Long-Term Assessment of Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy Potentials of Qatar
Abstract
1. Introduction
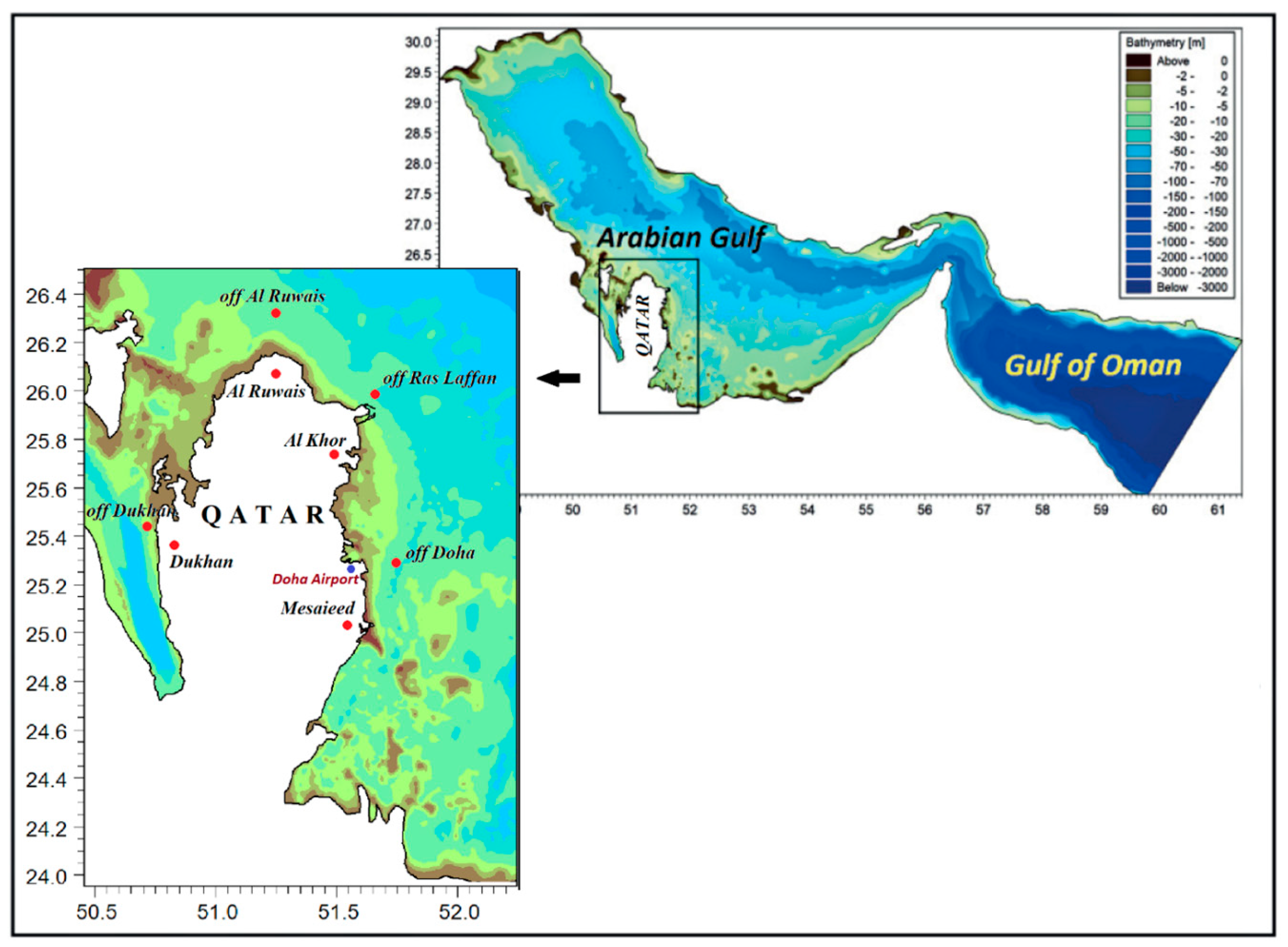
2. Area of Study
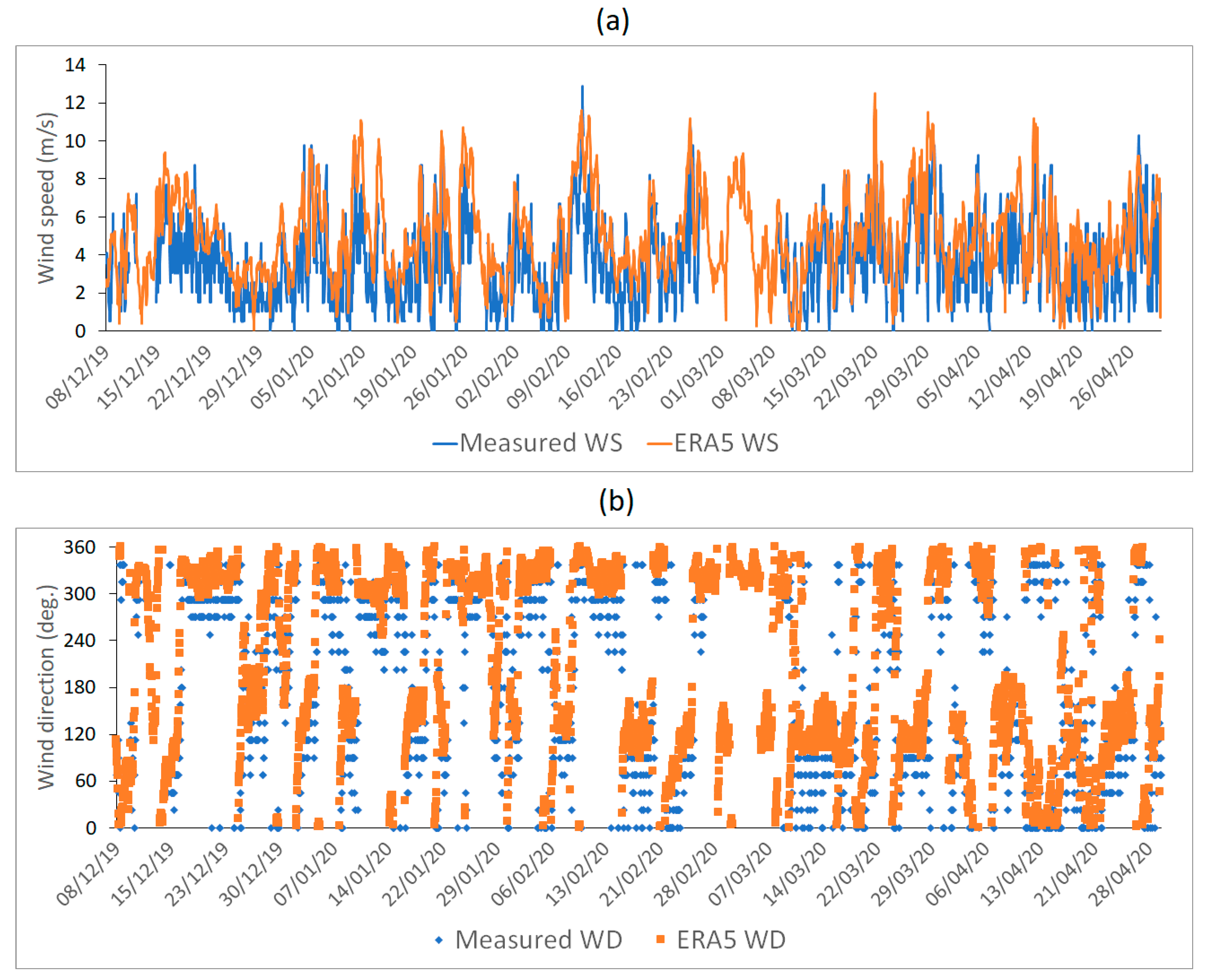
3. Data and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
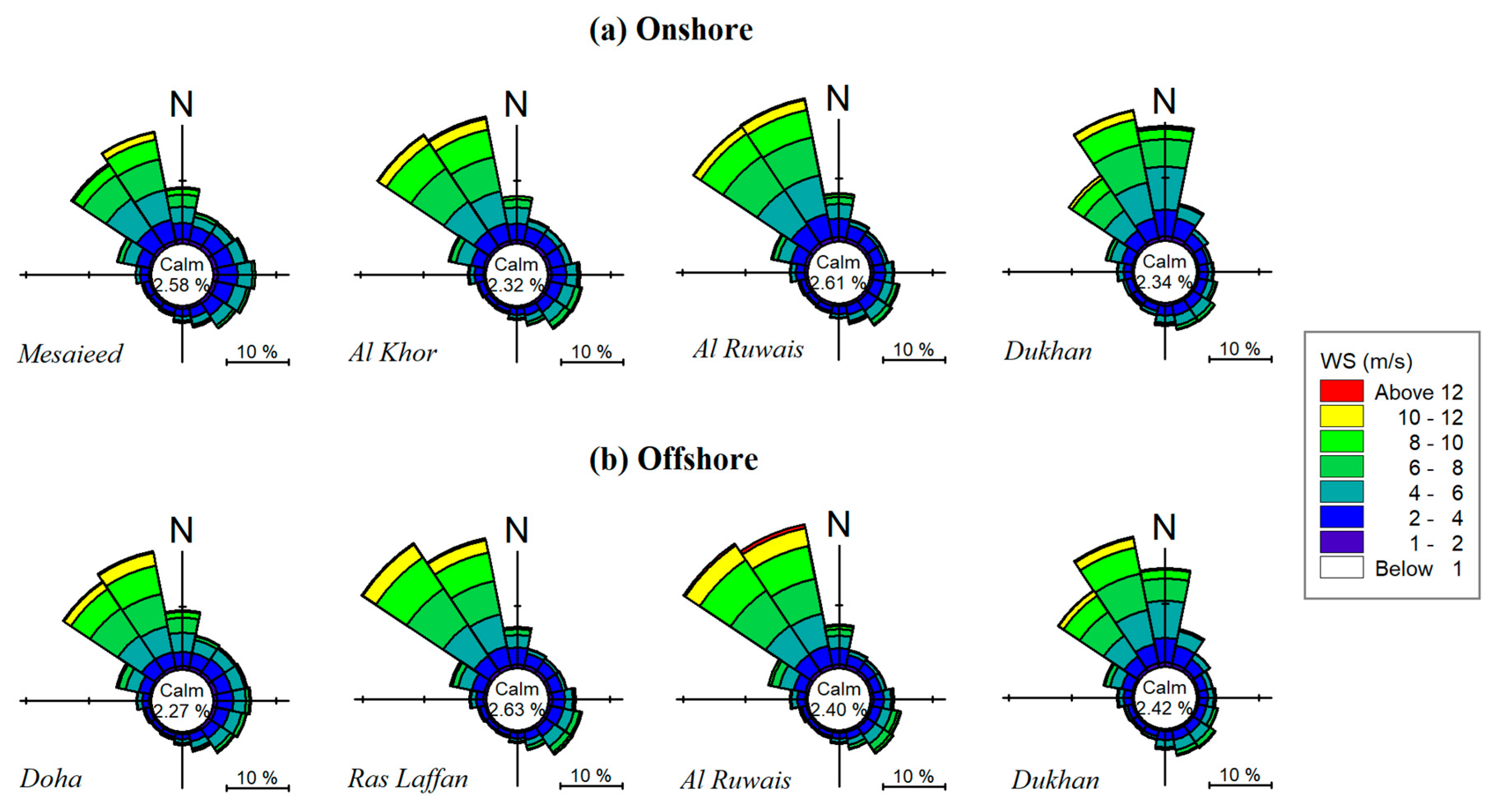
4.1. Wind Climate
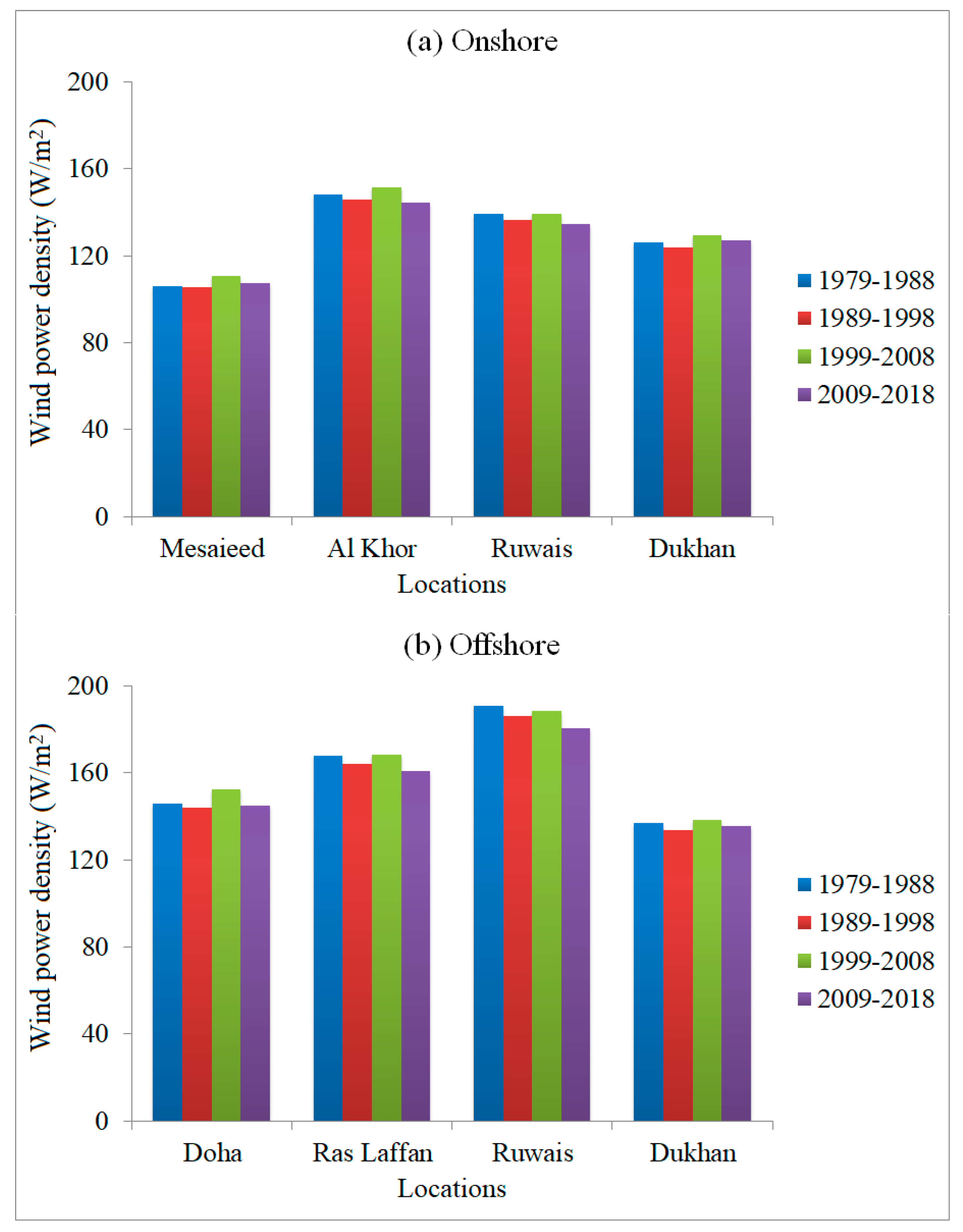
4.2. The Annual and Decadal Wind Power
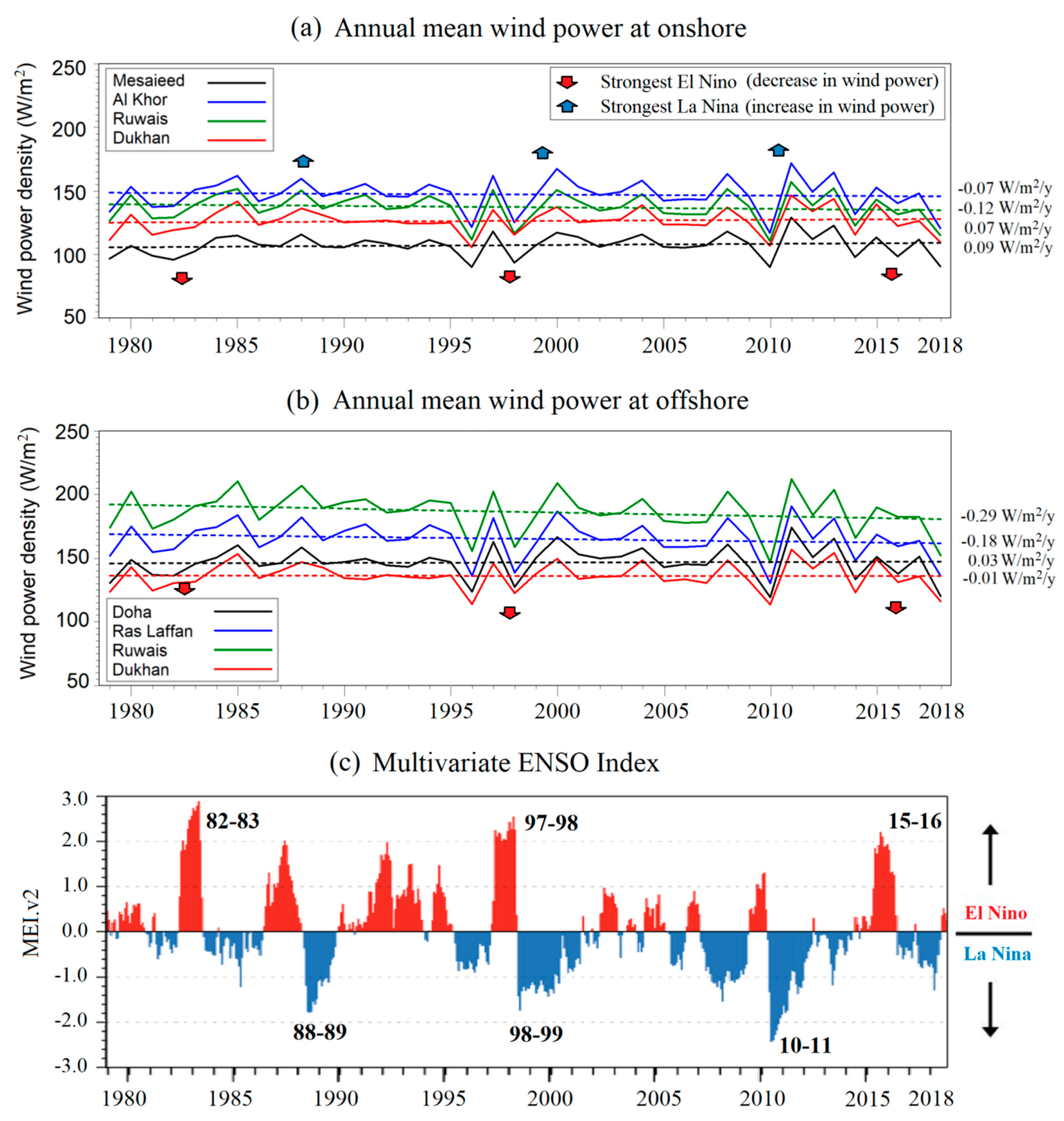
4.3. Inter-Annual Variability and Trends
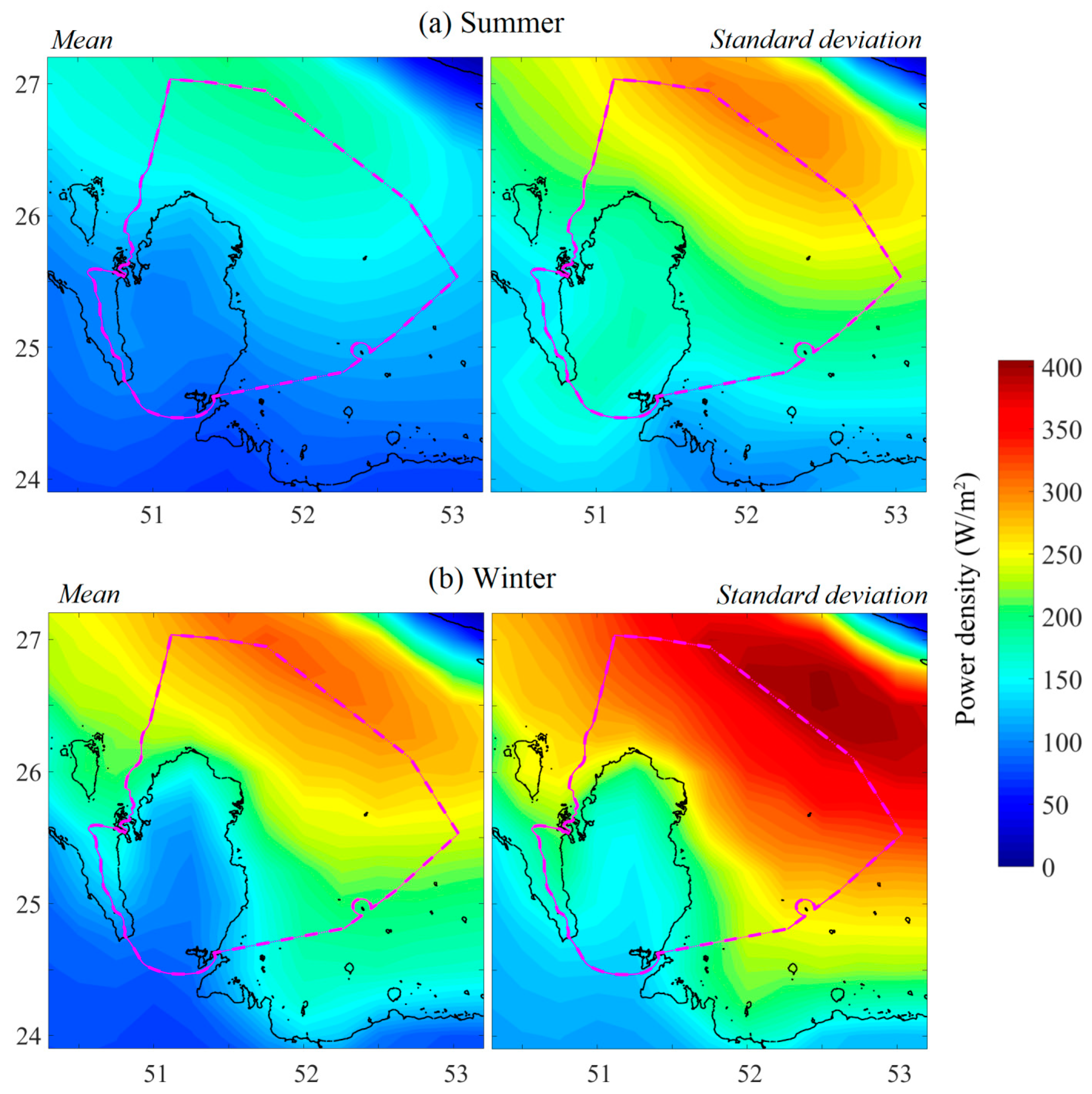
4.4. Seasonal Mean Wind Power
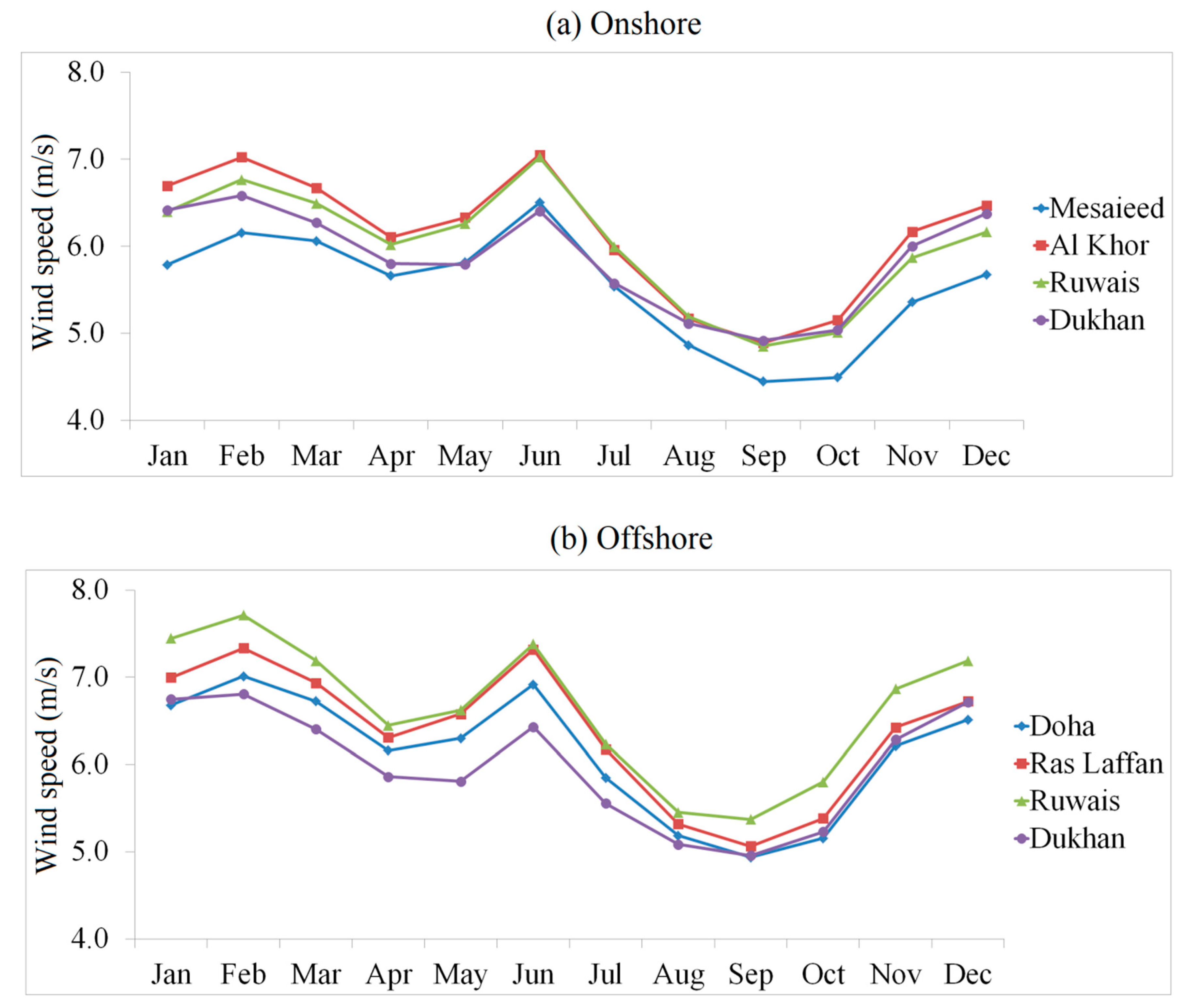
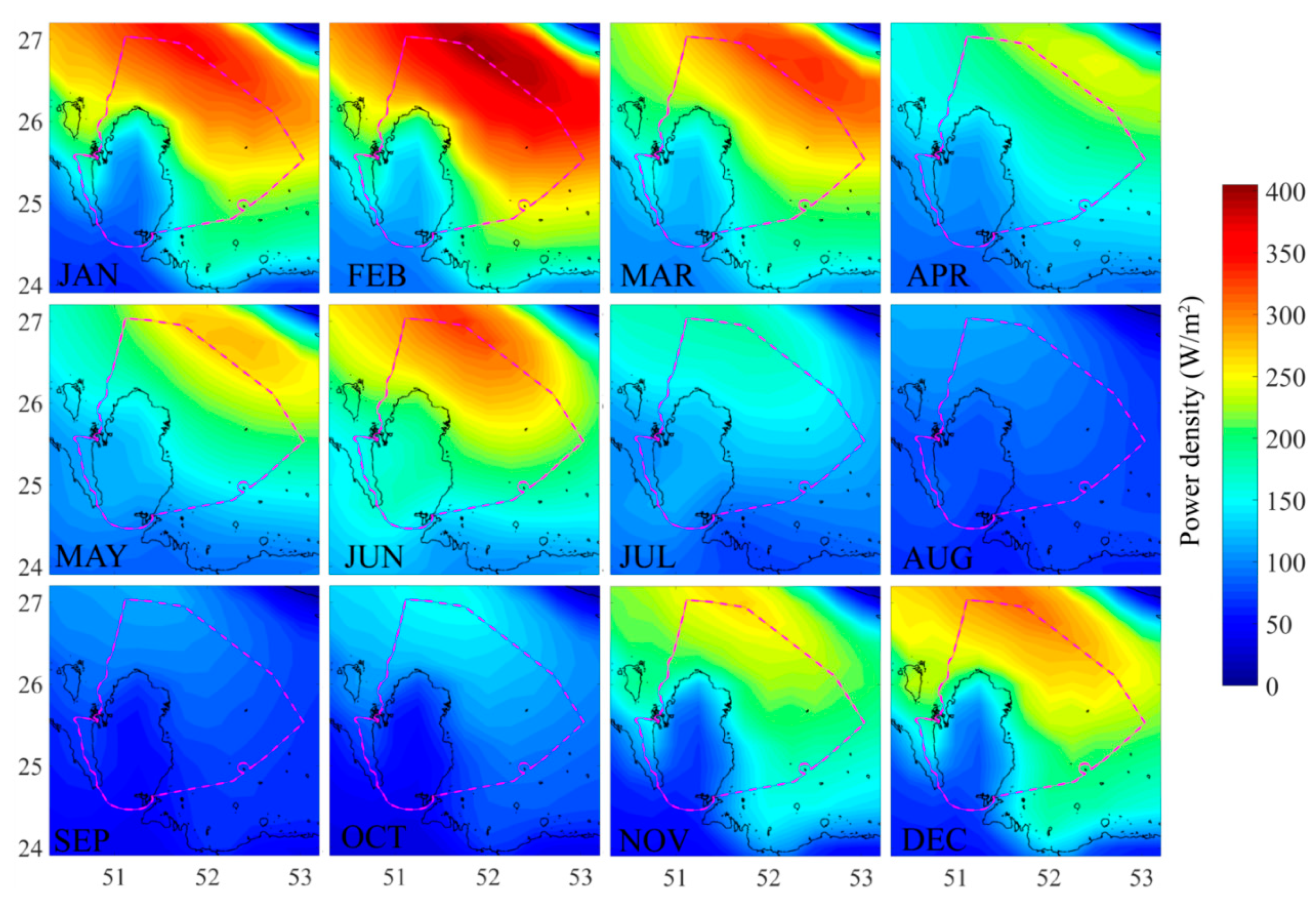
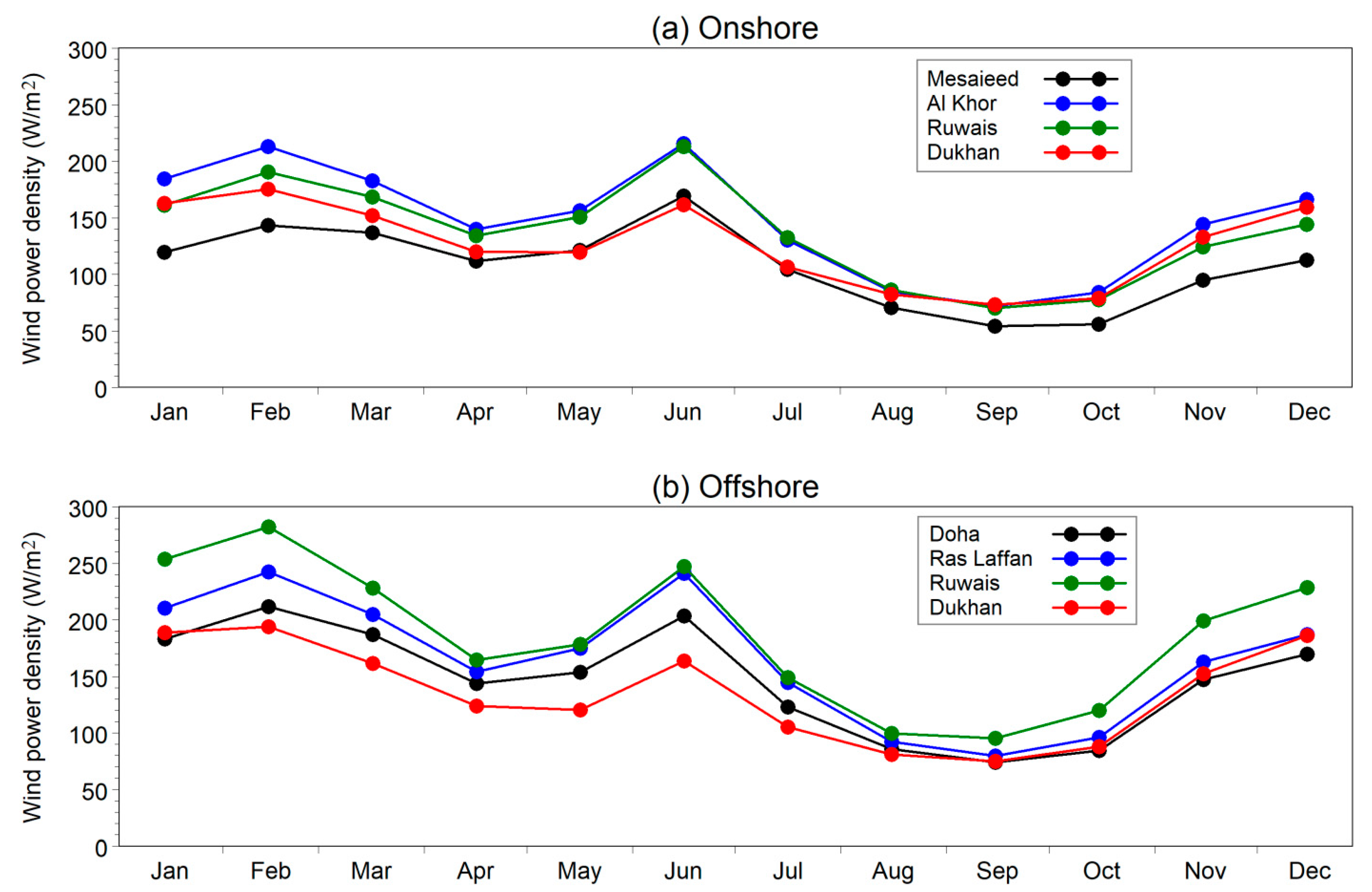
4.5. Monthly Mean Wind Power
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xiong, B. Energy revolution: From a fossil energy era to a new energy era. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2016, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, L.; El-Shennawy, T. Reducing Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Electricity Sector Using Smart Electric Grid Applications. J. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R. Global oil & gas depletion: An overview. Energy Policy 2002, 30, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, P.A.; Asumadu-Sarkodie, S. A review of renewable energy sources, sustainability issues and climate change mitigation. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1167990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, P.K.; Warudkar, V.; Ahmed, S. Wind energy development and policy in India: A review. Energy Strat. Rev. 2019, 24, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukali, S.; Dinçkal, Ç. Wind energy resource assessment of Izmit in the West Black Sea Coastal Region of Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Mansaray, L.R.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Huang, J. Assessing Global Ocean Wind Energy Resources Using Multiple Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Wan, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, D. Assessing temporal variability of wind resources in China and the spatial correlation of wind power in the selected regions. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2020, 12, 13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.-L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.-T.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Iredell, M.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Version 2. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; Mccarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.H.; et al. The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppala, S.M.; Kållberg, P.W.; Simmons, A.J.; Andrae, U.; Bechtold, V.D.C.; Fiorino, M.; Gibson, J.K.; Haseler, J.; Hernandez, A.; Kelly, G.A.; et al. The ERA-40 re-analysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2961–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrisford, P.; Dee, D.P.; Fielding, M.; Fuentes, M.; Kållberg, P.W.; Kobayashi, S.; Uppala, S. The ERA-Interim Archive. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/node/8173 (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.S.; Asok, A.B.; George, J.; Amrutha, M.M. Regional Study of Changes in Wind Power in the Indian Shelf Seas over the Last 40 Years. Energies 2020, 13, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Günther, G.; Li, D.; Stein, O.; Wu, X.; Griessbach, S.; Heng, Y.; Konopka, P.; Müller, R.; Vogel, B.; et al. From ERA-Interim to ERA5: The considerable impact of ECMWF’s next-generation reanalysis on Lagrangian transport simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 3097–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, M.B.; Stoffelen, A. Characterizing ERA-Interim and ERA5 surface wind biases using ASCAT. Ocean Sci. 2019, 15, 831–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulazia, A.; Sáenz, J.; Ibarra-Berastegi, G.; González-Rojí, S.J.; Carreno-Madinabeitia, S. Global estimations of wind energy potential considering seasonal air density changes. Energy 2019, 187, 115938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, J.; Lledó, L.; Torralba, V.; Soret, A.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J. What global reanalysis best represents near-surface winds? Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 3236–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olauson, J. ERA5: The new champion of wind power modelling? Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoppil, P.G.; Hogan, P.J. Persian Gulf response to a wintertime shamal wind event. Deep. Sea Res. Part I: Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2010, 57, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Notaro, M.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Garay, M.J. Climatology of summer Shamal wind in the Middle East. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Senafi, F.; Anis, A. Shamals and climate variability in the Northern Arabian/Persian Gulf from 1973 to 2012. Int. J. Clim. 2015, 35, 4509–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, T.J. Winter Shamal in the Persian Gulf; Naval Environmental Prediction Research Facility: Monterey, CA, USA, 1979; p. 180. [Google Scholar]
- Kamranzad, B. Persian Gulf zone classification based on the wind and wave climate variability. Ocean Eng. 2018, 169, 604–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eager, R.E.; Raman, S.; Wootten, A.; Westphal, D.L.; Reid, J.S.; Al Mandoos, A. A climatological study of the sea and land breezes in the Arabian Gulf region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeepan, B.; Panchang, V.G.; Nayak, S.; Kumar, K.K.; Kaihatu, J.M. Performance of the WRF Model for Surface Wind Prediction around Qatar. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlakas, P.; Stathopoulos, C.; Flocas, H.A.; Kalogeri, C.; Kallos, G. Regional Climatic Features of the Arabian Peninsula. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balog, I.; Ruti, P.M.; Tobin, I.; Armenio, V.; Vautard, R. A numerical approach for planning offshore wind farms from regional to local scales over the Mediterranean. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, M.D.C.R.; García-Díez, M.; Fita, L.; Fernández, J.; Mendez, F.J.; Gutiérrez, J.M. High-resolution sea wind hindcasts over the Mediterranean area. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 42, 1857–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calaudi, R.; Arena, F.; Badger, M.; Sempreviva, A.M. Offshore Wind Mapping Mediterranean Area Using SAR. Energy Procedia 2013, 40, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ucar, A.; Balo, F. Evaluation of wind energy potential and electricity generation at six locations in Turkey. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.M.A.; Gunturu, U.B.; Stenchikov, G.L. Wind resource characterization in the Arabian Peninsula. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nassar, W.; Neelamani, S.; Al-Salem, K.; Al-Dashti, H. Feasibility of offshore wind energy as an alternative source for the state of Kuwait. Energy 2019, 169, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shata, A.A.; Hanitsch, R. The potential of electricity generation on the east coast of Red Sea in Egypt. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 1597–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langodan, S.; Viswanadhapalli, Y.; Dasari, H.P.; Knio, O.; Hoteit, I. A high-resolution assessment of wind and wave energy potentials in the Red Sea. Appl. Energy 2016, 181, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, K.; Neelamani, S.; Al-Nassar, W. Wind Energy Map of Arabian Gulf. Nat. Resour. 2018, 9, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonkar, H. Complete Survey of Wind Behavior over the Arabian Gulf. J. King Abdulaziz Univ. Sci. 2009, 20, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A. Wind Meteorology of the Summer Shamal in the Arabian Gulf Region. Master’s Thesis, Boston University, Boston, NE, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.G.; Hatwar, H.R.; Al-Sulaiti, M.H.; Al-Mulla, A.H. Summer shamals over the Arabian Gulf. Weather 2003, 58, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirinia, G.; Mafi, S.; Mazaheri, S. Offshore wind resource assessment of Persian Gulf using uncertainty analysis and GIS. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaser, W.; Almohanadi, A. Wind and solar energy in Qatar. Energy 1990, 15, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marafia, A.-H.; Ashour, H.A. Economics of off-shore/on-shore wind energy systems in Qatar. Renew. Energy 2003, 28, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, C.; Bicer, Y. Qatar’s Wind Energy Potential with Associated Financial and Environmental Benefits for the Natural Gas Industry. Energies 2019, 12, 3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qaradawi, I.; Abdel-Moati, M.; Al-Yafei, M.A.-A.; Al-Ansari, E.; Al-Maslamani, I.A.; Holm, E.; Al-Shaikh, I.; Mauring, A.; Pinto, P.V.; Abdulmalik, D.; et al. Radioactivity levels in the marine environment along the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of Qatar. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.L.; Saleem, A.; Sadr, R. Recent warming trend in the coastal region of Qatar. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2015, 128, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboobacker, V.M.; Shanas, P.R.; Al-Ansari, E.M.A.S.; Sanil Kumar, V.; Vethamony, P. The maxima in northerly wind speeds and wave heights over the Arabian Sea, the Arabian/Persian Gulf and the Red Sea derived from 40 years of ERA5 data. Clim. Dyn. 2020. (In Press) [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, Z.; Zou, L. Evaluation of Near-Surface Wind Speed Changes during 1979 to 2011 over China Based on Five Reanalysis Datasets. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullaart, J.C.M.; Muis, S.; Bloemendaal, N.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Advancing global storm surge modelling using the new ERA5 climate reanalysis. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 54, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, K.; Ghassemi, H.; Razminia, A. Temporal and spatial characteristics of wave energy in the Persian Gulf based on the ERA5 reanalysis dataset. Energy 2019, 187, 115991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennekes, H. The Logarithmic Wind Profile. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Erdem, E.; Li, G.; Shi, J. Comprehensive evaluation of wind speed distribution models: A case study for North Dakota sites. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, A.; Erisoglu, M.; Pekgor, A.; Oturanc, G.; Hepbasli, A.; Ulgen, K. Estimation of Wind Power Potential Using Weibull Distribution. Energy Sources 2005, 27, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.P. Estimation of wind energy potential using different probability density functions. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Erdem, E. Estimation of Wind Energy Potential and Prediction of Wind Power; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 25–49. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Pillay, P.; Khan, A. PM Wind Generator Topologies. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Z. Design optimization and site matching of direct-drive permanent magnet wind power generator systems. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitano-Briggs, H. Low Speed Wind Turbine Design; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Verde, A.; Lastres, O.; Hernández, G.; Ibáñez, G.; Verea, L.; Sebastian, P. A new method for characterization of small capacity wind turbines with permanent magnet synchronous generator: An experimental study. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.S.; Shaaban, S.; Marsillac, E.; Mahmood, N.M. A methodology for improving wind energy production in low wind speed regions, with a case study application in Iraq. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 127, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shi, J.; Qu, X. Empirical investigation on using wind speed volatility to estimate the operation probability and power output of wind turbines. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 67, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Shi, J. Bivariate Modeling of Wind Speed and Air Density Distribution for Long-Term Wind Energy Estimation. Int. J. Green Energy 2010, 7, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, A.; Iyer, H.; Malm, W. Linear trend analysis: A comparison of methods. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 5211–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosseron, A.; Gunturu, U.B.; Schlosser, C.A. Characterization of the Wind Power Resource in Europe and its Intermittency. Energy Procedia 2013, 40, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornett, A.M. A global wave energy resource assessment. In Proceedings of the 18th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference (ISOPE), International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–11 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.; Hau, E.; Snel, H. Large Wind Turbines: Design and Economics; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Pan, J.; Li, J.-X. Assessing the China Sea wind energy and wave energy resources from 1988 to 2009. Ocean Eng. 2013, 65, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantusa, D.; Tomasicchio, G. Large-scale offshore wind production in the Mediterranean Sea. Cogent Eng. 2019, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, L.; Ganea, D.; Mereuta, E. A joint evaluation of wave and wind energy resources in the Black Sea based on 20-year hindcast information. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2017, 36, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J. Impact of Intermittency: How Wind Variability Could Change the Shape of the British and Irish Electricity Markets; Summary Report; Poyry Energy Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, K.R.; Kruk, M.C.; Levinson, D.H.; Diamond, H.J.; Neumann, C.J. The International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBTrACS). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naizghi, M.S.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J. Teleconnections and analysis of long-term wind speed variability in the UAE. Int. J. Clim. 2016, 37, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanas, P.; Aboobacker, V.; AlBarakati, A.M.; Zubier, K.M. Climate driven variability of wind-waves in the Red Sea. Ocean Model. 2017, 119, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboobacker, V.M.; Shanas, P.R. The climatology of shamals in the Arabian Sea-Part 1: Surface winds. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 38, 4405–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brano, V.L.; Galanis, G.; Spyrou, C.; Diamantis, D.; Baladima, F.; Koukoula, M.; Kallos, G.B. Assessing the European offshore wind and wave energy resource for combined exploitation. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Region | Locations | Geographical Co-Ordinates | Wind Speed (m/s) | % of Exploitable Wind Speed | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longitude (° E) | Latitude (° N) | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation | |||
| Onshore | Mesaieed | 51.5828 | 25.0444 | 15.4 | 4.6 | 2.3 | 73.9 |
| Al Khor | 51.4394 | 25.7534 | 16.2 | 5.1 | 2.6 | 77.1 | |
| Al Ruwais | 51.2202 | 26.0690 | 15.9 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 74.7 | |
| Dukhan | 50.8398 | 25.3355 | 15.7 | 4.9 | 2.4 | 77.5 | |
| Offshore | Doha | 51.7970 | 25.2755 | 15.5 | 5.1 | 2.5 | 78.5 |
| Ras Laffan | 51.6146 | 26.0131 | 16.5 | 5.2 | 2.7 | 76.5 | |
| Al Ruwais | 51.2992 | 26.2822 | 16.9 | 5.5 | 2.8 | 78.4 | |
| Dukhan | 50.7251 | 25.4767 | 16.1 | 5.0 | 2.4 | 78.2 | |
| Region | Statistics of Wind Power Density | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locations | Mean (W/m2) | Max (W/m2) | SD (W/m2) | CoV | Sk | K | |
| Onshore | Mesaieed | 107.4 | 2249.6 | 158.5 | 1.48 | 3.18 | 17.30 |
| Al Khor | 147.3 | 2604.2 | 202.6 | 1.38 | 2.52 | 11.43 | |
| Al Ruwais | 137.3 | 2467.1 | 192.0 | 1.40 | 2.57 | 11.93 | |
| Dukhan | 126.5 | 2378.5 | 173.3 | 1.37 | 2.75 | 13.48 | |
| Offshore | Doha | 146.7 | 2273.1 | 199.2 | 1.36 | 2.55 | 11.62 |
| Ras Laffan | 165.3 | 2783.8 | 224.7 | 1.36 | 2.32 | 9.84 | |
| Al Ruwais | 186.4 | 2960.3 | 245.4 | 1.32 | 2.22 | 9.42 | |
| Dukhan | 136.1 | 2547.7 | 183.1 | 1.35 | 2.61 | 12.31 | |
| Region | Locations | Annual Mean Wind Power (W/m2) during 1979–2018 | % of Variation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Highest | Lowest | Highest-Lowest | |||
| Onshore | Mesaieed | 129.1 | 90.0 | 39.1 | 43.4 |
| Al Khor | 171.8 | 117.0 | 54.8 | 46.8 | |
| Al Ruwais | 157.0 | 110.7 | 46.3 | 41.8 | |
| Dukhan | 146.6 | 105.6 | 41.0 | 38.8 | |
| Offshore | Doha | 174.0 | 119.2 | 54.8 | 46.0 |
| Ras Laffan | 190.7 | 130.1 | 60.6 | 46.6 | |
| Al Ruwais | 212.2 | 146.8 | 65.4 | 44.6 | |
| Dukhan | 156.9 | 113.4 | 43.5 | 38.4 | |
| Region | Locations | Mean Wind Power during 1979 | Increment in Mean Wind Power (W/m2) | Annual% of Increment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1979–2018 (40 Years) | Annual Rate of Increment | ||||
| Onshore | Mesaieed | 105.65 | +3.46 | +0.086 | +0.08 |
| Al Khor | 148.58 | −2.76 | −0.069 | −0.05 | |
| Al Ruwais | 139.58 | −4.61 | −0.115 | −0.08 | |
| Dukhan | 125.11 | +2.77 | +0.069 | +0.06 | |
| Offshore | Doha | 145.92 | +1.35 | +0.034 | +0.02 |
| Ras Laffan | 168.84 | −7.10 | −0.177 | −0.11 | |
| Al Ruwais | 192.23 | −11.57 | −0.289 | −0.15 | |
| Dukhan | 136.24 | −0.23 | −0.006 | 0.00 | |
| Region | Locations | Annual Variability Index | Seasonal Variability Index | Monthly Variability Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onshore | Mesaieed | 0.36 | 0.22 | 1.07 |
| Al Khor | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.98 | |
| Al Ruwais | 0.34 | 0.23 | 1.04 | |
| Dukhan | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.81 | |
| Offshore | Doha | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.94 |
| Ras Laffan | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.99 | |
| Al Ruwais | 0.35 | 0.42 | 1.00 | |
| Dukhan | 0.32 | 0.46 | 0.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aboobacker, V.M.; Shanas, P.R.; Veerasingam, S.; Al-Ansari, E.M.A.S.; Sadooni, F.N.; Vethamony, P. Long-Term Assessment of Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy Potentials of Qatar. Energies 2021, 14, 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14041178
Aboobacker VM, Shanas PR, Veerasingam S, Al-Ansari EMAS, Sadooni FN, Vethamony P. Long-Term Assessment of Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy Potentials of Qatar. Energies. 2021; 14(4):1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14041178
Chicago/Turabian StyleAboobacker, Valliyil Mohammed, Puthuveetil Razak Shanas, Subramanian Veerasingam, Ebrahim M. A. S. Al-Ansari, Fadhil N. Sadooni, and Ponnumony Vethamony. 2021. "Long-Term Assessment of Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy Potentials of Qatar" Energies 14, no. 4: 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14041178
APA StyleAboobacker, V. M., Shanas, P. R., Veerasingam, S., Al-Ansari, E. M. A. S., Sadooni, F. N., & Vethamony, P. (2021). Long-Term Assessment of Onshore and Offshore Wind Energy Potentials of Qatar. Energies, 14(4), 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14041178





