Hybrid Washer Fluid for Primary Cementing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Washing Liquid
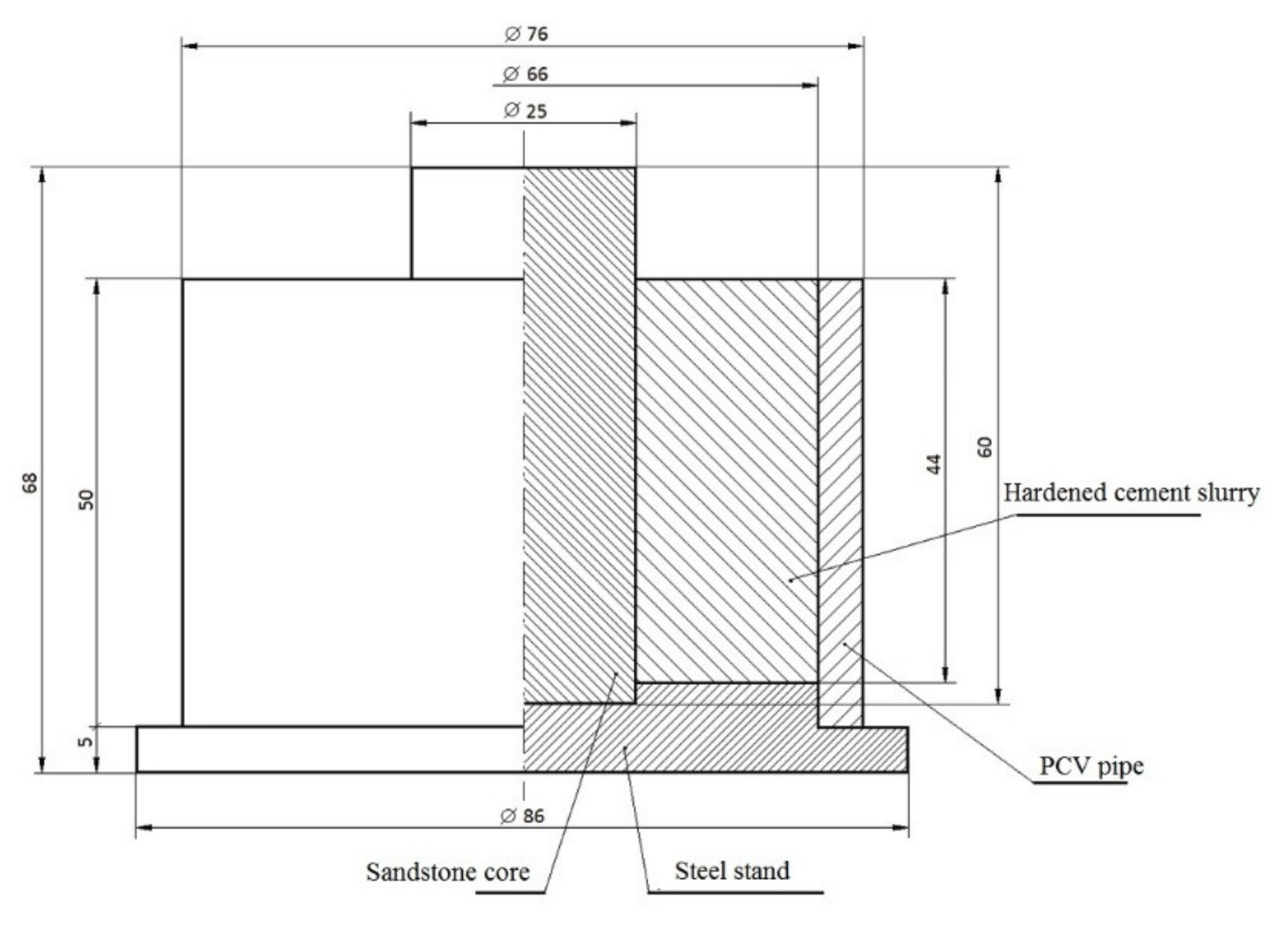
2.3. Preparation of the Cement Slurry
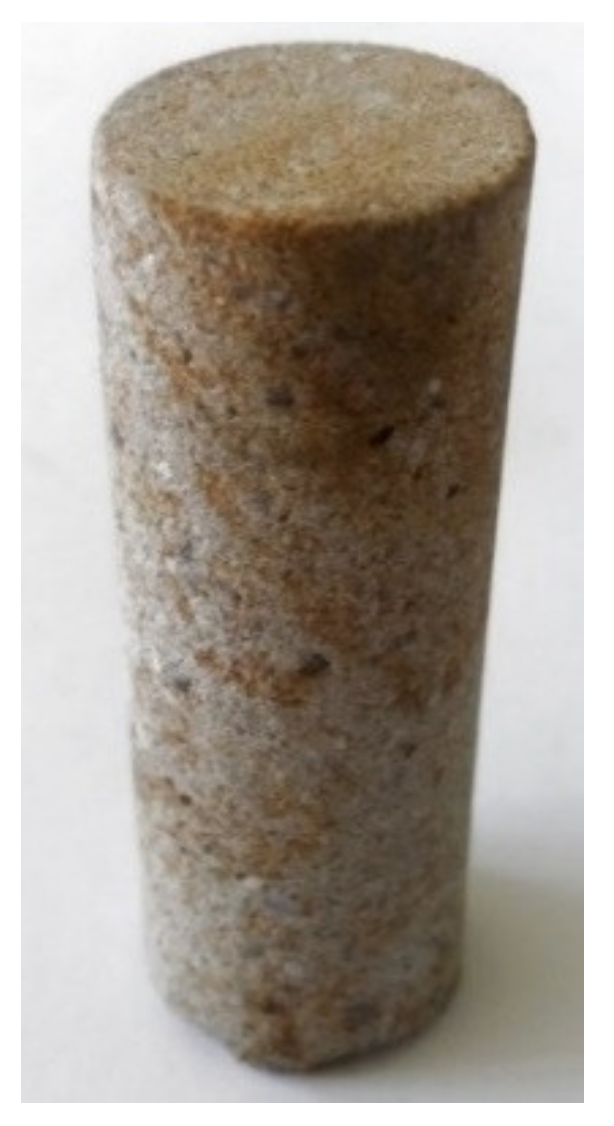
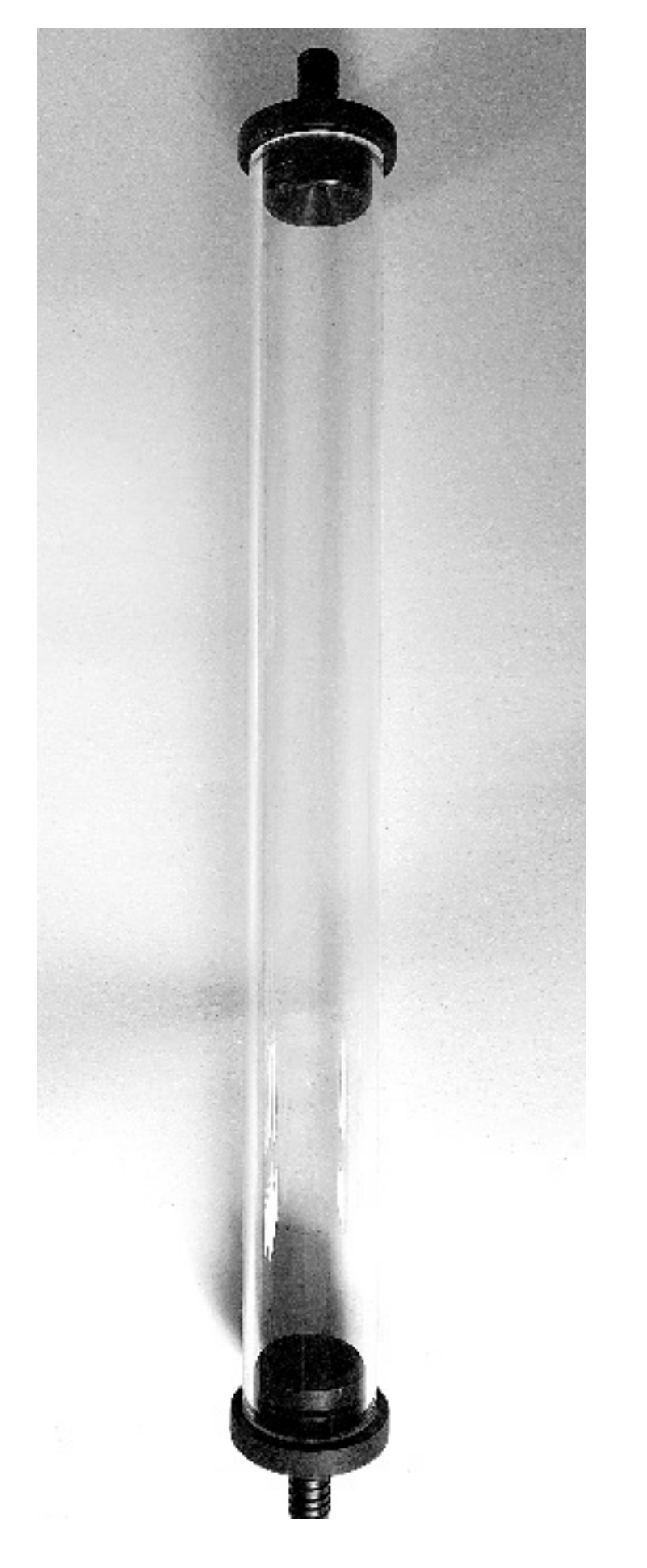
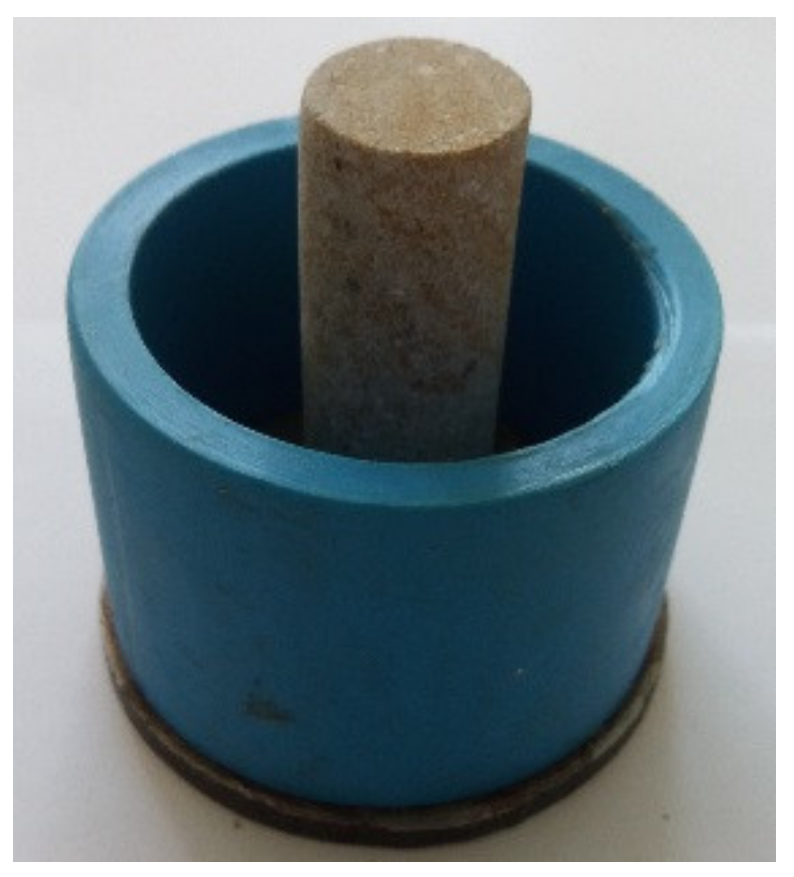
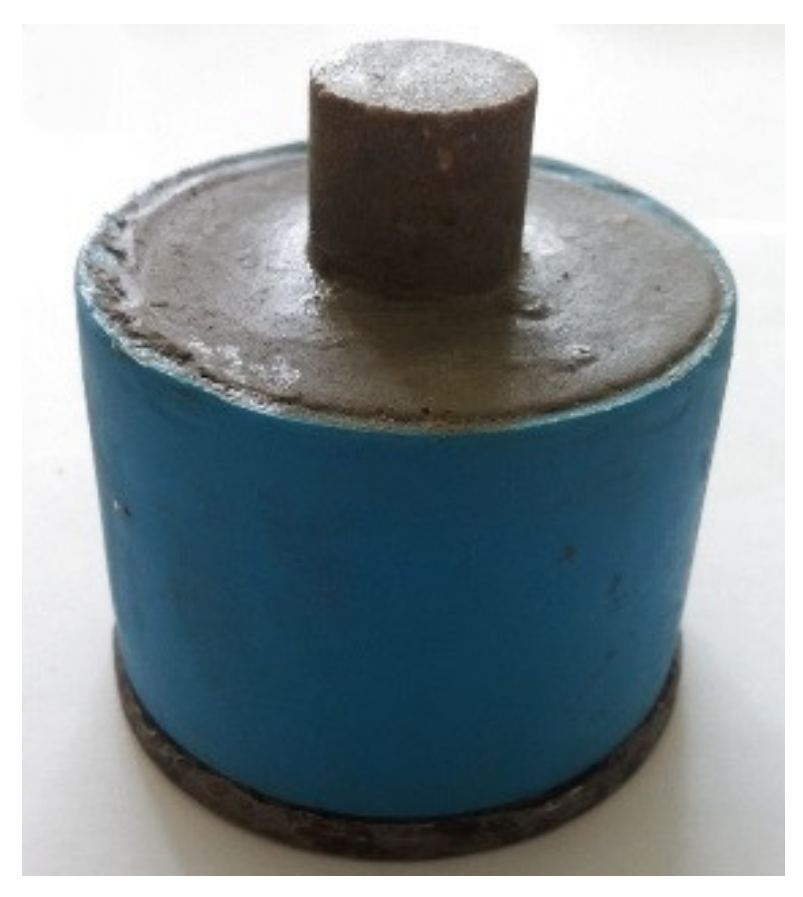
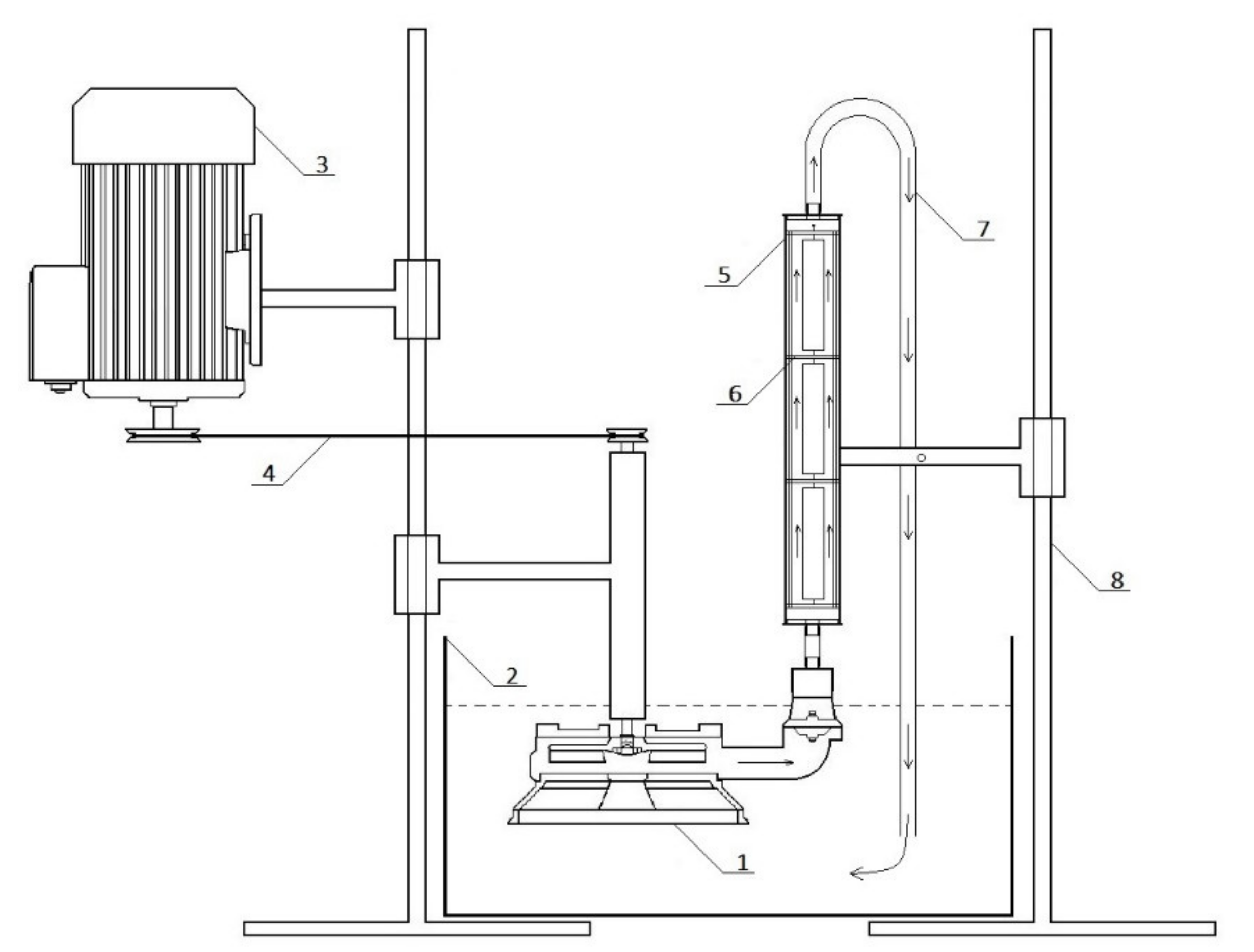
2.4. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- On the basis of the obtained test results, it can be stated that the best efficiency in removing the mud cake produced from the polymer–potassium scrubber was achieved using the washing liquid containing a mixture of suitably selected agents.
- The addition of fine-grained and coarse-grained abrasive fractions to the washing liquid resulted in an improvement in the mud-cake removal efficiency through additional mechanical stripping of the washing mud cake formed.
- The developed hybrid washer showed very good washing properties due to both its chemical and its mechanical influence on the washing mud cake formed on the rock surface.
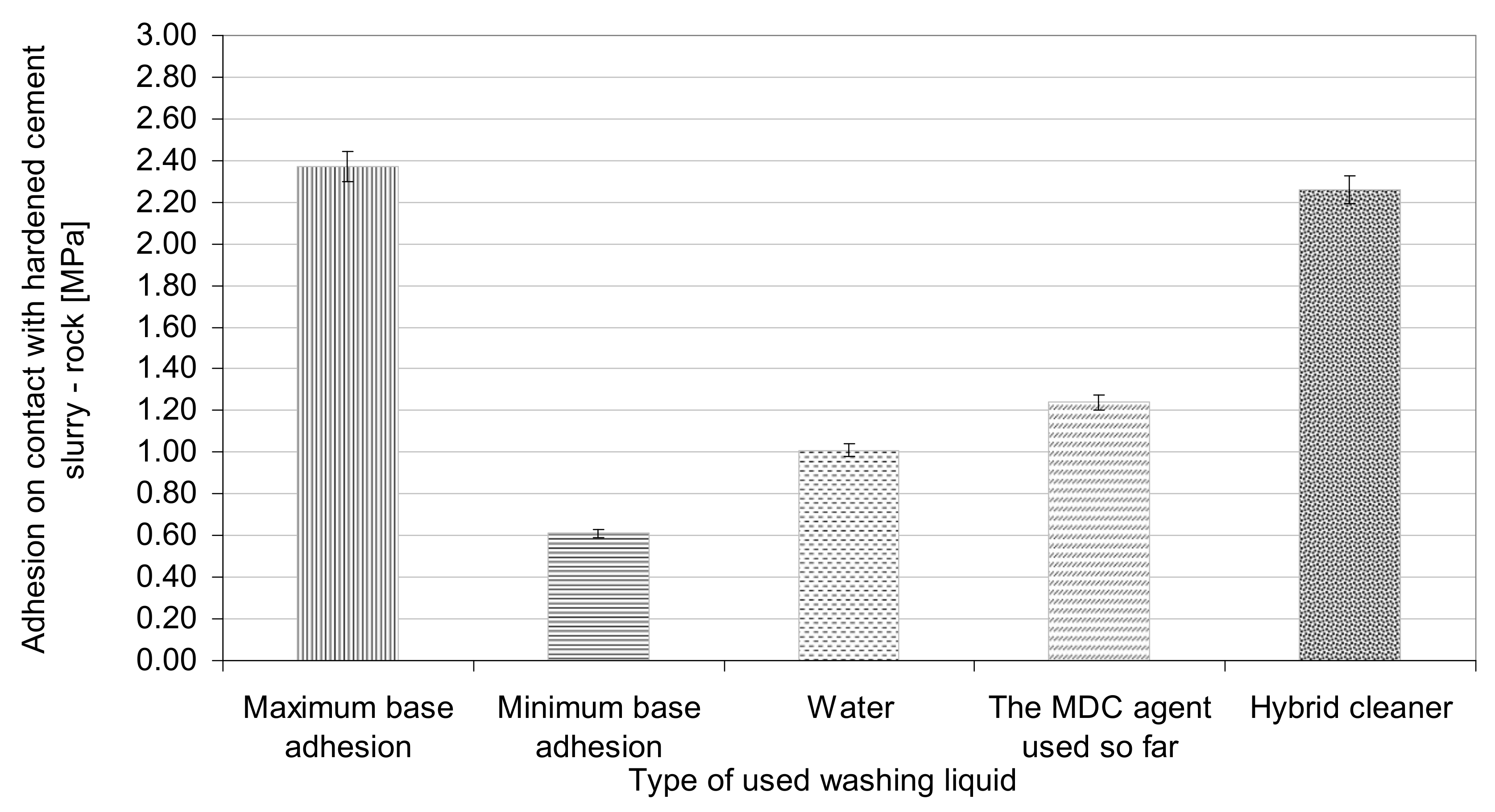
- The use of a hybrid washer resulted in an almost threefold increase in the value of adhesion to the contact between the hardened cement slurry and the rock formation. This value was almost comparable to the maximum base adhesion.
- The use of a hybrid washer caused a reduction of less than 5% in the adhesion value in relation to the maximum base value (adhesion to the contact between the hardened cement slurry and rock formation).
- The hybrid washer is considered to be the best liquid for removing mud cake from the polymer–potassium scrubber.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kremieniewski, M.; Rzepka, M. Przyczyny i Skutki Przepływu Gazu w Zacementowanej Przestrzeni Pierścieniowej Otworu Wiertniczego Oraz Metody Zapobiegania Temu Zjawisku; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2016; p. 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błaż, S. Nowe Rodzaje Cieczy Przemywających Osady z Płuczki Inwersyjnej Przed Zabiegiem Cementowania Otworów Wiertniczych; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 5, pp. 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremieniewski, M.; Kędzierski, M. Badanie Frakcjonowania Lekkich Materiałów Obniżających Gęstość Jako Wstępnego Parametru Podczas Projektowania Receptury Zaczynu Lekkiego; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 12, pp. 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.F.; Browne, S.V.; Burnham, M.P. Mud clean-up in horizontal wells: A major joint industry study. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, TX, USA, 22–25 October 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremieniewski, M. Ocena Skuteczności Oczyszczania Kolumny Rur Okładzinowych Przed Cementowaniem na Podstawie Badań Przy Użyciu Wiskozymetru Obrotowego; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 9, pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adari, R.B.; Miska, S.; Kuru, E.; Bern, P.A.; Saasen, A. Selecting drilling fluid properties and flow rates for effective hole cleaning in high-angle and horizontal wells. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, TX, USA, 1–4 October 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiński, B. Ocena Wpływu Cieczy Przemywającej na Jakość Zacementowania Rur w Otworze Wiertniczym po Użyciu Płuczki Glikolowo-Potasowej; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 6, pp. 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremieniewski, M. Korelacja Skuteczności Usuwania Osadu za Pomocą Cieczy na Osnowie Jonowych (Anionowych) i Niejonowych SPCz; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, M.; Jefferson, D.T.; Powell, J.W. Hole-cleaning study of polymer-based drilling fluids. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 October 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremieniewski, M.; Kędzierski, M.; Rzepka, M. Symulator Przepływu Cieczy Wiertniczych—Zasada Pomiaru i Możliwości Badawcze; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 7, pp. 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizhani, M.; Rodriguez Corredor, F.E.; Kuru, E. Quantitative evaluation of critical conditions required for effective hole cleaning in coiled-tubing drilling of horizontal wells. SPE Drill Compl. 2016, 31, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremieniewski, M. Recipe of lightweight slurry with high early strength of the resultant cement sheath. Energies 2020, 13, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremieniewski, M. Ultra-lightweight cement slurry to seal wellbore of poor wellbore stability. Energies 2020, 13, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.A.; Azar, J.J.; Bassal, A.A.; Martins, A.L. The effect of drillpipe rotation on hole cleaning during directional well drilling. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the SPE/IADC Drilling Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 4–6 March 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zima, G. Wpływ Właściwości Płuczek Wiertniczych na Jakość Cementowania w Gazonośnych Poziomach Miocenu; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 12, pp. 899–907. [Google Scholar]
- Kremieniewski, M. Badania nad Opracowaniem Hybrydowej Cieczy Buforowej; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyou, N.V.; Ismail, I.; Sulaiman, W.R.W.; Haddad, A.S.; Husein, N.; Hui, H.T.; Nadaraja, K. Experimental investigation of hole cleaning in directional drilling by using nano-enhanced water-based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 176, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremieniewski, M. Korelacja Skuteczności Działania Środków Dyspergujących o Różnym Mechanizmie Upłynniania; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpa, M.M.; Arnipally, S.K.; Kuru, E. Effect of the particle size on the near-wall turbulence characteristics of the polymer fluid flow and the critical velocity required for particle removal from the sand bed deposited in horizontal wells. Energies 2020, 13, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifferman, T.R.; Becker, T.E. Hole cleaning in full-scale inclined wellbores. SPE Drill Eng. 1992, 7, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Miska, S.; Yu, M.; Ozbayoglu, E.; Takach, N.; Osgouei, R.E. Is well clean enough? A fast approach to estimate hole cleaning for directional drilling. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the SPE/ICoTA Coiled Tubing & Well Intervention Conference & Exhibition, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 24–25 March 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saasen, A.; Løklingholm, G. The effect of drilling fluid rheological properties on hole cleaning. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the IADC/SPE Drilling Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 11 February 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayindla, S.; Lund, B.; Ytrehus, J.D.; Saasen, A. Hole-cleaning performance comparison of oil-based and water-based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 159, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniowski, R.; Skrzypaszek, K.; Małachowski, T. Selection of a suitable rheological model for drilling fluid using applied numerical methods. Energies 2020, 13, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Walker, S. Sensitivity analysis of hole cleaning parameters in directional wells. SPE J. 2001, 6, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okrajni, S.; Azar, J.J. The effects of mud rheology on annular hole cleaning in directional wells. SPE Drill Eng. 1986, 1, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgesu, H.; Nekkhil, I.M.; Ameri, S. Understanding the effect of drilling parameters on hole cleaning in horizontal and deviated wellbores using computational fluid dynamics. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the Eastern Regional Meeting, Lexington, KY, USA, 17–19 October 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Elkatatny, S.; Chen, W. The effect of weighting materials on oil-well cement properties while drilling deep wells. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valluri, S.G.; Miska, S.; Yu, M.; Ahmed, R.M.; Takach, N. Experimental study of effective hole cleaning using sweeps in horizontal wellbores. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 24–27 September 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Takach, N.; Nakamura, E.; David, R.; Shariff, M.M. An experimental study of hole cleaning under simulated downhole conditions. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 11–14 November 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubaii, A.; Murif, M.; Sehsah Ossama, R.; Omini, E. Approach to improve well drilling performance. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the SPE Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Annual Technical Symposium and Exhibition, Dammam, Saudi Arabia, 23–26 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saasen, A. Hole cleaning during deviated drilling—The effects of pump rate and rheology. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the European Petroleum Conference, The Hague, The Netherlands, 20–22 October 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadamosi Afeez, O.; Junin, R.; Oseh Jeffrey, O.; Agi, A.; Yekeen, N.; Abdalla, Y.; Ogiriki Shadrach, O.; Adeyinka, S.Y. Improving hole cleaning efficiency using nanosilica in water-based drilling mud. In Proceedings of the Paper Presented at the SPE Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition, Lagos, Nigeria, 6–8 August 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremieniewski, M.; Rzepka, M. Hybrydowa Ciecz Przemywająca Do Oczyszczania Przestrzeni Pierécieniowej Otworu Wiertniczego; Nafta-Gaz: Hünenber, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 5, pp. 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Ingredients | Concentration (%) |
|---|---|
| Water | 100 |
| Surfactant (C12–14 ethoxylated alcohols) | 0.2 |
| Surfactant (mixture of C12–15 ethoxylated alcohols and sodium salts) | 0.2 |
| Polyethyleneimine | 0.05 |
| Nut shells (fractions with dimensions of 100–250 µm) | 0.1 |
| Plastic shot (fractions with dimensions of 20–40 mesh) | 0.2 |
| Microspheric glass fractions with dimensions of 100–200 µm | 0.2 |
| Defoamer (product of saturated fatty alcohol ethoxylation and propoxylation) | 0.01 |
| Ingredients | % by Mass of Cement |
|---|---|
| Water–cement ratio | 0.45 |
| Plasticizer | 0.2 |
| Latex | 10.0 |
| Stabilizer | 1.0 |
| Defoaming agent | 0.5 |
| Antifiltrating agent | 0.2 |
| Setting accelerator | 4.0 |
| Microcement | 10.0 |
| Cement CEM I 42,5R | 100.0 |
| The Strength of Breaking Adhesion (kN) | Adhesion to Contact between HARDENED Cement Slurry and Rock (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum base adhesion | 8.2 | 2.37 |
| Minimum base adhesion | 2.1 | 0.61 |
| Type of Flushing Liquid | Adhesion Breaking Strength (kN) | Adhesion to Hardened Cement Slurry–Rock Contact (MPa) | Percentage Reduction in Adhesion Compared to the Maximum Base Adhesion | Percentage Increase in Adhesion Compared to the Minimum Base Adhesion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum base adhesion | 8.2 | 2.37 | ---- | ---- |
| Minimum base adhesion | 2.1 | 0.61 | ---- | ---- |
| Water | 3.5 | 1.01 | ↓ 57% | ↑ 66% |
| The MDC agent used so far | 4.3 | 1.24 | ↓ 48% | ↑ 103% |
| Hybrid drilling washer fluid | 7.8 | 2.26 | ↓ 5% | ↑ 271% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kremieniewski, M. Hybrid Washer Fluid for Primary Cementing. Energies 2021, 14, 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051295
Kremieniewski M. Hybrid Washer Fluid for Primary Cementing. Energies. 2021; 14(5):1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051295
Chicago/Turabian StyleKremieniewski, Marcin. 2021. "Hybrid Washer Fluid for Primary Cementing" Energies 14, no. 5: 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051295
APA StyleKremieniewski, M. (2021). Hybrid Washer Fluid for Primary Cementing. Energies, 14(5), 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051295






