Investigation of Steam Treatment on the Sorption Behavior of Rice Straw Pellets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Steam Explosion Pretreatment
2.3. Chemical Characterization
2.4. Moisture Sorption
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
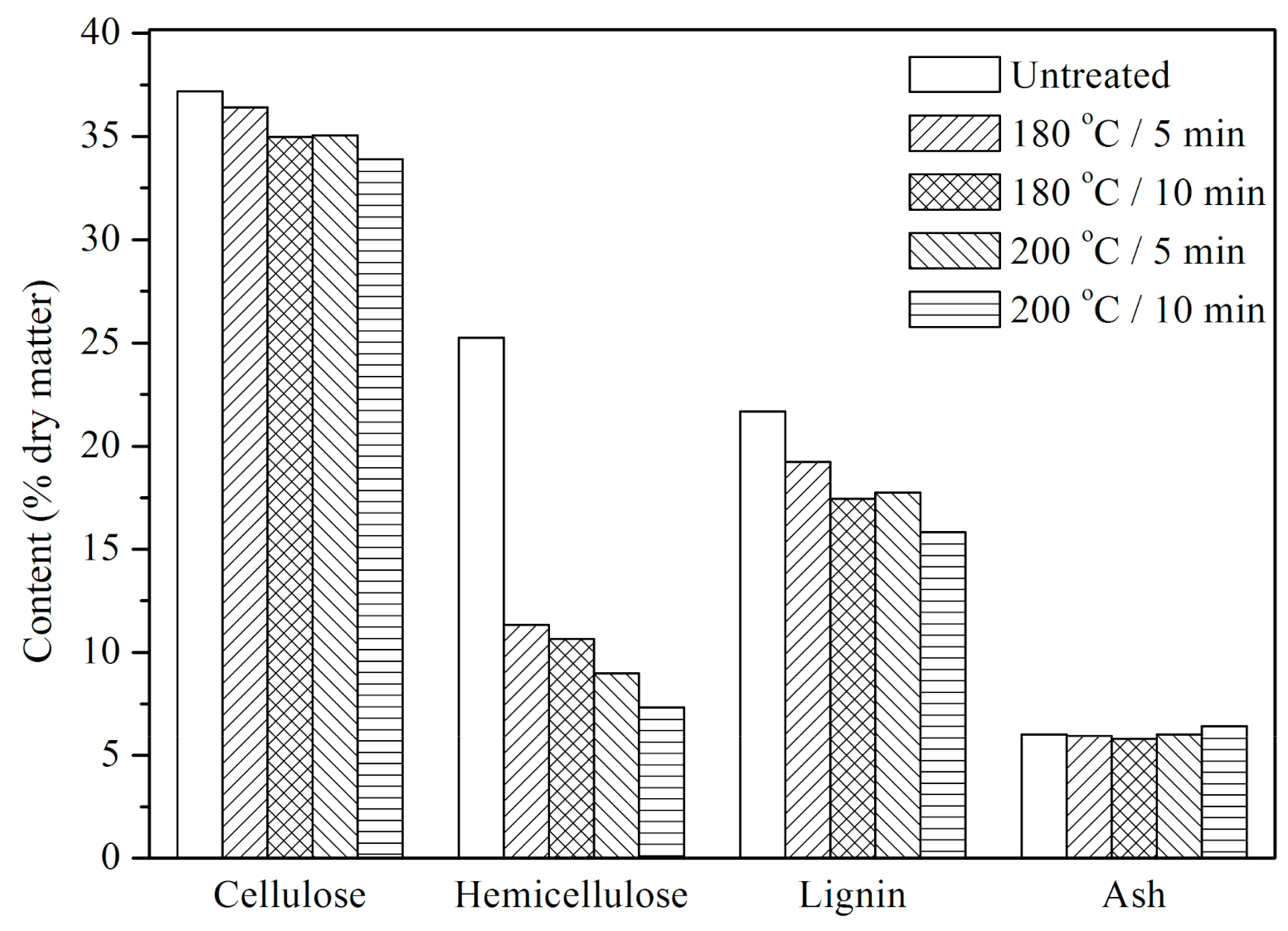
3.1. Effect of Steam Explosion on Chemical Properties
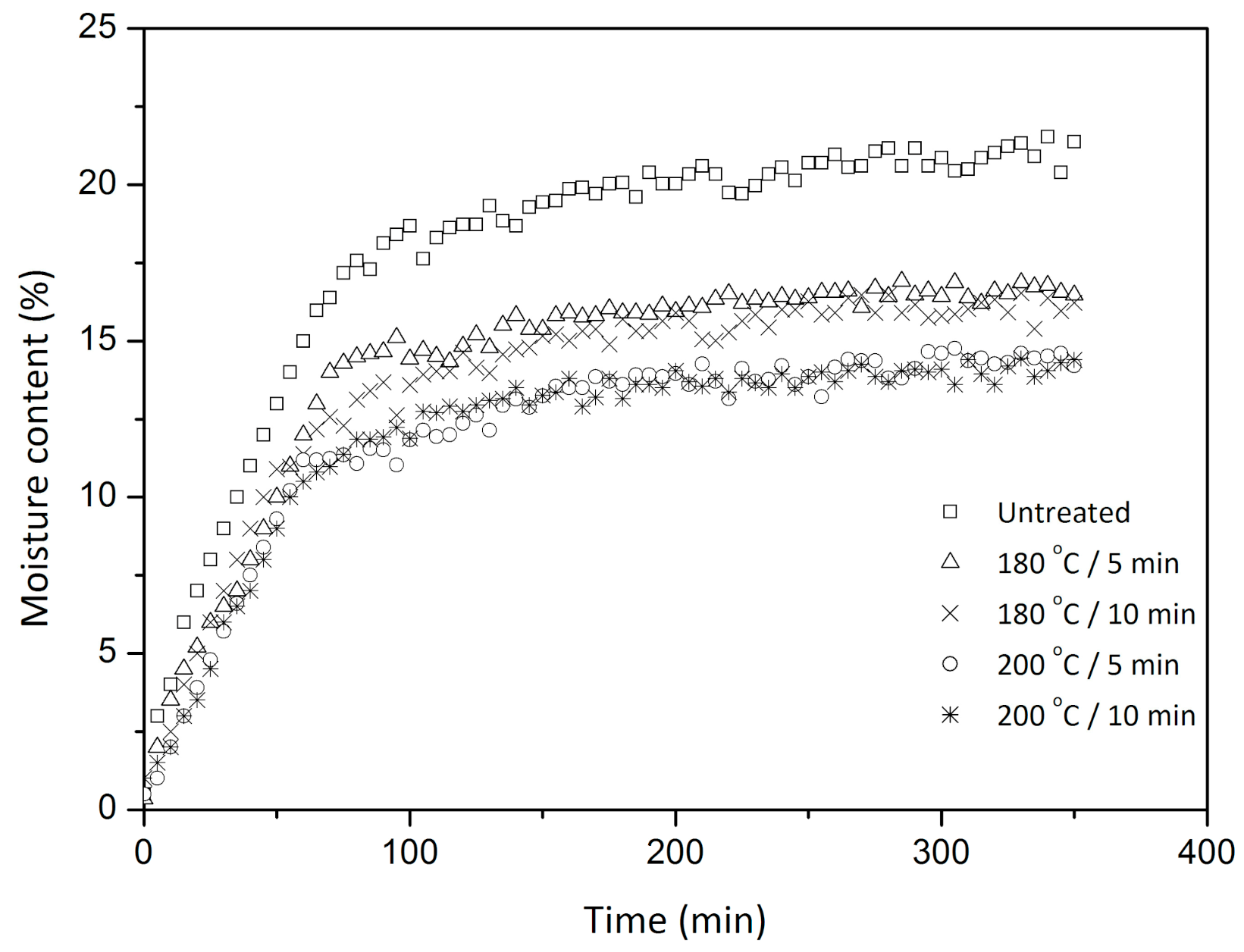
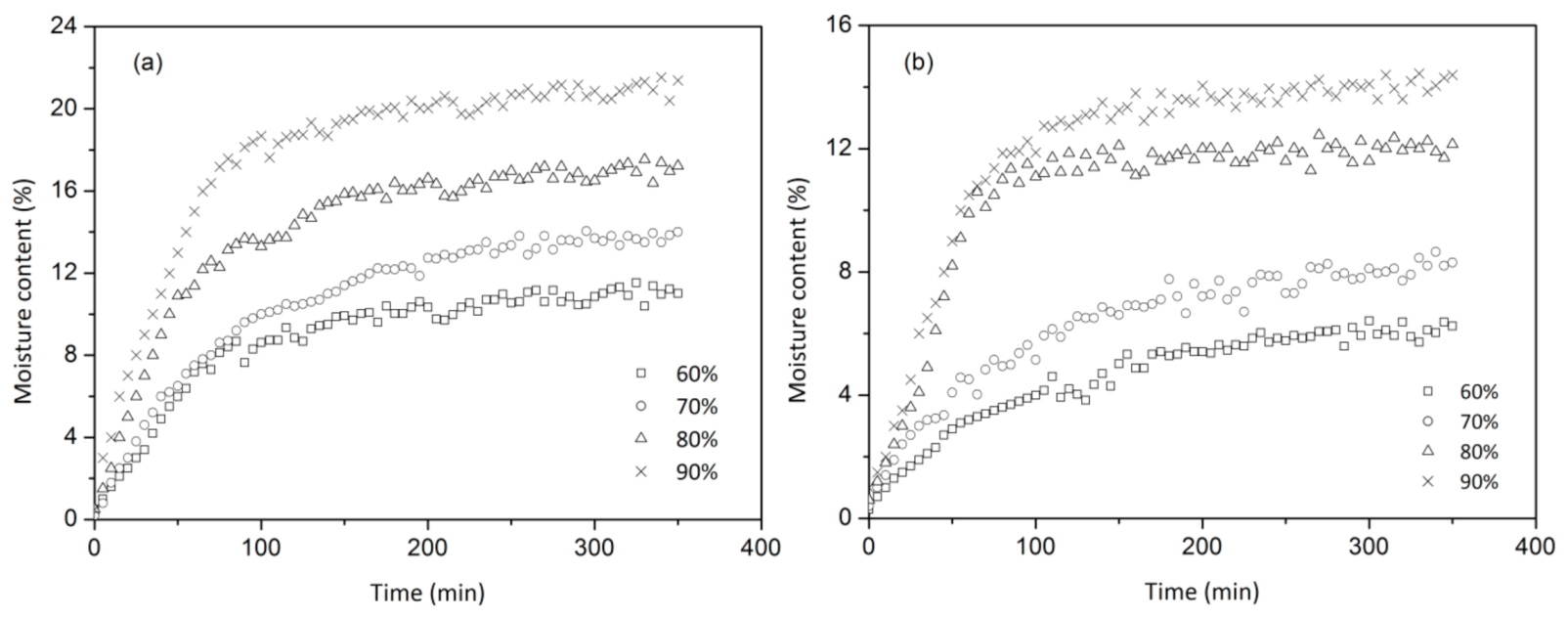
3.2. Effect of Steam Explosion on Moisture Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, J.; He, Y.; Yu, X.; Banks, S.W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, R.; Bridgwater, A.V. Review of physicochemical properties and analytical characterization of lignocellulosic biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, R.; Li, K.; Ma, R. A review of crop straw pretreatment methods forbiogas production by anaerobic digestion in China. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2019, 107, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Oryani, B.; Cho, J.; Talaiekhozani, A.; Sabbagh, F.; Hashemi, B.; Rupani, P.F.; Faraji, H. Different pretreatment technologies of lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol production: An overview. Energy 2020, 199, 117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutto, A.W.; Qureshi, K.; Harijan, K.; Abro, R.; Abbas, T.; Bazmi, A.A.; Karim, S.; Yu, G. Insight into progress in pre-treatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Energy 2017, 122, 724–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Acharjee, T.C.; Coronella, C.J.; Vásquez, V.R. Thermal pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2009, 28, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.A.; Zeshan; Visvanathan, C. Effect of thermal pretreatment on chemical composition, physical structure and biogas production kinetics of wheat straw. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 221, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auxenfans, T.; Crônier, D.; Chabbert, B.; Paës, G. Understanding the structural and chemical changes of plant biomass following steam explosion pretreatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aski, A.L.; Borghei, A.; Zenouzi, A.; Ashrafi, N.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Effect of steam explosion on the structural modification of rice straw for enhanced biodegradation and biogas production. Bioresources 2019, 14, 464–485. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Li, G.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z. Steam explosion enhances digestibility and fermentation of corn stover by facilitating ruminal microbial colonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damay, J.; Boboescu, I.; Duret, X.; Lalonde, O.; Lavoie, J.M. A novel hybrid firstand second generation hemicellulosic bioethanol production processthrough steam treatment of dried sorghum biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossatz, H.L.; Rose, S.H.; Viljoen-Bloom, M.; Van Zyl, W.H. Production of ethanol from steam exploded triticale straw in a simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process. Process. Biochem. 2017, 53, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yan, B.; Wang, Y.; Yong, X.Y.; Yang, Z.H.; Jia, H.; Jiang, M.; Wei, P. Effect of steam explosion pretreatment on the anaerobic digestion of rice straw. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88417–88425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanand, V.; Ryden, P.; Horn, S.J.; Tapp, H.S.; Wellner, N.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Waldron, K.W. Impact of steam explosion on biogas production from rape straw in relation to changes in chemical composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, W. Effects of steam explosion on lignocellulosic degradation of, and methane production from, corn stover by a co-cultured anaerobic fungus and methanogen. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 290, 121796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzir, N.M.; Aziz, M.A.; Ismail, S.; Abdullah, B.; Mahmood, N.A.N.; Umor, N.; Nooh, S.M. Agro-industrial waste to biobutanol production: Eco-friendly biofuels for next generation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manochio, C.; Andrade, B.; Rodriguez, R.P.; Moraes, B.S. Ethanol from biomass: A comparative overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.; Ghosh, S.K.; Bannerjee, S.; Aikat, K. Bioethanol production from agricultural wastes: An overview. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, F.; Li, Y. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enhanced biogas production. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2014, 42, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.S.; Sokhansanj, S.; Bi, X.T.; Lim, C.J.; Melin, S. Energy Input and Quality of Pellets Made from Steam-Exploded Douglas Fir (Pseudotsugamenziesii). Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooyserkani, Z.; Sokhansanj, S.; Bi, X.; Lim, C.J.; Lau, A.; Saddler, J.; Kumar, L.; Lam, P.S.; Melin, S. Steam treatment of softwood particles to produce torrefied material. Appl. Energy 2013, 103, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapa, P.; Tabil, L.; Schoenau, G.; Opoku, A. Pelleting characteristics of selected biomass with and without steam explosion pretreatment. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2010, 3, 62–79. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, M.; Karunakaran, C.; Tabil, L. Physicochemical characteristics of densified untreated and steam exploded poplar wood and wheat straw grinds. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 103, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.K.; Yang, W.; Blasiak, W. Steam pretreatment of Salix to upgrade biomass fuel for wood pellet production. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Cheng, W.; Deng, J.; Dai, C.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Q. Effect of pressurized steam treatment on selected properties of wheat straws. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2009, 30, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass; Technical Report NREL/TP-510-42618; Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); NREL: Colorado, CO, USA, 2012.
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C. Determination of Ash in Biomass; Technical Report NREL/TP-510-42622; Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); NREL: Colorado, CO, USA, 2008.
- American Society of Agricultural Engineers (ASAE). S358.2-Moisture Measurement-Forage; ASAE Standard: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Agricultural Engineers (ASAE). S448.2-Thin-Layer Drying of Agricultural Crops; ASAE Standard: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Iroba, K.L.; Tabil, L.G.; Sokhansanj, S.; Dumonceaux, T.J. Pretreatment and fractionation of barley straw using steam explosion at low severity factor. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 66, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Chang, X.; Chen, D.; Xue, Y.; Liu, P.; Lin, H.; Han, S. A review on the pretreatment of lignocellulose for high-value chemicals. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 160, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jiang, J.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.; Baird, M.S. Influence of steam pressure on the physic-chemical properties of degraded hemicelluloses obtained from steam-exploded lespedeza stalks. Bioresources 2010, 5, 1717–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Kurokochi, Y.; Sato, M. Steam treatment to enhance rice straw binderless board focusing hemicellulose and cellulose decomposition products. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chandra, R.P.; Sokhansanj, S.; Saddler, J.N. Influence of steam explosion processes on the durability and enzymatic digestibility of wood pellets. Fuel 2018, 211, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Deng, J.; Zhang, S.; Bicho, P.; Wu, Q. Effect of steam explosion treatment on characteristics of wheat straw. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 31, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharjee, T.C.; Coronella, C.J.; Vásquez, V. Effect of thermal pretreatment on equilibrium moisture content of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4849–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medic, D.; Darr, M.; Shah, A.; Rahn, S. Effect of torrefaction on water vapor adsorption properties and resistance to microbial degradation of com stover. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2386–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihranyan, A.; Strømme, M. Capillary condensation of moisture in fractal pores of native cellulose powders. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 393, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
| Treatment | C | H | N | S | O | Calorific Value (MJ/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (% Dry Matter) | |||||||
| Untreated | Average | 42.14 | 5.60 | 0.67 | 0.14 | 51.45 | 16.24 |
| Standard deviation | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.07 | |
| 180 °C, 5 min | Average | 42.82 | 5.48 | 0.68 | 0.07 | 50.95 | 16.47 |
| Standard deviation | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.004 | 0.09 | 0.05 | |
| 180 °C, 10 min | Average | 43.86 | 5.62 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 49.83 | 16.51 |
| Standard deviation | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.008 | 0.08 | 0.15 | |
| 200 °C, 5 min | Average | 45.63 | 5.51 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 48.06 | 16.95 |
| Standard deviation | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.007 | 0.10 | 0.09 | |
| 200 °C, 10 min | Average | 46.47 | 5.35 | 0.71 | 0.07 | 47.40 | 17.26 |
| Standard deviation | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.11 | 0.21 | |
| Treatment | Equilibrium Moisture Content (%) | Moisture Adsorption Rate (min−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Standard Deviation | Average | Standard Deviation | |
| Untreated | 21.0 | 0.12 | 0.0220 | 0.002 |
| 180 °C, 5 min | 17.1 | 0.14 | 0.0188 | 0.005 |
| 180 °C, 10 min | 16.5 | 0.20 | 0.0181 | 0.002 |
| 200 °C, 5 min | 14.3 | 0.08 | 0.0178 | 0.001 |
| 200 °C, 10 min | 14.2 | 0.15 | 0.0177 | 0.003 |
| Relative Humidity (%) | Equilibrium Moisture Content (%) | Moisture Adsorption Rate (min−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 200 °C, 10 min | Untreated | 200 °C, 10 min | ||
| 60 | Average | 11.2 | 6.1 | 0.0106 | 0.00839 |
| Standard deviation | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.001 | 0.0005 | |
| 70 | Average | 13.9 | 8.4 | 0.0141 | 0.0100 |
| Standard deviation | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| 80 | Average | 17.3 | 12.1 | 0.0187 | 0.0152 |
| Standard deviation | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| 90 | Average | 21.0 | 14.2 | 0.0220 | 0.0177 |
| Standard deviation | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Wang, L.; Lau, A. Investigation of Steam Treatment on the Sorption Behavior of Rice Straw Pellets. Energies 2020, 13, 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13205401
He X, Wang L, Lau A. Investigation of Steam Treatment on the Sorption Behavior of Rice Straw Pellets. Energies. 2020; 13(20):5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13205401
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiao, Lianjun Wang, and Anthony Lau. 2020. "Investigation of Steam Treatment on the Sorption Behavior of Rice Straw Pellets" Energies 13, no. 20: 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13205401
APA StyleHe, X., Wang, L., & Lau, A. (2020). Investigation of Steam Treatment on the Sorption Behavior of Rice Straw Pellets. Energies, 13(20), 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13205401




