Water and Energy Efficiency Assessment in Urban Green Spaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
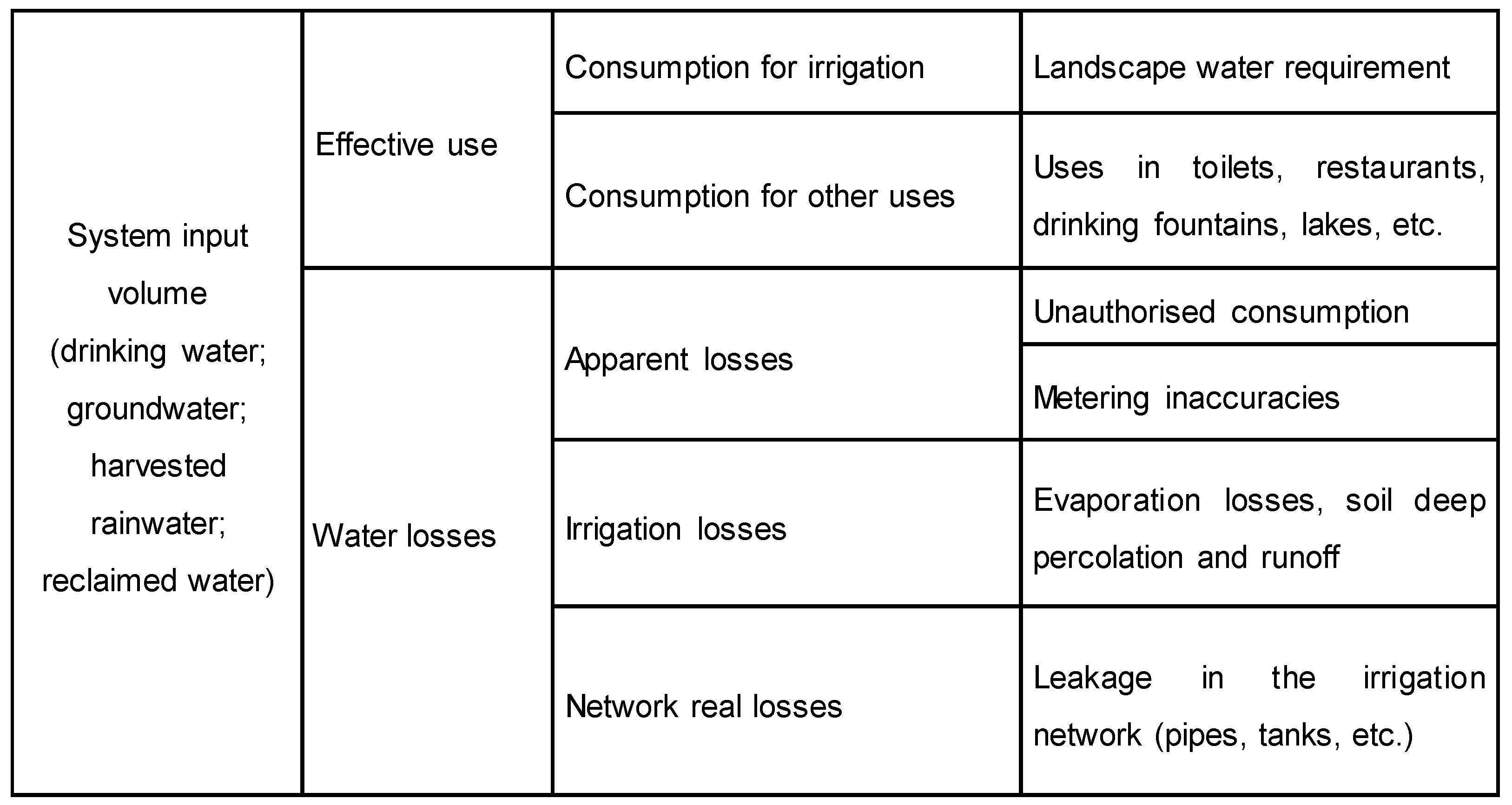
2.1. Water Balance
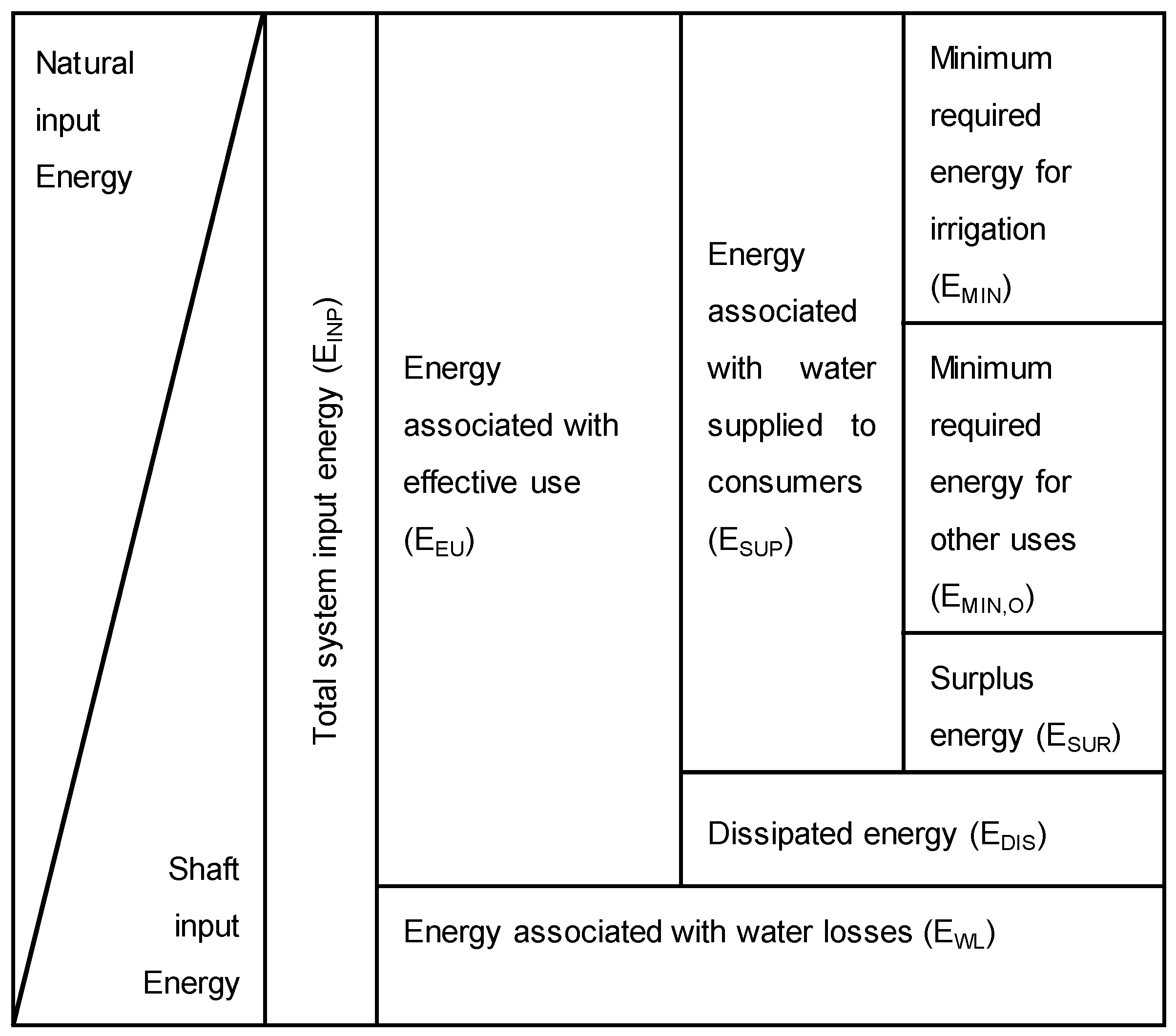
2.2. Water–Energy Balance
3. Case Studies Description
3.1. Case Study 1: Green Space with Smart Irrigation System
3.2. Case Study 2: Urban Park
4. Results and Discussion
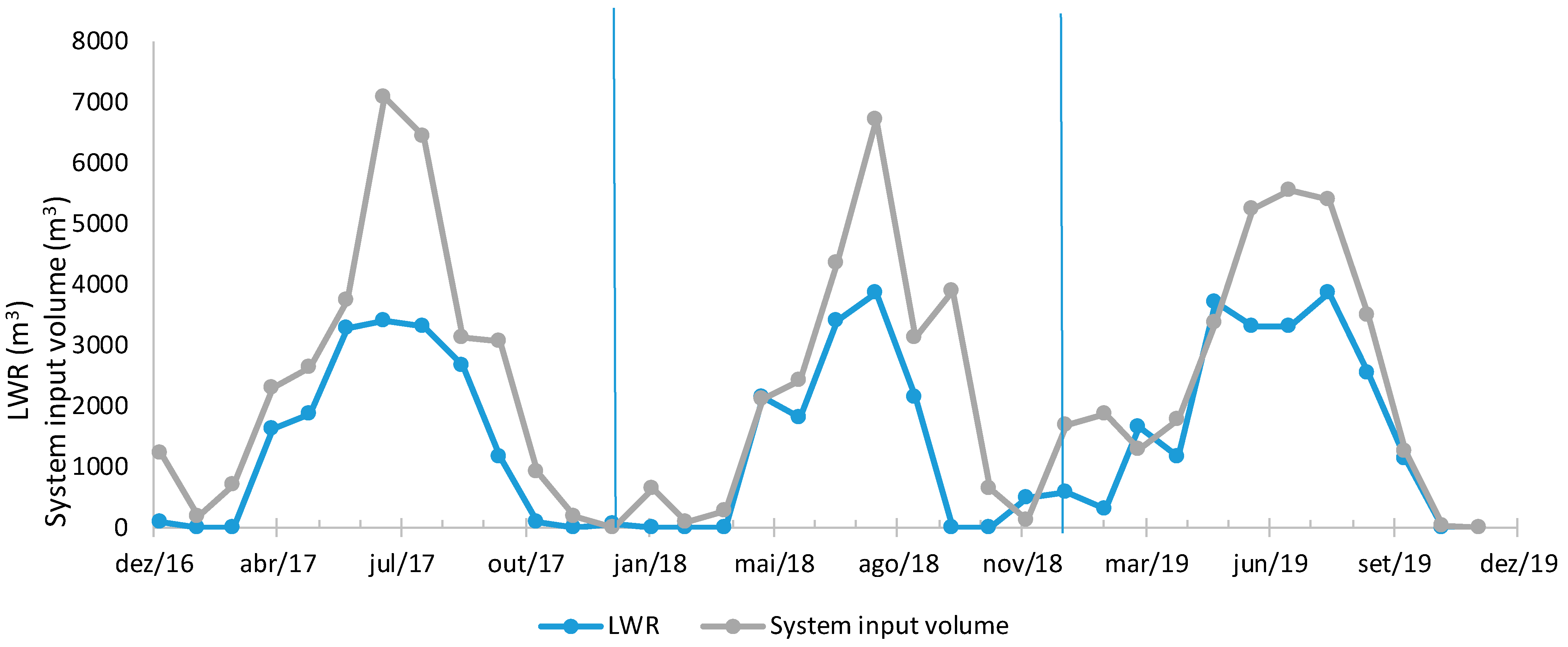
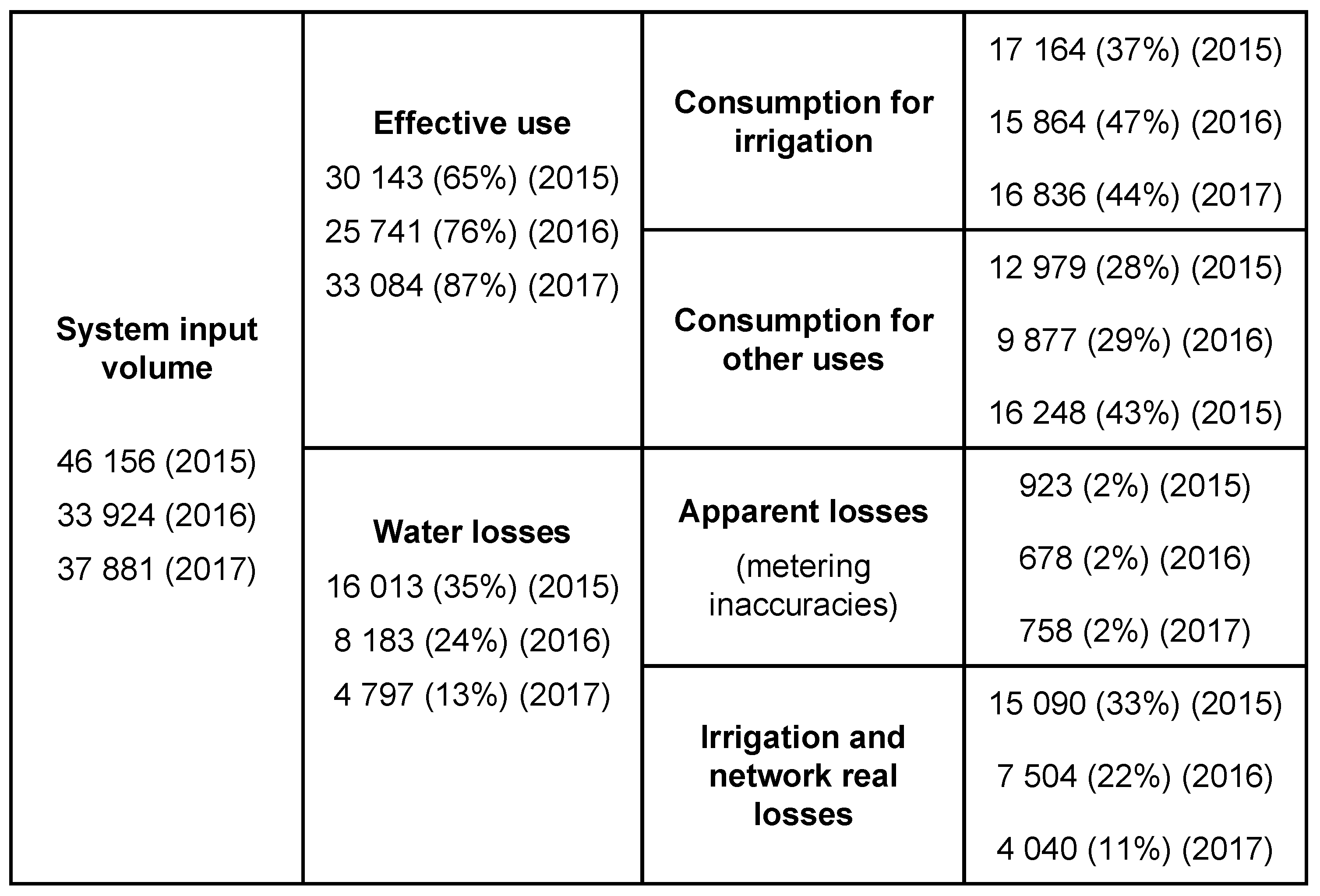
4.1. Water Balance Application to Case Study 1
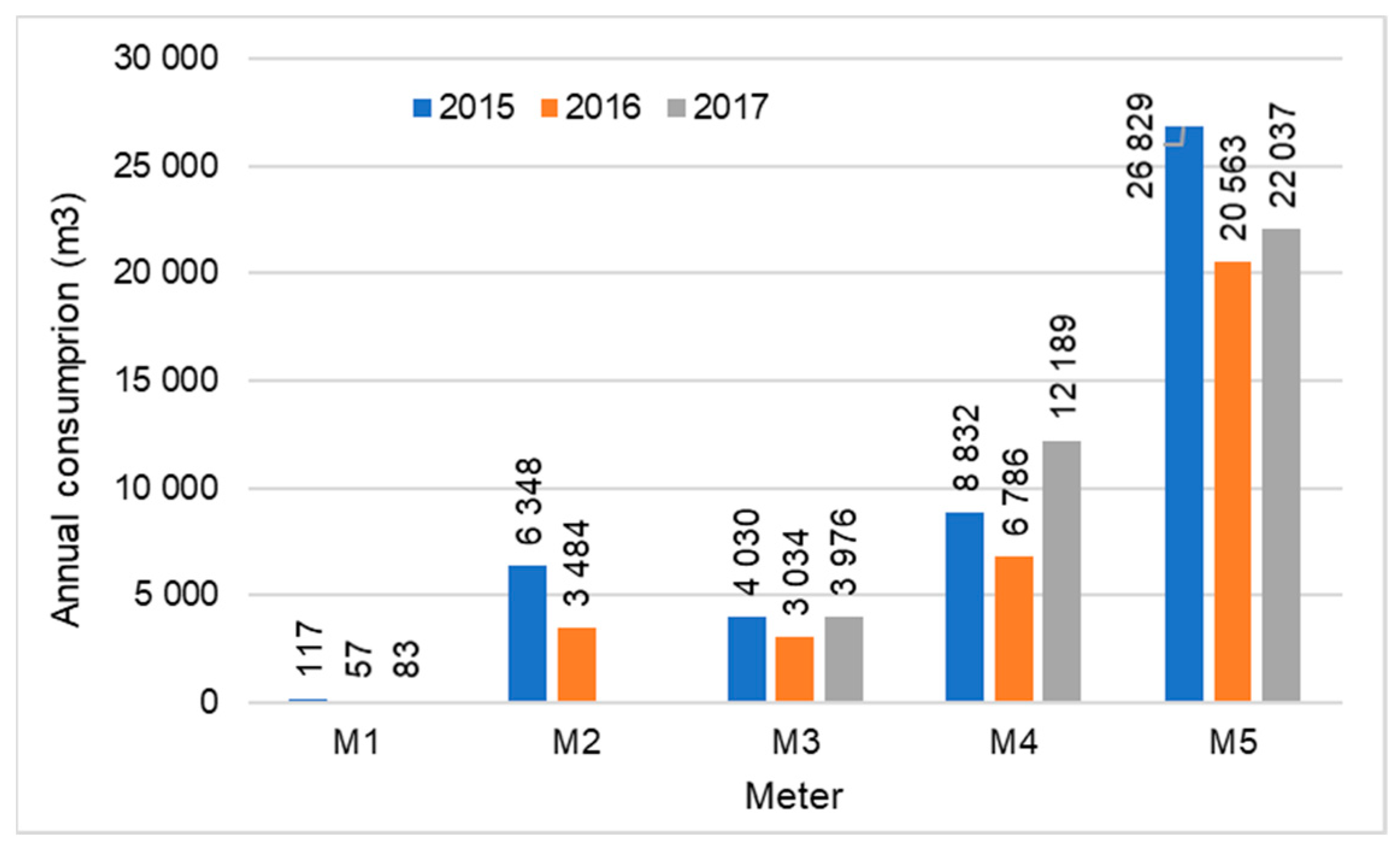
4.2. Water Balance Application to Case Study 2
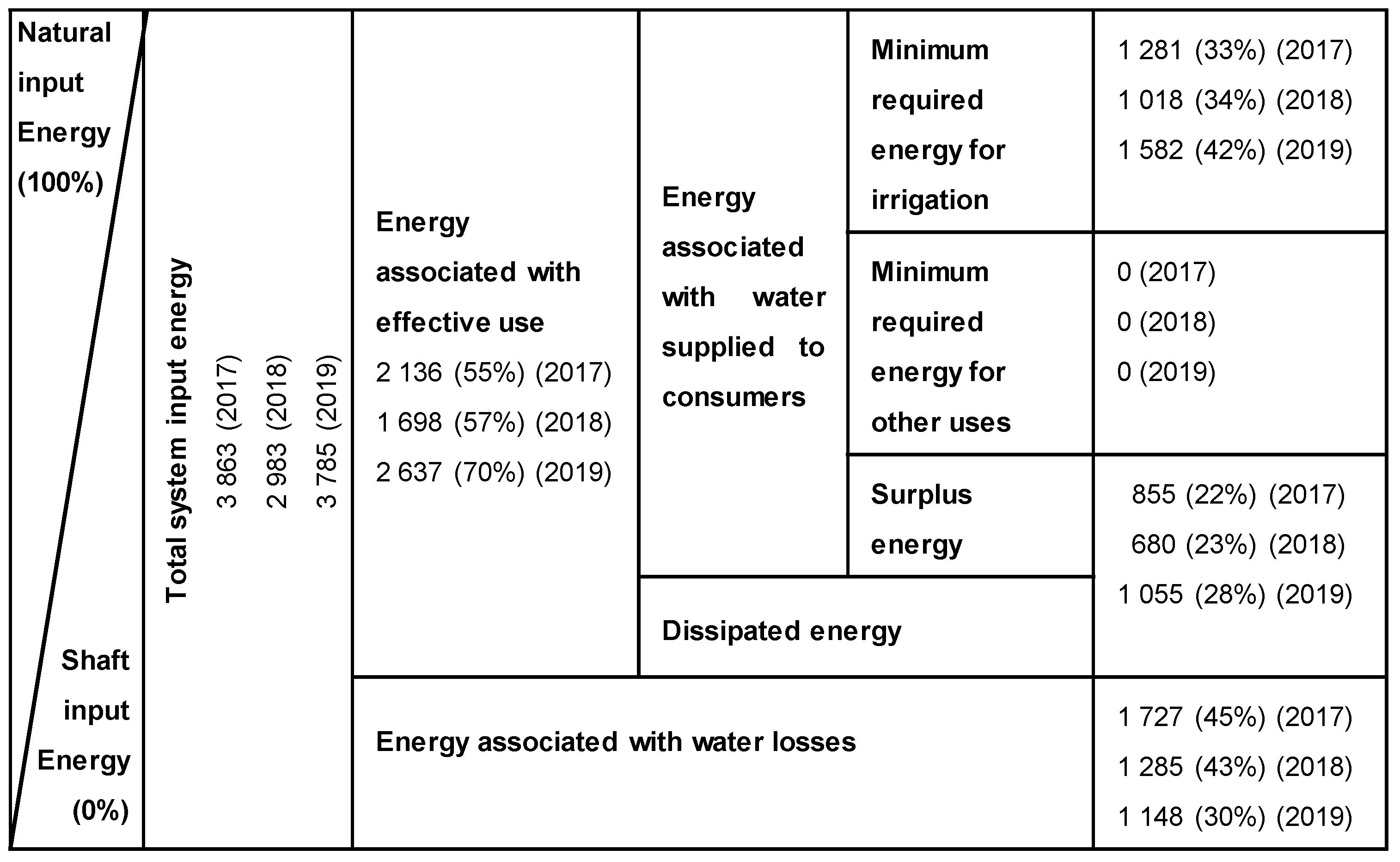
4.3. Water–Energy Balance Application to Case Study 1
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbesgaard, M. Blue growth: Savior or ocean grabbing? J. Peasant Stud. 2018, 45, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, G.; Janzen, C.; Maginnis, S. Nature-Based Solutions to Address Global SOCIETAL Challenges; ICUN: Gland, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 9782831718125. [Google Scholar]
- Geneletti, D.; Zardo, L. Ecosystem-based adaptation in cities: An analysis of European urban climate adaptation plans. Land Use Policy 2016, 50, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatzimentor, A.; Apostolopoulou, E.; Mazaris, A.D. A review of green infrastructure research in Europe: Challenges and opportunities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 198, 103775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Urban Green Spaces: A Brief for Action; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vicuña, S.; Gil, M.; Melo, O.; Donoso, G.; Merino, P. Water option contracts for climate change adaptation in Santiago, Chile. Water Int. 2018, 43, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USEPA. Water Efficiency Management Guide. Landscaping and Irrigation; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, H.; Chavoshi Borujeni, S.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The blue water footprint of urban green spaces: An example for Adelaide, Australia. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 190, 103613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Pérez, M.R.; Alba-Rodríguez, M.D.; Marrero, M. The water footprint of city naturalisation. Evaluation of the water balance of city gardens. Ecol. Model. 2020, 424, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa E-Nova. Matriz da Agua de Lisboa; Lisboa E-Nova: Lisboa, Portugal, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ayuntamiento de Madrid. Plan Municipal de Gestion de la Demanda de Agua en la Ciudad de Madrid; Ayuntamiento de Madrid: Madrid, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Parés-Franzi, M.; Saurí-Pujol, D.; Domene, E. Evaluating the environmental performance of urban parks in Mediterranean cities: An example from the Barcelona Metropolitan Region. Environ. Manag. 2006, 38, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, G.; Du, Y.; Ren, Y.; Lu, Y.; Fan, L.; Chang, J.; Ge, Y.; Bao, Z. Estimating irrigation water demand for green spaces in humid areas: Seeking a sustainable water management strategy. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvak, E.; Bijoor, N.S.; Pataki, D.E. Adding trees to irrigated turfgrass lawns may be a water-saving measure in semi-arid environments. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 1314–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Beecham, S.; Kazemi, F.; Hassanli, A.M. A review of ET measurement techniques for estimating the water requirements of urban landscape vegetation. Urban Water J. 2013, 10, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Paecke, S.; Gironás, J.; Melo, O.; Vicuña, S.; Herrera, J. Irrigation of green spaces and residential gardens in a Mediterranean metropolis: Gaps and opportunities for climate change adaptation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 182, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales-Ide, F.; Zubelzu, S.; Rodríguez-Sinobas, L. Irrigation systems in smart cities coping with water scarcity: The case of valdebebas, Madrid (Spain). J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.D.; Pandey, P.; Feijóo, A.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Bokde, N.D. Smart water technology for efficient water resource management: A review. Energies 2020, 13, 6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosson, C.; Tong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Q. Rainwater as a renewable resource to achieve net zero urban water in water stressed cities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, F.; Pitarma, R.; Reis, P. Intelligent management of urban garden irrigation. In Proceedings of the 9th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Barcelona, Spain, 18–21 June 2014; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.D.F.M.E.; Calijuri, M.L.; Sales, F.J.F.; Souza, M.H.B.; Lopes, L.S. Integration of technologies and alternative sources of water and energy to promote the sustainability of urban landscapes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 91, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. New Urban Agenda; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9789211327311. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, A.; Hirner, W. Losses from Water Supply Systems: Standard Terminology and Recommended Performance Measures; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mamade, A.; Loureiro, D.; Alegre, H.; Covas, D. Top-down and bottom-up approaches for water–energy balance in Portuguese supply systems. Water 2018, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glenn, D.T.; Endter-Wada, J.; Kjelgren, R.; Neale, C.M.U. Tools for evaluating and monitoring effectiveness of urban landscape water conservation interventions and programs. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 139, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunha, H.; Loureiro, D.; Sousa, G.; Covas, D.; Alegre, H. A comprehensive water balance methodology for collective irrigation systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 223, 105660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.R.; Matheny, N.P.; Clark, J.R. Estimating the irrigation water needs of landscape plantings in California: The landscape coefficient method. In A Guide to Estimating Irrigation Water Needs of Landscape Plantings in California; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2000; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Water Budget Approach; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaei, P.; Gheysari, M.; Myers, B.; Esmaeili, H. Quantifying microclimatic conditions: An attempt to more accurately estimate urban landscape water requirements. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 54, 126767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Washali, T.; Sharma, S.; Lupoja, R.; AL-Nozaily, F.; Haidera, M.; Kennedy, M. Assessment of water losses in distribution networks: Methods, applications, uncertainties, and implications in intermittent supply. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 152, 104515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, M.; Sánchez-Romero, F.J.; Ramos, H.M.; López-Jiménez, P.A. Energy recovery in existing water networks: Towards greater sustainability. Water 2017, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mamade, A.; Loureiro, D.; Alegre, H.; Covas, D. A comprehensive and well tested energy balance for water supply systems. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monteiro, L.; Cristina, R.; Covas, D. Water and Energy Efficiency Assessment in Urban Green Spaces. Energies 2021, 14, 5490. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175490
Monteiro L, Cristina R, Covas D. Water and Energy Efficiency Assessment in Urban Green Spaces. Energies. 2021; 14(17):5490. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175490
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonteiro, Laura, Raquel Cristina, and Dídia Covas. 2021. "Water and Energy Efficiency Assessment in Urban Green Spaces" Energies 14, no. 17: 5490. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175490
APA StyleMonteiro, L., Cristina, R., & Covas, D. (2021). Water and Energy Efficiency Assessment in Urban Green Spaces. Energies, 14(17), 5490. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175490





