Impurity Effects on the Mechanical Properties and Permeability Characteristics of Salt Rock
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Sample Preparation
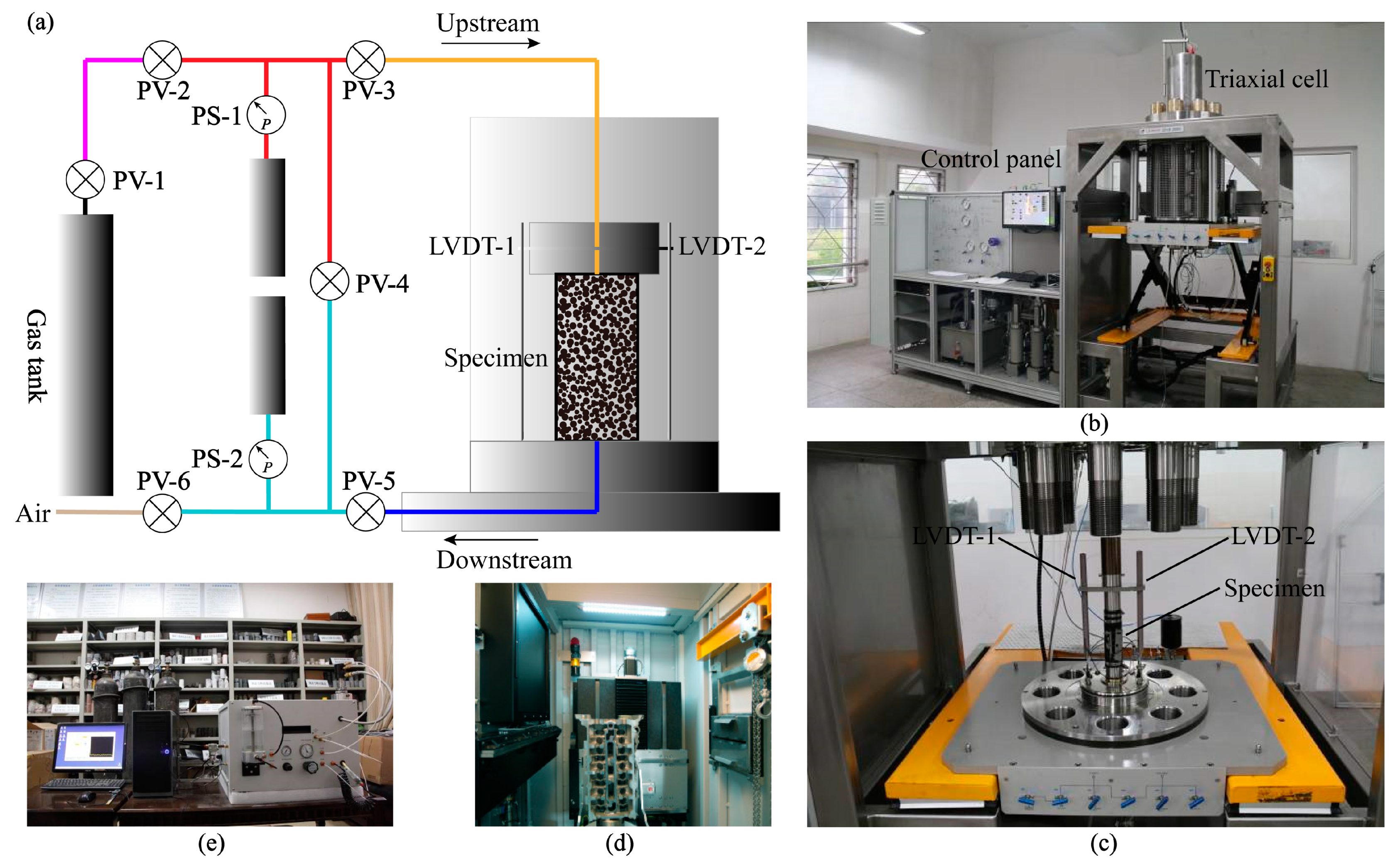
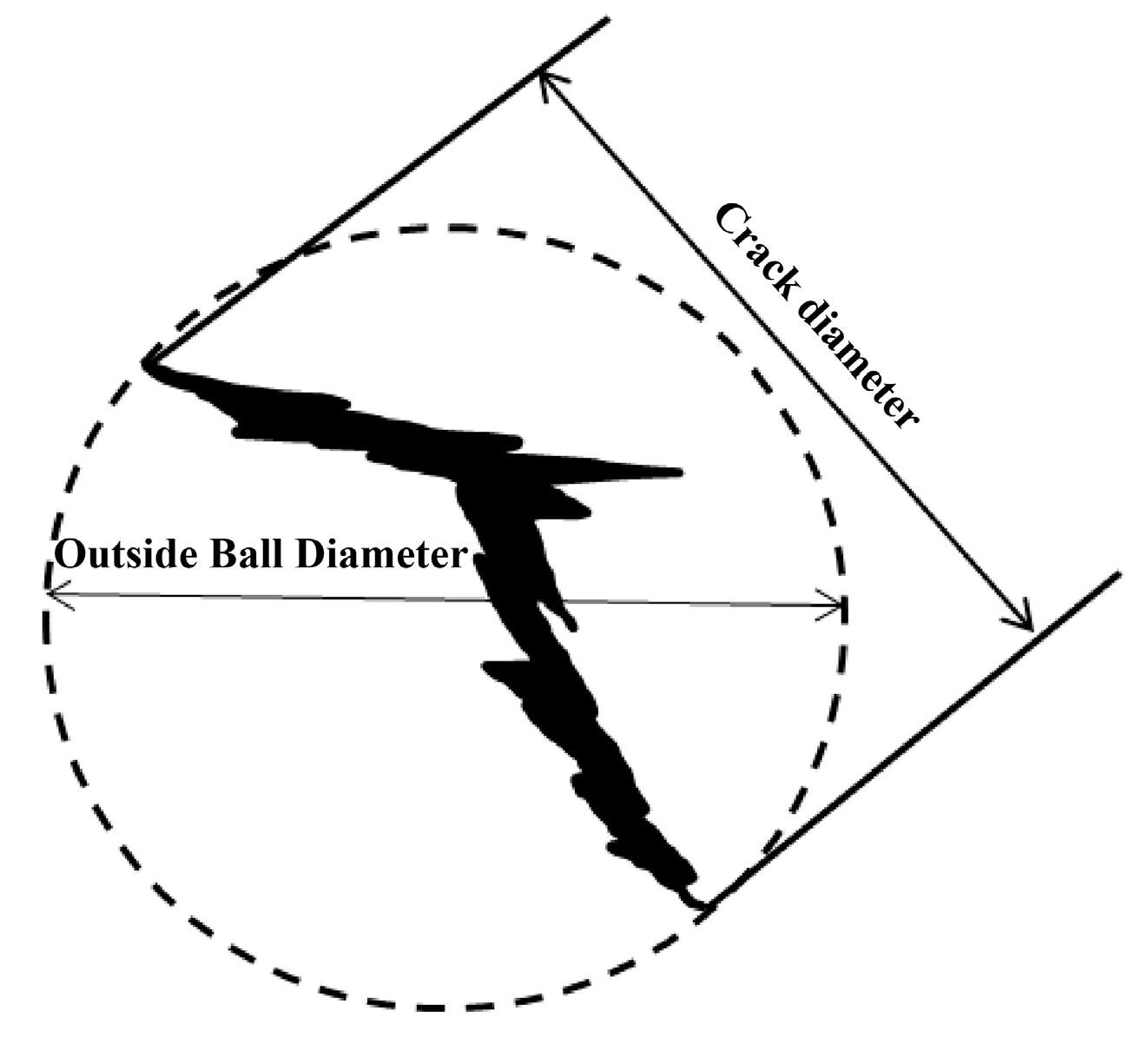
2.2. Testing Apparatus and Methods
3. Mechanical Test Results
3.1. Confining Pressure Effects on Mechanical Properties
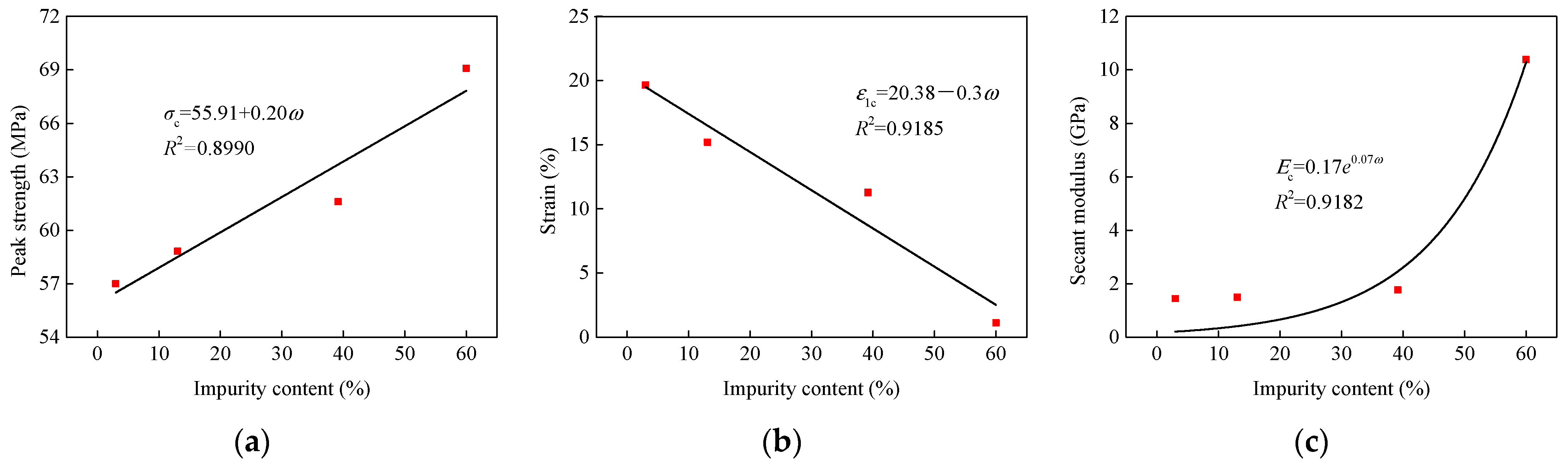
3.2. Impurity Effects on Mechanical Properties
4. Permeability Test Results
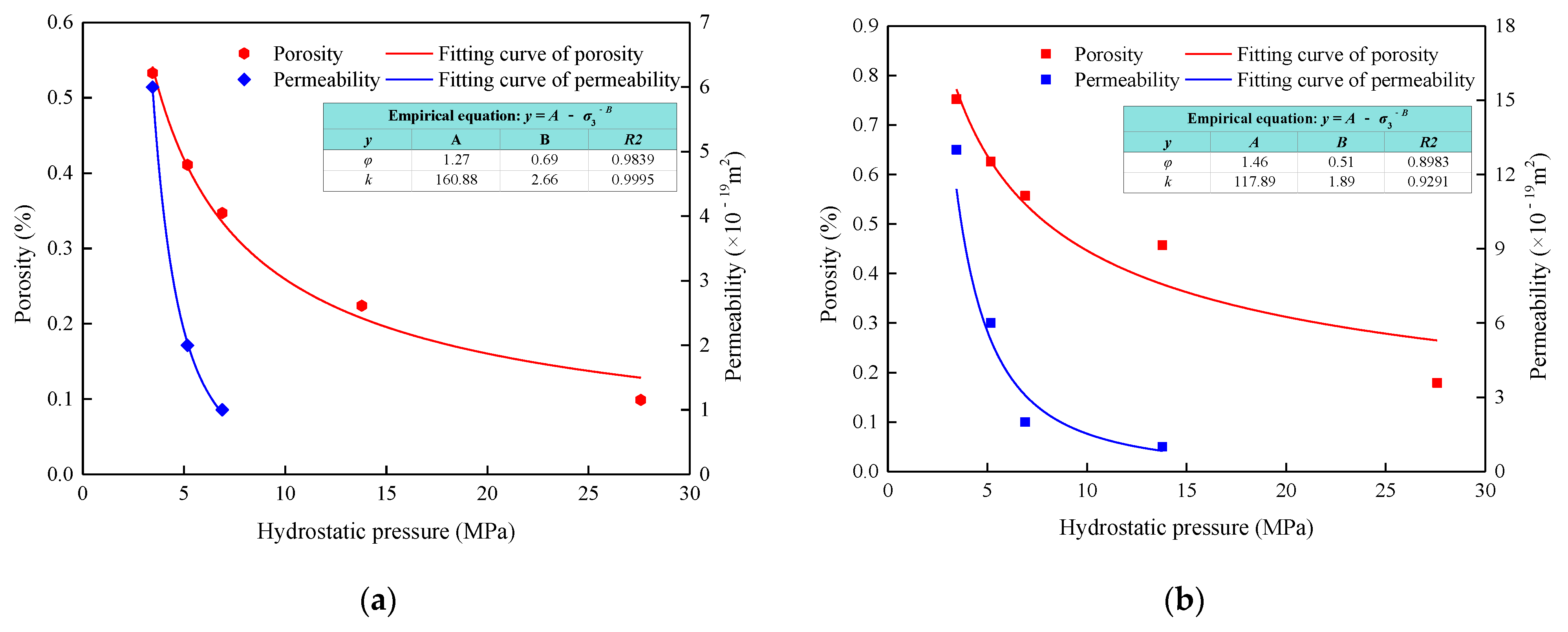
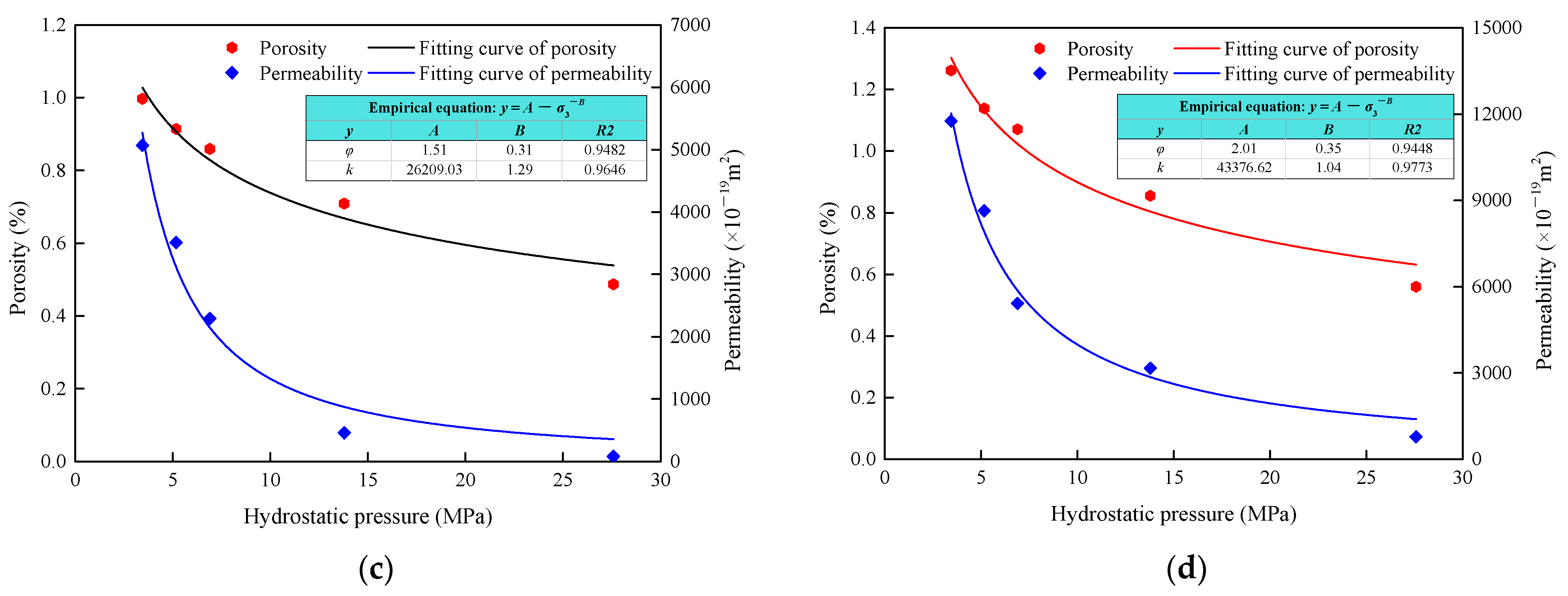
4.1. Porosity and Permeability under Hydrostatic Pressure
4.2. Confining Pressure Effects on Permeability under CTC
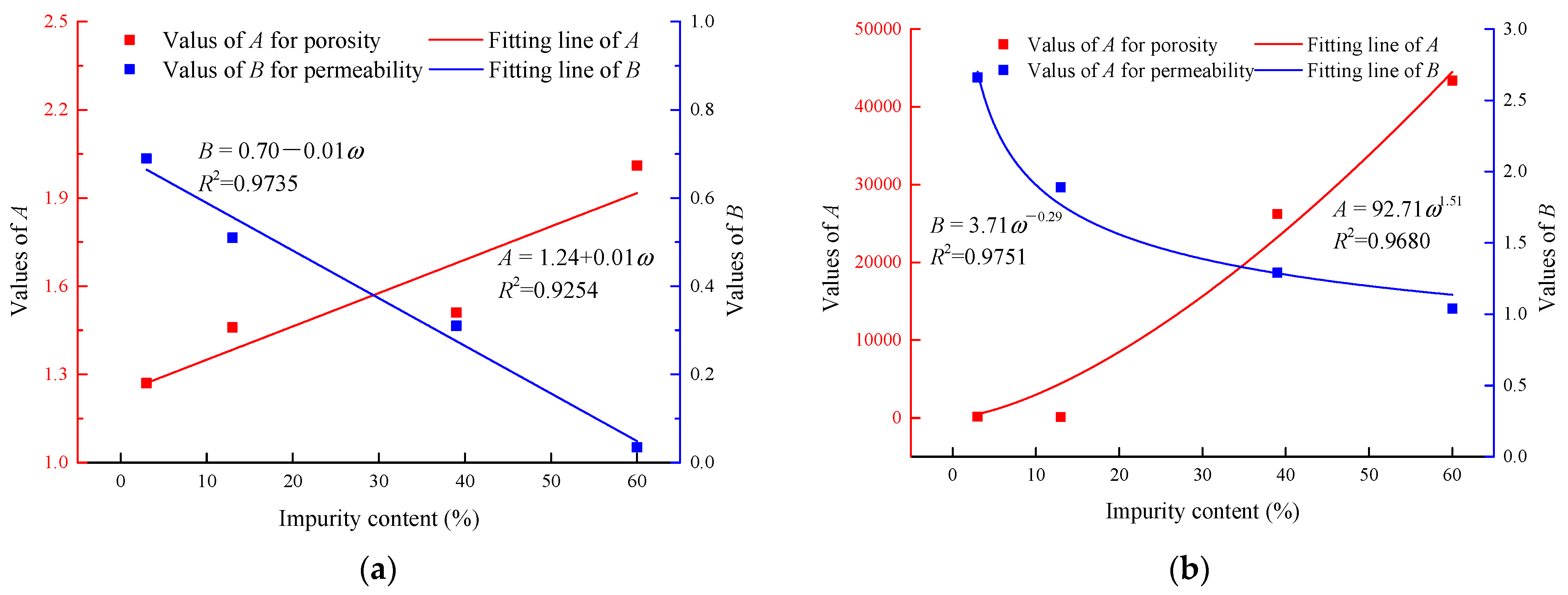
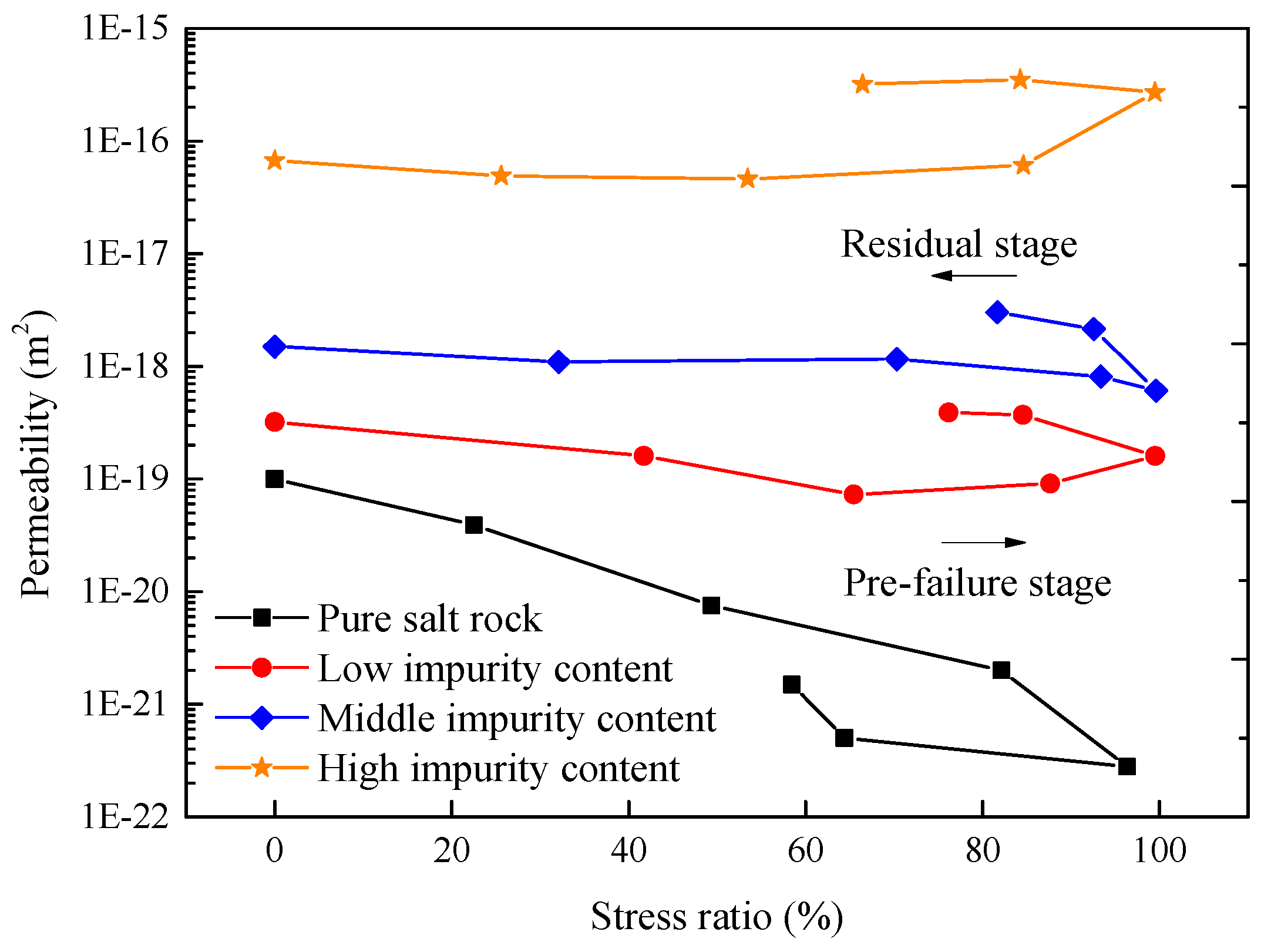
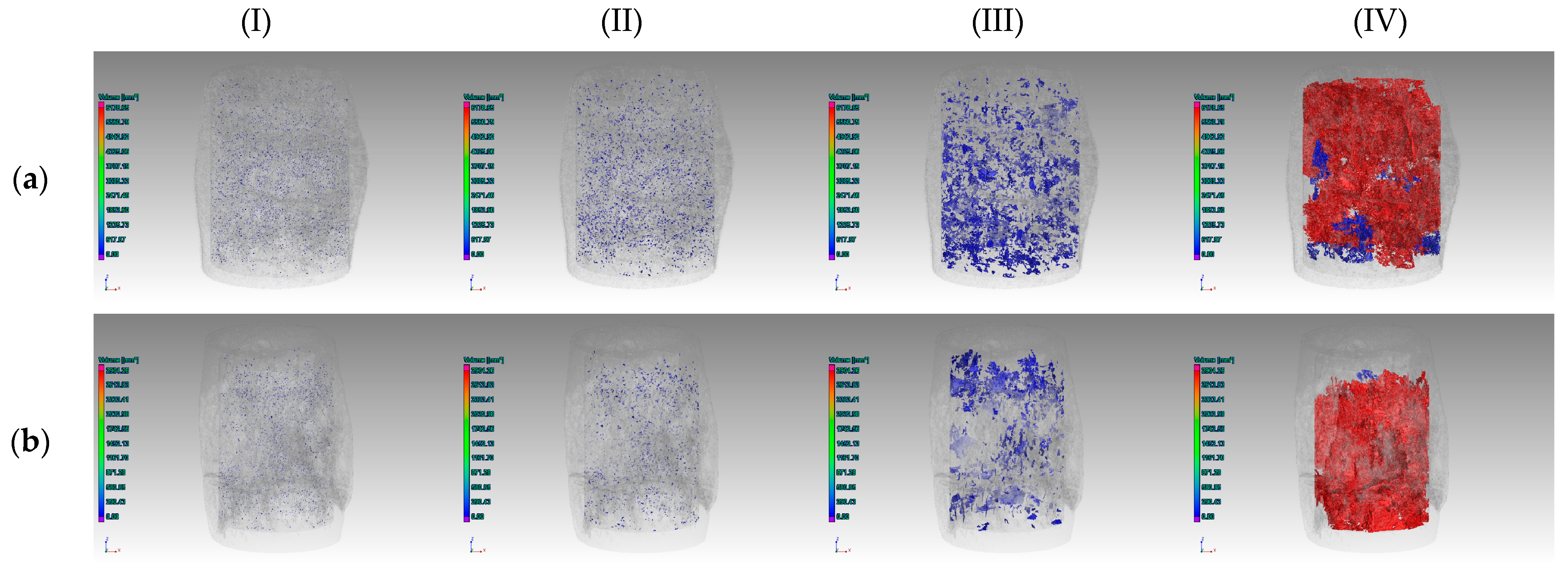
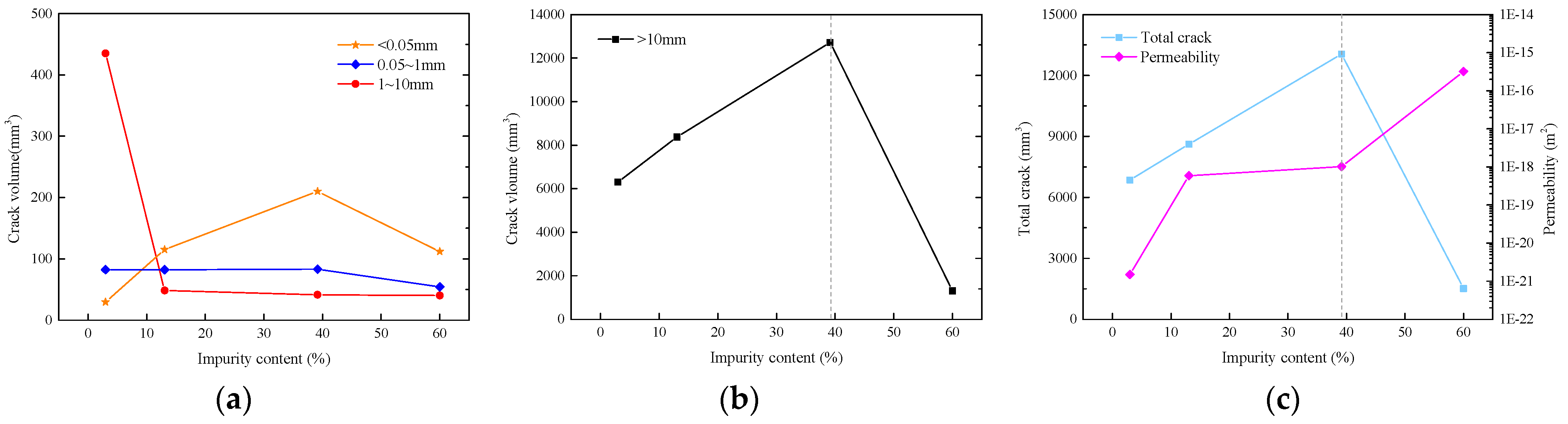
4.3. Impurity Effects on Permeability under CTC
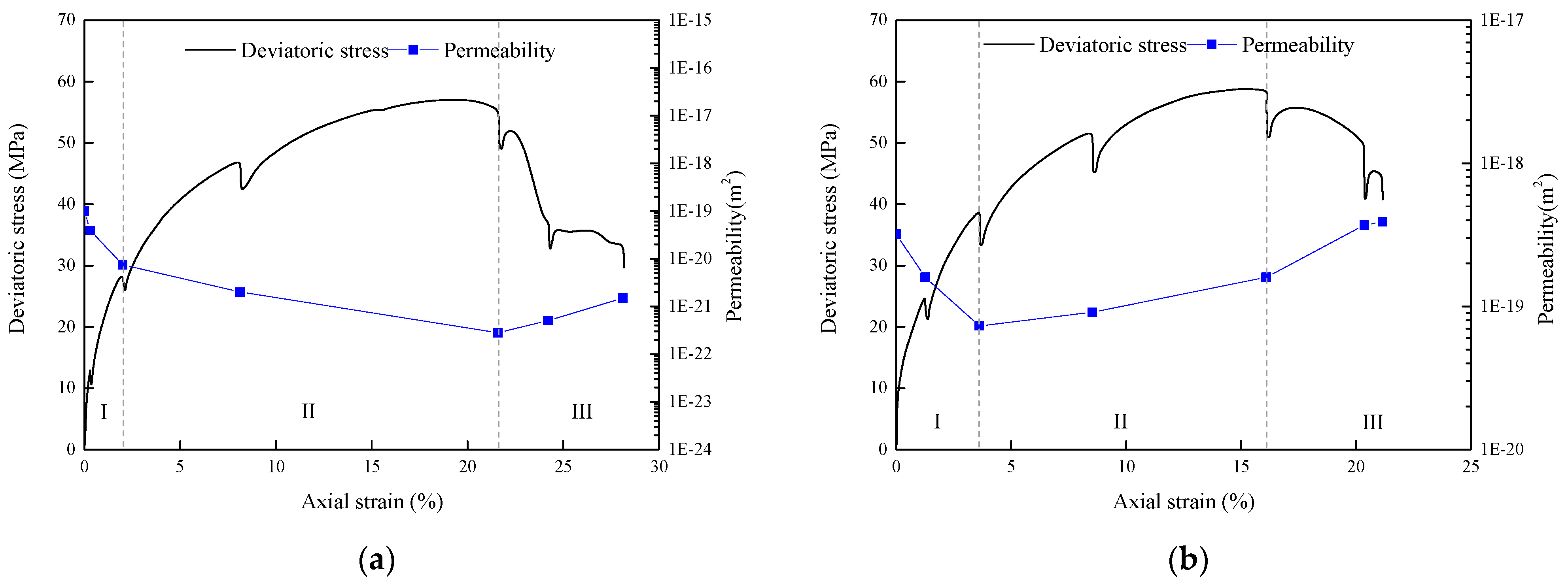
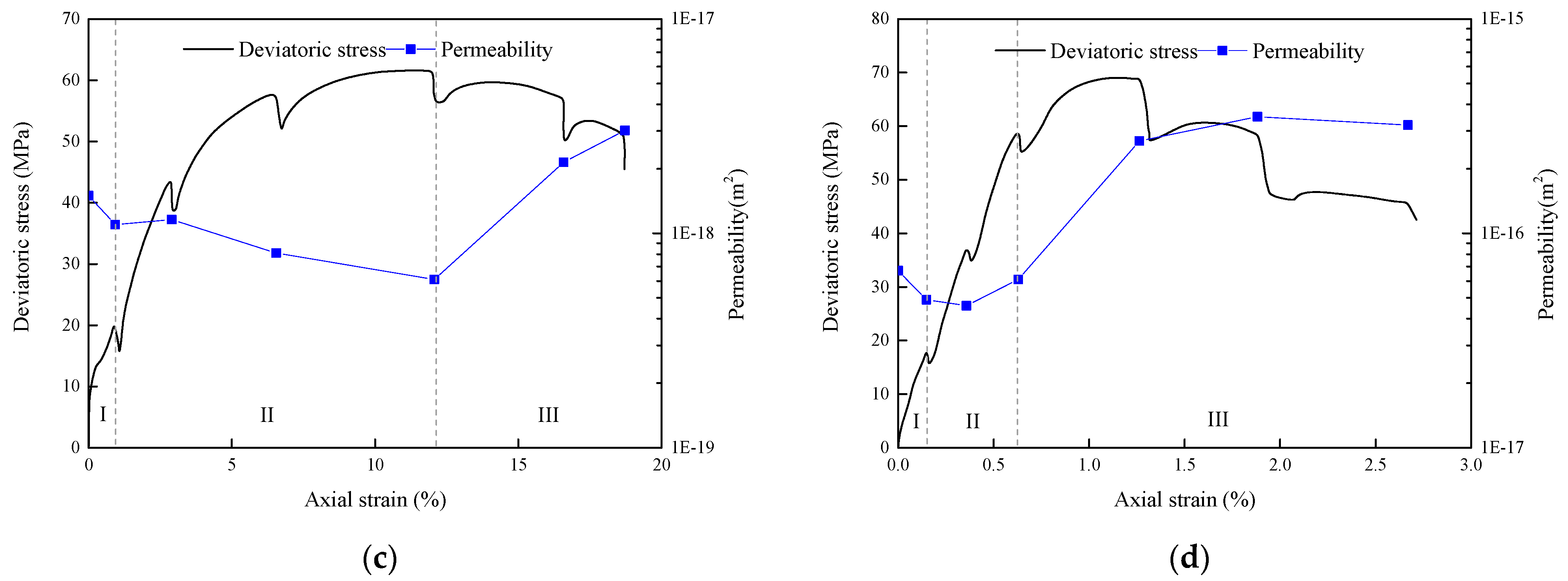
- Stage I: The decreasing stage, in which remaining cracks after the pre-compaction process are compacted in the first stage under the action of both confining pressure and axial stress. Consequently, the permeable channels in the rock gradually reduce, causing a considerable decrease in rock permeability.
- Stage II: The steady stage, in which the initiation and closure of the cracks are in a relatively dynamic equilibrium state. Here, permeability remains in a relatively steady with a slight increase or decrease.
- Stage III: The increasing stage in which the initiation rate of cracks exceeds the closure of cracks, and micro-cracks are progressively connected, with an increase in axial loading. Consequently, macroscopic cracks are formed, and a sharp increase in rock permeability occurs. Affected by the impurity content, the axial strain at the percolation threshold progressively decreases and reaches 22.01%, 16.13%, 12.04% and 0.63%.
5. Discussion
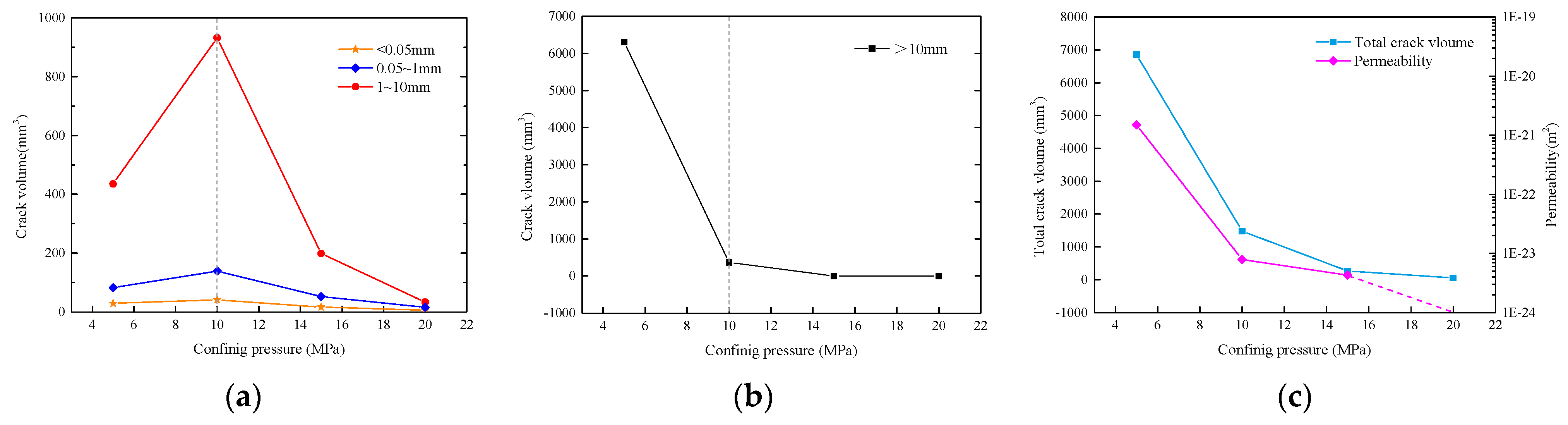
5.1. Confining Pressure Effects
5.2. Impurity Effects
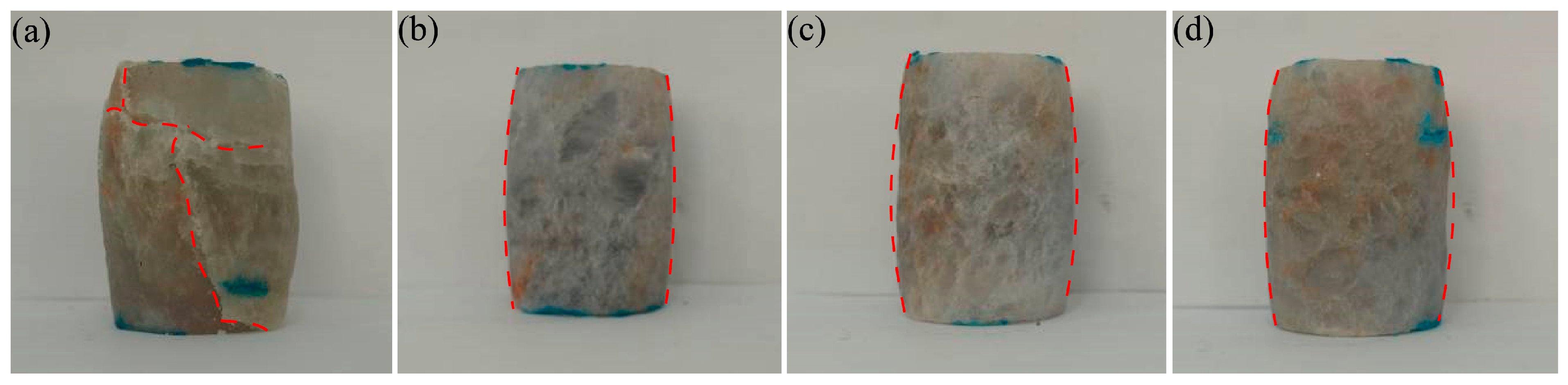
5.3. End Effects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hesser, J.; Kaiser, D.; Schmitz, H.; Spies, T. Measurements of Acoustic Emission and Deformation in a Repository of Nuclear Waste in Salt Rock. Eng. Geol. 2015, 6, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.; Shao, H.; Hesser, J.; Lege, C. In Situ Quantification of Hydrocarbon in an Underground Facility in Tight Salt Rock. Eng. Geol. 2015, 6, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Khaledi, K.; Miro, S.; König, D.; Schanz, T. Probabilistic Analysis of a Rock Salt Cavern with Application to Energy Storage Systems. Rock. Mech. Rock. Eng. 2017, 50, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Lux, K.H. A new coupling concept for the hydro-Mechanical interaction of clay stone and rock salt in underground waste repositories. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2004, 41, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, H.; Hou, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, L. Damage evolution of rock salt under cyclic loading in uniaxial tests. Acta Geotech. 2014, 9, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérest, P.; Brouard, B.; Djakeun-Djizanne, H.; Hévin, G. Thermomechanical effects of a rapid depressurization in a gas cavern. Acta Geotech. 2014, 9, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, K.H. Design of salt caverns for the storage of natural gas, crude oil and compressed air: Geo-Mechanical aspects of construction, operation and abandonment. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2019, 313, 93–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.S.; Bodner, S.R.; Fossum, A.F.; Munson, D.E. A constitutive model for inelastic flow and damage evolution in solids under triaxial compression. Mech. Mater. 1992, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.W.; Wang, C.P.; Mishnaevsky, L.; Duan, Z.Q.; Ding, J.Y. A fractional derivative approach to full creep regions in salt rock. Mech. Time-Depend. Mat. 2013, 17, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, H.; Ajalloeian, R. Mechanical behavior of salt rock under uniaxial compression and creep tests. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2018, 110, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, D.; Zhvick, V.; Ryzhikov, N.; Shako, V. Modeling of Rock Permeability Damage and Repairing Dynamics Due to Invasion and Removal of Particulate from Drilling Fluids. Transp. Porous Med. 2018, 121, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Hossein, M. Laboratory studies of creep behavior on thick-Walled hollow cylindrical salt rock specimens. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 5949–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.A.; Buchholz, S.A.; Mellegard, K.D.; Düsterloh, U. Cyclic Loading Effects on the Creep and Dilation of Salt Rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 2581–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düsterloh, U.; Lerche, S.; Lux, K.-H. Damage and Healing Properties of Rock Salt: Long-Term Cyclic Loading Tests and Numerical Back Analysis. Clean Energy Systems in the Subsurface: Production, Storage and Conversion. In Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering; Hou, M., Xie, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, German, 2013; pp. 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.S.; Hovorka, S.D. Relations between bromide content and depositional processes in bedded halite, Permian San Andres Formation, Palo Duro Basin, Texas. Carbonate Evaporite 1987, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, F.D.; Senseny, P.; Pfeifle, T.; Vogt, T. Influence of impurities on the creep of salt from the Palo Duro Basin. In the 29th US Symposium on Rock Mechanics (USRMS); A.A. Balkema Plubishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, M.S. Geomechanical analysis and design considerations for thin-bedded salt caverns. In Office of Scientific and Technical Information Technical Reports; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Zhao, J.; Düsterloh, U.; Hou, Z.M.; Xie, H.P.; Liu, J.F. Experimental study of mechanical and hydraulic properties of bedded rock salt from the Jintan location. Acta Geotech. 2014, 9, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Daemen, J. Stability and tightness evaluation of bedded rock salt formations for underground gas/oil storage. Acta Geotech. 2014, 9, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xing, W.; Hou, Z.; Were, P. Influence of water-Insoluble content on the short-Term strength of bedded rock salt from three locations in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6951–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Desseault, M.B.; Liu, J. Experimental investigation of mechanical properties of bedded salt rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2007, 44, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, C.; Daemen, J.J.K. Experimental investigation of mechanical behavior of bedded rock salt containing inclined interlayer. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2014, 69, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, Y. Research on Confining Pressure Effect on Mesoscopic Damage of Rock Salt Based on CT Scanning. In Proceedings of the Geo-Shanghai 2018 International Conference: Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, Singapore, 27–30 May 2018; pp. 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.G.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Y. Experimental Study of Temperature Effects on Physical and Mechanical Characteristics of Salt Rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2006, 39, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.L. Effect of Impurities on Engineering Mechanical Properties of Salt Rock. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Wuhan, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.X.; Wang, G.; Hou, Z.; Liu, J. Experimental study on the permeability characteristics of impure rock salt. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2017, 36, 2424–2430. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.D.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Zou, H.; Hu, C.; Li, J. Experimental study of permeability of salt rock with impurities in whole process of loading. Rock Soil Mech. 2017, 38, 402–408. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y. Study on penetration characteristics and mesoscopic features of impurity salt rock during loading process. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2019, 51, 85–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovari, K. Suggested methods for determining the strength of rock materials in triaxial compression: Revised version. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Geomech. Abstr. 1983, 20, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.; Liu, J.; Zou, H.; Xu, Y.; Deng, C.; Wu, C. Study of damage recovery of salt rock under confining pressures. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2017, 49, 135–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Experimental investigation into the damage-Induced permeability and deformation relationship of tectonically deformed coal from Huainan coalfield, China. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2018, 60, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedor, F.; Hámos, G.; Jobbik, A.; Máthé, Z.; Somodi, G.; Szűcs, I. Laboratory pressure pulse decay permeability measurement of Boda Claystone, Mecsek Mts., SW Hungary. Phys. Chem. Earth. 2008, 33, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabezloo, S.; Sulem, J.; Saint-Marc, J. Evaluation of a permeability–Porosity relationship in a low-Permeability creeping material using a single transient test. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 2009, 46, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, Y.M.; Sondergeld, C.H. Measuring low permeabilities of gas-Sands and shales using a pressure transmission technique. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2011, 48, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, M.; Tutuncu, A.N. Characterization of anisotropy in the permeability of organic-rich shales. J. Petro. Sci. Eng. 2015, 133, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Transient pulse test and morphological analysis of single rock fractures. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2017, 91, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brace, W.F.; Walsh, J.B.; Frangos, W.T. Permeability of granite under high pressure. J. Geophys. Res. 1968, 73, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Shao, J.; Skoczylas, F. The gas permeability properties of low-Permeability rock in the process of triaxial compression test. Mater. Lett. 2014, 116, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsoules, M.G.; Cripps, J.C. An Investigation of the Permeability of Yorkshire Chalk under Differing Pore Water and Confining Pressure Conditions. Energ. Sources 1982, 6, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zou, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, T. Investigation of the temperature effect on rock permeability sensitivity. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2017, 156, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Zou, J. Compact rock material gas permeability properties. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 2014, 449, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, T.; Kern, H.; Schulze, O. The evolution of dilatancy and permeability in rock salt during hydrostatic compaction and triaxial deformation. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 4061–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozeny, J. Uber kapillare Leitung des Wassers in Boden, Sitzungsber Akad. Wiss. Wien. 1927, 136, 271–306. [Google Scholar]
- Carman, P.C. Permeability of saturated sands, soils and clays. J. Agr. Sci.-Camb. 1939, 29, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, K. Experimental Rock Mechanics; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.T.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Kong, R.; Liu, X.; Peng, S. Evaluation and reduction of the end friction effect in true triaxial tests on hard rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2017, 97, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


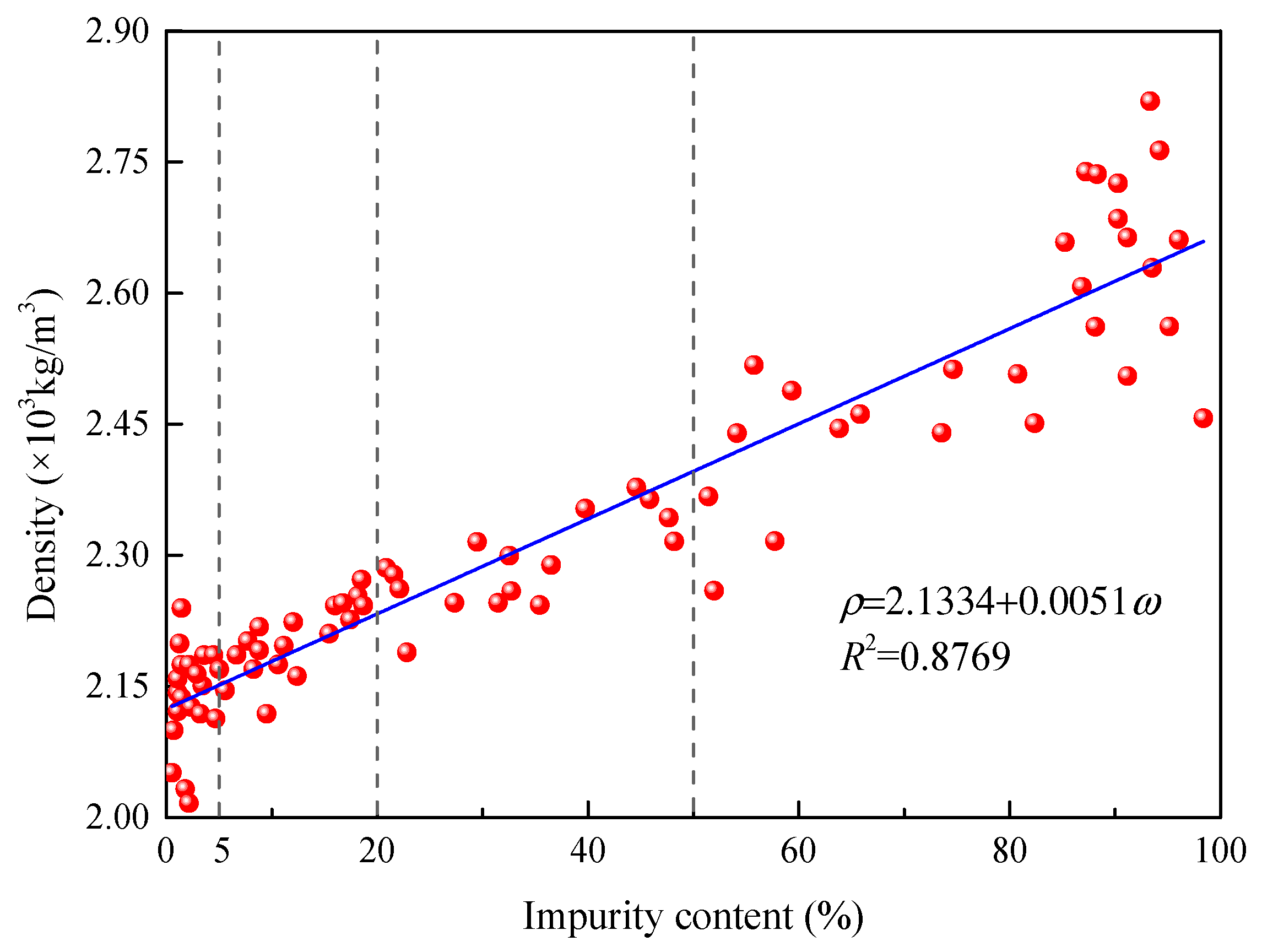







| Classification | Pure Salt Rock | Low-Impure Salt Rock | Middle-Impure Salt Rock | Salt Bearing Sedimentary Rock |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impurity content | ~5% | 5%–20% | 20%–50% | 50%–100% |
| Specimen | σ3 (MPa) | ωr (%) | H (mm) | D (mm) | ρ (g/cm3) | ωw (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR-1 | 5 | 3.00 | 75.36 | 37.65 | 2.19 | 0.25 |
| SR-2 | 10 | 2.75 | 76.03 | 38.02 | 2.16 | 0.31 |
| SR-3 | 15 | 1.98 | 76.12 | 38.04 | 2.17 | 0.13 |
| SR-4 | 20 | 4.02 | 75.77 | 37.91 | 2.23 | 0.39 |
| SR-5 | 5 | 13.07 | 75.89 | 38.11 | 2.22 | 1.25 |
| SR-6 | 5 | 39.16 | 76.19 | 37.87 | 2.49 | 0.54 |
| SR-8 | 5 | 60.02 | 75.92 | 38.00 | 2.67 | 1.02 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Luo, M.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Zou, H. Impurity Effects on the Mechanical Properties and Permeability Characteristics of Salt Rock. Energies 2020, 13, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13061366
Zhang Q, Liu J, Wang L, Luo M, Liu H, Xu H, Zou H. Impurity Effects on the Mechanical Properties and Permeability Characteristics of Salt Rock. Energies. 2020; 13(6):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13061366
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiangxing, Jianfeng Liu, Lu Wang, Min Luo, Hejuan Liu, Huining Xu, and Hang Zou. 2020. "Impurity Effects on the Mechanical Properties and Permeability Characteristics of Salt Rock" Energies 13, no. 6: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13061366
APA StyleZhang, Q., Liu, J., Wang, L., Luo, M., Liu, H., Xu, H., & Zou, H. (2020). Impurity Effects on the Mechanical Properties and Permeability Characteristics of Salt Rock. Energies, 13(6), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13061366





