A Multimodal Improved Particle Swarm Optimization for High Dimensional Problems in Electromagnetic Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Related Work
2.1. Proper Adjustment of Parameters
2.2. Mutation Methods
2.3. Topological Structure
2.4. Hybridization
3. The Proposed Work
4. Numerical Results Analysis
- A Particle swarm optimization with adaptive mutation for multimodal optimization (AMPSO) [20].
- A modified PSO algorithm with dynamic parameters for solving complex engineering design problem (MPSOED) [24].
- Analysis of gaussian & cauchy mutations in modified particle swarm optimization algorithm (GCMPSO) [25].
- Global Particle Swarm Optimization for High Dimension Numerical Functions Analysis (GPSO) [27].
- Modified particle swarm optimization algorithm for scheduling renewable generation (MPSO) [51].
- Modified particle swarm optimization with effective guides (MPSOEG) [52].
5. Discussion
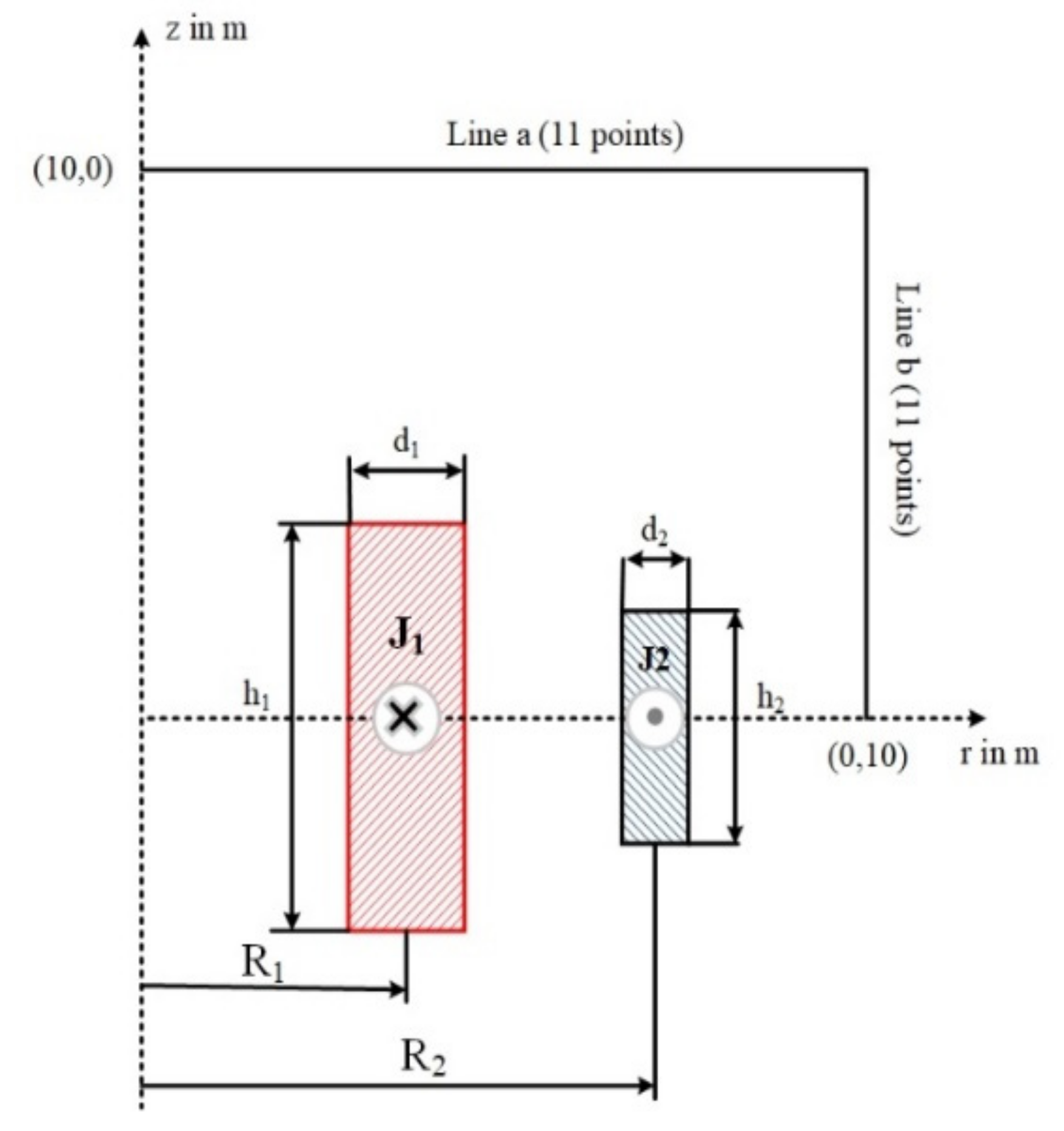
6. Application
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| IPSO | Improved Particle Swarm Optimization |
| C1 | Cognitive Constant |
| C2 | Social Constant |
| pbest | Personal Best |
| gbest | Global Best |
| W | Inertia Weight |
| SPSO | Smart Particle Swarm Optimization |
| CF | Convergence Factor |
| AIWF | Adaptive Inertia Weight Factor |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| SCA | Sine Cosine Algorithm |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| DE | Differential Evolution |
| PV | Photovoltaics |
| Mg | Maximum Generation |
| Rly | Rayleigh’s method |
| Std | Students |
| Out | Outcome |
| Q | Mutation Operator |
| SMES | Super Conducting Magnetic Storage System |
| TEAM | Testing Electromagnetic Analysis Method |
| Wm | Magnetic Energy |
| OF | Objective Function |
| Ji | Current Coil Density |
| Bmax | Maximum Magnetic Flux |
Appendix A
| f1 Rastrigin | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 6.70 | 1.10 |
| Mean | −12.18 | −2.14 | −2.10 | −1.49 | −0.62 | −0.21 | −3.80 |
| Variance | 4.14 | 0.77 | 1.13 | 0.84 | 0.68 | 3.45 | 2.35 |
| f2 De Jong’s | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 16.90 | 1.20 |
| Mean | −50.64 | −1.25 | −3.22 | −14.41 | −7.09 | −10.70 | −9.77 |
| Variance | 30.13 | 1.08 | 1.87 | 7.44 | 3.59 | 12.08 | 6.63 |
| f3 Bent Cigar | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.80 | 1.70 | 1.10 | 0.00 | 2.60 |
| Mean | −27.01 | −7.32 | −7.37 | −5.69 | −3.24 | −8.02 | −1.01 |
| Variance | 10.12 | 2.92 | 6.22 | 3.02 | 2.84 | 5.93 | 2.20 |
| f4 Step | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | −1.00 | 0.90 | 1.10 | 1.80 | 1.70 | 1.01 | 0.10 |
| Mean | −45.65 | −5.65 | −3.79 | −7.13 | −15.65 | −9.95 | −11.49 |
| Variance | 26.14 | 5.12 | 3.75 | 6.10 | 12.91 | 8.78 | 7.70 |
| f5 Quartic | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 |
| Mean | −54.37 | −11.58 | −7.79 | −22.93 | −5.77 | −11.18 | −8.16 |
| Variance | 16.18 | 8.70 | 5.52 | 14.99 | 3.76 | 10.00 | 6.71 |
| f6 Sphare | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | 0.80 | 0.90 | 1.60 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 1.41 | 0.93 |
| Mean | −5.55 | −1.09 | −1.18 | −2.85 | −2.90 | −0.82 | −3.73 |
| Variance | 3.90 | 1.05 | 1.43 | 2.67 | 2.62 | 0.90 | 2.09 |
| f7 Schwefel’s Problem 1.2 | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | 5.90 | 8.30 | 10.00 | 10.10 | 8.90 | 6.00 | 6.11 |
| Mean | −68.62 | −62.69 | −10.44 | −12.20 | −10.38 | −12.75 | −6.26 |
| Variance | 33.84 | 21.23 | 17.25 | 15.15 | 13.06 | 18.28 | 9.42 |
| f8 HappyCat | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | 1.90 | 2.40 | 2.30 | 2.50 | 2.60 | 8.00 | 1.19 |
| Mean | −0.75 | 0.60 | 1.46 | 1.88 | 1.17 | 1.77 | −0.44 |
| Variance | 1.17 | 0.43 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 1.34 | 0.71 |
| f9 Alpine1 | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | 0.00 | 3.20 | 2.90 | 0.90 | 3.00 | 2.90 | 3.30 |
| Mean | −14.57 | −2.28 | 1.74 | −4.37 | −1.34 | −0.28 | −1.69 |
| Variance | 6.33 | 1.70 | 1.25 | 2.62 | 4.15 | 2.43 | 4.20 |
| f10 Griewank | |||||||
| IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG | |
| Worst | 0.00 | 0.90 | 1.10 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 1.60 | 1.10 |
| Mean | −17.02 | −8.47 | −5.60 | −7.01 | −2.50 | −13.59 | −2.35 |
| Variance | 10.86 | 6.17 | 4.14 | 4.68 | 3.27 | 7.94 | 2.17 |
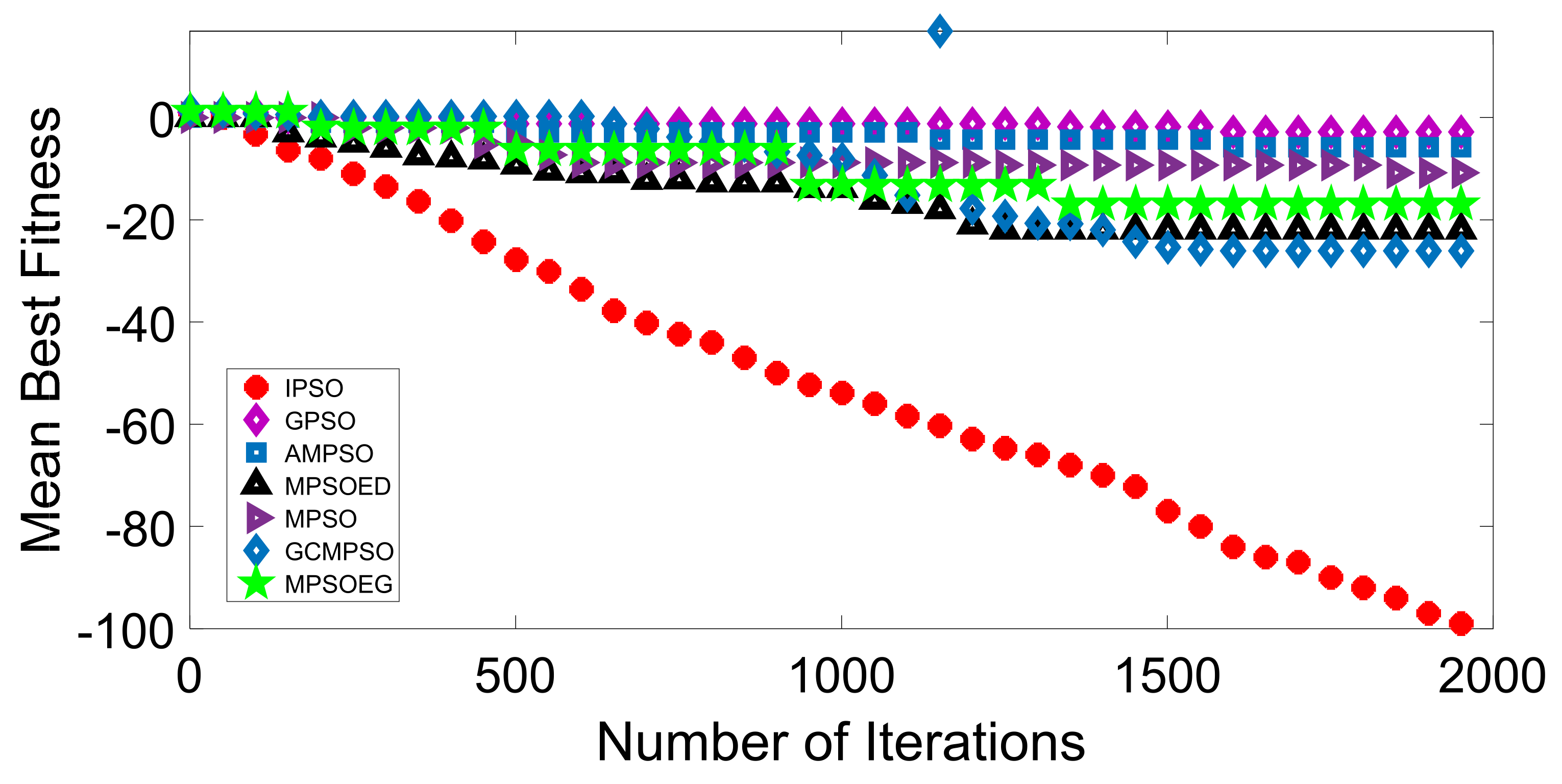
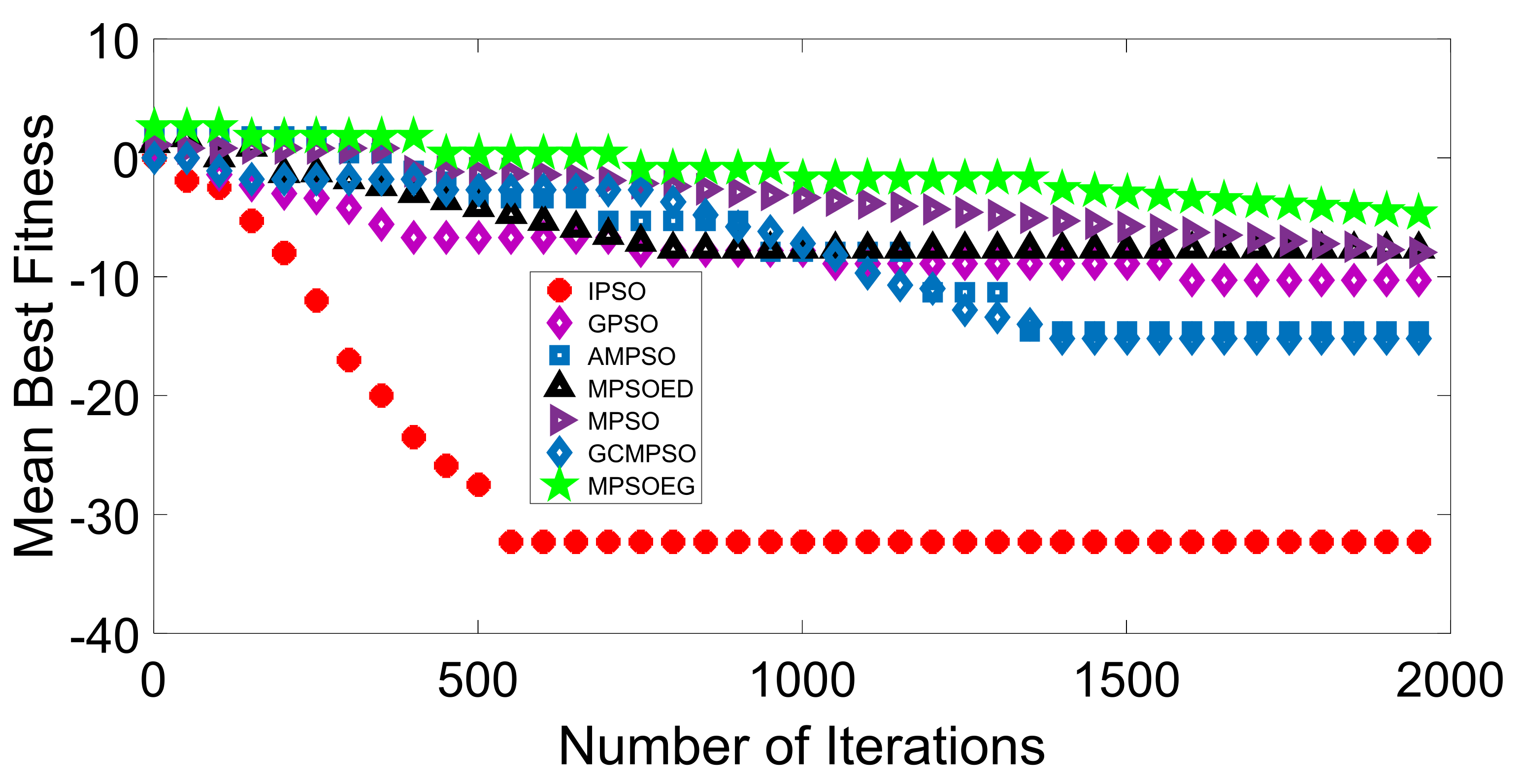
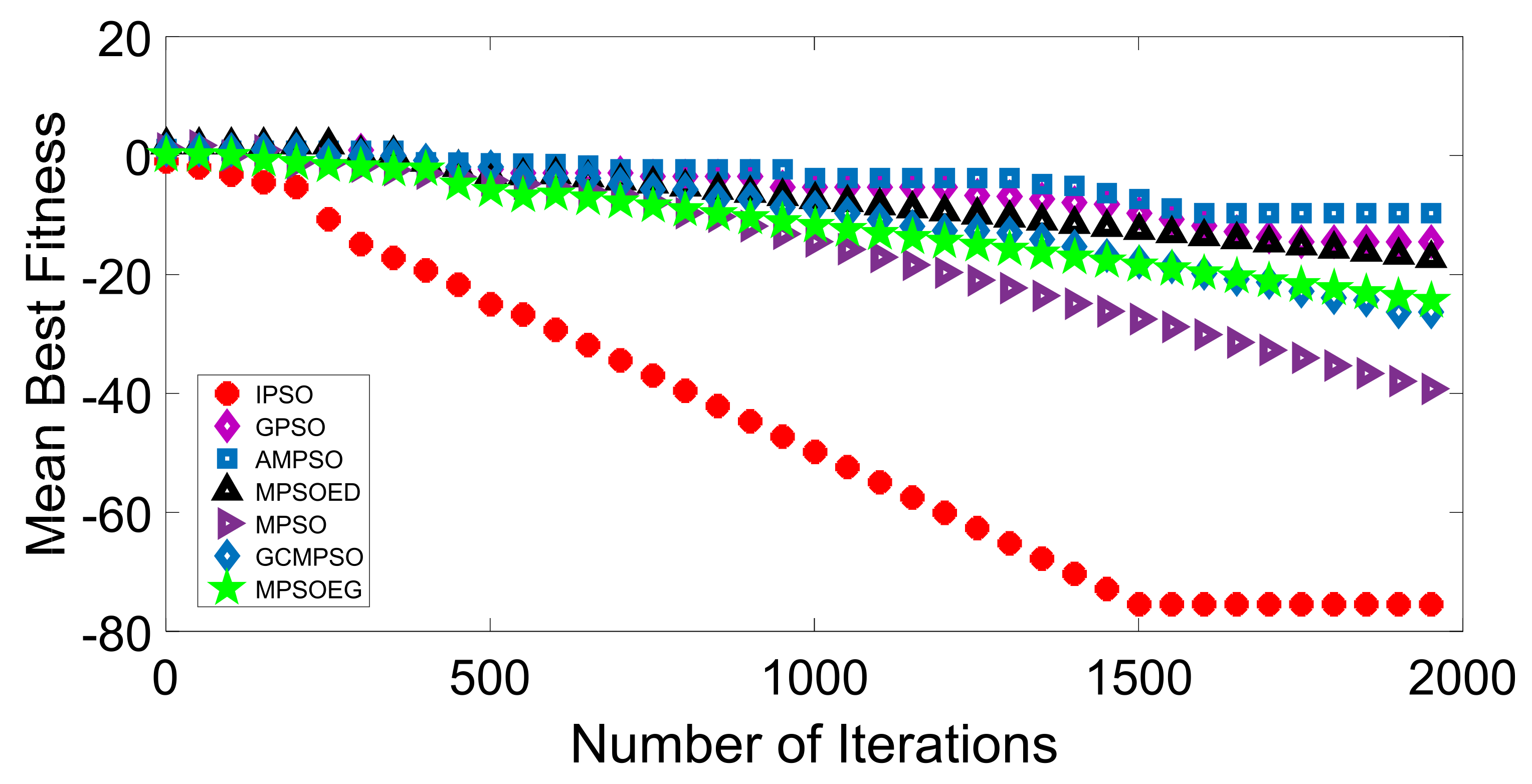
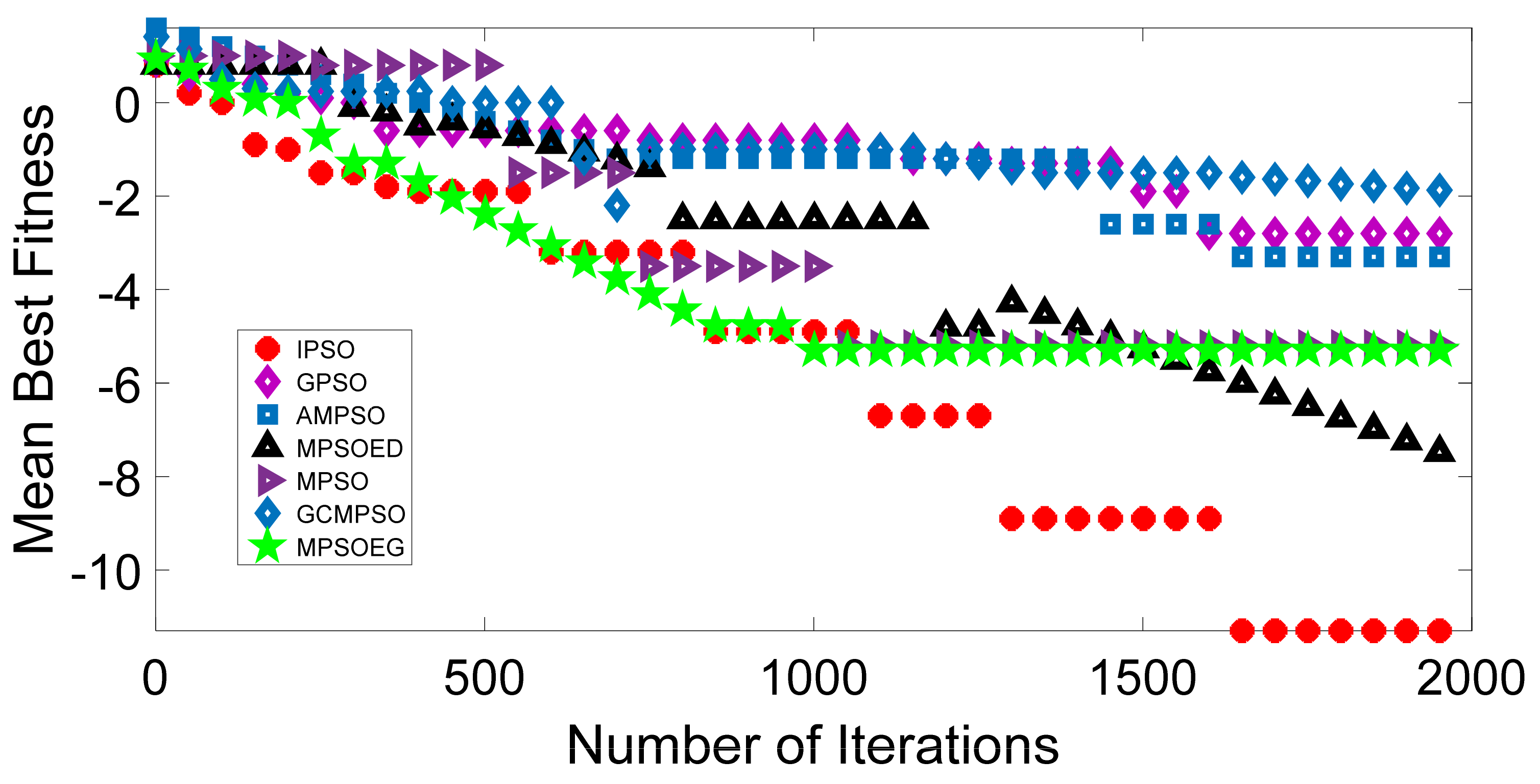
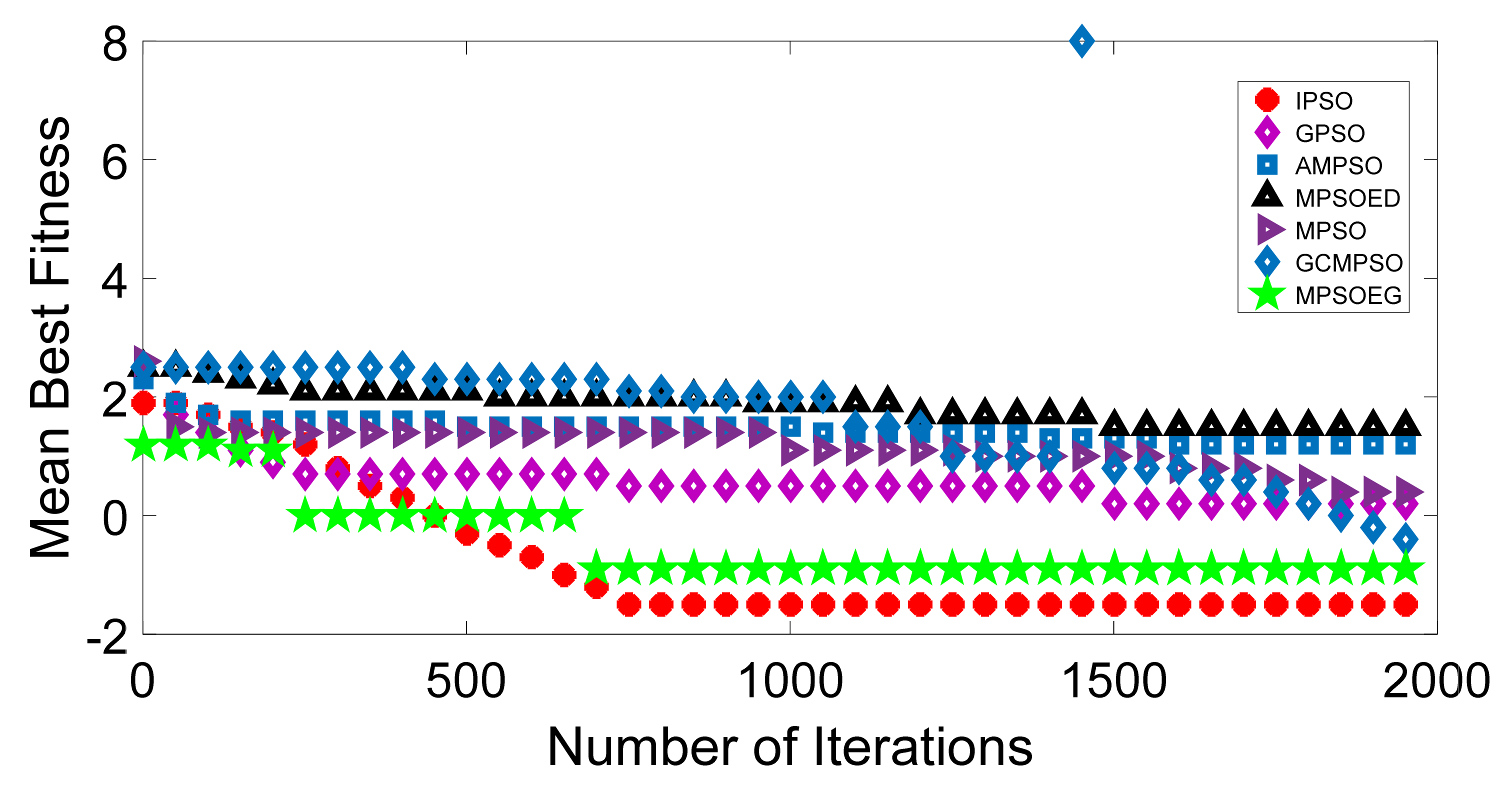
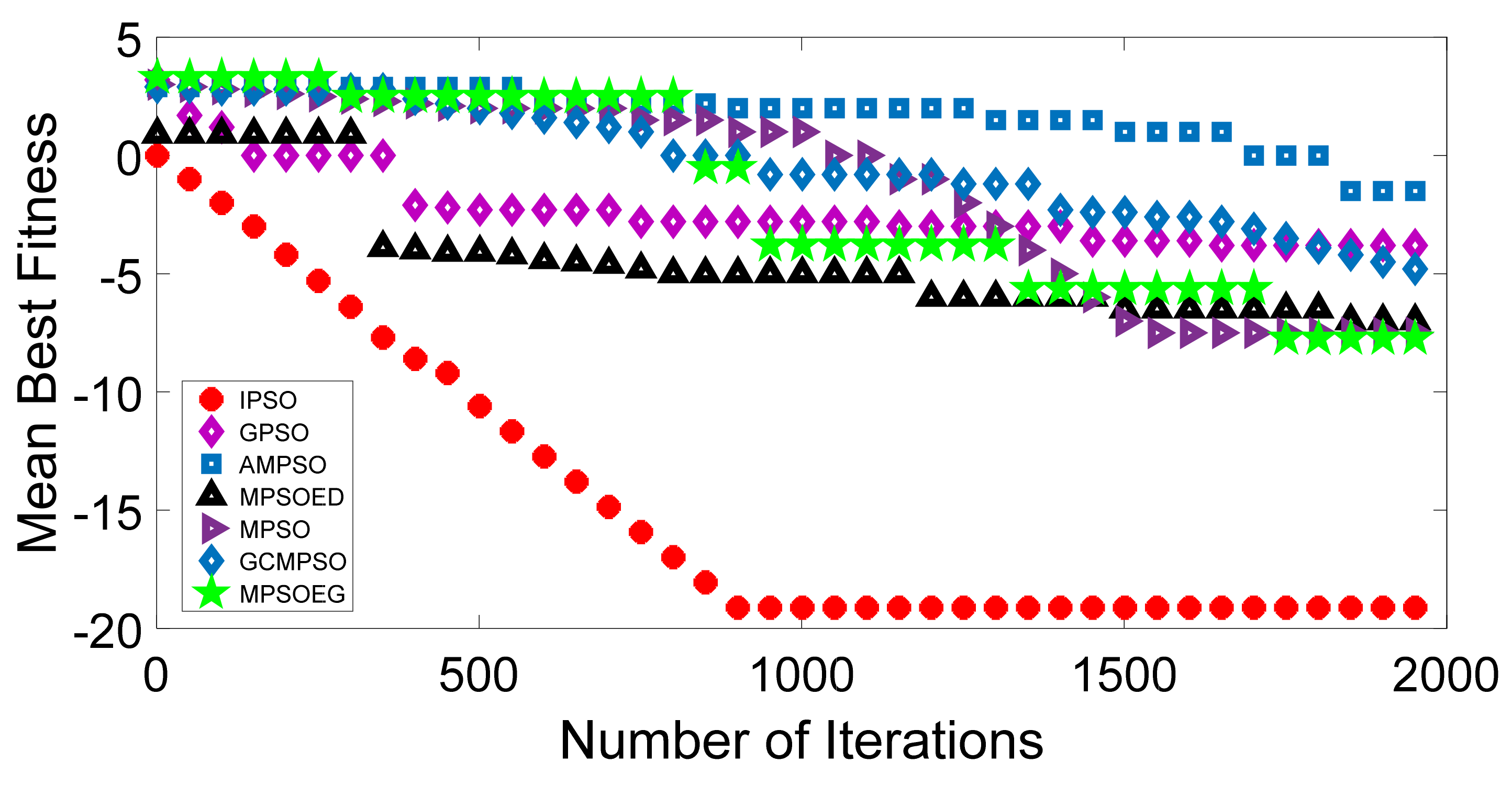
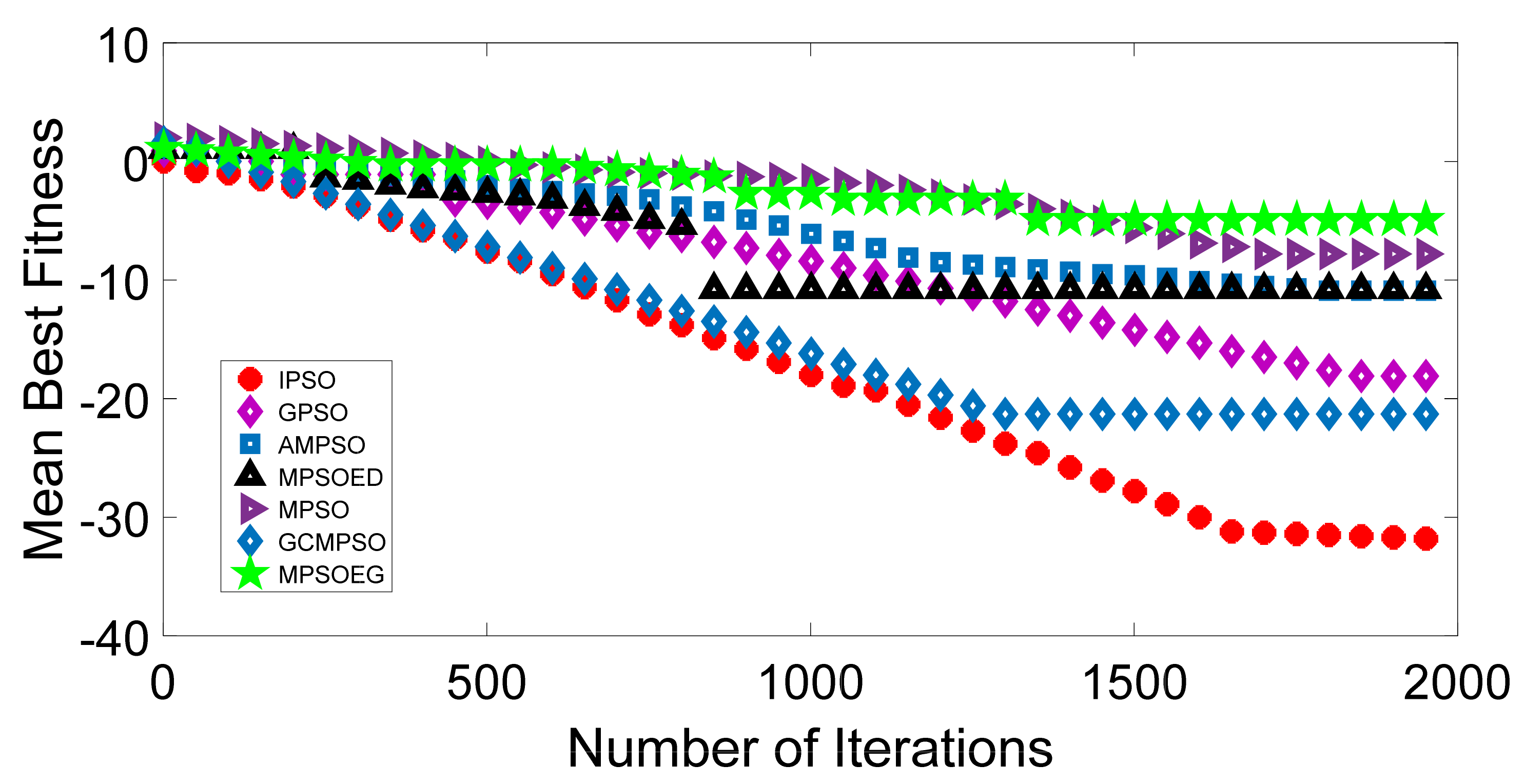
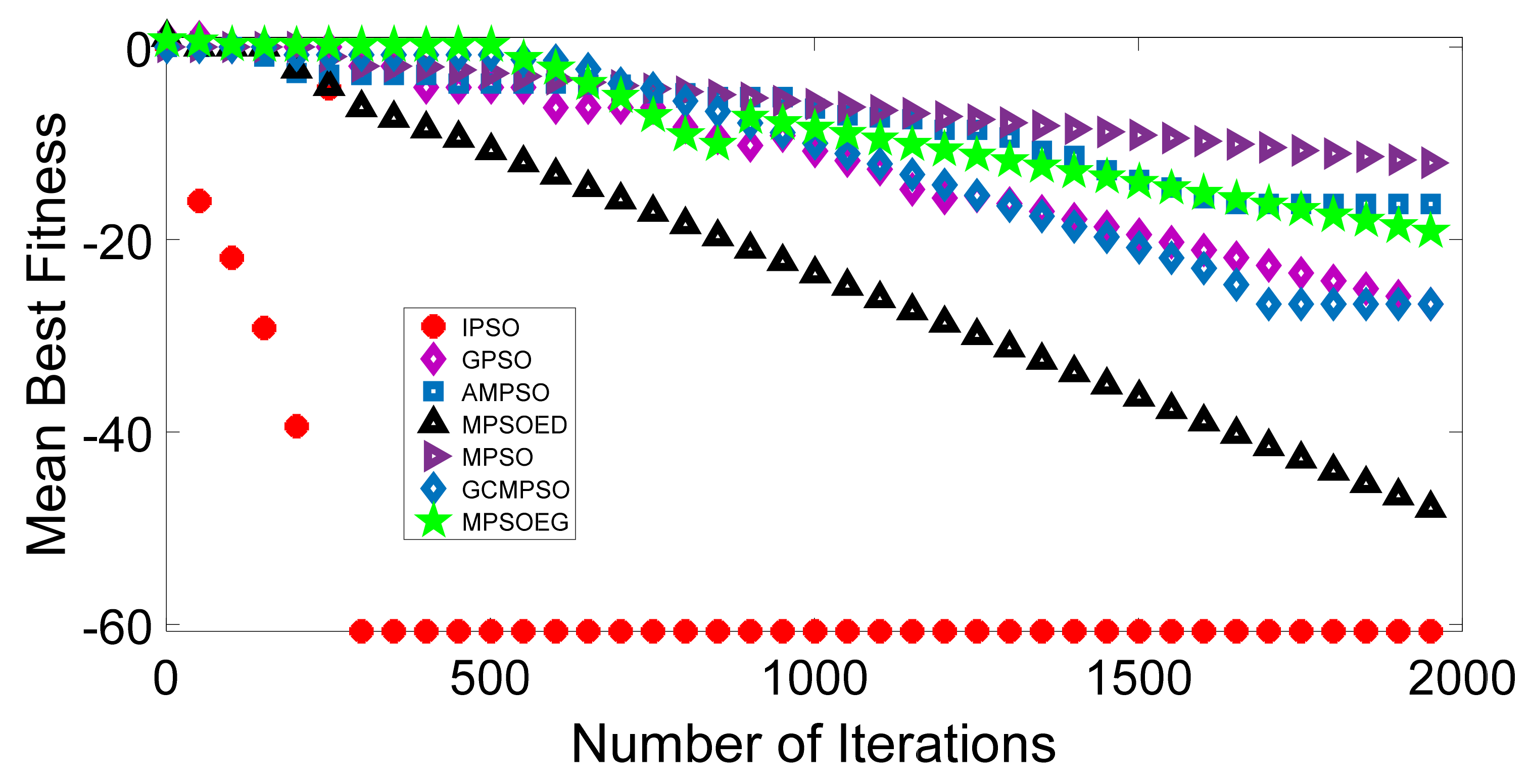
Discription of Mathematical Test Function
References
- Wahab, M.N.A.; Nefti-Meziani, S.; Atyabi, A. A Comprehensive Review of Swarm Optimization Algorithms. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R.C. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, D.; Lopes, L.G.; Morgado-Dias, F. Particle Swarm Optimization: A Historical Review up to the Current Developments. Entropy 2020, 22, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eberhart, R.C.; Shi, Y. Tracking and Optimizing Dynamic Systems with Particle Swarms. In Proceedings of the Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Seoul, Korea, 27–30 May 2001; pp. 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, A.; Vincent, J.; Anyakoha, C. A Review of Particle Swarm Optimization. Part II: Hybridisation, Combinatorial, Multicriteria and Constrained Optimization, and Indicative Applications. Nat. Comput. 2008, 7, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Hashim, R.; Khalid, N.E.A. An Overview of Particle Swarm Optimization Variants. Procedia Eng. 2013, 53, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, R.A.; Yang, S.; Fahad, S.; Khan, S.U.; Kalimullah. A Modified Particle Swarm Optimization with a Smart Particle for Inverse Problems in Electromagnetic Devices. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 99932–99943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, G. Sensor-Based Big Data Applications and Computationally Networked Urbanism in Smart Energy Management Systems. Geopolit. Hist. Int. Relat. 2020, 12, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Konecny, V.; Barnett, C.; Poliak, M. Sensing and Computing Technologies, Intelligent Vehicular Networks, and Big Data-Driven Algorithmic Decision-Making in Smart Sustainable Urbanism. In Contemporary Readings in Law and Social Justice; Addleton Academic Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 13, pp. 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Harrower, K. Networked and Integrated Urban Technologies in Sustainable Smart Energy Systems. Geopolit. Hist. Int. Relat. 2020, 12, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Nica, E.; Stehel, V. Internet of Things Sensing Networks, Artificial Intelligence-Based Decision-Making Algorithms, and Real-Time Process Monitoring in Sustainable Industry 4.0. J. Self Gov. Manag. Econ. 2021, 9, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Valderrama Bento da Silva, P.H.; Camponogara, E.; Seman, L.O.; Villarrubia González, G.; Reis Quietinho Leithardt, V. Decompositions for MPC of Linear Dynamic Systems with Activation Constraints. Energies 2020, 13, 5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; You, F. Machine Learning and Data-driven Techniques for the Control of Smart Power Generation Systems: An Uncertainty Handling Perspective. Engineering 2021, 7, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Yin, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.D.; Zhong, Y.R. Research on Active Disturbance Rejection Control with Parameter Autotune Mechanism for Induction Motors Based on Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm with Dynamic Inertia Weight. IEEE Trans. Power Electr. 2019, 34, 2841–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, A.T.; Nadeem, M.F.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, I.A.; Alkhammash, H.I.; Sajjad, I.A.; Hussain, B. An Improved Particle Swarm Optimization with Chaotic Inertia Weight and Acceleration Coefficients for Optimal Extraction of PV Models Parameters. Energies 2021, 14, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, T. Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of High-Speed Train Network System Based on Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry 2020, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, E.V.; Raaja, G.S.; Jerome, J. Adaptive PSO for Optimal LQR Tracking Control of 2 DOF Laboratory Helicopter. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 41, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Lee, H.P.; Liang, Y.; Wang, B.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C. Globally-Optimal Prediction-Based Adaptive Mutation Particle Swarm Optimization. Inf. Sci. 2017, 418–419, 186–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, S.; Qing, S.; Chang, P.C. A Novel Complex Network Community Detection Approach using Discrete Particle Swarm Optimization with Particle Diversity and Mutation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 81, 105476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Wu, Z. Particle Swarm Optimization with Adaptive Mutation for Multimodal Optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 221, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Y.; Kang, L.L.; Zhang, W.S. Opposition-Based Particle Swarm Optimization with Adaptive Mutation Strategy. Soft Comput. 2017, 21, 5081–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Liu, P.X.; Li, C.; Cheng, Q. Collision Detection for Virtual Environment using Particle Swarm Optimization with Adaptive Cauchy Mutation. Cluster Comput. 2017, 20, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Guo, W.; Li, Q.; Ren, C.; Liu, R. Multiple Scale Self-Adaptive Cooperation Mutation Strategy-Based Particle Swarm Optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 89, 1568–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Kamran, M.; Rehman, O.U.; Liu, L.; Yang, S. A Modified PSO Algorithm with Dynamic Parameters for Solving Complex Engineering Design Problem. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2017, 95, 2308–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, A.; Samal, S.; Sarangi, S.K. Analysis of Gaussian & Cauchy Mutations in Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 15–16 March 2019; pp. 463–467. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Qin, H.; Hao, Z.; Lim, A. Example-Based Learning Particle Swarm Optimization for Continuous Optimization. Inf. Sci. 2012, 182, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamian, J.J.; Abdullah, M.N.; Mokhlis, H.; Mustafa, M.W.; Bakar, A.H.A. Global Particle Swarm Optimization for High Dimension Numerical Functions Analysis. J. Appl. Math. 2014, 2014, 329193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedria, N.B. Improved Accelerated PSO Algorithm for Mechanical Engineering Optimization Problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 40, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.T.; Ling, H.S.; Mohan, S.A. Advanced Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm with Improved Velocity Update Strategy. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 3944–3949. [Google Scholar]
- Marinakis, Y.; Migdalas, A.; Sifaleras, A. A Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization-Variable Neighborhood Search algorithm for Constrained Shortest Path problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 261, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Chowdhury, K.R.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Q.; Lei, J. A Particle Swarm Optimization using Local Stochastic Search and Enhancing Diversity for Continuous Optimization. Neurocomputing 2014, 137, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H. A Hybrid GSA-GA Algorithm for Constrained Optimization Problems. Inf. Sci. 2019, 478, 499–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegini, S.N.; Bagheri, A.; Najafi, F. PSOSCALF: A new Hybrid PSO based on Sine Cosine algorithm and Levy Flight for Solving Optimization Problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 73, 697–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, F.A.; Gökçe, F.; Yüksel, A.S.; Yigit, T. A Novel Hybrid PSO–GWO Algorithm for Optimization Problems. Eng. Comput. 2019, 35, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xiang, K.; Pang, M. An Integrated Particle Swarm Optimization Approach Hybridizing a New Self-Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization with a Modified Differential Evolution. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 32, 4849–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, G.; Rojas, M.; Mendoza, J.; Farias, G.; Pizarro, F.T.; Martin, C.S.; Vera, E. Particle Swarm Optimization for the Fusion of Thermal and Visible Descriptors in Face Recognition Systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 42800–42811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, M.; Mafipour, M.S.; Mehrabi, P.; Bahadori, A.; Zandi, Y.; Salih, M.N.A.; Nguyen, H.; Dou, J.; Song, X.; Poi-Ngian, S. Application of a Hybrid Artificial Neural Network-Particle Swarm Optimization (ANN-PSO) Model in Behavior Prediction of Channel Shear Connectors Embedded in Normal and High-Strength Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yang, D.; Lian, M.; Li, M. Research on Intrusion Detection Based on Particle Swarm Optimization in IoT. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 38254–38268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Application of adaptive reliability importance sampling-based extended domain PSO on single mode failure in reliability engineering. Inf. Sci. 2021, 546, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantash, N.; Khatib, T.; Khammash, M. An Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Optimal Allocation of Distributed Generation Units in Radial Power Systems. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2020, 2020, 8824988. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Wei, E.; Ma, Z.; Wu, C.; Xu, S. Optimized CNNs to Indoor Localization through BLE Sensors Using Improved PSO. Sensors 2021, 21, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Z.; Shi, X.; Liao, L.; Zhou, C.J.; Zhou, H.; Su, Y.H. A Capacity Configuration Control Strategy to Alleviate Power Fluctuation of Hybrid Energy Storage System Based on Improved Particle Swarm Optimization. Energies 2019, 12, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arican, M.; Polat, K. Binary Particle Swarm Optimization (BPSO) Based Channel Selection in the EEG Signals and its Application to Speller Systems. J. Artif. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, A.; Joshi, G.P.; Ramachandran, A.; Subhalakshmi, R.T.; Khari, M.; Jha, S.; Shankar, K.; You, J. A Deep Learning Model Based on Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization for Scene Classification in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 135383–135393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edla, D.R.; Kongara, M.C.; Cheruku, R. A PSO Based Routing with Novel Fitness Function for Improving Lifetime of WSNs. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 104, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.; Latip, R.; Hussin, M.; Abdul Hamid, N.A.W. A Survey on QoS Requirements Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Scheduling Techniques for Workflow Scheduling in Cloud Computing. Symmetry 2020, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azab, M. Multi-Objective Design Approach of Passive Filters for Single-Phase Distributed Energy Grid Integration Systems using Particle Swarm Optimization. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshi, T.R.; Drake, J.H.; Ozcan, E. A Multimodal Particle Swarm Optimization-Based Approach for Image Segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 149, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, L. A Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Global Optimizations of Inverse Problems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, S.; Yang, S.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, S.; Khan, S.A. A Multimodal Smart Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization for Electromagnetic Design Optimization Problems. Energies 2021, 14, 4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, K.; Dehnavi, E. A Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Scheduling Renewable Generation in a Micro-Grid under Load Uncertainty. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 78, 496–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Isa, N.A.M.; Lim, W.H. Modified Particle Swarm Optimization with Effective Guides. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 188699–188725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotto, P.; Baumgartner, U.; Freschi, F. SMES Optimization Benchmark: TEAM Workshop Problem 22. COMPUMAG TEAM Workshop 2008; pp. 1–4. Available online: http://www.compumag.org/jsite/images/stories/TEAM/problem22.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Lowther, D.A.; Sykulski, J.K. A Benchmark TEAM Problem for Multi-Objective Pareto Optimization of Electromagnetic Devices. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Lei, G.; Bramerdorfer, G.; Peng, S.; Sun, X.; Zhu, J. Machine Learning for Design Optimization of Electromagnetic Devices: Recent Developments and Future Directions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Function’s Name | Mathematical Definition | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Rastrigin | [−600, 600] D | |
| De Jong’s | [−5.12, 5.12] D | |
| Bent Cigar | [−100, 100] D | |
| Step | [−100, 100] D | |
| Quartic | [−1.28, 1.28] D | |
| Sphare | [−100, 100] D | |
| Schwefel’s Problem 1.2 | and | [−100, 100] D |
| HappyCat | [−100, 100] D | |
| Alpine1 | [−10,10] D | |
| Griewank | [−100, 100] D |
| Function | IPSO | GPSO | AMPSO | MPSOED | MPSO | GCMPSO | MPSOEG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f1 | −14.30 | −3.10 | −4.00 | −2.60 | −1.70 | −5.40 | −7.35 |
| f2 | −99.00 | −2.80 | −5.80 | −22.00 | −10.80 | −26.10 | −16.94 |
| f3 | −32.30 | −10.30 | −14.60 | −7.68 | −7.96 | −15.20 | −4.65 |
| f4 | −75.46 | −14.50 | −9.70 | −17.28 | −39.22 | −26.30 | −24.38 |
| f5 | −60.70 | −26.71 | −16.30 | −47.93 | −12.04 | −26.70 | −19.15 |
| f6 | −11.30 | −2.80 | −3.30 | −7.48 | −5.20 | −2.20 | −5.30 |
| f7 | −95.00 | −72.00 | −29.00 | −32.40 | −28.40 | −46.20 | −22.49 |
| f8 | −1.50 | 0.20 | 1.20 | 1.50 | 0.40 | −0.40 | −0.90 |
| f9 | −19.12 | −3.80 | −1.50 | −7.00 | −7.50 | −4.80 | −7.73 |
| f10 | −31.80 | −18.10 | −10.90 | −10.80 | −7.80 | −21.30 | −4.90 |
| Algorithm | R2 | h2/2 | d2 | Objective Function Fitness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPSO | 2.9918 | 0.2028 | 0.2939 | 0.0717 |
| GPSO | 2.9713 | 0.2037 | 0.3192 | 0.1287 |
| AMPSO | 3.0017 | 0.6000 | 0.3201 | 0.1136 |
| MPSO | 3.0084 | 0.8265 | 0.2786 | 0.1356 |
| MPSOED | 2.8464 | 0.5729 | 0.3382 | 0.1123 |
| GCMPSO | 2.6050 | 0.2040 | 0.1000 | 0.1210 |
| MPSOEG | 3.1103 | 0.7325 | 0.2731 | 0.0821 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, R.A.; Yang, S.; Khan, S.; Fahad, S.; Kalimullah. A Multimodal Improved Particle Swarm Optimization for High Dimensional Problems in Electromagnetic Devices. Energies 2021, 14, 8575. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248575
Khan RA, Yang S, Khan S, Fahad S, Kalimullah. A Multimodal Improved Particle Swarm Optimization for High Dimensional Problems in Electromagnetic Devices. Energies. 2021; 14(24):8575. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248575
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Rehan Ali, Shiyou Yang, Shafiullah Khan, Shah Fahad, and Kalimullah. 2021. "A Multimodal Improved Particle Swarm Optimization for High Dimensional Problems in Electromagnetic Devices" Energies 14, no. 24: 8575. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248575
APA StyleKhan, R. A., Yang, S., Khan, S., Fahad, S., & Kalimullah. (2021). A Multimodal Improved Particle Swarm Optimization for High Dimensional Problems in Electromagnetic Devices. Energies, 14(24), 8575. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248575







