 | 0.234 | 0 | 4 | 0.133 |
| Glazing Area Distribution | 768 | 2.812 | 0 | 5 | 1.55 |
| Output Variables | Count | Mean | Min | Max | Std. |
| CL (kwh/m2) | 768 | 24.58 | 10.9 | 48.03 | 9.513 |
| Swarm Size | Training Dataset | Testing Dataset | Scoring | Total Score | Rank | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | Training | Testing | |||||
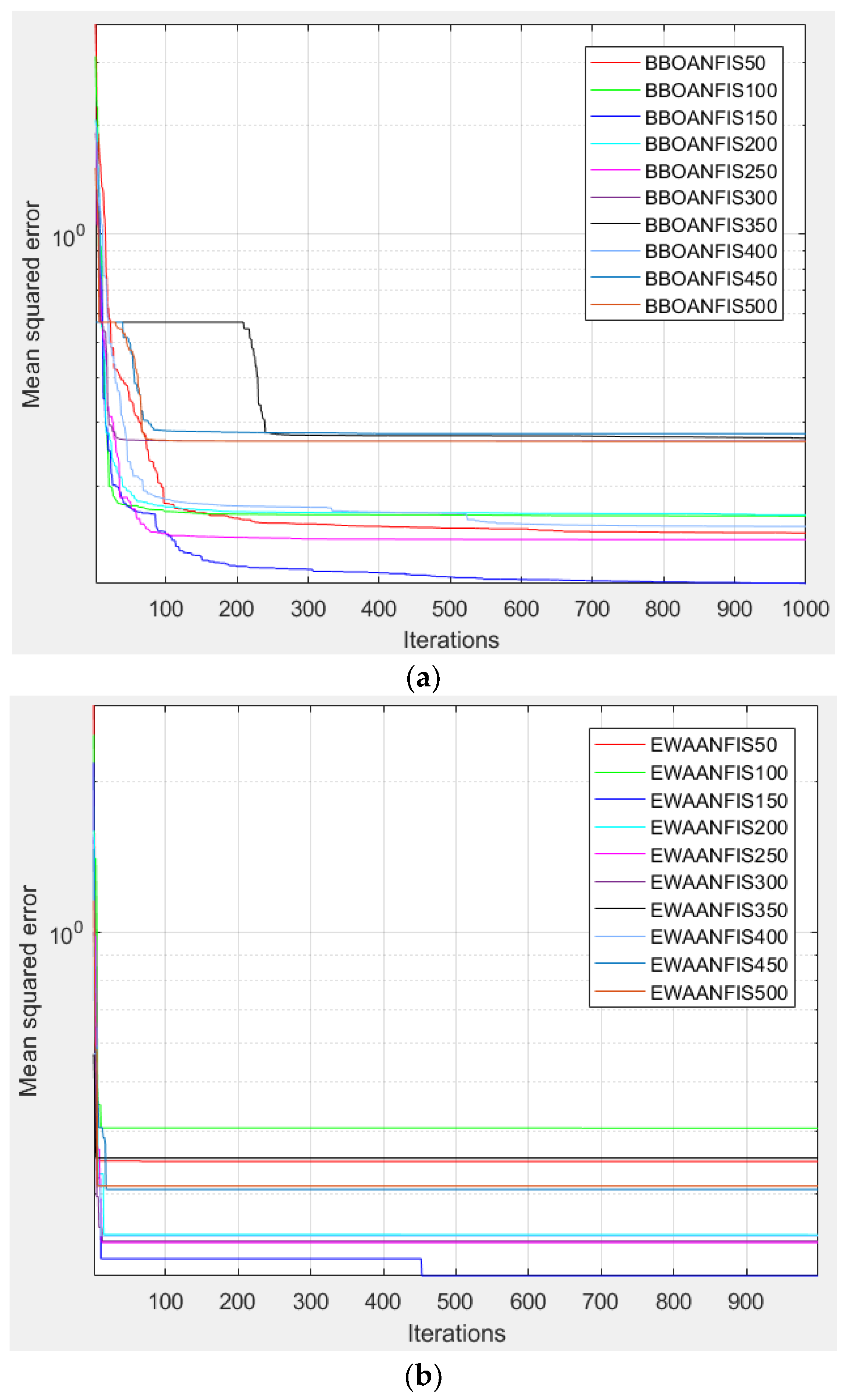
| 50 | 0.1482 | 0.95714 | 0.13877 | 0.96273 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 32 | 3 |
| 100 | 0.16536 | 0.94635 | 0.15491 | 0.95333 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 26 | 4 |
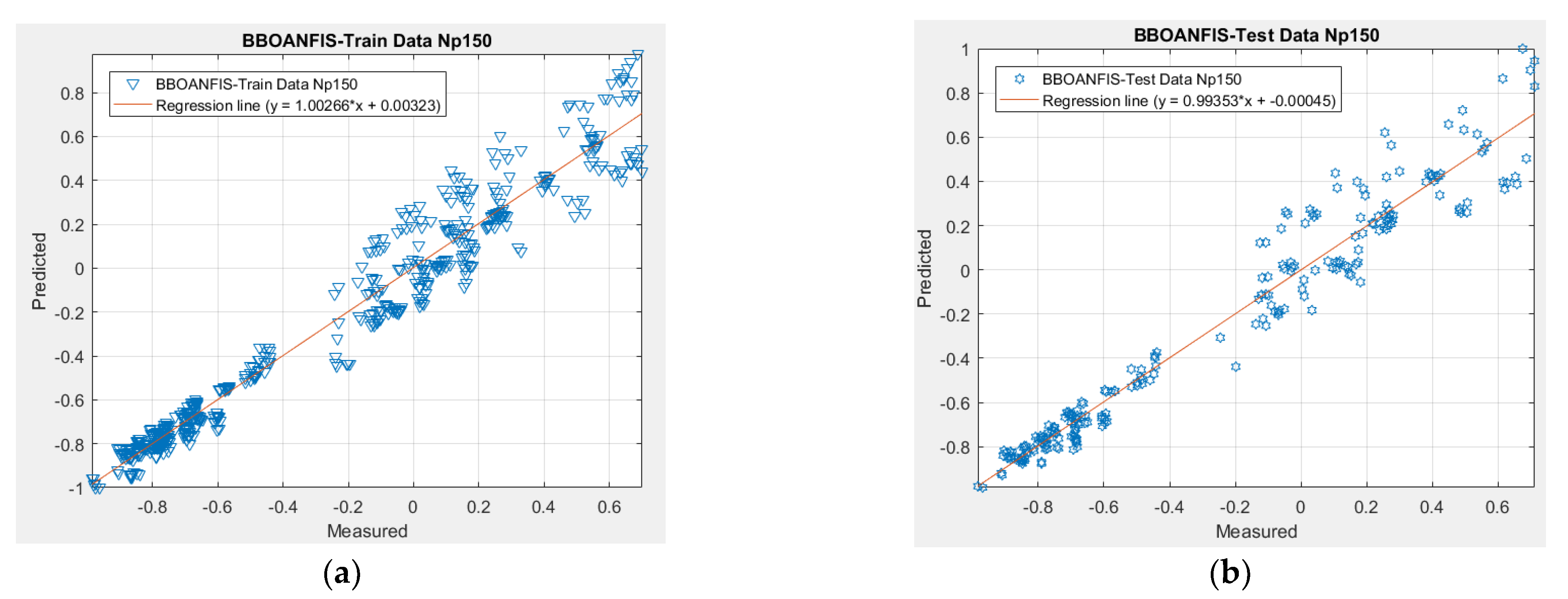
| 150 | 0.10731 | 0.97776 | 0.11282 | 0.97552 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 40 | 1 |
| 200 | 0.16644 | 0.94562 | 0.15983 | 0.95024 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 20 | 6 |
| 250 | 0.14229 | 0.96056 | 0.13831 | 0.96298 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 36 | 2 |
| 300 | 0.22812 | 0.89512 | 0.21526 | 0.90772 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 8 |
| 350 | 0.23762 | 0.88563 | 0.22298 | 0.90061 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 9 |
| 400 | 0.15479 | 0.95315 | 0.15504 | 0.95324 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 26 | 4 |
| 450 | 0.25089 | 0.87155 | 0.23661 | 0.8873 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 10 |
| 500 | 0.22509 | 0.89805 | 0.20959 | 0.91275 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 16 | 7 |
| Swarm Size | Training Dataset | Testing Dataset | Scoring | Total Score | Rank | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | Training | Testing | |||||
| 50 | 0.30417 | 0.80414 | 0.30231 | 0.80795 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 10 |
| 100 | 0.24549 | 0.8774 | 0.23744 | 0.88646 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 16 | 7 |
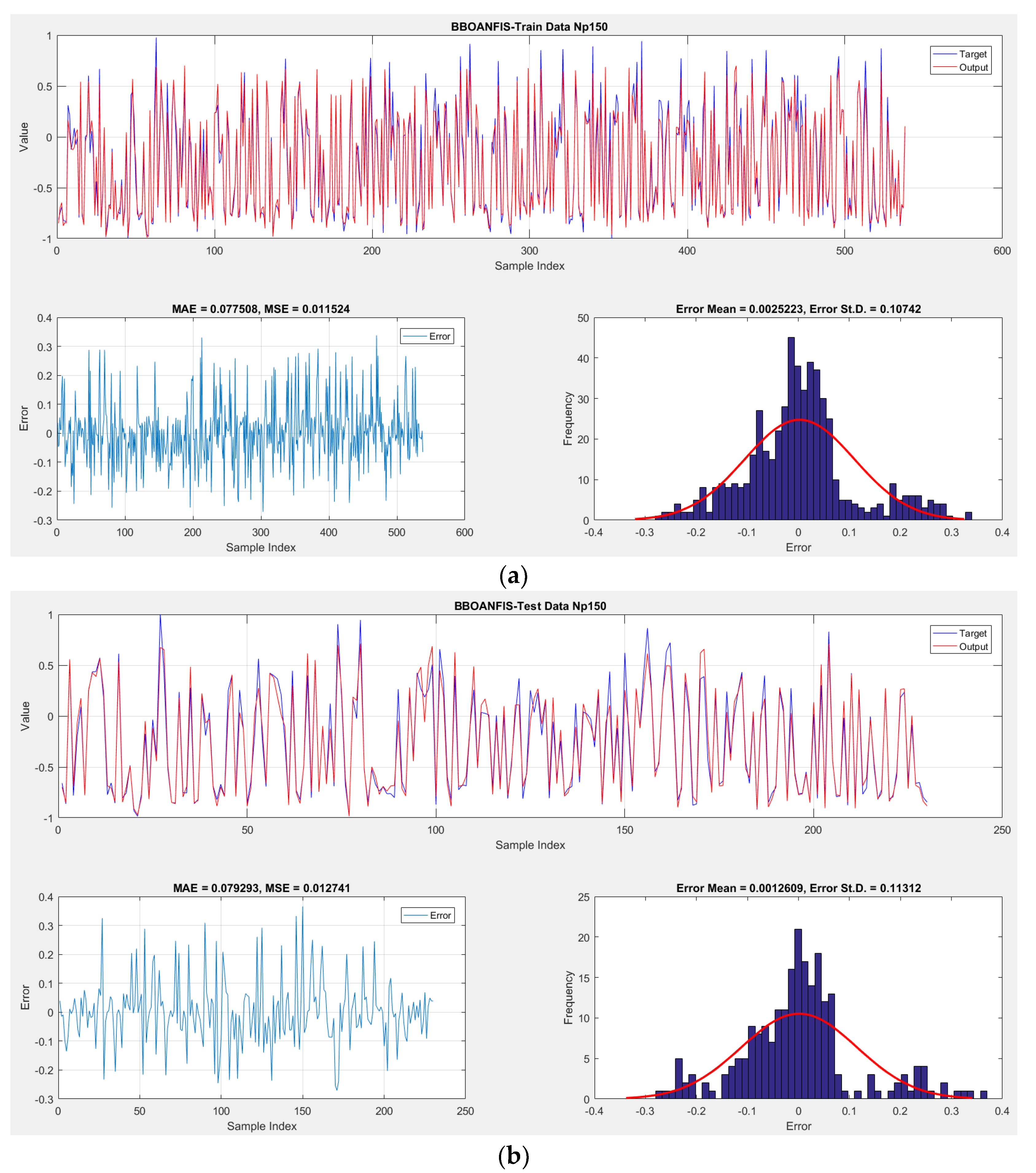
| 150 | 0.1936 | 0.92566 | 0.21073 | 0.91175 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 34 | 2 |
| 200 | 0.24025 | 0.88293 | 0.23395 | 0.88998 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 24 | 5 |
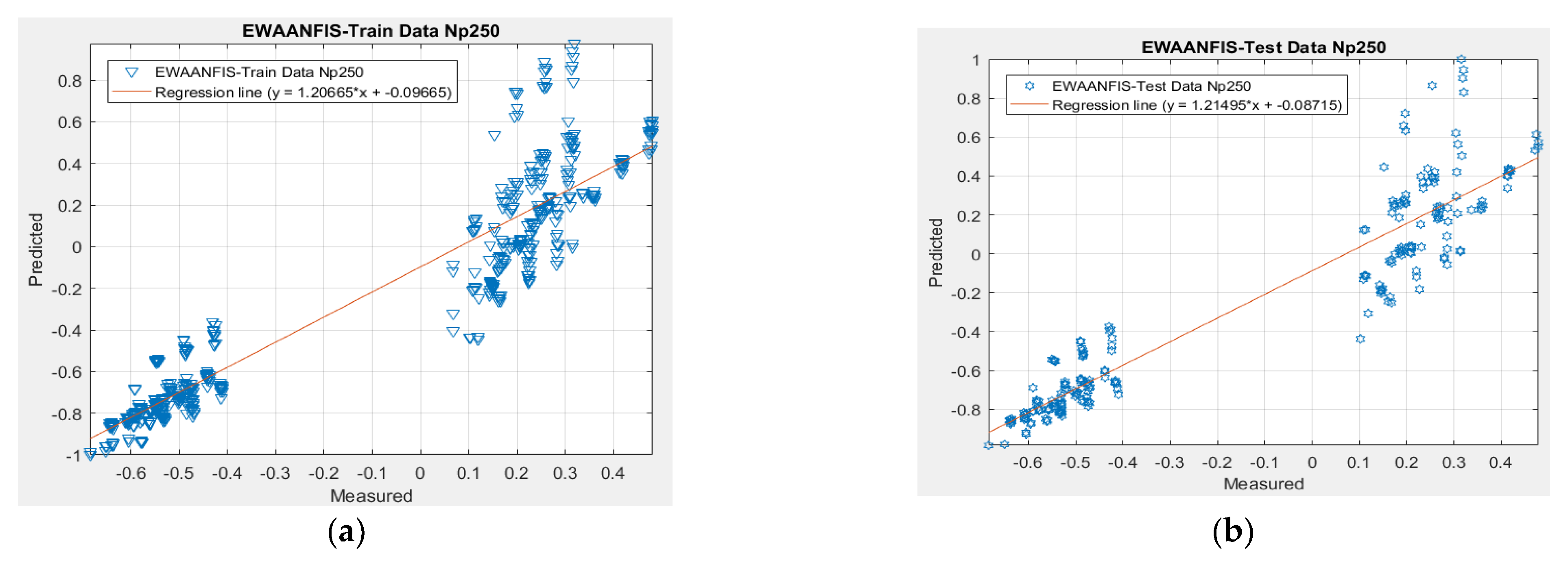
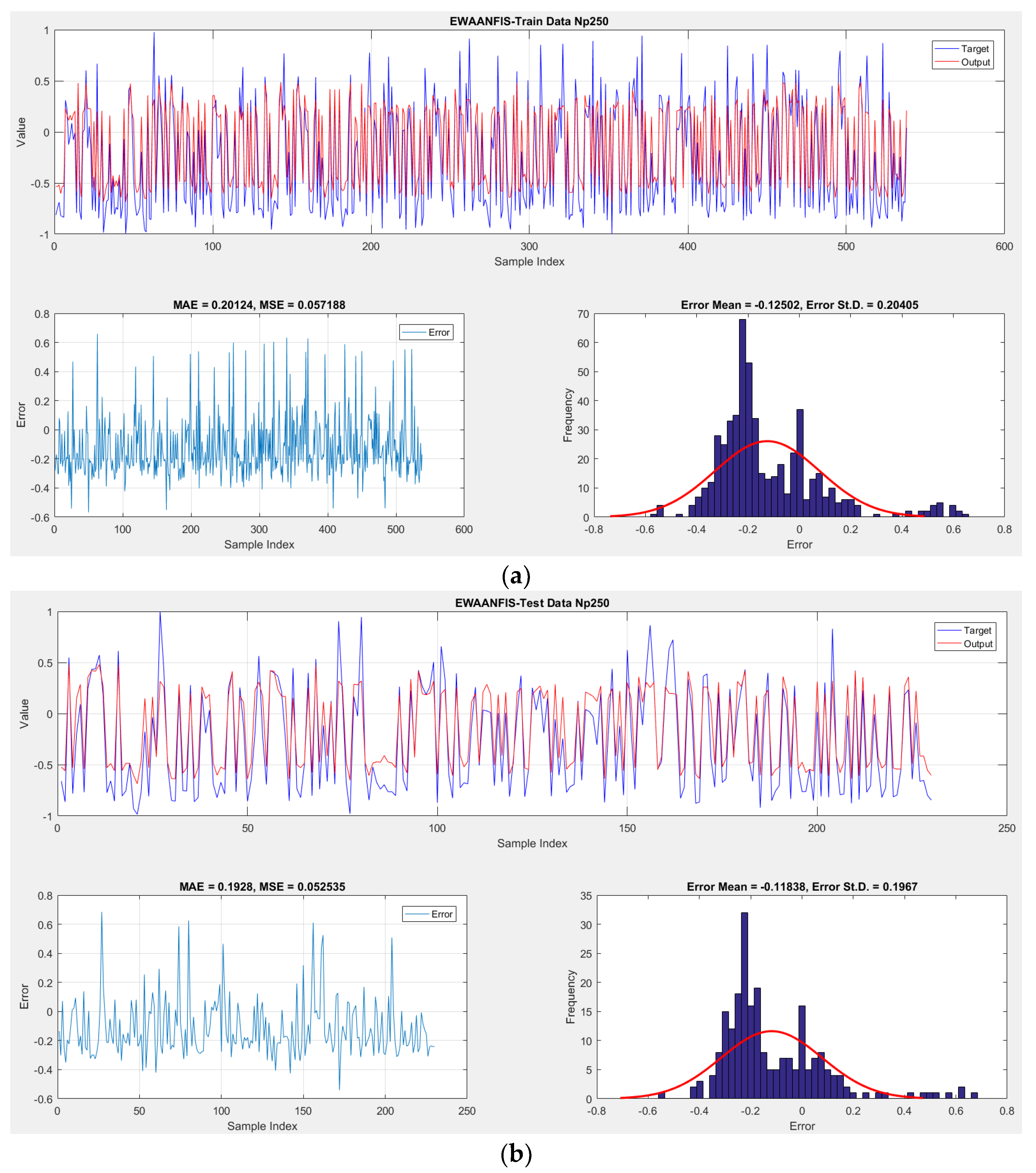
| 250 | 0.18682 | 0.93096 | 0.17681 | 0.93874 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 40 | 1 |
| 300 | 0.23089 | 0.89241 | 0.2214 | 0.9021 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 28 | 4 |
| 350 | 0.27511 | 0.84317 | 0.27416 | 0.84525 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 9 |
| 400 | 0.22259 | 0.90043 | 0.209 | 0.91326 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 34 | 2 |
| 450 | 0.26263 | 0.85824 | 0.26112 | 0.86078 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 8 |
| 500 | 0.2426 | 0.88046 | 0.23457 | 0.88936 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 20 | 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moayedi, H.; Le Van, B. The Applicability of Biogeography-Based Optimization and Earthworm Optimization Algorithm Hybridized with ANFIS as Reliable Solutions in Estimation of Cooling Load in Buildings. Energies 2022, 15, 7323. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15197323
Moayedi H, Le Van B. The Applicability of Biogeography-Based Optimization and Earthworm Optimization Algorithm Hybridized with ANFIS as Reliable Solutions in Estimation of Cooling Load in Buildings. Energies. 2022; 15(19):7323. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15197323
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoayedi, Hossein, and Bao Le Van. 2022. "The Applicability of Biogeography-Based Optimization and Earthworm Optimization Algorithm Hybridized with ANFIS as Reliable Solutions in Estimation of Cooling Load in Buildings" Energies 15, no. 19: 7323. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15197323
APA StyleMoayedi, H., & Le Van, B. (2022). The Applicability of Biogeography-Based Optimization and Earthworm Optimization Algorithm Hybridized with ANFIS as Reliable Solutions in Estimation of Cooling Load in Buildings. Energies, 15(19), 7323. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15197323





