Proposed Commutation Method for Performance Improvement of Brushless DC Motor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design Flow and Design for BLDC Motor
2.1. Design Flow for BLDC Motor
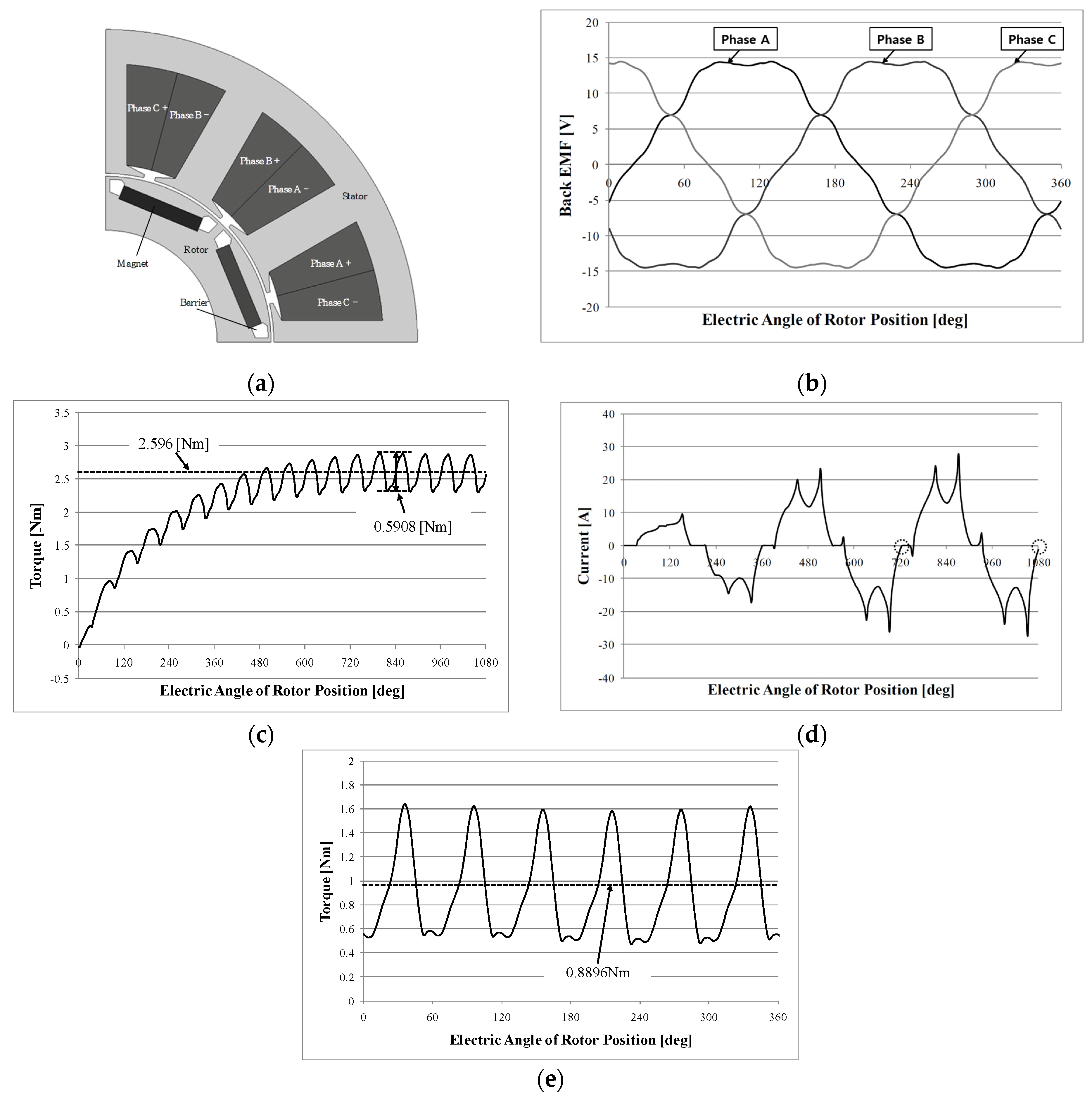
2.2. BLDC Motor Design Results
3. Comparison of Commutation Methods
3.1. Generating the Sinusoidal Current for BLDC Motor
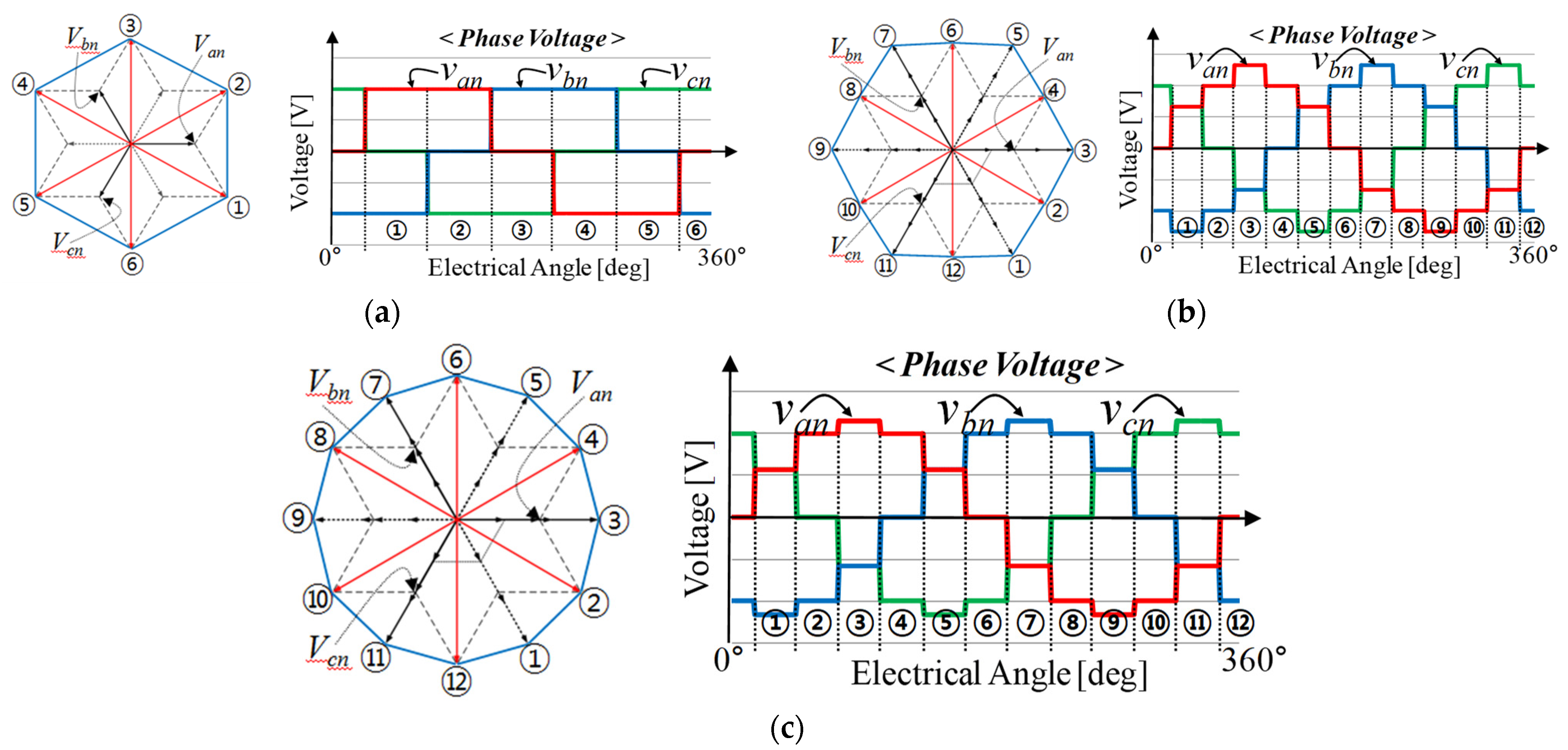
3.2. Definitions of Pole, Phase, and Neutral Voltage
3.3. Pole, Neutral, and Phase Voltages According to Commutation Methods
3.4. Extension of Improved 150° Commutation Method
3.5. Consideration of Commutation Methods
4. Applied Motor and Analysis Results
4.1. Applied Motor Specifications
4.2. Analysis Results of Co-Simulation
5. Experiment Results
5.1. Performance Testing of the BLDC Motor
5.2. Acoustic Noise and Vibration Testing of the BLDC Motor
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.W.; Park, Y.J.; Oh, S.T.; Jang, H.; Won, S.H.; Chun, Y.D.; Lee, J. A Study on the Rotor Design of Line Start Synchronous Reluctance Motor for IE4 Efficiency and Improving Power Factor. Energies 2020, 13, 5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.T.D.; Ferreira, F.J.T.E.; Baoming, G. Beyond, Induction Motors-Technology Trends to Move Up Efficiency. IEEE Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.T.D.; Ferreira, F.J.T.E.; Duarte, A.Q. Technical and Economical Considerations on Super High-Efficiency Three-Phase Motors. IEEE Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Singh, B.; Bist, V.; Al-Haddad, K.; Chandra, A. BLDC Motor Drive Based on Bridgeless Landsman PFC Converter With Single Sensor and Reduced Stress on Power Devices. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, S.; Qian, G.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. A Two-Step Strategy for Online Fault Detection of High-Resistance Connection in BLDC Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 3043–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L. Investigation of a Stator-Ironless Brushless DC Motor With Non-Ideal Back-EMF. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 28044–28054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.; Lajoie-Mazenc, M.; Fagundes, J.C.D.S. Analysis of torque ripple due to phase commutation in brushless DC machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1992, 28, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, W.; Shi, T. Torque ripple reduction in brushless dc drives based on reference current optimization using integral variable structure control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, T.C. New method to eliminate commutation torque ripple of brushless DC motor with minimum commutation time. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Kim, T.H.; Ehsani, M. Practical control for improving power density and efficiency of the BLDC generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Han, B.C.; Zheng, S.; Fang, J.C. High-Precision Sensorless Drive for High-Speed BLDC Motors Based on the Virtual Third Harmonic Back-EMF. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 1528–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, N.; Singh, S. Torque ripples control and speed regulation of Permanent magnet Brushless dc Motor Drive using Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the Recent Advances in Engineering and Computational Sciences (RAECS), Chandigarh, India, 6–8 March 2014; pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.U.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, D.K. Cogging Torque Reduction of Single-Phase Brushless DC Motor With a Tapered Air-Gap Using Optimizing Notch Size and Position. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 4455–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, C.; Champenois, G.; Bolopion, A. Commutation strategies for brushless DC motors: Influence on instant torque. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1993, 8, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, C.; Zeng, F.; Song, X. Sensorless BLDC motor commutation point detection and phase deviation correction method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 5880–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Seo, M.; Kim, Y.; Jung, S. Motor design and characteristics comparison of outer-rotor-type BLDC motor and BLAC motor based on numerical analysis. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 5205506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.N.; Kim, S.J.; Go, S.C.; Lee, H.W.; Chun, Y.D.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, J. Novel Configuration of the Magnetizing Fixture for a Brushless Permanent-Magnet Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2807–2810. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.W.; Lee, K.D.; Kim, W.H.; Jang, I.S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, J. Parameter Design of IPMSM With Concentrated Winding Considering Partial Magnetic Saturation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3653–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Park, H.W.; Lee, M.H.; Harashima, F. A new approach for minimum-torque-ripple maximum-efficiency control of BLDC motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2000, 47, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Qu, W. A new torque control method for torque ripple minimization of BLDC motors with un-ideal back EMF. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Conditions | Torque | Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Design point 1 (4 km/h at slop angle 15°) | 2.45 Nm | 1325 rpm |
| Design point 2 (30 km/h at slop angle 0°) | 0.45 Nm | 3930 rpm |
| Value | Unit | |
|---|---|---|
| Base Speed/Max. Speed | 1325/3930 | rpm/rpm |
| Torque @ Base/Max. Speed | 2.45/0.45 | Nm/Nm |
| Continuous Power | 340 | W |
| Outer Diameter | 110 | mm |
| Stack Length | 24.5 | mm |
| Air Gap Length | 0.5 | mm |
| Remanence of Permanent Magnet (NdFeB) | 1.25 | T (@20 °C) |
| Operating Temperature | 100 | °C |
| DC-Link 36V @1325 rpm | 120° Commutation | 150° Commutation | Improved 150° Commutation | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current | 9.58 | 13.57 | 12.25 | Arms |
| Average Torque | 1.8947 | 3.2085 | 2.9998 | Nm |
| Current/Torque | 5.06 | 4.23 | 4.08 | A/Nm |
| Torque Ripple | 24.1 | 13.6 | 12.03 | % |
| Copper Loss | 2.67 | 4.14 | 3.99 | W |
| Core Loss | 17.17 | 17.83 | 15.67 | W |
| Magnet Loss | 1.12 | 1.32 | 0.95 | W |
| Efficiency | 92.1 | 94.81 | 95.09 | % |
| @ 2 Nm | 120° Commutation | 150° Commutation | Improved 150° Commutation | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current | 10.35 | 8.62 | 7.96 | Arms |
| Current/Torque | 5.27 | 4.31 | 3.98 | A/Nm |
| THD | 0.287 | 0.112 | 0.055 | - |
| Value | No Commutation | 120° Commutation | 150° Commutation | Improved 150° Commutation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acoustic noise [dBA] | 19.3 | 51.1 | 47.7 | 47.5 |
| Vibration [m/s2] | 0.039 | 5.79 | 5.28 | 5.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, C.-S.; Kim, C.-M.; Kim, I.-J.; Jang, I. Proposed Commutation Method for Performance Improvement of Brushless DC Motor. Energies 2021, 14, 6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196023
Jin C-S, Kim C-M, Kim I-J, Jang I. Proposed Commutation Method for Performance Improvement of Brushless DC Motor. Energies. 2021; 14(19):6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196023
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Chang-Sung, Chang-Min Kim, In-Jin Kim, and Iksang Jang. 2021. "Proposed Commutation Method for Performance Improvement of Brushless DC Motor" Energies 14, no. 19: 6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196023
APA StyleJin, C.-S., Kim, C.-M., Kim, I.-J., & Jang, I. (2021). Proposed Commutation Method for Performance Improvement of Brushless DC Motor. Energies, 14(19), 6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196023







