Multi-Step Short-Term Wind Speed Prediction Models Based on Adaptive Robust Decomposition Coupled with Deep Gated Recurrent Unit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
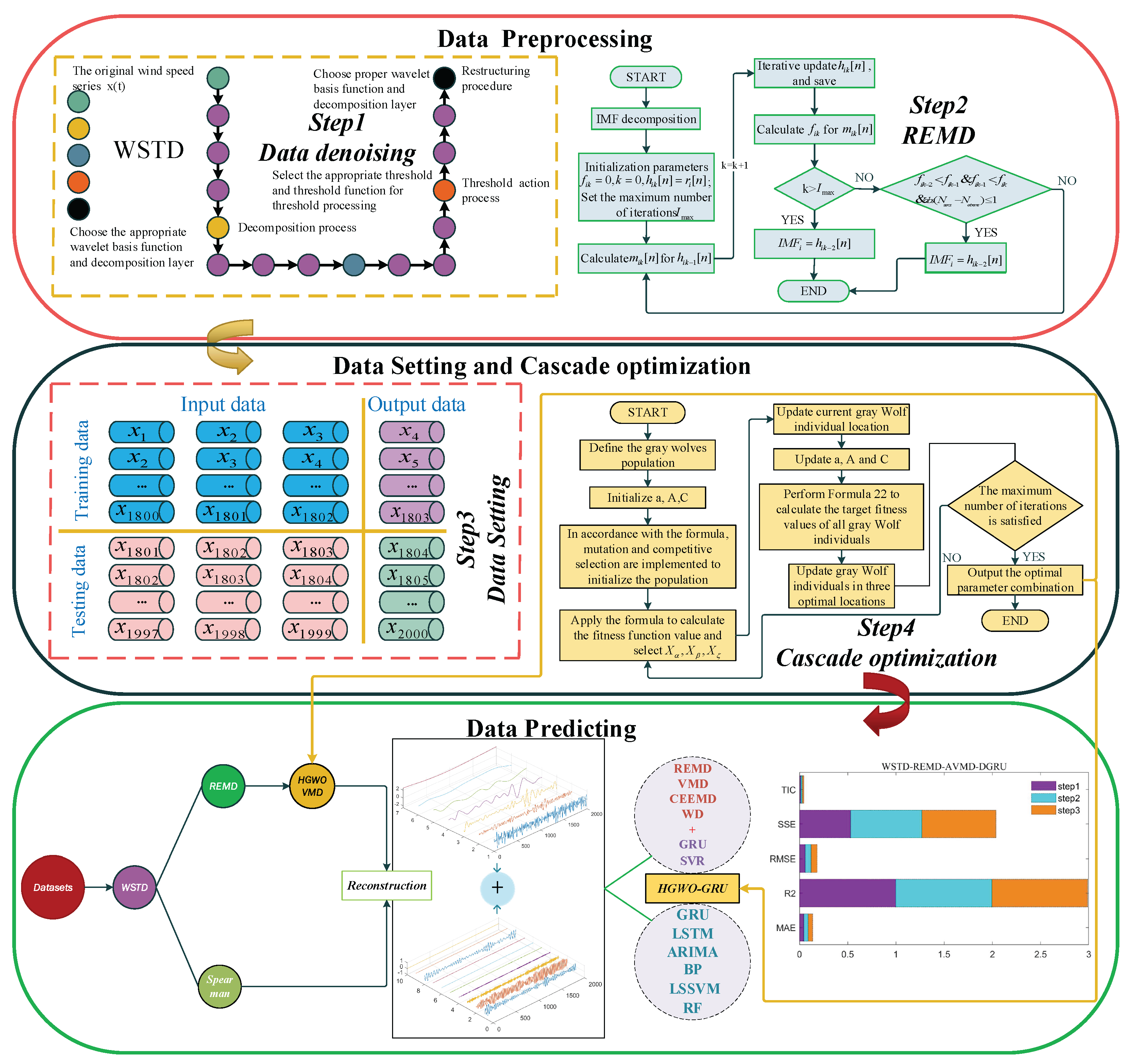
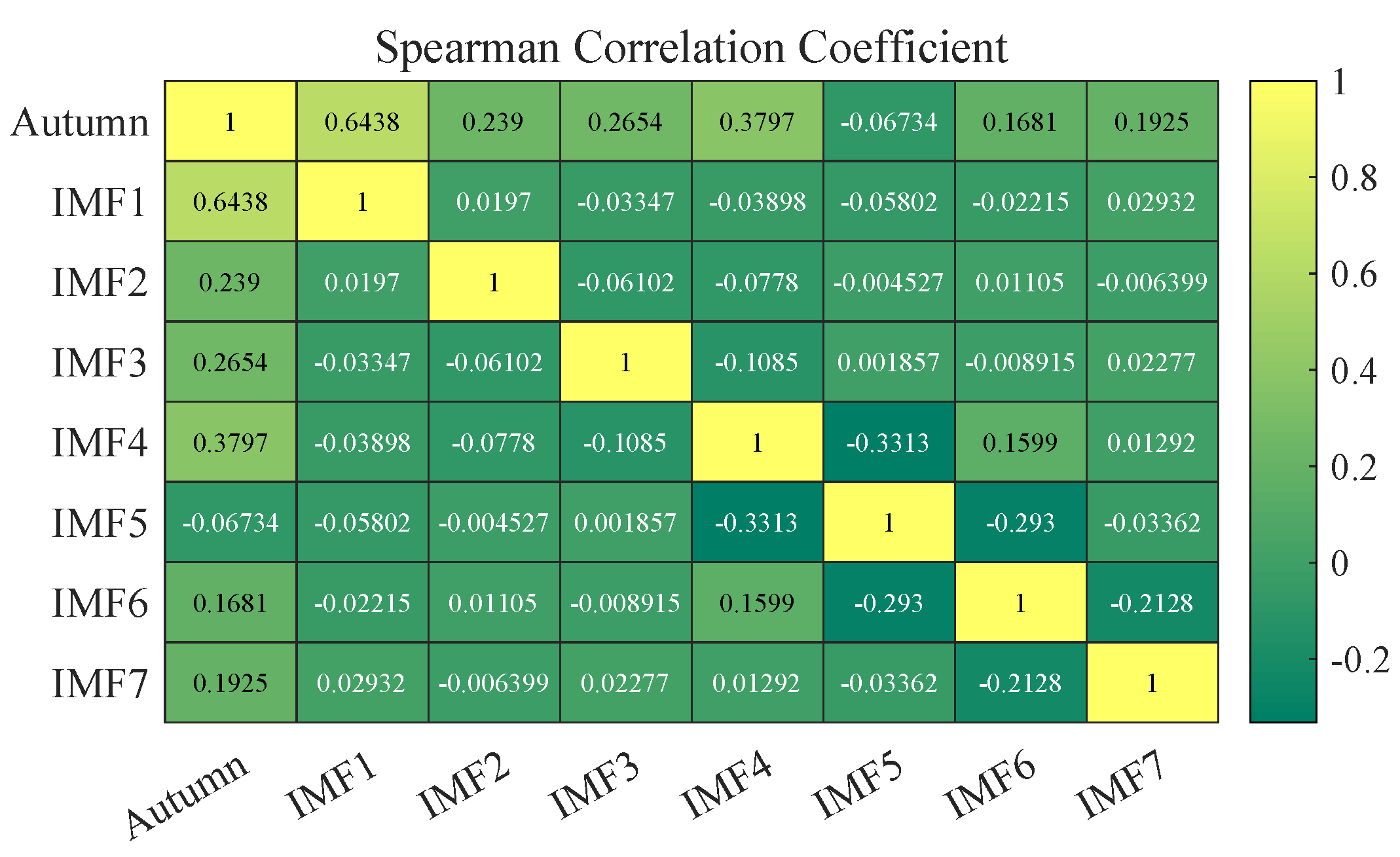
- Data preprocessing strategy: A novel and efficient two-stage data preprocessing technology is proposed. WSTD filters out the redundant noise of the original wind speed series. One-stage REMD decomposes to obtain a series of IMFs to eliminate random fluctuations. To reduce the error, Spearman correlation analysis is used to analyze the correlation between each IMF and the original wind speed time series, group reconstruction, reduce the accumulation of errors, and prepare high-quality data for prediction purposes.
- (2)
- Cascade optimization strategy: The cascading optimization strategy based on HGWO, which is used for the first time, and the optimized VMD is used to decompose the IMFs with strong correlation in the wind speed correlation series in the second stage to further explore the potential characteristic information of the wind speed. On this basis, it is more robust to deal with time series of complex characteristics.
- (3)
- Prediction strategy: The strategy of cascading optimization is adopted to dynamically analyze the optimal input parameters and optimal network structure of the GRU deep learning model, and the reorganized wind speed correlation sub-series are predicted and superimposed in the future time step to complete deeper wind speed characteristic extraction and learning, which greatly enhance the stability and generalization of the model.
- (4)
- The combined multi-step wind speed prediction method of WSTD, REMD, and HGWO-VMD-GRU is proposed, which integrates the advantages of each single model. The wind speed datasets of different seasons in the Shanghai Bay area are selected to verify the validity of the model, and the final conclusion is reached by testing and analyzing three different benchmark models with the classic single models, the decomposition optimization models, and other combined models.
2. Related Methodology
2.1. Data Preprocessing
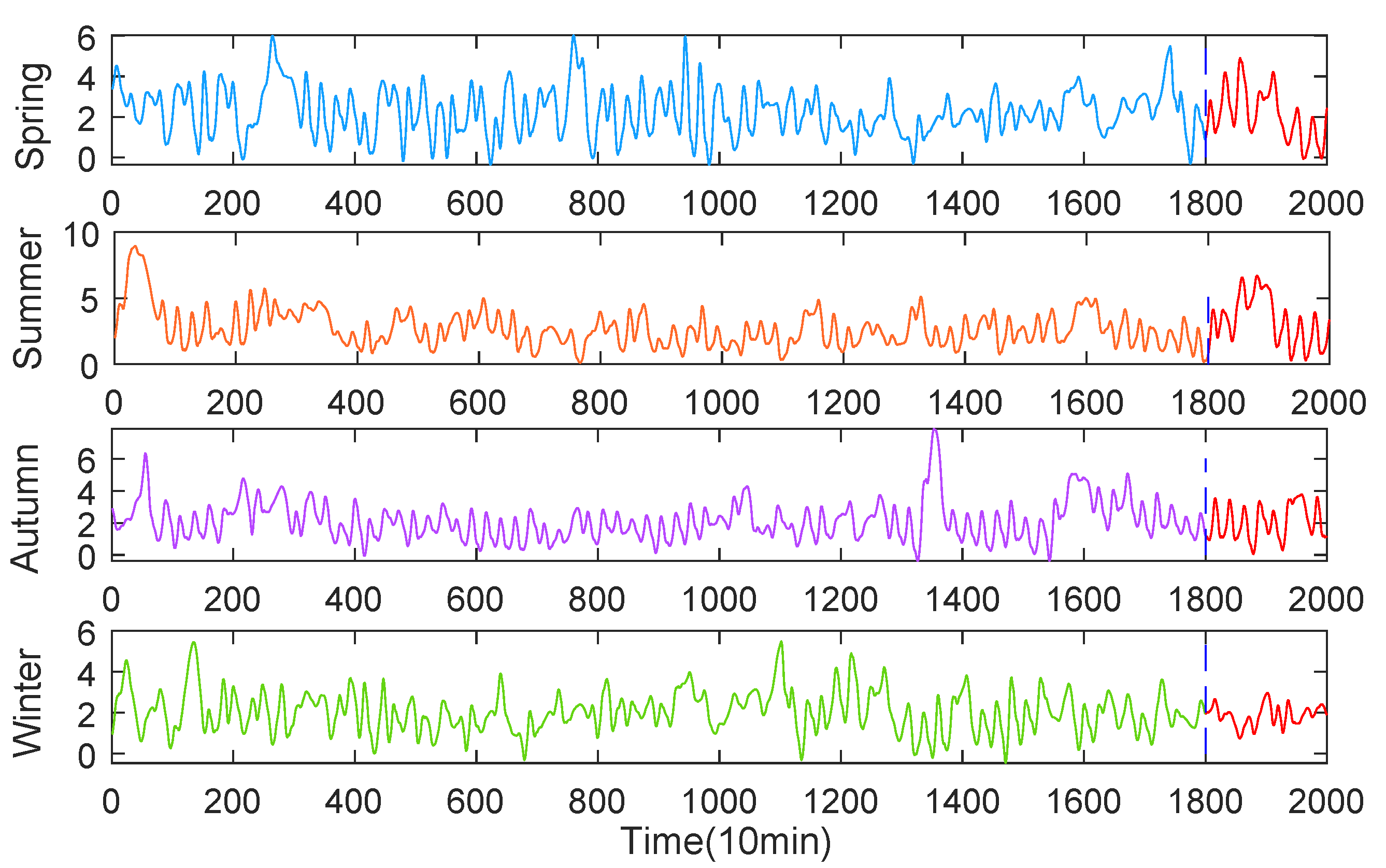
2.1.1. Data Collection
2.1.2. Data Denoising Based on WSTD
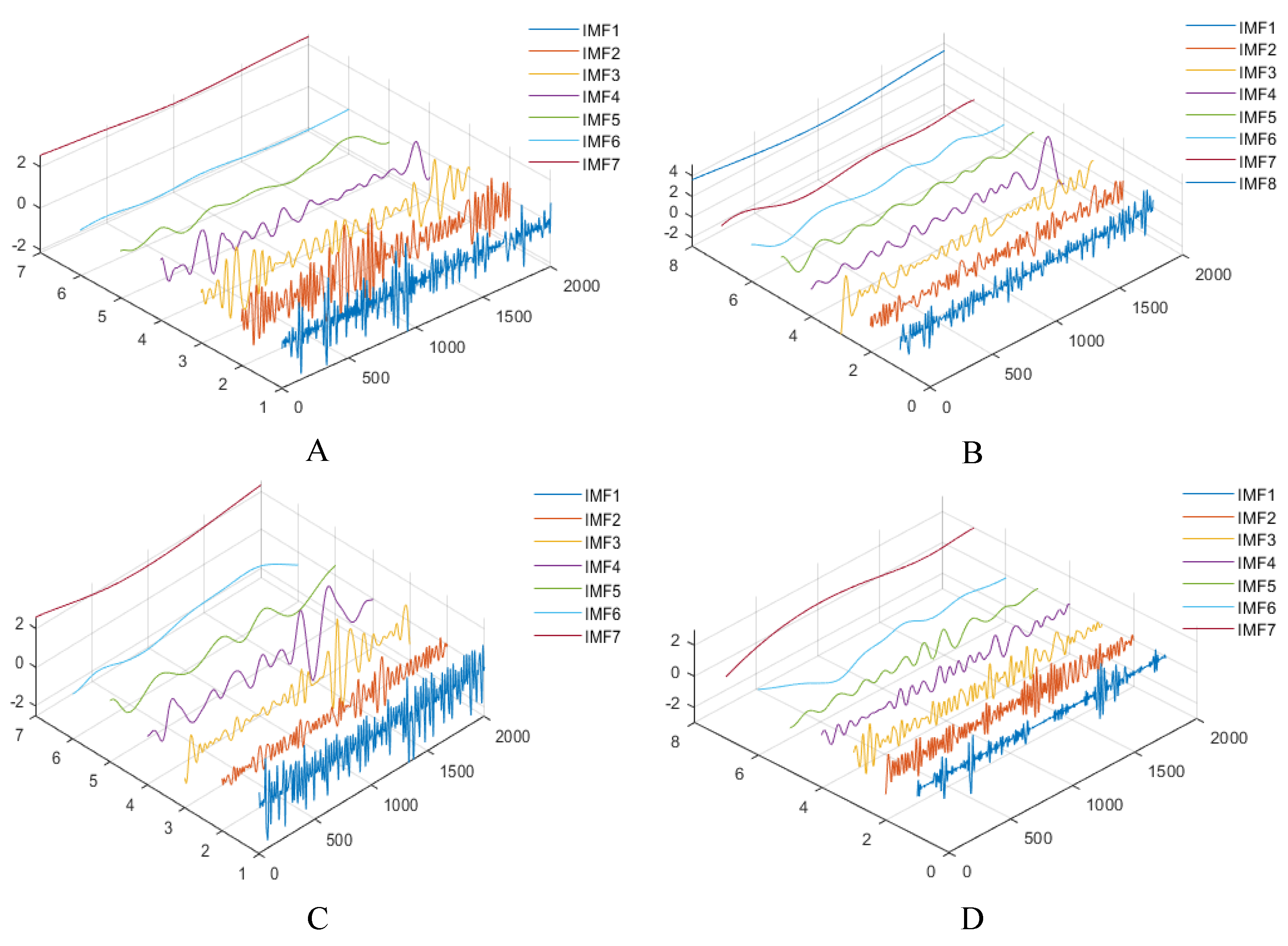
2.1.3. One-Stage Decomposition Based on REMD
- Step 1:
- Initialize parameters k and i, set the maximum number of sifting iterations ;
- Step 2:
- Find the maximum and minimum values of the wind speed signal . The upper and lower envelopes are obtained by cubic spline interpolation. Then, calculate the average value of the upper and lower envelopes :where indicates the signal after the ith IMF sifting k times;
- Step 3:
- Apply the objective function of SSC to calculate the objective value . The objective function is defined as follows:where stands for the arithmetic mean of ;
- Step 4:
- Execute SSC to determine the sifting stop process. If it is satisfied at the same time, stop and output; otherwise, return to step 2 and continue to iterate until the maximum number of sifting iterations is received, and output the k-2nd as . The two criteria are expressed as follows:
2.2. Cascade Optimization
2.2.1. The Hybridizing Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm
2.2.2. Two-Stage Decomposition Based on VMD
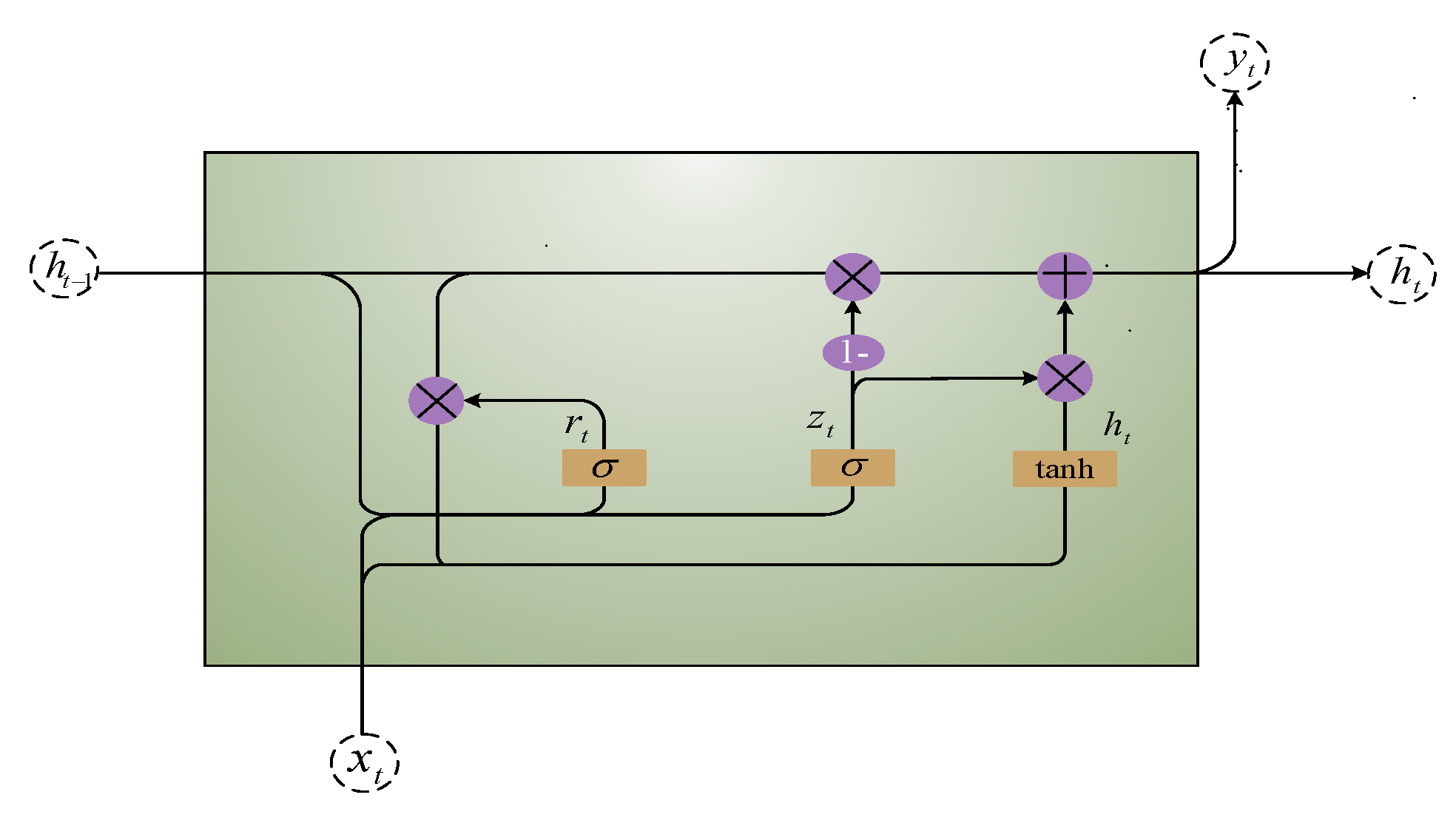
2.3. Prediction Model
Deep Gated Recurrent Unit
- Step 1:
- Define the parameters of HGWO, such as population size N, maximum number of iterations , and crossover probability parameters .
- Step 2:
- Initialize the parameters , implement DE mutation and competitive selection on the population individuals according to the formula, and generate the initial population.
- Step 3:
- Apply formula (12)–(21), calculate the objective function value of each grey wolf individual in the population, and select the positions of the three individual grey wolves , , and with the optimal value. Then, calculate the distance between other grey wolves in the population and the optimal individual position, and update the current position.
- Step 4:
- According to the formula (9)–(11), cross the positions of individuals and screen out new individuals.
- Step 5:
- Perform formula (22), calculate the target fitness value of all grey wolf individuals, and update the grey wolf individuals in the three optimal positions of , , and .
- Step 6:
- Cycle process, judge whether the maximum number of iterations is reached; if so, save the global optimal solution and exit. Otherwise, return to step 3 to continue the iterative update.
- Step 7:
- Output the optimal position, that is, . The GRU network determines the optimal combination parameters (GRU-size, Learning-rate).
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation Index
3.2. Denoising Verification
3.3. Experimental Results
3.3.1. Validation of REMD Method
3.3.2. Rationality of Adaptive VMD Method
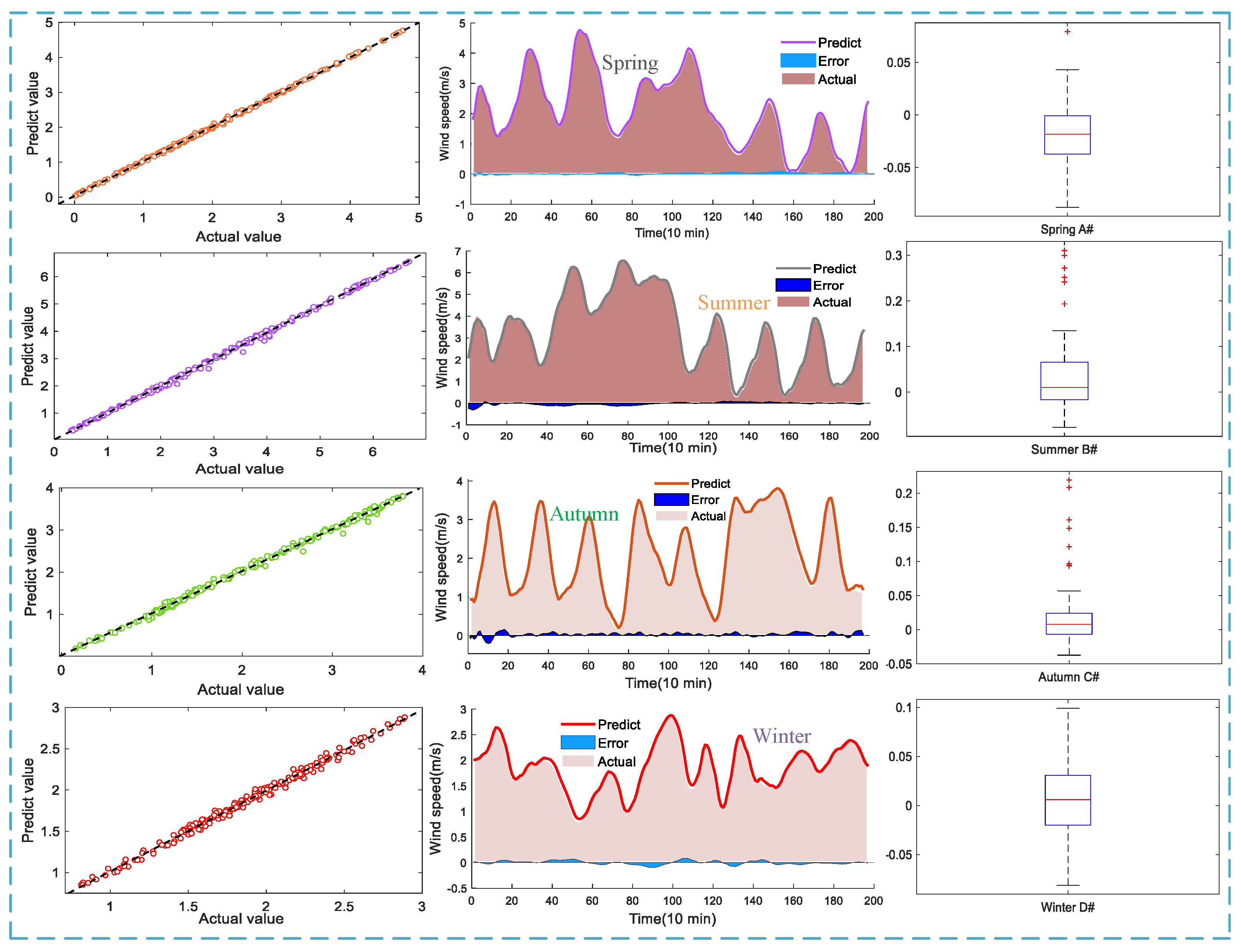
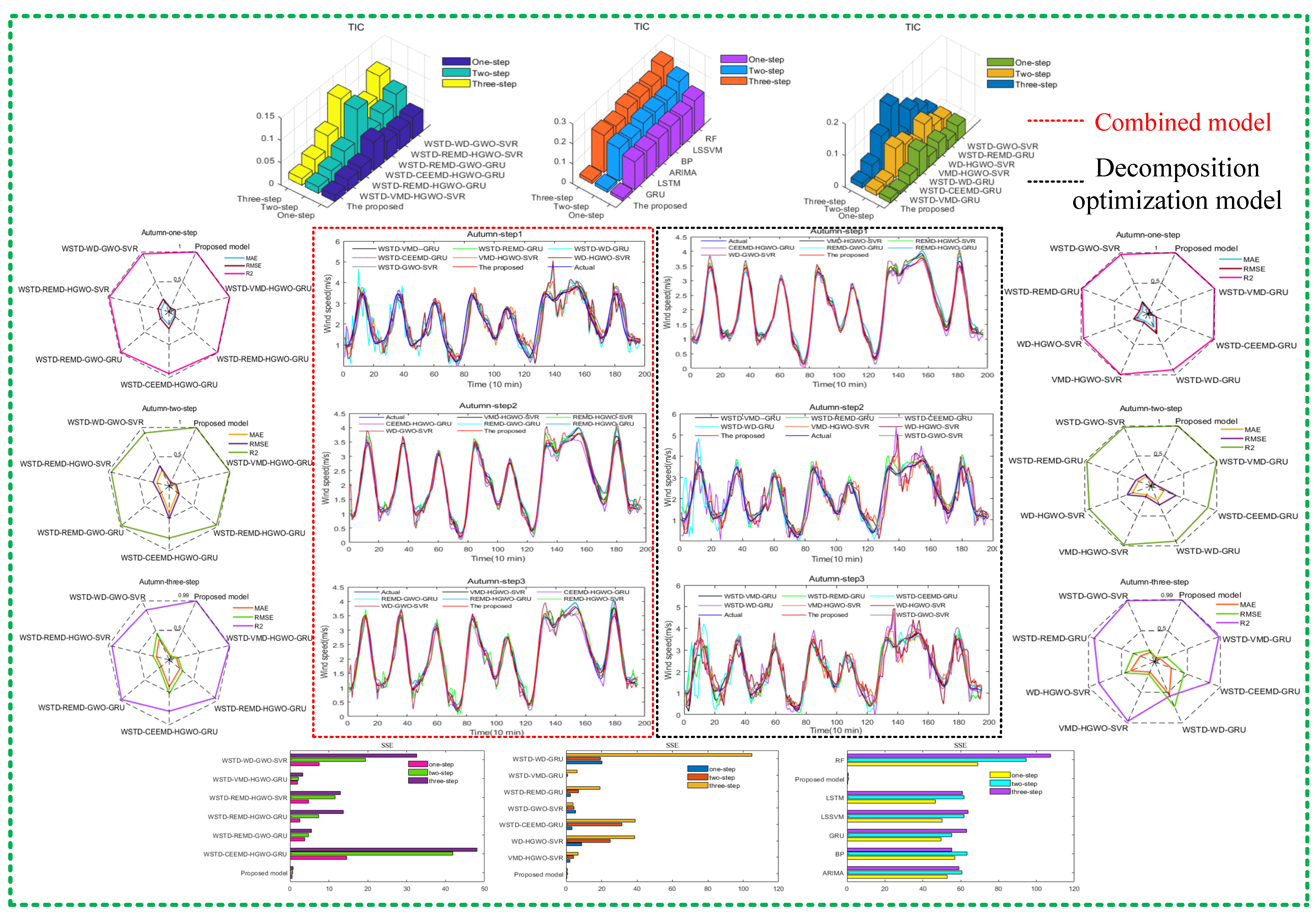
3.3.3. Prediction Results
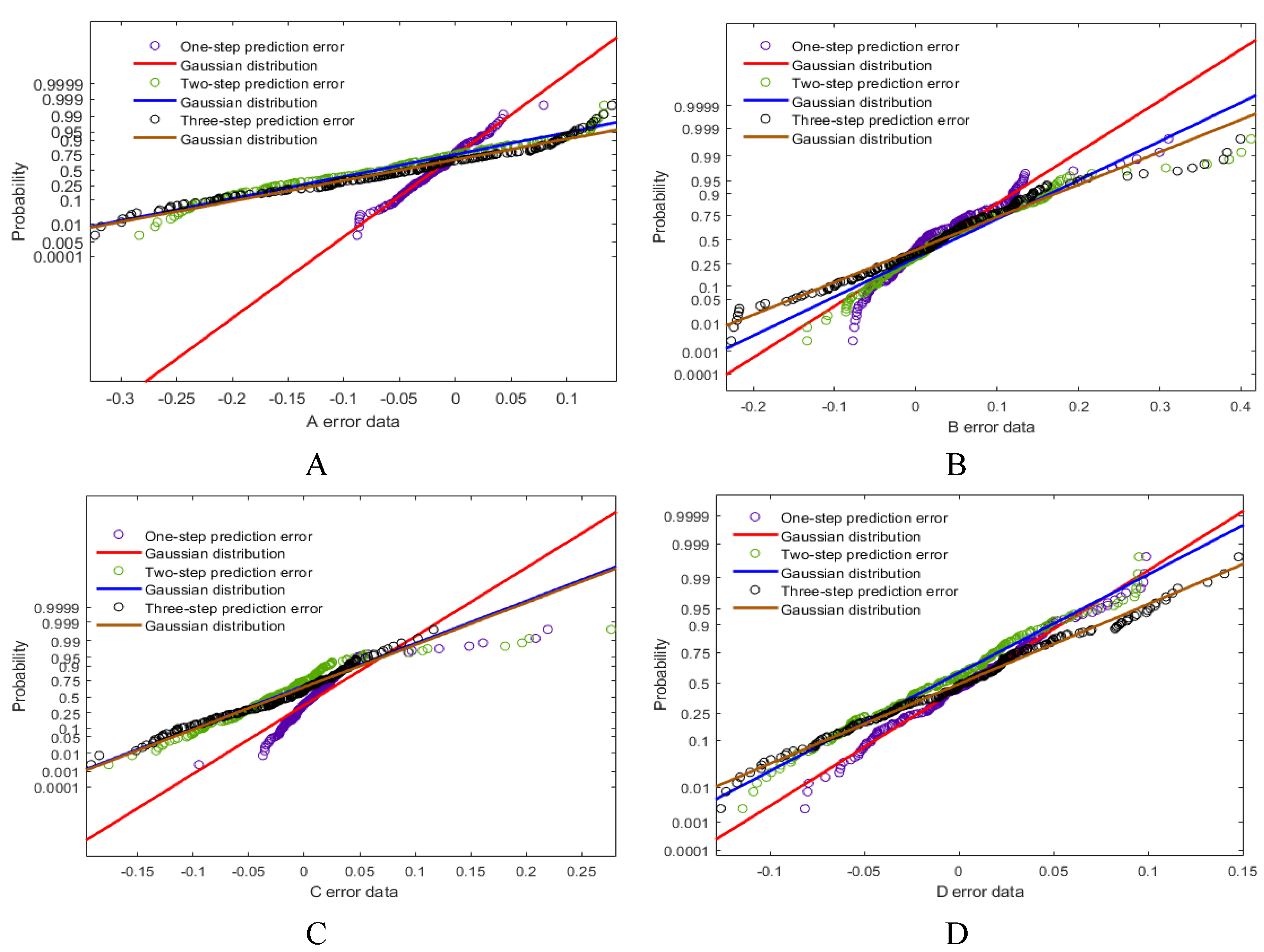
3.3.4. Error Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zou, R.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q. A review of wind speed and wind power forecasting with deep neural networks. Appl. Energy 2021, 304, 117766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chang, R.; He, G.; Tang, W. Optimizing wind/solar combinations at finer scales to mitigate renewable energy variability in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 156, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga, D.; Alvarez, A.; Giraldo, T. Short-term wind speed prediction based on robust Kalman filtering: An experimental comparison. Appl. Energy 2015, 156, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, B.; Lu, Z. A hybrid model based on data preprocessing strategy and error correction system for wind speed forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 212, 112779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, M.; Craciun, A.; Dumitrescu, A. Hybrid numerical models for wind speed forecasting. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2021, 220, 105669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzgou, H.; Benoudjit, N. Multiple architecture system for wind speed prediction. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, S.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, L. Sequence transfer correction algorithm for numerical weather prediction wind speed and its application in a wind power forecasting system. Appl. Energy 2019, 237, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, C. Short-term wind power prediction based on spatial model. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geibel, M.; Bangga, G. Data Reduction and Reconstruction of Wind Turbine Wake Employing Data Driven Approaches. Energies 2022, 15, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Lv, Q.; Sun, H. A novel wind speed prediction strategy based on Bi-LSTM, MOOFADA and transfer learning for centralized control centers. Energy 2021, 230, 120904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydia, M.; Kumar, S.; Selvakumar, A.; Kumar, G. Linear and non-linear autoregressive models for short-term wind speed forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 112, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, E.; Shi, J. ARMA based approaches for forecasting the tuple of wind speed and direction. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Banihabib, M.; Behbahani, S. Comparison of the ARMA, ARIMA, and the autoregressive artificial neural network models in forecasting the monthly inflow of Dez dam reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corba, B.; Egrioglu, E.; Dalar, A. AR–ARCH type artificial neural network for forecasting. Neural Process. Lett. 2020, 51, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziukynas, V.; Klementavicius, A. Short-term wind speed forecasting with ARIMA model. In Proceedings of the 2014 55th International Scientific Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering of Riga Technical University (RTUCON), Riga, Latvia, 14 October 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Wang, G.; Ren, Y. Short-term wind speed forecasting based on autoregressive moving average with echo state network compensation. Wind. Eng. 2020, 44, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Krishnaveny, R.; Vanitha, B.; Jisma, C. Forecasting of wind speed using ANN, ARIMA and hybrid models. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Instrumentation and Control Technologies (ICICICT), Kannur, India, 6–7 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Shukur, O.; Lee, M. Daily wind speed forecasting through hybrid KF-ANN model based on ARIMA. Renew. Energy 2015, 76, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Su, J.; Han, Z.; Zhou, D. Short-term wind speed predicting framework based on EEMD-GA-LSTM method under large scaled wind history. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 227, 113559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; An, N.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Hu, B.; Shang, D. Optimal parameters selection for BP neural network based on particle swarm optimization: A case study of wind speed forecasting. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 56, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, C.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tan, Q. Short-term wind power prediction based on LSSVM–GSA model. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 101, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Nie, G.; Chen, Y. The municipal solid waste generation distribution prediction system based on FIG–GA-SVR model. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1352–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiao, Z.; Xia, X.; Zou, W.; Zhang, C. A hybrid model based on synchronous optimisation for multi-step short-term wind speed forecasting. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M. Comparative study on three new hybrid models using Elman Neural Network and Empirical Mode Decomposition based technologies improved by Singular Spectrum Analysis for hour-ahead wind speed forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 147, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, M.; Venkaiah, C.; Kumar, D. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition based adaptive wavelet neural network method for wind speed prediction. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 168, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, E.; Cifuentes, J.; Marulanda, G. Short-Term Forecasting of Wind Energy: A Comparison of Deep Learning Frameworks. Energies 2021, 14, 7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, C. Data processing strategies in wind energy forecasting models and applications: A comprehensive review. Appl. Energy 2019, 249, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G. Hybrid forecasting system based on an optimal model selection strategy for different wind speed forecasting problems. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 1559–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Pei, Y.; Zareipour, H.; Chen, N. A review and discussion of decomposition-based hybrid models for wind energy forecasting applications. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Zhao, S. Wind speed prediction based on singular spectrum analysis and neural network structural learning. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 216, 112956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyükşahin, Ü.Ç.; Ertekin, Ş. Improving forecasting accuracy of time series data using a new ARIMA-ANN hybrid method and empirical mode decomposition. Neurocomputing 2019, 361, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, H. Multi-step short-term wind speed prediction based on integrated multi-model fusion. Appl. Energy 2021, 298, 117248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Pan, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F. A multi-stage predicting methodology based on data decomposition and error correction for ultra-short-term wind energy prediction. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 125981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Wang, P.; Ma, W.; Fang, S.; Hou, Z. A novel hybrid model based on nonlinear weighted combination for short-term wind power forecasting. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 134, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Liu, Z.; Deng, W. Short-term wind speed multistep combined forecasting model based on two-stage decomposition and LSTM. Wind. Energy 2021, 24, 991–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. A Novel Deep Learning Approach for Wind Power Forecasting Based on WD-LSTM Model. Energies 2020, 13, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Ye, L.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, B.; Pei, M.; Tang, Y. Review of meta-heuristic algorithms for wind power prediction: Methodologies, applications and challenges. Appl. Energy 2021, 301, 117446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, M.; Ding, L.; Ma, Y. Double-layer staged training echo-state networks for wind speed prediction using variational mode decomposition. Appl. Energy 2021, 301, 117461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Du, P.; Yang, W. A novel hybrid system based on multi-objective optimization for wind speed forecasting. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshat, M.; Nezhad, M.; Abbasnejad, E.; Mirjalili, S.; Tjernberg, L.; Garcia, D.; Alexander, B.; Wagner, M. A deep learning-based evolutionary model for short-term wind speed forecasting: A case study of the Lillgrund offshore wind farm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 236, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, H. A novel decomposition-ensemble prediction model for ultra-short-term wind speed. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 248, 114775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.; Wu, M.; Shih, H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.; Tung, C.; Liu, H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Y. A prediction approach using ensemble empirical mode decomposition-permutation entropy and regularized extreme learning machine for short-term wind speed. Wind. Energy 2020, 23, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xia, X.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Y. Combined model with secondary decomposition-model selection and sample selection for multi-step wind power forecasting. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Peng, S.; Fu, L.; Lu, B.; Tang, J.; Wang, K.; Li, W. A novel deep learning ensemble model with data denoising for short-term wind speed forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 207, 112524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Peng, D.; Zuo, M.; Xia, J.; Qin, Y. Improved Hilbert–Huang transform with soft sifting stopping criterion and its application to fault diagnosis of wheelset bearings. ISA Trans. 2021, 21, 0019–0578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z. Hybridizing grey wolf optimization with differential evolution for global optimization and test scheduling for 3D stacked SoC. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2015, 26, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivam, K.; Tzou, J.; Wu, S. Multi-Step Short-Term Wind Speed Prediction Using a Residual Dilated Causal Convolutional Network with Nonlinear Attention. Energies 2020, 13, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Wavelet Basis Function | SNR/dB | RMSE |
|---|---|---|
| db4 | 12.8588 | 0.5677 |
| haar | 11.3318 | 0.6768 |
| db3 | 12.5165 | 0.5905 |
| sym2 | 12.3492 | 0.6020 |
| Index | Meaning | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio | |
| MAE | Mean absolute error | |
| RMSE | Root mean square error | |
| Coefficient of determination | ||
| TIC | Theil inequality coefficient | |
| SSE | Square sum error |
| Model | MAE | RMSE | TIC | SSE | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | |
| The proposed | 0.0265 | ||||||||||||||
| WSTD-VMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.0873 | 0.0997 | 0.1105 | 0.0936 | 0.1203 | 0.1346 | 0.9942 | 0.9937 | 0.9902 | 0.0246 | 0.0287 | 0.0396 | 0.5648 | 1.6243 | 2.6591 |
| WSTD-REMD-HGWO-GRU | 0.1082 | 0.1394 | 0.1772 | 0.1257 | 0.1678 | 0.2177 | 0.9914 | 0.9821 | 0.9701 | 0.0296 | 0.0397 | 0.0515 | 2.3157 | 4.9175 | 7.8733 |
| WSTD-CEEMD-HGWO-GRU | 0.2381 | 0.3242 | 0.4317 | 0.3112 | 0.4662 | 0.5826 | 0.9459 | 0.8741 | 0.8050 | 0.0735 | 0.1106 | 0.1374 | 16.2923 | 39.2686 | 57.5463 |
| WSTD-REMD-GWO-GRU | 0.2029 | 0.2151 | 0.2266 | 0.2459 | 0.2569 | 0.2745 | 0.9740 | 0.9662 | 0.9595 | 0.0566 | 0.0597 | 0.0647 | 6.2862 | 9.9638 | 9.2274 |
| WSTD-REMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.1482 | 0.1554 | 0.4801 | 0.2364 | 0.2888 | 0.5893 | 0.9752 | 0.9461 | 0.7757 | 0.0542 | 0.0678 | 0.1417 | 7.3970 | 16.1000 | 59.1824 |
| WSTD-WD-GWO-SVR | 0.1631 | 0.2624 | 0.3381 | 0.2062 | 0.3430 | 0.4412 | 0.9758 | 0.9311 | 0.8829 | 0.0493 | 0.0809 | 0.1046 | 7.7958 | 20.7852 | 34.2191 |
| WSTD-VMD–GRU | 0.0289 | 0.0968 | 0.1045 | 0.0414 | 0.0916 | 0.1389 | 0.9970 | 0.9925 | 0.9866 | 0.0108 | 0.0219 | 0.0342 | 0.2666 | 0.9548 | 3.5586 |
| WSTD-CEEMD-GRU | 0.2256 | 0.2760 | 0.3255 | 0.3190 | 0.3605 | 0.3817 | 0.9366 | 0.9203 | 0.9132 | 0.0748 | 0.0850 | 0.0888 | 19.7238 | 25.5663 | 27.3503 |
| WSTD-WD-GRU | 0.2537 | 0.3061 | 0.4751 | 0.3380 | 0.4051 | 0.5911 | 0.9342 | 0.9058 | 0.8011 | 0.0826 | 0.0959 | 0.1314 | 22.5032 | 32.1648 | 68.1359 |
| VMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.1351 | 0.1786 | 0.1776 | 0.1634 | 0.2157 | 0.2160 | 0.9870 | 0.9774 | 0.9724 | 0.0383 | 0.0502 | 0.0509 | 3.3464 | 6.6253 | 7.0425 |
| WD-HGWO-SVR | 0.1634 | 0.2616 | 0.3354 | 0.2063 | 0.3396 | 0.4351 | 0.9867 | 0.9338 | 0.8917 | 0.0489 | 0.0799 | 0.1028 | 8.3818 | 22.6097 | 36.9103 |
| WSTD-REMD-GRU | 0.0510 | 0.1557 | 0.1725 | 0.0672 | 0.1883 | 0.2406 | 0.9970 | 0.9863 | 0.9654 | 0.0159 | 0.04433 | 0.0580 | 0.8734 | 4.0478 | 9.9962 |
| WSTD-GWO-SVR | 0.2002 | 0.2138 | 0.2258 | 0.2427 | 0.2560 | 0.2703 | 0.9732 | 0.9668 | 0.9577 | 0.0560 | 0.0595 | 0.0636 | 6.5164 | 7.8110 | 10.0248 |
| GRU | 0.5100 | 0.6724 | 0.7834 | 0.6597 | 0.8546 | 0.9884 | 0.7673 | 0.6078 | 0.4853 | 0.1541 | 0.1989 | 0.2262 | 55.3926 | 70.7938 | 69.7912 |
| LSTM | 0.5022 | 0.6801 | 0.7733 | 0.6515 | 0.8735 | 0.9701 | 0.7737 | 0.5942 | 0.4943 | 0.1526 | 0.2024 | 0.2241 | 53.0837 | 68.5102 | 79.3900 |
| ARIMA | 0.5056 | 0.6550 | 0.7655 | 0.6450 | 0.8205 | 0.9535 | 0.7722 | 0.6336 | 0.5084 | 0.1525 | 0.1930 | 0.2231 | 59.5121 | 74.0400 | 76.1862 |
| BP | 0.5153 | 0.6376 | 0.7578 | 0.6597 | 0.8394 | 0.9440 | 0.7632 | 0.6156 | 0.5191 | 0.1557 | 0.2015 | 0.2213 | 58.4474 | 82.8701 | 74.1387 |
| LSSVM | 0.5119 | 0.6616 | 0.7596 | 0.6499 | 0.8292 | 0.9538 | 0.7724 | 0.6317 | 0.5202 | 0.1537 | 0.1951 | 0.2233 | 53.9873 | 65.1392 | 61.5543 |
| RF | 0.5714 | 0.7492 | 0.8794 | 0.7190 | 0.9324 | 1.0929 | 0.7178 | 0.5325 | 0.3642 | 0.1700 | 0.2176 | 0.2562 | 79.6895 | 109.9353 | 119.3138 |
| Model | MAE | RMSE | TIC | SSE | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | |
| WSTD-VMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.1390 | 0.1518 | 0.1626 | 0.1788 | 0.1861 | 0.2010 | 0.9901 | 0.9891 | 0,9843 | 0.0270 | 0.0279 | 0.0301 | 6.0389 | 4.9523 | 5.7395 |
| WSTD-REMD-HGWO-GRU | 0.1952 | 0.2454 | 0.3140 | 0.2387 | 0.3039 | 0.4096 | 0.9858 | 0.9730 | 0.9479 | 0.0360 | 0.0456 | 0.0611 | 7.8560 | 15.2756 | 30.4725 |
| WSTD-CEEMD-HGWO-GRU | 0.2891 | 0.3531 | 0.4867 | 0.3697 | 0.4552 | 0.6076 | 0.9613 | 0.9443 | 0.8993 | 0.0555 | 0.0688 | 0.0913 | 24.8642 | 32.8804 | 54.8275 |
| WSTD-REMD-GWO-GRU | 0.1972 | 0.2117 | 0.2952 | 0.2332 | 0.3947 | 0.4950 | 0.9895 | 0.9538 | 0.9232 | 0.0350 | 0.0603 | 0.0745 | 5.5570 | 27.4678 | 47.3507 |
| WSTD-REMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.2649 | 0.3818 | 0.4564 | 0.3185 | 0.4751 | 0.5583 | 0.9715 | 0.9354 | 0.9108 | 0.0474 | 0.0707 | 0.0831 | 18.7953 | 39.9718 | 53.7150 |
| WSTD-WD-GWO-SVR | 0.4010 | 0.4073 | 0.4079 | 0.4735 | 0.4783 | 0.4850 | 0.9639 | 0.9620 | 0.9618 | 0.0723 | 0.0735 | 0.0746 | 14.9314 | 15.3618 | 15.3963 |
| WSTD-VMD–GRU | 0.1387 | 0.2000 | 0.2849 | 0.1810 | 0.2160 | 0.5525 | 0.9934 | 0.9849 | 0.9078 | 0.0278 | 0.0325 | 0.0826 | 3.0832 | 8.8005 | 59.2937 |
| WSTD-CEEMD-GRU | 0.3969 | 0.5127 | 0.6638 | 0.6430 | 0.9566 | 1.0510 | 0.9234 | 0.8393 | 0.8288 | 0.1013 | 0.1513 | 0.1728 | 59.4176 | 156.9631 | 170.2382 |
| WSTD-WD-GRU | 0.2893 | 0.3905 | 0.5251 | 0.3994 | 0.5134 | 0.6400 | 0.9544 | 0.9250 | 0.8841 | 0.0597 | 0.0765 | 0.0990 | 31.4280 | 51.6582 | 79.8677 |
| VMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.2329 | 0.3986 | 0.4242 | 0.3178 | 0.4100 | 0.5365 | 0.9720 | 0.9689 | 0.9312 | 0.0472 | 0.0514 | 0.0763 | 6.9342 | 23.7923 | 36.5286 |
| WD-HGWO-SVR | 0.2691 | 0.3872 | 0.4514 | 0.3249 | 0.4809 | 0.5544 | 0.9701 | 0.9342 | 0.9130 | 0.0484 | 0.0715 | 0.0824 | 20.8039 | 45.3356 | 59.9384 |
| WSTD-REMD-GRU | 0.1197 | 0.2083 | 0.3410 | 0.1600 | 0.3150 | 0.4440 | 0.9945 | 0.9760 | 0.8813 | 0.0243 | 0.0464 | 0.1052 | 3.4960 | 16.6538 | 34.7916 |
| WSTD-GWO-SVR | 0.3983 | 0.4048 | 0.4108 | 0.4751 | 0.4802 | 0.4858 | 0.9654 | 0.9633 | 0.9636 | 0.0726 | 0.0733 | 0.0736 | 14.1472 | 14.7856 | 14.4973 |
| GRU | 0.5302 | 0.7081 | 0.8722 | 0.6819 | 0.9143 | 1.1275 | 0.8722 | 0.7722 | 0.6566 | 0.1032 | 0.1390 | 0.1731 | 75.5531 | 114.9054 | 160.5826 |
| LSTM | 0.5649 | 0.8180 | 0.9325 | 0.7485 | 1.0120 | 1.1752 | 0.8453 | 0.7275 | 0.6305 | 0.1127 | 0.1560 | 0.1766 | 99.0382 | 127.8319 | 213.4905 |
| ARIMA | 0.5125 | 0.7678 | 0.9572 | 0.7233 | 0.9730 | 1.1723 | 0.8542 | 0.7396 | 0.6236 | 0.1087 | 0.1462 | 0.1776 | 88.6792 | 151.3385 | 184.1856 |
| BP | 0.6498 | 0.7737 | 0.9624 | 0.8109 | 0.9660 | 1.1717 | 0.8435 | 0.7497 | 0.6239 | 0.1251 | 0.1478 | 0.1780 | 69.9745 | 117.8563 | 175.6531 |
| LSSVM | 0.5950 | 0.7953 | 0.9820 | 0.7468 | 0.9849 | 1.1870 | 0.8480 | 0.7362 | 0.6179 | 0.1130 | 0.1498 | 0.1817 | 82.4907 | 123.8675 | 152.3672 |
| RF | 0.6588 | 0.8508 | 1.0154 | 0.8397 | 1.0670 | 1.2544 | 0.8069 | 0.6898 | 0.5753 | 0.1277 | 0.1628 | 0.1929 | 106.3476 | 161.5313 | 188.5835 |
| Model | MAE | RMSE | TIC | SSE | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | |
| The proposed | 0.0440 | ||||||||||||||
| WSTD-VMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.0865 | 0.0901 | 0.1166 | 0.1047 | 0.1138 | 0.1458 | 0.9895 | 0.9887 | 0.9821 | 0.0250 | 0.0270 | 0.0343 | 1.9670 | 2.1397 | 3.2653 |
| WSTD-REMD-HGWO-GRU | 0.0991 | 0.1640 | 0.2186 | 0.1243 | 0.2013 | 0.2724 | 0.9879 | 0.9647 | 0.9313 | 0.0294 | 0.0475 | 0.0642 | 2.5469 | 7.4293 | 13.6527 |
| WSTD-CEEMD-HGWO-GRU | 0.1971 | 0.4087 | 0.4118 | 0.2605 | 0.5005 | 0.5159 | 0.9372 | 0.8014 | 0.7835 | 0.0627 | 0.1179 | 0.1230 | 14.6358 | 41.9232 | 48.0972 |
| WSTD-REMD-GWO-GRU | 0.1450 | 0.1610 | 0.1615 | 0.1745 | 0.1931 | 0.1971 | 0.9806 | 0.9751 | 0.9709 | 0.0406 | 0.0450 | 0.0462 | 3.7592 | 4.7490 | 5.4628 |
| WSTD-REMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.1307 | 0.2025 | 0.2095 | 0.1808 | 0.2626 | 0.2607 | 0.9777 | 0.9482 | 0.9303 | 0.0424 | 0.0613 | 0.0618 | 4.8231 | 11.6438 | 12.9346 |
| WSTD-WD-GWO-SVR | 0.1611 | 0.2712 | 0.3614 | 0.2100 | 0.3456 | 0.4450 | 0.9667 | 0.9041 | 0.8389 | 0.0481 | 0.0816 | 0.1043 | 7.5073 | 19.4635 | 32.5792 |
| WSTD-VMD–GRU | 0.0226 | 0.0678 | 0.0952 | 0.0370 | 0.0628 | 0.1785 | 0.9988 | 0.9967 | 0.9691 | 0.0089 | 0.0149 | 0.0424 | 0.2404 | 0.6309 | 6.1653 |
| WSTD-CEEMD-GRU | 0.0776 | 0.1957 | 0.2532 | 0.1272 | 0.3812 | 0.4456 | 0.9848 | 0.8644 | 0.8288 | 0.0304 | 0.0916 | 0.1064 | 3.1937 | 31.4186 | 38.9903 |
| WSTD-WD-GRU | 0.2212 | 0.2427 | 0.5399 | 0.3211 | 0.3155 | 0.7330 | 0.9148 | 0.9179 | 0.5567 | 0.0785 | 0.0773 | 0.1738 | 20.3076 | 19.5159 | 104.7591 |
| VMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.1149 | 0.1456 | 0.1680 | 0.1420 | 0.1765 | 0.2053 | 0.9894 | 0.9781 | 0.9640 | 0.0348 | 0.0431 | 0.0496 | 2.1390 | 4.2846 | 6.6573 |
| WD-HGWO-SVR | 0.1663 | 0.2757 | 0.3611 | 0.2111 | 0.3563 | 0.4448 | 0.9632 | 0.9271 | 0.8367 | 0.0504 | 0.0839 | 0.1042 | 8.7813 | 24.8823 | 38.5802 |
| WSTD-REMD-GRU | 0.0870 | 0.1813 | 0.2141 | 0.1224 | 0.2266 | 0.3163 | 0.9883 | 0.9653 | 0.9087 | 0.0289 | 0.0526 | 0.0761 | 2.4138 | 7.1025 | 19.0146 |
| WSTD-GWO-SVR | 0.1612 | 0.1599 | 0.1504 | 0.1968 | 0.1921 | 0.1819 | 0.9713 | 0.9758 | 0.9801 | 0.0461 | 0.0447 | 0.0422 | 5.3970 | 4.5678 | 3.8964 |
| GRU | 0.4571 | 0.5368 | 0.6011 | 0.5844 | 0.6870 | 0.7726 | 0.7350 | 0.6345 | 0.5386 | 0.1405 | 0.1637 | 0.1859 | 49.5267 | 55.2589 | 63.1174 |
| LSTM | 0.4524 | 0.5246 | 0.5916 | 0.5788 | 0.6620 | 0.7439 | 0.7402 | 0.6615 | 0.5716 | 0.1384 | 0.1577 | 0.1760 | 46.5672 | 61.7483 | 60.8625 |
| ARIMA | 0.4785 | 0.5895 | 0.6983 | 0.6028 | 0.7429 | 0.8610 | 0.7180 | 0.5722 | 0.4257 | 0.1445 | 0.1782 | 0.2060 | 52.9226 | 60.7234 | 59.1549 |
| BP | 0.4778 | 0.5902 | 0.6930 | 0.6106 | 0.7447 | 0.8580 | 0.7142 | 0.5699 | 0.4321 | 0.1480 | 0.1782 | 0.2067 | 56.9368 | 63.3287 | 55.3472 |
| LSSVM | 0.4818 | 0.5973 | 0.7148 | 0.6030 | 0.7487 | 0.8709 | 0.7178 | 0.5641 | 0.4122 | 0.1443 | 0.1789 | 0.2072 | 50.0967 | 61.7453 | 63.9388 |
| RF | 0.5319 | 0.6997 | 0.8122 | 0.6806 | 0.8910 | 1.0285 | 0.6471 | 0.4123 | 0.2503 | 0.1646 | 0.2163 | 0.2496 | 68.8850 | 94.6278 | 107.4784 |
| Model | MAE | RMSE | TIC | SSE | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | 1-Step | 2-Step | 3-Step | |
| The proposed | 0.0309 | ||||||||||||||
| WSTD-VMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.0433 | 0.0663 | 0.0891 | 0.0522 | 0.0824 | 0.1101 | 0.9916 | 0.9808 | 0.9672 | 0.0139 | 0.0219 | 0.0291 | 0.4850 | 1.0614 | 1.7848 |
| WSTD-REMD-HGWO-GRU | 0.0436 | 0.0716 | 0.0905 | 0.0540 | 0.0904 | 0.1213 | 0.9886 | 0.9689 | 0.9453 | 0.0145 | 0.0243 | 0.0326 | 0.5424 | 1.3934 | 2.1183 |
| WSTD-CEEMD-HGWO-GRU | 0.2609 | 0.2667 | 0.3327 | 0.3548 | 0.3585 | 0.4742 | 0.7073 | 0.7018 | 0.5317 | 0.0957 | 0.0941 | 0.1248 | 18.6286 | 20.3429 | 35.7302 |
| WSTD-REMD-GWO-GRU | 0.0659 | 0.0860 | 0.1120 | 0.0831 | 0.1057 | 0.1368 | 0.9755 | 0.9566 | 0.9372 | 0.0223 | 0.0284 | 0.0371 | 1.0129 | 1.9540 | 2.7816 |
| WSTD-REMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.1647 | 0.1284 | 0.1945 | 0.2472 | 0.3176 | 0.3504 | 0.8809 | 0.6958 | 0.6593 | 0.0633 | 0.0845 | 0.0910 | 6.7752 | 19.6783 | 21.3897 |
| WSTD-WD-GWO-SVR | 0.1442 | 0.2172 | 0.2682 | 0.1870 | 0.2965 | 0.3525 | 0.9191 | 0.7941 | 0.7111 | 0.0502 | 0.0793 | 0.0946 | 5.8147 | 13.1518 | 18.5134 |
| WSTD-VMD–GRU | 0.0853 | 0.0952 | 0.2703 | 0.2217 | 0.2425 | 0.5223 | 0.8105 | 0.7838 | 0.4470 | 0.0595 | 0.0651 | 0.1397 | 9.5462 | 11.5238 | 53.1585 |
| WSTD-CEEMD-GRU | 0.1467 | 0.2385 | 0.2718 | 0.4163 | 0.5655 | 0.6323 | 0.5813 | 0.3350 | 0.2327 | 0.1103 | 0.1518 | 0.1715 | 34.6628 | 90.1783 | 137.5041 |
| WSTD-WD-GRU | 0.2199 | 0.2785 | 0.3247 | 0.3290 | 0.3685 | 0.4063 | 0.7460 | 0.6801 | 0.6134 | 0.0877 | 0.0989 | 0.1093 | 26.7563 | 21.2180 | 32.1939 |
| VMD-HGWO-SVR | 0.0610 | 0.0888 | 0.1199 | 0.0760 | 0.1131 | 0.1543 | 0.9876 | 0.9542 | 0.9206 | 0.0204 | 0.0385 | 0.0407 | 0.5707 | 1.8336 | 2.8740 |
| WD-HGWO-SVR | 0.1441 | 0.2173 | 0.2617 | 0.1860 | 0.2966 | 0.3405 | 0.9186 | 0.7936 | 0.7189 | 0.0498 | 0.0792 | 0.0928 | 6.8137 | 17.2469 | 23.4062 |
| WSTD-REMD-GRU | 0.0491 | 0.1258 | 0.1437 | 0.1049 | 0.2151 | 0.2820 | 0.9568 | 0.8595 | 0.7316 | 0.0281 | 0.0561 | 0.0748 | 2.1447 | 7.4762 | 15.1173 |
| WSTD-GWO-SVR | 0.0670 | 0.0843 | 0.1101 | 0.0840 | 0.1045 | 0.1358 | 0.9755 | 0.9573 | 0.9380 | 0.0225 | 0.0281 | 0.0368 | 1.0138 | 1.9295 | 2.7120 |
| GRU | 0.4448 | 0.5470 | 0.6011 | 0.5883 | 0.6957 | 0.7395 | 0.6546 | 0.5567 | 0.4347 | 0.1558 | 0.1824 | 0.1908 | 35.8524 | 37.3562 | 40.5836 |
| LSTM | 0.4490 | 0.5502 | 0.5809 | 0.5929 | 0.6935 | 0.7261 | 0.6436 | 0.5571 | 0.4912 | 0.1570 | 0.1800 | 0.1904 | 36.9078 | 36.6845 | 35.8163 |
| ARIMA | 0.4511 | 0.5359 | 0.5850 | 0.6012 | 0.6955 | 0.7390 | 0.5479 | 0.4617 | 0.3526 | 0.1596 | 0.1834 | 0.1921 | 43.9867 | 42.9321 | 37.8196 |
| BP | 0.4532 | 0.5419 | 0.5760 | 0.6007 | 0.6946 | 0.7172 | 0.5454 | 0.4739 | 0.3015 | 0.1600 | 0.1812 | 0.1914 | 42.9672 | 43.8373 | 36.1058 |
| LSSVM | 0.4423 | 0.5255 | 0.5745 | 0.5861 | 0.6798 | 0.7194 | 0.4601 | 0.3772 | 0.2928 | 0.1555 | 0.1793 | 0.1886 | 37.8521 | 39.0385 | 32.8654 |
| RF | 0.5283 | 0.5863 | 0.6179 | 0.6826 | 0.7481 | 0.7985 | 0.5758 | 0.4455 | 0.3592 | 0.1806 | 0.1968 | 0.2082 | 63.2678 | 65.9756 | 66.6372 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Wang, B.; Qiu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Multi-Step Short-Term Wind Speed Prediction Models Based on Adaptive Robust Decomposition Coupled with Deep Gated Recurrent Unit. Energies 2022, 15, 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124221
Yang K, Wang B, Qiu X, Li J, Wang Y, Liu Y. Multi-Step Short-Term Wind Speed Prediction Models Based on Adaptive Robust Decomposition Coupled with Deep Gated Recurrent Unit. Energies. 2022; 15(12):4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124221
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kui, Bofu Wang, Xiang Qiu, Jiahua Li, Yuze Wang, and Yulu Liu. 2022. "Multi-Step Short-Term Wind Speed Prediction Models Based on Adaptive Robust Decomposition Coupled with Deep Gated Recurrent Unit" Energies 15, no. 12: 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124221
APA StyleYang, K., Wang, B., Qiu, X., Li, J., Wang, Y., & Liu, Y. (2022). Multi-Step Short-Term Wind Speed Prediction Models Based on Adaptive Robust Decomposition Coupled with Deep Gated Recurrent Unit. Energies, 15(12), 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124221





