Optimization-Based Tuning of a Hybrid UKF State Estimator with Tire Model Adaption for an All Wheel Drive Electric Vehicle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vehicle Model
2.2. Sensors
2.3. Unscented Kalman Filter
2.4. Estimator Design and Tuning
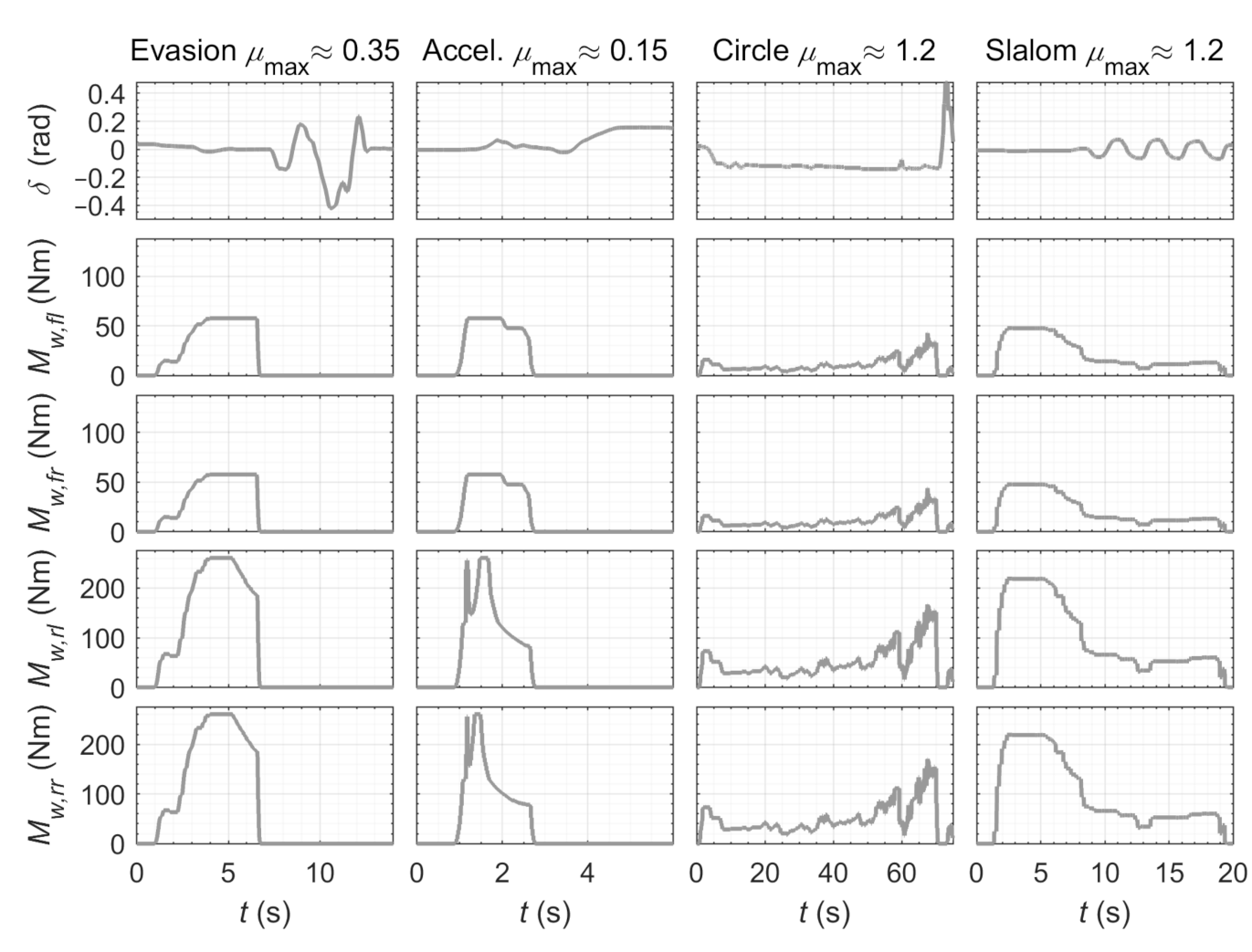
- a transient slalom maneuver on wet road surface with , an initial velocity of , and a distance of between the obstacles, where high lateral tire slip occurs;
- a transient all-wheel-drive acceleration maneuver from standstill on wet road surface with with excessive longitudinal tire slip; and
- steady-state circular driving on dry road surface with and a constant radius from standstill to a velocity of , where the vehicle starts to oversteer.
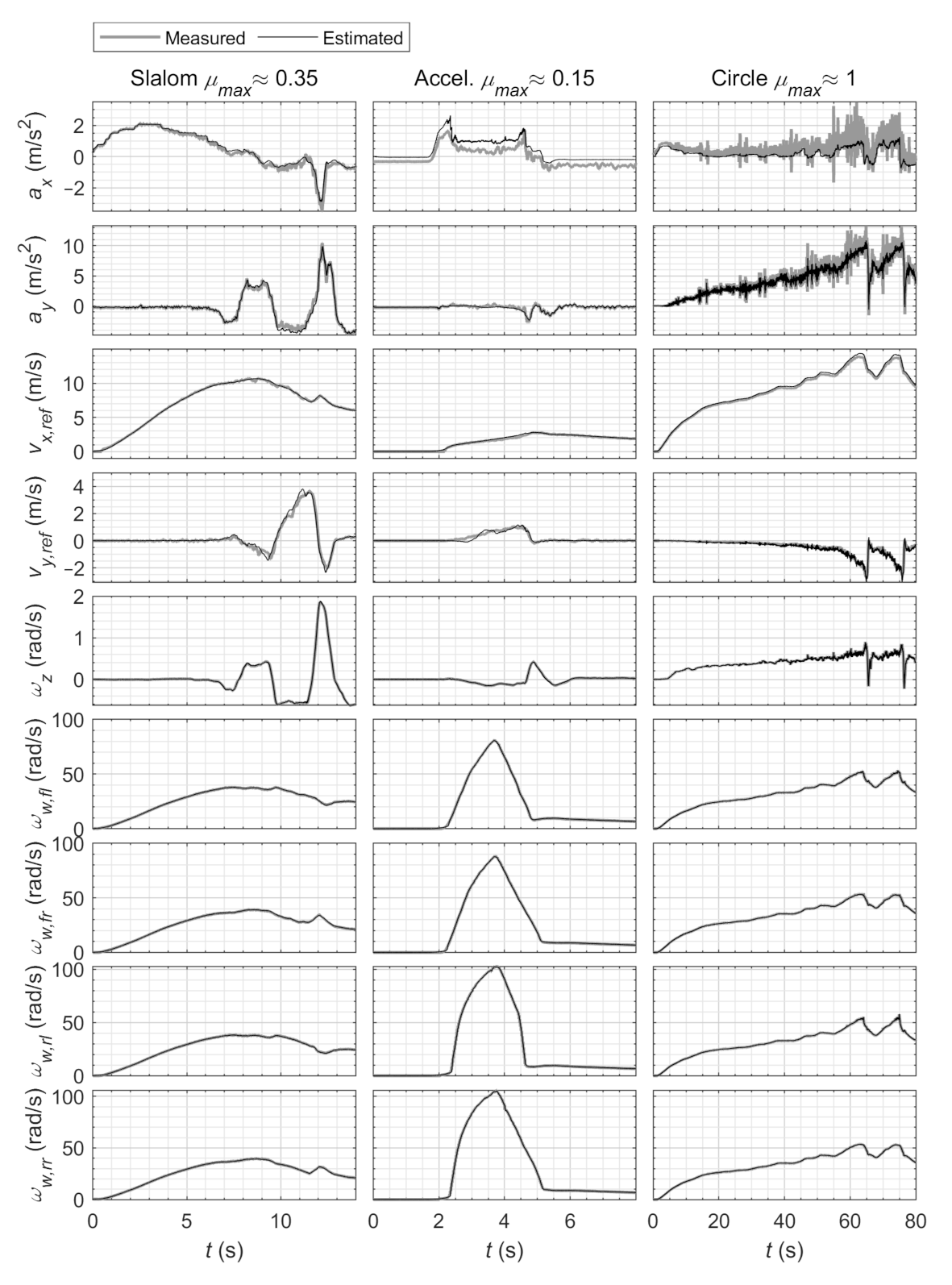
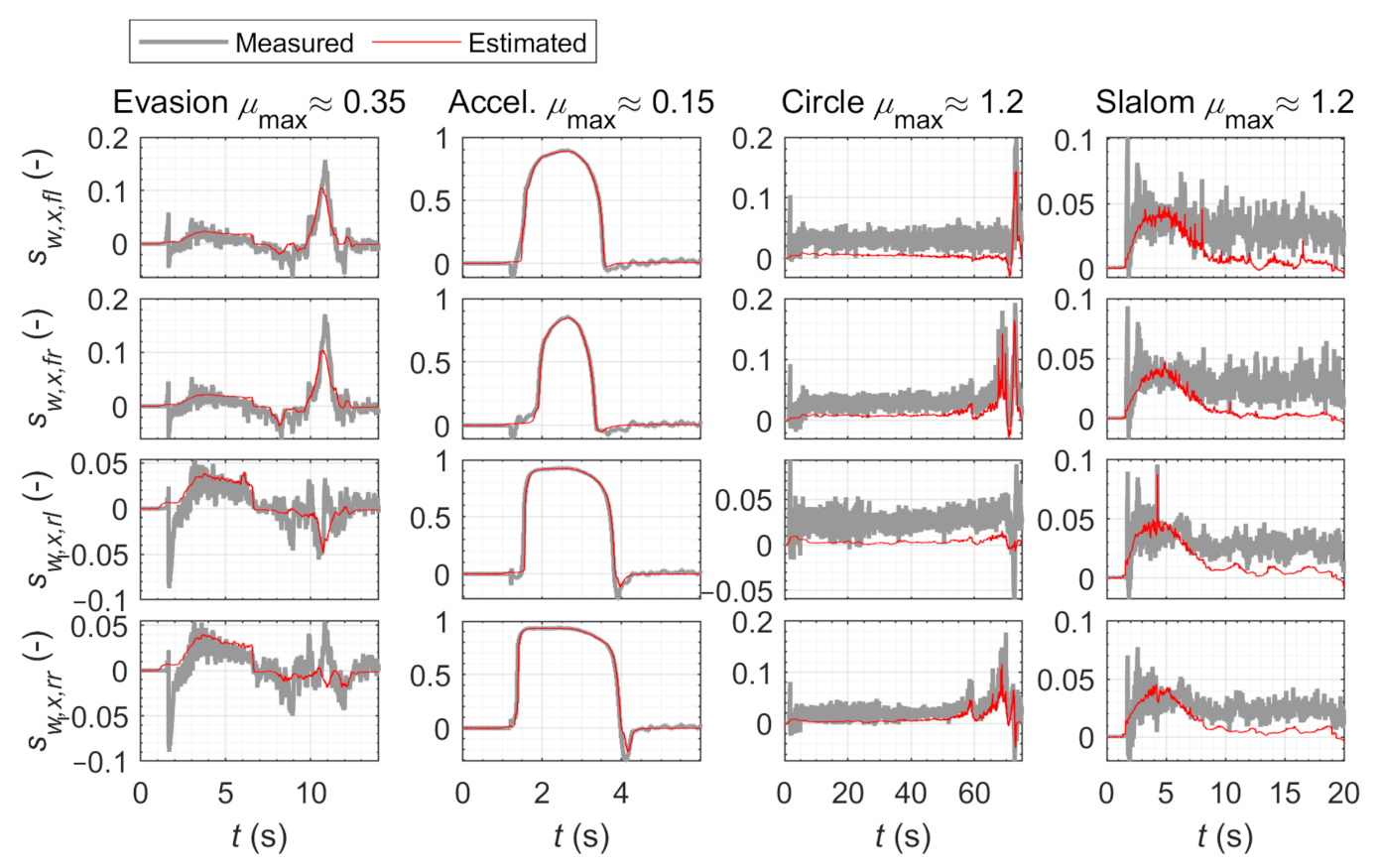
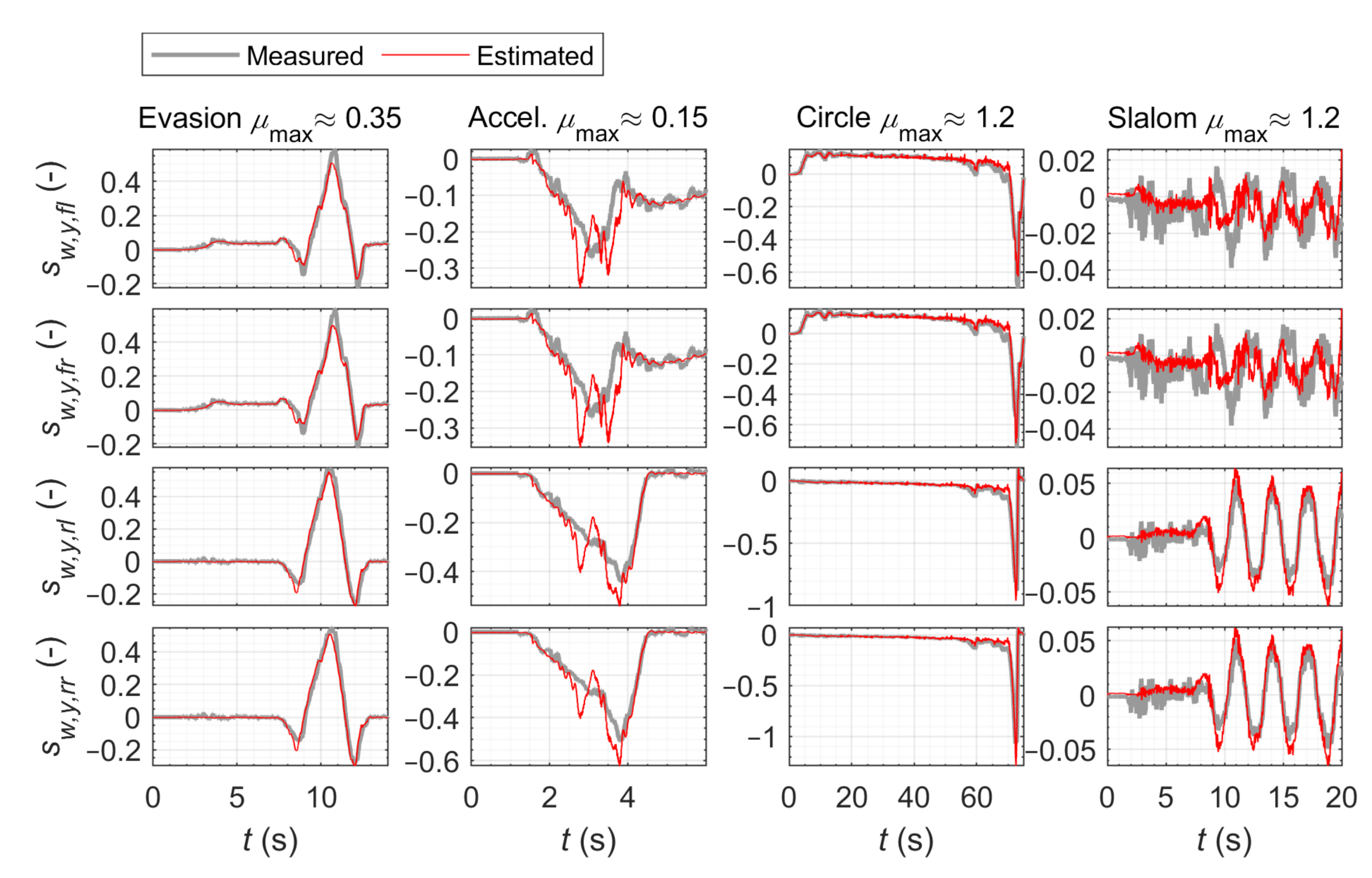
3. Results and Discussion
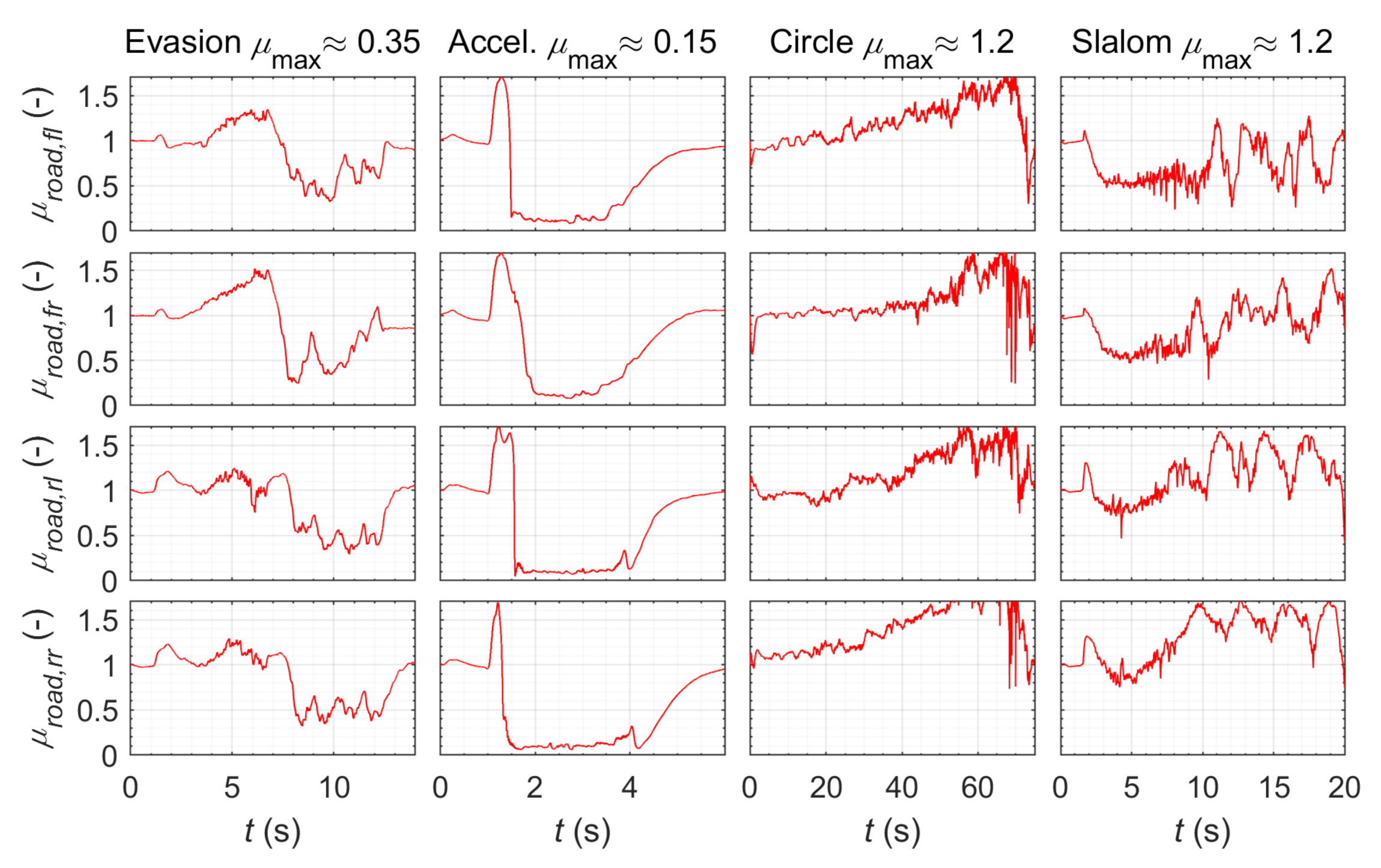
3.1. Wet Road Surface
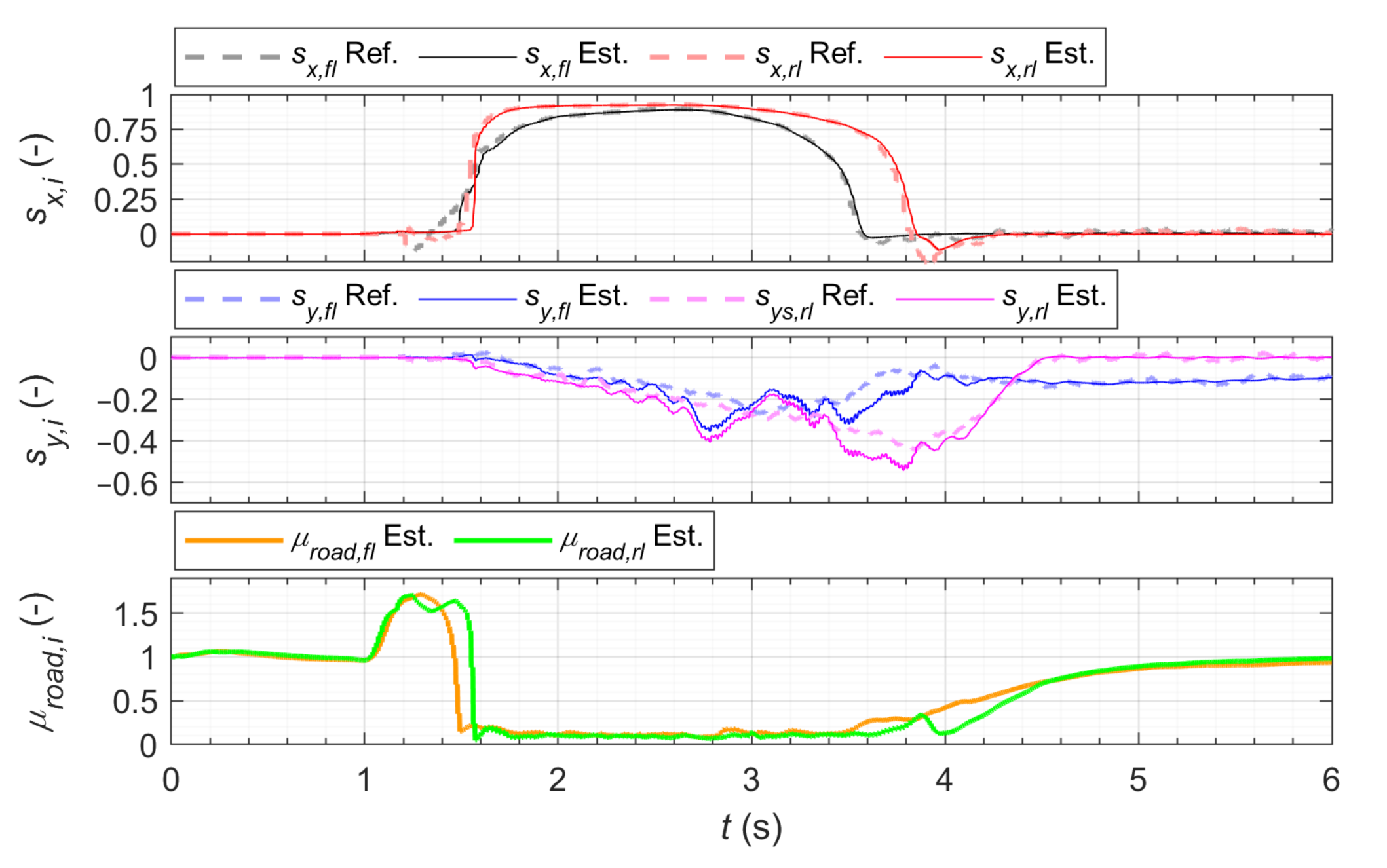
3.1.1. Acceleration Maneuver
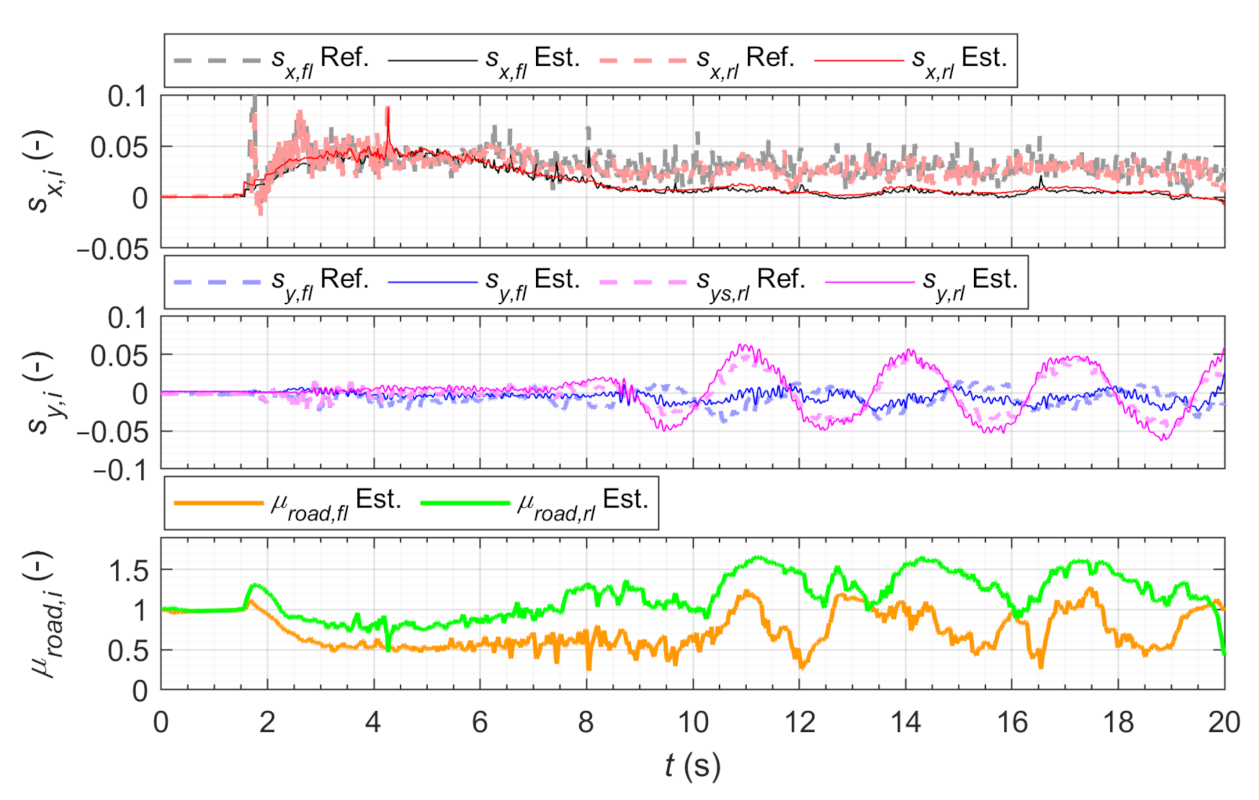
3.1.2. Emergency Evasion Maneuver
3.2. Dry Road Surface
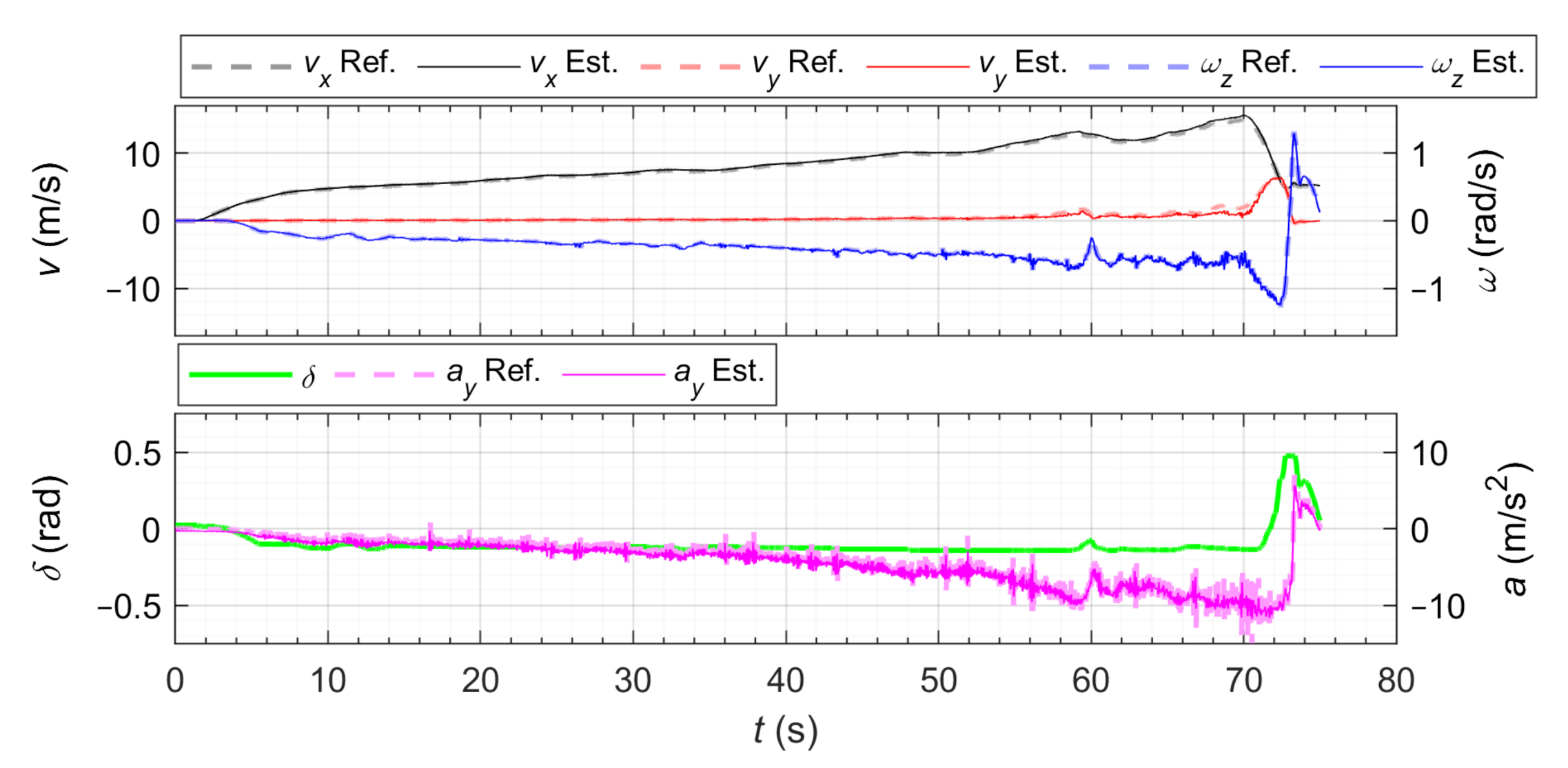
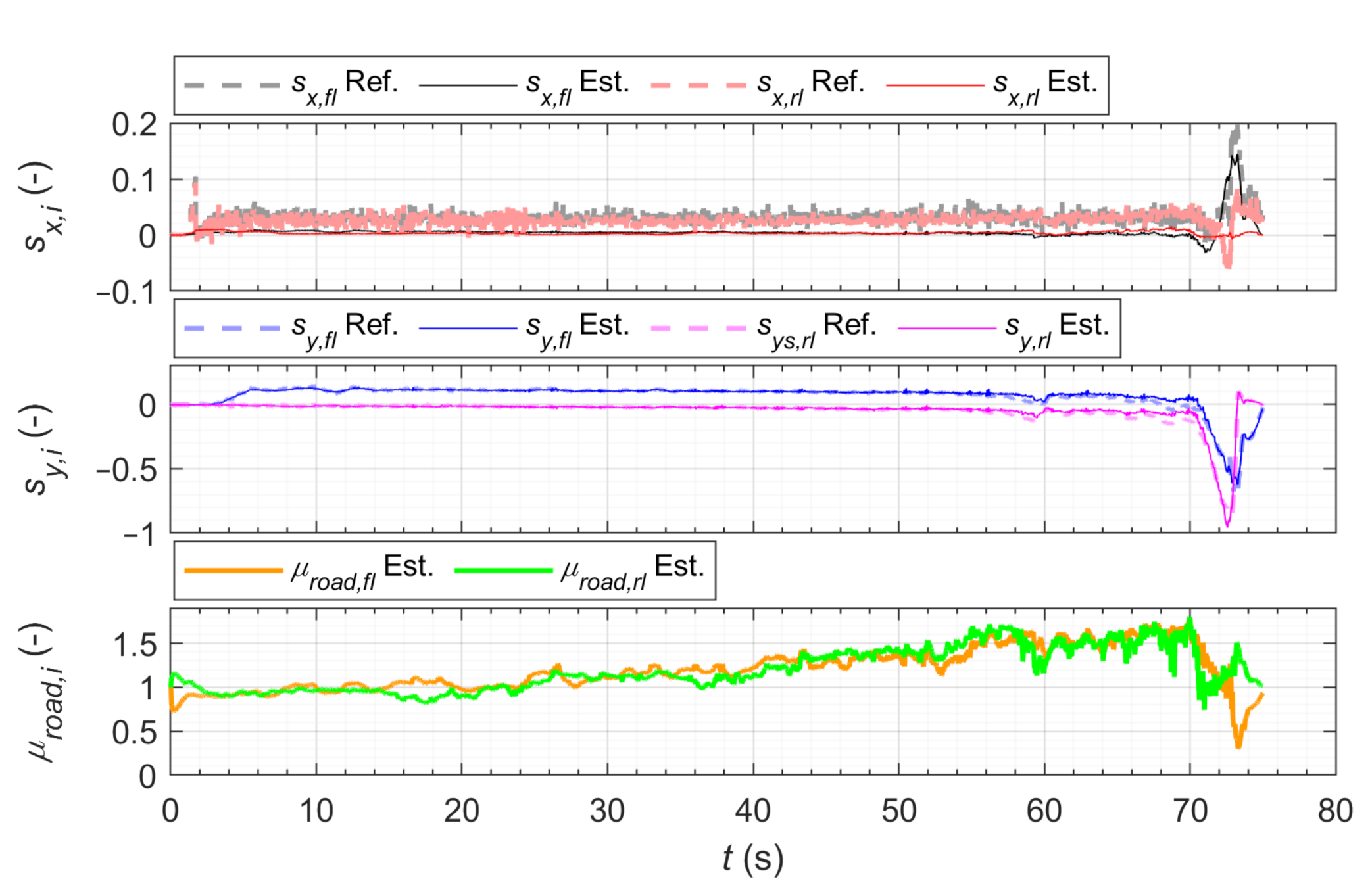
3.2.1. Steady-State Circular Driving
3.2.2. Slalom Maneuver
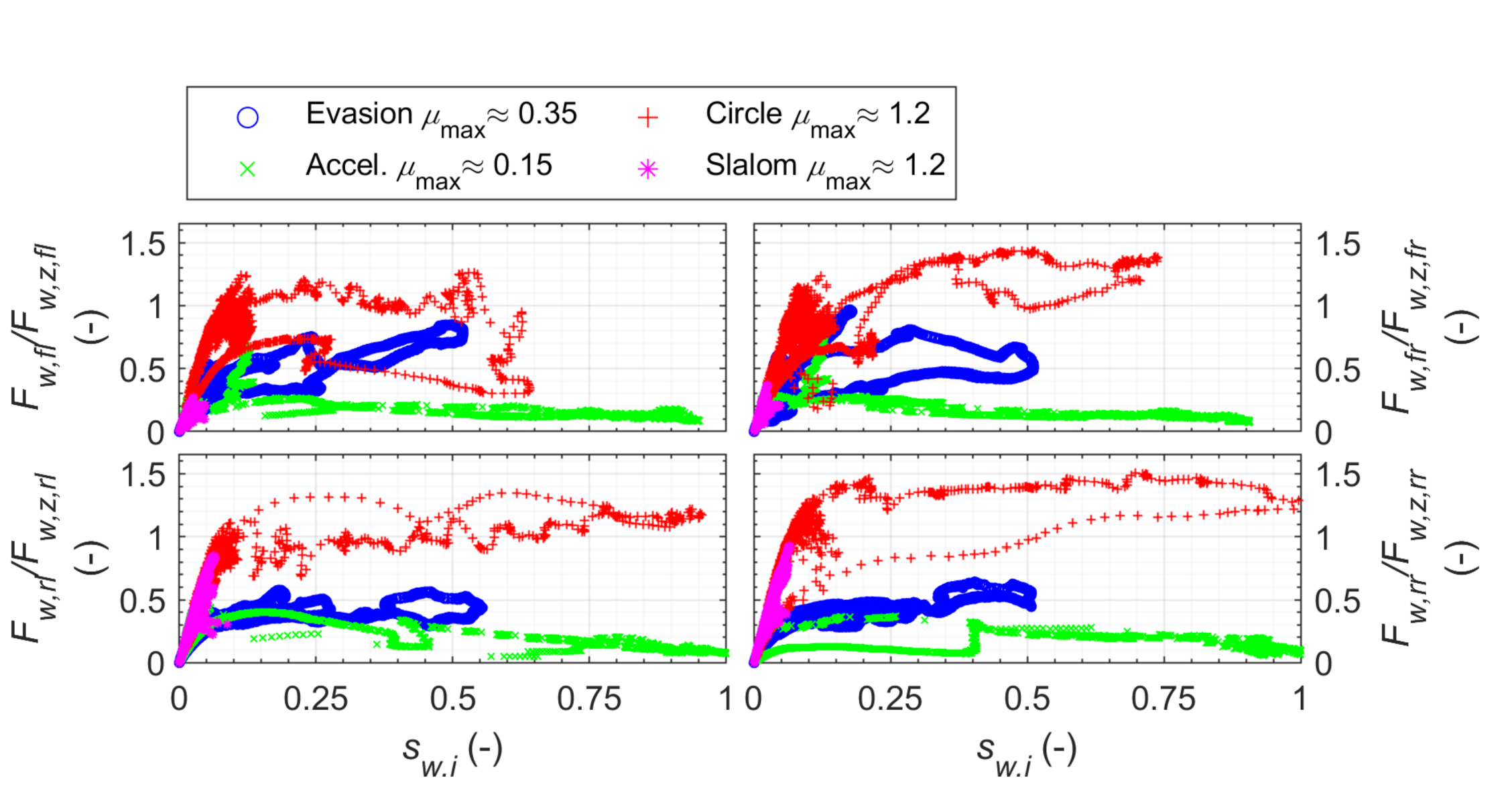
3.3. Estimated Tire Curves
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DGPS | Differential Global Positioning System |
| ECU | Electronic Control Unit |
| EKF | Extended Kalman Filter |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| MEMS | Microelectromechanical System |
| RCP | Rapid Control Prototyping |
| UKF | Unscented Kalman Filter |
Appendix A

Appendix B

References
- Chindamo, D.; Lenzo, B.; Gadola, M. On the Vehicle Sideslip Angle Estimation: A Literature Review of Methods, Models, and Innovations. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yin, G.; Chen, N. Advanced Estimation Techniques for Vehicle System Dynamic State: A Survey. Sensors 2019, 19, 4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, D. Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H [Infinity], and Nonlinear Approaches; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Julier, S.J.; Uhlmann, J.K. Unscented Filtering and Nonlinear Estimation. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Merwe, R. Sigma-Point Kalman Filters for Probabilistic Inference in Dynamic State-Space Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bechtloff, J.; Isermann, R. A redundant sensor system with driving dynamic models for automated driving. In Proceedings of the 15th Internationales Stuttgarter Symposium, Wiesbaden, Germany, 2 June 2015; Bargende, M., Reuss, H.C., Wiedemann, J., Eds.; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2015; pp. 755–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, S.; Fehn, A.; Kugi, A. Unscented Kalman filter for vehicle state estimation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2011, 49, 1497–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielitzka, M.; Busch, A.; Dagen, M.; Ortmaier, T. Unscented Kalman Filter for State and Parameter Estimation in Vehicle Dynamics. In Kalman Filters—Theory for Advanced Applications; Ginalber Luiz de Oliveira Serra; InTech: London, UK, 2018; pp. 56–75. [Google Scholar]
- Heidfeld, H.; Schünemann, M.; Kasper, R. UKF-based State and tire slip estimation for a 4WD electric vehicle. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2019, 58, 1479–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidfeld, H.; Schünemann, M.; Kasper, R. Experimental Validation of a GPS-Aided Model-Based UKF Vehicle State Estimator. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM), Ilmenau, Germany, 18–20 March 2019; pp. 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Fu, Z.; Xu, Q. An Adaptive Multi-Dimensional Vehicle Driving State Observer Based on Modified Sage-Husa UKF Algorithm. Sensors 2020, 20, 6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Feng, J.; Song, B.; Li, X. Huber-Based Robust Unscented Kalman Filter Distributed Drive Electric Vehicle State Observation. Energies 2021, 14, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, M.; Kanarachos, S. Optimized Vehicle Dynamics Virtual Sensing Using Metaheuristic Optimization and Unscented Kalman Filter. In Evolutionary and Deterministic Methods for Design Optimization and Control with Applications to Industrial and Societal Problems; Andrés-Pérez, E., González, L.M., Periaux, J., Gauger, N., Quagliarella, D., Giannakoglou, K., Eds.; Computational Methods in Applied Sciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 49, pp. 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Wei, Z.; He, J.; Yan, F.; Liu, L. A two-step parameter optimization method for low-order model-based state of charge estimation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, D.; Hiller, M.; Bardini, R. Vehicle Dynamics: Modeling and Simulation, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rill, G. Wheel Dynamics. In Proceedings of the XII International Symposium on Dynamic Problems of Mechanics (DINAME 2007), Ilhabela, Brazil, 26 February–2 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt, M. Radschlupf-Regelsysteme: Reifenverhalten, Zeitabläufe, Messung des Drehzustands der Räder, Anti-Blockier-System (ABS), Theorie Hydraulikkreisläufe, Antriebs-Schlupf-Regelung (ASR), Theorie Hydraulikkreisläufe, elektronische Regeleinheiten, Leistungsgrenzen, ausgeführte Anti-Blockier-Systeme und Antriebs-Schlupf-Regelungen, 1st ed.; Vogel-Fachbuch: Würzburg, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Pacejka, H.B. Tyre and Vehicle Dynamics, 2nd ed.; Elsevier/Butterworth-Heinemann: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tanelli, M.; Piroddi, L.; Piuri, M.; Savaresi, S.M. Real-time identification of tire-road friction conditions. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Antonio, TX, USA, 3–5 September 2008; IEEE Service Center: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindfield, G.R.; Penny, J. Numerical Methods: Using MATLAB, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, R.K. Optimization: Algorithms and Applications; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]





| m | 760 | A | ||||||
| 532 | ||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||
| Sensor | Variable | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accelerometer | |||
| Gyroscope | |||
| Wheel speed sensor |
| Acceleration | Evasion | Circular Driving | Slalom | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heidfeld, H.; Schünemann, M. Optimization-Based Tuning of a Hybrid UKF State Estimator with Tire Model Adaption for an All Wheel Drive Electric Vehicle. Energies 2021, 14, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051396
Heidfeld H, Schünemann M. Optimization-Based Tuning of a Hybrid UKF State Estimator with Tire Model Adaption for an All Wheel Drive Electric Vehicle. Energies. 2021; 14(5):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051396
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeidfeld, Hannes, and Martin Schünemann. 2021. "Optimization-Based Tuning of a Hybrid UKF State Estimator with Tire Model Adaption for an All Wheel Drive Electric Vehicle" Energies 14, no. 5: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051396
APA StyleHeidfeld, H., & Schünemann, M. (2021). Optimization-Based Tuning of a Hybrid UKF State Estimator with Tire Model Adaption for an All Wheel Drive Electric Vehicle. Energies, 14(5), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051396






