A Stepped-Segmentation Method for the High-Speed Theoretical Elevator Car Air Pressure Curve Adjustment
Abstract
1. Introduction
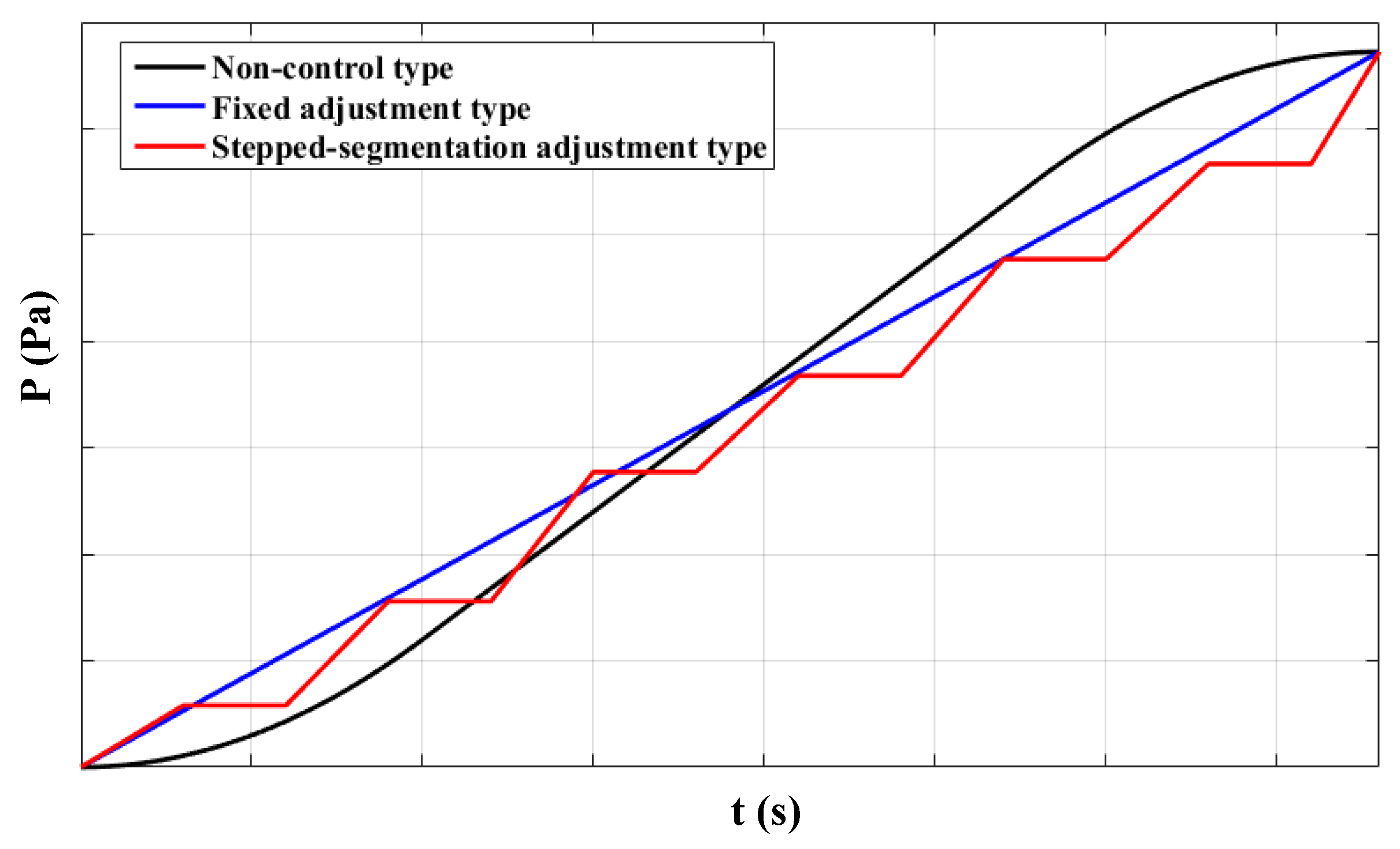
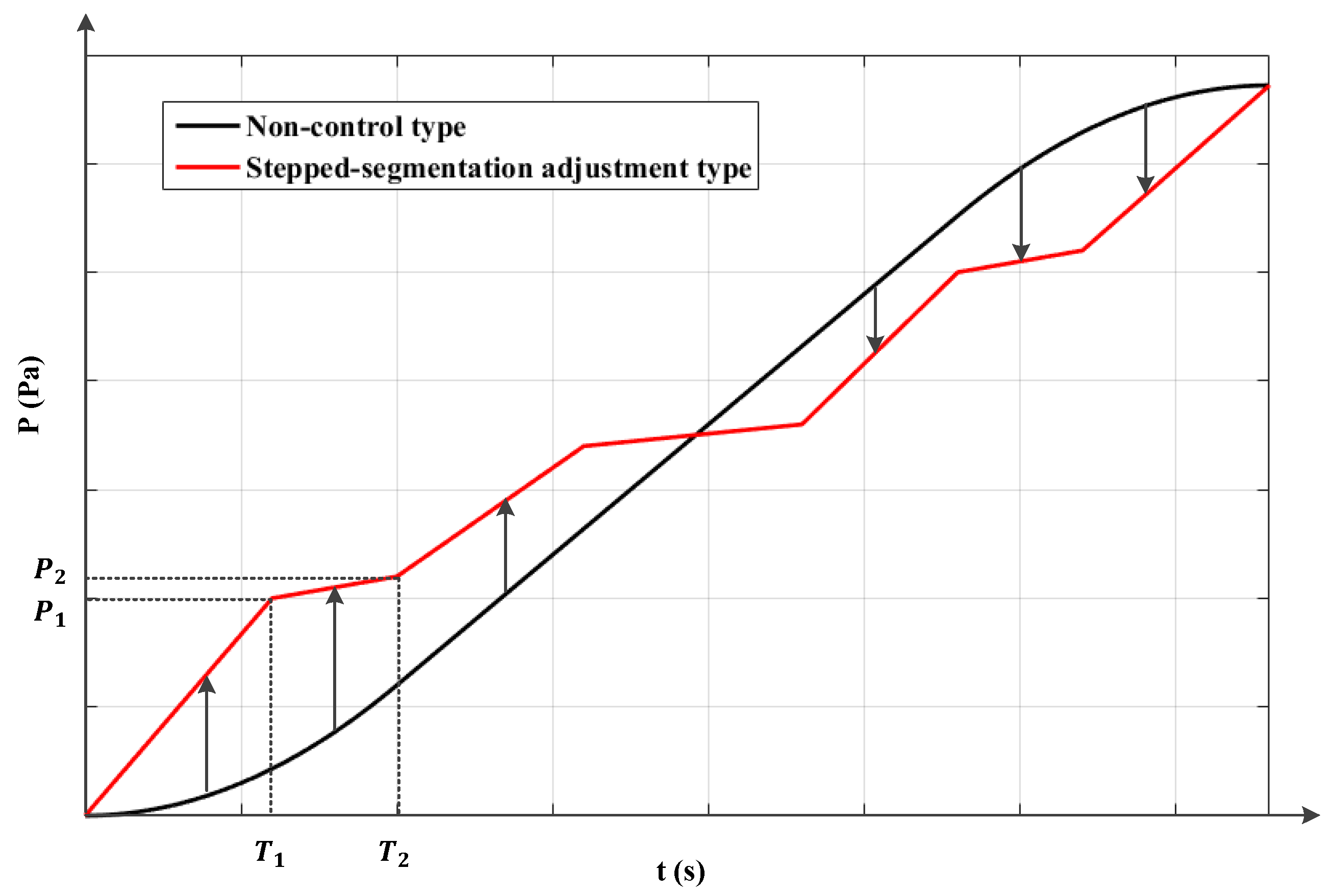
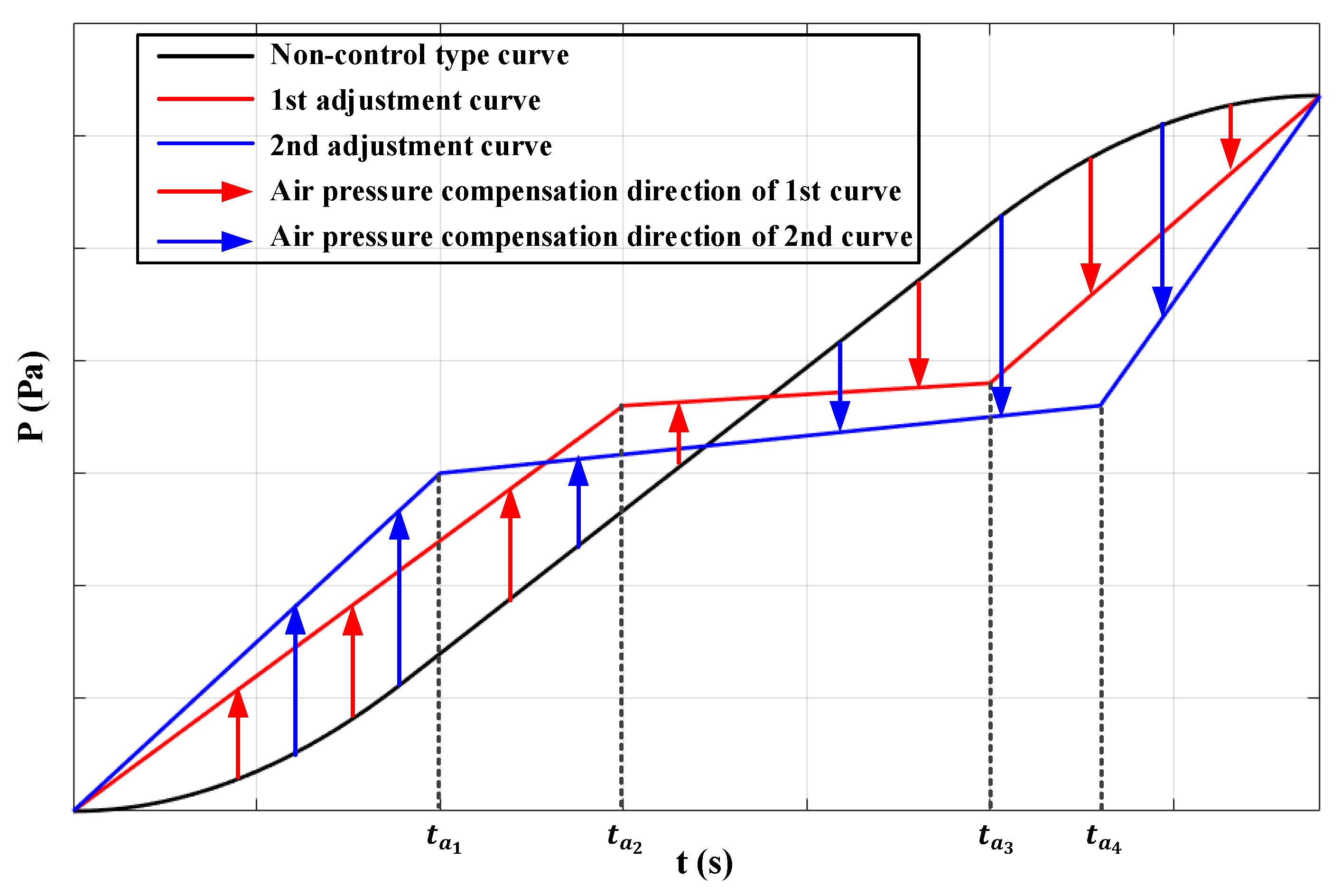
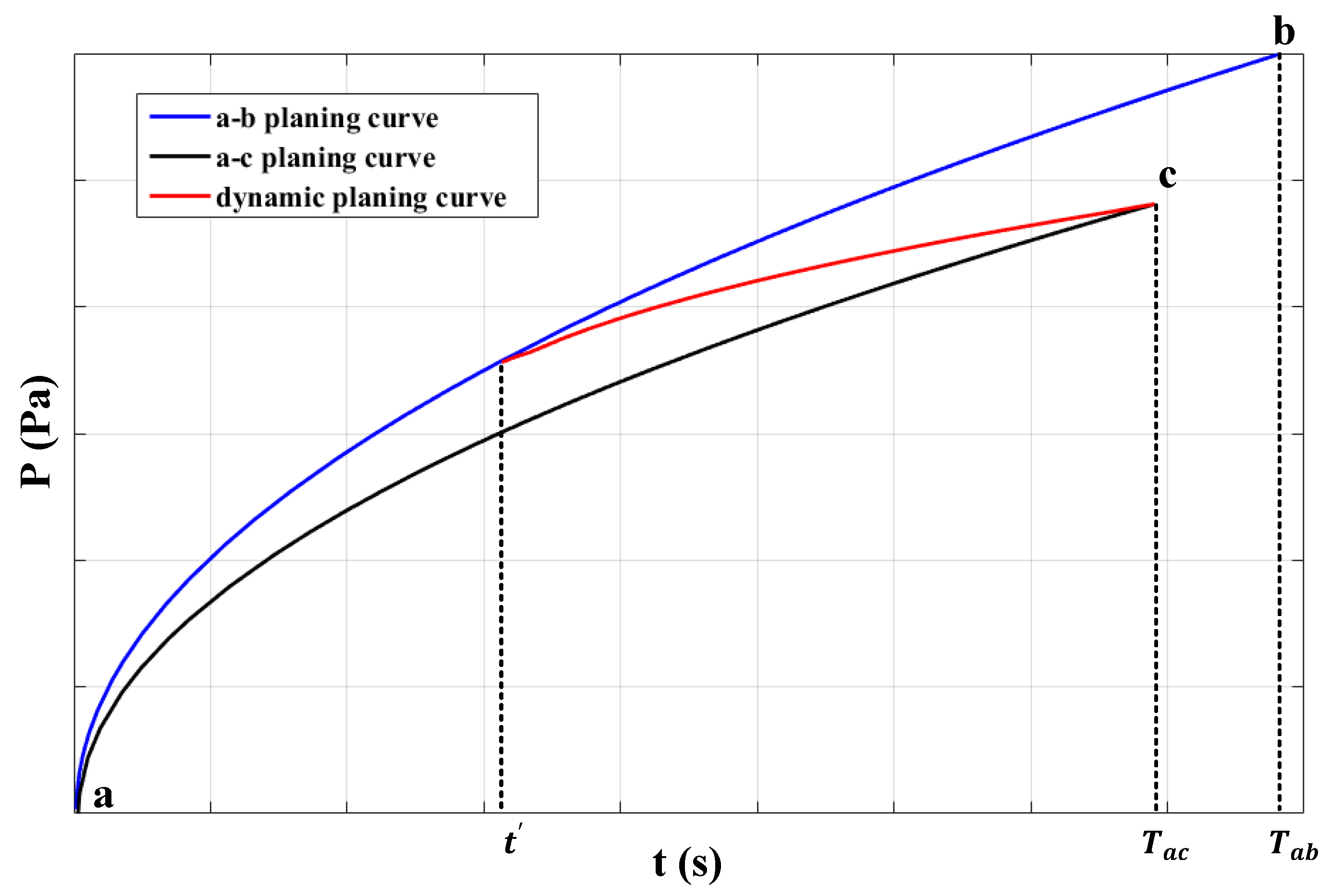
2. Theoretical Elevator Car Air Pressure Adjustment Curve Selection
- (a)
- Non-Control Type
- (b)
- Fixed Adjustment Type
- (c)
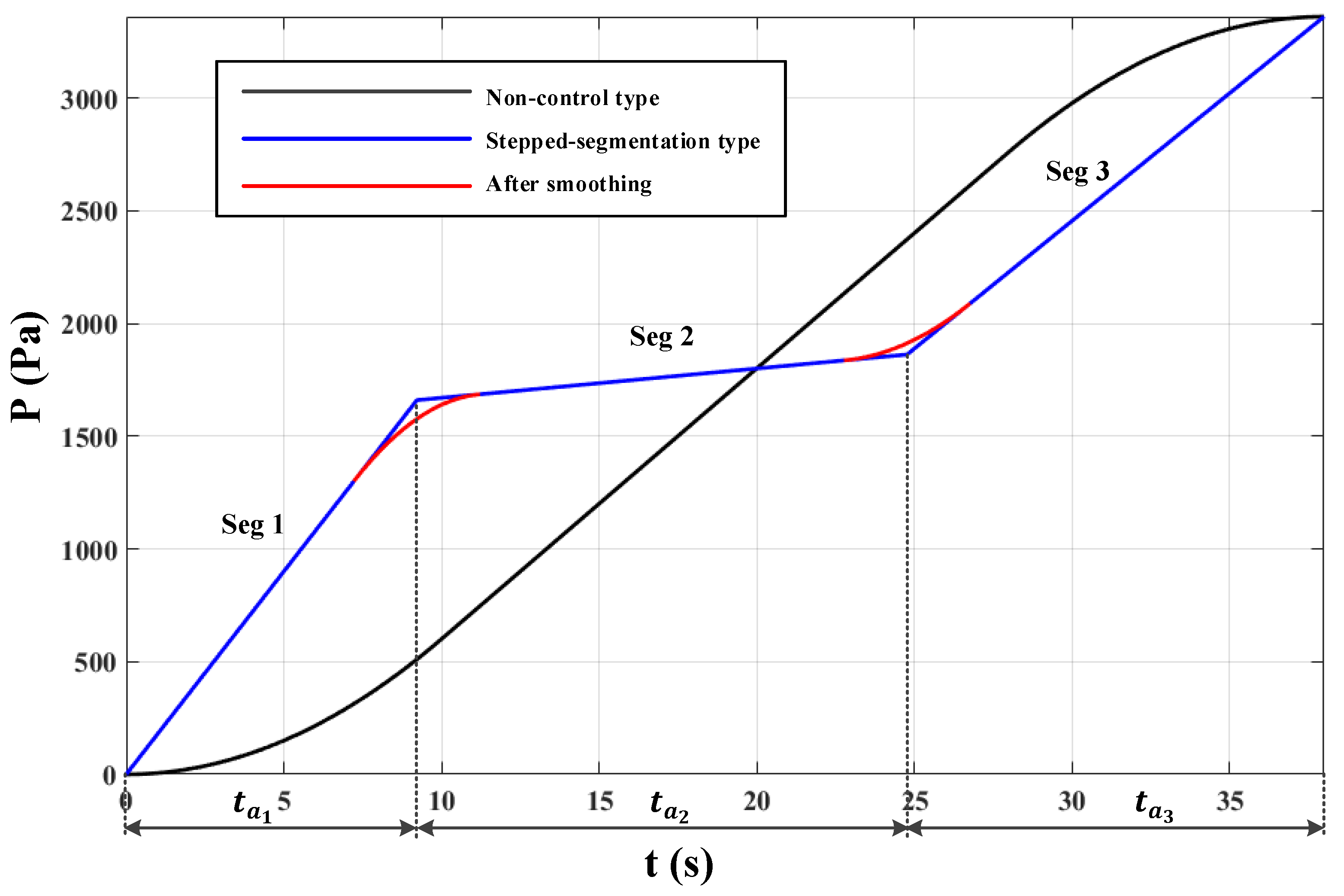
- Stepped-Segmentation Adjustment Type
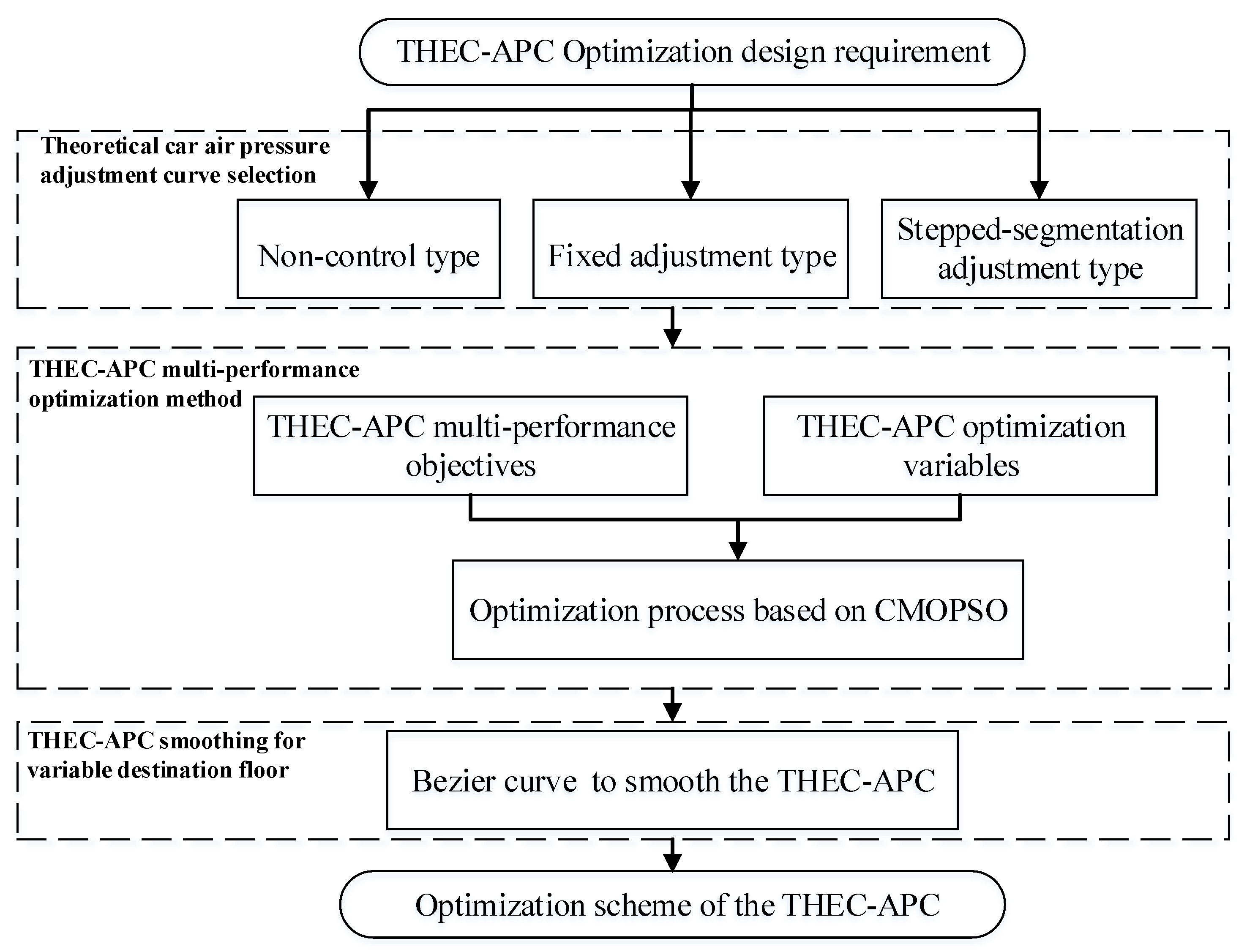
3. THEC-APC Multi-Performance Optimization Method
3.1. THEC-APC Multi-Performance Objectives
- A.
- Passenger comfort index
- B.
- Energy-saving index
- C.
- Precision pressure adjustment index
3.2. THEC-APC Optimization Variables
- A.
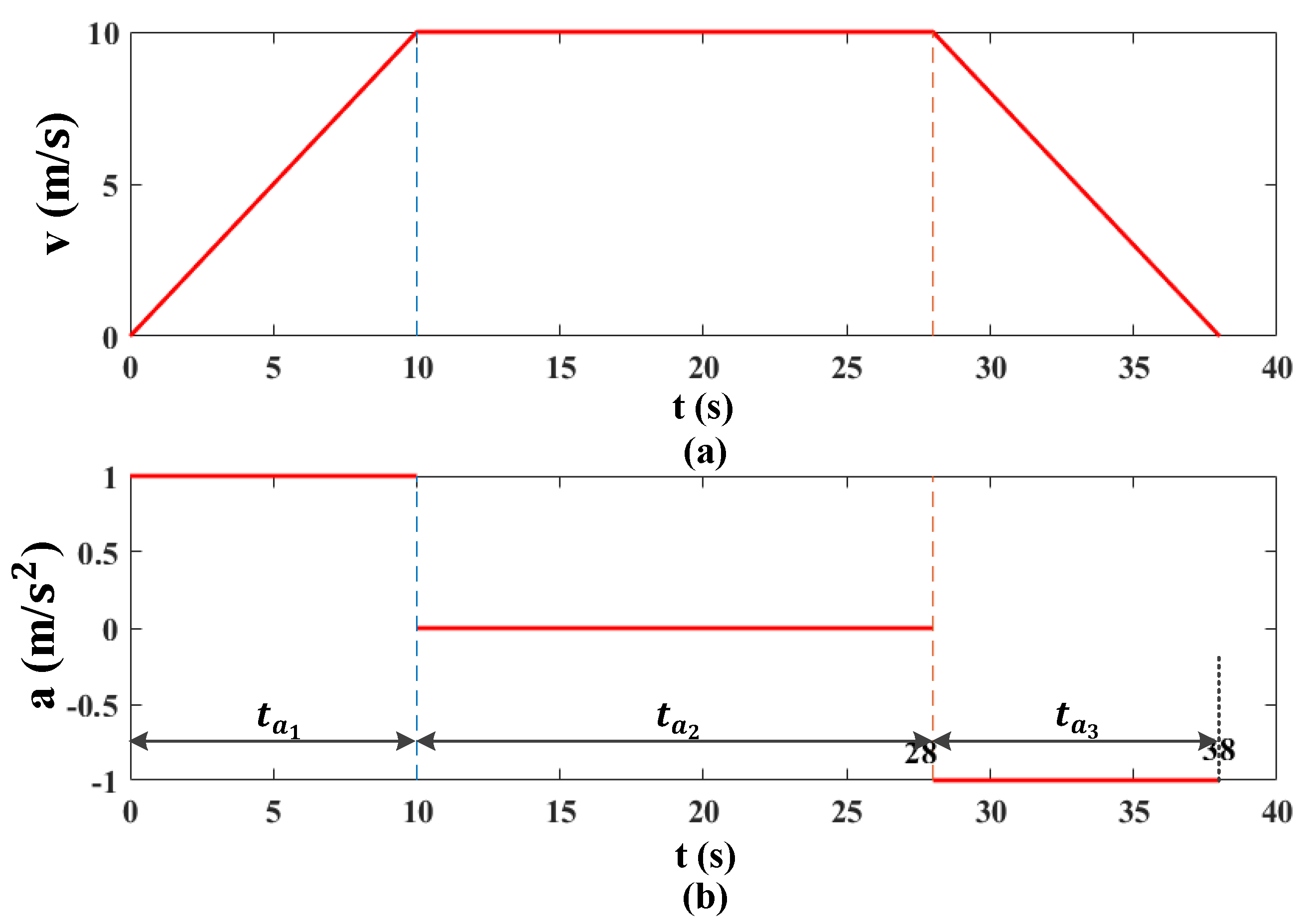
- Elevator Car Air Pressure Change Rate () and Corresponding Time ()
- B.
- Elevator Constant Speed () and Corresponding Acceleration Time ()
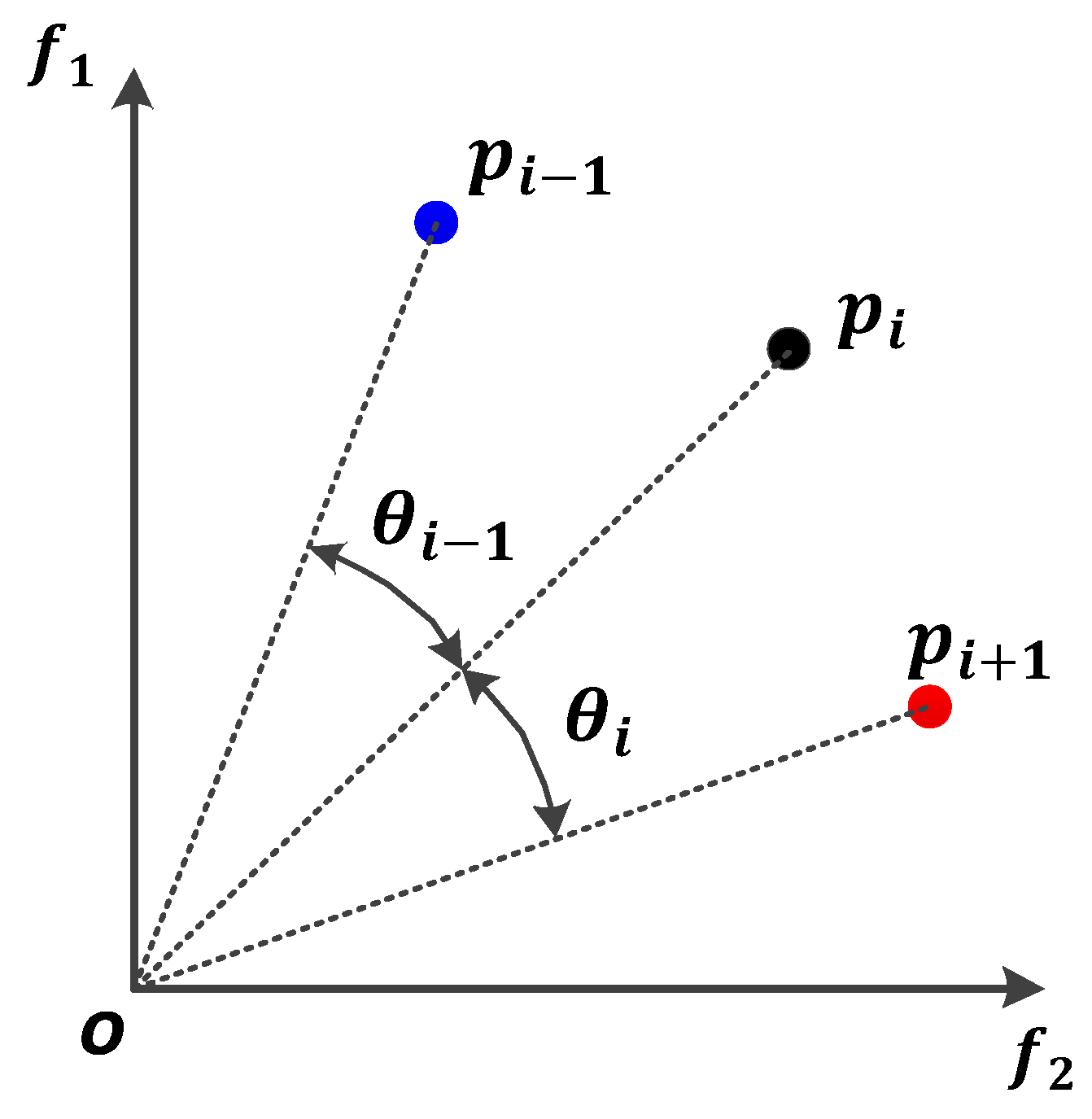
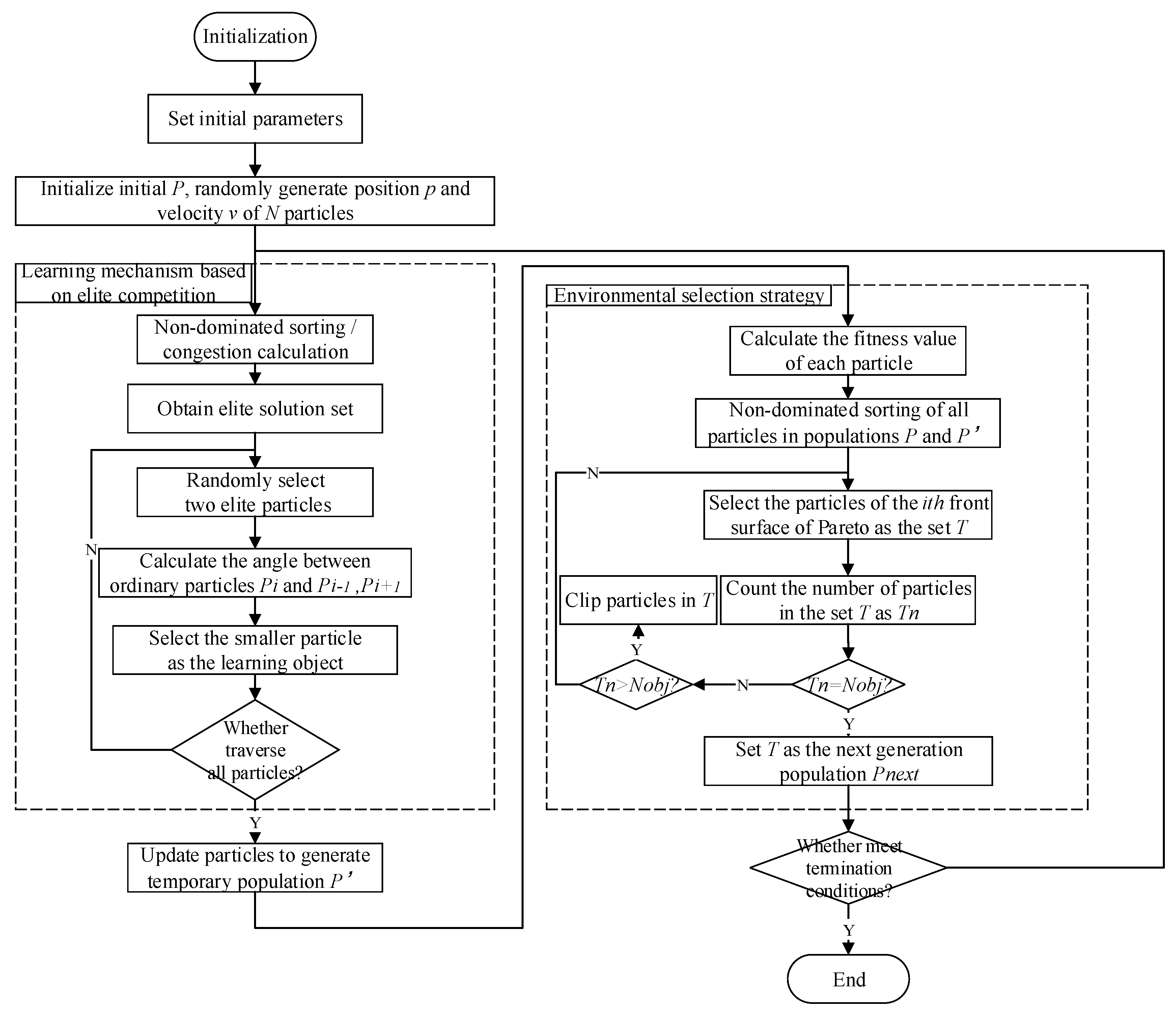
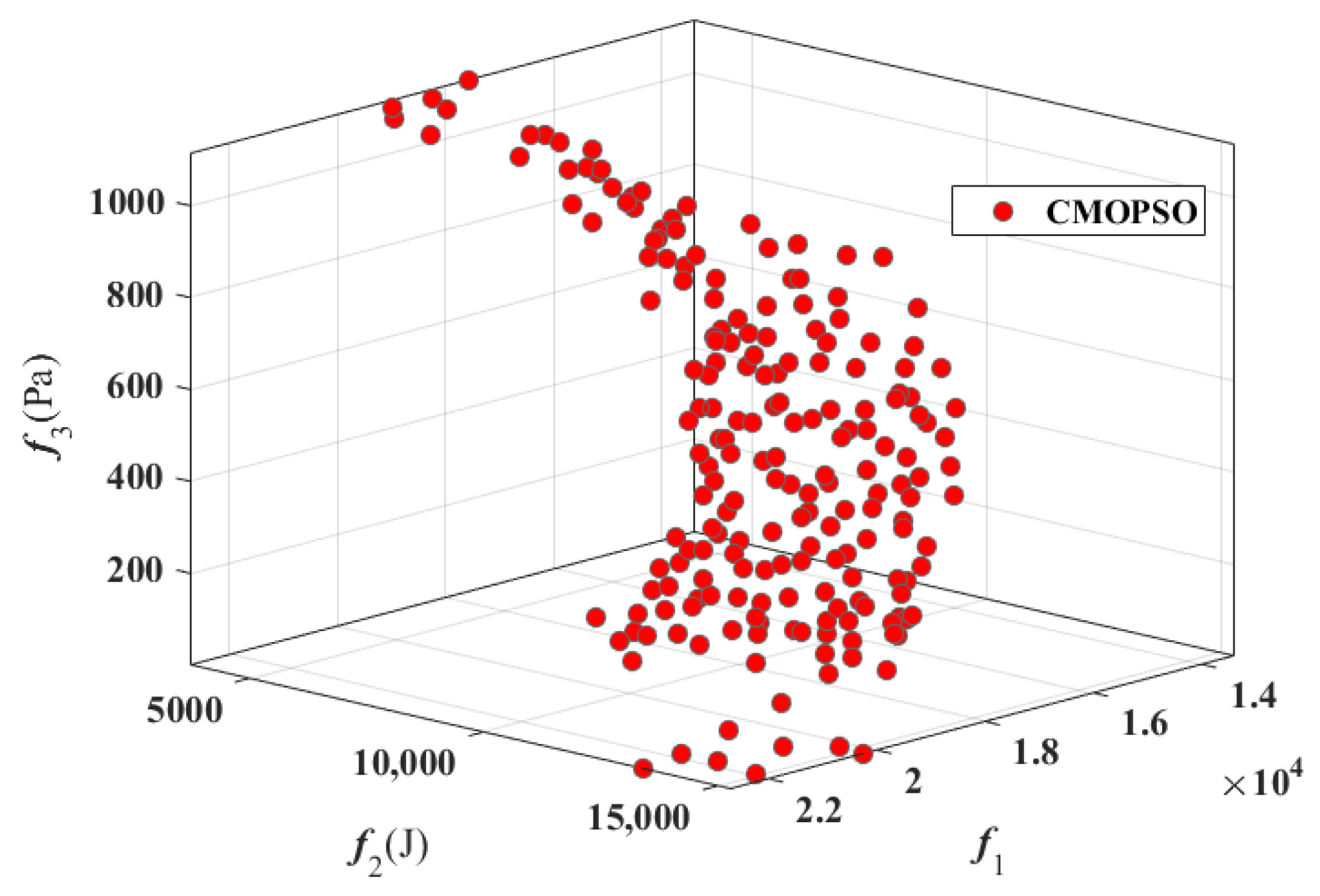
3.3. THEC-APC Multi-Performance Optimization Process Based on CMOPSO
- Step 1. Randomly initialize particle swarm , including the initialization of population particle position and velocity .
- Step 2. Obtain the N fitness values of each particle through the objective function and update the temporary particle swarm using the learning mechanism based on elite competition.
- Step 3. Use a non-dominated sorting-based environment selection strategy to select the next-generation population containing N particles from populations P and .
- Step 4. If the optimal solution end requirement is met, stop searching; otherwise, go to Step 2.
4. THEC-APC Smoothing for Variable Destination Floor
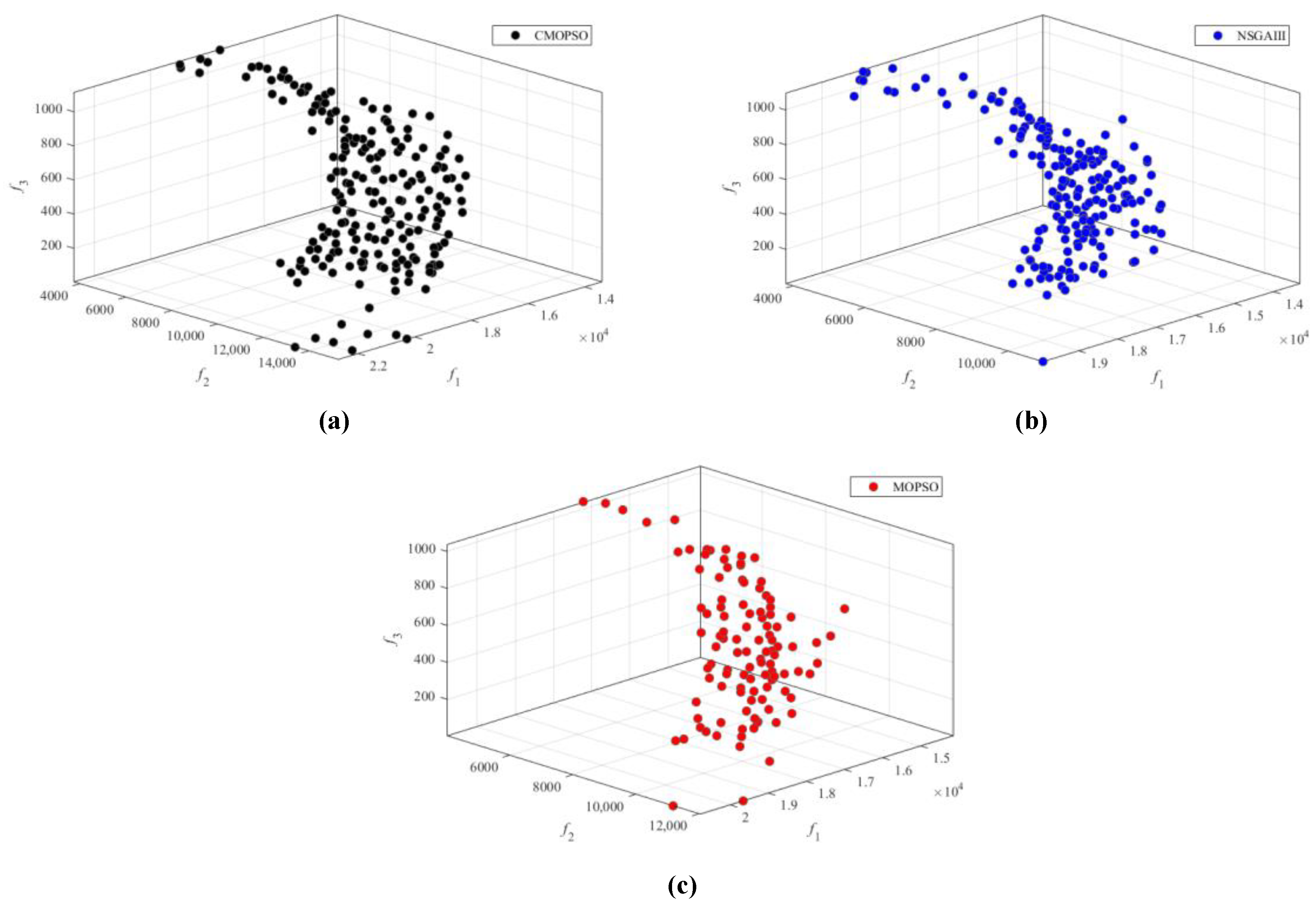
5. Numerical Experiment Verification
6. Conclusions
7. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability Statement
References
- Ding, B.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Peng, X.-Y.; Li, Q.-C.; Tang, H.-Y. A hybrid approach for the analysis and prediction of elevator passenger flow in an office building. Autom. Constr. 2013, 35, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharif, L.; Abu Alqumsan, A.M.; Aal, O.F.A. Automated optimal design methodology of elevator systems using rules and graphical methods (the HARint plane). Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2012, 34, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepyne, D.L.; Cassandras, C.G. Design and implementation of an adaptive dispatching controller for elevator systems during up-peak traffic. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1998, 6, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cortés, P.; Onieva, L.; Muñuzuri, J.; Guadix, J. A viral system algorithm to optimize the car dispatching in elevator group control systems of tall buildings. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2013, 64, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biotto, C.; Proverbio, A.; Ajewole, O.; Waterson, N.P.; Peiró, J. On the treatment of transient area variation in 1D discontinuous Galerkin simulations of train-induced pressure waves in tunnels. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2012, 71, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.; Lee, S. Efficient prediction methods for the micro-pressure wave from a high-speed train entering a tunnel using the Kirchhoff formulation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 110, 2379–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linic, S.; Ocokoljic, G.; Ristic, S.; Lucanin, V.; Kozić, M.; Rašuo, B.; Jegdić, B. Boundary-layer transition detection by thermography and numerical method around bionic train model in wind tunnel test. Therm. Sci. 2018, 22, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthoine, J. Alleviation of Pressure Rise from a High-Speed Train Entering a Tunnel. AIAA J. 2009, 47, 2132–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanitz, S.; Wittkowski, M.; Rolny, V.; Samel, C.; Basner, M. Continuous assessments of pressure comfort on a train—A field-laboratory comparison. Appl. Ergon. 2013, 44, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diedrichs, B.; Krajnović, S.; Berg, M. On The Aerodynamics of Car Body Vibrations of High-Speed Trains Cruising Inside Tunnels. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2008, 2, 51–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Shen, G.; So, A. Experimental-based study of the aerodynamics of super-high-speed elevators. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2005, 26, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Shen, G.X.; Zhang, Y.G. Aerodynamic testing simulation facility for high-speed elevator. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2004, 30, 444–447. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Teppo, L. Design and analysis of a scaled model of a high-rise, high-speed elevator. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 264, 707–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.-Q.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Jin, S.-Y.; Cao, Z.-M. Numerical Simulation of Unsteady Turbulent Flow Induced by Two-Dimensional Elevator Car and Counter Weight System. J. Hydrodyn. 2007, 19, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H. Cause and modification of the aerodynamic noise on high speed elevator. J. INCE Jpn. 1994, 18, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Lin, Z.; Tang, P.; Ling, Z. Research of the blockage ratio on the aerodynamic performances of high speed elevator. In Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Mechatronics, Materials, Chemistry and Computer Engineering, Xi’an, China, 12–13 December 2015; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Taplak, H.; Erkaya, S.; Yildirim, Ş.; Uzmay, I.; Yıldırım, Ş. The Use of Neural Network Predictors for Analyzing the Elevator Vibrations. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2013, 39, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Rui, Y. Research on vibration Control of traction elevator. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Industrial Informatics and Computer Engineering Conference, Xi’an, China, 10–11 January 2015; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, R. Intelligent control of active shock absorber for high-speed elevator car. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2018, 233, 3804–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusset, A.M.; Santo, D.R.; Balthazar, J.M.; Piccirillo, V.; Santos, L.C.C.D.; Brasil, R.M.L.R.F. Active vibration control of an elevator system using magnetorheological damper actuator. Int. J. Nonlinear Dyn. Control. 2017, 1, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.-H.; Jeong, J.-E.; Jeong, U.-C.; Kim, J.-S.; Oh, J.-E. Improvement of noise reduction performance for a high-speed elevator using modified active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 79, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, R.; Hironaka, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Daikoku, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Nishimura, M. Noise and Vibration Analysis of Elevator Traction Machine(Mechanical Systems). Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Ser. C 2010, 76, 2032–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Xie, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, K.; Chen, Z.; Luan, K. Robust Optimization of Power Consumption for Public Buildings Considering Forecasting Uncertainty of Environmental Factors. Energies 2018, 11, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbao, E.; Barrade, P.; Etxeberria-Otadui, I.; Rufer, A.; Luri, S.; Gil, I. Optimal Energy Management Strategy of an Improved Elevator With Energy Storage Capacity Based on Dynamic Programming. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 50, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Mao, C.; Lu, J.; Yang, J. Design and Implementation of an Energy Feedback Digital Device Used in Elevator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4636–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Su, Q.; Huo, J. A multi-objective genetic algorithm designed for energy saving of the elevator system with complete information. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Energy Conference, Manama, Bahrain, 18−22 December 2010; pp. 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zong, Q. Energy-saving scheduling optimization under up-peak traffic for group elevator system in building. Energy Build. 2013, 66, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zong, Q. Energy-saving-oriented group-elevator dispatching strategy for multi-traffic patterns. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2014, 35, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desdouits, C.; Alamir, M.; Boutin, V.; Le Pape, C. Multisource elevator energy optimization and control. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Control Conference (ECC), Linz, Austria, 15−17 July 2015; pp. 2315–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, P.F.; Yao, J.; Ding, B. A Novel Reconstruction Approach to Elevator Energy Conservation Based on a DC Micro-Grid in High-Rise Buildings. Energies 2018, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Kawase, K.; Sato, S.; Nakagawa, T. Experimental Verification of Effects in an Emergency Stop by Installation of Magnetorheological Fluid Damper to an Elevator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, B.; Li, C.; Xu, D. Weight-transducerless control strategy based on active disturbance rejection theory for gearless elevator drives. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L. Transverse Vibration Response of a Super High-Speed Elevator under Air Disturbance. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2019, 19, 1950103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.-H.; Hou, T.; Zhang, R.-J. Dynamic analysis of high-speed traction elevator and traction car–rope time-varying system. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2019, 50, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Palazzola, M.A.; Allen, S.D.; Frank, D.; Xu, J. Linear Motor for an Elevator; ThyssenKrupp Elevator AG: Essen, Germany, 2016; EP17708489.4. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, H.; Sudo, K.; Miyoshi, W.; Miyada, H. Elevator Equipment and its Pressure Control Method; State Intellectual Property Office Intellectual Property Press: Beijing, China, 2007; CN200810184378.6. [Google Scholar]
- Hekun, Y.; Shi, W.L.; Hagiwara, T.; Miyada, H.; Miyoshi, W. Control Method of Internal Pressure of Elevator Car; State Intellectual Property Office Intellectual Property Press: Beijing, China, 2016; CN201610453048.7. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K.; Shinji, L.; Suzuki, I. Elevator Air Pressure Control Device. United States. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (Tokyo, JP). 9017153. Available online: http://www.freepatentsonline.com/9017153.html (accessed on 28 April 2015).
- Fuller, J.W. Control of pressure—Comfort and motion in mega-rise elevators. Elev. World 1999, 47, 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Funai, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Koizumi, T.; Tsujiuchi, N. Analysis of tympanic membrane behavior and ear pressure discomfort for super high speed elevators. Elev. World 2006, 54, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L. Selected Applications of Convex Optimization; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, R.; Qiu, J.; Jin, Y. A competitive mechanism based multi-objective particle swarm optimizer with fast convergence. Inf. Sci. 2018, 427, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
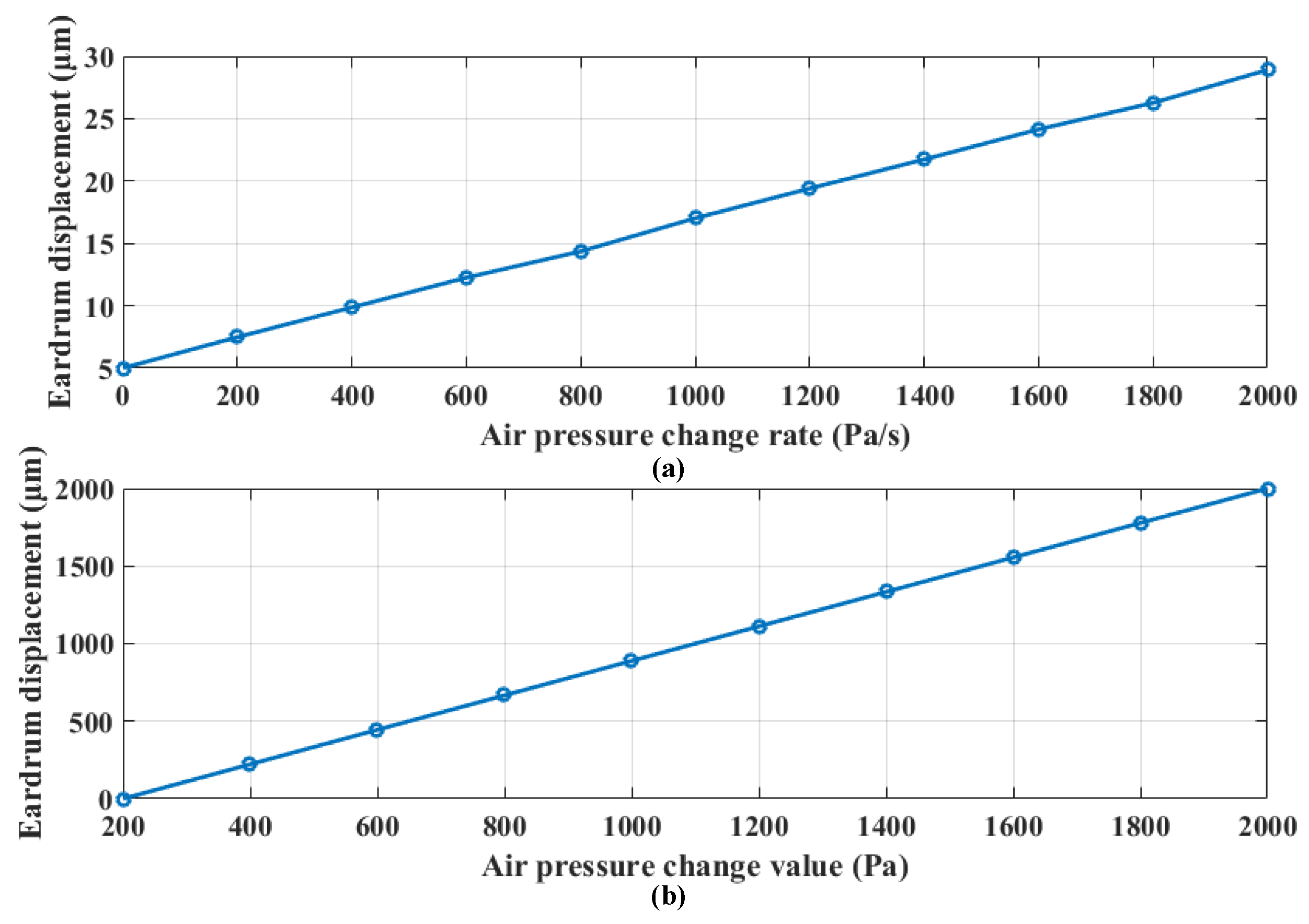
| Comfort level (J) | Comfort Evaluation Description | Ear Tympanic Membrane Displacement |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | No feeling | 1 |
| 2 | Comfortable | 10.1 |
| 3 | Slight discomfort | 19.2 |
| 4 | Noticeable discomfort | 28.3 |
| 5 | Extreme discomfort | 37.4 |
| Scheme No. | (m/s) | (s) | (s) | (Pa/s) | (s) | (Pa/s) | (s) | (Pa/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.09 | 9.00 | 17.99 | 161.42 | 9.00 | 12.57 | 14.40 | 161.84 |
| 2 | 9.96 | 9.76 | 19.65 | 165.71 | 9.08 | 12.63 | 14.33 | 163.86 |
| …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… |
| 50 | 10.48 | 9.80 | 20.00 | 162.96 | 9.00 | 13.43 | 14.08 | 161.01 |
| …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… |
| 55 | 10.79 | 9.17 | 16.67 | 160.00 | 9.22 | 15.55 | 12.05 | 162.37 |
| …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… | …… |
| 99 | 11.35 | 9.90 | 20.00 | 162.05 | 9.00 | 13.97 | 14.06 | 160.00 |
| 100 | 11.60 | 10.21 | 19.29 | 162.44 | 9.29 | 10.82 | 14.82 | 162.34 |
| Scheme No. | Passenger Comfort Index | Energy-Saving Index (J) | Precision Pressure Adjustment Index (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15,378.00 | 5949.00 | 968.00 |
| 2 | 14,833.00 | 9375.00 | 347.00 |
| …… | …… | …… | …… |
| 50 | 15,688.00 | 10,614.00 | 141.00 |
| …… | …… | …… | …… |
| 55 | 8920 | 28,275.6 | 5.7 |
| …… | …… | …… | …… |
| 99 | 18,715.00 | 12,134.00 | 155.00 |
| 100 | 21,268.00 | 11,240.00 | 318.00 |
| Scheme | Passenger Comfort Index | Energy-Saving Index (J) | Precision Pressure Adjustment Index (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| stepped-segmentation type | 8921.5 | 28,275.6 | 5.7 |
| non-control curve | 54,342.3 | 17,342.9 | 4.3 |
| Algorithms | (m/s) | (s) | (s) | (Pa/s) | (s) | (Pa/s) | (s) | (Pa/s) |
| CMOPSO | 10.79 | 9.17 | 16.67 | 160.00 | 9.22 | 12.05 | 15.55 | 162.37 |
| NSGA-III | 10.24 | 9.18 | 19.29 | 166.11 | 9.82 | 10.40 | 15.84 | 160.37 |
| MOPSO | 10.65 | 10.29 | 19.44 | 165.42 | 10.28 | 10.76 | 15.95 | 161.17 |
| Algorithm | Passenger Comfort Index | Energy-Saving Index (J) | Precision Pressure AdjustmentIndex (Pa) | |||||
| CMOPSO | 8920 | 28275.6 | 5.7 | |||||
| NSGA-III | 9891 | 29246.3 | 14.3 | |||||
| MOPSO | 10404 | 30161.4 | 10.2 | |||||
| Algorithms | Convergence Iterations | Running Time/s | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMOPSO | 32 | 11.16 | 1.475 | 1.432 |
| NSGA-III | 45 | 10.92 | 1.609 | 1.665 |
| MOPSO | 47 | 10.95 | 1.556 | 1.765 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, L.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Lou, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L. A Stepped-Segmentation Method for the High-Speed Theoretical Elevator Car Air Pressure Curve Adjustment. Energies 2020, 13, 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102585
Qiu L, Zhou H, Wang Z, Lou W, Zhang S, Zhang L. A Stepped-Segmentation Method for the High-Speed Theoretical Elevator Car Air Pressure Curve Adjustment. Energies. 2020; 13(10):2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102585
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Lemiao, Huifang Zhou, Zili Wang, Wenqian Lou, Shuyou Zhang, and Lichun Zhang. 2020. "A Stepped-Segmentation Method for the High-Speed Theoretical Elevator Car Air Pressure Curve Adjustment" Energies 13, no. 10: 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102585
APA StyleQiu, L., Zhou, H., Wang, Z., Lou, W., Zhang, S., & Zhang, L. (2020). A Stepped-Segmentation Method for the High-Speed Theoretical Elevator Car Air Pressure Curve Adjustment. Energies, 13(10), 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102585






