Abstract
Separating oil-water mixtures is critical in a variety of practical applications, including the treatment of industrial wastewater, oil spill cleanups, as well as the purification of petroleum products. Among various methodologies that have been utilized, membranes are the most attractive technology for separating oil-water emulsions. In recent years, selective wettability membranes have attracted particular attention for oil-water separations. The membrane surfaces with hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic wettability have demonstrated enhanced effectiveness for oil-water separations in comparison with underwater oleophobic membranes. However, developing a hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic surface for a membrane is not a trivial task. The coating delamination process is a critical challenge when applying these membranes for separations. Inspired by the above, in this study we utilize poly(ethylene glycol)diacrylate (PEGDA) and 1H,1H,2H,2H-heptadecafluorodecyl acrylate (F-acrylate) to fabricate a hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic coating on a filter. We utilize methacryloxypropyl trimethoxysilane (MEMO) as an adhesion promoter to enhance the adhesion of the coating to the filter. The filter demonstrates robust oil repellency preventing oil adhesion and oil fouling. Utilizing the filter, gravity-driven and continuous separations of surfactant-stabilized oil-water emulsions are demonstrated. Finally, we demonstrate that the filter can be reused multiple times upon rinsing for further oil-water separations.
1. Introduction
Oil-water separation is a crucial step in a wide variety of industries [1,2]. For example, 140,000 L of oil-contaminated water is produced during conventional mining operations on a daily basis [3]. Additionally, oil leakage and spillage during marine transportation not only pose a threat to the marine environment and ecosystem but is a waste of valuable natural resources [4,5]. Typically, an oil-water mixture can be classified into three categories based on the dispersed phase size (diameter, d)-as free oil-water, if d > 150 μm, as a dispersion if 20 μm < d < 150 μm, or as an emulsion if d < 20 μm [6]. Oil-water emulsions are stable in the presence of the adsorbed interface-active chemicals (e.g., surfactant) [7]. Spontaneous separation of stable oil-water emulsions can be impractically time-consuming. Further, the separation process becomes more challenging with the decrease in the size of the dispersed phase [8].
There have been extensive efforts devoted to developing effective separation technologies for oil-water emulsions [8]. Membrane-based technologies are the most attractive because they can separate oil and water without requiring chemical additives [9,10,11,12,13,14]; thus, they are relatively energy-saving and applicable to a broad range of industrial effluents [15,16,17]. The working principle and operation of these technologies are simple. A membrane can regulate the transportation of two phases (e.g., oil and water) by allowing the selective passage of one phase while inhibiting the permeation of another phase [18,19]. Various methods have been employed to enable the permeation of one phase through a membrane while repelling another phase. For example, a careful modulation of the applied pressure can overcome the hydraulic resistance of one phase while being insufficient for another phase [11,14,20,21]. Additionally, we [20,21] and others [22,23,24] have demonstrated that a water-in-oil emulsion can be demulsified upon applying an electric field due to the coalescence of the dispersed water droplets. The resulting free oil and water can be readily separated under gravity.
While membranes have become an industry benchmark to compare the performance of conventional separation technologies, they are limited by fouling when continuously operated [13,14,25,26,27]. When a membrane is subjected to an oil-water mixture, oils and organic substances are deposited onto its surface. This membrane fouling can result in a decrease in permeability over time [28]. To compensate for this compromised performance, membrane operation often requires an increase in the applied trans-membrane pressure (i.e., TMP, the pressure gradient generated across the two opposite membrane sides [29]), which results in an increase in the energy consumption [30]. In some instances, the oil-water mixture treatment system becomes oversized to compensate for the permeate flux loss [30]. Further, due to fouling, membranes undergo periodic cleaning protocols that include backwashing, forward washing, and chemically enhanced cleaning to restore membrane permeability [31]. Although these cleaning protocols allow a membrane to restore its inherent permeability and selectivity, they may shorten the membrane’s lifespan due to mechanical or chemical damage [32,33].
The development of fouling-resistant membranes has been an active research topic for decades [34,35]. A membrane with hydrophilic (i.e., water contact angle, θwater < 90°) or superhydrophilic (θwater = 0°) wettability can retain a hydration layer on its surface when subjected to water, which can reduce the adhesion of organic substances such as oil [20,36]. While these membranes show resistance to oil fouling, they become vulnerable when a hydration layer disappears [37]. For example, the hydration layer can be evaporated or compromised due to a large exerted drag force (e.g., applied pressure), which results in direct contact and deposition of an oily phase on the membrane surface [38,39].
Hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic (i.e., oil contact angle, θoil > 90°) membranes can overcome this limitation by providing oil repellency, not only underwater, but also in the air [20,40]. This enables them to exhibit unique features in oil-water separations. For example, there is no need to prewet the membrane to introduce a hydration layer. Additionally, water-in-oil emulsions can be separated without prewetting, as long as the breakthrough pressure for oil (Pb, i.e., the lowest applied pressure required to force a liquid permeation through a porous filter) is higher than the operating pressure.
Fabricating a hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic membrane requires one to reconcile two conflicting design criteria. It should possess low solid surface energy to repel oil, while water should wet the surface. Given that the water surface tension (γlv = 72.1 mN m−1, T = 22 °C) is higher than that of oils (γlv = 20–30 mN m−1, T = 22 °C), a large volume of reports [9,41,42,43,44,45,46] have utilized materials composed of a low surface energy component along with a hydrogen-bond-capable hydrophilic moiety as the membrane coating to achieve selective wettability for water over oil [20,47,48,49,50,51] For example, Brown et al [52]. utilized a fluorosurfactant as a low surface energy material and poly(diallyl dimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA) for hydrophilic moieties. Yang et al [49]. fabricated a membrane coated with a mixture of PDDA, chitosan, and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). These surfaces often exhibit selective reconfiguration of the coating components. Upon contact with water, a hydrophilic component will expand to the surface for enthalpic gain, while a low surface energy material (e.g., fluorinated moiety) minimizes its contact with water [20,47]. When oil comes into contact, the surface reverts back to its inherent configuration to lower the overall free energy.
Utilizing surface reconfiguration, herein we report on a superhydrophilic and in-air oleophobic filter by grafting a composite mixture of poly(ethylene glycol)diacrylate (PEGDA) and 1H,1H,2H,2H-heptadecafluorodecyl acrylate (F-acrylate) via silane chemistry. This enables the resulting coating (F-PEGDA) to firmly attach to the filter surface. The filter exhibits ultralow oil adhesion forces, both in air and underwater, which results in resistance to oil fouling during oil-water separation. Utilizing this filter, separation of surfactant-stabilized oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions is demonstrated. Finally, we demonstrate that the filter can be reused multiple times upon cleansing for further oil-water separations.
2. Result and Discussion
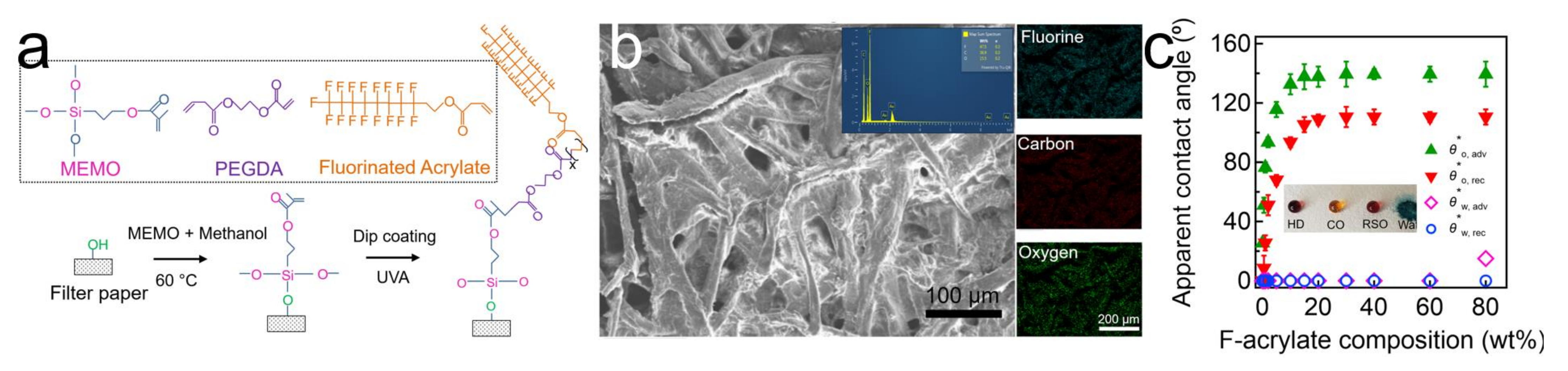
We fabricated a hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic filter by coating it with F-PEGDA, utilizing filters with nominal pore sizes of 6.0 µm and 2.0 µm (Experimental Section). Note that we utilized varying compositions of PEGDA and F-acrylate, while the photo-initiator concentration remained at 5.0 wt.% with respect to the mass of the PEGDA and F-acrylate mixture. The filters were irradiated by a long-wavelength ultraviolet (UV) light, which resulted in the grafting of F-PEGDA to the MEMO-treated filter surface (Figure 1a and Section S1). We analyzed the filter surface’s morphology using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Figure 1b). It was clear that the surface morphology remained nearly unaffected after coating with F-PEGDA. Additionally, the uniform coating of F-PEGDA on the filter surface was verified by the energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis. The EDS elemental mapping demonstrated a uniform coverage of fluorine (F) across the filter surface (Figure 1b, insets).
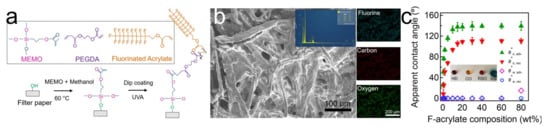
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic demonstrating the grafting of the filter surface with MEMO and the subsequent coating with F-PEGDA. (b) SEM image showing the morphology of the filter after coating with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%). Inset shows the elemental EDS spectrum and the elemental mappings for fluorine. (c) The measured apparent advancing and receding contact angles of water and oil (n-hexadecane) on the F-PEGDA-coated filter surface with varied compositions of F-acrylate. A filter with a 6.0 µm inherent nominal pore size was used.
It is critical to ensure that the F-PEGDA coating has a negligible effect on the pore size of the filters. We measured the nominal pore size of the filters after coating with F-PEGDA (Table 1). The results indicated that filters coated with F-PEGDA with a higher PEGDA composition demonstrate more decreased pore sizes. For example, the filter coated with F-PEGDA with 20 wt.% F-acrylate (F-PEGDA (20 wt.%)) exhibited a pore size of 5.0 µm ± 0.5 µm, while the filter coated with F-PEGDA (80 wt.%) showed 5.5 µm ± 0.5 µm. We attributed this to an increase in the viscosity of the coating solution with an increase in the PEGDA composition (i.e., decrease in the F-acrylate composition), which resulted in an increase in the coating thickness (Section S2).

Table 1.
Pore size of as-purchased filters and those coated with F-PEGDA with various F-acrylate compositions.
The wettability of our F-PEGDA-coated filters was analyzed by measuring the apparent contact angles for water (deionized (DI) water, γlv =72.1 mN m−1, T = 22 °C) and oil (n-hexadecane, γlv = 27.5 mN m−1, T = 22 °C) in the air (Figure 1c). The results showed that the filter (inherent nominal pore size = 6.0 µm) coated with F-PEGDA with a higher F-acrylate composition exhibited higher oil apparent contact angles. When the composition reached 20 wt.%, the advancing (θ*oil,adv) and receding (θ*oil,rec) apparent contact angles for oil were measured as 131°± 3° and 108° ± 3°, respectively, while those for water remained at zero (θ*water,adv = 0 and θ*water,rec = 0). Further increases in the F-acrylate composition in F-PEGDA had a negligible effect on the oil apparent contact angles, which can be attributed to the complete coverage of the filter surface by F-acrylate (see also Figure 1b inset). When the F-acrylate composition reached 80 wt.% in the F-PEGDA coating, the value for θ*water,adv reached 25° ± 3°. We attributed this to the reduced presence of -OH moieties, which are responsible for inducing hydrophilicity and creating more fluorine moieties, which are responsible for omniphobic wettability.
In previous reports, we [20] and others [47,53,54] have shown that a water droplet can gradually wet the surface with hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic wettability due to surface reconfiguration. The required time for a water droplet to completely spread on a given reconfigurable surface is defined as the time of wetting (ToW) [20]. The measured initial contact angles and the time of wetting for water on our F-PEGDA surfaces are included in Section S3. We also calculated the solid surface energy (γsv) values of the F-PEGDA surfaces (Section S4). Furthermore, the measured apparent contact angles for water and oil on the filters with an inherent nominal pore size of 2.0 µm are included in Section S5. Based on these results, a filter coated with 20 wt.% of F-acrylate (F-PEGDA (20 wt.%)) was utilized for the rest of the study.
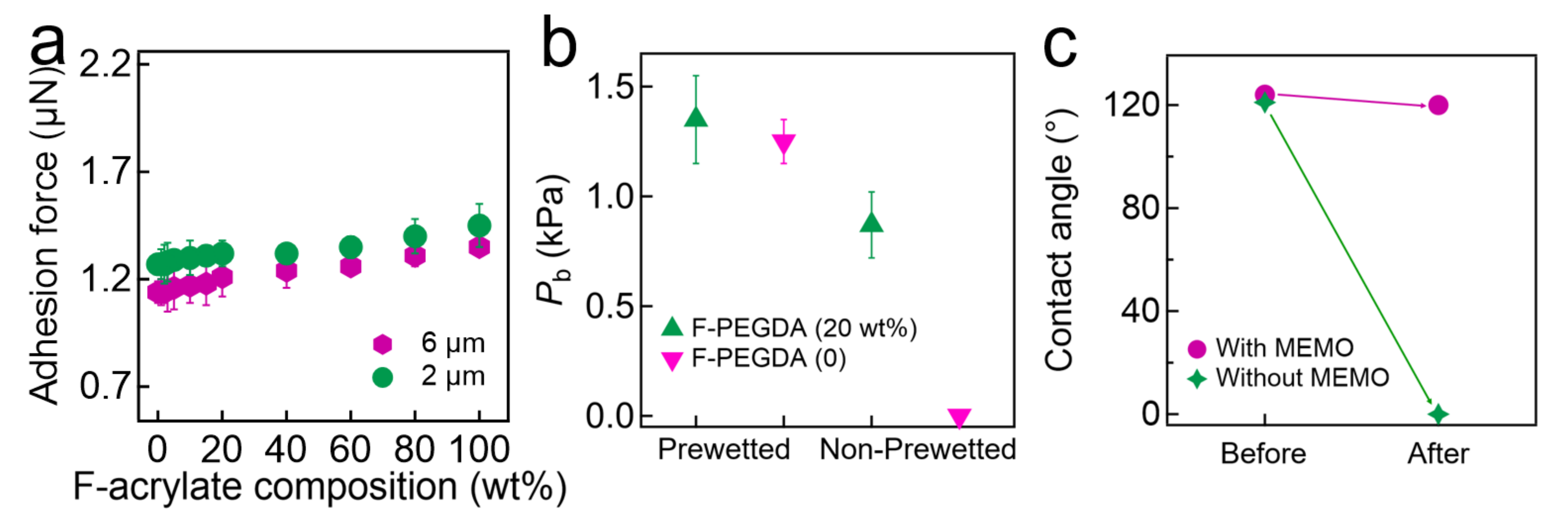
We measured the adhesion force of a sessile oil droplet on the filters submerged in DI water using a high-precision microelectromechanical system (Figure 2a, see also Experimental Section). The results showed that the adhesion force values were nearly constant (≈1.32 µN ± 0.10 µN) on filters with an inherent nominal pore size of 6.0 µm, which were coated with F-PEGDA, irrespective of the F-acrylate composition. Note that the adhesion force value measured on the neat PEGDA-coated filter was slightly lower (1.27 µN ± 0.10 µN), while that measured on the neat F-acrylate-coated filter was slightly higher (1.45 µN ± 0.10 µN). The measured adhesion forces of an oil droplet on a filter with an inherent nominal pore size of 2.0 µm are also demonstrated in Figure 2a. This ultralow oil adhesion was a direct consequence of the underwater superoleophobic wettability (i.e., apparent oil contact angle > 150° on a surface submerged in water) (Section S6). Additionally, the experimental results regarding water uptake by F-PEGDA-coated filters are provided in Section S7.
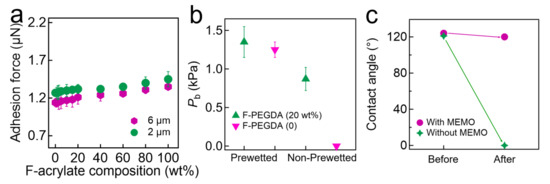
Figure 2.
(a) The measured adhesion force of a sessile oil (n-hexadecane) droplet on the filter surfaces coated with F-PEGDA with various F-acrylate concentrations. (b) The breakthrough pressure of oil on prewetted and dry filters coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%). The data obtained from a filter coated with neat PEGDA are also provided for comparison. (c) The measured apparent contact angles of oil on the F-PEGDA (20 wt.%), which was prepared with MEMO before and after being submerged in water for 1 h. For comparison, the data for F-PEGDA (20 wt.%) prepared without MEMO are also shown.
Filters exhibiting hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic wettability do not need to undergo prewetting in order to introduce a hydration layer before conducting oil-water separation. This is because the in-air superoleophobic wettability plays a key role in resistance to oil adhesion on the surface by repelling it [38]. In contrast, an in-air superoleophilic surface such as a neat PEGDA-coated filter or an unmodified filter allows oil to wet and adhere to the surface.
We measured the breakthrough pressure (Pb) for oil of an F-PEGDA-coated filter. It was observed that filters coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%) and with neat PEGDA (i.e., F-PEGDA (0)) can both exhibit high Pb values for oil. For example, a filter coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%) exhibited Pb = 1.35 ± 0.2 kPa while another filter coated with neat PEGDA showed Pb = 1.25 ± 0.1 kPa when they were prewetted (Figure 2b). When the filters were dry, the neat PEGDA-coated filter immediately allowed oil to pass through (Pb 0), whereas the filter coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%) maintained a breakthrough pressure of Pb = 0.87 ± 0.2 kPa.
Filters grafted with MEMO can prevent delamination of the F-PEGDA coating from the surface after being submerged in water. To test this, we measured the apparent contact angles of in-air oil on a filter coated with F-PEGDA after being submerged in DI water for 1 h. For comparison, we conducted the same experiment using a filter without MEMO grafting. The results showed that the apparent contact angles of oil remained almost unchanged on the filters coated with MEMO and F-PEGDA, while those on the filter without MEMO grafting equaled zero (Figure 2c). This was the direct consequence of delamination of the F-PEGDA coating from the filter surface (Section S8). Consequently, the oil droplet contacts the underlying filter surface and completely wets it due to the absence of fluorine on the filter surface.
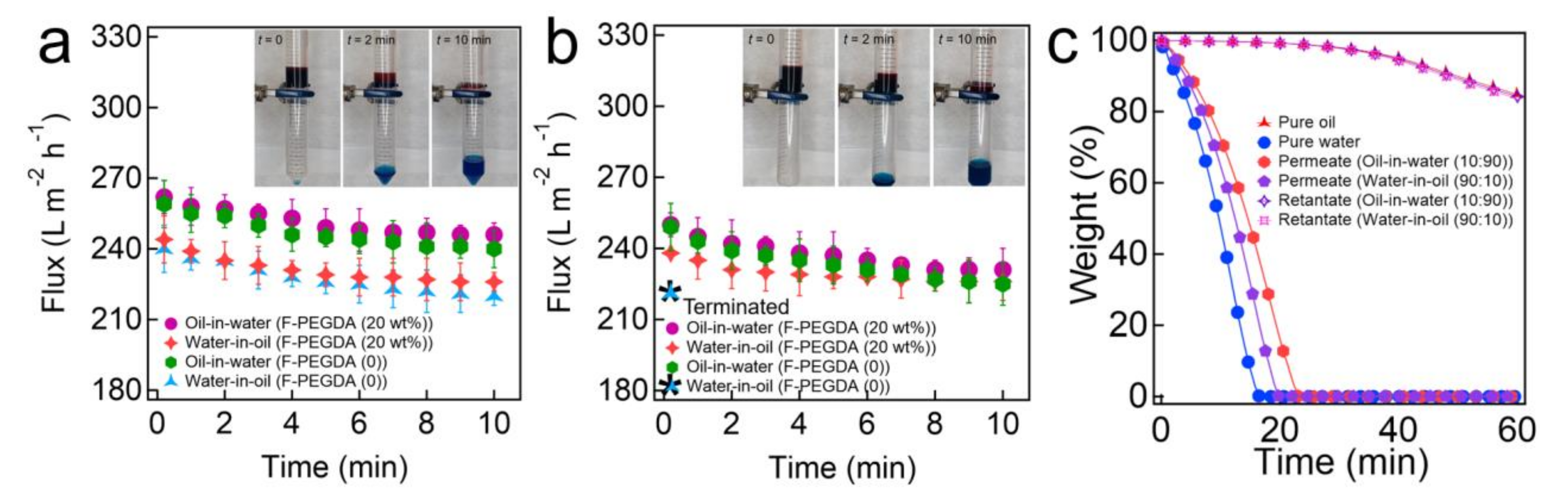
Using our hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic filter, we separated oil-water mixtures under gravity. Here, we utilized a surfactant-stabilized oil-in-water emulsion (10 vol% n-hexadecane in water) and a water-in-oil emulsion (90 vol% water in n-hexadecane) (see Experimental Section and Section S9). The separation apparatus consisted of two vertical tubes and a filter coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%), which was sandwiched between them. Here, we utilized a filter with an inherent nominal pore size of 6.0 µm Upon introducing an emulsion (15 mL) into an upper tube, a filter allows the water-rich phase to permeate through, while the oil-rich phase is retained above it within 11.2 ± 2 min (Figure 3a). We also calculated the flux (J = ∆m(Aρ∆t)−1, where ∆m is the mass change of the water-rich permeate in a given time interval (i.e., ∆t = 1 min), A is the projected area of the filter surface, and ρ is the permeate density) values by periodically measuring the volume of the water-rich permeate through filters prewetted with water for 30 min. The results for the oil-in-water emulsion showed that the permeate flux gradually declined from J (t = 0) = 261 ± 10 L m−2 h−1 and reached J (t = 10 min) = 245 ± 10 L m−2 h−1. This can be attributed to the decreased height of the emulsion column as the water-rich phase permeated through the filter, which resulted in a decrease in the exerted pressure. The filter also separated the water-in-oil emulsion in 13.1 ± 2 min. Similarly, the permeate flux values were determined as J (t = 0) = 242 ± 10 L m−2 h−1 and J (t = 10 min) = 225 ± 10 L m−2 h−1. Note that almost all water droplets dispersed in an emulsion can come into contact with the filter surface under gravity. For comparison, we conducted the same experiments using a filter coated with F-PEGDA (0) after prewetting with water for 30 min. The results showed that the filter can separate both oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions in 11.9 ± 2 min and 13.5 ± 2 min, respectively (Figure 3a). The permeate flux values were measured as J (t = 10 min) = 239 ± 10 L m−2 h−1 and J (t = 10 min) = 219 ± 10 L m−2 h−1 for the separation of the oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions, respectively.
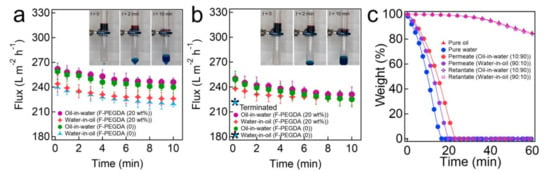
Figure 3.
(a–c) Time-dependent flux measurements during the separation of oil-water mixtures under gravity by (a) prewetted and (b) dry filters coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%) and neat PEGDA. The inset shows images of the oil-water separation experiments with oil-in-water emulsions by utilizing a filter coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%). (c) The TGA plots of the permeate and retentates after the separation of both oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions using a filter coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%). The TGA data for pure water and oil are also shown for comparison.
When a filter coated with F-PEGDA (0) is subjected to a water-in-oil emulsion without prewetting, both oil and water immediately pass through. Note that the filter exhibited similar separation performance for the oil-in-water emulsion (Figure 3b). This is attributed to the water as a continuous medium in the emulsion, which provides a hydration layer on the filter surface and prevents oil droplets from permeating. The filter coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%) exhibited similar water-rich permeate flux values for both oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions (J (t = 10 min) = 231 ± 10 L m−2 h−1 and J (t = 10 min) = 222 ± 20 L m−2 h−1). Figure 3c shows the TGA plots of the permeates and retentates after the separation experiments for oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions using a filter coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%). The results showed that our filter can separate both oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions with very high efficiency (>98%). Please note that our F-PEGDA filter surfaces after the separation remained clean (i.e., no fouling). We attributed this to a combinatorial effect of fouling resistance due to hydrophilic wettability and a relatively lower surfactant concentration (0.03 wt.%, see Experimental Section). It is anticipated that our F-PEGDA-coated filter surface may suffer from a cake layer when it is subjected to emulsions stabilized by high-concentration surfactants [55,56,57] Additionally, it should be noted that the surfactants used in this study were either anionic (sodium dodecyl sulfate for the oil-in-water emulsion) or nonionic (Tween 80 for the water-in-oil emulsion). Given that the seta potential (ξ) value of our F-PEGDA (20 wt.%)-coated filter surface was measured as −0.83 mV ± 0.19 mV, it is anticipated that our filter may be fouled by emulsions stabilized with cationic or amphoteric surfactants [55,58,59].
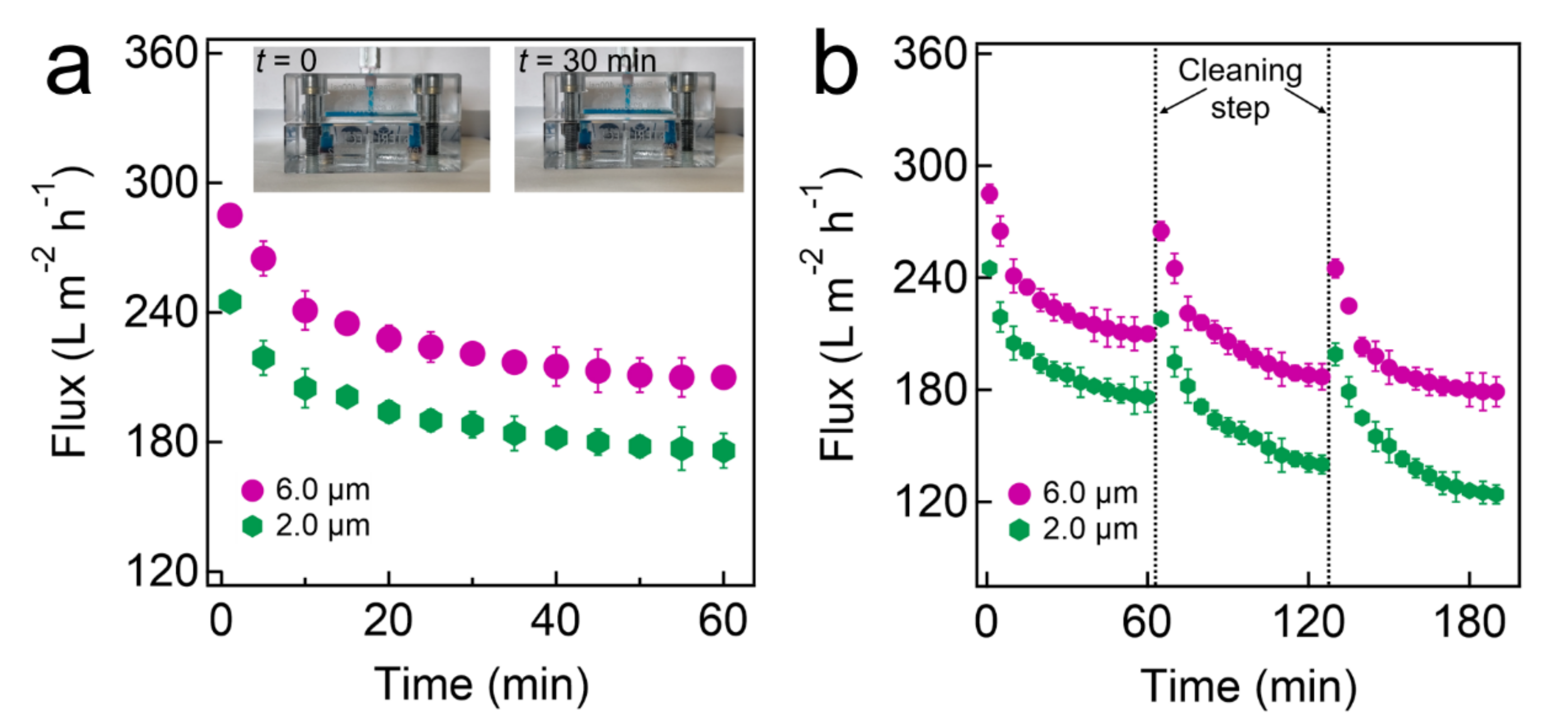
Finally, we continuously separated an oil-in-water emulsion utilizing a cross-flow apparatus (Experimental Section). An emulsion (total volume = 20 L) was gradually introduced into a cell in which a filter (inherent nominal pore size = 6.0 µm. coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%) was mounted. We measured the volume of the water-rich permeates every 5 min for the entire 60 min of operation. The TMP value was maintained at 0.90 kPa ± 0.20 kPa. The results showed that J (t = 0) = 285 ± 10 L m−2 h−1, after which it declined and reached J (t = 60 min) = 210 ± 10 L m−2 h−1 (Figure 4a). We conducted the same experiments using a filter with an inherent nominal pore size of 2.0 µm. The results showed that J (t = 0) = 245 ± 10 L m−2 h−1, after which it declined over time and reached J (t = 60 min) = 176 ± 10 L m−2 h−1. Unlike the flux decline during batch separation, which was primarily caused by a decrease in the exerted pressure (see Figure 3a,b), the continuous separation was conducted at a constant TMP. Therefore, we attributed the flux decline to the oil droplet accumulation above the membrane surface [4]. Although our filter exhibits very low oil adhesion forces (see Figure 2a), oil can still accumulate on the surfaces and pore walls due to transmembrane pressure. The accumulation of oil can cause pore blockages. As a consequence, the volume of water passing through the filter in a given period of time (i.e., permeate flux) decreases. This results in a decline of the flux. We cleaned the filter by first rinsing it with ethanol for 10 s followed by washing it with DI water for 30 s (flow rate ≈ 20.0 L min−1). The cleansed filter was subjected to the same separation experiments. The results showed that the filter nearly recovered its inherent flux values (Figure 4b). An analysis of the separation efficiency is included in Section S10. The flux values for the continuous separation experiment over 50 h are presented in Section S11.
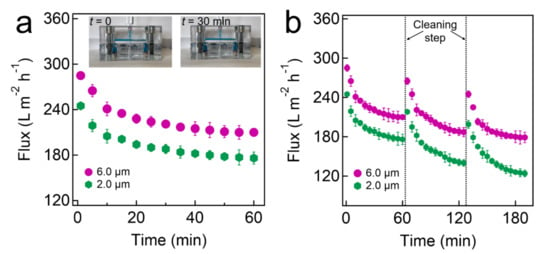
Figure 4.
(a) Time-dependent flux measurements during the continuous separation of oil-water mixtures using prewetted filters with various inherent nominal pore sizes, which were coated with F-PEGDA (20 wt.%). The inset demonstrates the separation experiment using a cross-flow apparatus. (b) Time-dependent flux measurements during the continuous separation of oil-in-water emulsion with cleaning steps in between.
3. Conclusions
In this work, we prepared robust hydrophilic and in-air oleophobic F-PEGDA-coated filters to separate oil-water mixtures. We utilized MEMO as an adhesion promoter to enhance coating adhesion to the filter. The prepared surfaces were then subjected to fouling conditions representative of conventional oil-water separation applications. The results of the study demonstrated that the F-PEGDA-coated filter showed low oil adhesion forces and was able to withstand fouling conditions without delamination. Subsequently, gravity-driven oil-water separations were conducted by utilizing oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions. The F-PEGDA-coated filter was able to separate both emulsions and maintained high flux values, while the filter with underwater oleophobicity failed to separate the water-in-oil emulsion, highlighting the advantages of in-air oleophobicity. Further, the F-PEGDA surface demonstrated good reusability upon cleansing.
4. Experimental Section
Grafting MEMO on filter surface: The filters (6 µm (Whatman Grade 3, Whatman, Marlborough, MA, USA) and 2 µm (Whatman Grade 602 h)) were rinsed with DI water followed by drying at room temperature. They were dip-coated in a 10 wt.% methacryloxypropyl trimethoxysilane (MEMO) solution in methanol for 30 min. Subsequently, the dip-coated filters were heated using a hot plate at 60° C for 1 h. Finally, the filters were thoroughly rinsed using DI water and ethanol to remove any unreacted MEMO molecules.
Coating F-PEGDA on filter: A solution of F-PEGDA was prepared by adding PEGDA, F-acrylate, and Darokur 1173 (Photo-initiator) to water with an overall concentration of 30 mg ml−1. The MEMO-grafted filters were then dip-coated in F-PEGDA solution for 30 min. Varying compositions of PEGDA and F-acrylate (i.e., 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100 wt.% of F-acrylate) were utilized. Note that the concentration of Darocur 1173 was maintained at 5.0 wt.% with respect to the PEGDA and F-acrylate mixture. Consequently, the filters were removed and exposed to UV light (100 W, λ = 365 nm, Analytikjena, Upland, CA, USA) for 5 min.
Measuring pore size of filters: A capillary flow porometer (Particle Technology Labs, Downers Grove, IL, USA) was utilized to measure the nominal size and the distribution of the filter pores, as described elsewhere [60]. A commercial wetting liquid (Porefil) was utilized to wet the filter. The nitrogen gas pressure and flow were controlled and recorded using a pressure transducer and a flow meter, respectively.
Contact angle measurements: A Ramé-Hart 200-F1 goniometer (Ramé-Hart, Succasunna, NJ, USA) was employed to measure the advancing and receding contact angles of liquid droplets (≈5 μL) on the filter surfaces. The initial advancing contact angle for water was measured based on the instantaneous value observed when a water droplet first contacted a filter surface, while the initial receding water contact angle was measured by gradually withdrawing a small volume of water from the same droplet. The time-dependent advancing and receding water contact angle measurements were conducted in a controlled environment (T = 22° ± 1°, relative humidity = 79% ± 4%) to minimize the evaporation effect. A sessile water droplet was placed on a filter surface followed by periodic measurements of contact angles. The measurements were conducted three times to ensure the accuracy of the values. A typical error in the goniometry was ±2°.
Zeta potential measurements: Zeta potential measurements were conducted using a Brookhaven ZetaPALS instrument, Holtsville, NY, USA [61]. The electrophoretic velocity was calculated using a laser light-scattering phase analyzer. Then, the Smoluchowski model was utilized to calculate the zeta potential values.
Fabrication of oil-water emulsions: An oil-in-water emulsion was fabricated via vigorously stirring of n-hexadecane and DI water (10:90 vol%:vol% n-hexadecane:water). Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, 0.03 wt.%) was introduced as a surfactant. Similarly, a water-in-oil emulsion (10:90 vol%:vol% n-hexadecane/water) was fabricated using Tween 80 (0.03 wt.%) as the surfactant. Please note that slight demulsification was observed over time in these emulsions. A multimeter was utilized to verify the type of emulsion. Note that the surfactant concentration (0.03 wt.%) employed in this work was similar or even higher than those reported in the literature [62,63].
Dispersed phase size measurements: The average size of the dispersed phase in an emulsion was characterized using dynamic light scattering (DLS) (ZetaPALS, Brookhaven Instruments, Holtsville, NY, USA).
Filter surface topology characterization: The PEGDA-coated filter surface’s morphology was characterized using an SEM (FEI Versa 3D DualBeam, Hillsboro, OR, USA). A thin layer of gold (7 nm) was applied to the filter surface.
Underwater adhesion force measurements: A small piece of a filter (4 cm2) was attached to the bottom of the container. The container was filled with DI water. Subsequently, a needle tip holding a droplet of n-hexadecane (≈5 µL) was immersed in the water (3 cm below the water surface). Then, the entire container was gradually elevated at a constant speed (6.0 mm min−1) until the filter contacted the oil droplet. Subsequently, the container was gradually descended to detach the oil droplet from the filter. The force between the oil and filter surface was recorded using Data-Physics DCAT 11(Data Physics, Filderstadt, Germany). The adhesion force was determined by the force at the detachment point.
Thermogravimetric analyses (TGA): PerkinElmer PYRIS 1 (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) was utilized for TGA measurements. A sample (≈50 mg) was heated to 110 °C at a rate of 5 °C per minute, then the temperature was maintained for 60 min. The TGA data were compared with the data for DI water and as-obtained n-hexadecane to measure the purity of the permeate or retentate after the separation.
Continuous separation apparatus: We utilized a custom-made apparatus [9,10] for the continuous separation experiments. The apparatus consisted of a cross-flow cell CF042A, Sterlitech, Kent, WA, USA) onnected to a container that stored the feed emulsion, a peristaltic pump (Model 2002, Vector, Minneapolis, MN, USA), a differential pressure gauge (DPG409-500DWU, OMEGA, Stamford, CT, USA), and a permeate tank. A filter (surface area 42 cm2) was mounted to the cell. The feed oil-water emulsion was supplied from one side (feed in) of the apparatus while the permeate was collected at the opposite side of the apparatus. Note that the raffinate was readded to the feed emulsion storage container.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/en14217429/s1: Section S1: Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy analysis of F-PEGDA; Section S2: Effect of F-PEGDA solution viscosity on the pore size of a filter; Section S3: Initial contact angles and Time of Wetting values for water on F-PEGDA surfaces; Section S4: Calculation of the solid surface energy of F-PEGDA surfaces; Section S5: Apparent contact angles for water and oil on F-PEGDA coated filter with 2.0 µm of inherent pore size; Section S6: Apparent contact angles for oil on a filter submerged in water; Section S7: Measurements of water uptake by F-PEGDA coated filters; Section S8: Delamination of F-PEGDA coating from a filter without MEMO grafting; Section S9: Size distribution of the dispersed phases in oil-water emulsions; Section S10: TGA data for permeates from continuous separation of oil-water emulsion by cross-flow apparatus; Section S11: The measured flux values of continuous separation of oil-in-water emulsion.
Author Contributions
B.S. and M.E. conducted the experiments and collected and analyzed the data. G.K. conceived the project. B.S., M.E. and G.K. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We thank the financial support from National Science Foundation (grant number: CBET-1944314), NASA Kansas EPSCoR (grant number: R52123-20-02314), and US Poultry and Egg Association (grant number: F091).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during this study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Cheryan, M.; Rajagopalan, N. Membrane processing of oily streams. Wastewater treatment and waste reduction. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 151, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, X.; Akbulut, O.; Hu, J.; Suib, S.L.; Kong, J.; Stellacci, F. Superwetting nanowire membranes for selective absorption. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, T.F. Heavy equipment maintenance wastes and environmental management in the mining industry. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-C.; Xu, Z.-K. Mineral-coated polymer membranes with superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity for effective oil/water separation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lian, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Weng, Z.; Yu, H. Nanosecond laser-induced underwater superoleophobic and underoil superhydrophobic mesh for oil/water separation. Langmuir 2018, 34, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Bilal, M.; Khan, A.; Ali, F.; Iqbal, H.M. Design, engineering and analytical perspectives of membrane materials with smart surfaces for efficient oil/water separation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Weng, D.; Mahmood, A.; Chen, S.; Wang, J. Separation mechanism and construction of surfaces with special wettability for oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11006–11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhru’l-Razi, A.; Pendashteh, A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Biak, D.R.A.; Madaeni, S.S.; Abidin, Z.Z. Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 530–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezazi, M.; Shrestha, B.; Kim, S.I.; Jeong, B.; Gorney, J.; Hutchison, K.; Lee, D.H.; Kwon, G. Selective Wettability Membrane for Continuous Oil−Water Separation and In Situ Visible Light-Driven Photocatalytic Purification of Water. Glob. Chall. 2020, 4, 2000009. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, B.; Ezazi, M.; Kwon, G. Engineered Nanoparticles with Decoupled Photocatalysis and Wettability for Membrane-Based Desalination and Separation of Oil-Saline Water Mixtures. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, U.; Matin, A.; Gondal, M.; Zubair, S. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic, superoleophilic photocatalytic membrane for efficient oil-water separation and removal of hazardous organic pollutants. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondal, M.A.; Sadullah, M.S.; Qahtan, T.F.; Dastageer, M.A.; Baig, U.; McKinley, G.H. Fabrication and wettability study of WO 3 coated photocatalytic membrane for oil-water separation: A comparative study with ZnO coated membrane. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.; Liu, W.; Yang, M.; Liu, C.; He, S.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z. Robust multifunctional superhydrophobic fabric with UV induced reversible wettability, photocatalytic self-cleaning property, and oil-water separation via thiol-ene click chemistry. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Cha, D.; Wang, P. A self-cleaning underwater superoleophobic mesh for oil-water separation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henthorne, L. Evaluation of Membrane Pretreatment for Seawater Reverse Osmosis Desalination; US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Reclamation, Technical Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Duraisamy, R.T.; Beni, A.H.; Henni, A. State of the Art Treatment of Produced Water. Water Treatment; Intech: London, UK, 2013; pp. 199–222. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, A.W.; Teow, Y.; Ang, W.; Chung, Y.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membranes review: Recent advances and future prospects. Desalination 2015, 356, 226–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Han, N.; Zhang, X. A novel PVDF/graphene composite membrane based on electrospun nanofibrous film for oil/water emulsion separation. Compos. Commun. 2016, 2, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaki, M.; Murali, R.S.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A. Membrane technology enhancement in oil–water separation. A review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil–water separation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, G.; Post, E.; Tuteja, A. Membranes with selective wettability for the separation of oil–water mixtures. MRS Commun. 2015, 5, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, T.; Nakajima, Y. Rapid demulsification of dense oil-in-water emulsion by low external electric field.: II. Theory. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 242, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Kang, Y. Demulsification of oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion in bidirectional pulsed electric field. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8923–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hano, T.; Ohtake, T.; Takagi, K. Demulsification kinetics of W/0 emulsion in an AC electric field. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1988, 21, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Yan, D.Y.; Lam, F.L.-Y.; Deka, B.J.; Lv, X.; Ng, Y.H.; An, A.K. Self-cleaning BiOBr/Ag photocatalytic membrane for membrane regeneration under visible light in membrane distillation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, S.; Tomoishi, S.; Kameshima, Y.; Fujii, E.; Miyake, M. Self-cleaning efficiency of titanium dioxide surface under simultaneous UV irradiation of various intensities and water flow. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 122, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Mane, A.U.; Yang, X.; Xia, Z.; Barry, E.F.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y.; Elam, J.W.; Darling, S.B. Visible-light-activated photocatalytic films toward self-cleaning membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qahtan, T.F.; Gondal, M.A.; Dastageer, M.A.; Kwon, G.; Ezazi, M.; Al-Kuban, M.Z. Thermally Sensitized Membranes for Crude Oil–Water Remediation under Visible Light. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 48572–48579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defrance, L.; Jaffrin, M. Comparison between filtrations at fixed transmembrane pressure and fixed permeate flux: Application to a membrane bioreactor used for wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 152, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheryan, M. Ultrafiltration Handbook; Technomic Publishing, Co. Inc.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, J.; Ding, L.; Jaffrin, M.Y. A review on flux decline control strategies in pressure-driven membrane processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2843–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsirai, T.; Buzatu, P.; Aerts, P.; Judd, S. Efficacy of relaxation, backflushing, chemical cleaning and clogging removal for an immersed hollow fibre membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4499–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchanathan, D.; Kwon, G.; Qahtan, T.F.; Gondal, M.A.; Varanasi, K.K.; McKinley, G.H. Kinetics of photoinduced wettability switching on nanoporous titania surfaces under oil. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Z. Improved antifouling property of PVDF membranes by incorporating an amphiphilic block-like copolymer for oil/water emulsion separation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 21349–21359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.; Kota, A.K.; Li, Y.; Sohani, A.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. On-demand separation of oil-water mixtures. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3666–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Huo, J.; Hou, X. Superoleophobic surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4168–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuteja, A.; Choi, W.; Ma, M.; Mabry, J.M.; Mazzella, S.A.; Rutledge, G.C.; McKinley, G.H.; Cohen, R.E. Designing superoleophobic surfaces. Science 2007, 318, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Tu, W.; Wee, K.-H.; Bai, R. Effective and low fouling oil/water separation by a novel hollow fiber membrane with both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Boban, M.; Snyder, S.A.; Kobaku, S.P.; Kwon, G.; Mehta, G.; Tuteja, A. Paper-based surfaces with extreme wettabilities for novel, open-channel microfluidic devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 6121–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tang, Z.; Park-Lee, K.J.; Hess, D.W.; Breedveld, V. Fabrication of non-fluorinated hydrophilic-oleophobic stainless steel mesh for oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 184, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, K.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Z.; Dai, J.; Andreasen, J.; Hu, L. A cellulose based hydrophilic, oleophobic hydrated filter for water/oil separation. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13296–13299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; You, C.; Kowall, C.; Li, L. A Nanometer-Thick, Mechanically Robust, and Easy-to-Fabricate Simultaneously Oleophobic/Hydrophilic Polymer Coating for Oil–Water Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 15395–15399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordjazi, S.; Kamyab, K.; Hemmatinejad, N. Super-hydrophilic/oleophobic chitosan/acrylamide hydrogel: An efficient water/oil separation filter. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2020, 3, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Pan, X.; Huang, Z. Cu mesh’s super-hydrophobic and oleophobic properties with variations in gravitational pressure and surface components for oil/water separation applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Chi, H.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y. One-pot fabrication of hydrophilic-oleophobic cellulose nanofiber-silane composite aerogels for selectively absorbing water from oil–water mixtures. Cellulose 2021, 28, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Atkinson, O.; Badyal, J. Ultrafast oleophobic–hydrophilic switching surfaces for antifogging, self-cleaning, and oil–water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7504–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, S.; Guo, R.; Xu, W. Durable superoleophobic fabric surfaces with counterintuitive superwettability for polar solvents. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 2752–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, X.; Men, X.; Zhou, X. Superhydrophilic–superoleophobic coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2834–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, H.; Ikematsu, Y.; Kawase, T.; Hayakawa, Y. Synthesis and surface properties of novel fluoroalkylated flip-flop-type silane coupling agents. Langmuir 1996, 12, 3529–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, G.; Bhat, S.D. Simultaneous tuning of methanol crossover and ionic conductivity of sPEEK membrane electrolyte by incorporation of PSSA functionalized MWCNTs: A comparative study in DMFCs. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.S.; Bhushan, B. Mechanically durable, superoleophobic coatings prepared by layer-by-layer technique for anti-smudge and oil-water separation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Alcaraz, M.L.; Rubner, M.F.; Cohen, R.E. Zwitter-wettability and antifogging coatings with frost-resisting capabilities. ACS nano 2013, 7, 2172–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, F.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. Coexistence of superhydrophilicity and superoleophobicity: Theory, experiments and applications in oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 15057–15063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchik, L.D. Advances in Membrane-Based Oil/Water Separation; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, I.-S.; Chung, C.-M.; Han, S.-H. Treatment of oily wastewater by ultrafiltration and ozone. Desalination 2001, 133, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummons, E.N.; Chew, J.W.; Fane, A.G.; Tarabara, V.V. Ultrafiltration of saline oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by an anionic surfactant: Effect of surfactant concentration and divalent counterions. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wei, W.; Li, S.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, F.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J. The effect of membrane surface charges on demulsification and fouling resistance during emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Tarabara, V.V.; Bruening, M.L. Adsorption of anionic or cationic surfactants in polyanionic brushes and its effect on brush swelling and fouling resistance during emulsion filtration. Langmuir 2015, 31, 11790–11799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaulsky, E.; Nejati, S.; Boo, C.; Perreault, F.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Post-fabrication modification of electrospun nanofiber mats with polymer coating for membrane distillation applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barati, R.; Johnson, S.J.; McCool, S.; Green, D.W.; Willhite, G.P.; Liang, J.T. Polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles for protection and delayed release of enzymes in alkaline pH and at elevated temperature during hydraulic fracturing of oil wells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Herrmann, N.; McClements, D. Ostwald ripening of hydrocarbon emulsion droplets in surfactant solutions. Langmuir 1999, 15, 6652–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, T.; Schroën, C.; Boom, R. Separation kinetics of an oil-in-water emulsion under enhanced gravity. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 71, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).