Biopolymers in Aerobic Granular Sludge—Their Role in Wastewater Treatment and Possibilities of Re-Use in Line with Circular Economy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Composition of Polymers in Biomass
3. Methods of EPS Isolation
4. Effect of Operational Parameters on Polymer Production and the Effect of Polymer Content on Wastewater Treatment and Sludge Management
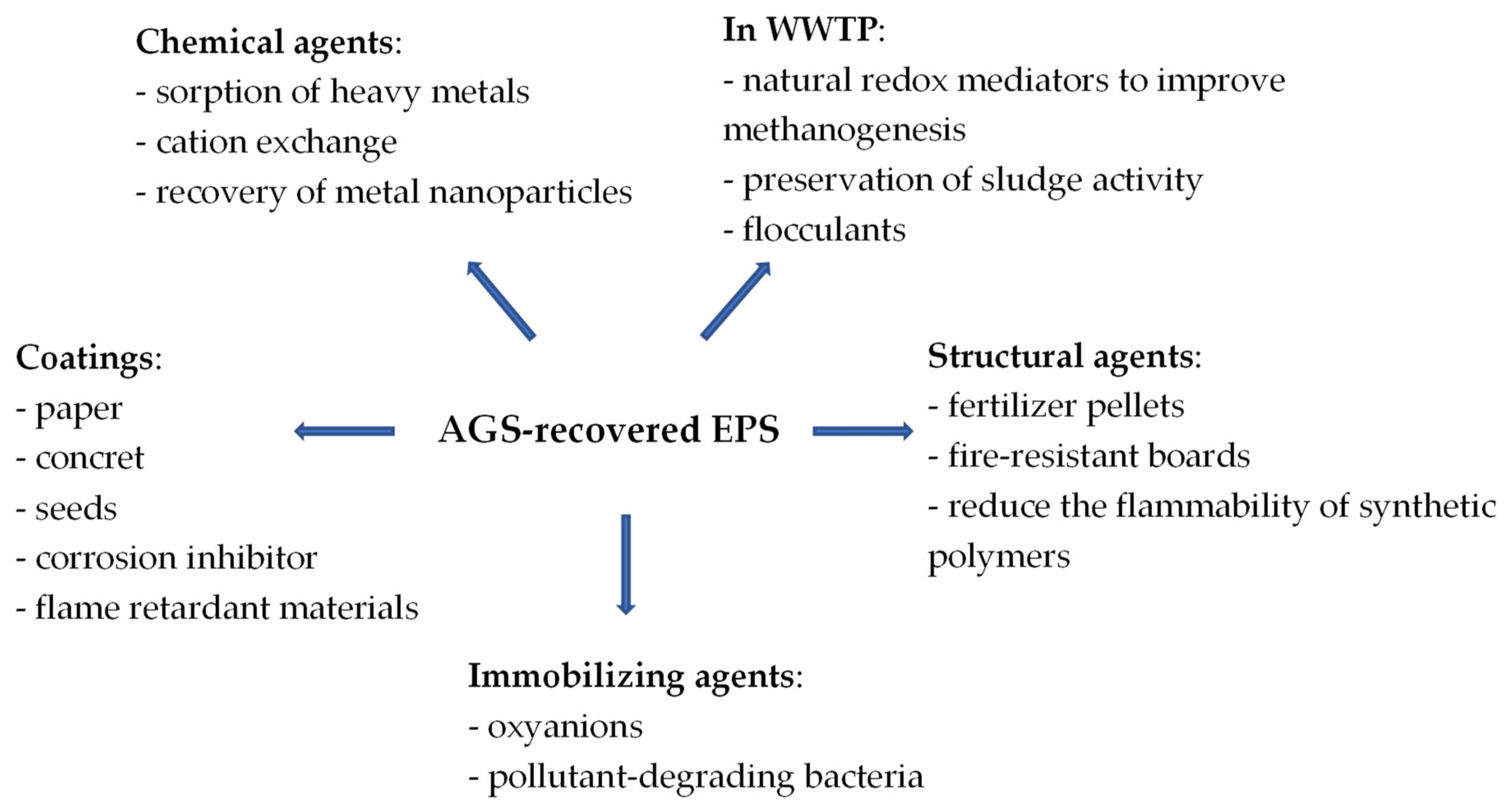
5. Possibilities for Utilizing Granule-Derived Polymers
5.1. Coatings, Agricultural Agents, Flame-Retardants
5.2. Sorption, Ion Exchange, Immobilization
5.3. Re-Use in WWTP
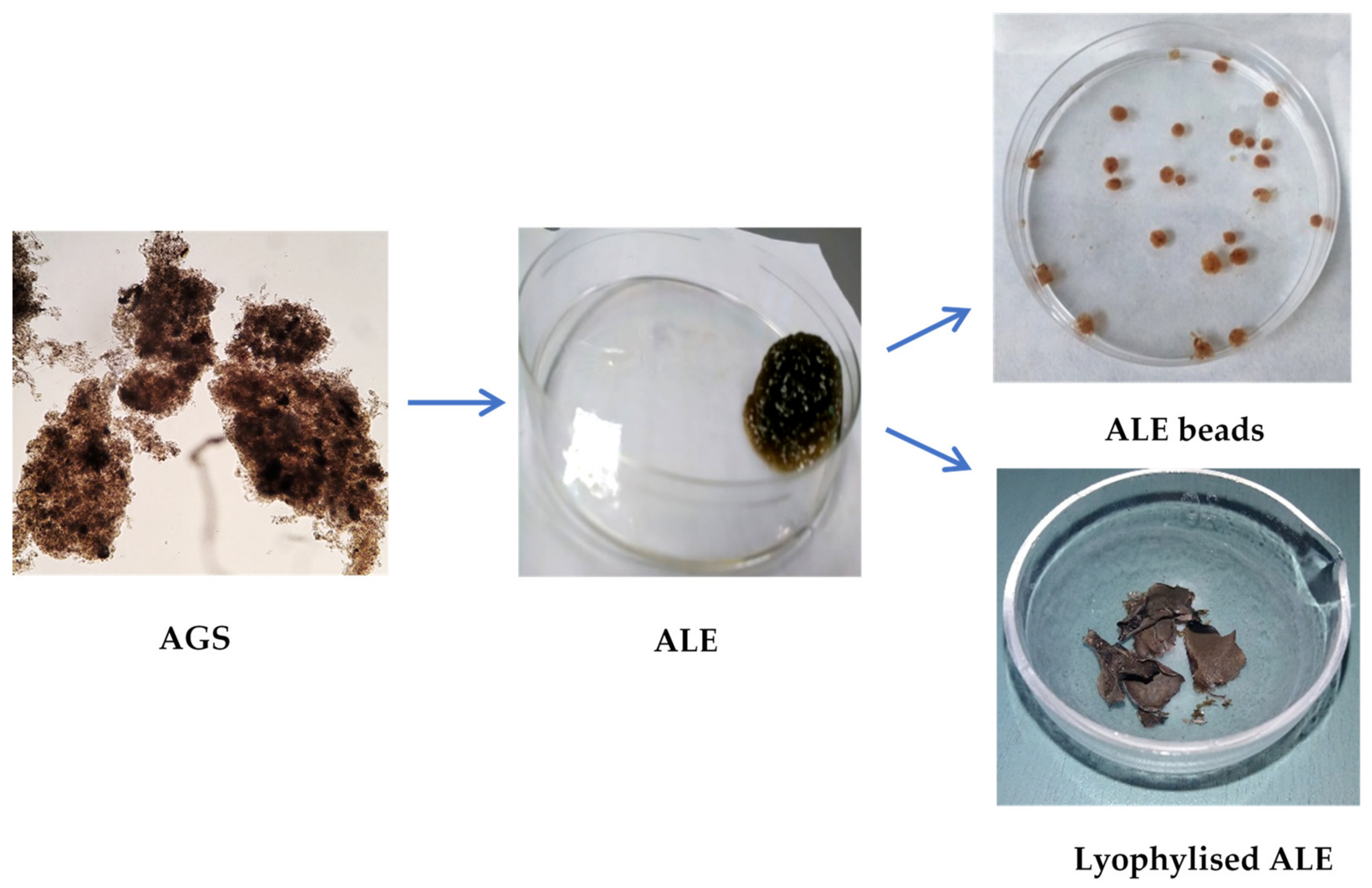
5.4. ALE
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bates, B. Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/426381925/Ohio-Biosolids-Nereda-Seminar-2017 (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Podlasek, M.; Nosek, D.; Jaskulska, B. Treatment efficiency and characteristics of biomass in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant with aerobic granular sludge. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inocencio, P.; Coelho, F.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Giesen, A. The future of sewage treatment: Nereda technology exceeds high expectation. Water 2013, 21, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Rusanowska, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Świątczak, P.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I. Changes in extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) content and composition in aerobic granule size-fractions during reactor cycles at different organic loads. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seviour, T.; Pijuan, M.; Nicholson, T.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. Understanding the properties of aerobic sludge granules as hydrogels. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felz, S.; Neu, T.R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y. Aerobic granular sludge contains hyaluronic acid-like and sulfated glycosaminoglycans-like polymers. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Fang, F.; Guo, J. Insight into the role of exopolysaccharide in determining the structural stability of aerobic granular sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhou, J.; Lv, M.; Yu, H.; Zhao, H.; Xu, X. Specific component comparison of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in flocs and granular sludge using EEM and SDS-PAGE. Chemosphere 2015, 121, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kończak, B.; Miksch, K. Influence of calcium, magnesium and iron ions on the molecular mass of exoproteins during biogranulation. Chem. Process Eng. 2020, 41, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Wan, C. Understanding the role of cations and hydrogen bonds on the stability of aerobic granules from the perspective of the aggregation and adhesion behavior of extracellular polymeric substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 95, 148659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Liu, X.; Wan, C.; Sun, S.; Lee, D.J. Accelerated aerobic granulation using alternating feed loadings: ALE-like exopolysaccharides. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotti, T.; Carretti, E.; Berti, D.; Montis, C.; Del Buffa, S.; Lubello, C.; Feng, C.; Malpei, F. Hydrogels formed by anammox extracellular polymeric substances: Structural and mechanical insights. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.S.; Amorim, C.L.; Ramos, M.A.; Mesquita, D.P.; Inocêncio, P.; Ferreira, E.C.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Castro, P.M.L. Variability in the composition of extracellular polymeric substances from a full-scale aerobic granular sludge reactor treating urban wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cescutti, P.; Foschiatti, M.; Furlanis, L.; Lagatolla, C.; Rizzo, R. Isolation and characterisation of the biological repeating unit of cepacian, the exopolysaccharide produced by bacteria of the Burkholderiacepacia complex. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, L.; Saracevic, E.; Svardal, K.; Krampe, J. Anaerobic biodegradation and dewaterability of aerobic granular sludge. J. Chem. Technol. 2019, 94, 2908–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Hui, C.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Du, L.; Jiang, H. Enhanced excretion of extracellular polymeric substances associated with nonylphenol tolerance in Dictyosphaerium sp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Ye, Z. Insight into the role of extracellular polymeric substances in denitrifying biofilms under nitrobenzene exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seviour, T.; Yuan, Z.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y. Aerobic sludge granulation: A tale of two polysaccharides? Water Res. 2012, 46, 4803–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felz, S.; Vermeulen, P.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y.M. Chemical characterization methods for the analysis of structural extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Water Res. 2019, 157, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schambeck, C.M.; Girbal-Neuhauser, E.; Böni, L.; Fischer, P.; Bessière, Y.; Paul, E.; da Costa, R.H.R.; Derlon, N. Chemical and physical properties of alginate-like exopolymers of aerobic granules and flocs produced from different wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.L.; Wang, H.H.; Alam, F.; Cui, Y.W. Granulation of halophilic sludge inoculated with estuarine sediments for saline wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 532–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Graaff, D.R.; Felz, S.; Neu, T.R.; Pronk, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y. Sialic acids in the extracellular polymeric substances of seawater-adapted aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2019, 155, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Reino, C.; Carrera, J.; Pérez, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Glycosylated amyloid-like proteins in the structural extracellular polymers of aerobic granular sludge enriched with ammonium-oxidizing bacteria. Microbiologyopen 2018, 7, e00616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kończak, B.; Karcz, J.; Miksch, K. Influence of Calcium, Magnesium, and Iron Ions on Aerobic Granulation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Ming, J.; Yoza, B.A.; Liang, J.; Li, Q.X.; Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, Q. Characterization of aerobic granular sludge used for the treatment of petroleum wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Gao, D.W.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Y. Comparison of Ca2+ and Mg2+ enhancing aerobic granulation in SBR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.-W.; Huang, J.-L.; Alam, F. Fast granulation of halophilic activated sludge treating low-strength organic saline wastewater via addition of divalent cations. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Song, W.; Song, T.; Li, J. Study on rapid formation of aerobic granular sludge promoted by addition of Fe2+. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 2021, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Liu, Y.; Tay, J.H. Biodegradability of extracellular polymeric substances produced by aerobic granules. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenen, E.J.T.M. Nitrification by Artificially Immobilized Cells: Model and Practical System. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.-C.; Zhu, J.-R. Role of N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL)-based quorum sensing (QS) in aerobic sludge granulation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7623–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, C.; Li, Y.; Hao, W.; Zhu, J. The effect of quorum sensing and extracellular proteins on the microbial attachment of aerobic granular activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Zhang, P.; Lee, D.-J.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, S.; Pan, X. Disintegration of aerobic granules: Role of second messenger cyclic di-GMP. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Zeng, W.; Meng, Q.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y. Identification of partial denitrification granulation enhanced by low C/N ratio in the aspect of metabolomics and quorum sensing. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basuvaraj, M.; Fein, J.; Liss, N. Protein and polysaccharide content of tightly and loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances and the development of a granular activated sludge floc. Water Res. 2015, 82, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felz, S.; Al-Zuhnairy, S.; Aarstas, O.A.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y.M. Extraction of structural polymeric substances from aerobic granular sludge. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 115, e54534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Q.; Fu, B.; Yang, E.; Fang, F.; Feng, Q.; Luo, J. Revealing the characteristics and formation mechanisms of partial denitrification granular sludge for efficient nitrite accumulation driven by glycerol. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.B.; Yan, S.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) producing bacterial strains of municipal wastewater sludge: Isolation, molecular identification, EPS characterization and performance for sludge settling and dewatering. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2253–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouha, K.; Yan, S.; Tyadi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. EPS producting microorganisms from municipal wastewater activated sludge. J. Pet. Environ. Biotechnol. 2015, 7, 1000255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, C.H.; Koh, K.S.; Xie, C.; Tay, M.; Zhou, Y.; Williams, R.; Ng, W.J.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. The role of quorum sensing signalling in EPS production and the assembly of a sludge community into aerobic granules. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Bacterial structure of aerobic granules is determined by aeration mode and nitrogen load in the reactor cycle. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 181, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, A.M.S.; Amorim, C.L.; Costa, J.; Mesquita, D.P.; Ferreira, E.C.; Castro, P.M.L. Long-term stability of a non-adapted aerobic granular sludge process treating fish canning wastewater associated to EPS producers in the core microbiome. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, I.; Paoletti, S. Material properties of ALEs. In ALEs: Biology and Applications; Rehm, B.H.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, I.D.; Rehman, Z.U.; Moradali, M.F.; Wang, Y.; Rehm, B.H.A. Microbial alginate production, modification and its applications. Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ertesvåg, H.; Valla, S.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Enzymatic ALE Modification. In ALEs: Biology and Applications; Rehm, B.H.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, I.D.; Gatland, K.; Campisano, A.; Jordens, J.Z.; Rehm, B.H. Impact of ALE overproduction on attachment and biofilm architecture of a super mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6022–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabra, W.; Zeng, A.P. Microbial production of ALEs physiology and process aspects In ALEs: Biology and Applications; Rehm, B.H.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 153–173. [Google Scholar]
- Giesen, A.; van Loosdrecht, M.; de Bruin, B.; van der Roest, H.; Pronk, M. Full-scale experiences with aerobic granular biomass technology for treatment of urban and industrial wastewater. In Proceedings of the International Water Week, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 4–8 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Nosek, D.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Mikulski, A. Efficient dewatering of polymer-rich aerobic granular sludge with cationic polymer containing hydrocarbons. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bales, P.M.; Renke, E.M.; May, S.L.; Shen, Y.; Nelson, D.C. Purification and characterization of biofilm-associated EPS exopolysaccharides from ESKAPE organisms and other pathogens. PLoS ONE 2008, 8, 67950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 1996, 30(8), 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.J. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from aerobic granule with compact interior structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y. Comparison and optimization of extraction methods of extracellular polymeric substances in anammox granules: From maintaining protein secondary structure perspective. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSwain, B.S.; Irvine, R.L.; Hausner, M.; Wilderer, P.A. Composition and distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic flocs and granular sludge. Appl. Environ. Biotechnol. 2005, 71, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, W.; Tang, B.; Fu, F.; Huang, S.; Zhao, S.; Bin, L.; Ding, J.; Chen, C. A new insight into resource recovery of excess sewage sludge: Feasibility of extracting mixed amino acids as an environment-friendly corrosion inhibitor for industrial pickling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Nosek, D.; Gusiatin, Z.M.; Zielińska, M.; Bernat, K.; Kulikowska, D.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I. Optimization of extraction parameters of alginate from aerobic granular sludge. In Proceedings of the 6th International Environmental Best Practices Conference, Olsztyn, Poland, 22–26 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.M.; Wang, L.; Chi, Z.M.; Liu, X.Y. Bacterial ALE role in aerobic granular bio-particles formation and settle ability improvement. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątczak, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Performance and microbial characteristics of biomass in a full-scale aerobic granular sludge wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q.; Li, X.Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Xiang, R.; Yu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Organic load rate (OLR) regulation for enhancement of aerobic sludge granulation: Role of key microorganism and their function. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, A.J.; Yuan, Q. Long-term stability and nutrient removal efficiency of aerobic granules at low organic loads. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, B.; Wang, M.; Ma, C.; Tian, Q.; Song, X.; Sand, W. Granulation process in an expanded granular sludge blanked (EGSB) reactor for domestic sewage treatment: Impact of extracellular polymeric substances compositions and evolution of microbial population. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remmas, N.; Melidis, P.; Zerva, I.; Kristoffersen, J.B.; Nikolaki, S.; Tsiamis, G.; Ntougias, S. Dominance of candidate Saccharibacteria in a membrane bioreactors treating medium age landfill leachte: Effects of organic load on microbial communities hydrolytic potential and extracellular polymeric substances. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 248, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, Y. Evolution of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in aerobic sludge granulation: Composition, adherence and viscoelastic properties. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; She, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, C.; Guo, L.; Li, K.; Gao, M. Impact of carbon/nitrogen ratio on the performance and microbial community of sequencing batch biofilm reactor treating synthetic mariculture wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Ren, X.; Cui, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Z. Impacts of influent COD/N ratio on floc physicochemical characteristics and microbial community of nitrifying sludge under high-strength ammonia conditions. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decho, A.W.; Gutierrez, T. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) in ocean systems. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsino, S.F.; Capodici, M.; Pippo, D.F.; Tandoi, V.; Torregrossa, M. Comparison between kinetics of autochthons marine bacteria in activated sludge and granular sludge systems at different salinity and SRTs. Water Res. 2019, 148, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, S.B.; de La Parra, C.J.; Temmink, H.; van Lier, J.B. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors operated under high salinity conditions. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsino, S.F.; Capodici, M.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Physical properties and extracellular polymeric substances pattern of aerobic granular sludge treating hypersaline wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Luo, J.; Guo, G.; Mackey, H.R.; Hao, T.; Chen, G. Seawater-based wastewater accelerates development of aerobic granular sludge: A laboratory proof-of-concept. Water Res. 2017, 115, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Liu, D.; Pan, Y.; Xi, L.; Yang, D.; Huang, W. Enhanced amount and quality of alginate-like exopolysaccharides in aerobic granular sludge for the treatment of salty wastewater. BioResources 2019, 14, 139–165. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Sun, S.P.; Ma, B.Y.; Zhang, C.; Wan, C.L.; Lee, D.J. Understanding of aerobic granulation enhanced by starvation in the perspective of quorum sensing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3747–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinyua, M.N.; Elliott, M.; Wett, B.; Murthy, S.; Chandran, K.; Bott, C.B. The role extracellular polymeric substances on carbon capture in a high rate activated sludge A-stage system. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Cao, R.; Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. A novel mode of air recycling favored stable operation of the aerobic granular sludge process via calcium accumulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. The connection between aeration regimes and EPS composition in nitritation biofilm. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-M.; Liao, X.-W.; Guo, J.-S.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Chen, Y.-P.; Fang, F.; Yan, P. New insights into filamentous sludge bulking: The potential role of extracellular polymeric substances in sludge bulking in the activated sludge process. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; He, X.; Wang, P.; Xu, B.; Li, K.; Lu, B.; Jin, W.; Tang, S. Effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on extracellular polymeric substance composition of activated sludge: The role of surface functional groups. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, W.; Lin, L.; Wu, Z. Effects of microplastics accumulation on performance of membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junaid, M.; Wang, J. Interaction of nanoplastics with extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in the aquatic environment: A special reference to eco-corona formation and associated impacts. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premnath, N.; Mohanrasu, K.; Rao, R.G.R.; Dinesh, G.H.; Prakash, G.S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Govarthanan, M.; Kumar, P.; Arun, A. Effect of C/N substrates for enhanced extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production and Poly Cyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) degradation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.S.; Amorim, C.L.; Mesquita, D.P.; Ferreira, E.C.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Castro, P.M.L. Increased extracellular polymeric substances production contributes for the robustness of aerobic granular sludge during long-term intermittent exposure to 2-fluorophenol in saline wastewater. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 40, 101977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, H.; Chen, G.; Chen, X. A subcellular level study of copper speciation reveals the synergistic mechanism of microbial cells and EPS involved in copper binding in bacterial biofilms. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wan, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Lee, D.-J. Understanding of the mechanism of extracellular polymeric substances of aerobic granular sludge against tetracycline from the perspective of fluorescence properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ma, B.; She, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, C.; Gao, M. Effect of norfloxacin on performance, microbial enzymatic activity and microbial community of a sequencing batch reactor. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Gao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Cheng, J.; Jin, L.; Lyu, Y.; Du, Z.; Guo, M. Multiple roles of Ca2+ in the interaction of ciprofloxacin with activated sludge: Spectroscopic investigations of extracellular polymeric substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 142246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.-H.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, G.-P. Quantifying the occurrence and transformation potential of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)-associated antibiotic resistance genes in activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernat, K.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Karczewska, M. Physicochemical properties and biogas productivity of aerobic granular sludge and activated sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 117, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudmalis, D.; Mubita, T.M.; Gagliano, M.C.; Dinis, E.; Zeeman, G.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Temmink, H. Cation exchange membrane behaviour of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in salt adapted granular sludge. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Enhancing anaerobic digestion of kitchen wastes via combining ethanol-type fermentation with magnetite: Potential for stimulating secretion of extracellular polymeric substances. Waste Manag. 2021, 127, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, H.; Lou, Z.; Zhu, N. Synergy between denitrification and calcium bridging improves dewaterability of waste activated sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Ge, D.; Wang, G.; Dong, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, N.; Yuan, H. Enhancement of waste activated sludge dewaterability by ultrasound-activated persulfate oxidation: Operation condition, sludge properties, and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Jin, W.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q. Role of extracellular polymeric substances in anaerobic granular sludge: Assessing dewaterability during Fe(II)-peroxydisulfate conditioning and granulation processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Li, N.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yu, W.; Liang, S.; Hou, H.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; et al. Deciphering the impacts of composition of extracellular polymeric substances on sludge dewaterability: An often overlooked role of amino acids. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.B.; Song, J.L.; Yao, Q.J.; Chen, Z.X.; Wei, Y.; Li, H.L.; Wang, M.X.; Wang, B.J.; Zhou, J.M. Effects of dissolved oxygen on the sludge dewaterability and extracellular polymeric substances distribution by bioleaching. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hoek, J.P.; De Fooij, H.; Struker, A. Wastewater as a resource: Strategies to recover resources from Amsterdam’s wastewater. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 113, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Roest, H.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Langkamp, E.J.; Uijterlinde, C. Recovery and reuse of Bio-ALE from granular Nereda sludge. Water 2015, 21, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Kroiss, H. What is the potential for utilizing the resources in sludge? Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROYAL HASKONINGDHV. 2019. Available online: https://www.royalhaskoningdhv.com/en-gb/news-room/news/launching-new-sustainable-raw-material-kaumera/10149 (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Hogendoorn, A. Enhanced Digestion and Bio-ALE-Like Exopolysaccharides Extraction from Nereda Sludge. Master’s Thesis, University of Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 2013. Available online: https://repository.tudelft.nl/islandora/object/uuid:b1c86da0-3786-4fd7-b2c6-1cf0d3da8865?collection=education (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- ROYAL HASKONINGDHV. 2017. Available online: https://www.royalhaskoningdhv.com/en-gb/news-room/news/new-raw-material-from-nereda-wastewater/6794 (accessed on 30 November 2017).
- Lin, Y.M.; Nierop, K.G.J.; Girbal-Neuhauser, E.; Adriaanse, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Sustainable polysaccharide-based biomaterial recovered from waste aerobic granular sludge as a surface coating material. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2015, 4, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Go, L.C.; Holmes, W.; Depan, D.; Hernandez, R. Evaluation of extracellular polymeric substances extracted from waste activated sludge as a renewable corrosion inhibitor. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.K.; Mao, N.; Lin, R.; Bhattacharyya, D.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y. Flame retardant property of flax fabrics coated by extracellular polymeric substances recovered from both activated sludge and aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.K.; Lin, R.; Bhattacharyya, D.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y. Insight on how biopolymers recovered from aerobic granular wastewater sludge can reduce the flammability of synthetic polymers. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, B.; Gupta, B.; Thakur, I.S. Biosorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) produced by Parapedobacter sp. ISTM3 strain isolated from Mawsmai cave, Meghalaya, India. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajao, V.; Nam, K.; Chatzopoulos, P.; Spruijt, E.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H.; Temmink, H. Regeneration and reuse of microbial extracellular polymers immobilised on a bed column for heavy metal recovery. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Liu, G.; Zhou, J.; Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Jin, R. Roles of molecular weight-fractionated extracellular polymeric substance in transformation of Au(III) to Au nanoparticles in aqueous environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, K.; Huang, S.; Zhu, X.; Kang, F. Spontaneous assembly of microbial extracellular polymeric substances into microcapsules involved in trapping and immobilizing degradation-resistant oxoanions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, A.; Cheng, X.; Wang, C.; Kang, L.; Chen, P.; He, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ye, J.; Zhou, S. Extracellular polymeric substances trigger an increase in redox mediators for enhanced sludge methanogenesis. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Y.-H.; Xia, W.-J.; Ni, S.-K.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Fan, N.-S.; Huang, B.-C.; Jin, R.-C. Exogenous extracellular polymeric substances as protective agents for the preservation of anammox granules. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, C.; Silva, L.; Paulo, J.; Faria, M.; Nogueira, N.; Cordeiro, N. Microalgal-based biopolymer for nano- and microplastic removal: A possible biosolution for wastewater treatment. Environ. Poll. 2020, 263, 114385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragett, K.I.; Taylor, C. Chemical, physical and biological properties of ALEs and their biomedical implications. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Sharma, P.K.; van Loosedrecht, M.C.M. The chemical and mechanical differences between ALE-like exopolysaccharides isolated form aerobic flocculent sludge and aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2013, 47, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, M.; Neu, T.R.; van Loosedrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y.M. The acid souble extracellular polymeric substance of aerobic granular sludge dominated by Defluvuiicoccus sp. Water Res. 2017, 122, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, K.; De Vries, E.; Koop, S.; Roest, K. The Energy & Raw Materials Factory: Role and Potential Contribution to the Circular Economy of the Netherlands. Environ. Manag. 2018, 61, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladnorg, S.; Libardi, N., Jr.; Dall’Agnol, P.; Domingos, D.G.; Magnus, B.S.; Wichern, M.; Gehring, T.; de Costa, R.H.R. ALE-like exopolysaccharide extracted from aerobic granular sludge as biosorbent for methylene blue: Termodynamic, kinetics and isotherm studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Biopolymers in Aerobic Granular Sludge—Their Role in Wastewater Treatment and Possibilities of Re-Use in Line with Circular Economy. Energies 2021, 14, 7219. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14217219
Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A. Biopolymers in Aerobic Granular Sludge—Their Role in Wastewater Treatment and Possibilities of Re-Use in Line with Circular Economy. Energies. 2021; 14(21):7219. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14217219
Chicago/Turabian StyleCydzik-Kwiatkowska, Agnieszka. 2021. "Biopolymers in Aerobic Granular Sludge—Their Role in Wastewater Treatment and Possibilities of Re-Use in Line with Circular Economy" Energies 14, no. 21: 7219. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14217219
APA StyleCydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. (2021). Biopolymers in Aerobic Granular Sludge—Their Role in Wastewater Treatment and Possibilities of Re-Use in Line with Circular Economy. Energies, 14(21), 7219. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14217219




