Magnéli TiO2 as a High Durability Support for the Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Catalysts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Catalyst Synthesis and Electrode Preparation
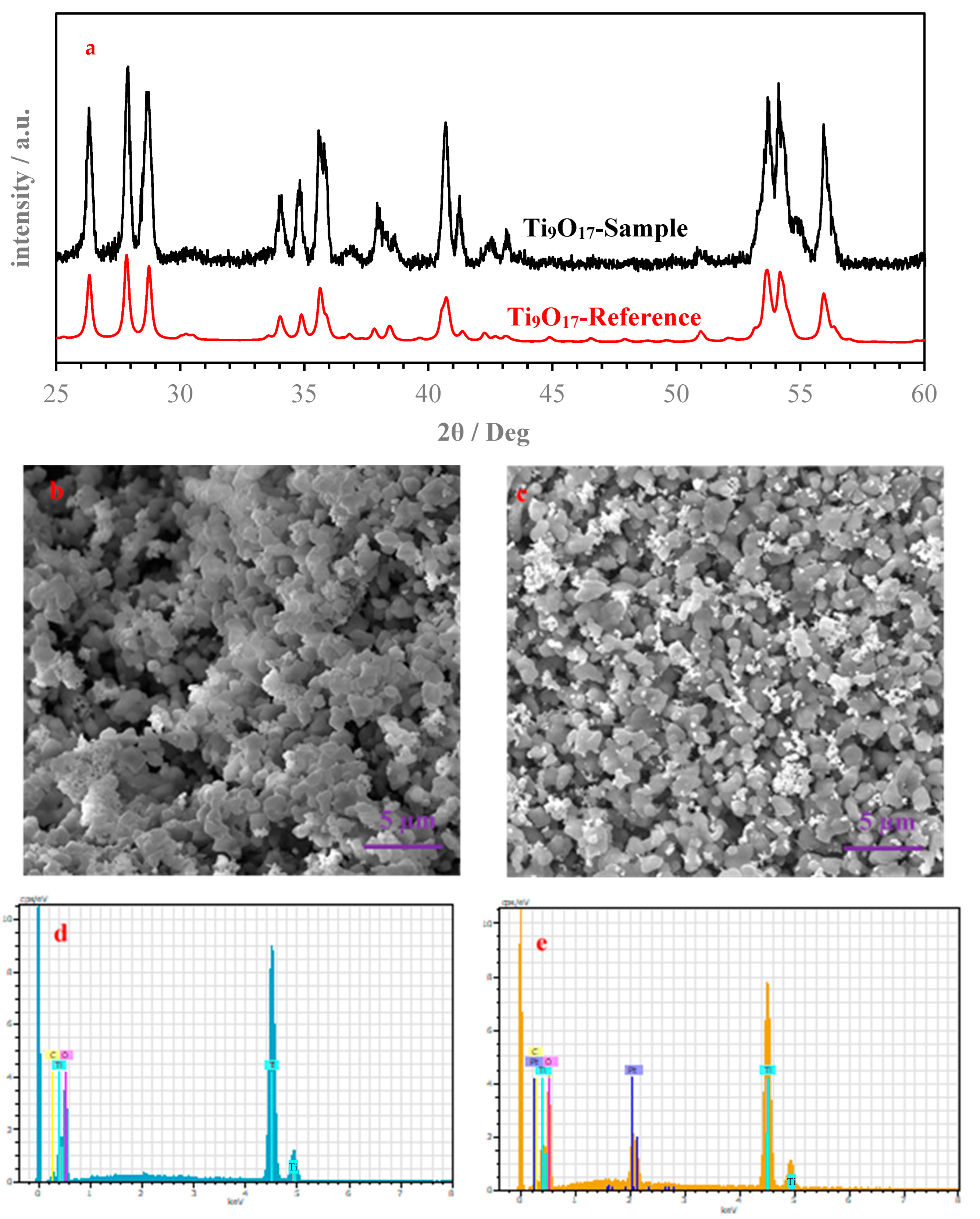
2.2.1. Synthesis of Ti9O17
2.2.2. Synthesis of 30% Pt/Ti9O17
2.2.3. Electrode Preparation
Pt /Ti9O17 (30%) Electrode
Pt/C (20%) Electrode
2.3. Surface Characterizations
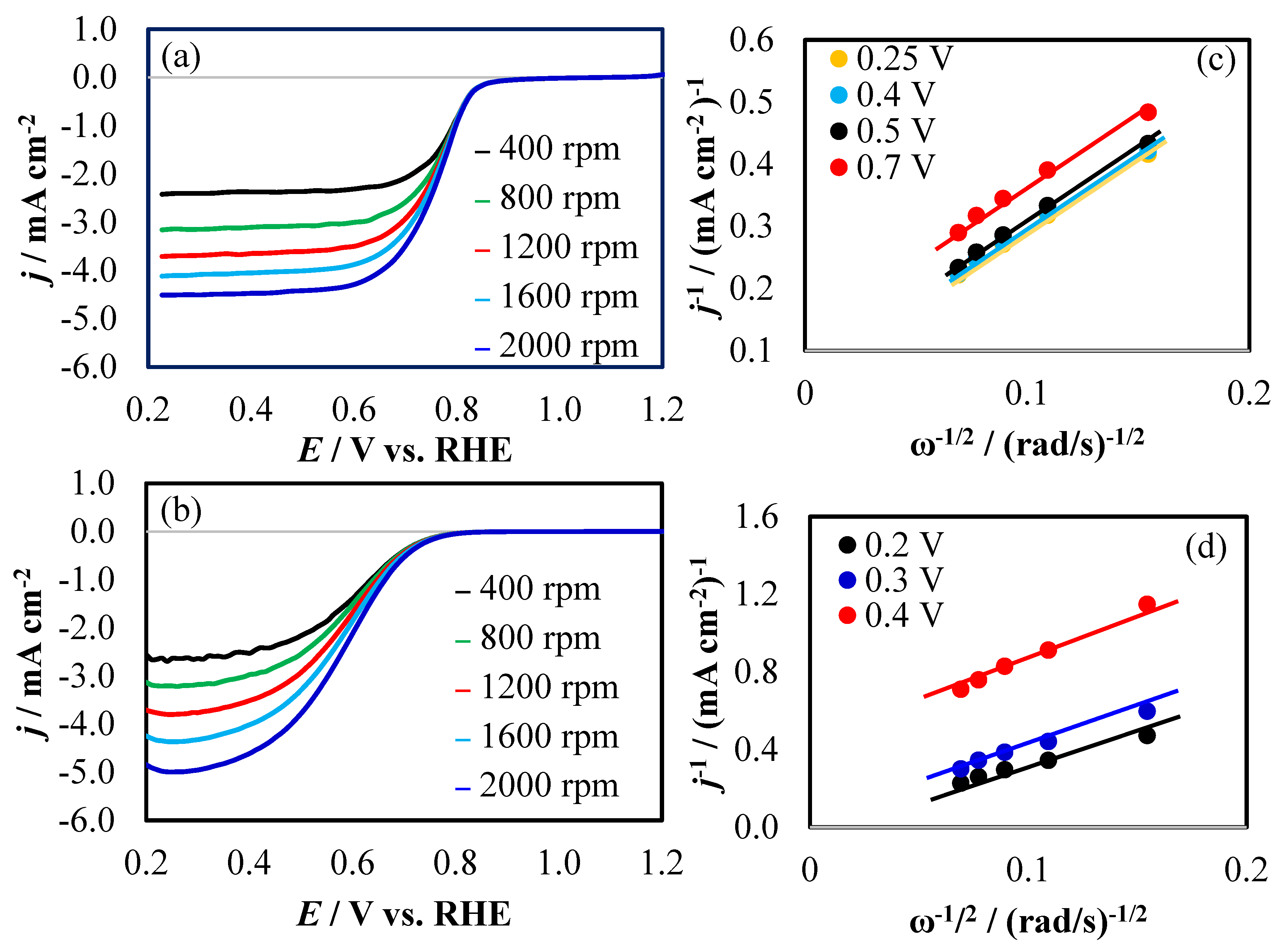
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
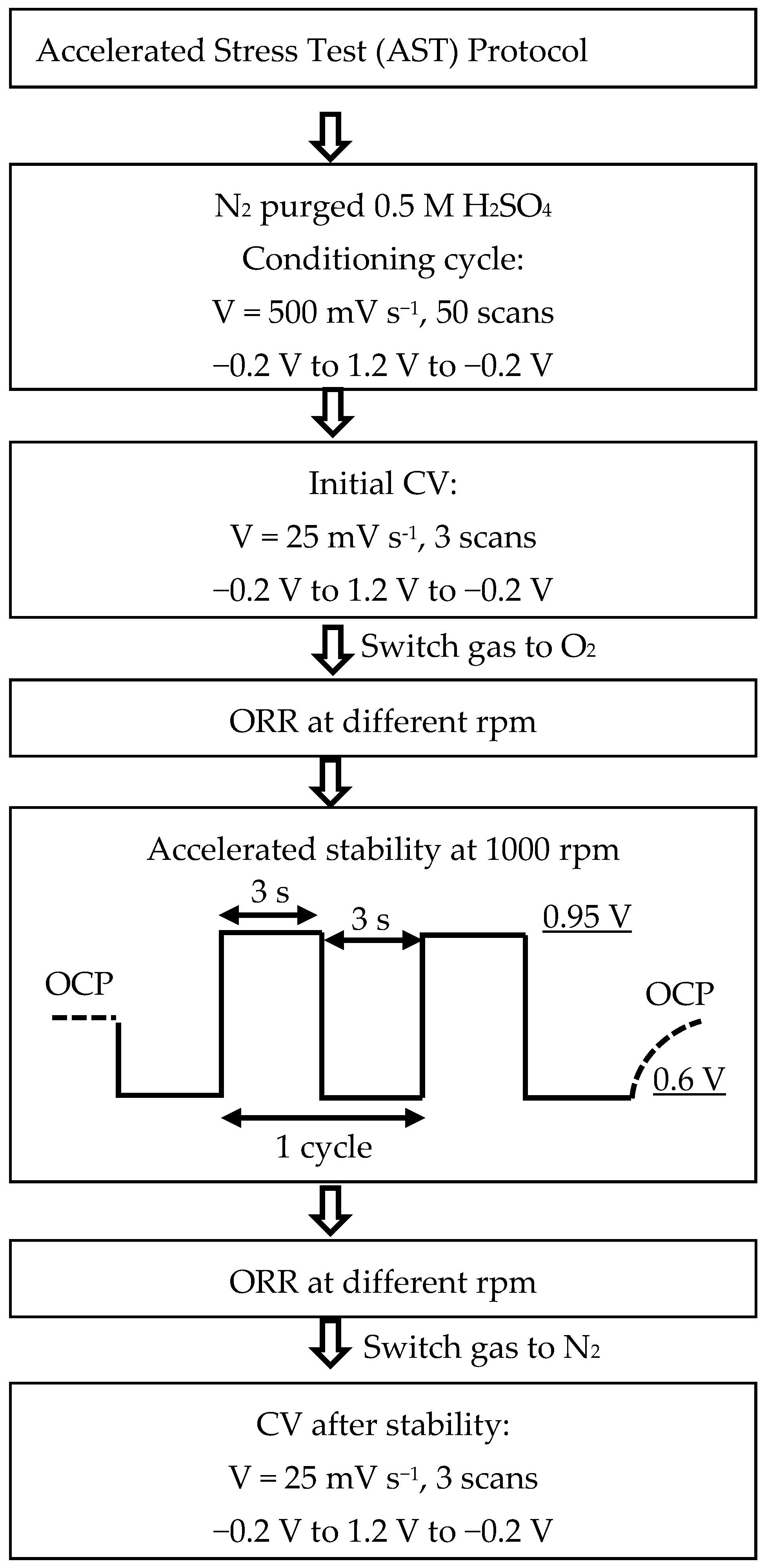
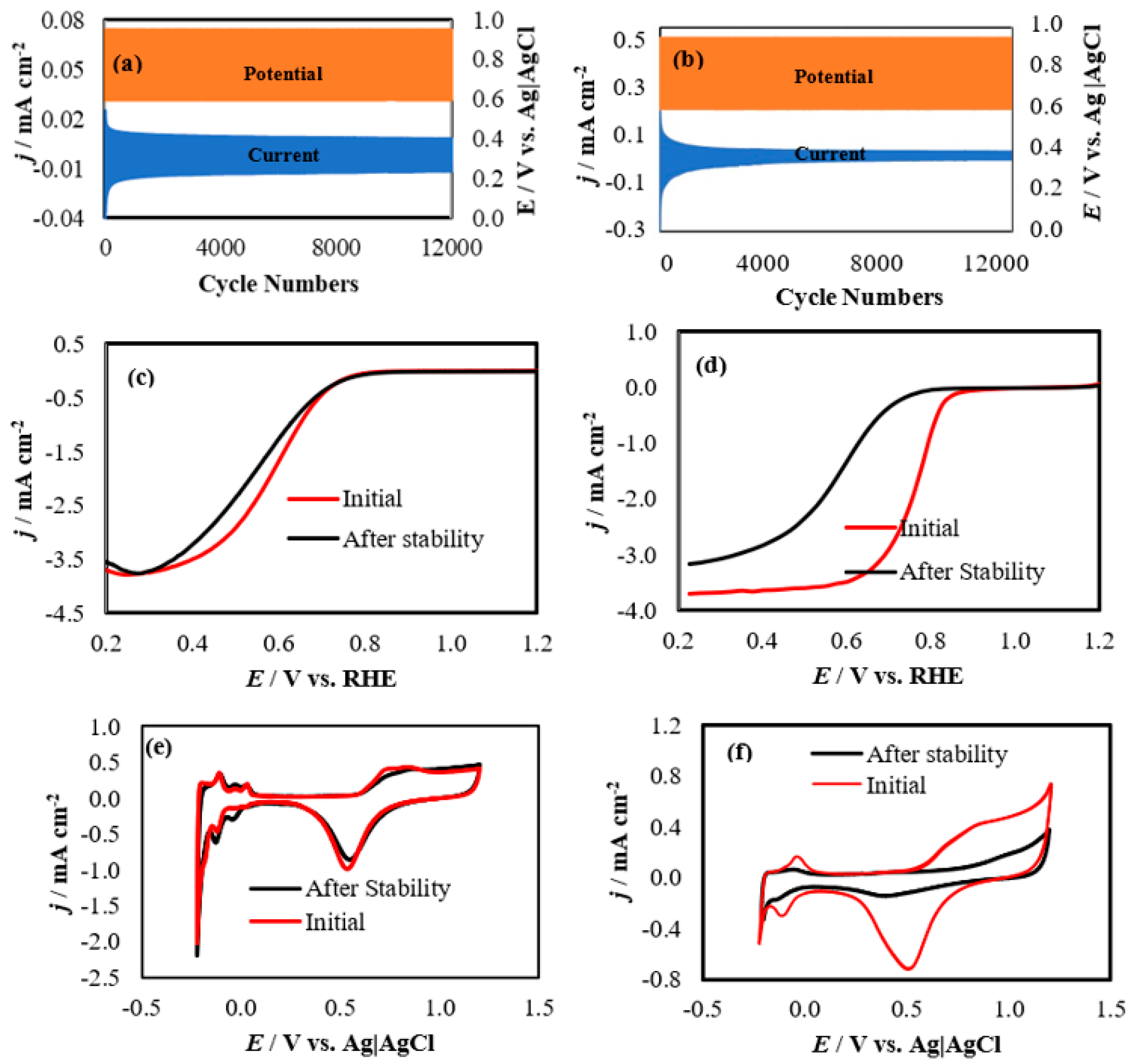
2.5. Accelerated Stress Test (AST) via Start-Stop Cycles
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ning, F.; He, X.; Shen, Y.; Jin, H.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Li, S.; Zhan, Y.; Du, Y.; Jiang, J.; et al. Flexible and Lightweight Fuel Cell with High Specific Power Density. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5982–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Peng, C.; Yin, C. Review of System Integration and Control of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2020, 3, 466–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheepers, F.; Stähler, M.; Stähler, A.; Rauls, E.; Müller, M.; Carmo, M.; Lehnert, W. Temperature optimization for improving polymer electrolyte membrane-water electrolysis system efficiency. Appl. Energy 2021, 283, 116270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochner, T.; Kluge, R.M.; Fichtner, J.; El-Sayed, H.A.; Garlyyev, B.; Bandarenka, A.S. Temperature Effects in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzjaie, H.A.; Mustain, W.E. Catalytic Advantages, Challenges, and Priorities in Alkaline Membrane Fuel Cells. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Lv, Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, A.; Wu, G. Current progress of Pt and Pt-based electrocatalysts used for fuel cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2020, 4, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Bera, S.; Kim, C.M.; Koh, E.K.; Hong, W.P.; Oh, S.J.; Cho, E.A.; Kwon, S.H. Synthesis of highly dispersed Pt nanoparticles into carbon supports by fluidized bed reactor atomic layer deposition to boost PEMFC performance. NPG Asia Mater. 2020, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolini, E. Carbon supports for low-temperature fuel cell catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 88, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharwar, Y.P.; Akula, S.; Sahu, A.K.; Ramanujam, K. Highly Durable Pt-Based Catalyst Supported on Carbon Derived from Tamarind Seeds for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in PEM Fuel Cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 104515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Zou, Y.; Dai, L. Carbon-Based Metal-Free Electrocatalysis for Energy Conversion, Energy Storage, and Environmental Protection. Electrochem. Energ. Rev. 2018, 1, 84–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, N.; Reddy, A.L.M.; Shaijumon, M.M.; Rajalakshmi, N.; Ramaprabhu, S. Pt–Ru/multiwalled carbon nanotubes as electrocatalysts for direct methanol fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribov, E.N.; Kuznetsov, A.N.; Golovin, V.A.; Krasnikov, D.V.; Kuznetsov, V.L. Effect of modification of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with nitrogen-containing polymers on the electrochemical performance of Pt/CNT catalysts in PEMFC. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2019, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppannan, M.; Kim, Y.; Gok, S.; Lee, E.; Hwang, J.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Lim, T.; Sung, Y.E.; Kwon, O.J. A highly durable carbon-nanofiber-supported Pt–C core–shell cathode catalyst for ultra-low Pt loading proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Facile carbon encapsulation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2820–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Wang, Y.; Bian, L.; Zhang, J.; Meng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, R.; Qu, X.; Ren, S. Graphene growth on nanodiamond as a support for a Pt electrocatalyst in methanol electrooxidation. Carbon 2012, 50, 3032–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, R.I.; Rajalakshmi, N.; Ramaprabhu, S. Nitrogen doped graphene nanoplatelets as catalyst support for oxygen reduction reaction in proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7114–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganyecz, Á.; Kállay, M. Oxygen Reduction Reaction on N-Doped Graphene: Effect of Positions and Scaling Relations of Adsorption Energies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 8551–8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Chan, K.Y.; Ren, J.; Xiao, F.S. Platinum and platinum-ruthenium nanoparticles supported on ordered mesoporous carbon and their electrocatalytic performance for fuel cell reactions. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 3131–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Tian, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhong, H.; Liang, Y.; Yi, B. Microporous layer with composite carbon black for PEM fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 49094915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lia, J.; Wei, Z. Transition-metal-oxide-based catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 8194–8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kelly, T.G.; Chen, J.G.; Mustain, W.E. Metal Carbides as Alternative Electrocatalyst Supports. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Zhang, J. Recent Progresses in Oxygen Reduction Reaction Electrocatalysts for Electrochemical Energy Applications. Electrochem. Energ. Rev. 2019, 2, 518–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wilkinson, P.D.; Zhang, J. Noncarbon Support Materials for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Electrocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7625–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Ganesan, P.; Park, S.; Popov, B.N. Development of a Titanium DioxideSupported Platinum Catalyst with Ultrahigh Stability for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13898–13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, A.D.; Wu, Y.C.; Su, W.N.; Pan, C.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Chen, H.M.; Lee, J.F.; Sheu, H.S.; Ho, V.T.T.; Hwang, B.J. In Situ Confined Synthesis of Ti4O7 Supported Platinum Electrocatalysts with Enhanced Activity and Stability for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Yin, G.; Gao, Y. Understanding and approaches for the durability issues of Pt-based catalysts for PEM fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.A.; Hicks, M.T.; Haugen, G.M.; Dahn, J.R. Ex Situ and In Situ Stability Studies of PEMFC Catalysts: Effect of Carbon Type and Humidification on Degradation of the Carbon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, A.F.; Balgis, R.; Ogi, T.; Iskandar, F.; Kinoshita, A.; Nakamura, K.; Okuyama, K. Highly conductive nano-sized Magnéli phases titanium oxide (TiOx). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, J.; Thakare, J.; Aulich, T.; Mann, M.; Zhao, J.X. Magnéli Phase Ti9O17− Catalyst Support Materials for ORR. In ECS Meeting Abstracts; MA2020-02 2849; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Stariha, S.; Macauley, N.; Sneed, B.T.; Langlois, D.; More, K.L.; Mukundan, R.; Borup, R.L. Recent Advances in Catalyst Accelerated Stress Tests for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Doshin, W.; Tsukamoto, H.; Yonezawa, T. Black TiO2 Nanoparticles by a Microwave-induced Plasma over Titanium Complex Aqueous Solution. Chem. Lett. 2015, 44, 1327–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, J.; Nguyen, T.V.; Singh, N.; McFarland, E.; Ikenberry, M.; Hohn, K.; Pan, C.J.; Hwang, B.J. A RhxSy/C Catalyst for the Hydrogen Oxidation and Hydrogen Evolution Reactions in HBr. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F455–F462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Masud, J.; Nath, M. Co7Se8 Nanostructures as Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction with High Methanol Tolerance. ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thakare, J.; Masud, J. Magnéli TiO2 as a High Durability Support for the Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Catalysts. Energies 2022, 15, 4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124437
Thakare J, Masud J. Magnéli TiO2 as a High Durability Support for the Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Catalysts. Energies. 2022; 15(12):4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124437
Chicago/Turabian StyleThakare, Jivan, and Jahangir Masud. 2022. "Magnéli TiO2 as a High Durability Support for the Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Catalysts" Energies 15, no. 12: 4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124437
APA StyleThakare, J., & Masud, J. (2022). Magnéli TiO2 as a High Durability Support for the Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Catalysts. Energies, 15(12), 4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124437






