Rehydrogenation of Sodium Borates to Close the NaBH4-H2 Cycle: A Review
Abstract
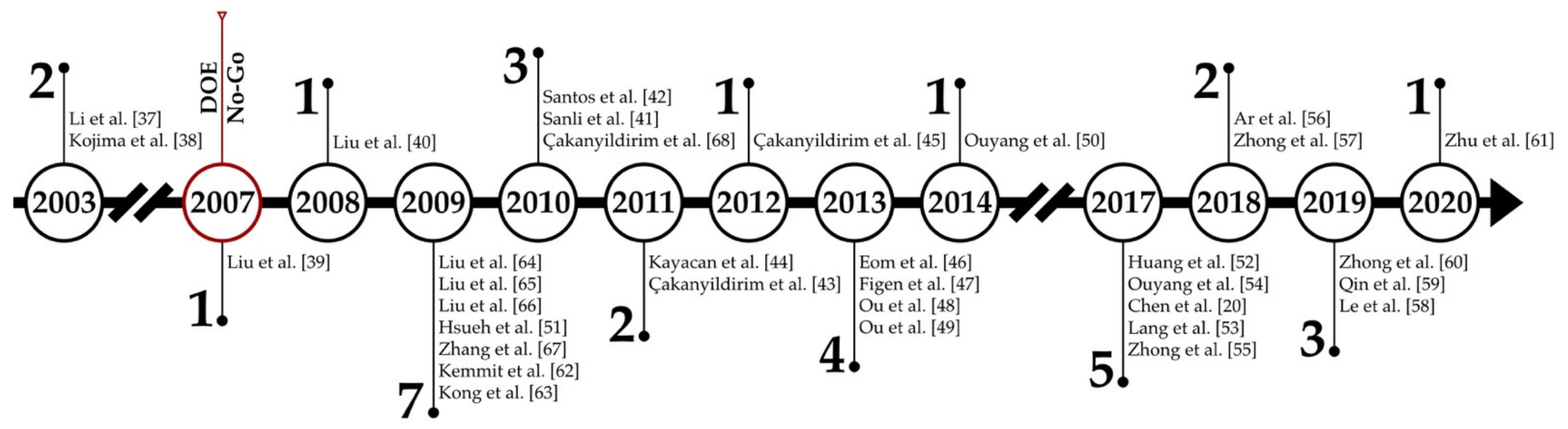
:1. Introduction
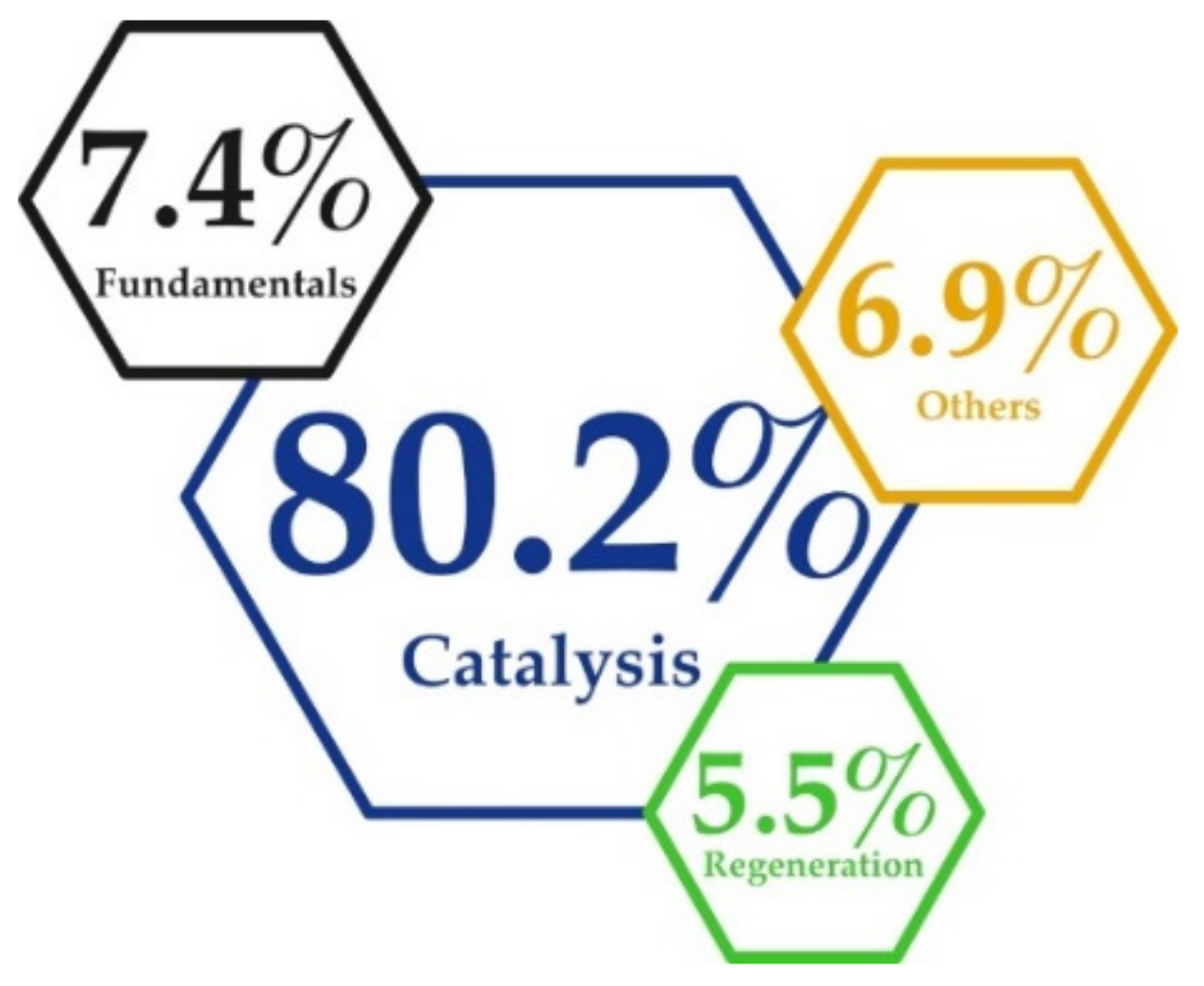
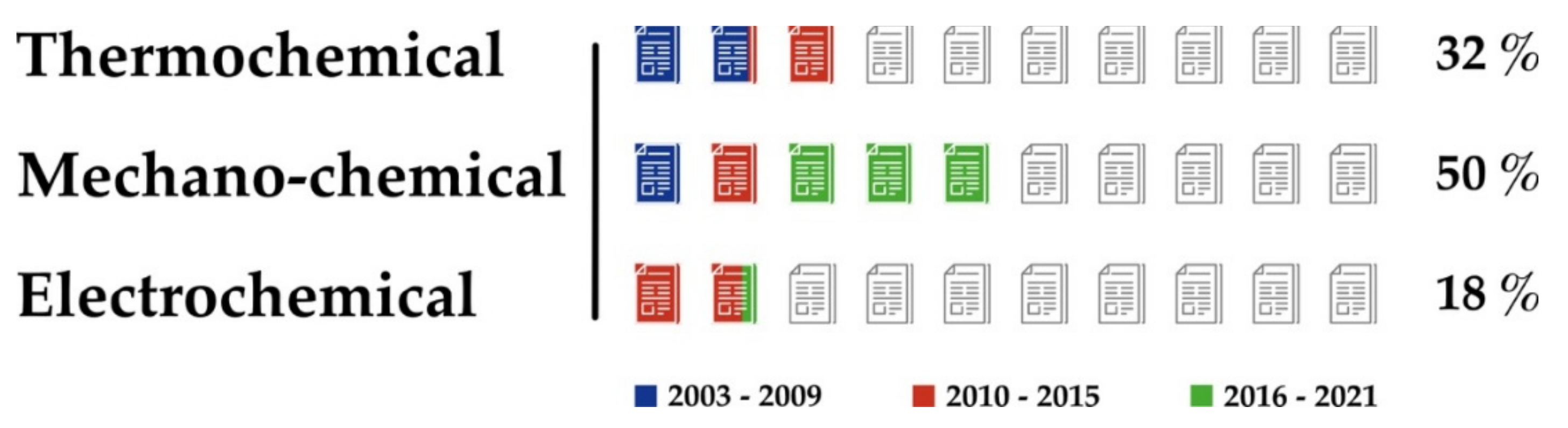
2. Regeneration of NaBH4
2.1. Thermochemical Processes
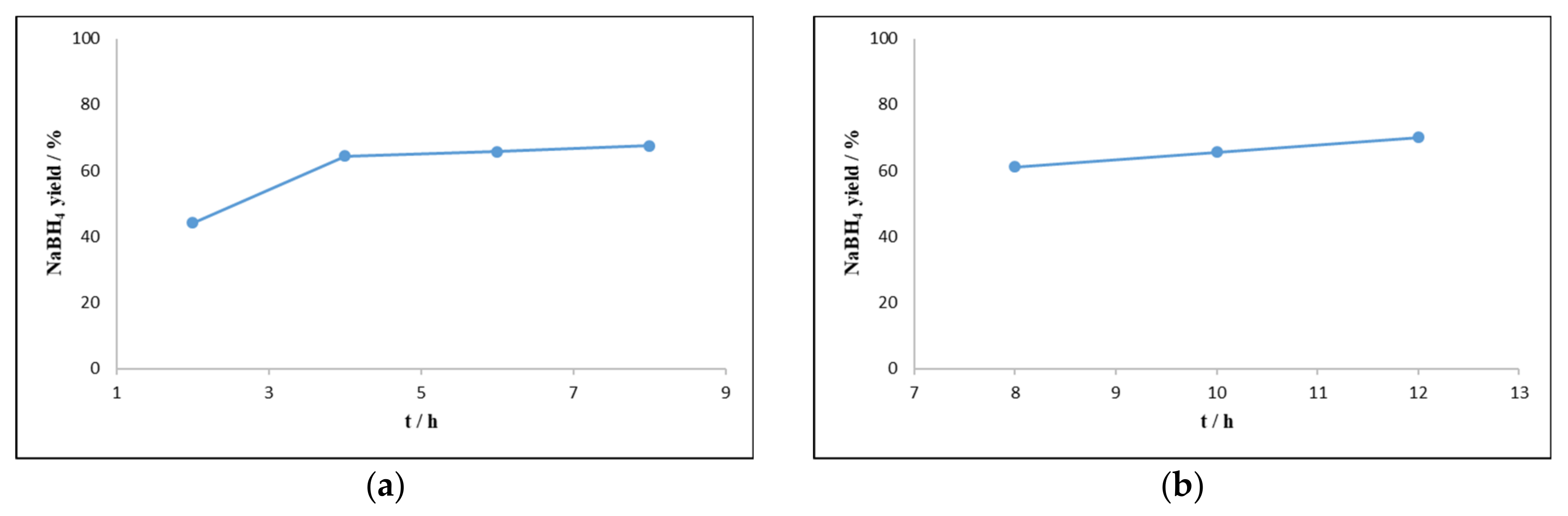
2.1.1. Effect of Temperature, Pressure, and Time of Reaction
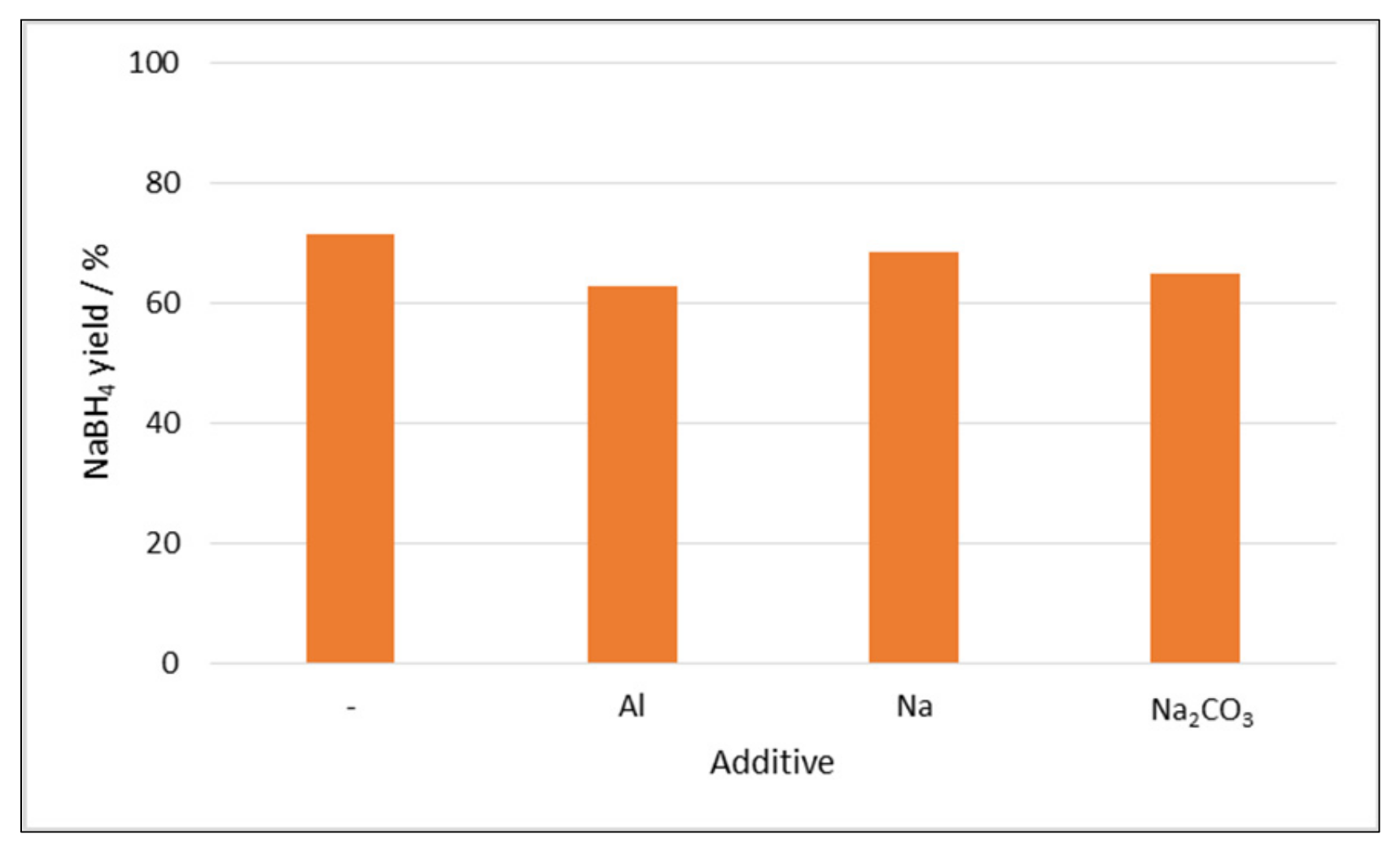
2.1.2. Effect of Additives and the Hydration of the Boron Compound
2.2. Mechano-Chemical Processes
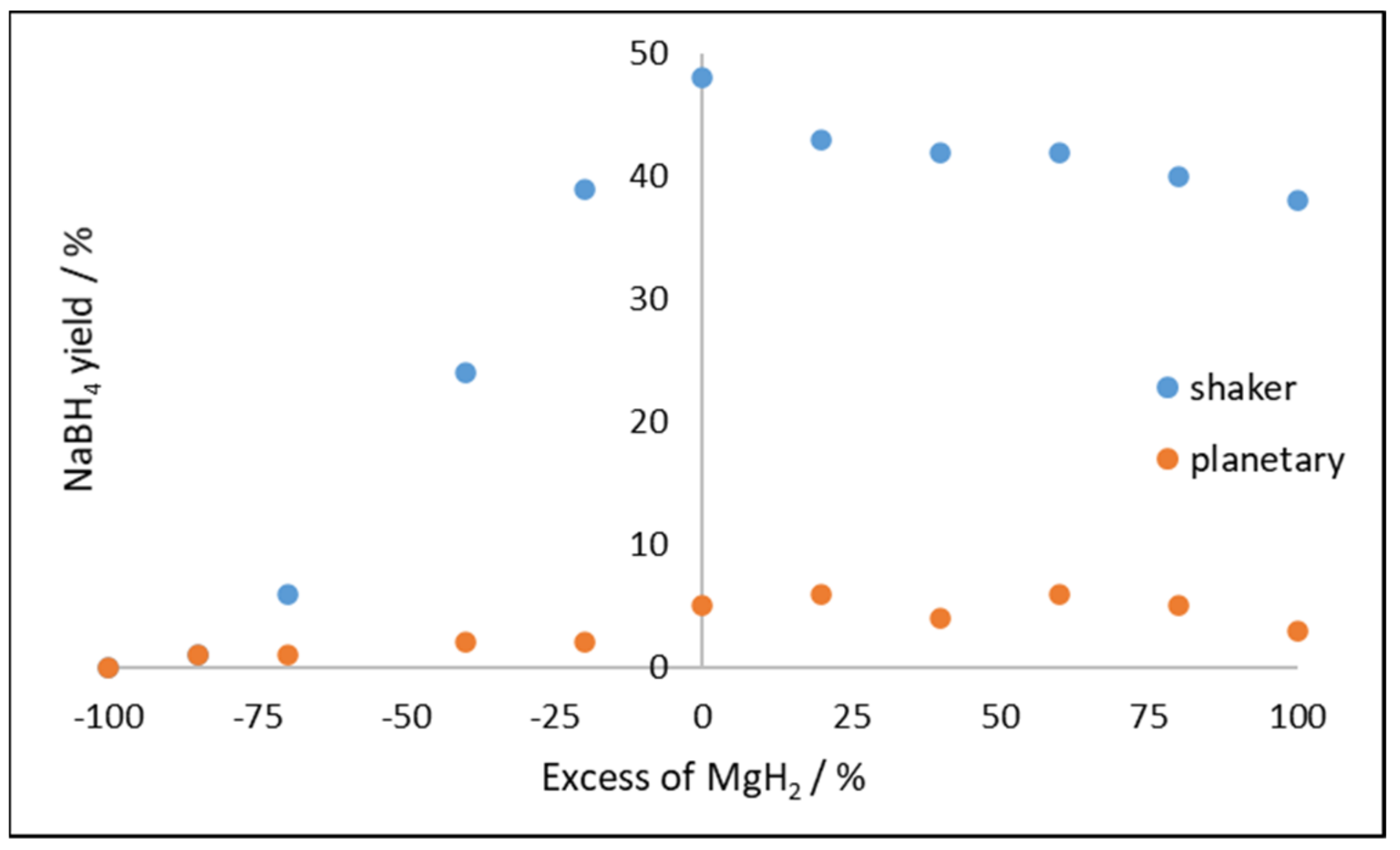
2.2.1. Effect of Time, Ball to Powder Ratio, and Excess of Reactant
2.2.2. Effect of Additives and the Hydration of the Boron Compound
2.2.3. Effect of the Mill
2.2.4. NaBH4 Formation and Energy Efficiency
2.3. Electrochemical Processes
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fazelpour, F.; Markarian, E.; Soltani, N. Wind energy potential and economic assessment of four locations in Sistan and Balouchestan province in Iran. Renew. Energy 2017, 109, 646–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, E.S.; Deane, J.; Gallachóir, B.P.Ó. The role of hydrogen in low carbon energy futures—A review of existing perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3027–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, S.C. A safe, portable, hydrogen gas generator using aqueous borohydride solution and Ru catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2000, 25, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzac, G.; Fernandez, A.; Justo, A.; Sarmiento, B.; Jimenez, M.M. Optimized hydrogen generation in a semicontinuous sodium borohydride hydrolysis reactor for a 60W-scale fuel cell stack. J. Power Source 2011, 196, 4388–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopian, K.; Daud, W.R.W. Challenges and future developments in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lototskyy, M.V.; Tolj, I.; Pickering, L.; Sita, C.; Barbir, F.; Yartys, V. The use of metal hydrides in fuel cell applications. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2017, 27, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawood, F.; Anda, M.; Shafiullah, G. Hydrogen production for energy: An overview. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 3847–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras, T.D.S.; Mozer, T.S.; da Costa Rubim Messeder dos Santos, D.; César, A. Hydrogen: Trends, production and characterization of the main process worldwide. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 2018–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, S.Z. Hydrogen: A brief overview on its sources, production and environmental impact. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 10605–10614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.B.; Akdim, O.; Hannauer, J.; Chamoun, R.; Miele, P. Cobalt, a reactive metal in releasing hydrogen from sodium borohydride by hydrolysis: A short review and a research perspective. Sci. China Ser. B Chem. 2010, 53, 1870–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, H.; Ferreira, M.; Rangel, C.; Pinto, A. Hydrogen generation and storage by aqueous sodium borohydride (NaBH4) hydrolysis for small portable fuel cells (H2–PEMFC). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 15426–15432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, S.C.; Sharp-Goldman, S.L.; Janjua, M.; Kelly, M.T.; Petillo, P.J.; Binder, M. An ultrasafe hydrogen generator: Aqueous, alkaline borohydride solutions and Ru catalyst. ACS Div. Fuel Chem. Prepr. 1999, 44, 864–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.B.; Miele, P. Sodium tetrahydroborate as energy/hydrogen carrier, its history. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2009, 12, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Sequeira, C. Sodium borohydride as a fuel for the future. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3980–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, H.I.; Brown, H.C.; Finholt, A.E. The Preparation of Sodium Borohydride by the High Temperature Reaction of Sodium Hydride with Borate Esters1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Suzuki, K.-I.; Fukumoto, K.; Sasaki, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Kawai, Y.; Hayashi, H. Hydrogen generation using sodium borohydride solution and metal catalyst coated on metal oxide. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2002, 27, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, P.; Dann, S.E.; Wijayantha, K.G.U. Heterogeneous and homogenous catalysts for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of aqueous sodium borohydride (NaBH4) solutions. Energy Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrero-Alfonso, E.Y.; Gray, J.R.; Davis, T.A.; Matthews, M.A. Minimizing water utilization in hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: The role of sodium metaborate hydrates. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 4723–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, N.; Uvarov, V.; Popov, I.; Sasson, Y. Study of by-product of NaBH4 hydrolysis and its behavior at a room temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 7378–7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ouyang, L.; Liu, J.; Yao, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, M. Hydrolysis and regeneration of sodium borohydride (NaBH4)—A combination of hydrogen production and storage. J. Power Source 2017, 359, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.B. The hydrogen cycle with the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: A statistical approach for highlighting the scientific/technical issues to prioritize in the field. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 2673–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.B. Impact of H.I. Schlesinger’s discoveries upon the course of modern chemistry on B-(N-)H hydrogen carriers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 21048–21062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Alligier, D.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.-F.; Demirci, U.B. Hydrogen generation from a sodium borohydride-nickel core@shell structure under hydrolytic conditions. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2707–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tignol, P.; Demirci, U.B. Nickel-based catalysts for hydrogen evolution by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: From structured nickel hydrazine nitrate complexes to reduced counterparts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 14207–14216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, K.; Kulaklı, B.N.; Filiz, B.C.; Alligier, D.; Demirci, U.B.; Figen, A.K. Closing the hydrogen cycle with the couple sodium borohydride-methanol, via the formation of sodium tetramethoxyborate and sodium metaborate. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 11405–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.; Garin, F. Kinetics of Ru-promoted sulphated zirconia catalysed hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium tetrahydroborate. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008, 279, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Gales, L.; Fernandes, V.; Rangel, C.M.; Pinto, A. Alkali free hydrolysis of sodium borohydride for hydrogen generation under pressure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9869–9878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.B.; Miele, P. Cobalt-based catalysts for the hydrolysis of NaBH4 and NH3BH3. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 6872–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahri, H.; Flaud, V.; Touati, R.; Miele, P.; Demirci, U.B. Reaction intermediate/product-induced segregation in cobalt–copper as the catalyst for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102498–102503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugénio, S.; Demirci, U.B.; Silva, T.M.; Carmezim, M.J.; Montemor, M.F. Copper-cobalt foams as active and stable catalysts for hydrogen release by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 8438–8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koska, A.; Toshikj, N.; Hoett, S.; Bernaud, L.; Demirci, U.B. Volcano Plot for Bimetallic Catalysts in Hydrogen Generation by Hydrolysis of Sodium Borohydride. J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 94, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.B. About the Technological Readiness of the H2 Generation by Hydrolysis of B(-N)-H Compounds. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirci, Ü.B. Sodium borohydride for the near-future energy: A rough diamond for Turkey. Turk. J. Chem. 2018, 42, 193–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Energy. Go/No-Go Recommendation for Sodium Borohydride for On-Board Vehicular Hydrogen Storage; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci, U.; Akdim, O.; Miele, P. Ten-year efforts and a no-go recommendation for sodium borohydride for on-board automotive hydrogen storage. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 2638–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Zhong, H.; Li, H.-W.; Zhu, M. A Recycling Hydrogen Supply System of NaBH4 Based on a Facile Regeneration Process: A Review. Inorganics 2018, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.P.; Morigazaki, N.; Liu, B.H.; Suda, S. Preparation of sodium borohydride by the reaction of MgH2 with dehydrated borax through ball milling at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 349, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Haga, T. Recycling process of sodium metaborate to sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2003, 28, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Li, Z.P.; Zhu, J.K.; Morigasaki, N.; Suda, S. Sodium Borohydride Synthesis by Reaction of Na2O Contained Sodium Borate with Al and Hydrogen. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, Z.; Morigasaki, N.; Suda, S. Kinetic characteristics of sodium borohydride formation when sodium meta-borate reacts with magnesium and hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanli, A.E.; Kayacan, I.; Uysal, B.Z.; Aksu, M.L. Recovery of borohydride from metaborate solution using a silver catalyst for application of direct rechargable borohydride/peroxide fuel cells. J. Power Source 2010, 195, 2604–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Sequeira, C. On the electrosynthesis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9851–9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakanyildirim, Ç.; Gürü, M. The Production of NaBH4 from Its Elements by Mechano-chemical Reaction and Usage in Hydrogen Recycle. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2011, 33, 1912–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayacan, I.; Dogan, Ö.M.; Uysal, B.Z. Effect of magnesium on sodium borohydride synthesis from anhydrous borax. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 7410–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakanyildirim, Ç.; Gürü, M. The Processing of NaBH4from Na2B4O7by Mechano-chemical Synthesis and Its Catalytic Dehydrogenation. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2012, 34, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, K.; Cho, E.; Kim, M.; Oh, S.; Nam, S.-W.; Kwon, H. Thermochemical production of sodium borohydride from sodium metaborate in a scaled-up reactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 2804–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figen, A.K.; Pişkin, S. Microwave assisted green chemistry approach of sodium metaborate dihydrate (NaBO2·2H2O) synthesis and use as raw material for sodium borohydride (NaBH4) thermochemical production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 3702–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, T.; Giuliano, A.; Panizza, M.; Barbucci, A.; Cerisola, G. Thermochemical recycling of hydrolyzed NaBH4. Part I: In-Situ and Ex-Situ evaluations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 15269–15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, T.; Panizza, M.; Barbucci, A. Thermochemical recycling of hydrolyzed NaBH4. Part II: Systematical study of parameters dependencies. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 15940–15945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Zhong, H.; Li, Z.; Cao, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, M. Low-cost method for sodium borohydride regeneration and the energy efficiency of its hydrolysis and regeneration process. J. Power Source 2014, 269, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, C.-L.; Liu, C.-H.; Chen, B.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-C.; Hwang, K.-J.; Ku, J.-R. Regeneration of spent-NaBH4 back to NaBH4 by using high-energy ball milling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhong, H.; Ouyang, L.; Peng, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, W.; Fang, F.; Zhu, M. Efficient regeneration of sodium borohydride via ball milling dihydrate sodium metaborate with magnesium and magnesium silicide. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 729, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Jia, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.; Zhu, M.; Yao, X. NaBH4 regeneration from NaBO2 by high-energy ball milling and its plausible mechanism. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 13127–13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Felderhoff, M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M. Enhancing the Regeneration Process of Consumed NaBH4for Hydrogen Storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Ye, J.S.; Liu, J.W.; Wang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhu, M. An one-step approach towards hydrogen production and storage through regeneration of NaBH4. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 7, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ar, I.; Güler, Ö.U.; Gürü, M. Synthesis and characterization of sodium borohydride and a novel catalyst for its dehydrogenation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20214–20233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Ouyang, L.; Liu, J.; Peng, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, W.; Fang, F.; Zhu, M. Sodium borohydride regeneration via direct hydrogen transformation of sodium metaborate tetrahydrate. J. Power Source 2018, 390, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.; Pistidda, C.; Puszkiel, J.; Milanese, C.; Garroni, S.; Emmler, T.; Capurso, G.; Gizer, G.; Klassen, T.; Dornheim, M. Efficient Synthesis of Alkali Borohydrides from Mechanochemical Reduction of Borates Using Magnesium-Aluminum-Based Waste. Metals 2019, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Shao, H.; Zhu, M. Regulation of high-efficient regeneration of sodium borohydride by magnesium-aluminum alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29108–29115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.Z.; Ouyang, L.; Zeng, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Shao, H.; Felderhoff, M.; Zhu, M. Realizing facile regeneration of spent NaBH4 with Mg–Al alloy. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 10723–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Zhong, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Shao, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, M. Closing the Loop for Hydrogen Storage: Facile Regeneration of NaBH4 from its Hydrolytic Product. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8623–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmitt, T.; Gainsford, G. Regeneration of sodium borohydride from sodium metaborate, and isolation of intermediate compounds. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 5726–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Cui, X.; Jin, H.; Wu, J.; Du, H.; Xiong, T. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Sodium Borohydride by Recycling Sodium Metaborate. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 5049–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Li, Z.P.; Suda, S. Influences of alkali in borates on recovery of sodium borohydride. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 474, L6–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Li, Z.P.; Suda, S. Improving MgH2 formation kinetics and its effect on NaBH4 synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 474, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Li, Z.P.; Zhu, J.K. Sodium borohydride formation when Mg reacts with hydrous sodium borates under hydrogen. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, L16–L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, S.; Fang, F.; Chen, G.; Sang, G.; Sun, D. Synthesis of NaBH4 based on a solid-state reaction under Ar atmosphere. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakanyıldırım, Ç.; Gürü, M. Processing of NaBH4 from NaBO2 with MgH2 by ball milling and usage as hydrogen carrier. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1895–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, G.; Moury, R.; Demirci, U.B.; Şener, T.; Miele, P. Boron-based hydrides for chemical hydrogen storage. Int. J. Energy Res. 2013, 37, 825–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. A review on hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 726–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Kelly, M.T.; Ortega, J.V. Review of Chemical Processes for the Synthesis of Sodium Borohydride; Under DOE Cooperative Agreement DE-FC36-04GO14008; Millennium Cell Inc.: Eatontown, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Çakanyıldırım, Ç.; Guru, M. Hydrogen cycle with sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 4634–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, Z. A review: Hydrogen generation from borohydride hydrolysis reaction. J. Power Source 2009, 187, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, S.S.; Yao, X. Progress in sodium borohydride as a hydrogen storage material: Development of hydrolysis catalysts and reaction systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 5983–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Gregory, D.H. Recent Advances in the Use of Sodium Borohydride as a Solid State Hydrogen Store. Energies 2015, 8, 430–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Pan, Z.; Yu, X. Metal B-N-H hydrogen-storage compound: Development and perspectives. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 794, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-C.; Wang, F.-C. The development of a sodium borohydride hydrogen generation system for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 3038–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, G.; Zeng, C. Synthesis of ruthenium nanoparticles deposited on graphene-like transition metal carbide as an effective catalyst for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 14927–14934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hou, X.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Han, S. Co-Mo nanoparticles loaded on three-dimensional graphene oxide as efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29075–29082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, N.; Chen, B.H.; Smith, K.J. Activity and kinetics of ruthenium supported catalysts for sodium borohydride hydrolysis to hydrogen. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29371–29377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Zhang, T.; Wang, G.; Xie, G. Hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solution using supported amorphous alloy catalysts (Ni-Co-P/γ-Al2O3). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 14935–14941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, G. Properties of Cu Co P/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for efficient hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of alkaline NaBH4 solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 5749–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, F.; Zhao, S.; Xia, X. Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of NaBH4 based on high stable NiB/NiFe2O4 catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 3971–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Huang, H. Magnetic sensitive Hericium erinaceus residue chitin/Cu hydrogel nanocomposites for H2 generation by catalyzing NaBH4 hydrolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.A.; Chang, H.-A. Efficient hydrogen production from NaBH4 hydrolysis catalyzed by a magnetic cobalt/carbon composite derived from a zeolitic imidazolate framework. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 296, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Du, X.; Mi, G.; Dong, Y. Immobilization of Amorphous NiB Nanoparticles on Mesoporous Supports: Superior Catalysis for Controllably Hydrolyzing NaBH4 to Release H2. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4372794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, K.; Du, G.; Asiri, A.M.; Sun, X. Self-supported CoP nanosheet arrays: A non-precious metal catalyst for efficient hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13053–13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, K.; Jiang, J. Magnetic CoOx@C-Reduced graphene oxide composite with catalytic activity towards hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28163–28172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, G.; Zhang, X.; Xing, C.; Du, C.; Cao, H.; Li, B. Co-Co3O4@carbon core–shells derived from metal−organic framework nanocrystals as efficient hydrogen evolution catalysts. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3035–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loghmani, M.H.; Shojaei, A.F. Hydrogen production through hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: Oleic acid stabilized Co–La–Zr–B nanoparticle as a novel catalyst. Energy 2014, 68, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loghmani, M.H.; Shojaei, A.F.; Khakzad, M. Hydrogen generation as a clean energy through hydrolysis of sodium borohydride over Cu-Fe-B nano powders: Effect of polymers and surfactants. Energy 2017, 126, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Fu, F.; Yang, X.; Wei, J.; Wang, C.; Zhu, J.; Huang, D.; Astruc, D.; Zhao, P. Highly Efficient and Selective Co@ZIF-8 Nanocatalyst for Hydrogen Release from Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.; Hu, P.-A. Iron-Doped Ni5P4 Ultrathin Nanoporous Nanosheets for Water Splitting and On-Demand Hydrogen Release via NaBH4 Hydrolysis. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiabadi, M.; Shamspur, T.; Mostafavi, A. Performance improvement of oxygen on the carbon substrate surface for dispersion of cobalt nanoparticles and its effect on hydrogen generation rate via NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 1706–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, J.; Roy, B.; Pareek, D.; Sharma, P. Hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis using Co-B/AlPO4 and Co-B/bentonite catalysts. Catal. Struct. React. 2017, 3, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manna, J.; Roy, B.; Sharma, P. Efficient hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis using silica sulfuric acid catalyst. J. Power Source 2015, 275, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, J.; Roy, B.; Vashistha, M.; Sharma, P. Effect of Co+2/BH4-ratio in the synthesis of Co-B catalysts on sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkina, V.G.; Shabunya, S.I.; Kalinin, V.I.; Smirnova, A. Hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride solutions for stationary applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 9227–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostajeran, M.; Prévot, V.; Mal, S.S.; Mattiussi, E.; Davis, B.R.; Baker, R.T. Base-metal catalysts based on porous layered double hydroxides for alkaline-free sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 20092–20102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, S.S.; Chen, Z.; Wood, B.J.; Wang, L.; Lu, G.; Yao, X. New electroless plating method for preparation of highly active Co-B catalysts for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabid, M.R.; Bide, Y.; Fereidouni, N. Boron and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots as a metal-free catalyst for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. N. J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8823–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimharao, K.; Abu-Zied, B.M.; Alfaifi, S.Y. Cobalt oxide supported multi wall carbon nanotube catalysts for hydrogen production via sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 6404–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netskina, O.; Kochubey, D.I.; Prosvirin, I.P.; Kellerman, D.G.; Simagina, V.I.; Komova, O.V. Role of the electronic state of rhodium in sodium borohydride hydrolysis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 390, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netskina, O.; Komova, O.; Mukha, S.; Simagina, V. Aqueous-alkaline NaBH4 solutions: The influence of hydride decomposition on catalytic properties of Co3O. Catal. Commun. 2016, 85, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netskina, O.; Komova, O.; Simagina, V.; Odegova, G.; Prosvirin, I.; Bulavchenko, O. Aqueous-alkaline NaBH4 solution: The influence of storage duration of solutions on reduction and activity of cobalt catalysts. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netskina, O.V.; Pochtar, A.A.; Komova, O.V.; Simagina, V.I. Solid-State NaBH4 Composites as Hydrogen Generation Material: Effect of Thermal Treatment of a Catalyst Precursor on the Hydrogen Generation Rate. Catalysts 2020, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Netskina, O.V.; Tayban, E.S.; Ozerova, A.M.; Komova, O.V.; Simagina, V.I. Solid-State NaBH4/Co Composite as Hydrogen Storage Material: Effect of the Pressing Pressure on Hydrogen Generation Rate. Energies 2019, 12, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Netskina, O.; Tayban, E.; Prosvirin, I.; Komova, O.; Simagina, V. Hydrogen storage systems based on solid-state NaBH4/Co composite: Effect of catalyst precursor on hydrogen generation rate. Renew. Energy 2020, 151, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.H.; Gang, B.G.; Kim, H.; Kwon, S. Sodium borohydride hydrogen generator using Co-P/Ni foam catalysts for 200 W proton exchange membrane fuel cell system. Energy 2015, 90, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumus, E.; San, F.G.B.; Okur, O.; Turk, B.E.; Cengelci, E.; Kilic, M.; Karadağ, Ç.; Cavdar, M.; Turkmen, A.; Yazici, M.S. Development of boron-based hydrogen and fuel cell system for small unmanned aerial vehicle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Kim, T. Electroless Plated Co-Ni-P-B/Ni Foam Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Sodium Borohydride. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 1740–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.N.; Prasad, D.; Bhanushali, J.T.; Kim, H.; Atar, A.B.; Nagaraja, B.M.; Jadhav, A.H. Sustainable Hydrogen Generation by Catalytic Hydrolysis of NaBH4 Using Tailored Nanostructured Urchin-like CuCo2O4 Spinel Catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 586–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornea, A.M.; Abebe, M.W.; Kim, H. Ternary NiCoP urchin like 3D nanostructure supported on nickel foam as a catalyst for hydrogen generation of alkaline NaBH4. Chem. Phys. 2019, 516, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.; Patil, K.N.; Sandhya, N.; Chaitra, C.; Bhanushali, J.T.; Samal, A.K.; Keri, R.S.; Jadhav, A.H.; Nagaraja, B.M. Highly efficient hydrogen production by hydrolysis of NaBH4 using eminently competent recyclable Fe2O3 decorated oxidized MWCNTs robust catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 489, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnamma, R.; Novais, A.; Rangel, C.M.; Yu, L.; Matthews, M.A. Kinetic modeling of self-hydrolysis of aqueous NaBH4 solutions by model-based isoconversional method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 6567–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivarolo, M.; Improta, O.; Magistri, L.; Panizza, M.; Barbucci, A. Thermo-economic analysis of a hydrogen production system by sodium borohydride (NaBH4). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ö.; Izgi, M.S.; Onat, E.; Saka, C. Influence of the using of methanol instead of water in the preparation of Co-B-TiO2 catalyst for hydrogen production by NaBH4 hydrolysis and plasma treatment effect on the Co-B-TiO2 catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 2539–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ö.; Kılınç, D.; Saka, C. Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride with a novel palladium metal complex catalyst. J. Energy Inst. 2016, 89, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ö.; Kılınç, D.; Saka, C. Bimetallic Co-Ni based complex catalyst for hydrogen production by catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride with an alternative approach. J. Energy Inst. 2016, 89, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Yasar, A.O. H2 generation from NaBH4 and NH3BH3 using metal catalysts prepared within p(VI) capsule particles. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 125, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Yasar, A.O.; Aktaş, N. An alternative to metal catalysts: Poly(4-vinyl pyridine)-based polymeric ionic liquid catalyst for H2 generation from hydrolysis and methanolysis of NaBH4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 20562–20572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, C.; Eygi, M.S.; Balbay, A. CoB doped acid modified zeolite catalyst for enhanced hydrogen release from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 15086–15099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Das, D.; Das, N.S.; Nanda, K.K. An efficient on-board metal-free nanocatalyst for controlled room temperature hydrogen production. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2994–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvitepe, N.; Balbay, A.; Saka, C. Optimisation of sepiolite clay with phosphoric acid treatment as support material for CoB catalyst and application to produce hydrogen from the NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 16387–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiz, L.; Abdullayeva, N.; Sankir, M. Nanoporous Pt and Ru catalysts by chemical dealloying of Pt-Al and Ru-Al alloys for ultrafast hydrogen generation. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 744, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavi, R.; Jadhav, A.H.; Lee, K.; Gil Seo, J. Sulfonated Nanolayers of H+-Montmorillonite as an Efficient Acidic Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Sodium Borohydride. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 10980–10985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, W.; Lv, G.; Yang, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, X.; Dai, Z. Hydrolysis of NH3BH3 and NaBH4 by graphene quantum dots-transition metal nanoparticles for highly effective hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, B.; Ding, W. CoB supported on Ag-activated TiO2 as a highly active catalyst for hydrolysis of alkaline NaBH4 solution. Energy 2015, 90, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, Z.; Jian, Z.; Guo, F.; Gao, C. Carbon nanotubes-promoted Co-B catalysts for rapid hydrogen generation via NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 19868–19877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Xie, W.; Jian, Z.; Liao, X.; Wang, Y. Graphene modified Co-B catalysts for rapid hydrogen production from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 17954–17962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Lu, L.; Zhu, S.; Liu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, J.; Ruan, Z.; Liu, Y. Ultra small cobalt nanoparticles supported on MCM41: One-pot synthesis and catalytic hydrogen production from alkaline borohydride. Catal. Commun. 2019, 118, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Das, T. Generation of hydrogen from NaBH4 solution using metal-boride (CoB, FeB, NiB) catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 29360–29369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Zabihi, M. Hydrogen generation by catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride using the nano-bimetallic catalysts supported on the core-shell magnetic nanocomposite of activated carbon. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 12331–12346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.; Rangel, C.M. A dynamic two phase flow model for a pilot scale sodium borohydride hydrogen generation reactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5291–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamboli, A.; Chaugule, A.A.; Sheikh, F.A.; Chung, W.-J.; Kim, H. Synthesis and application of CeO2-NiO loaded TiO2 nanofiber as novel catalyst for hydrogen production from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Energy 2015, 89, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboli, A.H.; Gosavi, S.; Terashima, C.; Fujishima, A.; Pawar, A.A.; Kim, H. Synthesis of cerium and nickel doped titanium nanofibers for hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboli, A.H.; Jadhav, A.; Chung, W.-J.; Kim, H. Structurally modified cerium doped hydrotalcite-like precursor as efficient catalysts for hydrogen production from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Energy 2015, 93, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Huang, G.; Gao, C.; Li, X.; Qiu, H. Co nanoparticles supported 3D structure for catalytic H2 production. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 191, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, M.; Xia, F.; Gao, C.; Qiu, H. Preparation of magnetically recyclable CuFe2O4/RGO for catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 13058–13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomboc, G.R.M.; Tamboli, A.; Kim, H. Synthesis of Co3O4 macrocubes catalyst using novel chitosan/urea template for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. Energy 2017, 121, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, D.D.; Lin, K.-Y.A. ZIF-67-derived Co3O4 rhombic dodecahedron as an efficient non-noble-metal catalyst for hydrogen generation from borohydride hydrolysis. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, D.D.; Lin, K.-Y. Ruthenium supported on ZIF-67 as an enhanced catalyst for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzundurukan, A.; Devrim, Y. Hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis by multi-walled carbon nanotube supported platinum catalyst: A kinetic study. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 17586–17594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-C.; Fang, W.-H. The development of a PEMFC hybrid power electric vehicle with automatic sodium borohydride hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 10376–10389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ke, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Han, S. Efficient hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride catalyzed by cobalt nanoparticles supported on three–dimensional graphene oxide. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 95, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ashraf, S.; Jiang, J.; Han, G.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.; Li, B. Pitaya pulp structural cobalt-carbon composite for efficient hydrogen generation from borohydride hydrolysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 808, 151774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Xie, G. Hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution using electroless-deposited Co-W-P supported on γ-Al2O3. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 7965–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wang, G.; Xie, G. Hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution using Co-Ni-Mo-P/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xie, G. Hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution using electroless-deposited Co-Ni-W-P/γ-Al2O3 as catalysts. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 702, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Hao, W.; Guo, Y. Highly efficient ferromagnetic Co-B-O catalyst for hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 17164–17171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ouyang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M. Hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis accelerated by zinc chloride without catalyst: A kinetic study. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 717, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Tian, J. Promoted Mo incorporated Co-Ru-B catalyst for fast hydrolysis of NaBH4 in alkaline solutions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 16202–16211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, X.; Jing, C.; Hu, W.; Tian, S.; Tian, J. In Situ synthesis of cobalt-based tri-metallic nanosheets as highly efficient catalysts for sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Preparation and catalytic activity of PVP-protected Au/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of basic NaBH4 solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liao, J.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, R. Solid-state-reaction synthesis of cotton-like CoB alloy at room temperature as a catalyst for hydrogen generation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 475, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liao, J.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, R. Preparation of pompon-like Co-B nanoalloy by a room-temperature solid-state-reaction as a catalyst for hydrolysis of borohydride solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 6646–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, S.; Wei, Y.; Meng, W.; Xie, Y.; Cui, Y.; Lian, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. Hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution using nanostructured Co-Ni-P catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 16529–16537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Bai, S.; Qi, K.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Wang, D. Catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride via nanostructured cobalt–boron catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, S.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Liu, H.; Xin, S. Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride using nanostructured NiB catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 16077–16086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Qi, K.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S. Nanostructured cobalt-phosphorous catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solution. Renew. Energy 2016, 89, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, K.; Zhang, D.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, G.; Li, G.; Bai, S. Cobalt-copper-boron nanoparticles as catalysts for the efficient hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 9845–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Dong, X.; Ma, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Q. Co3O4 hollow fiber: An efficient catalyst precursor for hydrolysis of sodium borohydride to generate hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Dong, X.-L.; Yang, Y.-M.; Shi, Q.-Y.; Lu, Y.-H.; Liu, H.-Y.; Yu, Y.-N.; Zhang, M.-H.; Qi, M.; Wang, Q. Co-O-P composite nanocatalysts for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 10745–10753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, D. Synthesis of bifunctional non-noble monolithic catalyst Co-W-P/carbon cloth for sodium borohydride hydrolysis and reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 25860–25868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Meng, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Qi, K.; Zhang, K. Fast hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis catalyzed by nanostructured Co-Ni-B catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 6072–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H. Highly efficient and reactivated electrocatalyst of ruthenium electrodeposited on nickel foam for hydrogen evolution from NaBH4 alkaline solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, J.; Isimjan, T.T.; Yang, X. Palladium nanoclusters decorated partially decomposed porous ZIF-67 polyhedron with ultrahigh catalytic activity and stability on hydrogen generation. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Mao, X.; Zi, Q.; Zhang, R.; Dou, T.; Yip, A.C.K. Mechanism and kinetics of sodium borohydride hydrolysis over crystalline nickel and nickel bordie and amorphous nickel-boron nanoparticles. J. Power Source 2014, 268, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Jiang, D.; She, Z.; Zou, Y.; Chu, H.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Tang, C.; Sun, L. Hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride using a cobalt–zinc–boron/graphene nanocomposite treated with sodium hydroxide. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 4111–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Wang, K.; Du, G.; Asiri, A.M.; Sun, X. 3D hierarchical CuO/Co3O4 core-shell nanowire array on copper foam for on-demand hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88846–88850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Kinetic study of NaBH4 catalytic hydrolysis using supported NiCo2O4. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 125530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Dai, P.; Wang, C.; Gao, J.; Liu, X. Stability and kinetic studies of MOF-derived carbon-confined ultrafine Co catalyst for sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 3702–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of NaBH4 and NH3BH3 composite promoted by AlCl3. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 16344–16351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, H. Protonated Poly(ethylene imine)-Coated Silica Nanoparticles for Promoting Hydrogen Generation from the Hydrolysis of Sodium Borohydride. ChemPlusChem 2020, 85, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Matthews, M.A. A reactor model for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride and water vapor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 3830–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Pellechia, P.; Matthews, M.A. Kinetic models of concentrated NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. Hierarchical porous ZIF-8 for hydrogen production via the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 4416–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. Facile synthesis and characterization of nano-Pd loaded NiCo microfibers as stable catalysts for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 743, 137170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabielaitė, A.; Balčiūnaitė, A.; Stalnionienė, I.; Lichušina, S.; Šimkūnaitė, D.; Vaičiūnienė, J.; Šimkūnaitė-Stanynienė, B.; Selskis, A.; Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, L.; Norkus, E. Fiber-shaped Co modified with Au and Pt crystallites for enhanced hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 23310–23318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Cheng, L.; Hou, X.; Li, Y.; Han, S. Non-noble Co anchored on nanoporous graphene oxide, as an efficient and long-life catalyst for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 563, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhangab, H.; Xuc, G.; Zhangab, L.; Wangb, W.; Miaob, W.; Chenb, K.; Chengb, L.; Lib, Y.; Hanab, S. Ultrafine cobalt nanoparticles supported on carbon nanospheres for hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Renew. Energy 2020, 162, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhangab, H.; Zhangab, L.; Rodríguez-Pérez, I.A.; Miaob, W.; Chenb, K.; Wangb, W.; Lib, Y.; Hanab, S. Carbon nanospheres supported bimetallic Pt-Co as an efficient catalyst for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 540, 148296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, J.; Ma, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, Z. Polyvinylpyrrolidone stabilized-Ru nanoclusters loaded onto reduced graphene oxide as high active catalyst for hydrogen evolution. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2017, 19, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, F.; Yang, L.; Dong, H. Highly dispersed Ru/Co catalyst with enhanced activity for catalyzing NaBH4 hydrolysis in alkaline solutions. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2512–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, F.; Yang, L.; He, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, D.; Dong, H. Ultrasmall Ru nanoparticles supported on chitin nanofibers for hydrogen production from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2019–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, K.; Fan, G.; Jiang, W. Efficient Hydrogen Generation from the NaBH4 Hydrolysis by Cobalt-Based Catalysts: Positive Roles of Sulfur-Containing Salts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 9376–9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, D.; Tao, X.; Dai, P.; Guo, Q.; Liu, X. Synthesis of MOF-derived Co@C composites and application for efficient hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 469, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. UiO-66 as a catalyst for hydrogen production via the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 10851–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, Q.; Meng, X. Catalytic hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride solution for hydrogen evolution in a micro-scale fluidized bed reactor. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 6758–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Su, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B. A novel Enteromorpha based hydrogel for copper and nickel nanoparticle preparation and their use in hydrogen production as catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 6746–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Rao, X.; Yan, P.; Isimjan, T.T.; Yang, X. Structure-regulated Ru particles decorated P-vacancy-rich CoP as a highly active and durable catalyst for NaBH4 hydrolysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 591, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fang, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Liu, H.; Ge, H. Hydrogen generation mechanism of BH4− spontaneous hydrolysis: A sight from ab initio calculation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 22668–22676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.-W.; Dai, H.-B.; Zhong, Y.-J.; Sun, L.-X.; Wang, P. A new reactivation method towards deactivation of honeycomb ceramic monolith supported cobalt-molybdenum-boron catalyst in hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 9373–9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Huang, P.; Xiang, C.; Chu, H.; Qiu, S.; Yan, E.; Xu, F.; Sun, L. Effects of the Preparation Solvent on the Catalytic Properties of Cobalt–Boron Alloy for the Hydrolysis of Alkaline Sodium Borohydride. Metals 2017, 7, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xiang, C.; Chu, H.; Qiu, S.; Yan, E.; Xu, F.; Sun, L. Chitosan-mediated Co-Ce-B nanoparticles for catalyzing the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 4912–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zied, B.M.; Alamry, K.A. Green synthesis of 3D hierarchical nanostructured Co3O4/carbon catalysts for the application in sodium borohydride hydrolysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 798, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Gao, X.; Jiang, J. In situ synthesis of cobalt stabilized on macroscopic biopolymer hydrogel as economical and recyclable catalyst for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. J. Power Source 2014, 257, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, S.; Özkar, S. Inverse relation between the catalytic activity and catalyst concentration for the ruthenium(0) nanoparticles supported on xonotlite nanowire in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 424, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Khan, Z.; Malik, M.A. Bimetallic Ag-Ni nanoparticles as an effective catalyst for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 16452–16466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M. Enhanced H2 generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis and methanolysis by cellulose micro-fibrous cottons as metal templated catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 6539–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, D.; Alkahlawy, A.; Zaki, T. Hydrolysis of NaBH4 using ZVI/Fe2(MoO4)3 nanocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18289–18295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.; Hasimoglu, A.; Ozdemir, O.K. Kinetic properties of Cobalt-Titanium-Boride (Co-Ti-B) catalysts for sodium borohydride hydrolysis reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbay, A.; Saka, C. Effect of phosphoric acid addition on the hydrogen production from hydrolysis of NaBH4 with Cu based catalyst. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2018, 40, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkanli, E.; Figen, H.E. Sodium borohydride hydrolysis by using ceramic foam supported bimetallic and trimetallic catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 9959–9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandal, H.; Jadhav, A.; Kim, H. Cobalt impregnated magnetite-multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite as magnetically separable efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation by NaBH4 hydrolysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 699, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydaroglu, F.; Ozdemir, E.; Hasimoglu, A. An effective synthesis route for improving the catalytic activity of carbon-supported Co-B catalyst for hydrogen generation through hydrolysis of NaBH4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baye, A.F.; Abebe, M.W.; Appiah-Ntiamoah, R.; Kim, H. Engineered iron-carbon-cobalt (Fe3O4@C-Co) core-shell composite with synergistic catalytic properties towards hydrogen generation via NaBH4 hydrolysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 543, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekirogullari, M. Hydrogen production from sodium borohydride by ZnCl2 treated defatted spent coffee ground catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 9733–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boran, A.; Erkan, S.; Eroglu, I. Hydrogen generation from solid state NaBH4 by using FeCl3 catalyst for portable proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 18915–18926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, G.; Özer, A.; Yurtcan, A.B. Hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride with Ni and Co based catalysts supported on Co3O4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 22205–22214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, G.; Özer, A.; Yurtcan, A.B. Development of effective catalysts for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride: Ru, Pt, Pd nanoparticles supported on Co3O4. Energy 2019, 180, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Lu, P.; Dong, J. Robust nickel-polymer nanocomposite particles for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. Fuel 2016, 166, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyhan, A.A.; Edebali, S.; Fangaj, E. A study on hydrogen generation from NaBH4 solution using Co-loaded resin catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 34761–34772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Bandal, H.A.; Appiah-Ntiamoah, R.; Jadhav, A.R.; Kim, H. Cobalt nanoparticles supported on magnetic core-shell structured carbon as a highly efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 9296–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, H. Fabrication of amorphous Co-Cr-B and catalytic sodium borohydride hydrolysis for hydrogen generation. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, A.; Jadhav, A.H.; Puguan, J.M.C.; Appiah-Ntiamoah, R.; Kim, H. Fabrication of ionic liquid/polymer nanoscale networks by electrospinning and chemical cross-linking and their application in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of NaBH4. Energy 2015, 79, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, A.; Puguan, J.M.C.; Chung, W.-J.; Kim, H. Hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride using chemically modified multiwalled carbon nanotubes with pyridinium based ionic liquid and decorated with highly dispersed Mn nanoparticles. J. Power Source 2015, 293, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-C.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Chen, B.-H. Hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride using bimetallic Ni–Co nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide as catalysts. Energy 2015, 90, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, B.C.; Figen, A.K. The Molecular-Kinetic Approach to Hydrolysis of Boron Hydrides for Hydrogen Production. Kinet. Catal. 2019, 60, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, B.C.; Figen, A.K. Hydrogen production from sodium borohydride originated compounds: Fabrication of electrospun nano-crystalline Co3O4 catalyst and its activity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 9883–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, B.C.; Figen, A.K. Insight into the role of solvents in enhancing hydrogen production: Ru-Co nanoparticles catalyzed sodium borohydride dehydrogenation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28471–28482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Cobalt Carbonate Hydroxide Nanowire Array on Ti Mesh: An Efficient and Robust 3D Catalyst for On-Demand Hydrogen Generation from Alkaline NaBH4 Solution. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 14831–14835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ma, J. In situ synthesis of graphene supported Co-Sn-B alloy as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Zhao, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, C.; Tao, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, J. Preparation, characterization, and properties of Pt/Al2O3/cordierite monolith catalyst for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride in a flow reactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28463–28470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.; Sahiner, N. Superior reusability of metal catalysts prepared within poly(ethylene imine) microgels for H2 production from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 127, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.B.; Miele, P. Reaction mechanisms of the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: A discussion focusing on cobalt-based catalysts. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deonikar, V.; Rathod, P.V.; Pornea, A.M.; Puguan, J.M.C.; Park, K.; Kim, H. Hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride by a Cu and Mo promoted Co catalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 86, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didehban, A.; Zabihi, M.; Babajani, N. Preparation of the efficient nano-bimetallic cobalt-nickel catalysts supported on the various magnetic substrates for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride in alkaline solutions. Polyhedron 2020, 180, 114405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didehban, A.; Zabihi, M.; Shahrouzi, J.R. Experimental studies on the catalytic behavior of alloy and core-shell supported Co-Ni bimetallic nano-catalysts for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20645–20660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Shangguan, J.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, K. The coralline cobalt oxides compound of multiple valence states deriving from flower-like layered double hydroxide for efficient hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of NaBH4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 2390–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, Q.; Su, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Zhou, W. Preparation and catalytic activity of wheat straw cellulose based hydrogel-nanometal composites for hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 9978–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Rao, X.; Yan, P.; Isimjan, T.T.; Yang, X. Shaggy-like Ru-clusters decorated core-shell metal-organic framework-derived CoOx@NPC as high-efficiency catalyst for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 7772–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, S.; Kaya, B.; Caf, F.; Enez, B.; Fincan, S.A. Innovative hydrogen release from sodium borohydride hydrolysis using biocatalyst-like Fe2O3 nanoparticles impregnated on Bacillus simplex bacteria. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 15410–15430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, S.; Özkar, S. Ceria supported manganese(0) nanoparticle catalysts for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 15262–15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durano, M.M.; Tamboli, A.; Kim, H. Cobalt oxide synthesized using urea precipitation method as catalyst for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 520, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangaj, E.; Ali, A.A.; Güngör, F.; Bektaş, S.; Ceyhan, A.A. The use of metallurgical waste sludge as a catalyst in hydrogen production from sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 13322–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, R.; Scirè, S.; Venezia, A. Carbon supported bimetallic Ru-Co catalysts for H2 production through NaBH4 and NH3 BH3 hydrolysis. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ding, C.; Wang, J.; Ding, G.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, P.; Gao, X. Cobalt nanoparticles packaged into nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from metal-organic framework nanocrystals for hydrogen production by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 8365–8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Hou, Y.; Li, B. Facile synthesis of a hollow Ni–Fe–B nanochain and its enhanced catalytic activity for hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25873–25880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Hou, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, Y. Novel Ni-Co-B hollow nanospheres promote hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 15245–15254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, B.; Yanga, D.; Wana, Z.; Yana, P.; Tiana, J.; Isimjan, T.T.; Yanga, X. Rugae-like Ni2P-CoP nanoarrays as a bi-functional catalyst for hydrogen generation: NaBH4 hydrolysis and water reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 265, 118584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Yan, P.; Tian, J.; Shen, X.; Isimjan, T.T.; Yang, X. Hierarchically structured rugae-like RuP3-CoP arrays as robust catalysts synergistically promoting hydrogen generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 8865–8872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wu, Q.; Sun, J.; Chen, T.; Feng, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, B.; Ding, W. Highly stable and controllable CoB/Ni-foam catalysts for hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 21063–21072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qian, J.; Iqbal, A.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Qin, W. Pd nanoparticles immobilized on magnetic carbon dots@Fe3O4 nanocubes as a synergistic catalyst for hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 15167–15177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansu, T.A.; Caglar, A.; Sahin, O.; Kivrak, H. Hydrolysis and electrooxidation of sodium borohydride on novel CNT supported CoBi fuel cell catalyst. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostert, L.; Neiva, E.G.C.; Zarbin, A.J.G.; Orth, E.S. Nanocatalysts for hydrogen production from borohydride hydrolysis: Graphene-derived thin films with Ag- and Ni-based nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 22226–22233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.P.; Ho, C.Y.; Hsu, L.C.; Chang, Y.-J. Synergistic effect on hydrolytic sodium borohydride adding waste Al for hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 10334–10341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, D.; Cheng, D. Porous Co2P nanowires as high efficient bifunctional catalysts for 4-nitrophenol reduction and sodium borohydride hydrolysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 507, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.; Dushatinski, T.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Gold nanoparticle/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite as novel catalyst for hydrogen evolution reactions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 18985–18990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokawa, H.; Driss, H.; Trovela, F.; Miyaoka, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Kojima, Y.; Zaman, S.F.; Al-Zahrani, A.; Alhamed, Y.; Petrov, L. Catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride on Co catalysts. Int. J. Energy Res. 2016, 40, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irum, M.; Zaheer, M.; Friedrich, M.; Kempe, R. Mesoporous silica nanosphere supported platinum nanoparticles (Pt@MSN): One-pot synthesis and catalytic hydrogen generation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10438–10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izgi, M.S.; Şahin, Ö.; Saka, C. Hydrogen production from NaBH4 using Co-Cu-B catalysts prepared in methanol: Effect of plasma treatment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-C.; Hung, C.-J.; Hu, C.-C. Kinetics of hydrogen generation on NaBH4 powders using cobalt catalysts. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 87, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.A.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Fouad, D.M.; Ibrahim, S.A. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and MOFs-derived CuO@C for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 31230–31238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, D.; Tao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Han, S. Kinetics study on hydrolytic dehydrogenation of alkaline sodium borohydride catalyzed by Mo-modified Co–B nanoparticles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 7308–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibar, M.E.; Engintepe, E.; Özdemir, E.; Kaplan, Ö.; Çelik, C.; Akın, A.N. Effect of morphology of activated carbon supports for cobalt boride catalysts on the hydrolysis reaction of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2018, 50, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, D.; Sahin, O. Highly active and stable CeO2 supported nickel-complex catalyst in hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, S.S.; Li, W.; Fortner, J.D. Towards optimizing cobalt based metal oxide nanocrystals for hydrogen generation via NaBH4 hydrolysis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 589, 117303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Oh, T.H.; Kwon, S. Simple catalyst bed sizing of a NaBH4 hydrogen generator with fast startup for small unmanned aerial vehicles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılınç, D.; Şahin, Ö. Synthesis of polymer supported Ni (II)-Schiff Base complex and its usage as a catalyst in sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 10717–10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılınç, D.; Şahin, Ö. Al2O3 based Co-Schiff Base complex catalyst in hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28391–28401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılınç, D.; Şahin, Ö. Effective TiO2 supported Cu-Complex catalyst in NaBH4 hydrolysis reaction to hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 18858–18865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılınç, D.; Şahin, Ö.; Saka, C. Salicylaldimine-Ni complex supported on Al2O3: Highly efficient catalyst for hydrogen production from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindtworth, E.; Delidovich, I.; Palkovits, R. Borohydride in ionic liquids for tailored hydrogen release. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20772–20782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-M.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, S.; Kim, T. Development of a high-storage-density hydrogen generator using solid-state NaBH4 as a hydrogen source for unmanned aerial vehicles. Appl. Energy 2019, 251, 113331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lale, A.; Wasan, A.; Kumar, R.; Miele, P.; Demirci, U.B.; Bernard, S. Organosilicon polymer-derived mesoporous 3D silicon carbide, carbonitride and nitride structures as platinum supports for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 15477–15488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, H.; Choi, K.S.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.-Y.; Yu, H.K. Carbon layer supported nickel catalyst for sodium borohydride (NaBH4) dehydrogenation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.-S.; A Shin, H.; Jo, Y.S.; Jeong, H.; Sohn, H.; Yoon, C.W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, K.-B.; Nam, S.W. Surface area enhancement of nickel foam by low-temperature chemical alloying/dealloying and its application for sodium borohydride hydrolysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 843, 155759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Lu, M.-T.; Lai, Y.-H.; Yang, J.-T. Design and testing of a novel catalytic reactor to generate hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 886, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hong, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Huang, P.; Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Zou, Y.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; et al. Encapsulated cobalt nanoparticles as a recoverable catalyst for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 27, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ma, M.; Xie, L.; Yao, Y.; Kong, R.; Du, G.; Asiri, A.M.; Sun, X. Monolithically integrated NiCoP nanosheet array on Ti mesh: An efficient and reusable catalyst in NaBH4 alkaline media toward on-demand hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19028–19034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Zhang, L. Synergistical photo-thermal-catalysis of Zn2GeO4:xFe3+ for H2 evolution in NaBH4 hydrolysis reaction. Catal. Commun. 2021, 156, 106321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, W.; Li, F.; Cui, A.; Hong, J. Preparation of CoB/ZIF-8 supported catalyst by single step reduction and its activity in hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakko-Saksa, P.T.; Cook, C.; Kiviaho, J.; Repo, T. Liquid organic hydrogen carriers for transportation and storing of renewable energy—Review and discussion. J. Power Source 2018, 396, 803–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.-B.; Gao, L.-L.; Liang, Y.; Kang, X.-D.; Wang, P. Promoted hydrogen generation from ammonia borane aqueous solution using cobalt–molybdenum–boron/nickel foam catalyst. J. Power Source 2010, 195, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, X.; Sun, T.; Jia, J. Innovative Desulfurization Process of Coal Water Slurry under Atmospheric Condition via Sodium Metaborate Electroreduction in the Isolated Slot. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 5007–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Sun, T.; Jia, J. A novel desulphurization process of coal water slurry via sodium metaborate electroreduction in the alkaline system. Fuel 2012, 96, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Sun, T.; Jia, J.; Lou, Z. A novel desulfurization process of gasoline via sodium metaborate electroreduction with pulse voltage using a boron-doped diamond thin film electrode. Fuel 2013, 113, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Lai, F.; Zhu, F.; Luo, D. Optimal extractive and reductive desulfurization process using sodium borohydride in situ generated via sodium metaborate electroreduction in ionic liquid. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2020, 150, 107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Chen, B.-H. The Concept about the Regeneration of Spent Borohydrides and Used Catalysts from Green Electricity. Materials 2015, 8, 3456–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varin, R.; Jang, M.; Czujko, T.; Wronski, Z. The effect of ball milling under hydrogen and argon on the desorption properties of MgH2 covered with a layer of Mg(OH)2. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 493, L29–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.-Y.; Zhu, C.-G.; Wang, F.-W.; Wei, Y.-J. Preparation of Sodium Borohydride by Copper Electrolysis. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 7749–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
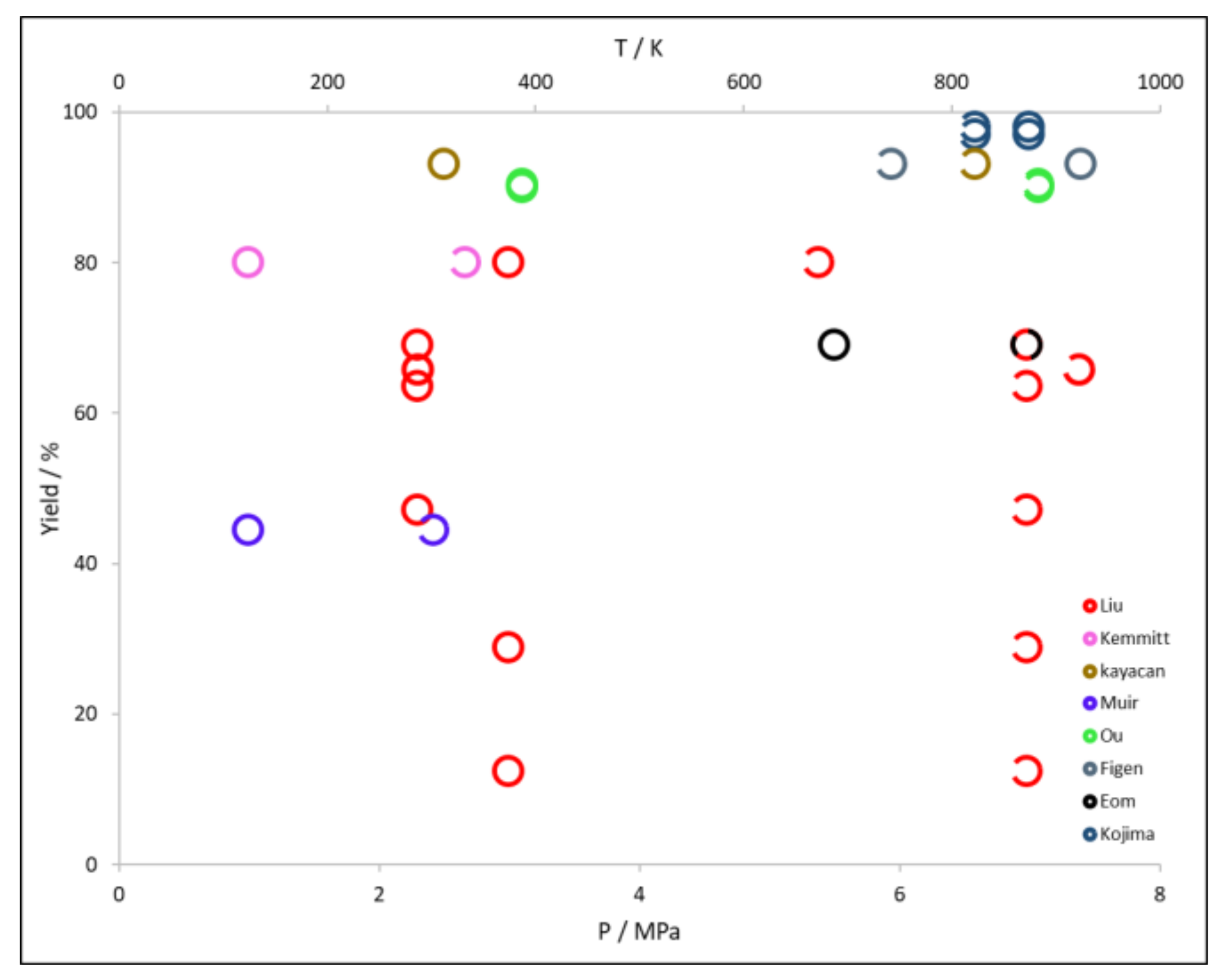
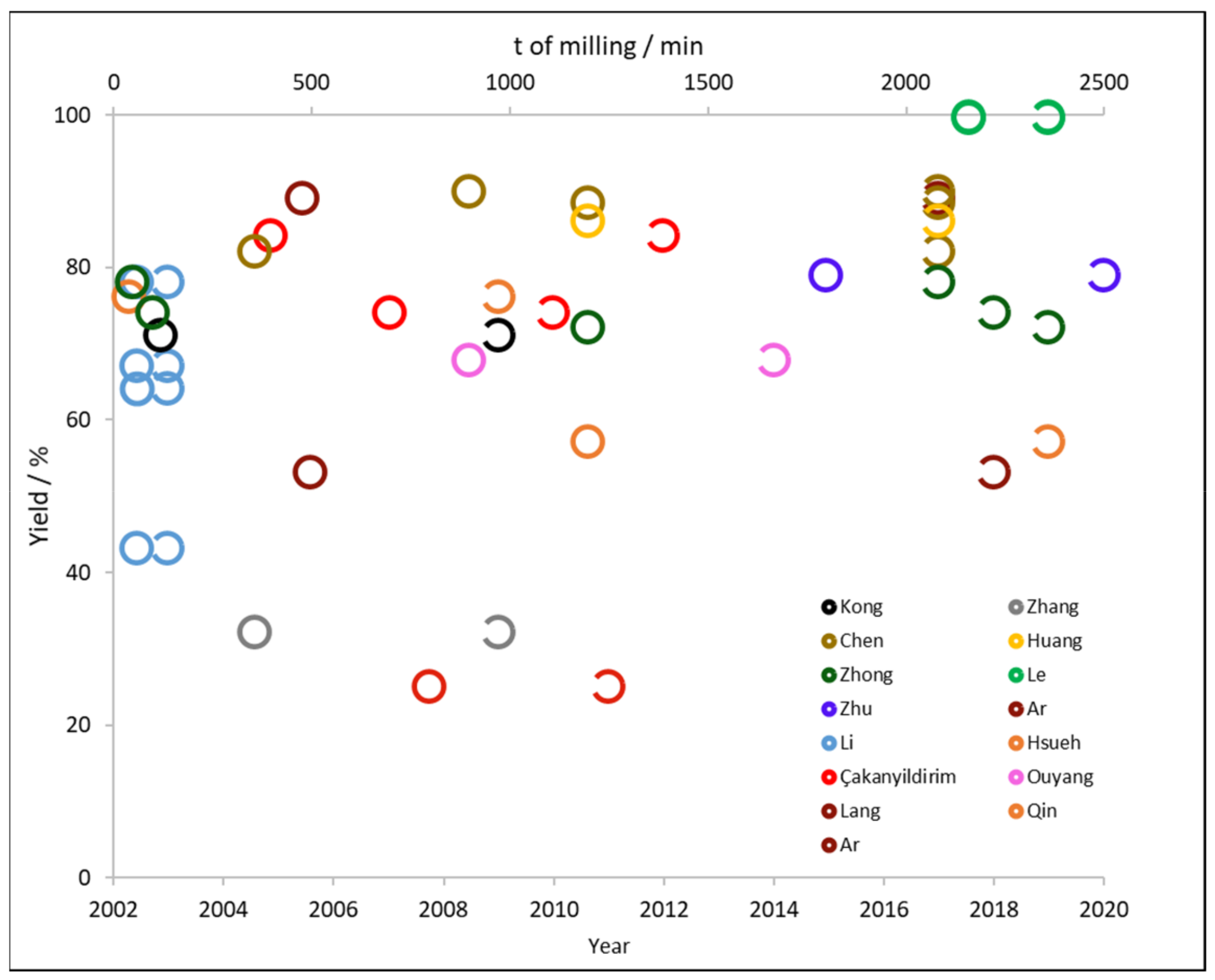
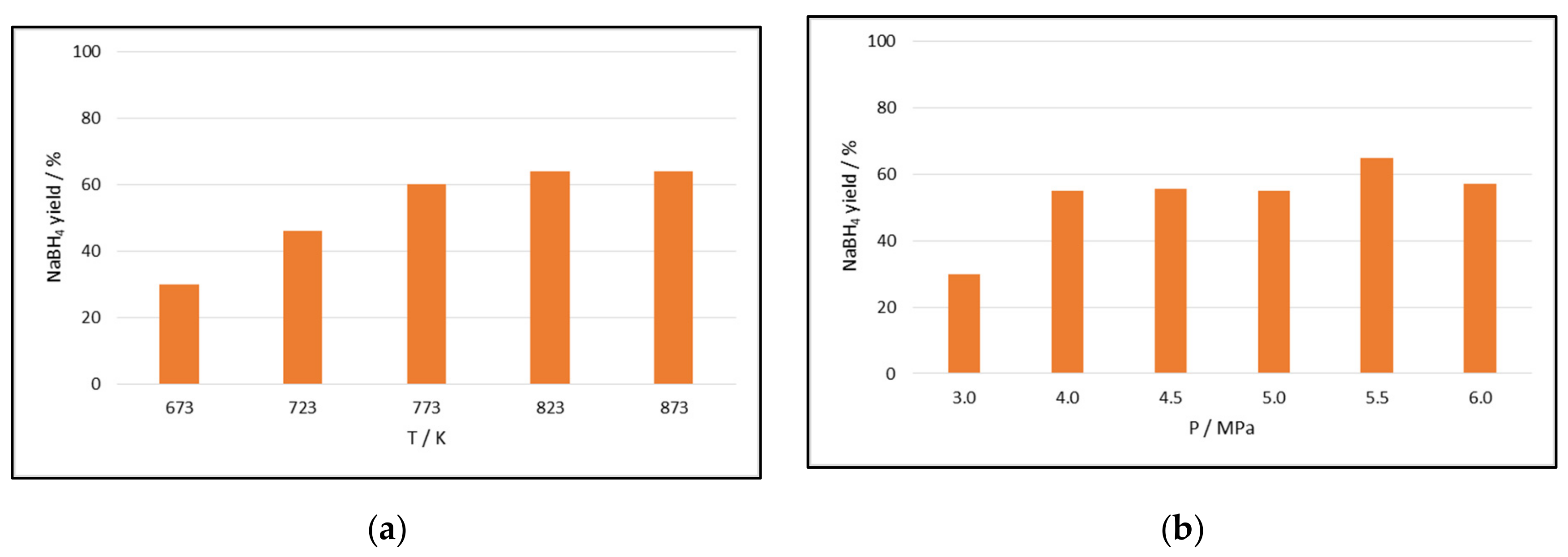
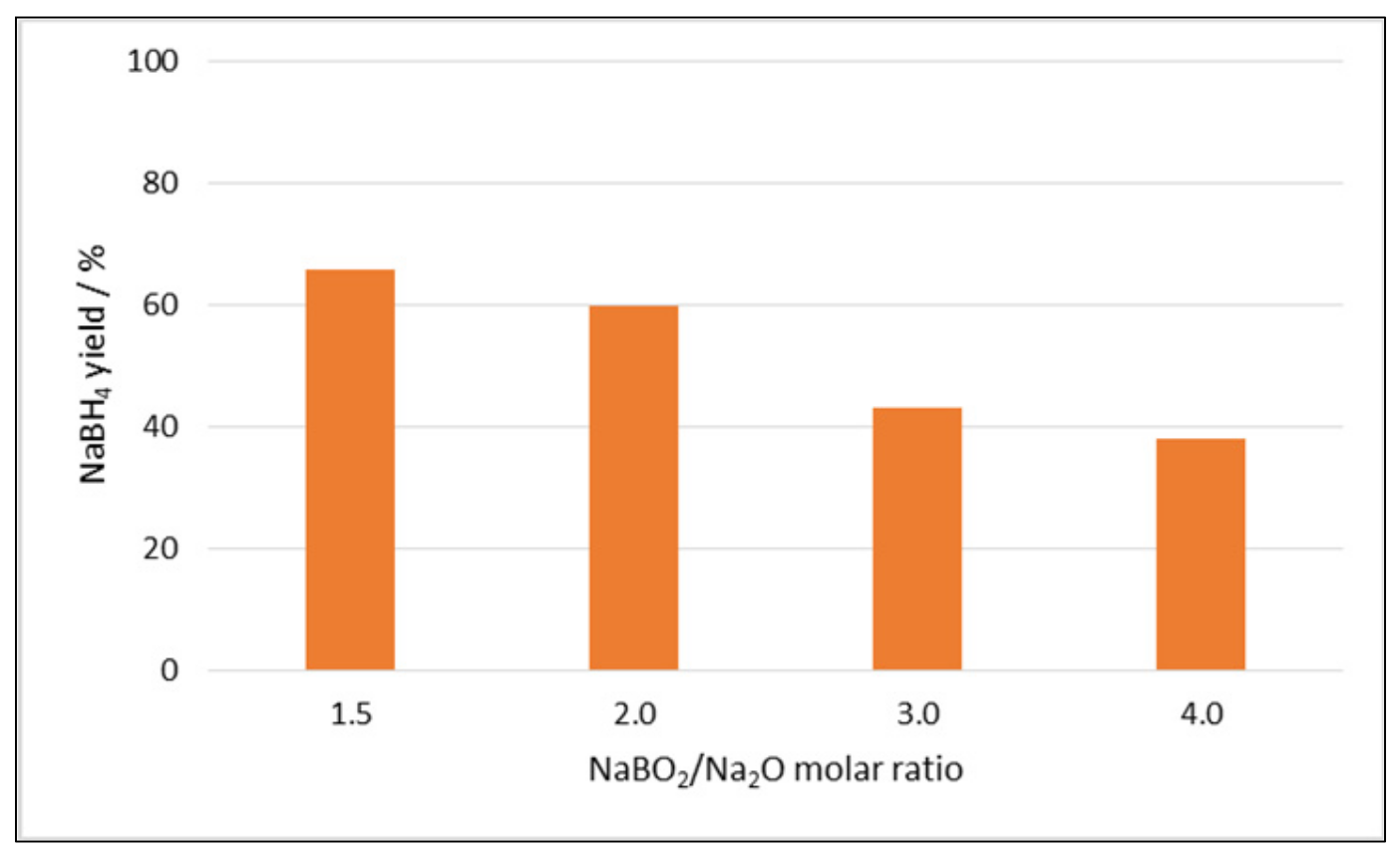
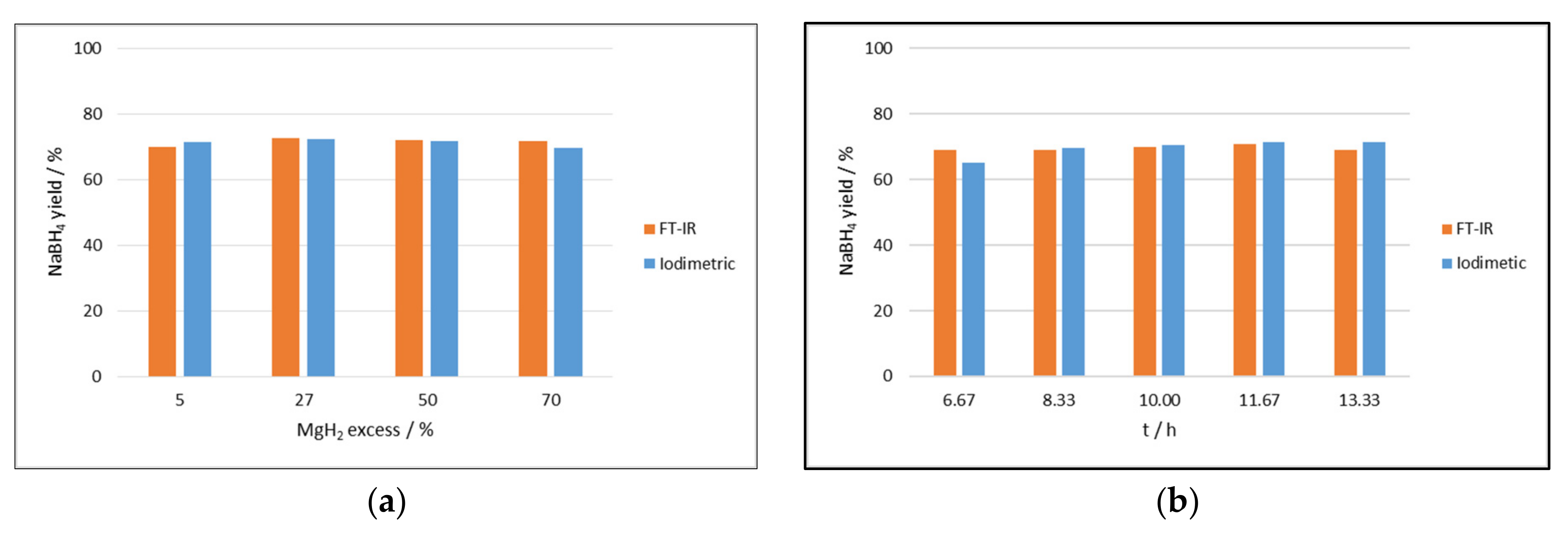
| Author | Boron Compound | Other Reactants | Yield/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kojima | 97.0 | [38] | ||
| Mg, Si | 98.0 | |||
| Liu | Al, , | 65.8 | [39] | |
| Si | 47.0 | [40] | ||
| Al | 69.0 | [64] | ||
| Mg | 63.5 | [66] | ||
| Mg | 28.8 | |||
| Mg | 12.3 | |||
| Mg + 23.5% Ni | 80.0 | [65] | ||
| Kemmitt | 80.0 | [62] | ||
| Kayacan | 93.0 | [44] | ||
| Ou | 90.4 | [48] | ||
| 90.0 | [49] | |||
| Figen | 93.0 | [47] | ||
| Eom | Mg | 69.0 | [46] |
| Author | Borate | Other Reactants | Excess of Reactant/% | Additive | t/min | Yield/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | 100 | - | 60 | 43.0 | [37] | ||
| 2.70 | 67.0 | ||||||
| - | NaOH | 64.0 | |||||
| 15.50 | 78.0 | ||||||
| Hsueh | 40 | - | 120 | 76.0 | [51] | ||
| Kong | 3.50 | - | 120 | 71.0 | [63] | ||
| Zhang | - | - | 360 | 32.0 | [67] | ||
| Çakanyldirim | 27 | - | 700 | 73.9 | [68] | ||
| 30 | Na | 800 | 25.0 | [43] | |||
| 10 | - | 400 | 84.0 | [45] | |||
| Ouyang | Mg | 37.50 | - | 900 | 67.7 | [54] | |
| Lang | 35 | 480 | 89.0 | [53] | |||
| Chen | 25 | - | 900 | 89.8 | [20] | ||
| 37.50 | - | 1 200 | 88.3 | ||||
| 40 | - | 360 | 82.0 | ||||
| Huang | Mg, | 25 | - | 1 200 | 86.0 | [52] | |
| Zhong | 50 | - | 1 200 | 78.0 | [55] | ||
| 100 | - | 1 200 | 74.0 | [57] | |||
| Ar | 30 | - | 500 | 53.0 | [56] | ||
| Qin | - | NaH | 1 200 | 57.0 | [59] | ||
| Le | Mg, Al | - | - | 2 160 | 99.7 | [58] | |
| - | - | 2 160 | 99.5 | ||||
| Zhu | Mg, | 23.75 | - | 1 800 | 78.9 | [61] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nunes, H.X.; Silva, D.L.; Rangel, C.M.; Pinto, A.M.F.R. Rehydrogenation of Sodium Borates to Close the NaBH4-H2 Cycle: A Review. Energies 2021, 14, 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123567
Nunes HX, Silva DL, Rangel CM, Pinto AMFR. Rehydrogenation of Sodium Borates to Close the NaBH4-H2 Cycle: A Review. Energies. 2021; 14(12):3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123567
Chicago/Turabian StyleNunes, Helder X., Diogo L. Silva, Carmen M. Rangel, and Alexandra M. F. R. Pinto. 2021. "Rehydrogenation of Sodium Borates to Close the NaBH4-H2 Cycle: A Review" Energies 14, no. 12: 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123567
APA StyleNunes, H. X., Silva, D. L., Rangel, C. M., & Pinto, A. M. F. R. (2021). Rehydrogenation of Sodium Borates to Close the NaBH4-H2 Cycle: A Review. Energies, 14(12), 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123567








