A Grey-System Theory Approach to Assess the Safety of Gas-Supply Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Approach
2.1. The Risk Matrix
- negligible (0,0,1,2),
- low (1,2,3,4),
- medium (3,4,6,7),
- high (6,7,8,9),
- very high (8,9,10,10).
- : no gas supply disruption,
- : short disruption,
- : medium disruption,
- : long disruption,
- : critical disruption.
- The weight scale of a given type of failure mode (P):
- −
- , negligible,
- −
- , low,
- −
- , medium,
- −
- , high,
- −
- , very high.
- The weight scale (F) according the annual-longitudinal rate of failure λ along the gas-supply network:
- −
- , negligible,
- −
- , low,
- −
- , medium,
- −
- , high,
- −
- , very high.
- Supply disruption criticality level (NC) as a function of the disruption duration:
- −
- , negligible,
- −
- , low,
- −
- , medium,
- −
- , high,
- −
- , very high.
2.2. Grey-System Theory
- negligible: (i = 1)
- low: (i = 2)
- medium: (i = 3)
- high: (i = 4)
- very high: (i = 5)
3. Results
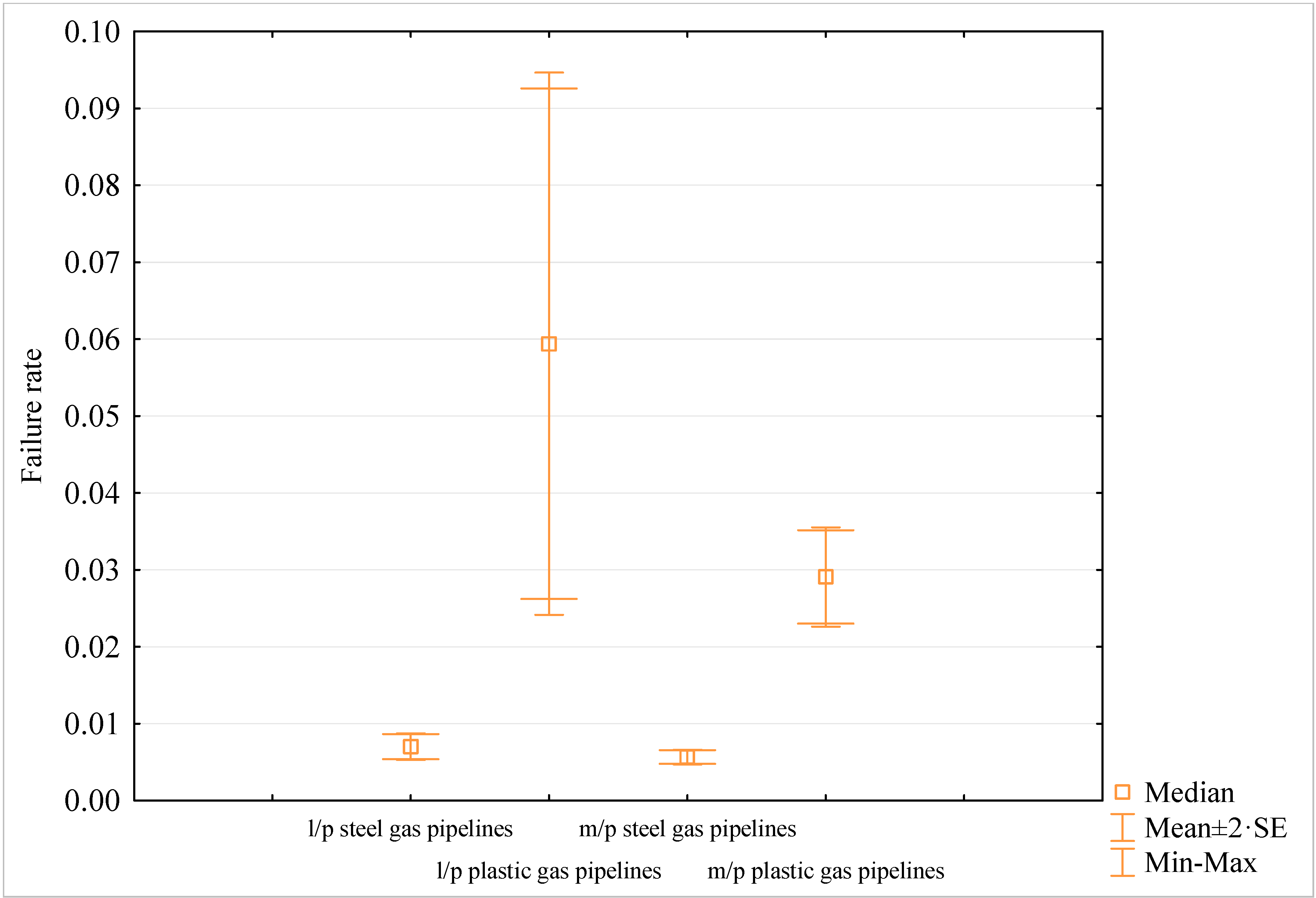
3.1. Analysing a Gas-Supply Network’s Technical State
3.2. Undesirable Events Prioritisation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Majid, Z.A.; Mohsin, R.; Yusof, M.Z. Experimental and computational failure analysis of natural gas pipe. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2012, 19, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, H.M.; Riad, W.T.; Alhazza, A.A.; Behbehani, M.H. Failure analysis of fuel supply pipeline. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2006, 13, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Akbar, A.; Maqbool, S.; Sokolová, M.; Haider, S.A.; Naz, S.; Danish, S.M. Corporate Risk Tolerance and Acceptability towards Sustainable Energy Transition. Energies 2022, 15, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, R.; Majid, Z.A. Erosive failure of natural gas pipes. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. 2014, 5, 818–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckhoener, C.; Lochner, S.; Lindenberger, D. Simulating the Effects of European Natural Gas Infrastructure Developments. Oil Gas-Eur. Mag. 2010, 36, 174–185. [Google Scholar]
- Ondrejka Harbulakova, V.; Estokova, A.; Kovalcikova, M. Correlation Analysis between Different Types of Corrosion of Concrete Containing Sulfate Resisting Cement. Environments 2017, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpak, D. Method for Determining the Probability of a Lack of Water Supply to Consumers. Energies 2020, 13, 5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchorzewska-Cieslak, B.; Boryczko, K.; Eid, M. Failure scenarios in water supply system by means of fault tree analysis. Adv. Saf. Reliab. Risk Manag. 2011, 2011, 2492–2499. [Google Scholar]
- Parka, A.; Kuliczkowska, E.; Kuliczkowski, A.; Zwierzchowska, A. Selection of pressure linings used for trenchless renovation of water pipelines. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 98, 103218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, R.; Octaviano, R.; Blokland, H.; Busking, T. Security of Supply in Gas and Hybrid Energy Networks. Energies 2021, 14, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Tchórzewska-Cieślak, B.; Eid, M. Water Network-Failure Data Assessment. Energies 2020, 13, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.M.; Zhang, C.S.; Shao, H.; Wang, M.T. Baye network quantitative risk analysis for failure of natural gas pipelines. J. Northeast Univ. 2011, 32, 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, H.U.; Ismail, M.C.; Nosbi, N. Permeation Damage of Polymer Liner in Oil and Gas Pipelines: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, M.; Spada, M.; Kadziński, M.; Miebs, G.; Burgherr, P. Advancing Hazard Assessment of Energy Accidents in the Natural Gas Sector with Rough Set Theory and Decision Rules. Energies 2019, 12, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, M.-S. Fifteen years of grey system theory research: A historical review and bibliometric analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 2767–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S.; Garrick, B.J. On the quantitative definition of risk. Risk Anal. 1981, 1, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, A.; Guzzini, A.; Pellegrini, M.; Saccani, C. Natural gas distribution system: A statistical analysis of accidents data. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2018, 168, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y. Optimal Maintenance Decision Method for Urban Gas Pipelines Based on as Low as Reasonably Practicable Principle. Sustainability 2019, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Camacho, G.J.; Carbone, F.; Pastor, E.; Bubbico, R.; Casal, J. Assessing the consequences of pipeline accidents to support land-use planning. Saf. Sci. 2017, 97, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.L. Control Problems of Grey Systems. Syst. Control Lett. 1982, 1, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpak, D.; Tchorzewska-Cieslak, B. The Use of Grey Systems Theory to Analyze the Water Supply Systems Safety. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4141–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.L.; Wei, C.C.; Lee, Y.H. Failure mode and effects analysis using fuzzy method and grey theory. Kybernetes 1999, 28, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, A.; Wang, J. Modified failure mode and effects analysis using approximate reasoning. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe 2003, 79, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.B.; Klien, C.M. A simple approach to ranking a group of aggregated fuzzy utilities. IEEE Trans Syst. Man. Cybernet Part B Cybernet 1997, 27, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.L. Introduction to Grey System Theory. J. Grey Syst. 1989, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tchórzewska-Cieślak, B.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Urbanik, M. Analysis of the gas network failure prediction using the Monte Carlo simulation method. Eksploat. Niezawodn. 2016, 18, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchórzewska-Cieślak, B.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Urbanik, M.; Rak, J.R. Approaches for Safety Analysis of Gas-Pipeline Functionality in Terms of Failure Occurrence: A Case Study. Energies 2018, 11, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbanik, M.; Tchórzewska-Cieślak, B.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K. Analysis of the Safety of Functioning Gas Pipelines in Terms of the Occurrence of Failures. Energies 2019, 12, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilmott, M.J.; Diakow, D.A. Factors influencing stress corrosion cracking of gas transmission pipelines: Detailed studies following a pipeline failure. Part 2: Pipe metallurgy and mechanical testing. Proc. Int. Pipeline Conf. 2016, 1, 573–585. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, K.M.; Hart, R.F. Quantitative Methods for Quality Improvement; ASQC Quality Press: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]






| No. | Failure Causes | % of the Total | Average Length of Time over Which the Supply Was Interrupted [h] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | mechanical damage | 30.5 (P = medium) | 4.50 (N = medium) |
| 2 | operating wear of material | 26 (P = medium) | 3.35 (N = low) |
| 3 | defects in workmanship | 23 (P = medium) | 6.15 (N = medium) |
| 4 | corrosion | 13.5 (P = low) | 1.62 (N = negligible) |
| 5 | landslide | 3.75 (P = negligible) | 4.15 (N = medium) |
| 6 | other | 3.25 (P = negligible) | 3.15 (N = low) |
| No. | % of the Total—P | γP | Failure Rate—F | γI | Gas Supply Disruption—NC | γN | Relation Degree Γ | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | medium | 0.333 | Low | 0.533 | medium | 0.333 | 0.383 | 1 |
| 2 | medium | 0.333 | low | 0.533 | low | 0.533 | 0.483 | 2 |
| 3 | medium | 0.333 | low | 0.533 | medium | 0.333 | 0.383 | 1 |
| 4 | low | 0.533 | low | 0.533 | negligible | 1.000 | 0.767 | 5 |
| 5 | negligible | 1.000 | low | 0.533 | medium | 0.333 | 0.550 | 3 |
| 6 | negligible | 1.000 | low | 0.533 | low | 0.533 | 0.650 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szpak, D.; Tchórzewska-Cieślak, B.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Eid, M. A Grey-System Theory Approach to Assess the Safety of Gas-Supply Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124240
Szpak D, Tchórzewska-Cieślak B, Pietrucha-Urbanik K, Eid M. A Grey-System Theory Approach to Assess the Safety of Gas-Supply Systems. Energies. 2022; 15(12):4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124240
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzpak, Dawid, Barbara Tchórzewska-Cieślak, Katarzyna Pietrucha-Urbanik, and Mohamed Eid. 2022. "A Grey-System Theory Approach to Assess the Safety of Gas-Supply Systems" Energies 15, no. 12: 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124240
APA StyleSzpak, D., Tchórzewska-Cieślak, B., Pietrucha-Urbanik, K., & Eid, M. (2022). A Grey-System Theory Approach to Assess the Safety of Gas-Supply Systems. Energies, 15(12), 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124240









