Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition and Recurrence Quantification for the Multiscale, Spatiotemporal Analysis of Electricity Demand—A Case Study of Japan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Empirical Mode Decomposition
| Algorithm 1 Empirical mode decomposition (EMD). |
|
2.3. Noise-Assisted Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition
| Algorithm 2 Multivariate empirical mode decomposition (MEMD). |
|
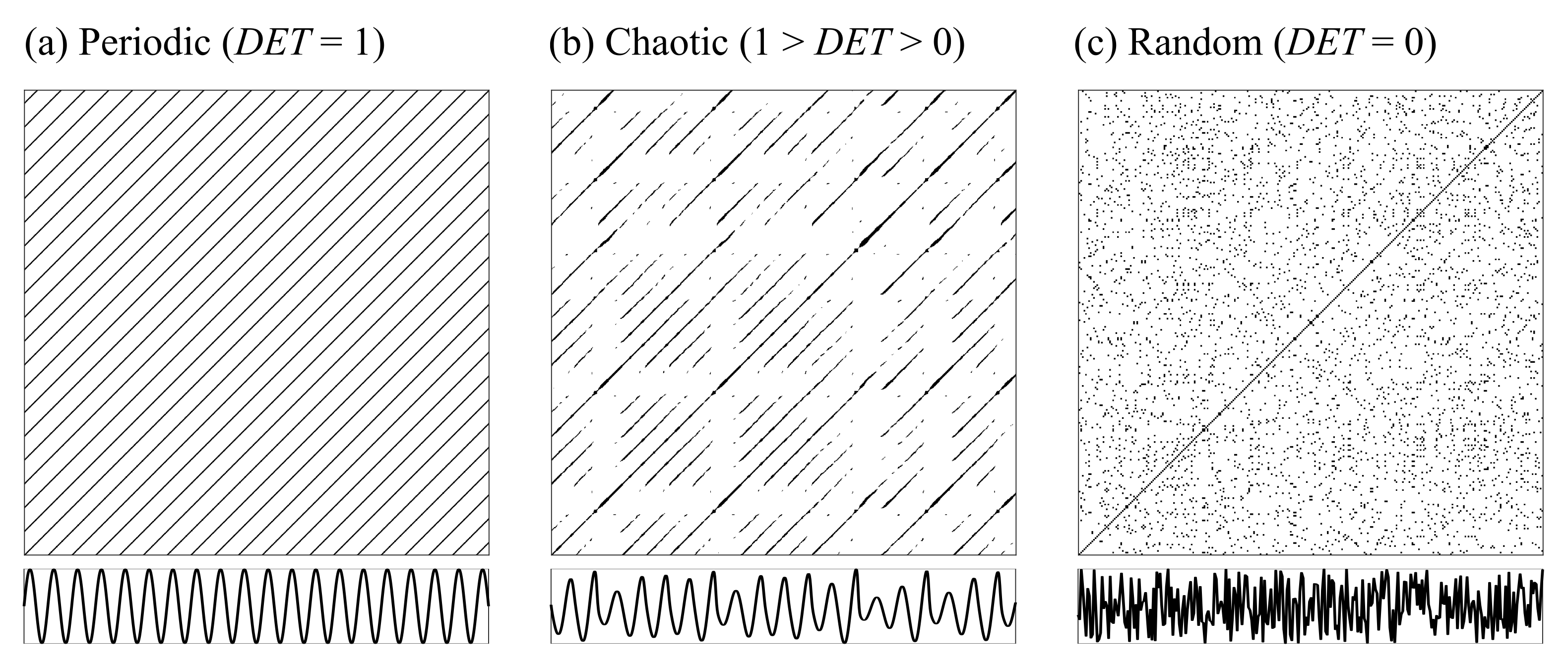
2.4. Recurrence Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
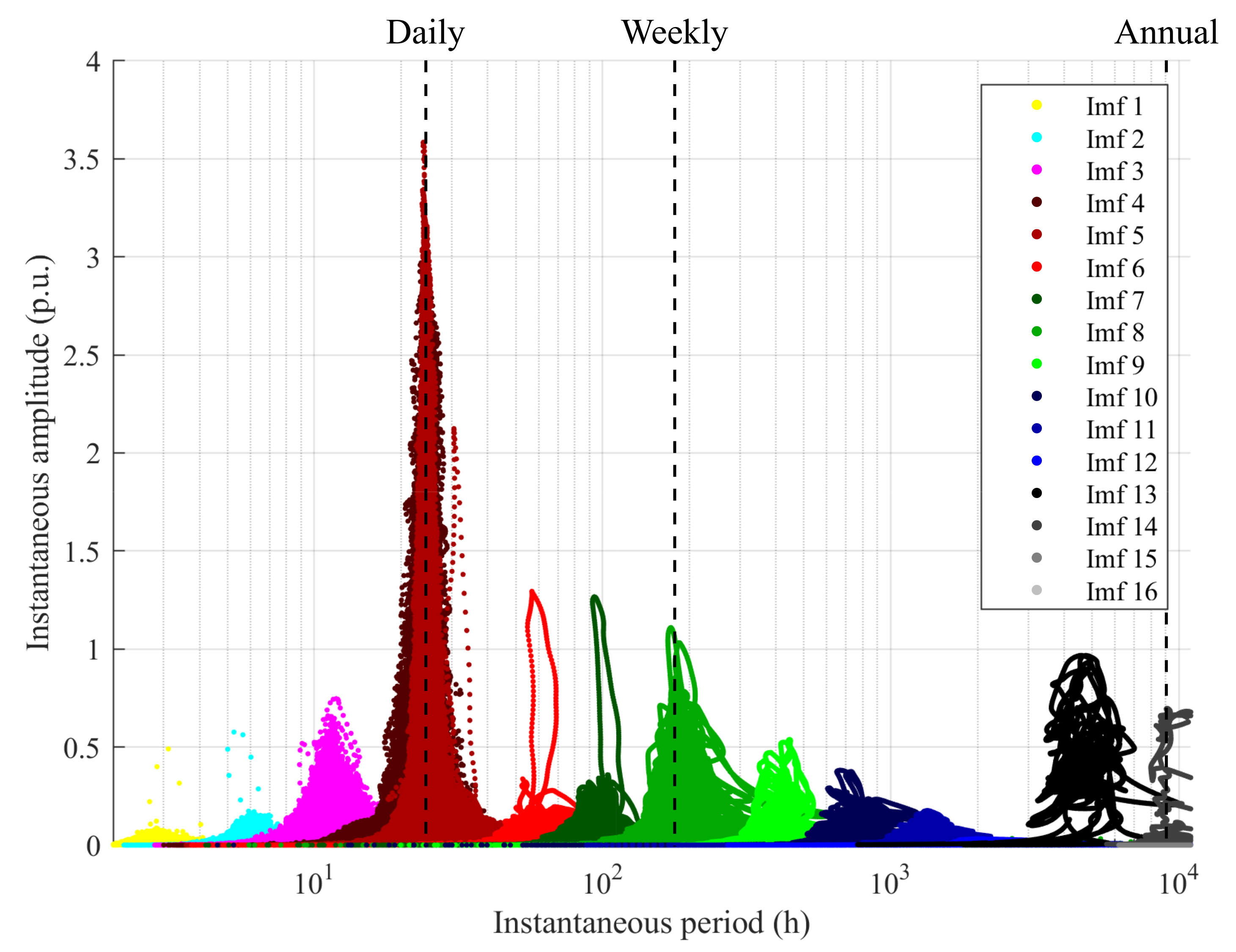
3.1. IMFs Selection
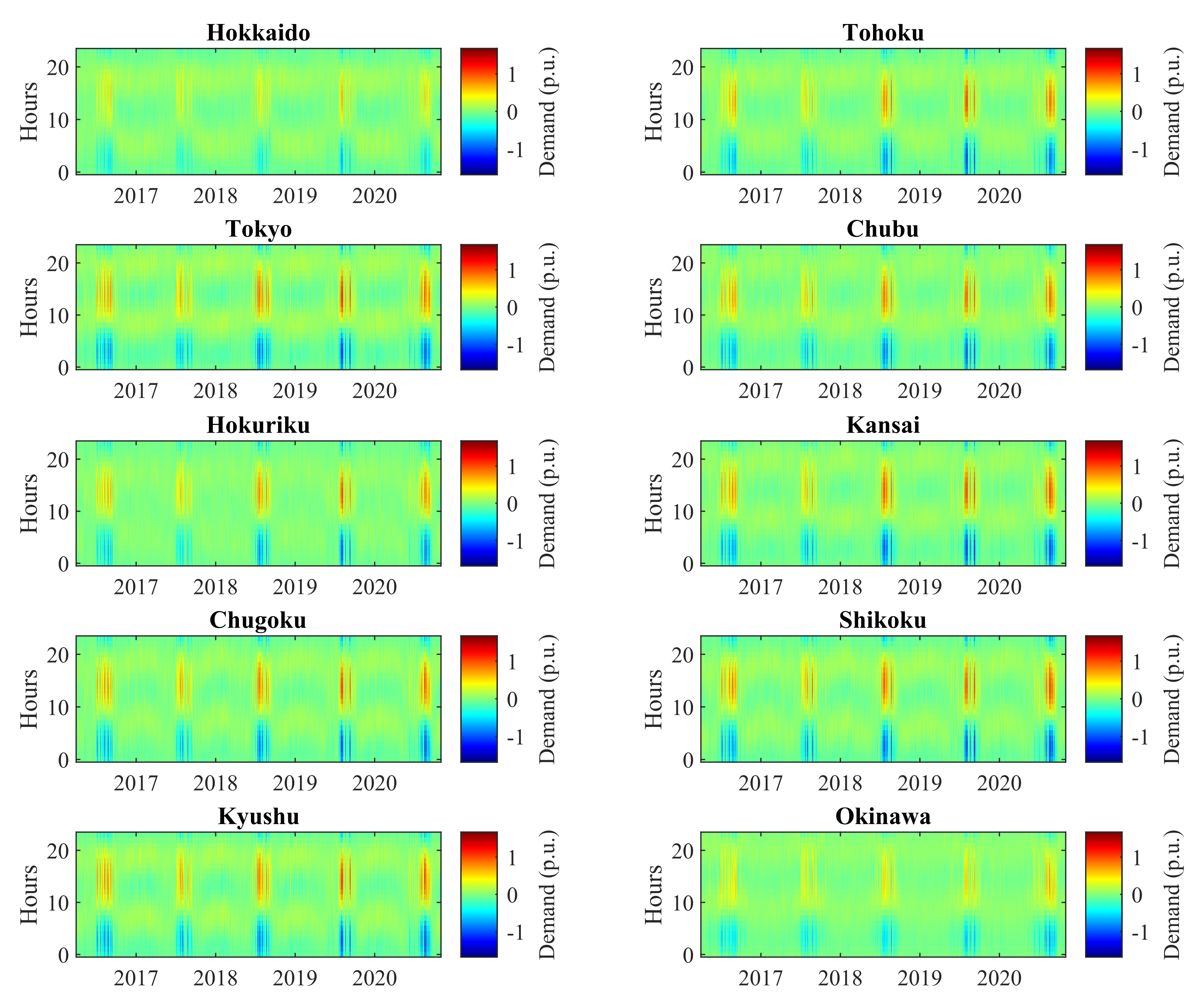
3.2. Annual Period
3.3. Semi-Annual Period
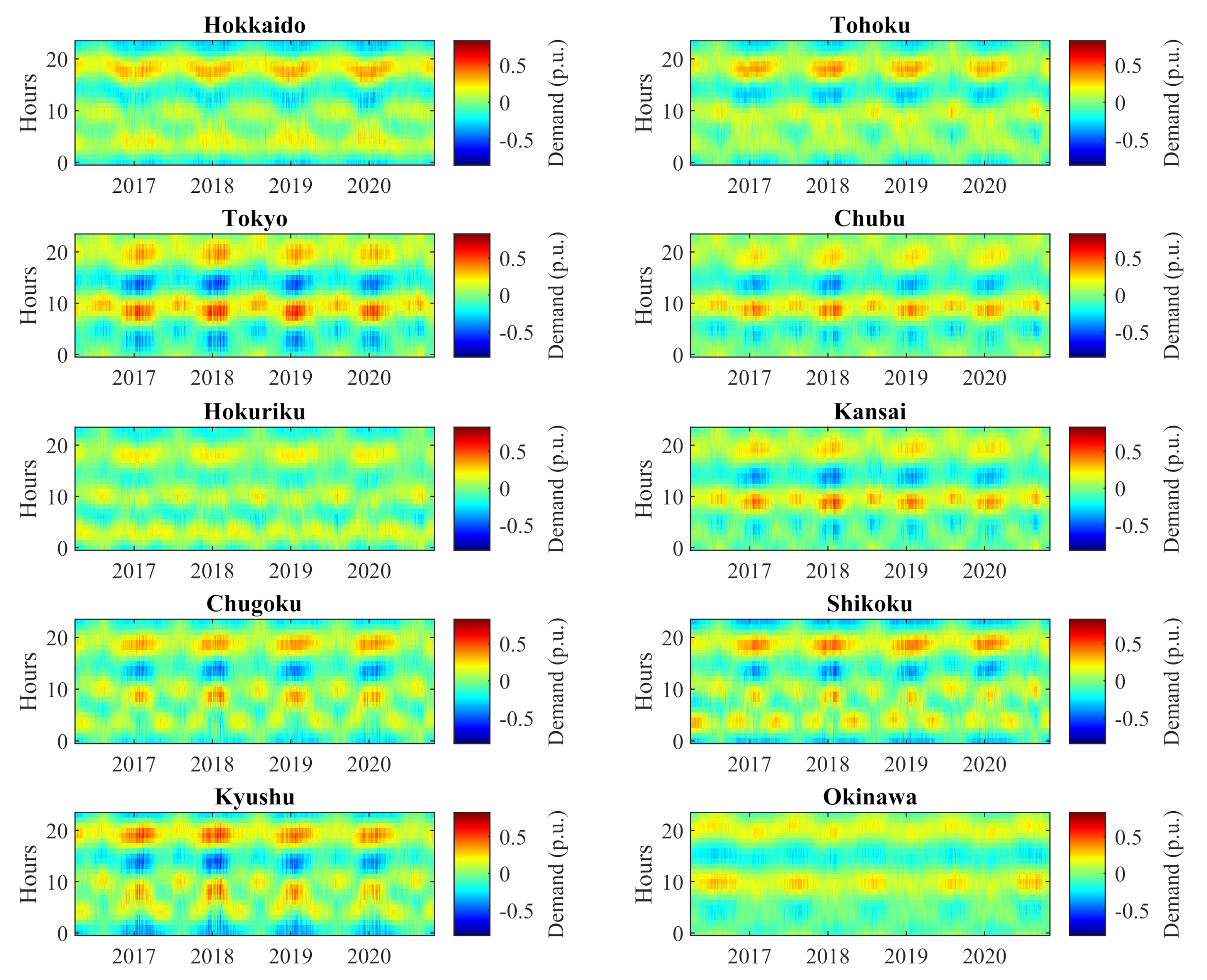
3.4. Weekly Period
3.5. Daily Period
3.6. Semi-Daily Period
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EMD | Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| IMF | Intrinsic Mode Function |
| EEMD | Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| CEEMD | Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| MEMD | Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| NA-MEMD | Noise-Assisted Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| RP | Recurrence Plot |
| RQA | Recurrence Quantification Analysis |
References
- Nakata, T.; Silva, D.; Rodionov, M. Application of energy system models for designing a low-carbon society. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2011, 37, 462–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinius, M.; Otto, A.; Heuser, P.; Welder, L.; Syranidis, K.; Ryberg, D.; Grube, T.; Markewitz, P.; Peters, R.; Stolten, D. Linking the power and transport sectors—Part 1: The principle of sector coupling. Energies 2017, 10, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Schlachtberger, D.; Kies, A.; Schramm, S.; Greiner, M. Synergies of sector coupling and transmission reinforcement in a cost-optimised, highly renewable European energy system. Energy 2018, 160, 720–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruf, M.N.I. Sector coupling in the north sea region—A review on the energy system modelling perspective. Energies 2019, 12, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Werner, S.; Wlitshire, R.; Svendsen, S.; Thorsen, J.E.; Hvelplund, F.; Mathiesen, B.V. 4th Generation District Heating (4GDH): Integrating smart thermal grids into future sustainable energy systems. Energy 2012, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.A.; Becker, S.; Andresen, G.B.; Heide, D.; Greiner, M. Transmission needs across a fully renewable European power system. Renew. Energy 2014, 63, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhoff, K.; Bach, S.; Diekmann, J.; Beznoska, M.; El-Laboudy, T. Distributional effects of energy transition: Impacts of renewable electricity support in Germany. Econ. Energy Environ. Policy 2013, 2, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, C.S.E.; Varga, L.; Foxon, T.J. Energy and complexity: New ways forward. Appl. Energy 2015, 138, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delage, R.; Nakata, T. Machine learning for modeling energy systems complexity. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Efficiency, Cost, Optimization, Simulation and Environmental Impact of Energy Systems, Osaka, Japan, 29 June–3 July 2020; pp. 2405–2414. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Horsch, J.; Schlachtberger, D. PyPSA: Python for Power System Analysis. J. Open Res. Softw. 2018, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfenninger, S.; Pickering, B. Calliope: A multi-scale energy systems modelling framework. J. Open Res. Softw. 2018, 3, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, V.; Henry, A.D. Agent-based modelling of consumer energy choices. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylatt, M.; Gammon, R.; Boait, P.; Varga, L.; Allen, P.; Savill, M.; Snape, R.; Lemon, M.; Ardestani, B.; Pakka, V.; et al. Cascade: An agent based framework for modeling the dynamics of smart electricity systems. Emerg. Complex. Organ. 2013, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kremers, E. Modelling and Simulation of Electrical Energy Systems through a Complex Systems Approach Using Agent-Based Models, 1st ed.; KIT Scientific Publishing: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Logenthiran, T.; Srinivasan, D.; Shun, T.Z. Multi-Agent System for Demand Side Management in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Ninth International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems, Singapore, 5–8 December 2011; pp. 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, S.M.; Borries, S.; Bornholdt, S. Econophysics of adaptive power markets:When a market does not dampen fluctuations but amplifies them. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 012815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morstyn, T.; Farrell, N.; Evins, L.A.; Bollinger, L.A.; Carmeliet, J. Using peer-to-peer energy-trading platforms to incentivize prosumers to form federated power plants. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Long, C. Evaluation of peer-to-peer energy sharing mechanisms based on a multiagent simulation framework. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 993–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deissenroth, M.; Klein, M.; Nienhaus, K.; Reeg, M. Assessing the Plurality of Actors and Policy Interactions: Agent-Based Modelling of Renewable Energy Market Integration. Complexity 2017, 2017, 7494313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappin, E.J.L.; de Vries, L.J.; Richstein, J.C.; Bhagwat, P.; Iychettira, K.; Khan, S. Simulating climate and energy policy with agent-based modelling: The Energy Modelling Laboratory (EMLab). Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 96, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calikus, E.; Nowaczyk, S.; Sant’Anna, A.; Gadd, H.; Werner, S. A data-driven approach for discovering heat load patterns in district heating. Appl. Energy 2019, 252, 113409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystrup, P.; Madsen, H.; Blomgren, E.M.V.; de Zotti, G. Clustering commercial and industrial load patterns for long-term energy planning. Smart Energy 2021, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Salimi, M.; Ardabili, S.F.; Rabczuk, T.; Shamshirband, S.; Varkonyi-Koczy, A.R. State of the art of machine learning models in energy systems, a systematic review. Energies 2019, 12, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.M.; Hossain, M.A.; French, R.H.; Abramson, A.R. Building electricity consumption: Data analytics of building operations with classical time series decomposition and case based subsetting. Energy Build. 2018, 177, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolov, A.; Lepri, B.; Larcher, R.; Antonelli, F.; Pianesi, F.; Pentland, A. Energy consumption prediction using people dynamics derived from cellular network data. EPJ Data Sci. 2016, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Tam, K.S. Hierarchical Classification of Load Profiles Based on Their Characteristic Attributes in Frequency Domain. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 2434–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukseltan, E.; Yucekaya, A.; Bilge, A.H. Hourly electricity demand forecasting using Fourier analysis with feedback. Energy Strategy Rev. 2020, 31, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, F.; Smith, N.D. Load Characterization and Low-Order Approximation for Smart Metering Data in the Spectral Domain. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prema, V.; Uma Rao, K. Time series decomposition model for accurate wind speed forecast. Renewables 2015, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Dang, W.; Cai, Q.; Wang, Z.; Marwan, N.; Boccaletti, S.; Kurths, J. Reconstructing multi-mode networks from multivariate time series. Europhys. Lett. 2017, 119, 50008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, J.; Anguita, D.; Perez, F.; Denda, R. Spectral Analysis of Electricity Demand Using Hilbert–Huang Transform. Sensors 2020, 20, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Wang, Z. Drivers analysis and empirical mode decomposition based forecasting of energy consumption structure. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looney, D.; Hemakom, A.; Mandic, D.P. Intrinsic multi-scale analysis: A multi-variate empirical mode decomposition framework. Proc. R. Soc. A 2015, 471, 20140709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwan, N.; Romano, M.C.; Thiel, M.; Kurths, J. Recurrence plots for the analysis of complex systems. Phys. Rep. 2007, 438, 237–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, R.V.; Zou, Y.; Donges, J.F.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J. Recurrence networks—A novel paradigm for nonlinear time series analysis. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 033025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charakopoulos, A.; Karakasidis, T.; Sarris, I. Pattern identification for wind power forecasting via complex network and recurrence plot time series analysis. Energy Policy 2019, 133, 110934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenji, A.E.; Olusola, O.I.; Njah, A.N. Comparative study of chaotic features in hourly wind speed using recurrence quantification analysis. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 025102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, N.; Kurths, J.; Marwan, N. Complex systems approaches for Earth system data analysis. J. Phys. Complex. 2021, 2, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhui, P.; Senroy, N. Application of Recurrence Quantification Analysis to Power System Dynamic Studies. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delage, R.; Matsuoka, T.; Nakata, T. Spatial–Temporal Estimation and Analysis of Japan Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy Potential. Energies 2021, 14, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Sustainable Energy Policies. Electricity Generation and Demand. Available online: https://isep-energychart.com/en/graphics/ (accessed on 13 July 2021).
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Outline of the Operational Numerical Weather Prediction. Available online: https://www.jma.go.jp/jma/jma-eng/jma-center/nwp/outline2019-nwp/index.htm (accessed on 13 July 2021).
- Kyoto University. Japan Meteorological Agency Data. Available online: http://database.rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp/arch/jmadata/ (accessed on 11 March 2021).
- Japan Ministry of Economy. Trade and Industry: Energy Consumption Statistics by Prefectures. Available online: https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/statistics/energy_consumption/ec002/results.html (accessed on 13 July 2021).
- Huang, N.E.; Wu, M.L.; Long, S.R.; Shen, S.S.P.; Qu, W.; Gloersen, P.; Fan, K.L. A confidence limit for the empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 2003, 459, 2317–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilling, G.; Flandrin, P.; Goncalves, P. On Empirical Mode Decomposition and its Algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE-EURASIP Workshop on Nonlinear Signal and Image Processing, NSIP-03, Grado, Italy, 8–11 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mandic, D.P.; Rehman, N.; Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Time-Frequency Analysis of Multivariate Signals. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2013, 30, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwan, N.; Schinkel, S.; Kurths, J. Recurrence plots 25 years later—Gaining confidence in dynamical transitions. EPL 2013, 101, 20007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, N.H.; Crutchfield, J.P.; Farmer, J.D.; Shaw, R.S. Geometry from a Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennel, M.B.; Brown, R.; Abarbanel, H.D. Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 45, 3403–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
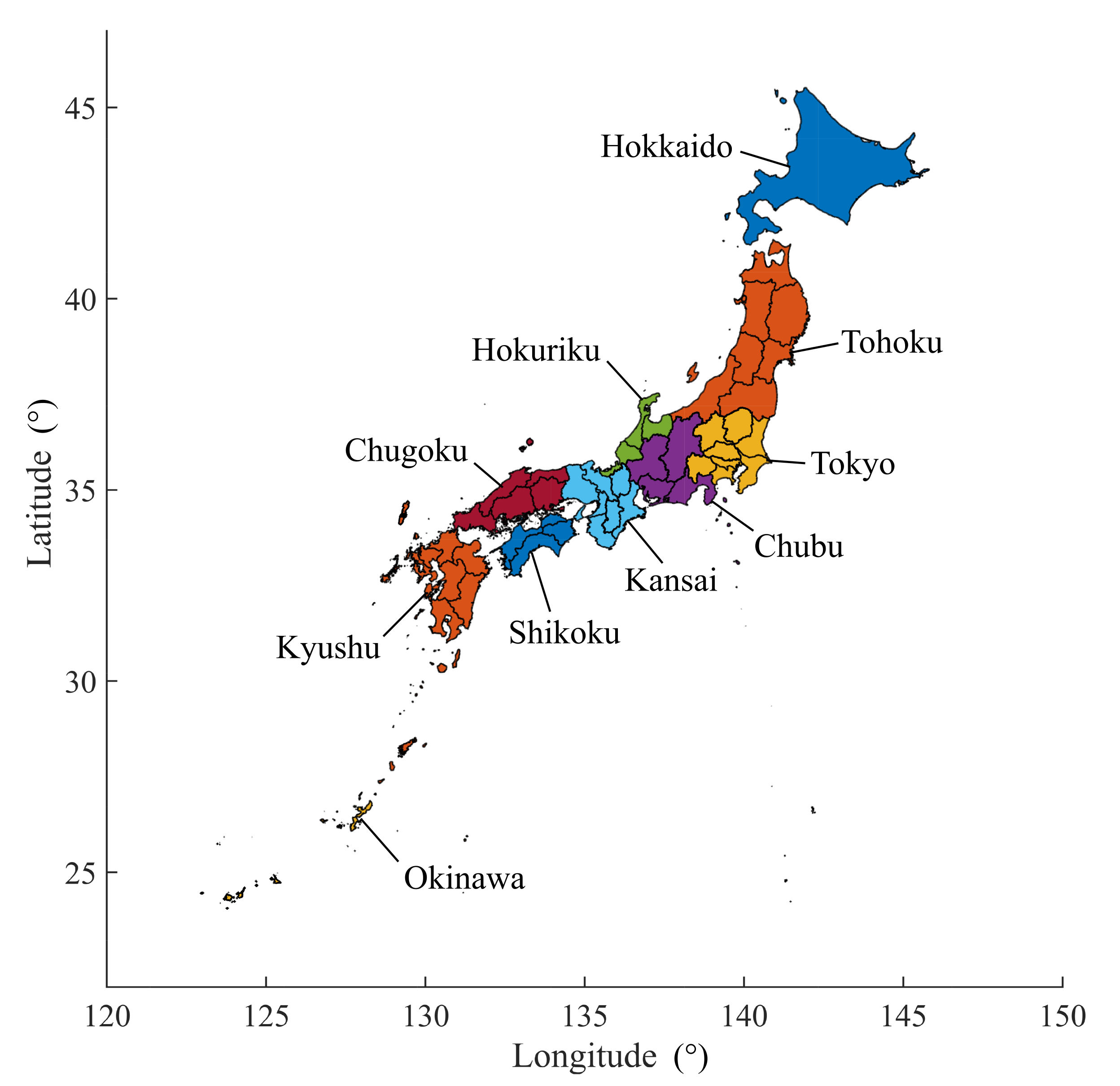
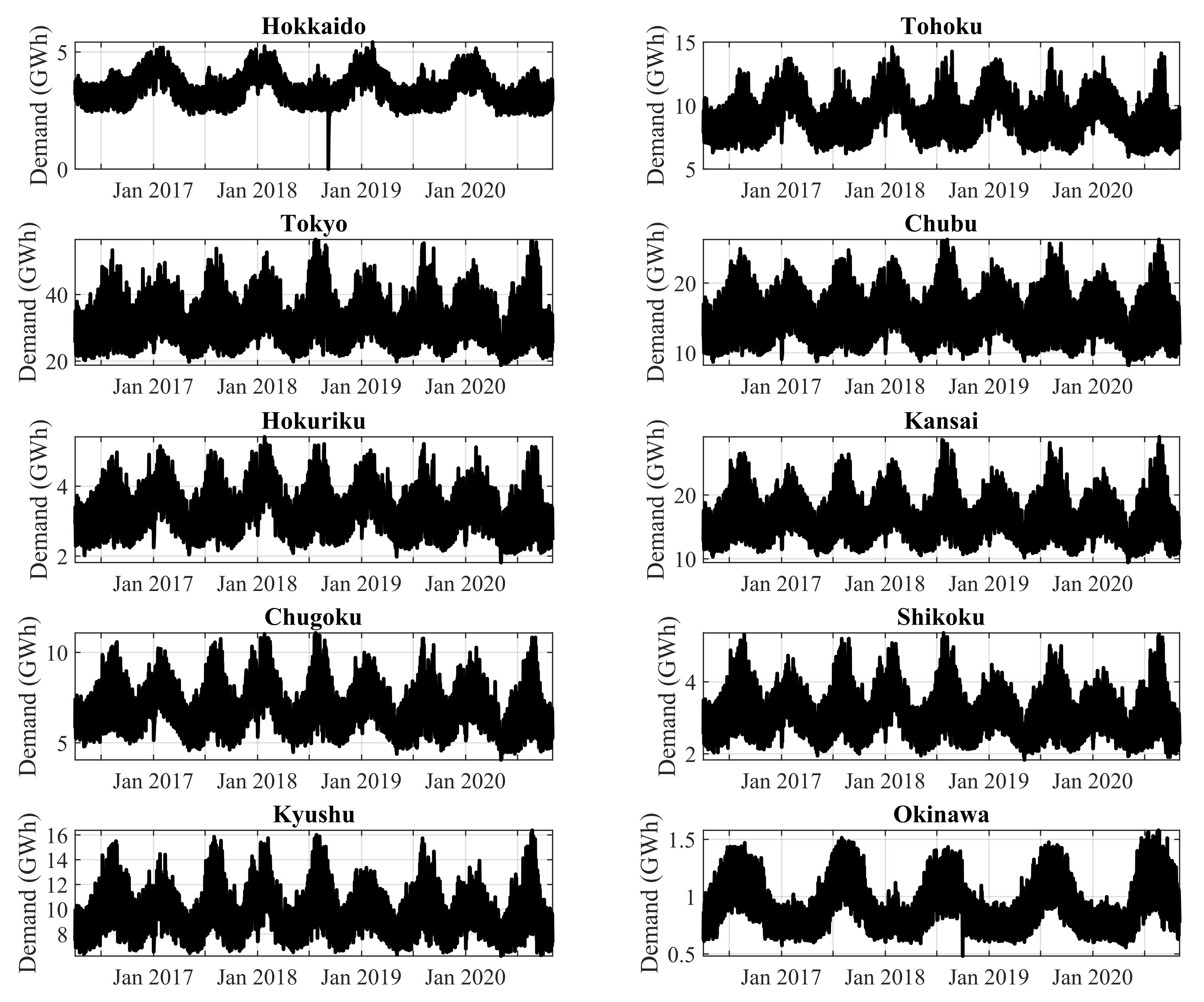
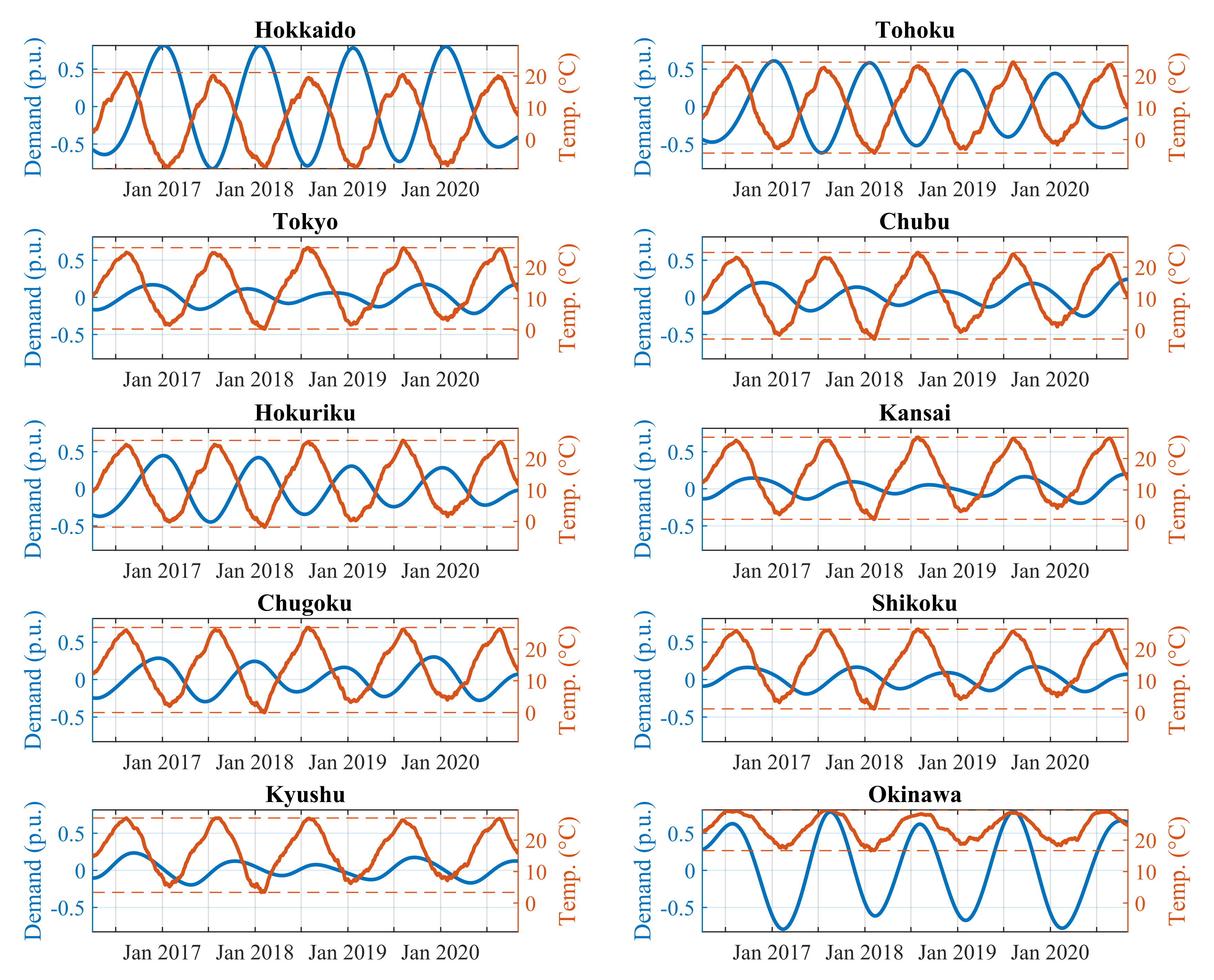
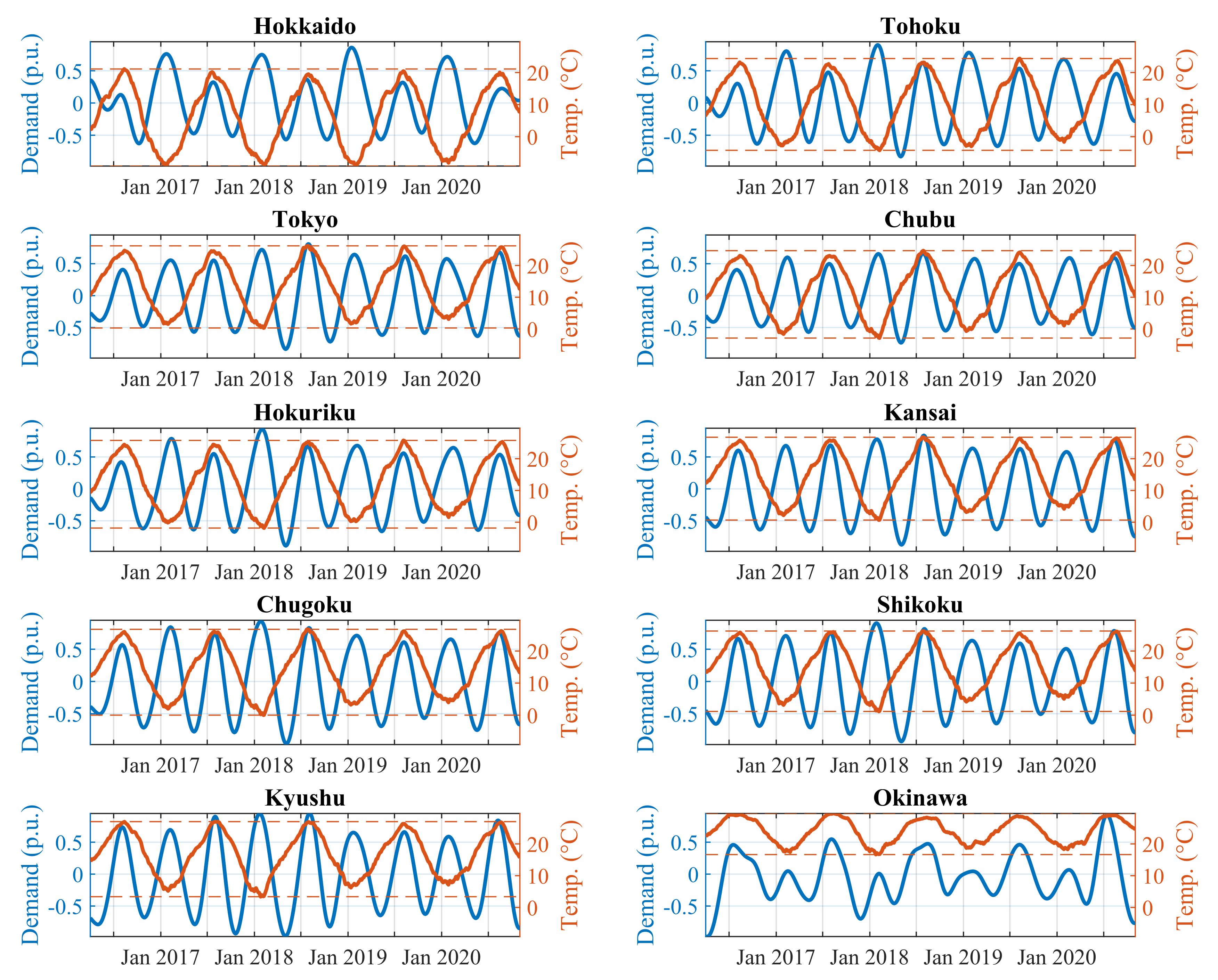
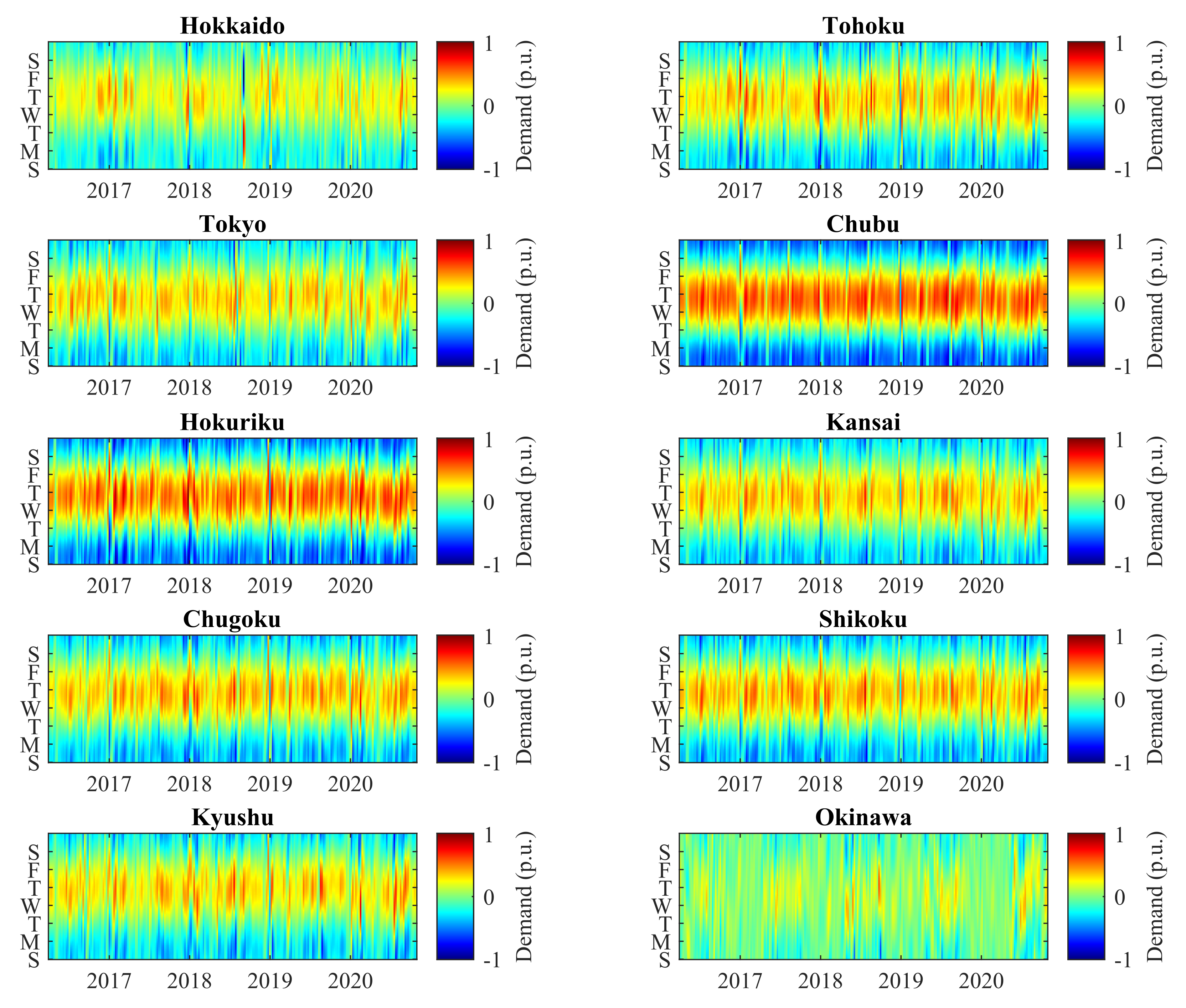
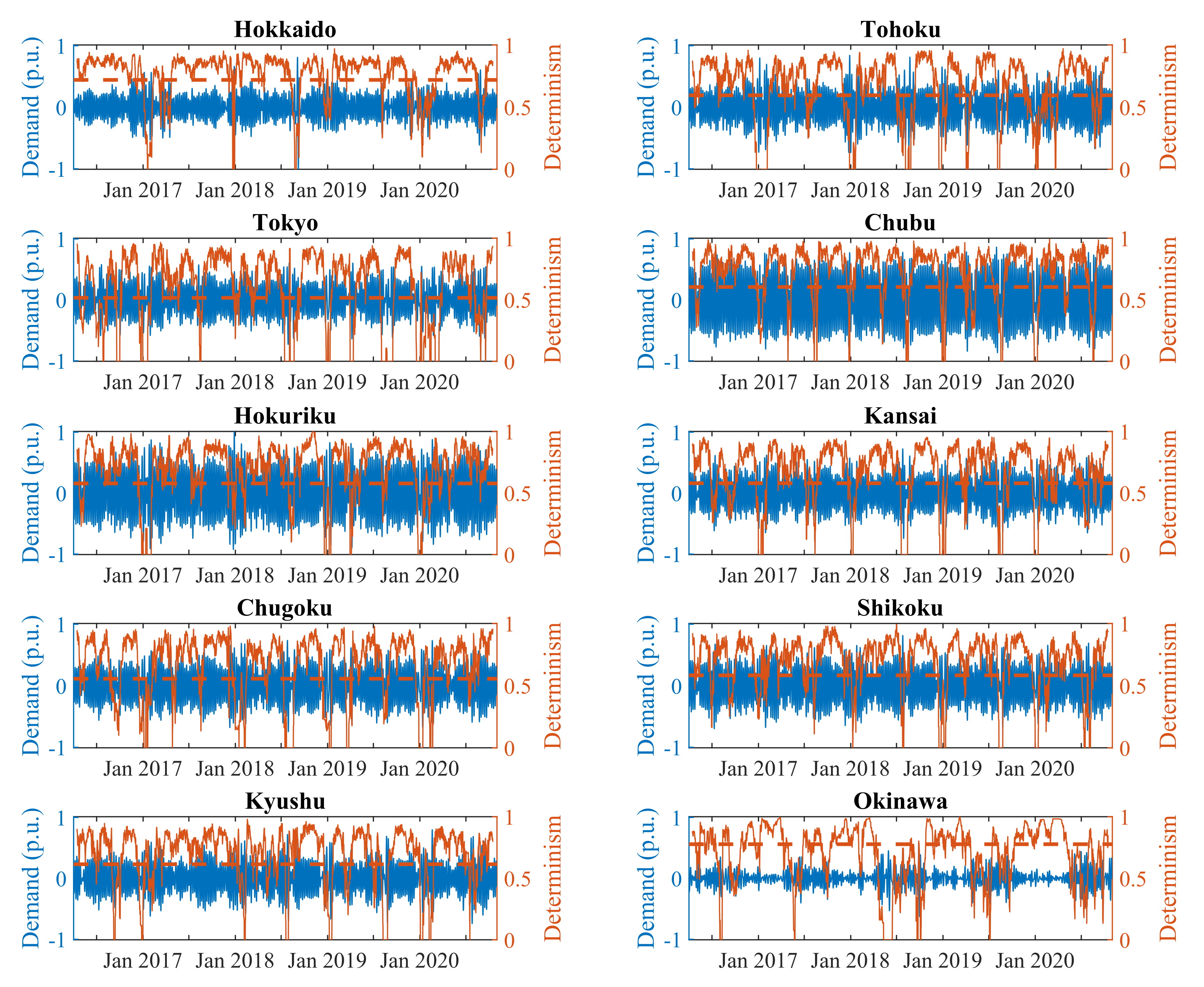

| Industrial (%) | Commercial (%) | Residential (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hokkaido | 18.1 | 43.4 | 38.5 |
| Tohoku | 31.1 | 33.8 | 35.2 |
| Tokyo | 24.3 | 45.2 | 30.5 |
| Chubu | 37.8 | 32.6 | 29.7 |
| Hokuriku | 35.9 | 26.8 | 37.3 |
| Kansai | 29.9 | 39.8 | 30.3 |
| Chugoku | 45.8 | 27.7 | 26.6 |
| Shikoku | 37.7 | 30.3 | 32.1 |
| Kyushu | 34.6 | 34.7 | 30.7 |
| Okinawa | 10.2 | 54.4 | 35.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delage, R.; Nakata, T. Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition and Recurrence Quantification for the Multiscale, Spatiotemporal Analysis of Electricity Demand—A Case Study of Japan. Energies 2022, 15, 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176292
Delage R, Nakata T. Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition and Recurrence Quantification for the Multiscale, Spatiotemporal Analysis of Electricity Demand—A Case Study of Japan. Energies. 2022; 15(17):6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176292
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelage, Rémi, and Toshihiko Nakata. 2022. "Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition and Recurrence Quantification for the Multiscale, Spatiotemporal Analysis of Electricity Demand—A Case Study of Japan" Energies 15, no. 17: 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176292
APA StyleDelage, R., & Nakata, T. (2022). Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition and Recurrence Quantification for the Multiscale, Spatiotemporal Analysis of Electricity Demand—A Case Study of Japan. Energies, 15(17), 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176292







