The Optimal Pumping Power under Different Ice Slurry Concentrations Using Evolutionary Strategy Algorithms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
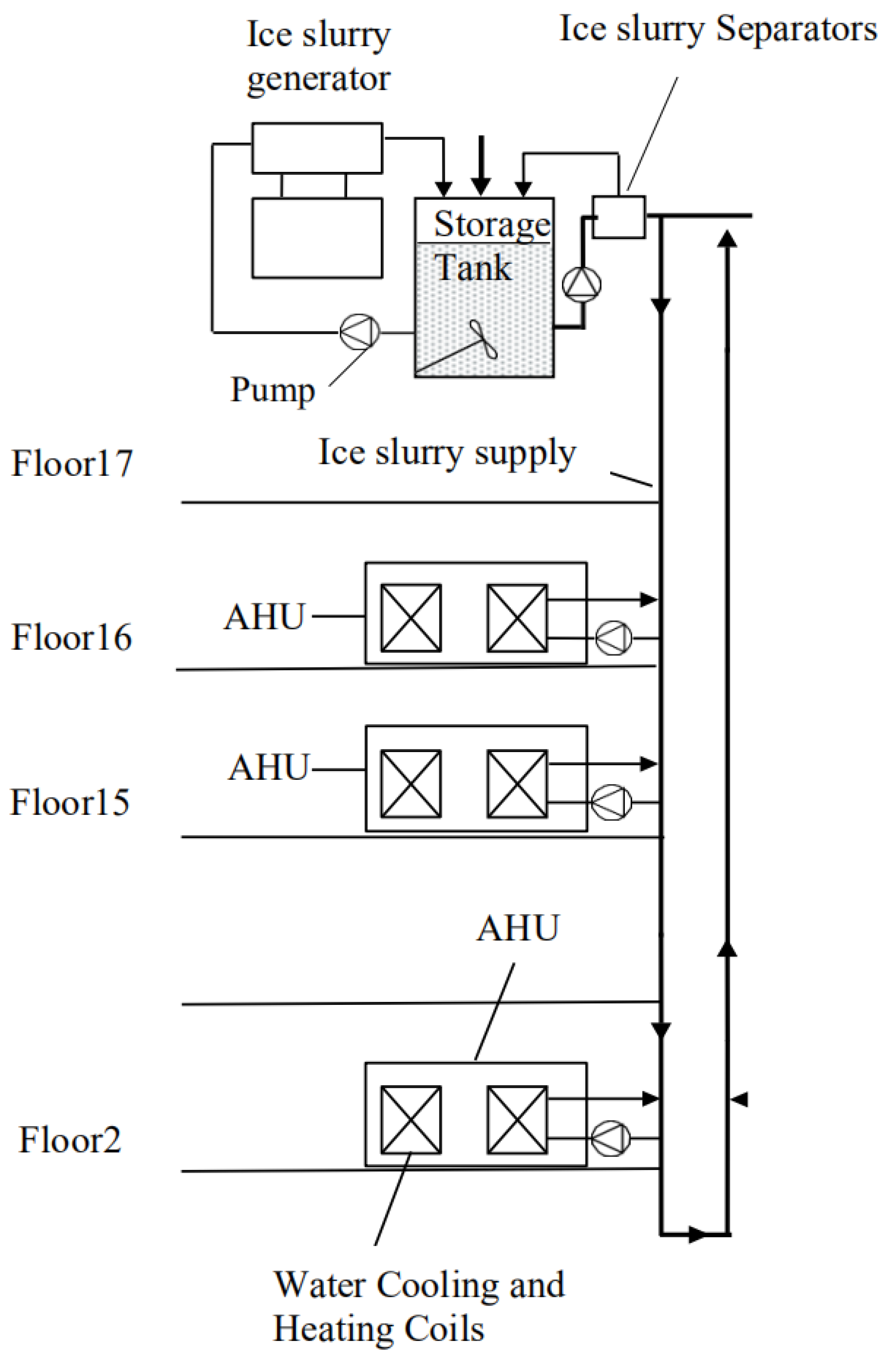
2.1. Ice Slurry Refrigeration System
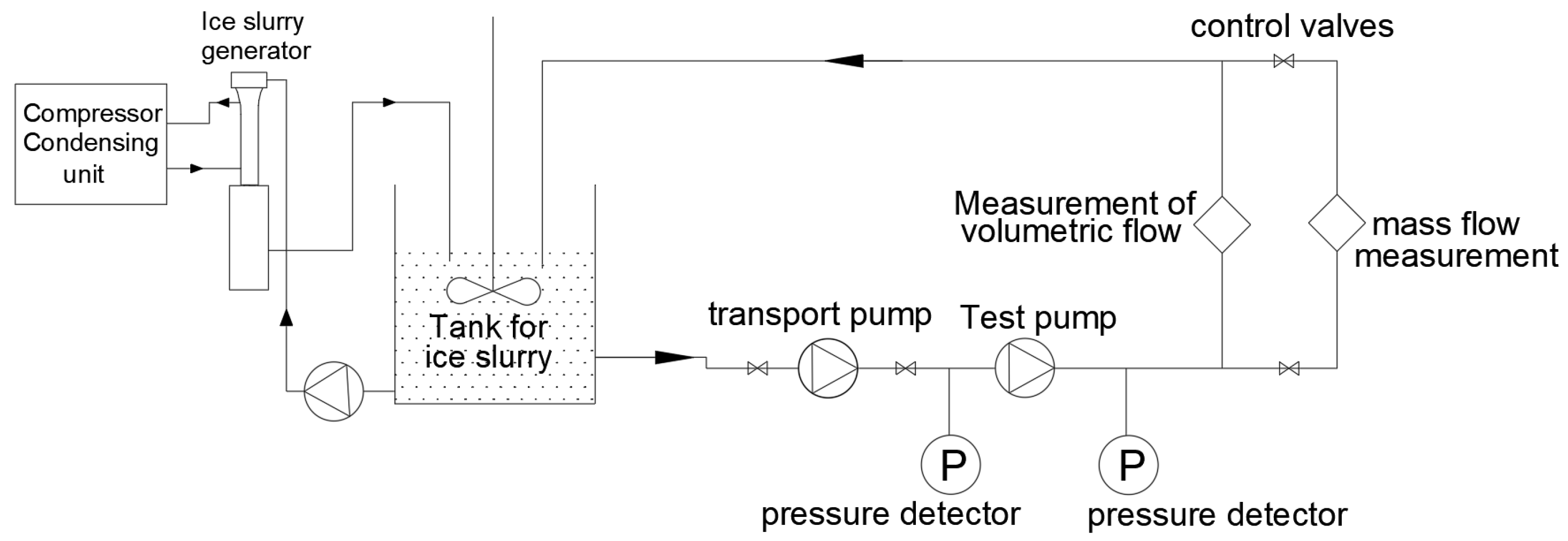
2.2. Simulation Models/Methods
3. Results
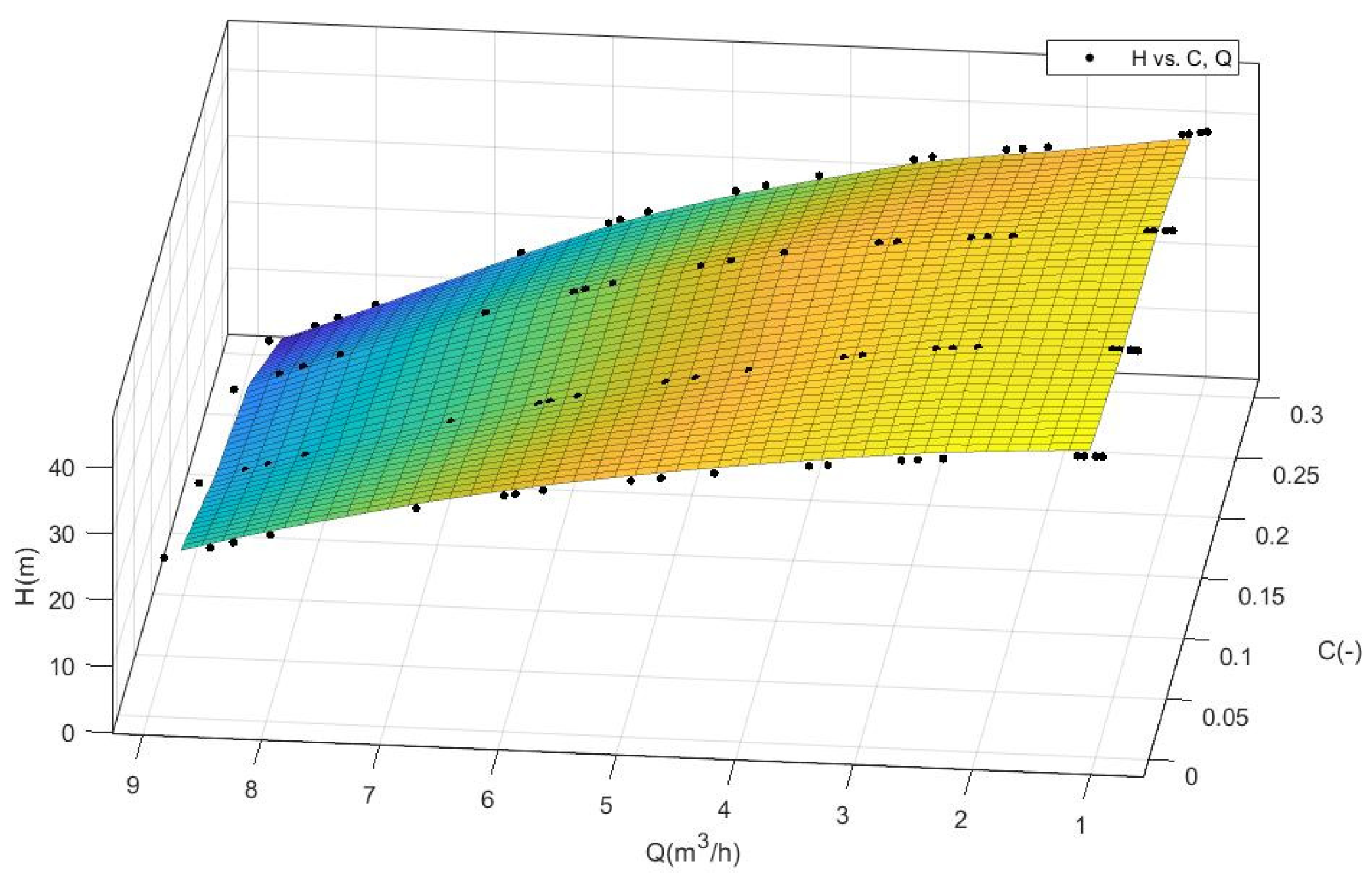
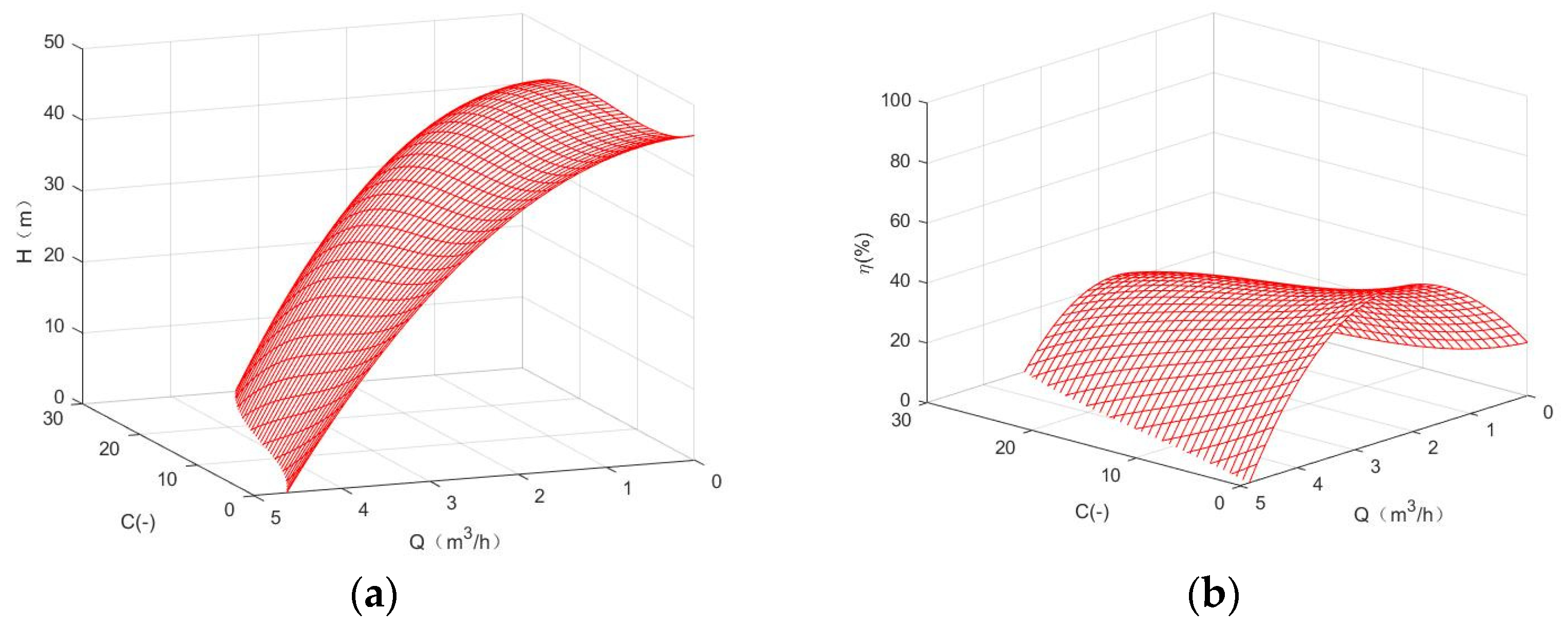
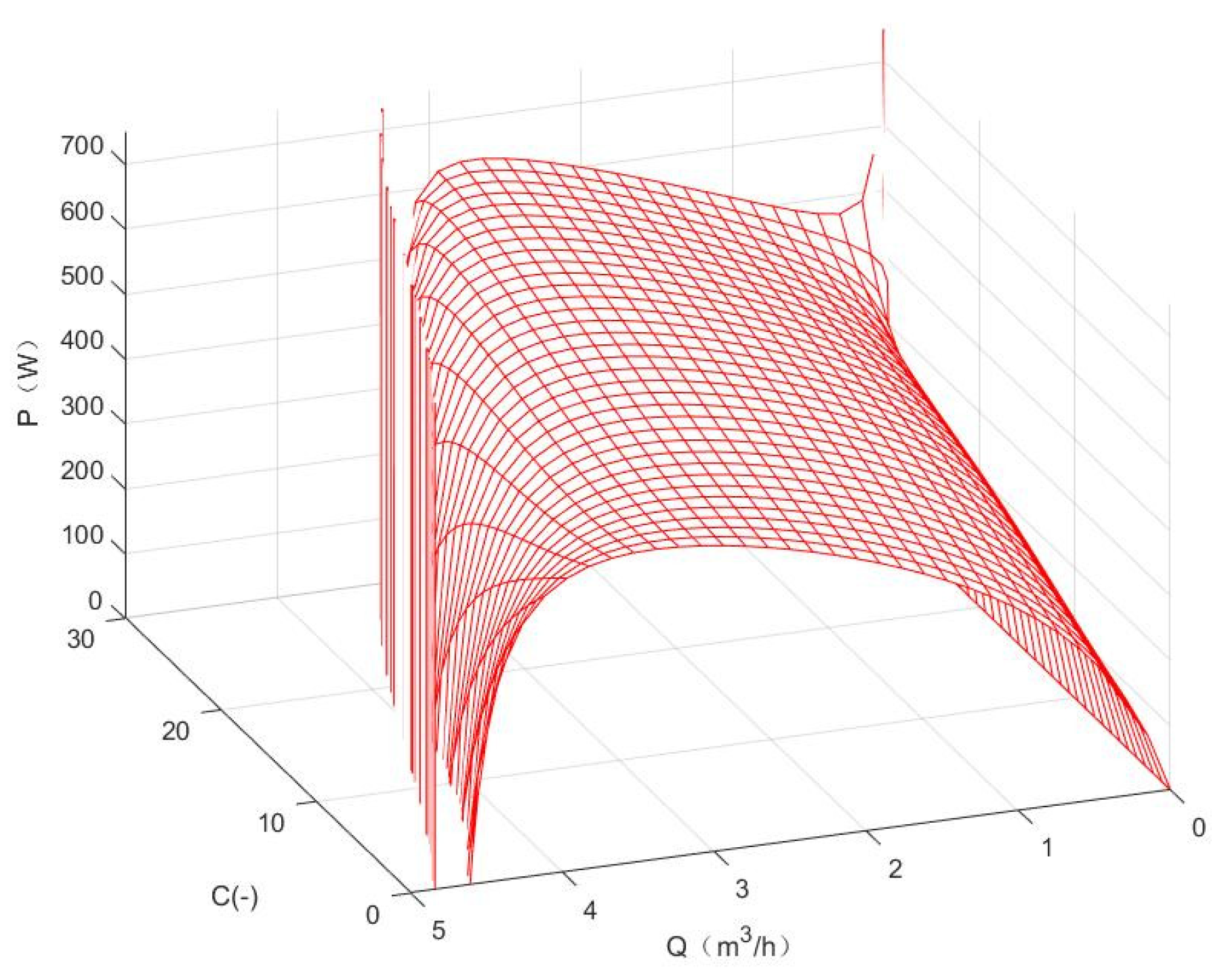
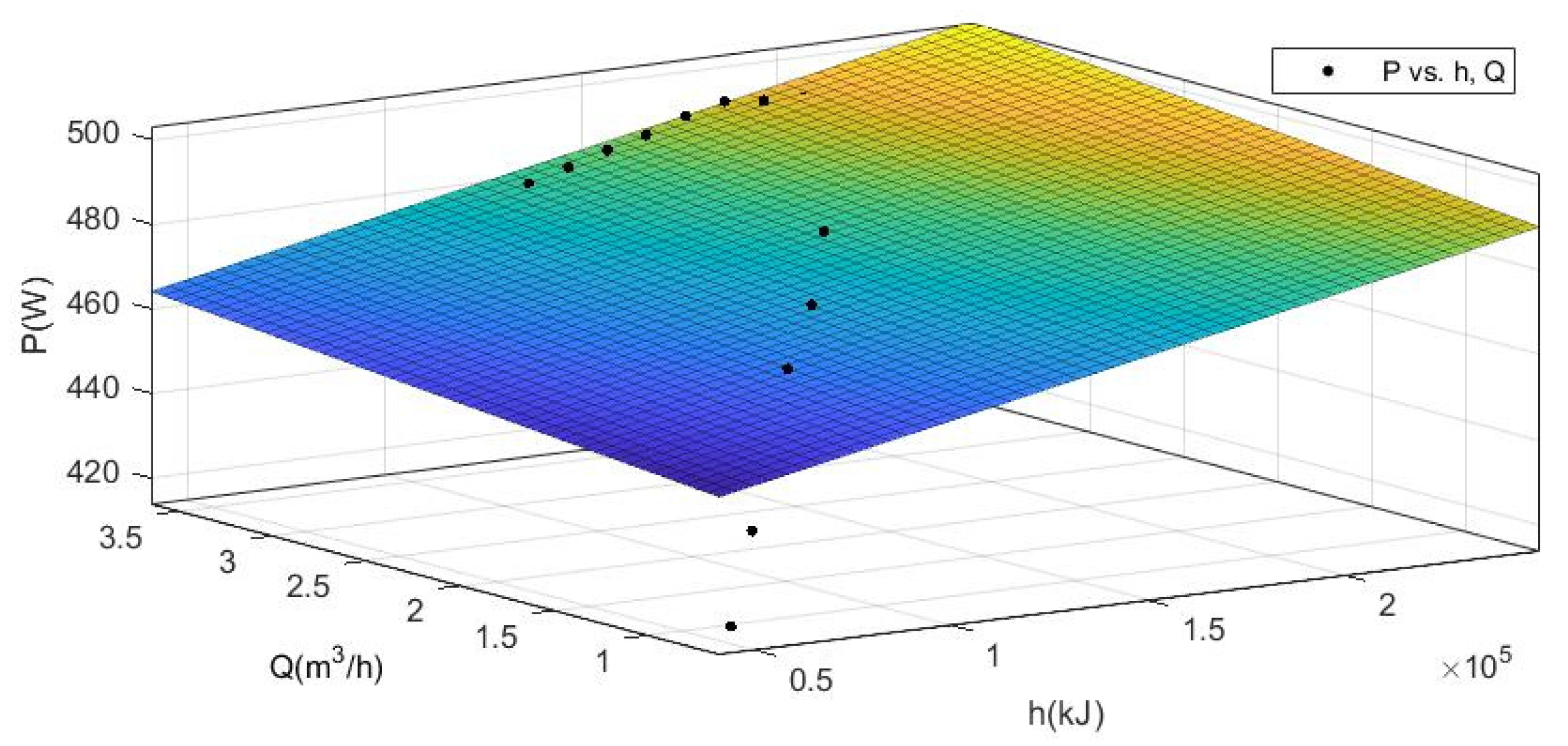
3.1. Empirical Function Diagram
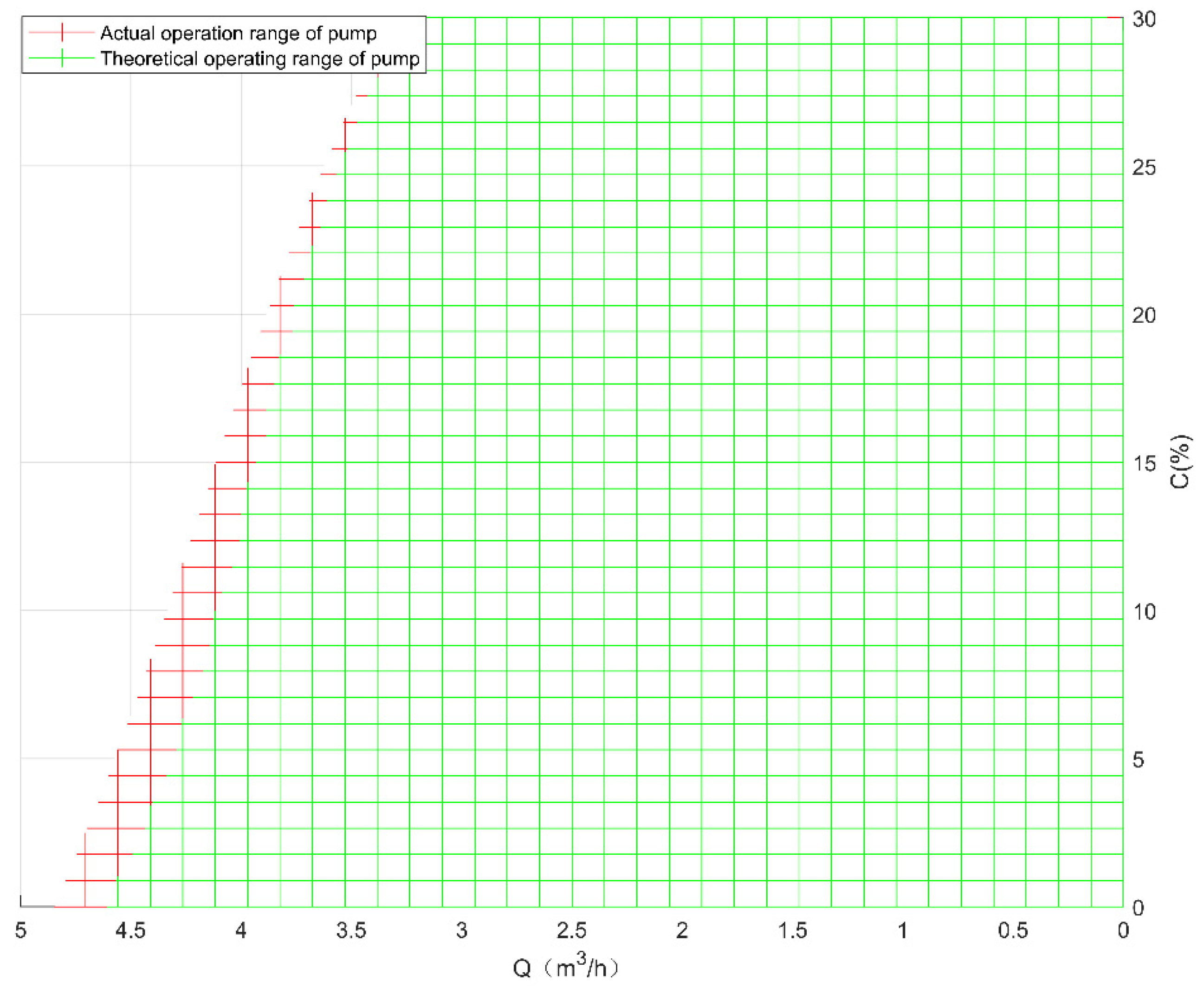
3.2. The Operation Range of Pump
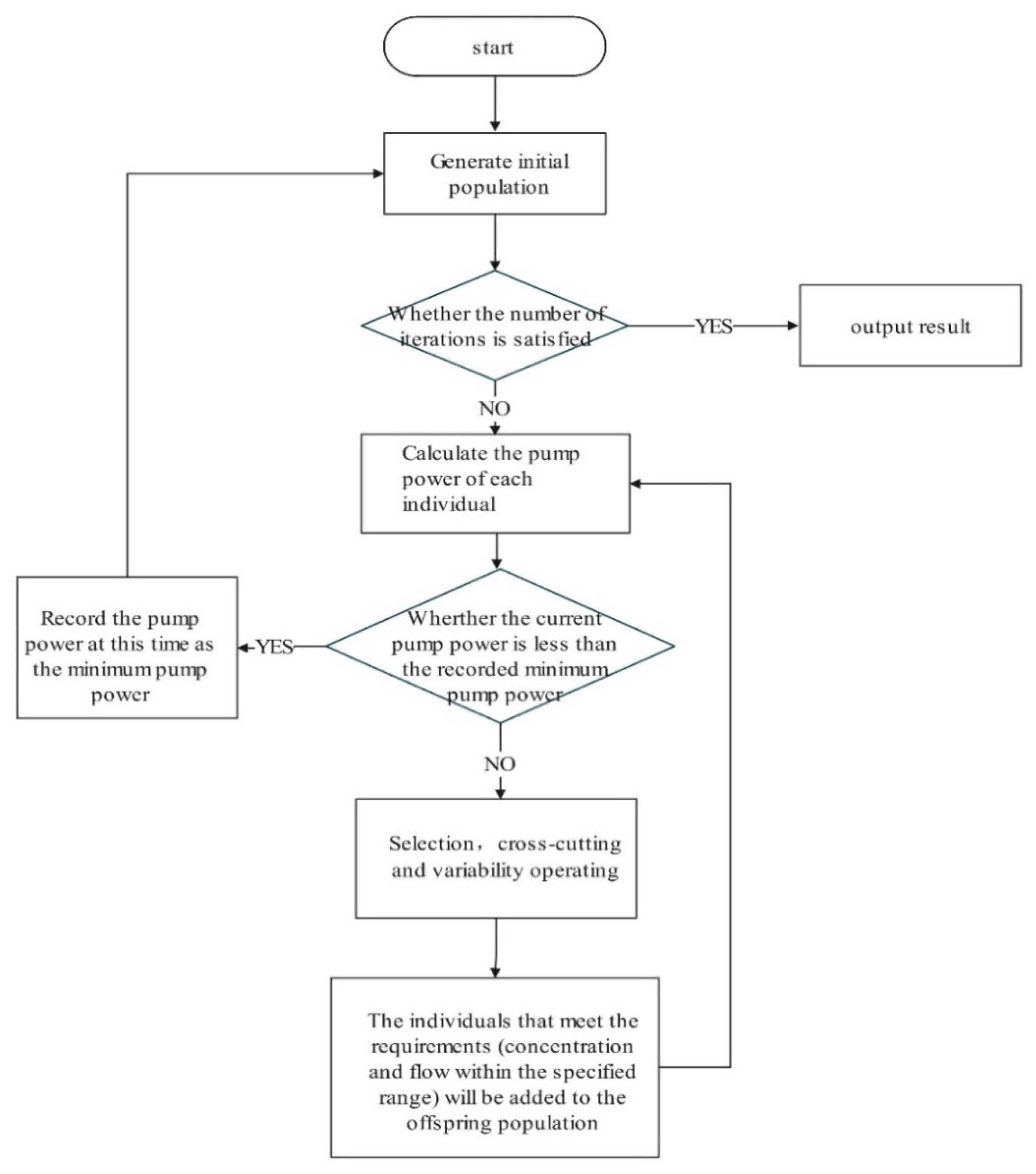
3.3. Apply the Optimal Algorithm
3.4. Comparison under Different Cooling Capacity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Illán, F.; Viedma, A. Heat exchanger performance modeling using ice slurry as secondary refrigerant. Int. J. Refrig. 2012, 35, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, J.E.; Ribeiro, R.P.P.L.; Castro, P.J.; Mota, J.P.B.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Absorption of Fluorinated Greenhouse Gases Using Fluorinated Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20769–20778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, P.; Oglund-Isaksson, L.H. Global emissions of fluorinated greenhouse gases 2005–2050 with abatement potentials and costs. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2795–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sosa, J.E.; Malheiro, C.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Castro, P.J.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Araújo, J.M.; Plantier, F.; Mota, J.P.; Pereiro, A.B. Adsorption of fluorinated greenhouse gases on activated carbons: Evaluation of their potential for gas separation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 1892–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, I.; Tassou, S.A. Present and future applications of ice slurries. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumano, H.; Hirata, T.; Shirakawa, M.; Shouji, R.; Hagiwara, Y. Flow characteristics of ice slurry in narrow tubes. Int. J. Refrig. 2010, 33, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffeld, M.; Wang, M.J.; Goldstein, V.; Kasza, K.E. Ice slurry applications. Int. J. Refrig. 2010, 33, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vetterli, J.; Benz, M. Cost-optimal design of an ice-storage cooling system using mixed-integer linear programming techniques under various electricity tariff schemes. Energy Build. 2012, 49, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze, G.P.; Krarti, M.; Brandemuehl, M.J. Guidelines for improved performance of ice storage systems. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Chen, Y.T.; Wu, T. Optimization for ice-storage air-conditioning system using particle swarm algorithm. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ise, H.; Tanino, M.; Kozawa, Y. Ice Storage System in Kyoto Station Building. In Proceedings of the Information Booklet for the Technical Tour of the Fourth IIR Workshop on Ice Slurries, Kyoto, Japan, 13 November 2001; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kousksou, T.; Arid, A.; Majid, J.; Zeraouli, Y. Numerical modeling of double-diffusive convection in ice slurry storage tank. Int. J. Refrig. 2010, 33, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, B.; Huber, H. Characteristics of different pump types operating with ice slurry. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgaard, E.; Sørensen, T.A.; Hansen, T.M.; Kauffeld, M. Performance of components of ice slurry systems: Pumps, plate heat exchangers, and fittings. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumano, H.; Hirata, T.; Shouji, R.; Shirakawa, M. Experimental study on heat transfer characteristics of ice slurry. Int. J. Refrig. 2010, 33, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žurovec, D.; Jezerská, L.; Nečas, J.; Hlosta, J.; Diviš, J.; Zegzulka, J. Spiral Vibration Cooler for Continual Cooling of Biomass Pellets. Processes 2021, 9, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.H.; Ledesma, J.R.; Carrêlo, I.B.; Narvarte, L.; Ferrara, G.; Antipodi, L. A new pump selection method for large-power PV irrigation systems at a variable frequency. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 174, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Sha, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Performance evaluation and working fluid selection of combined heat pump and power generation system (HP-PGs) using multi-objective optimization. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 221, 113164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chao, Q.; Xu, B. Analysis of the cylinder block tilting inertia moment and its effect on the performance of high-speed electro-hydrostatic actuator pumps of aircraft. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warguła, A.; Kukla, M. Determination of maximum torque during carpentry waste comminution. Wood Res.-Slovak. 2020, 65, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, E.; Shin, Y.; Kim, S.; Min, S.; Ahn, S. Power Consumption Assessment of Machine Tool Feed Drive Units. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 7, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nang, N.; Matsuo, T.; Koumoto, T.; Inaba, S. Measurement of the properties of agricultural tire for tractor dynamic analyses (Part 1)-Determination of drive tire stiffness and damping from static tests. J. Jpn. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2009, 71, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Klarecki, K.; Rabsztyn, D.; Hetmańczyk, M.P. Influence of the Controller Settings on the Behaviour of the Hydraulic Servo Drive; Awrejcewicz, J., Szewczyk, R., Trojnacki, M., Kaliczyńska, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Warguła, A.; Kukla, M.; Krawiec, P.; Wieczorek, B. Impact of Number of Operators and Distance to Branch Piles on Woodchipper Operation. Forests 2020, 11, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paryanto; Brossog, M.; Bornschlegl, M.; Franke, J. Reducing the energy consumption of industrial robots in manufacturing systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 78, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchmacz, J.; Niezgoda-Żelasko, B. Ice slurry flow through a vertical slit channel. Int. J. Refrig. 2021, 128, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, T.; Komatsu, W.; Kimata, H.; Kato, M.; Kumano, H. Solidification behavior of an ice slurry flowing in a rectangular channel. Int. J. Refrig. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffeld, M.; Kawaji, M.; Egolf, P.W. Handbook_on_ice_slurries. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 3, 415–427. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, T.W. Slurry ice as a heat transfer fluid with a large number of application domains. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanovski, A.; Vuarnoz, D.; Ata-Caesar, D.; Egolf, P.W.; Hansen, T.M.; Doetsch, C. The fluid dynamics of ice slurry. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Gen, M.; Chien, C. Hybrid Sampling Strategy-based Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2012, 12, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Pedrycz, W.; Suganthan, P.N.; Mallipeddi, R. A variable reduction strategy for evolutionary algorithms handling equality constraints. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 37, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, E.F.; Kagan, N.; Ribeiro, P.F. Three-phase harmonic distortion state estimation algorithm based on evolutionary strategies. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2010, 80, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Hou, W.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Z. Two new reference vector adaptation strategies for many-objective evolutionary algorithms. Inf. Sci. 2019, 483, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Yan, Q.; Tian, W.; Guan, D.; Lee, S. Replica creation strategy based on quantum evolutionary algorithm in data gird. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2013, 42, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lin, W.; Lin, Q.; Ming, Z. Balancing Convergence and Diversity in Multiobjective Immune Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Dali, China, 14–16 August 2020; pp. 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, N.; Tsang, E. Bargaining strategies designed by evolutionary algorithms. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 4701–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.S. Optimization of thermoelectric modules for maximum cooling capacity. Cryogenics 2021, 114, 103241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
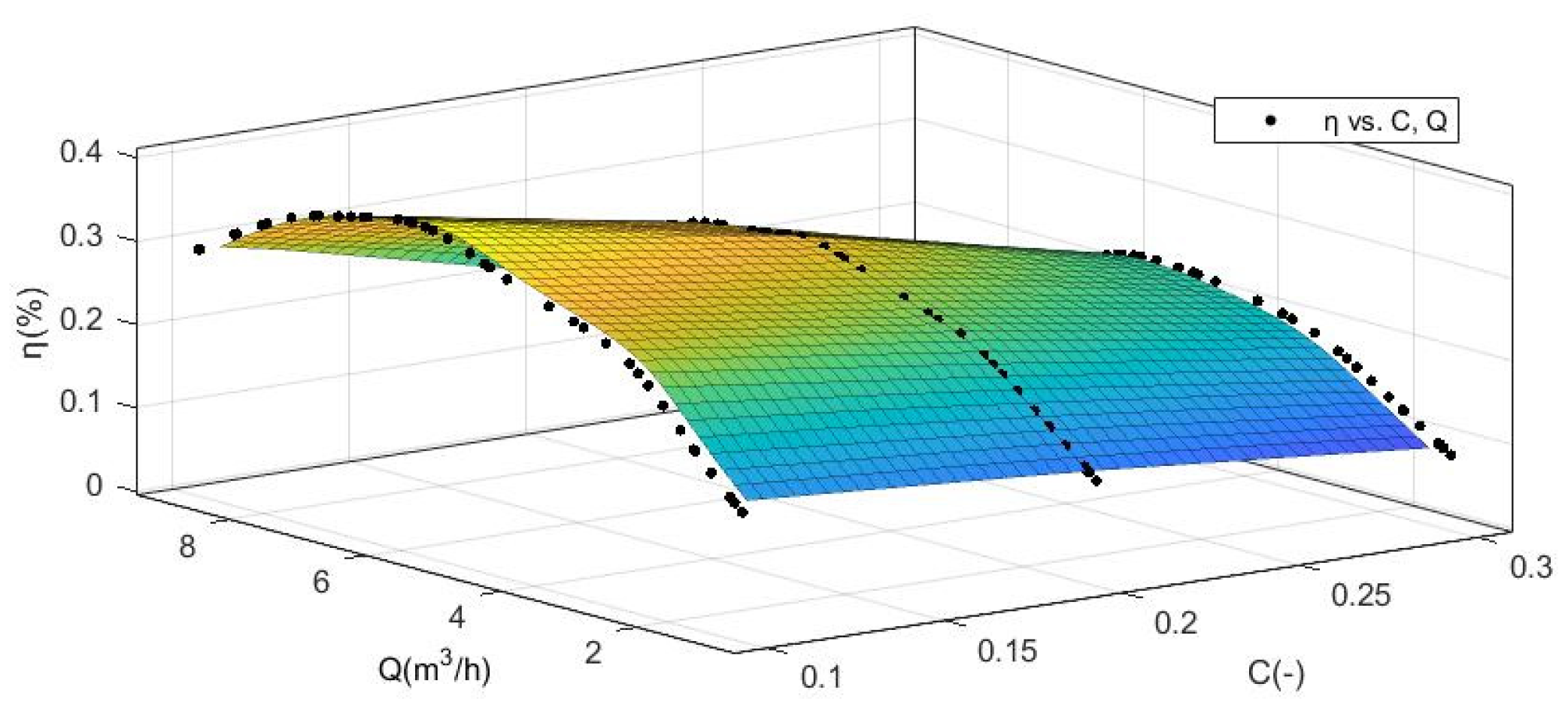

| Q | (C = 0%) | (C = 10%) | (C = 20%) | (C = 30%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ×10−4 (m3/s) | % | % | % | % |
| 0.933 | 17.832 | 14.991 | 12.151 | 8.581 |
| 1.043 | 19.777 | 15.882 | 12.928 | 9.182 |
| 1.098 | 20.715 | 16.324 | 13.316 | 9.483 |
| 1.116 | 21.022 | 16.471 | 13.446 | 9.583 |
| 1.391 | 25.338 | 18.725 | 15.386 | 11.084 |
| 1.629 | 28.636 | 20.821 | 17.062 | 12.381 |
| 1.647 | 28.903 | 20.988 | 17.190 | 12.481 |
| 1.848 | 32.093 | 22.861 | 18.597 | 13.571 |
| 2.104 | 35.093 | 25.246 | 20.366 | 14.946 |
| 2.324 | 36.718 | 27.193 | 21.849 | 16.103 |
| 2.470 | 37.715 | 28.361 | 22.808 | 16.853 |
| 2.598 | 38.627 | 29.240 | 23.614 | 17.477 |
| 2.946 | 40.710 | 30.935 | 25.387 | 18.889 |
| 3.276 | 42.162 | 32.063 | 26.370 | 19.836 |
| 3.422 | 42.737 | 32.508 | 26.787 | 20.179 |
| 3.788 | 44.070 | 33.544 | 27.907 | 20.915 |
| 4.410 | 46.024 | 35.407 | 29.855 | 21.878 |
| 4.666 | 46.678 | 36.316 | 30.629 | 22.170 |
| 4.739 | 46.849 | 36.578 | 30.843 | 22.240 |
| 4.959 | 47.334 | 37.346 | 31.445 | 22.407 |
| 5.288 | 48.030 | 38.391 | 32.026 | 22.511 |
| 5.508 | 48.535 | 38.920 | 31.804 | 22.454 |
| 5.618 | 48.896 | 39.097 | 31.615 | 22.373 |
| 5.801 | 49.279 | 39.226 | 31.406 | 22.130 |
| 5.856 | 49.316 | 39.224 | 31.357 | 22.022 |
| 6.020 | 49.387 | 39.123 | 31.227 | 21.547 |
| 6.459 | 49.388 | 38.440 | 30.904 | 19.186 |
| 6.533 | 49.362 | 38.300 | 30.838 | 18.774 |
| 6.716 | 49.254 | 37.943 | 30.618 | 17.795 |
| 6.899 | 49.069 | 37.595 | 30.252 | 16.857 |
| 7.191 | 48.607 | 37.044 | 29.317 | 15.393 |
| 7.265 | 48.463 | 36.881 | 29.048 | 15.029 |
| 7.594 | 47.727 | 35.925 | 27.773 | 13.280 |
| 7.960 | 46.862 | 34.453 | 26.241 | 10.687 |
| 7.978 | 46.818 | 34.371 | 26.160 | 10.537 |
| 8.033 | 46.688 | 34.118 | 25.910 | 10.080 |
| 8.399 | 45.825 | 32.301 | 23.738 | 6.817 |
| 8.436 | 45.740 | 32.109 | 23.456 | 6.478 |
| 8.948 | 44.348 | 29.261 | 19.119 | 1.624 |
| 8.966 | 44.285 | 29.153 | 18.943 | 1.449 |
| Q | H (C = 0%) | H (C = 10%) | H (C = 20%) | H (C = 30%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ×10−4 (m3/s) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) |
| 0.938 | 45.336 | 43.123 | 43.024 | 39.705 |
| 0.996 | 45.311 | 43.113 | 42.942 | 39.552 |
| 1.094 | 45.268 | 43.097 | 42.806 | 39.298 |
| 1.152 | 45.239 | 43.087 | 42.724 | 39.146 |
| 2.285 | 44.004 | 42.499 | 41.103 | 36.381 |
| 2.500 | 43.657 | 42.208 | 40.776 | 35.960 |
| 2.637 | 43.425 | 41.978 | 40.561 | 35.704 |
| 3.262 | 42.274 | 40.501 | 39.485 | 34.142 |
| 3.418 | 41.966 | 40.050 | 39.179 | 33.615 |
| 4.219 | 40.264 | 37.500 | 37.132 | 30.550 |
| 4.668 | 39.213 | 36.037 | 35.529 | 28.731 |
| 4.922 | 38.584 | 35.189 | 34.515 | 27.696 |
| 5.664 | 36.567 | 32.477 | 31.333 | 24.050 |
| 5.898 | 35.862 | 31.530 | 30.265 | 22.634 |
| 5.996 | 35.558 | 31.122 | 29.810 | 22.015 |
| 6.738 | 33.037 | 27.828 | 26.119 | 16.992 |
| 7.969 | 28.075 | 21.828 | 18.798 | 8.209 |
| 8.281 | 26.679 | 20.206 | 16.766 | 5.994 |
| 8.477 | 25.786 | 19.167 | 15.485 | 4.639 |
| 8.867 | 23.939 | 17.024 | 12.915 | 2.052 |
| h (kJ) | C (−) | Q (m3/h) | P (W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50,000 | 0.2019 | 0.742 | 417.7741 |
| 60,000 | 0.2145 | 0.838 | 438.0961 |
| 70,000 | 0.2259 | 0.9281 | 455.7548 |
| 80,000 | 0.2244 | 1.068 | 471.3064 |
| 90,000 | 0.2324 | 1.1488 | 484.3047 |
| 100,000 | 0.2321 | 1.2917 | 498.7775 |
| 110,000 | 0.2045 | 3.4994 | 475.4409 |
| 120,000 | 0.2357 | 3.499 | 477.3328 |
| 130,000 | 0.2014 | 3.4985 | 480.6834 |
| 140,000 | 0.2219 | 3.4963 | 483.3599 |
| 150,000 | 0.2056 | 3.4978 | 486.1921 |
| 160,000 | 0.2136 | 3.4999 | 488.5491 |
| 170,000 | 0.2145 | 3.4994 | 491.9074 |
| 180,000 | 0.2096 | 3.4987 | 494.1524 |
| 190,000 | 0.2101 | 3.4998 | 493.1199 |
| 200,000 | 0.2121 | 3.4978 | 492.5956 |
| 210,000 | 0.2125 | 3.4984 | 491.9436 |
| 220,000 | 0.2118 | 3.4996 | 491.8095 |
| 230,000 | 0.2122 | 3.4995 | 491.532 |
| 240,000 | 0.2115 | 3.4993 | 492.2494 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, S.; Zhou, W.; Lu, J.; Wang, J. The Optimal Pumping Power under Different Ice Slurry Concentrations Using Evolutionary Strategy Algorithms. Energies 2021, 14, 6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206738
Hao S, Zhou W, Lu J, Wang J. The Optimal Pumping Power under Different Ice Slurry Concentrations Using Evolutionary Strategy Algorithms. Energies. 2021; 14(20):6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206738
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Shuai, Wenjie Zhou, Junliang Lu, and Jiajun Wang. 2021. "The Optimal Pumping Power under Different Ice Slurry Concentrations Using Evolutionary Strategy Algorithms" Energies 14, no. 20: 6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206738
APA StyleHao, S., Zhou, W., Lu, J., & Wang, J. (2021). The Optimal Pumping Power under Different Ice Slurry Concentrations Using Evolutionary Strategy Algorithms. Energies, 14(20), 6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206738





