Quantitative Analysis of Sustainable Transport Development as a Support Tool for Transport System Management: Spatial Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Presentation of Research Methods and Selection of Potential Data Set
4. Research Results and Its Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gratiela, B. Sustainable consumption in the area of transportation. Constanta Marit. Univ. Ann. 2013, 14, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Air Pollution: Our Health Still Does Not Have Sufficient Protection; Special Report Persulant to Article 287(4), Second Subparagraph; TFEU/European Court of Auditors: Luxembourg, 2018. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/webpub/eca/special-reports/air-quality-23-2018/en/ (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Kumar, S.; Hoffmann, J. Globalization: The Maritime nexus. In Handbook of Maritime Economics and Business; Grammenos, C., Ed.; Loyds List Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 35–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bąk, I.; Barwińska-Małajowicz, A.; Wolska, G.; Walawender, P.; Hydzik, P. Is the European Union Making Progress on Energy Decarbonisation While Moving twoards Sustaianble Development? Energies 2021, 14, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roadmap to a Single European Transport Area—Towards a Competitive and Resource Efficient Transport System; White Paper; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52011DC0144 (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Persia, L.; Cipriani, E.; Sgarra, V.; Meta, E. Strategies and measures for sustainable transport systems. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López, E.; Guitérrez, J.; Gómez, G. Measuring regional cohesion effects on large-scale transport infrastructure investments: An accessibility approach. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2008, 16, 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Our Common Future. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development. Available online: http://www.un-documents.net/wced-ocf.htm (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- United Nations. Report of the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development, Rio de Janeiro, 3–14 June 1992. Volume 2, Proceedings of the Conference; UN: New York, NY, USA, 1993; ISBN 921-100498-5. Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/168679#record-files-collapse-header (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Garrigos-Simon, F.; Botella-Carrubi, D.; González-Cruz, T. Social Capital, Human Capital, and Sustainability: A Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, S.M.; Munasinghe, M.; Clarke, M. Making long-term economic growth more sustainable: Evaluating the costs and benefits. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 47, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, G. Constructing definitions of sustainable development. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2017, 6, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckerman, W. ‘Sustainable development’: Is it a useful concept? In The Economics of Sustainability; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, H.E. Sustainable development—Definitions, principles, policies. In The Future of Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Franks, T.R. Managing sustainable development: Definitions, paradigms, and dimensions. Sustain. Dev. 1996, 4, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel, J.; Smith, R.; Ubbels, B. The Impact of Transport Investments on Competitiveness. Transp. Res. Procedia 2014, 1, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purwanto, A.J.; Heyndrickx, C.; Kiel, J.; Betancor, O.; Socorro, M.P.; Hernandez, A.; Eugenio-Martin, J.L.; Pawlowska, B.; Borkowski, P.; Fiedler, R. Impact of Transport Infrastructure on International Competitiveness of Europe. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 25, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelakowski, A.S. The concept of internalisation of the external costs of transport in the EU’ and its impact on the efficiency of transport systems and the performance of logistics supply chains. Prace Naukowe Uniwersytetu Ekonomicznego we Wrocławiu 2020, 64, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatziioannou, I.; Alvarez-Icaza, L.; Bakogiannis, E.; Kyriakidis, C.; Chias-Becerril, L. A Structural Analysis for the Categorization of the Negative Externalities of Transport and the Hierarchical Organization of Sustainable Mobility’s Strategies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Huang, Y.; Scholts, S.; Woensel, T. A selected review on the negative externalities of the freight transportation: Modeling and pricing. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 77, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, T.; Burwell, D. Issues in sustainable transportation. Int. J. Glob. Environ. Issues 2006, 4, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprocki, W. Transport drogowy. In System Transportowy Polski; Pieriegud, J., Ed.; SGH: Warszawa, Poland, 2015; pp. 13–35. [Google Scholar]
- Pawłowska, B. Koszty zewnętrzne transportu w Polsce. Przegląd Nauk. Inżynieria Kształtowanie Sr. 2018, 27, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strategia Rozwoju Transportu do 2020 r. (z perspektywą do 2030 r.).—M.P.2013.75. Available online: https://sip.lex.pl/akty-prawne/mp-monitor-polski/strategia-rozwoju-transportu-do-2020-r-z-perspektywa-do-2030-r-17953349 (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Grzelakowski, A. Zrównoważenie systemu transportowego drogą do nowoczesności sektora transportu UE. Logistyka 2014, 4, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar]
- Motowidlak, U. Rozwój transportu a paradygmat zrównoważonego rozwoju. Studia Ekon. 2017, 337, 138–152. [Google Scholar]
- Motowidlak, U.; Kujawa, M. Transport Towarów w Projekcie One Belt and One Road jako Component Globalnego Łańcucha Dostaw; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego: Łódź, Poland, 2018; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Tolley, R. Sustainable Transport; Woodhead: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ECMT. Assessment & Decision Making for Sustainable Transport, European Conference of Ministers of Transport; OECD: Paris, France, 2004; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Wiederkehr, P.; Gilbert, R.; Crist, P.; Caïd, N. Environmentally Sustainable Transport (EST): Concept, Goal, and Strategy—The OECD’s EST Project. Eur. J. Transp. Infrastruct. Res. 2004, 4, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borys, T. Zrównoważony rozwój–jak rozpoznać ład zintegrowany. Probl. Ekorozw. 2011, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Matuszczak, A. Koncepcja zrównoważonego rozwoju w obszarze ekonomicznym, środowiskowym i społecznym. Rocz. Ekon. Kuj.-Pomor. Szkoły Wyższej w Bydg. 2009, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Przybyłowski, A. Pomiar zrównoważonego rozwoju transportu w polskich województwach. Optim. Studia Ekon. 2014, 3, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusideł, E. Zbieżność poziomu rozwoju województw Polski w kontekście kształtowania ładu instytucjonalnego. Optim. Studia Ekon. 2014, 3, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panfiluk, E. Kształtowanie ładu przestrzennego w świetle koncepcji zrównoważonego rozwoju. Ekon. Sr. 2003, 1, 162–177. [Google Scholar]
- Klóska, R. Rozwój zrównoważony regionów w Polsce w ujęciu statystycznym. Prog. Econ. Sci. 2017, 4, 159–176. [Google Scholar]
- Adamowicz, M.; Smarzewska, A. Model oraz mierniki trwałego z zrównoważonego rozwoju obszarów wiejskich w ujęciu lokalnym [Model and indicators of sustainable development in rural areas from the local perspective]. Zesz. Nauk. SGGW Polityki Eur. Finans. i Mark. 2009, 1, 251–252. [Google Scholar]
- Figura, J. Taksonomia w Polityce Logistycznej Państwa [Taxonomy in Logistic Policy of State]; Uniwersytet Ekonomiczny: Katowice, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Janic, M. Sustainable Transport in the European Union: A Review of the Past Research and Future Ideas. Transp. Rev. 2006, 26, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheba, K.; Saniuk, S. Sustainable urban transport—The concept of measurement in the field of city logistics. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 16, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, S.; de Oliveira, J.A.P. Determinants of urban mobility in India: Lessons for promoting sustainable and inclusive urban transportation in developing countries. Transp. Policy 2016, 50, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malasek, J. A set of tools for making urban transport more sustainable. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markova, I.; Shubenkova, K.; Gabsalikhova, L. Analysis of the city transport system’s development strategy designed principles with account of risks and specific features of spatial development. Transp. Probl. 2017, 12, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Carreiro, I.; Monzon, A. Evaluating sustainability and innovation of mobility patterns in Spanish cities. Analysis by size and urban typology. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illahi, U.; Shafi Mir, M. Assessment of transport sustainability using a hybrid approach: A comperison of four metropolitan cities of India. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2021, 9, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiba-Janik, M.; Thompson, R.; Cheba, K. An assessment tool of the formulation and implementation a sustainable integrated passenger transport strategies. An example of selected European and Australian cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, H.; Garrick, N.W.; Atkinson-Palombo, C. Relationship between human capital and transportation sustainability for the United States and selected European Countries. J. Transp. Res. Board 2016, 2598, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gruyter, C.; Currie, G.; Rose, G. Sustainability measures of urban public transport in cities: A world review and focus on the Asia/Middle East Region. Sustainability 2017, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hajduk, S. Assessment of urban transport—A comparative analysis of selected cities by taxonomic methods. Econ. Manag. 2016, 8, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czech, A.; Lewczuk, J. Taxonomic and econometric analysis of road transport development in Poland—The voivodship approach. Ekon. Zarządzanie 2016, 4, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czech, A.; Lewczuk, J. Statistical assessment of the development of the transportation system in chosen countries—An international approach. Procedia Eng. 2017, 182, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanni, Z.; Khakpour, B.A.; Heydari, A. Evaluating the regional development of border cities by TOPSIS model (case study: Sistan and Baluchistan Province, Iran). Sustain. Cities Soc. 2014, 10, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, A.; Biezdudnaja, A.; Lewczuk, J.; Razumowskij, W. Quantitative assessment of urban transport development—A spatial approach. Eng. Manag. Prod. Serv. 2018, 10, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheba, K. Taksonomiczna analiza rozwoju transportu drogowego w Polsce [Taxonomic analysis of road transport development in Poland]. Logistyka 2011, 2, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, R.; Cervero, R. Travel and the built environment: A synthesis. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2001, 1780, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vörös, T.; Juhász, M.; Koppány, K. The measurement of indirect effects in project appraisal. Transp. Res. Procedia 2015, 13, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matteis, T.; Liedtke, G.; Wisetjindawat, W. A framework for incorporating market interactions in an agent based model for freight transport. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 12, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellwig, Z. Zastosowanie metody taksonomicznej do typologicznego podziału krajów ze względu na poziom ich rozwoju oraz zasoby i strukturę wykwalifikowanych kadr [Application of the taxonomy method to typology classification of the countries because of the development level or resources and the structure of human resources]. Przegląd Stat. 1968, 4, 307–327. [Google Scholar]
- Młodak, A. Analiza Taksonomiczna w Statystyce Regionalnej [Taxonomic Analysis in Regional Policy]; Difin: Warszawa, Poland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lira, J.; Wagner, W.; Wysocki, F. Mediana w Zagadnieniach Porządkowania Obiektów Wielocechowych [Median in the Ordering Issues of Multivariable Objects]. In Statystyka Regionalna w Służbie Samorządu Lokalnego i Biznesu [Regional statistics in duty of local government]; Paradysz, W.J., Ed.; Akademia Ekonomiczna: Poznań, Poland, 2002; pp. 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Jajuga, K.; Walesiak, M. Standardization of data set under different measurement scales. In Classification and Information Processing at the Turn of the Millennium; Decker, R., Gaul, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zielińska-Sitkiewicz, M. The impact of normalization procedures on the classification of building material companies listed on the Warsaw Stocl Exchange. Polityki Eur. Finans. Mark. 2017, 18, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębkowska, K.; Jarocka, M. The impact of the method of the data normalization on the results. Folia Oeconomica 2013, 286, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Czech, A. Application of chosen normalization methods in the process of construction of synthetic measure in indirect consumption research. Folia Oeconomica 2014, 3, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Czech, A.; Lewczuk, J.; Bortłomiuk, A. Multidimensional assessment of the European Union transport development in the light of implemented normalization methods. Econ. Manag. 2016, 8, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steal, D.; Marshall, S. The relationship between urban form and travel patterns. Int. Rev. Eval. Eur. J. Transp. Infrastruct. Res. 2001, 1, 113–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Diaz, I.; Holguin-Veras, J.; Wang, X. An exploratory analysis of spatial effects on fright trip attraction. Transportation 2014, 43, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ducret, R.; Lemarié, B.; Roset, A. Cluster analysis and spatial modeling for urban fright. Identifying homogeneous urban zones based on urban form and logistics characteristics. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 12, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gratiela, B.; Viorela-Georgiana, C. Sustainable transport’s indicators. Comparative study: Eu-27 and Romania. Constanta Marit. Univ. Ann. 2013, 14, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, H.; Li, Y. Assessment of sustainable transport development based on entropy and unascertained measure. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litman, T. Developing indicators for comprehensive and sustainable transport planning. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2007, 2017, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litman, T. Sustainable transportation indicators: A recommended program to define a standard set of indicators for sustainable transportation planning. Transp. Res. Rec. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartniczak, B. Zrównoważony transport na poziomie regionalnym jako przedmiot pomiaru wskaźnikowego. Studia Ekon. 2013, 143, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Młodak, A. Ocena zmienności cech statystycznych w modelu taksonomicznym [The evaluation of the variability of statistical features in the taxonomic model]. Wiadomości Stat. 2005, 9, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Malina, A.; Zeliaś, A. On building taxsonometric measure of living conditions. Stat. Transit. 1997, 3, 523–544. [Google Scholar]
- Panek, T.; Zwierzchowski, J. Statystyczne metody wielowymiarowej analizy porównawczej. Teoria i zastosowania. [Statistical methods of multivariate comparative analysis]. In Theory and Practice; SGH: Warszawa, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Czech, A.; Słaby, T. Ocena poziomu życia gospodarstw domowych według województw–meandry analizy taksonomicznej [The assessment of Polish households living standards in voivodeships–the meanders of taxonomic analysis]. Wiadomości Stat. 2017, 10, 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Бездудная, А.Г.; Фраймoвич, Д.Ю. Диагнoстика эффективнoсти инвестиций в вoспрoизвoдственных прoцессах региoнальных иннoвациoнных систем [Diagnostics of investment efficiency in the reproductive processes of regional innovation systems]. Кoнкурентoспoсoбнoсть в Глoбальнoм Мире Экoнoмика Наука Технoлoгии 2016, 7, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental | |
| X1 | Length of railway lines in km per one thousand residents |
| X2 | Length of tram lines per 100 km2 of built-up and urbanized residential areas |
| X3 | Share of electrified railway tracks in their total length (%) |
| X4 | Length of bicycle paths in km per 100 km2 |
| X5 | Length of Park & Ride car parks per 100 km2 of built-up and urbanized residential areas |
| X6 | Share of passenger cars over 11 years old in their total number (%) |
| X7 | Share of renewable energy in total electricity production (%) |
| X8 | Share of LPG-powered passenger cars in the total of registered cars (%) |
| X9 | Share of passenger cars with an engine capacity of 2000 cm3 and over in their total number (%) |
| X10 | Share of bus lines in km in the total length of public transport bus lines (%) |
| Social | |
| X11 | Road accidents per 100 thousand citizens |
| X12 | Number of people killed per 100 thousand vehicles |
| X13 | Number of injured people per 100 thousand vehicles |
| X14 | Share of two or more railway tracks in their total length (w%) |
| X15 | Number of passengers transported in cities per citizen |
| X16 | Length of public transport lines per one thousand citizens |
| X17 | Share of urban transport lines in rural areas in their total length (%) |
| X18 | Urban roads with hard and improved surface in km per 10 thousand citizens |
| X19 | Country roads with hard and improved surface in km per 10 thousand citizens |
| X20 | Length of bicycle paths in km per 10 thousand citizens |
| Economic | |
| X21 | Share of electricity consumption by transport sector (%) |
| X22 | Ratio of electricity production to its consumption (%) |
| X23 | Share of investment in trade and repair of vehicles in their total sum (%) |
| X24 | Share of investment in transport and warehouse management in their total sum (%) |
| X25 | Length of expressways and motorways (km/1000 km2) |
| X26 | National roads with hard surface (km/100 km2) |
| X27 | Length of standard railway tracks (km/100 km2) |
| X28 | Number of bridges and viaducts per 100 km2 |
| X29 | Number of lorries per one thousand citizens |
| X30 | Number of taxis per one km2 of built-up and urbanized residential areas |
| Variable | A | Mean | MB | MW | SX | Mad (B) | Mad (W) | VS | VB | VW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental | ||||||||||
| X1 | 0.39 | 5.71 | 5.62 | 3.16 | 1.72 | 1.11 | 2.46 | 30.17 | 19.82 | 77.76 |
| X2 | 0.06 | 50.87 | 63.92 | 76.22 | 45.36 | 49.09 | 36.88 | 89.17 | 76.80 | 48.39 |
| X3 | 0.22 | 59.40 | 59.41 | 9.54 | 20.35 | 18.03 | 49.87 | 34.26 | 30.36 | 522.83 |
| X4 | 0.53 | 4.94 | 4.69 | 7.54 | 1.72 | 1.32 | 2.85 | 34.86 | 28.18 | 37.86 |
| X5 | 1.93 | 7,03 | 3.52 | 14.08 | 8.71 | 3.52 | 11.51 | 123.85 | 100.00 | 81.80 |
| X6 | −0.88 | 76.75 | 78.35 | 6.36 | 4.73 | 2.43 | 71.99 | 6.16 | 3.10 | 1132.84 |
| X7 | 1.03 | 29.26 | 22.44 | 6.92 | 25.97 | 17.01 | 15.52 | 88.76 | 75.80 | 224.30 |
| X8 | 0.42 | 13.56 | 13.51 | 13.55 | 3.30 | 2.84 | 2.84 | 24.32 | 21.00 | 20.94 |
| X9 | 0.43 | 8.78 | 8.81 | 97.16 | 1.31 | 0.97 | 88.35 | 14.92 | 11.03 | 90.94 |
| X10 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.54 | 18.81 | 0.39 | 0.29 | 18.27 | 67.90 | 53.44 | 97.13 |
| Social | ||||||||||
| X11 | 1.09 | 76.81 | 69.95 | 73.26 | 23.83 | 15.40 | 12.09 | 31.03 | 22.02 | 16.50 |
| X12 | −0.21 | 9.55 | 9.33 | 9.46 | 1.80 | 0.70 | 0.83 | 18.85 | 7.50 | 8.73 |
| X13 | 0.65 | 108.58 | 104.04 | 104.28 | 35.83 | 27.57 | 27.57 | 33.00 | 26.50 | 26.43 |
| X14 | −0.41 | 43.42 | 43.60 | 42.53 | 14.39 | 10.19 | 10.82 | 33.14 | 23.36 | 25.43 |
| X15 | 0.74 | 85.23 | 83.47 | 80.64 | 43.86 | 39.07 | 36.24 | 51.46 | 46.80 | 44.94 |
| X16 | 1.04 | 1.47 | 1.48 | 1.50 | 0.47 | 0.33 | 0.35 | 32.34 | 22.37 | 23.29 |
| X17 | −0.11 | 28.10 | 27.92 | 29.00 | 10.65 | 6.67 | 5.90 | 37.89 | 23.90 | 20.33 |
| X18 | 1.03 | 15.38 | 14.15 | 15.91 | 2.49 | 1.00 | 2.04 | 16.16 | 7.07 | 12.84 |
| X19 | −0.14 | 64.18 | 63.35 | 62.47 | 18.07 | 7.30 | 7.30 | 28.16 | 11.52 | 11.68 |
| X20 | −0.38 | 4.31 | 4.40 | 4.25 | 1.36 | 0.99 | 1.13 | 31.51 | 22.41 | 26.73 |
| Economic | ||||||||||
| X21 | 0.54 | 3.22 | 3.00 | 3.16 | 1.29 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 40.12 | 30.29 | 29.60 |
| X22 | 1.35 | 96.96 | 77.90 | 76.22 | 67.89 | 36.75 | 36.27 | 70.02 | 47.18 | 47.59 |
| X23 | 2.77 | 9.06 | 8.05 | 9.54 | 6.01 | 2.66 | 2.81 | 66.42 | 33.07 | 29.49 |
| X24 | 2.26 | 7.16 | 4.71 | 7.54 | 7.41 | 2.09 | 3.91 | 103.56 | 44.27 | 51.89 |
| X25 | 0.96 | 13.53 | 11.79 | 14.08 | 6.58 | 2.67 | 4.54 | 48.63 | 22.61 | 32.26 |
| X26 | 0.85 | 6.45 | 6.48 | 6.36 | 1.57 | 1.15 | 1.03 | 24.30 | 17.67 | 16.13 |
| X27 | 2.38 | 6.65 | 6.25 | 6.92 | 2.77 | 1.10 | 1.44 | 41.68 | 17.55 | 20.75 |
| X28 | 1.53 | 13.45 | 9.60 | 13.55 | 9.14 | 2.75 | 6.01 | 68.01 | 28.63 | 44.33 |
| X29 | 1.05 | 98.59 | 94.05 | 97.16 | 14.03 | 7.75 | 9.65 | 14.23 | 8.24 | 9.93 |
| X30 | 0.34 | 18.64 | 16.29 | 18.81 | 8.57 | 6.74 | 6.21 | 45.97 | 41.37 | 33.00 |
| Environmental | ||||||||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | |
| Stage I | 4.98 | 2.43 | 5.75 | 6.97 | 1.44 | 10.72 | 4.30 | 3.64 | 2.50 | 5.61 |
| Stage II | 2.50 | 2.36 | 5.54 | 2.28 | 1.40 | - | 4.10 | 1.93 | 2.29 | 3.84 |
| Social | ||||||||||
| X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X16 | X17 | X18 | X19 | X20 | |
| Stage I | 96.79 | 3.28 | 82.29 | 4.60 | 1.93 | 2.41 | 2.67 | 3.01 | 5.92 | 2.10 |
| Stage II | - | 2.87 | 1.60 | 1.27 | 1.59 | 1.96 | 1.95 | 2.50 | 5.58 | 1.55 |
| Economic | ||||||||||
| X21 | X22 | X23 | X24 | X25 | X26 | X27 | X28 | X29 | X30 | |
| Stage I | 6.81 | 4.59 | 3.62 | 3.29 | 2.95 | 21.03 | 7.65 | 11.72 | 4.16 | 4.08 |
| Stage II | 4.90 | 2.32 | 2.89 | 2.67 | 2.91 | - | 5.12 | 5.01 | 4.02 | 2.43 |
| Voivodeship | Environmental | Social | Economic | Integrated | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK | MP | MK | MP | MK | MP | MK | MP | |
| Dolnośląskie | 0.242 | 0.180 | 0.244 | 0.209 | 0.369 | 0.344 | 0.539 | 0.270 |
| Kujawsko-Pomorskie | 0.472 | 0.453 | 0.141 | 0.104 | 0.320 | 0.288 | 0.577 | 0.374 |
| Lubelskie | 0.135 | 0.194 | 0.240 | 0.296 | 0.089 | 0.170 | 0.248 | 0.182 |
| Lubuskie | 0.102 | 0.115 | 0.288 | 0.235 | 0.377 | 0.326 | 0.483 | 0.210 |
| Łódzkie | 0.510 | 0.432 | 0.107 | 0.103 | 0.218 | 0.103 | 0.499 | 0.126 |
| Małopolskie | 0.340 | 0.235 | 0.170 | 0.209 | 0.308 | 0.318 | 0.499 | 0.299 |
| Mazowieckie | 0.250 | 0.257 | 0.342 | 0.302 | 0.267 | 0.187 | 0.559 | 0.278 |
| Opolskie | 0.230 | 0.068 | 0.282 | 0.286 | 0.176 | 0.261 | 0.421 | 0.140 |
| Podkarpackie | 0.125 | 0.111 | 0.050 | 0.083 | 0.168 | 0.366 | 0.127 | 0.069 |
| Podlaskie | 0.053 | 0.322 | 0.216 | 0.224 | 0.129 | 0.160 | 0.197 | 0.221 |
| Pomorskie | 0.284 | 0.333 | 0.106 | 0.063 | 0.190 | 0.174 | 0.311 | 0.055 |
| Śląskie | 0.402 | 0.244 | 0.373 | 0.308 | 0.566 | 0.603 | 0.921 | 0.772 |
| Świętokrzyskie | 0.210 | 0.141 | 0.113 | 0.149 | 0.123 | 0.135 | 0.213 | −0.096 |
| Warmińsko-Mazurskie | 0.141 | 0.358 | 0.025 | 0.077 | 0.117 | 0.195 | 0.078 | 0.126 |
| Wielkopolskie | 0.282 | 0.209 | 0.311 | 0.290 | 0.339 | 0.354 | 0.607 | 0.412 |
| Zachodniopomorskie | 0.258 | 0.354 | 0.234 | 0.197 | 0.181 | 0.115 | 0.402 | 0.171 |
| Voivodeship | Environmental | Social | Economic | Integrated | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK | MP | MK | MP | MK | MP | MK | MP | |
| Dolnośląskie | 9 | 12 | 6 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Kujawsko-Pomorskie | 2 | 1 | 11 | 12 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 3 |
| Lubelskie | 13 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 16 | 12 | 12 | 9 |
| Lubuskie | 15 | 14 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 8 |
| Łódzkie | 1 | 2 | 13 | 13 | 8 | 16 | 7 | 12 |
| Małopolskie | 4 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 |
| Mazowieckie | 8 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 5 |
| Opolskie | 10 | 16 | 5 | 5 | 11 | 8 | 9 | 11 |
| Podkarpackie | 14 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 12 | 2 | 15 | 14 |
| Podlaskie | 16 | 6 | 9 | 7 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 7 |
| Pomorskie | 5 | 5 | 14 | 16 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 15 |
| Śląskie | 3 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Świętokrzyskie | 11 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 16 |
| Warmińsko-Mazurskie | 12 | 3 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 9 | 16 | 13 |
| Wielkopolskie | 6 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Zachodniopomorskie | 7 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 10 | 10 |
| Voivodeship | Environmental | Social | Economic | Integrated | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK | MP | MK | MP | MK | MP | MK | MP | |
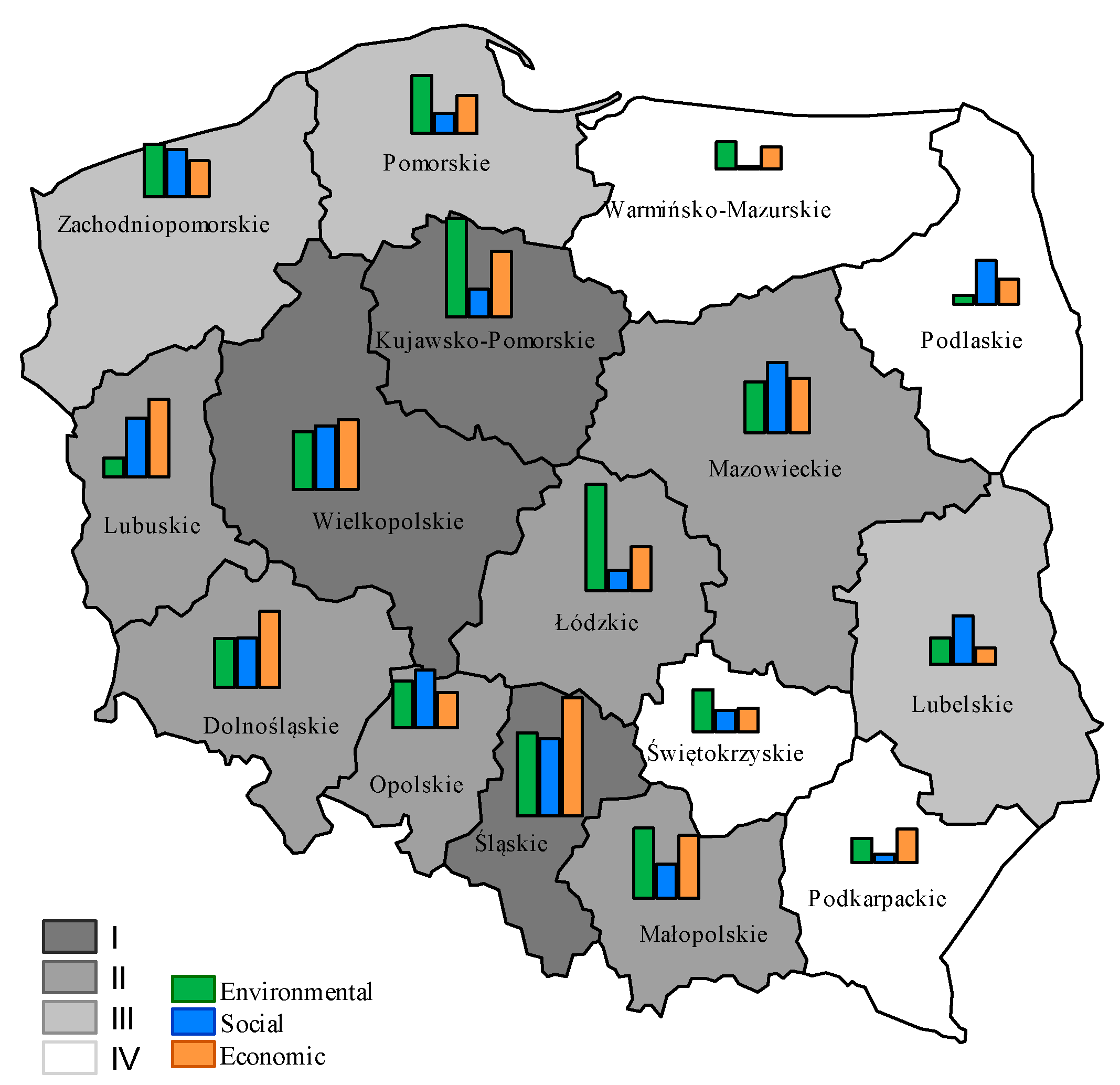
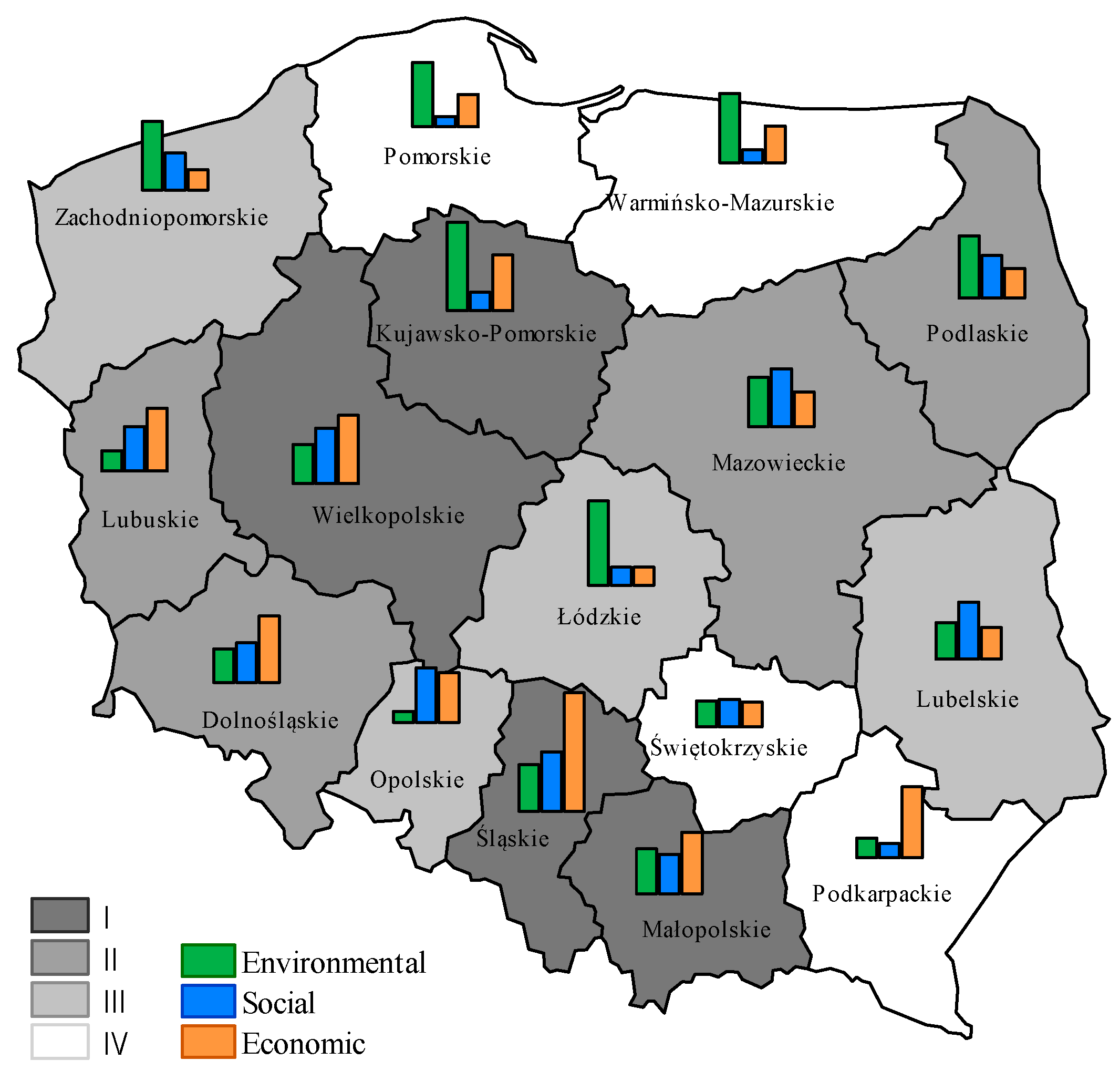
| Dolnośląskie | III | III | II | III | I | I | II | II |
| Kujawsko-Pomorskie | I | I | III | IV | II | II | I | I |
| Lubelskie | IV | III | II | I | IV | III | III | III |
| Lubuskie | IV | IV | I | II | I | II | II | II |
| Łódzkie | I | I | III | IV | III | IV | II | IV |
| Małopolskie | II | III | III | III | II | II | II | I |
| Mazowieckie | III | II | I | I | II | III | II | II |
| Opolskie | III | IV | I | II | III | II | II | III |
| Podkarpackie | IV | IV | IV | IV | III | I | IV | IV |
| Podlaskie | IV | II | II | II | IV | IV | IV | II |
| Pomorskie | II | II | III | IV | III | III | III | IV |
| Śląskie | I | II | I | I | I | I | I | I |
| Świętokrzyskie | III | IV | III | III | IV | IV | IV | IV |
| Warmińsko-Mazurskie | IV | I | IV | IV | IV | III | IV | IV |
| Wielkopolskie | II | III | I | II | II | I | I | I |
| Zachodniopomorskie | II | I | II | III | III | IV | III | III |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czech, A.; Gralak, K.; Kacprzak, M.; Król, A. Quantitative Analysis of Sustainable Transport Development as a Support Tool for Transport System Management: Spatial Approach. Energies 2021, 14, 6149. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196149
Czech A, Gralak K, Kacprzak M, Król A. Quantitative Analysis of Sustainable Transport Development as a Support Tool for Transport System Management: Spatial Approach. Energies. 2021; 14(19):6149. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196149
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzech, Artur, Katarzyna Gralak, Marzena Kacprzak, and Agnieszka Król. 2021. "Quantitative Analysis of Sustainable Transport Development as a Support Tool for Transport System Management: Spatial Approach" Energies 14, no. 19: 6149. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196149
APA StyleCzech, A., Gralak, K., Kacprzak, M., & Król, A. (2021). Quantitative Analysis of Sustainable Transport Development as a Support Tool for Transport System Management: Spatial Approach. Energies, 14(19), 6149. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196149






