Voltage-Based Droop Control of Electric Vehicles in Distribution Grids under Different Charging Power Levels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- three currently available charging power levels ( kW, kW, 11 kW);
- a full range of EV penetrations (5%, 10–100%, in steps of 10%);
- long term simulations (half a year);
- real distribution grid topology and load data.
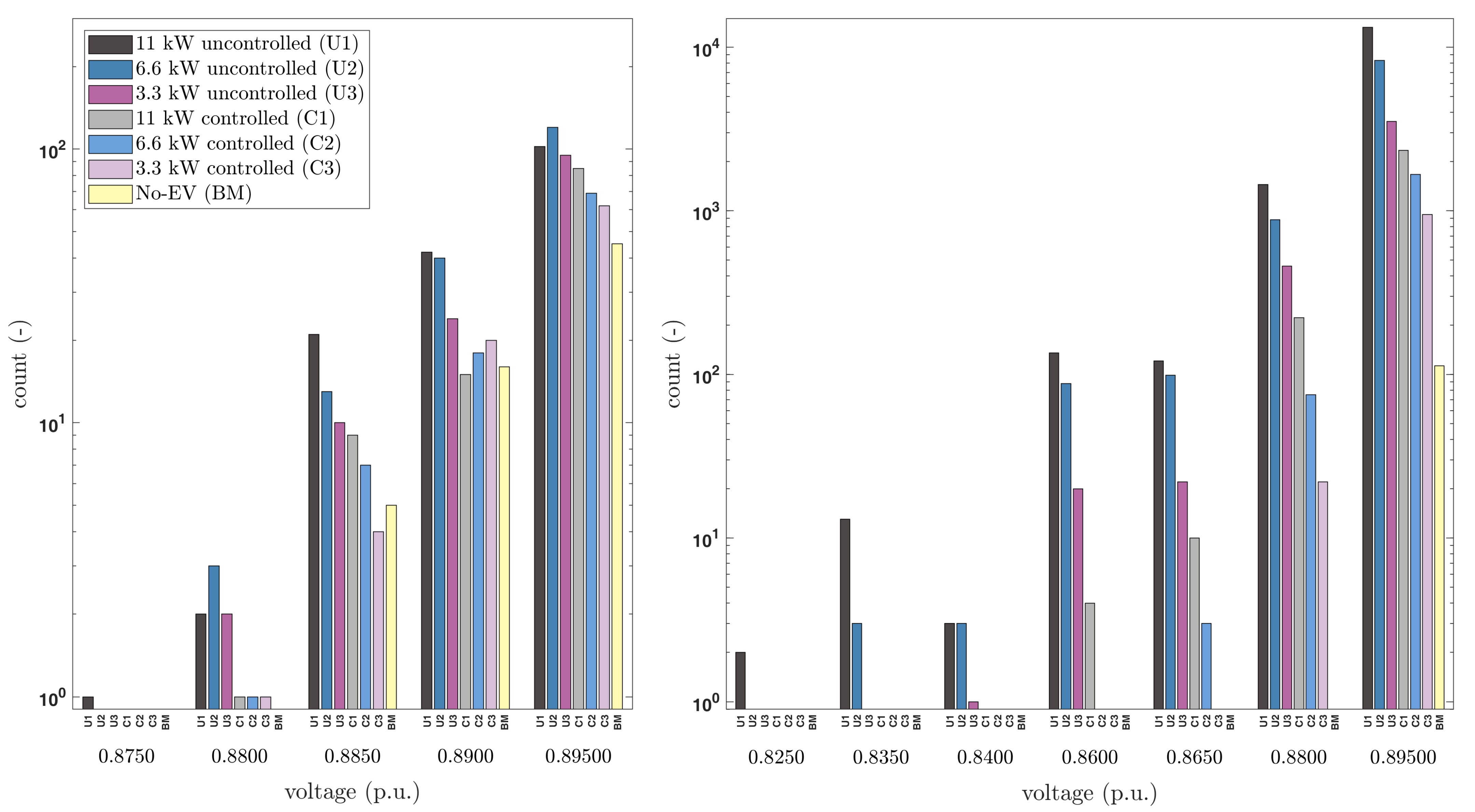
- the voltage magnitude compliance with the standards;
- the peak power in the grid;
- the average charging rates over a range of EV penetrations and three charging power levels.
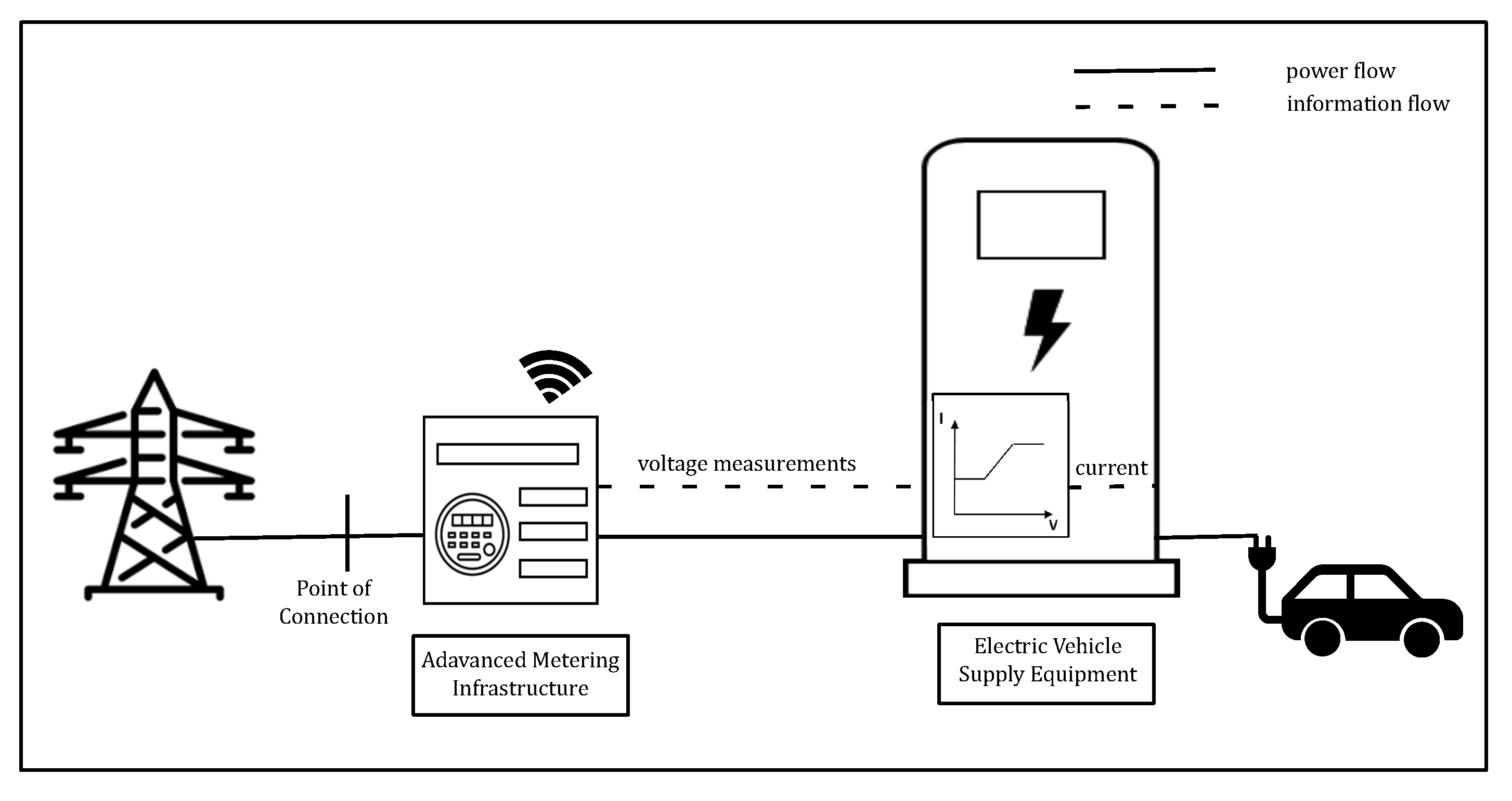
2. System Modeling
2.1. Voltage Based Controller Characteristics
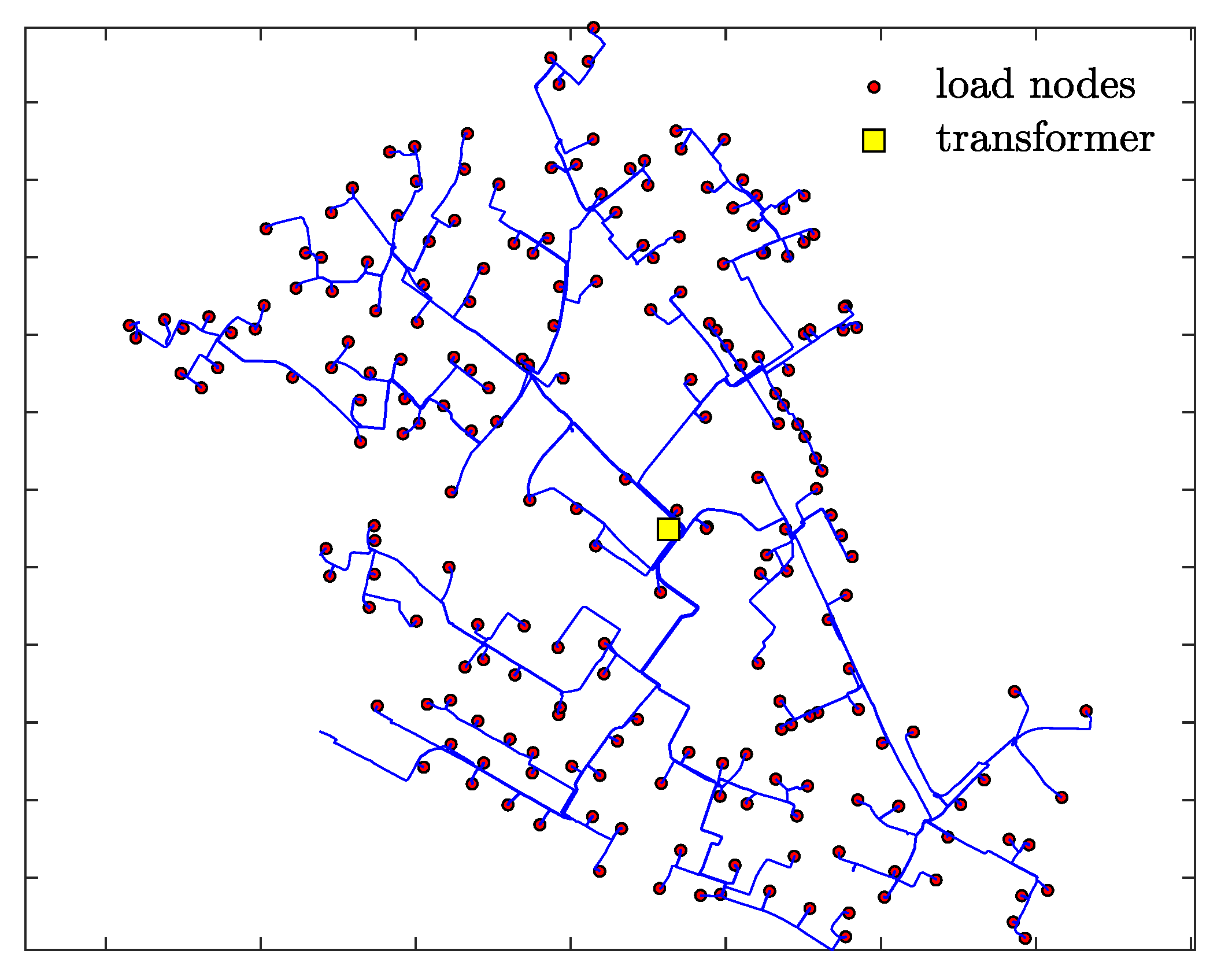
2.2. Simulation Framework
2.3. EV Model
2.4. Scenarios
3. Results
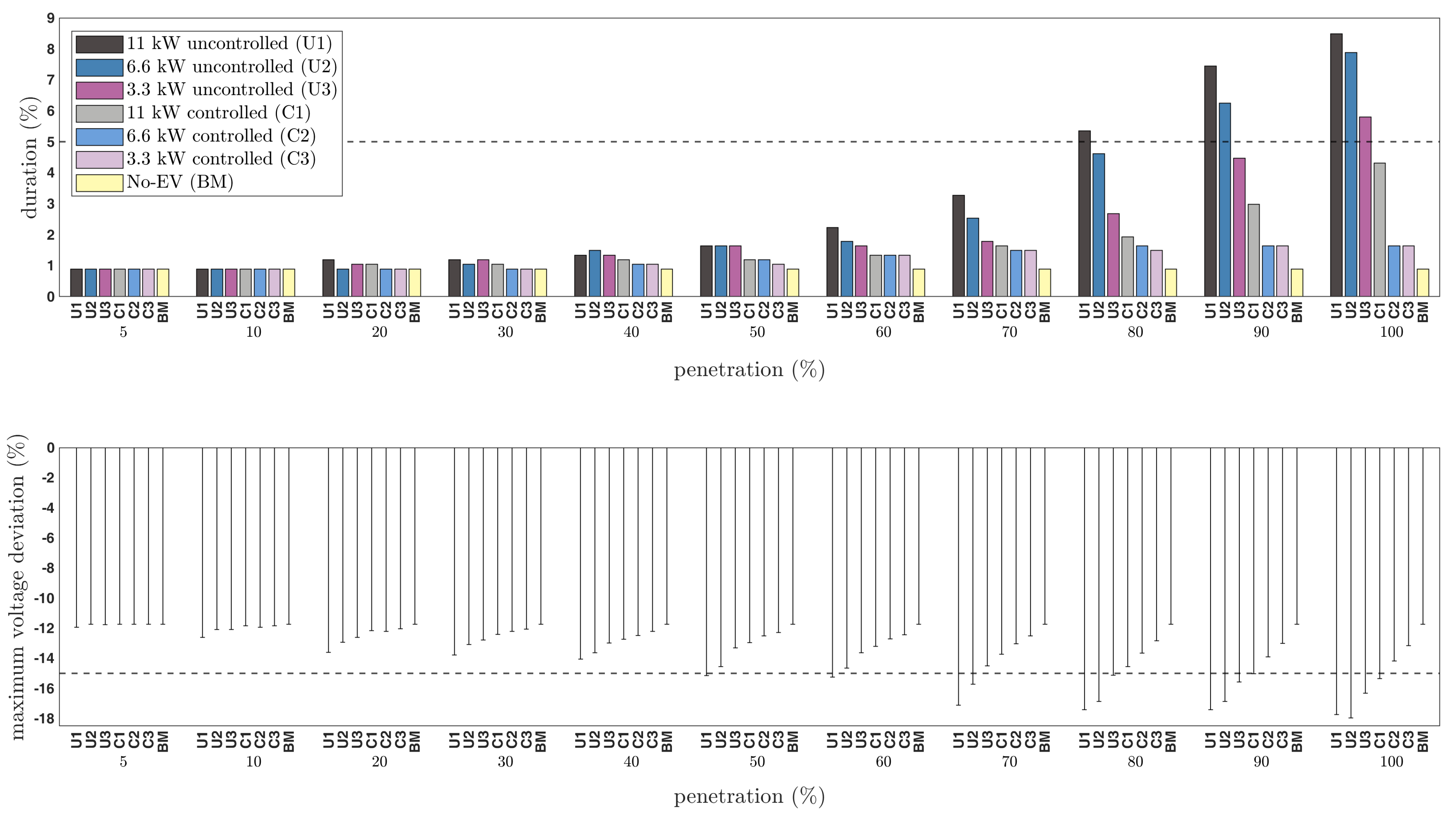
3.1. Compliance of the Voltage with the International Standard EN50160
3.2. Average Charging Rate
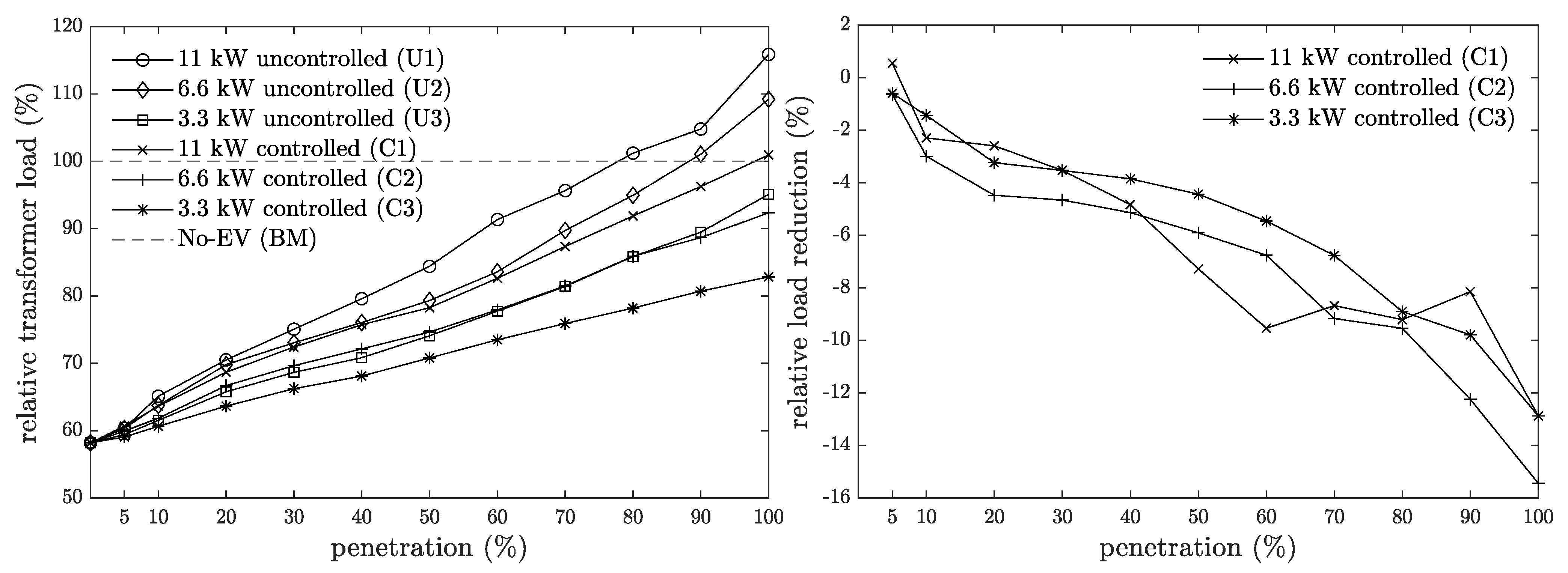
3.3. Peak Power
3.4. Nodal Voltages
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, S.; Pipattanasomporn, M.; Rahman, S. Grid integration of electric vehicles and demand response with customer choice. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babrowski, S.; Heinrichs, H.; Jochem, P.; Fichtner, W. Load shift potential of electric vehicles in Europe. J. Power Sources 2014, 255, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, R.C., II; Wang, L.; Alam, M. The impact of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles on distribution networks: A review and outlook. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, L.; Rowe, A.; Wild, P. Analyzing the impacts of plug-in electric vehicles on distribution networks in British Columbia. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Electrical Power &Energy Conference (EPEC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 22–23 October 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, K.; Haesen, E.; Driesen, J. Coordinated charging of multiple plug-in hybrid electric vehicles in residential distribution grids. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, Seattle, WA, USA, 15–18 March 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Awami, A.T.; Sortomme, E.; Akhtar, G.M.A.; Faddel, S. A voltage-based controller for an electric-vehicle charger. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 65, 4185–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.A.P.; Soares, F.J.; Almeida, P.M.R. Integration of electric vehicles in the electric power system. Proc. IEEE 2010, 99, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shareef, H.; Islam, M.M.; Mohamed, A. A review of the stage-of-the-art charging technologies, placement methodologies, and impacts of electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, N.; Wu, Q.; Østergaard, J.; Nielsen, A.H.; Cha, S.T.; Ding, Y. Electric vehicle (EV) charging management with dynamic distribution system tariff. In Proceedings of the 2011 2nd IEEE PES International Conference and Exhibition on Innovative Smart Grid Technologies, Manchester, UK, 5–7 December 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Amjad, M.; Ahmad, A.; Rehmani, M.H.; Umer, T. A review of EVs charging: From the perspective of energy optimization, optimization approaches, and charging techniques. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 386–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Villalobos, J.; Zamora, I.; San Martín, J.I.; Asensio, F.J.; Aperribay, V. Plug-in electric vehicles in electric distribution networks: A review of smart charging approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanke, T.U.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Yong, J.Y.; Pasupuleti, J.; Kasinathan, P.; Rajagopalan, A. A review of strategic charging–discharging control of grid-connected electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2020, 28, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geth, F.; Leemput, N.; Van Roy, J.; Büscher, J.; Ponnette, R.; Driesen, J. Voltage droop charging of electric vehicles in a residential distribution feeder. In Proceedings of the 2012 3rd IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT Europe), Berlin, Germany, 14–17 October 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Leemput, N.; Geth, F.; Van Roy, J.; Delnooz, A.; Büscher, J.; Driesen, J. Impact of electric vehicle on-board single-phase charging strategies on a flemish residential grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, J.N.; Knezović, K.; Marinelli, M. Analysis and comparison of voltage dependent charging strategies for single-phase electric vehicles in an unbalanced Danish distribution grid. In Proceedings of the 2016 51st International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Coimbra, Portugal, 6–9 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Mareels, I.; Alpcan, T.; Brazil, M.; de Hoog, J.; Thomas, D.A. A distributed electric vehicle charging management algorithm using only local measurements. In Proceedings of the ISGT 2014, Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 February 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Faddel, S.; Al-Awami, A.T.; Mohammed, O.A. Charge control and operation of electric vehicles in power grids: A review. Energies 2018, 11, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CENELEC. Voltage Characteristics of Electricity Supplied by Public Electricity Networks; Technical Report EN50160; German Institute for Standardisation: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mohassel, R.R.; Fung, A.; Mohammadi, F.; Raahemifar, K. A survey on advanced metering infrastructure. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 63, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vorarlberger Energienetze GmbH. Available online: https://www.vorarlbergnetz.at/ (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Schuler, M.; Faessler, B.; Preißinger, M.; Kepplinger, P. A Method for Grid Simulation Assessing Demand Side Management Strategies. In Tagungsband des 12. Forschungsforum der österreichischen Fachhochschulen (FFH) 2018; Fachhochschule Salzburg GmbH: Salzburg, Austria, 2018; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- MATLAB. Version: 9.7.0,1165820 (R2019a); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ghatak, U.; Mukherjee, V. An improved load flow technique based on load current injection for modern distribution system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2017, 84, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- illwerke vkw AG. Available online: https://www.vkw.at/ (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Synthetic Load Profiles APCS—Power Clearing & Settlement. Available online: https://www.apcs.at/en/clearing/physical-clearing/synthetic-load-profiles (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Nissan-Leaf-Data-Sheet. Available online: https://goelectricyyc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Nissan-Leaf-Data-Sheet.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Tomschy, R.; Herry, M.; Sammer, G.; Klementschitz, R.; Riegler, S.; Follmer, R.; Gruschwitz, D.; Josef, F.; Gensasz, S.; Kirnbauer, R.; et al. Österreich Unterwegs 2013/2014; Bundesministerium für Verkehr, Innovation und Technologie: Wien, Juni, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy, J.; Leemput, N.; De Breucker, S.; Geth, F.; Tant, P.; Driesen, J. An availability analysis and energy consumption model for a flemish fleet of electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the European Electric Vehicle Congress (EEVC), Brussels, Belgium, 26–28 October 2011. [Google Scholar]

| Ref. | Penetration | Nominal Charging Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| [6] | ||
| [13] | 10 EVs | 4 |
| [14] | 39 EVs | |
| [15] | 43 EVs | |
| [16] | undefined | |
| [this paper] | 5%, 10–100% | , , 11 |
| (in steps of 10%) |
| Scenario | Nominal Power (Kw) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BM | - | benchmark, no EVs are connected to the grid |
| U1 | 11 | EVs charge at nominal power as soon they arrive home |
| U2 | EVs charge at nominal power as soon they arrive home | |
| U3 | EVs charge at nominal power as soon they arrive home | |
| C1 | 11 | EVs charging with voltage droop control |
| C2 | EVs charging with voltage droop control | |
| C3 | EVs charging with voltage droop control |
| Scenario | Penetration (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | |
| U1 | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/+ | −/+ | −/+ | +/+ | +/+ | +/+ |
| C1 | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/+ | −/+ |
| U2 | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/+ | −/+ | +/+ | +/+ |
| C2 | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− |
| U3 | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/+ | −/+ | +/+ |
| C3 | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− | −/− |
| Penetration (%) | C1 | C2 | C3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.67 | 0.74 | 0.80 |
| 10 | 0.65 | 0.72 | 0.79 |
| 20 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.78 |
| 30 | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.78 |
| 40 | 0.64 | 0.70 | 0.77 |
| 50 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.76 |
| 60 | 0.62 | 0.69 | 0.75 |
| 70 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.74 |
| 80 | 0.60 | 0.66 | 0.72 |
| 90 | 0.59 | 0.64 | 0.71 |
| 100 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 0.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ireshika, M.A.S.T.; Lliuyacc-Blas, R.; Kepplinger, P. Voltage-Based Droop Control of Electric Vehicles in Distribution Grids under Different Charging Power Levels. Energies 2021, 14, 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14133905
Ireshika MAST, Lliuyacc-Blas R, Kepplinger P. Voltage-Based Droop Control of Electric Vehicles in Distribution Grids under Different Charging Power Levels. Energies. 2021; 14(13):3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14133905
Chicago/Turabian StyleIreshika, Muhandiram Arachchige Subodha Tharangi, Ruben Lliuyacc-Blas, and Peter Kepplinger. 2021. "Voltage-Based Droop Control of Electric Vehicles in Distribution Grids under Different Charging Power Levels" Energies 14, no. 13: 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14133905
APA StyleIreshika, M. A. S. T., Lliuyacc-Blas, R., & Kepplinger, P. (2021). Voltage-Based Droop Control of Electric Vehicles in Distribution Grids under Different Charging Power Levels. Energies, 14(13), 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14133905







