Sizing and Energy Management of Parking Lots of Electric Vehicles Based on Battery Storage with Wind Resources in Distribution Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Objective Function
- Cost of power loss
- Cost of purchased power from main network
- Cost of wind power
- Cost of parking lots
2.2. Constraints
- Power balance
- Power purchased from the main network
- Vehicle’s battery capacity
- Voltage
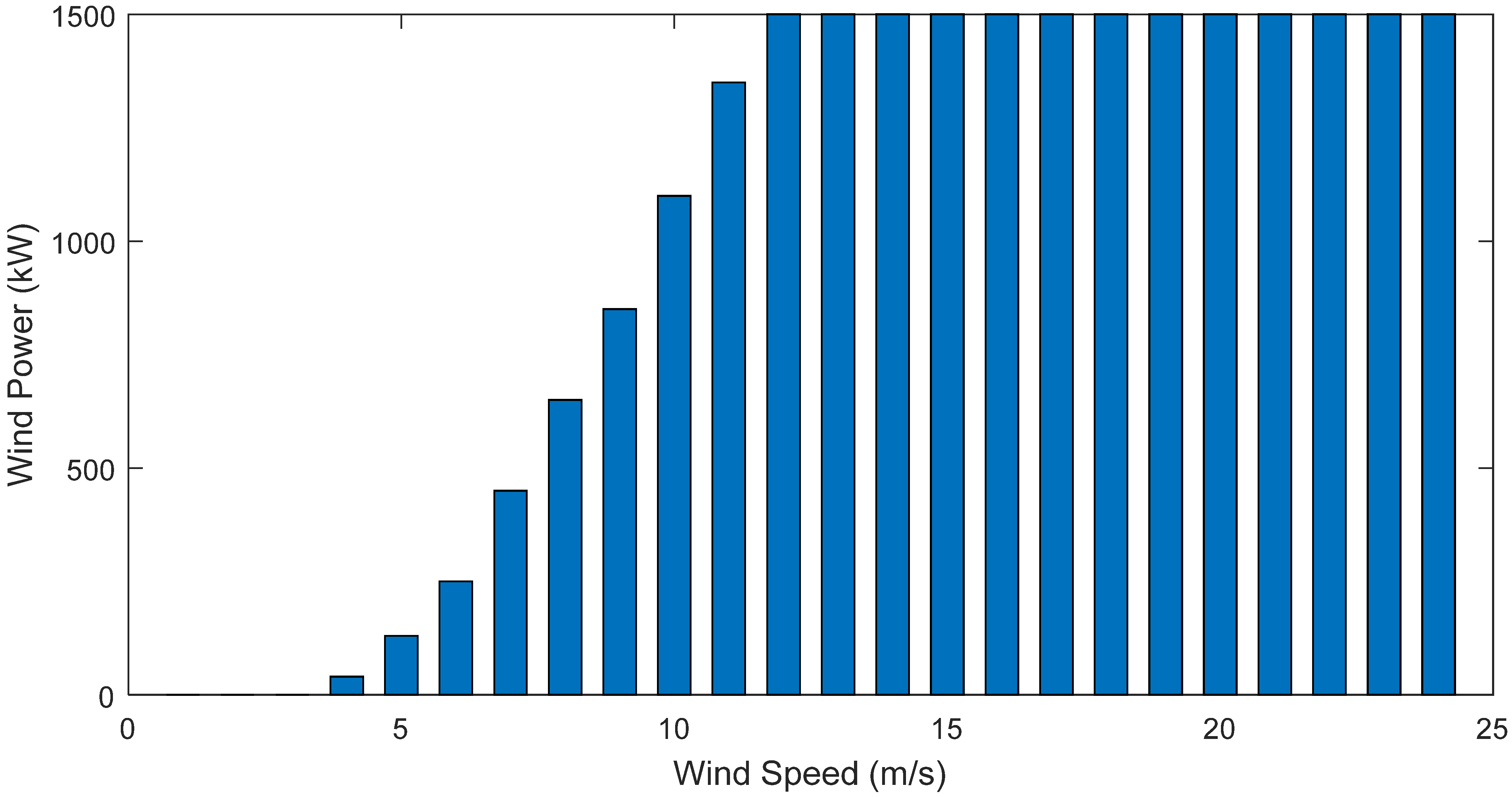
- Power of wind generator
- Allowable power of network lines (thermal limit)
2.3. Energy Management Strategy
- If the power output of wind turbines is more than the load demand and if the amount of parking battery charge is less than the maximum allowable value, then the parking battery will be charged based on the allowable charging capacity.
- If the power output of wind turbines is less than the load demand and if the amount of parking battery charge is more than the maximum allowable value, then considering the allowable charging capacity, the parking battery will be discharged to load supply.
- If the capacity of wind resources in addition to charging electric parking lots is less than the demand, then in proportion to the load shortage, the power can be purchased from the main grid.
3. Proposed Optimization Method
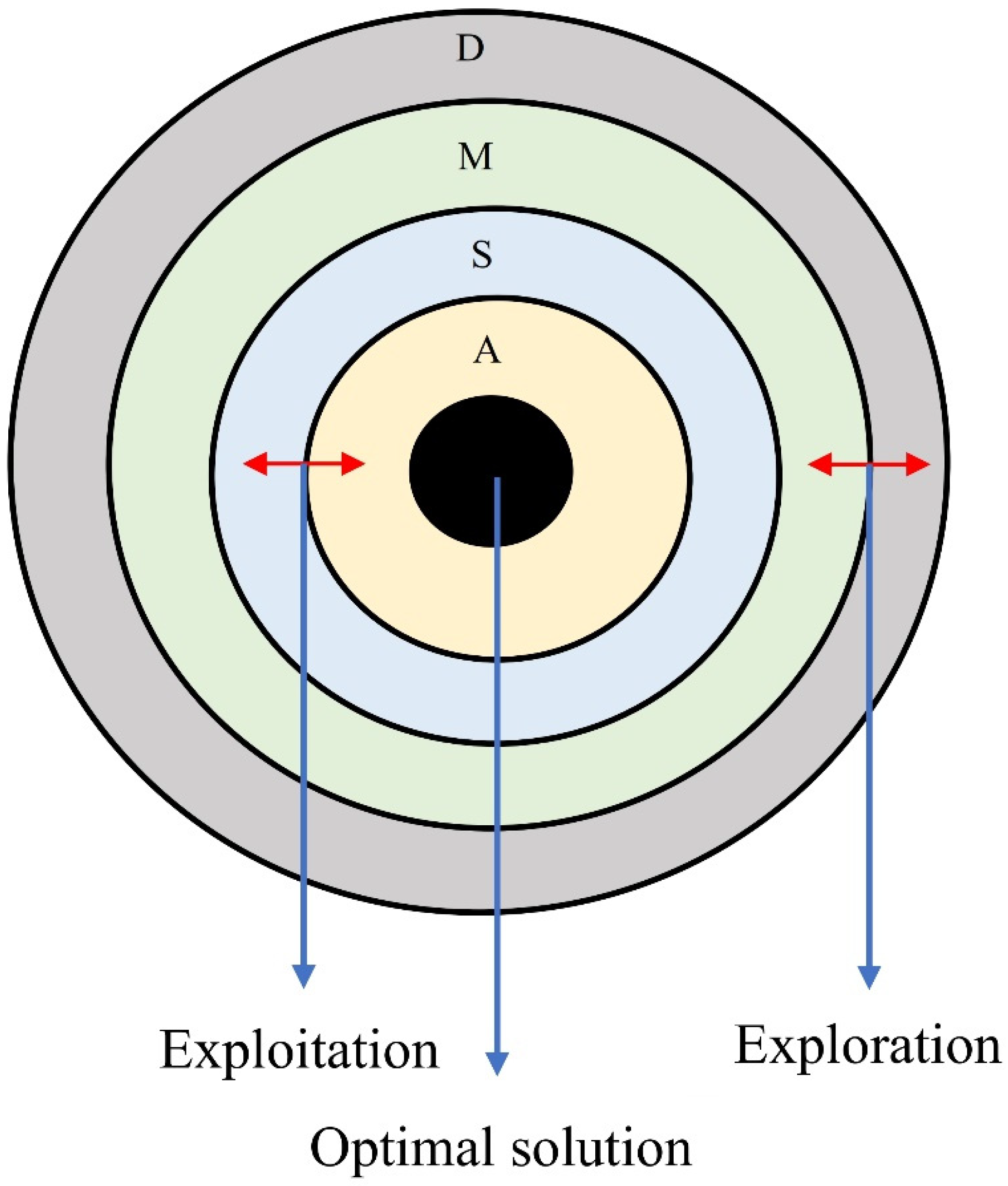
3.1. Overview of AOA
3.1.1. Preparation Stage
3.1.2. Exploration Stage
3.1.3. Exploitation Phase
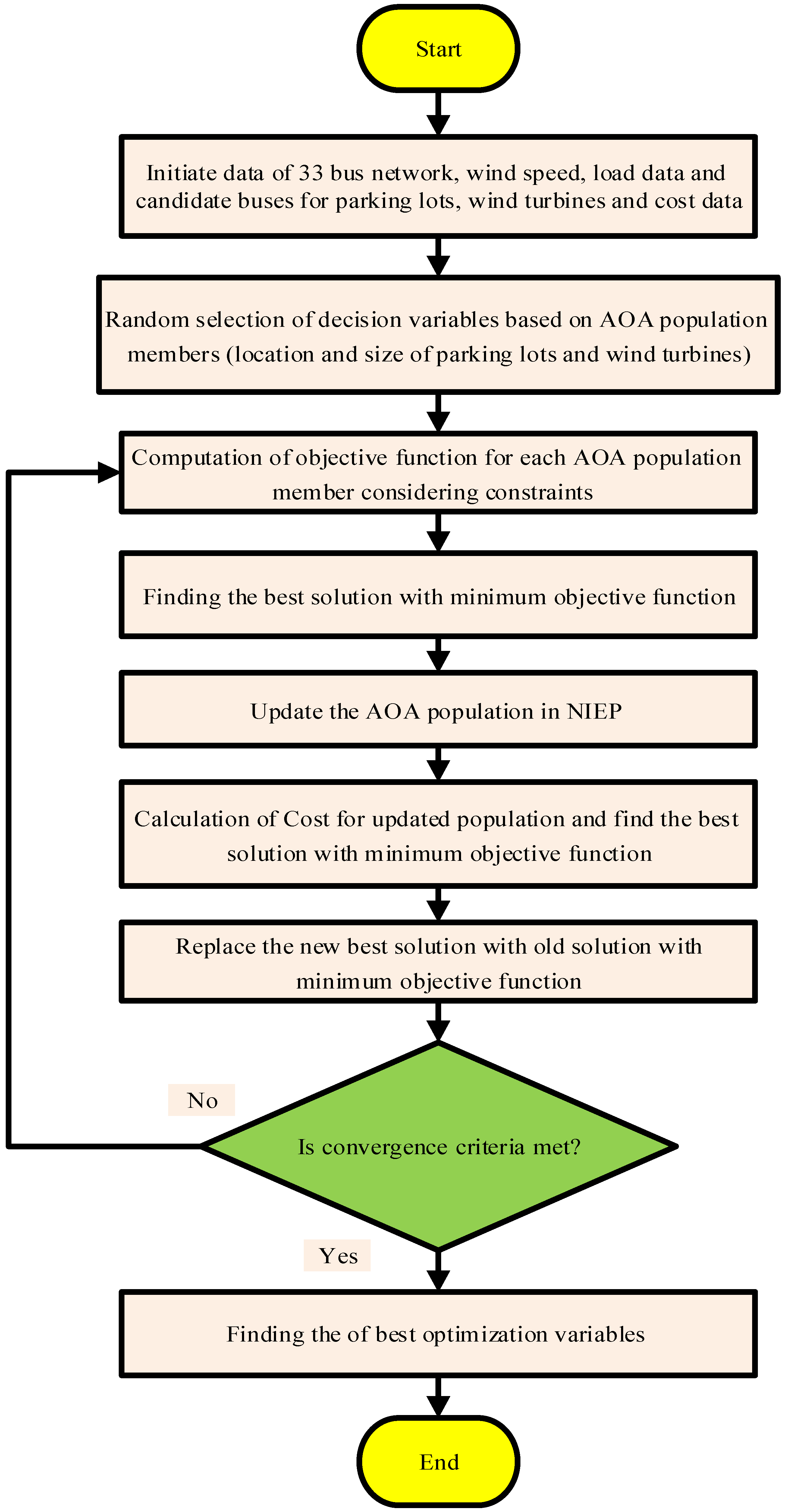
3.2. Implementation of the AOA
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Test Network
4.2. Simulation Cases
4.3. Comparison of the Results
4.3.1. Power Loss
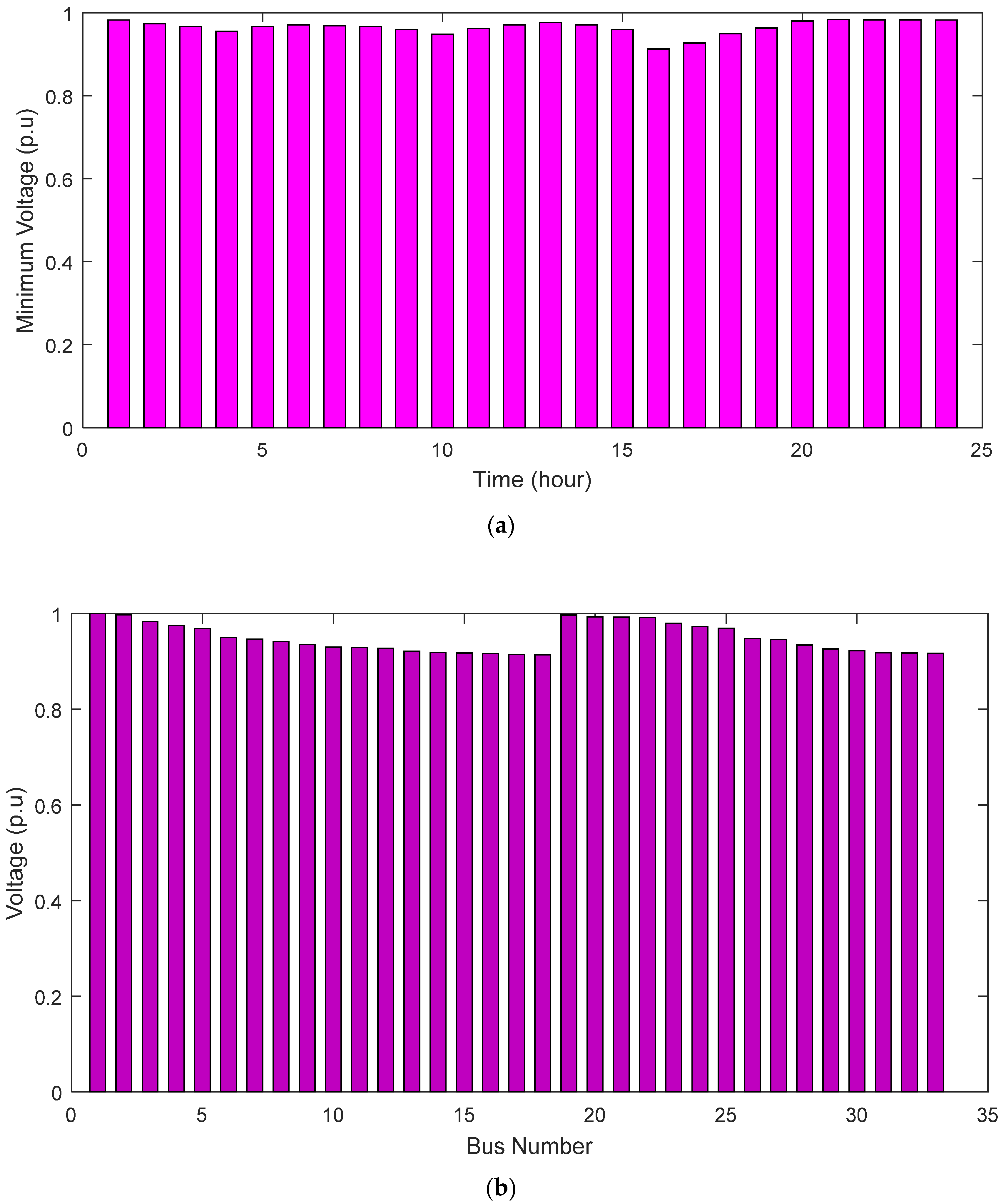
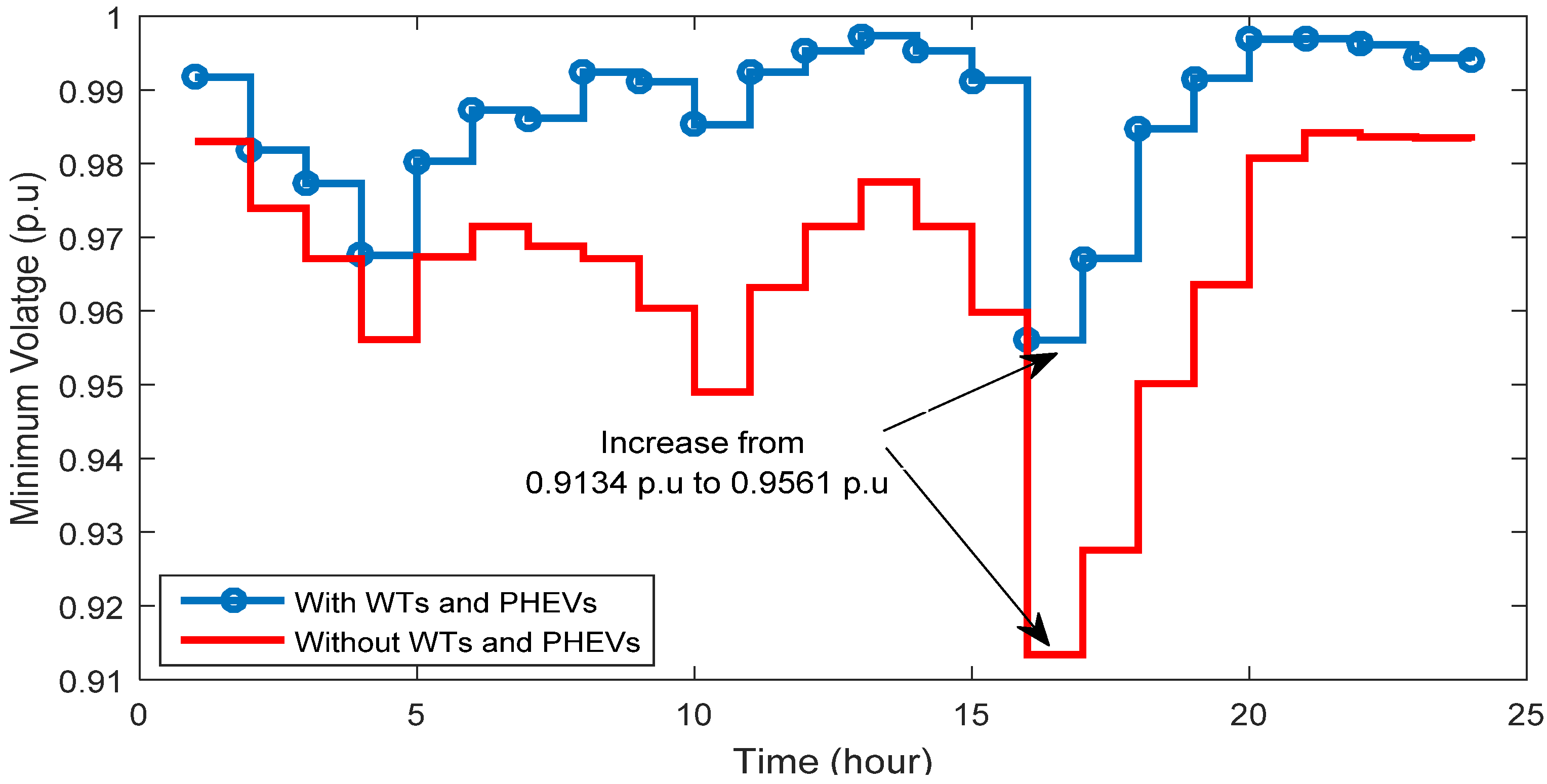
4.3.2. Minimum Voltage
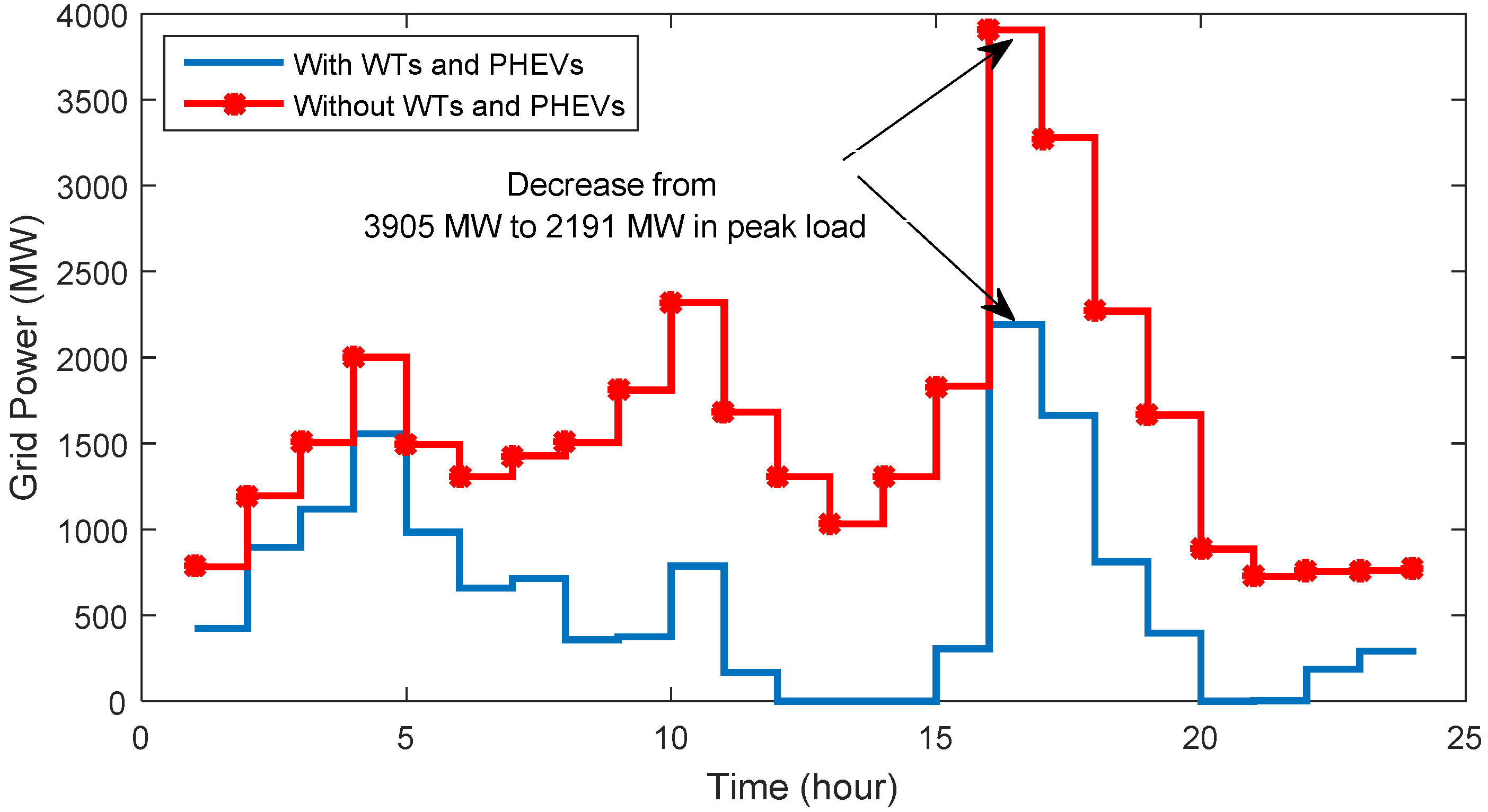
4.3.3. Grid Power
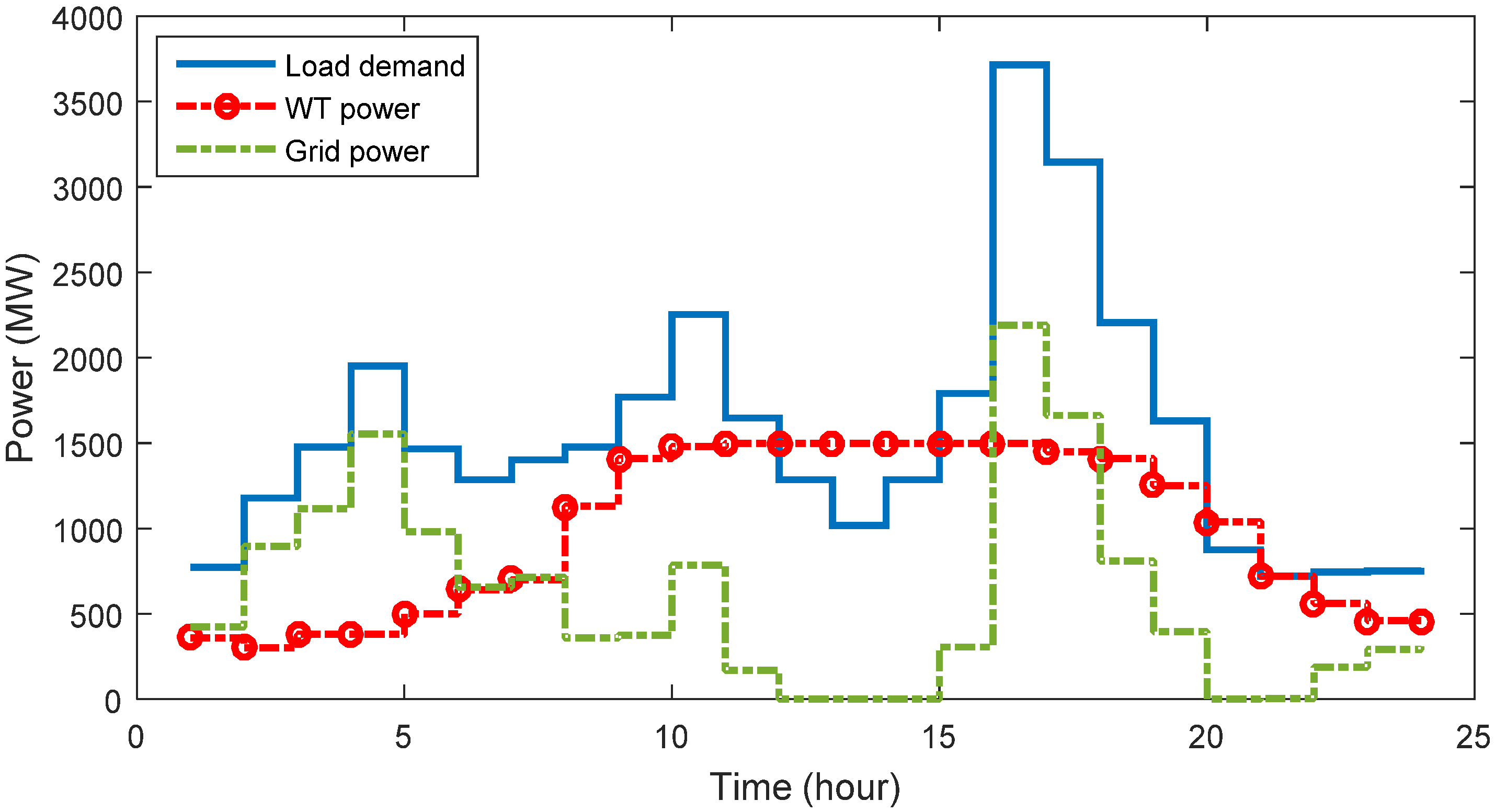
4.3.4. Contribution of the Wind Resources and Grid
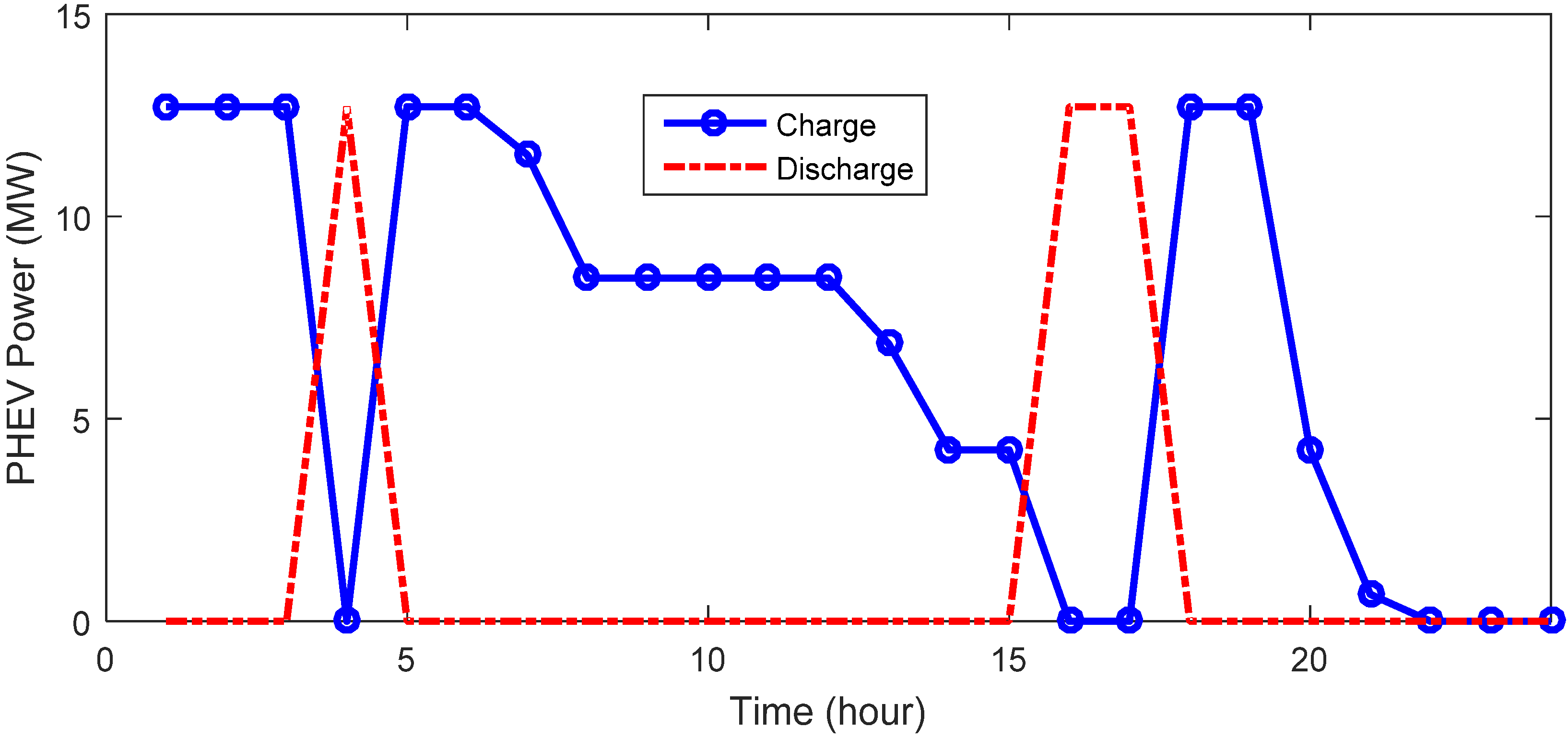
4.3.5. Charge and Discharge of the Batteries
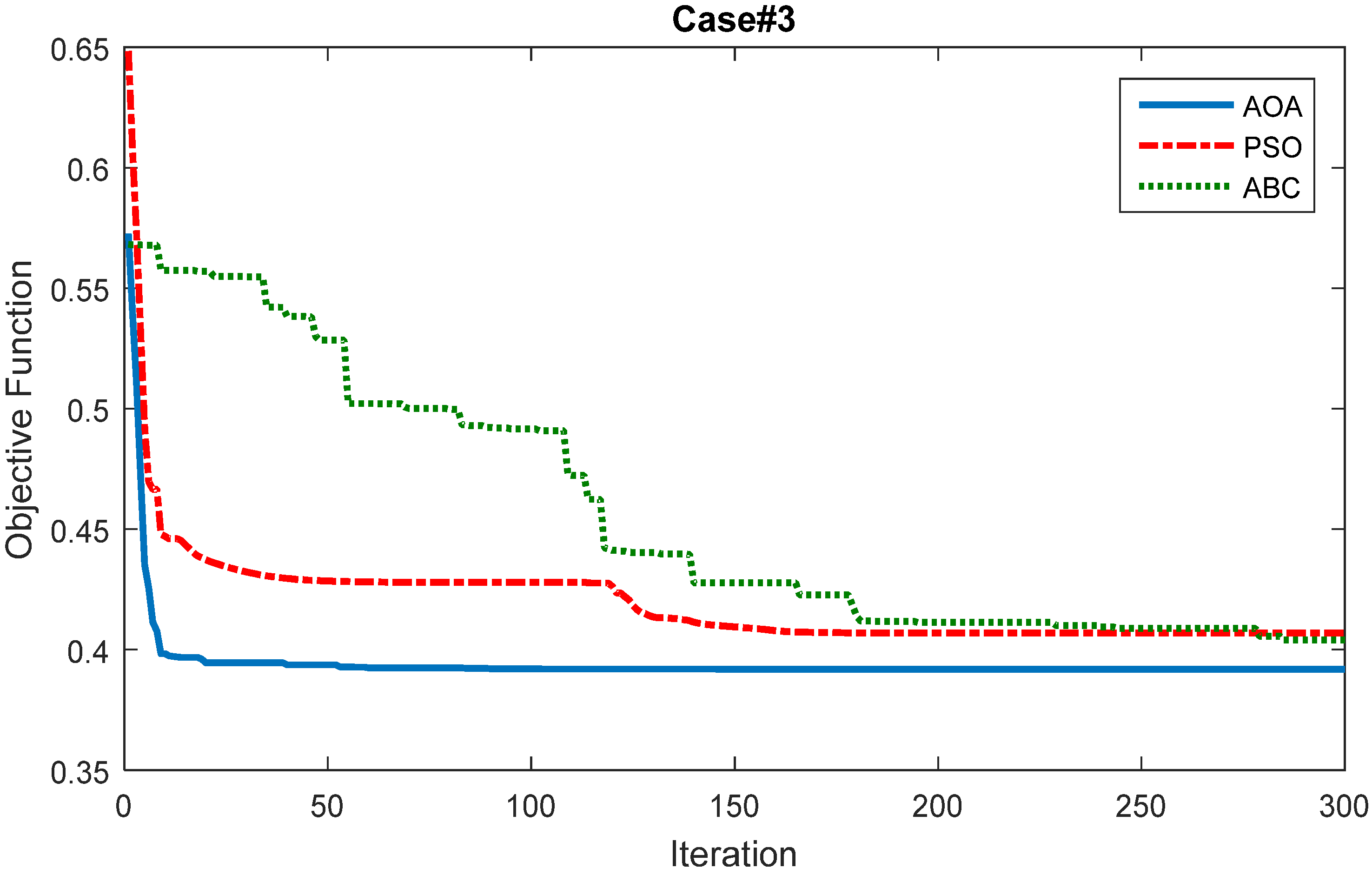
4.4. Comparison of the AOA Results with PSO and ABC
4.5. Comparison Results of the AOA with Previous Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turan, M.T.; Ates, Y.; Erdinc, O.; Gokalp, E.; Catalão, J.P. Effect of electric vehicle parking lots equipped with roof mounted photovoltaic panels on the distribution network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 109, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. Competition over resource optimization algorithm for optimal allocating and sizing parking lots in radial distribution network. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, H.; Dong, H. Optimal Public Parking Lot Allocation and Management for Efficient PEV Accommodation in Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 5984–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderipour, A.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Nowdeh, S.A.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Kalam, A.; Guerrero, J. Optimal allocation for combined heat and power system with respect to maximum allowable capacity for reduced losses and improved voltage profile and reliability of microgrids considering loading condition. Energy 2020, 196, 117124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savari, G.F.; Krishnasamy, V.; Sathik, J.; Ali, Z.; Aleem, S.H.A. Internet of Things based real-time electric vehicle load forecasting and charging station recommendation. ISA Trans. 2020, 97, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradijoz, M.; Moghaddam, M.P.; Haghifam, M.; Alishahi, E. A multi-objective optimization problem for allocating parking lots in a distribution network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 46, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatpanah, H.; Sabourikenari, M.; Mohammadian, M.; Rashidinejad, M. Optimal placement and determine parking capacity of electric vehicles to improve VSM and congestion. In Proceedings of the Iranian Conference on Smart Grids, Mashhad, Iran, 14–16 May 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Moradijoz, M.; Ghazanfarimeymand, A.; Moghaddam, M.P.; Haghifam, M.R. Optimum placement of distributed generation and parking lots for loss reduction in distribution networks. In Proceedings of the 2012 17th Conference on Electrical Power Distribution, Tehran, Iran, 2–3 May 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, I.; Vasant, P.M.; Singh, B.S.M.; Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M. On the performance of accelerated particle swarm optimization for charging plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clement-Nyns, K.; Haesen, E.; Driesen, J. The impact of vehicle-to-grid on the distribution grid. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2011, 81, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.; Morais, H.; Soares, J.; Vale, Z. Day-ahead resource scheduling in smart grids considering Vehicle-to-Grid and network constraints. Appl. Energy 2012, 96, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, J.; Gonzalez, R.; Gimenez, A.; Lopez, J. Energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. A comparative study. Appl. Energy 2013, 113, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, C.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K.; Corzine, K.A. Intelligent scheduling of hybrid and electric vehicle storage capacity in a parking lot for profit maximization in grid power transactions. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Energy 2030 Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–18 November 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fazelpour, F.; Vafaeipour, M.; Rahbari, O.; Rosen, M.A. Intelligent optimization to integrate a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle smart parking lot with renewable energy resources and enhance grid characteristics. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 77, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Han, S.; Sezaki, K. Development of an optimal vehicle-to-grid aggregator for frequency regulation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2010, 1, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsenzadeh, A.; Pazouki, S.; Ardalan, S.; Haghifam, M.-R. Optimal placing and sizing of parking lots including different levels of charging stations in electric distribution networks. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2017, 39, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenzadeh, A.; Pazouki, S.; Haghifam, M.R.; Pang, C. Optimal planning of parking lots and demand response programs in distribution network considering power loss and voltage profile. 2015 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Bangko, Thailand, 17–20 February 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sattarpour, T.; Farsadi, M. Parking lot allocation with maximum economic benefit in a distribution network. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2016, 27, e2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, C.; Song, H.; Jermsittiparsert, K. Optimal sizing and sitting of EVCS in the distribution system using metaheuristics: A case study. Energy Rep. 2020, 7, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderipour, A.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Nowdeh, S.A.; Kamyab, H.; Ramtin, A.R.; Shahrokhi, S.; Klemeš, J. Comparative evaluation of hybrid photovoltaic, wind, tidal and fuel cell clean system design for different regions with remote application considering cost. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar-Nowdeh, A.; Babanezhad, M.; Arabi-Nowdeh, S.; Naderipour, A.; Kamyab, H.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K. Meta-heuristic matrix moth–flame algorithm for optimal reconfiguration of distribution networks and placement of solar and wind renewable sources considering reliability. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, M.J.H.; Kalam, A.; Shi, J.; Nowdeh, S.A.; Gandoman, F.H.; Ahmadi, A. A New Model for Reconfiguration and Distributed Generation Allocation in Distribution Network Considering Power Quality Indices and Network Losses. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 3530–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Diabat, A.; Mirjalili, S.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Gandomi, A.H. The arithmetic optimization algorithm. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 376, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, M.; Jangir, P.; Kumar, B.S.; Sowmya, R.; Alhelou, H.H.; Abualigah, L.; Yildiz, A.R.; Mirjalili, S. A New Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm for Solving Real-World Multiobjective CEC-2021 Constrained Optimization Problems: Diversity Analysis and Validations. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 84263–84295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. On the performance of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2008, 8, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 7 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- El-Zonkoly, A.; dos Santos Coelho, L. Optimal allocation, sizing of PHEV parking lots in distribution system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 67, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderipour, A.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Nowdeh, S.A.; Gandoman, F.H.; Moghaddam, M.J.H. A Multi-Objective Optimization Problem for Optimal Site Selection of Wind Turbines for Reduce Losses and Improve Voltage Profile of Distribution Grids. Energies 2019, 12, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arabi-Nowdeh, S.; Nasri, S.; Saftjani, P.B.; Naderipour, A.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Kamyab, H.; Jafar-Nowdeh, A. Multi-criteria optimal design of hybrid clean energy system with battery storage considering off- and on-grid application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowdeh, S.A.; Davoudkhani, I.F.; Moghaddam, M.H.; Najmi, E.S.; Abdelaziz, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Razavi, S.; Gandoman, F. Fuzzy multi-objective placement of renewable energy sources in distribution system with objective of loss reduction and reliability improvement using a novel hybrid method. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 77, 761–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ebadi, A.G.; Toughani, M.; Nowdeh, S.A.; Naderipour, A.; Abdullah, A. Designing framework of hybrid photovoltaic-biowaste energy system with hydrogen storage considering economic and technical indices using whale optimization algorithm. Energy 2022, 238, 121555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahannoush, M.; Nowdeh, S.A. Optimal designing and management of a stand-alone hybrid energy system using meta-heuristic improved sine–cosine algorithm for Recreational Center, case study for Iran country. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 96, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.; Wu, F. Network reconfiguration in distribution systems for loss reduction and load balancing. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1989, 4, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization of Renewable Energy and Electricity Energy Efficiency, Tehran, Iran. Available online: http://www.satba.gov.ir/ (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Taylor, M.; Ralon, P.; Anuta, H.; Al-Zoghoul, S. Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2019; International Renewable Energy Agency: Masdar City, United Arab Emirates, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, E.; Abd-Elazim, S.; Abdelaziz, A. Ant Lion Optimization Algorithm for optimal location and sizing of renewable distributed generations. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaaeldin, I.; Abdel Aleem, S.; El-Rafei, A.; Abdelaziz, A.; Zobaa, A.F. Optimal network reconfiguration in active distribution networks with soft open points and distributed generation. Energies 2019, 12, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Item | Cost of Power Loss (USD) | Cost of Grid Power (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Min Voltage (p.u) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 57.02 | 75,011 | 75,068 | 0.9134 |
| Size/@Bus | WT 1 | WT 2 | WT 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case#1 | 429/@6 | --/-- | 500/@30 |
| Case#2 | 500/@8 | --/-- | 500/18 |
| Case#3 | 500/@6 | 500/@18 | 500/@30 |
| Size/@Bus | PHEV 1 | PHEV 2 | PHEV 3 | PHEV 4 | PHEV 5 | PHEV 6 | PHEV 7 | PHEV 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case#1 | 2000/@12 | 2000/@15 | 2000/@17 | 2000/@28 | 2000/@32 | 2000/@21 | --/-- | 2000/@24 |
| Case#2 | --/-- | 1601/@17 | --/-- | 1974/@21 | --/-- | 1697/@24 | --/-- | 1204/@32 |
| Case#3 | --/-- | 1059/@8 | --/-- | 1789/@16 | --/- | 1195/@28 | 1059/@32 | --/-- |
| Item/Case | Case#1 | Case#2 | Case#3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost of power loss (USD) | 29.68 | 31.25 | 44.60 |
| Cost of grid (USD) | 47012 | 45,876 | 29,271 |
| Cost of PHEV (USD) | 547.16 | 312.84 | 201.28 |
| Cost of WTs (USD) | 995.17 | 1071.22 | 1606.84 |
| Total cost (USD) | 48,584 | 47,291 | 31,123 |
| Voltage deviation (p.u) | 0.1779 | 0.0504 | 0.0631 |
| Method/Size/@Bus | WT 1 | WT 2 | WT 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AOA | 500/@6 | 500/@18 | 500/@30 |
| PSO | 500/@8 | 500/@16 | 500/@29 |
| ABC | 495/@6 | 467/@18 | 495/@28 |
| Method/Size/@Bus | PHEV 1 | PHEV 2 | PHEV 3 | PHEV 4 | PHEV 5 | PHEV 6 | PHEV 7 | PHEV 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOA | --/@-- | 1059/@8 | --/@-- | 1789/@16 | --/@- | 1195/@28 | 1059/@32 | --/@-- |
| PSO | --/@-- | 2000/@12 | --/@-- | 2000/@17 | --/@-- | --/@-- | 2000/@28 | 2000/@32 |
| ABC | --/@-- | 1536/@15 | --/@-- | 1962/@21 | --/@- | 1006/@30 | --/@-- | --/@-- |
| Item/Case | AOA | PSO | ABC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost of power loss (USD) | 44.60 | 44.81 | 45.07 |
| Cost of grid (USD) | 29,271 | 29,364 | 30,690 |
| Cost of PHEV (USD) | 201.28 | 238.50 | 184.33 |
| Cost of WTs (USD) | 1606.84 | 1617.35 | 1560.77 |
| Total cost (USD) | 31,123 | 31,264 | 32,480 |
| Voltage deviation (p.u) | 0.0631 | 0.0648 | 0.0726 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahrokhi, S.; El-Shahat, A.; Masoudinia, F.; Gandoman, F.H.; Abdel Aleem, S.H.E. Sizing and Energy Management of Parking Lots of Electric Vehicles Based on Battery Storage with Wind Resources in Distribution Network. Energies 2021, 14, 6755. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206755
Shahrokhi S, El-Shahat A, Masoudinia F, Gandoman FH, Abdel Aleem SHE. Sizing and Energy Management of Parking Lots of Electric Vehicles Based on Battery Storage with Wind Resources in Distribution Network. Energies. 2021; 14(20):6755. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206755
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahrokhi, Saman, Adel El-Shahat, Fatemeh Masoudinia, Foad H. Gandoman, and Shady H. E. Abdel Aleem. 2021. "Sizing and Energy Management of Parking Lots of Electric Vehicles Based on Battery Storage with Wind Resources in Distribution Network" Energies 14, no. 20: 6755. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206755
APA StyleShahrokhi, S., El-Shahat, A., Masoudinia, F., Gandoman, F. H., & Abdel Aleem, S. H. E. (2021). Sizing and Energy Management of Parking Lots of Electric Vehicles Based on Battery Storage with Wind Resources in Distribution Network. Energies, 14(20), 6755. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206755








