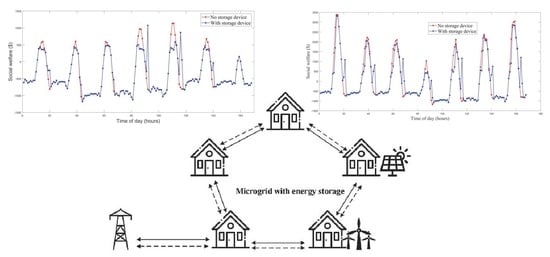
Iterative Auction for P2P Renewable Energy Trading with Dynamic Energy Storage Management
Abstract
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, T. Iterative Auction for P2P Renewable Energy Trading with Dynamic Energy Storage Management. Energies 2020, 13, 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184963
Zhang C, Wang Y, Yang T. Iterative Auction for P2P Renewable Energy Trading with Dynamic Energy Storage Management. Energies. 2020; 13(18):4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184963
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chen, Yong Wang, and Tao Yang. 2020. "Iterative Auction for P2P Renewable Energy Trading with Dynamic Energy Storage Management" Energies 13, no. 18: 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184963
APA StyleZhang, C., Wang, Y., & Yang, T. (2020). Iterative Auction for P2P Renewable Energy Trading with Dynamic Energy Storage Management. Energies, 13(18), 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184963