Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Wiener Processes with Considering the Relaxation Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivations and Technical Challenges
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Original Contributions and Outline of Paper
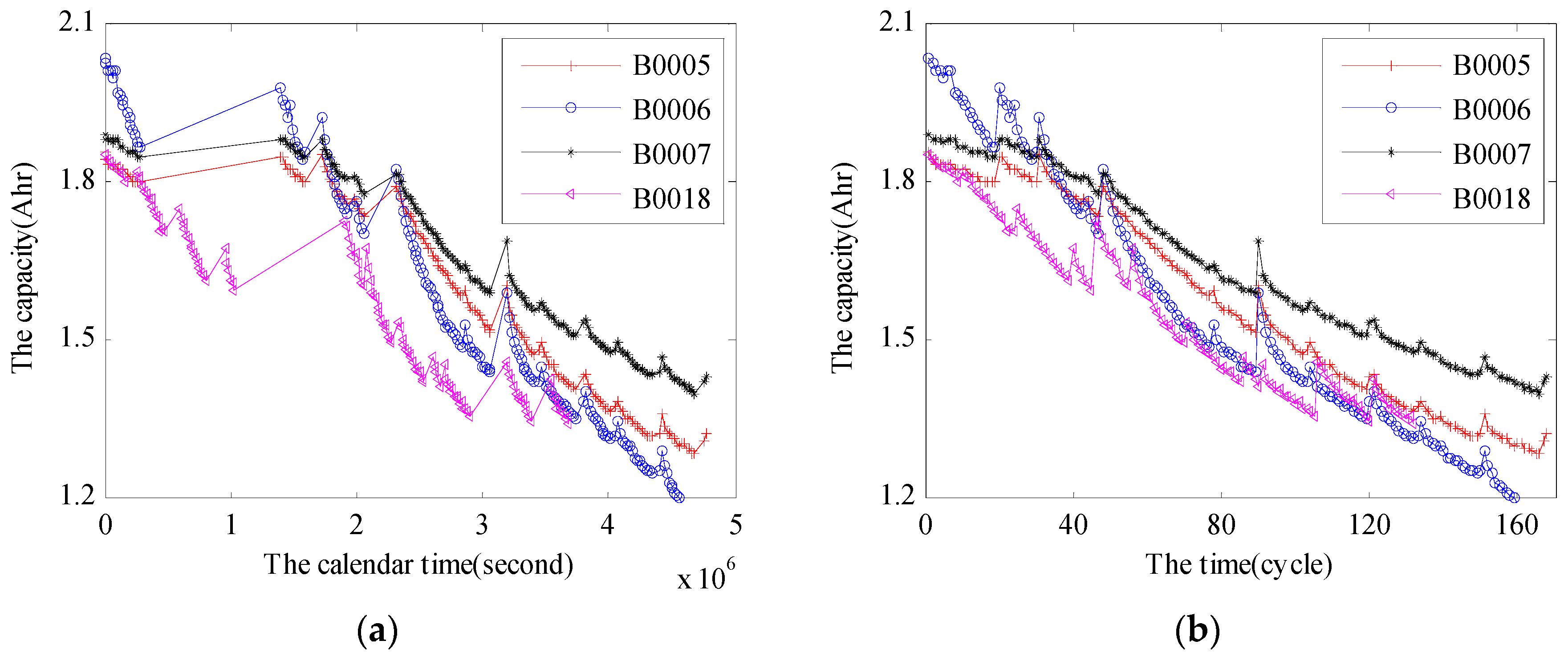
2. Relaxation Effect Analysis
3. RUL Prediction for the Degradation Model with Elimination of the Relaxation Effect
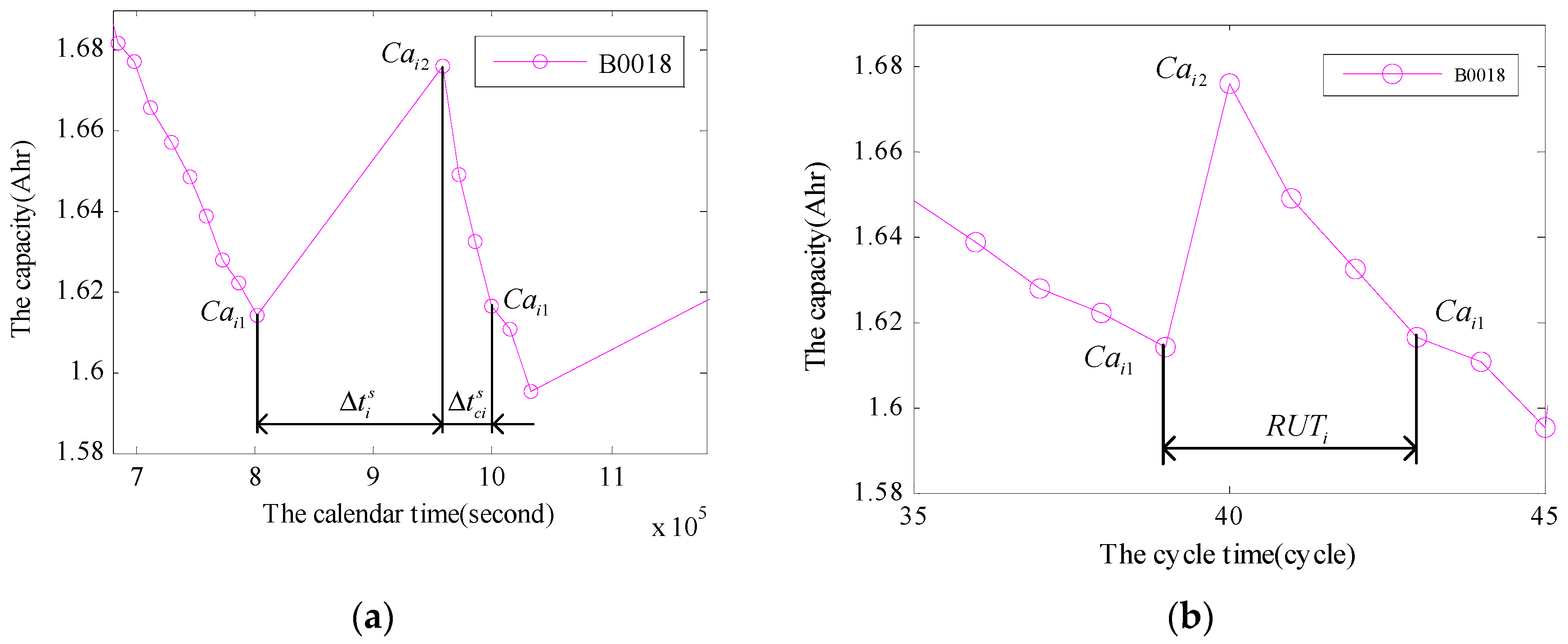
3.1. The Method for Eliminating the Relaxation Effect
3.2. Degradation Modeling
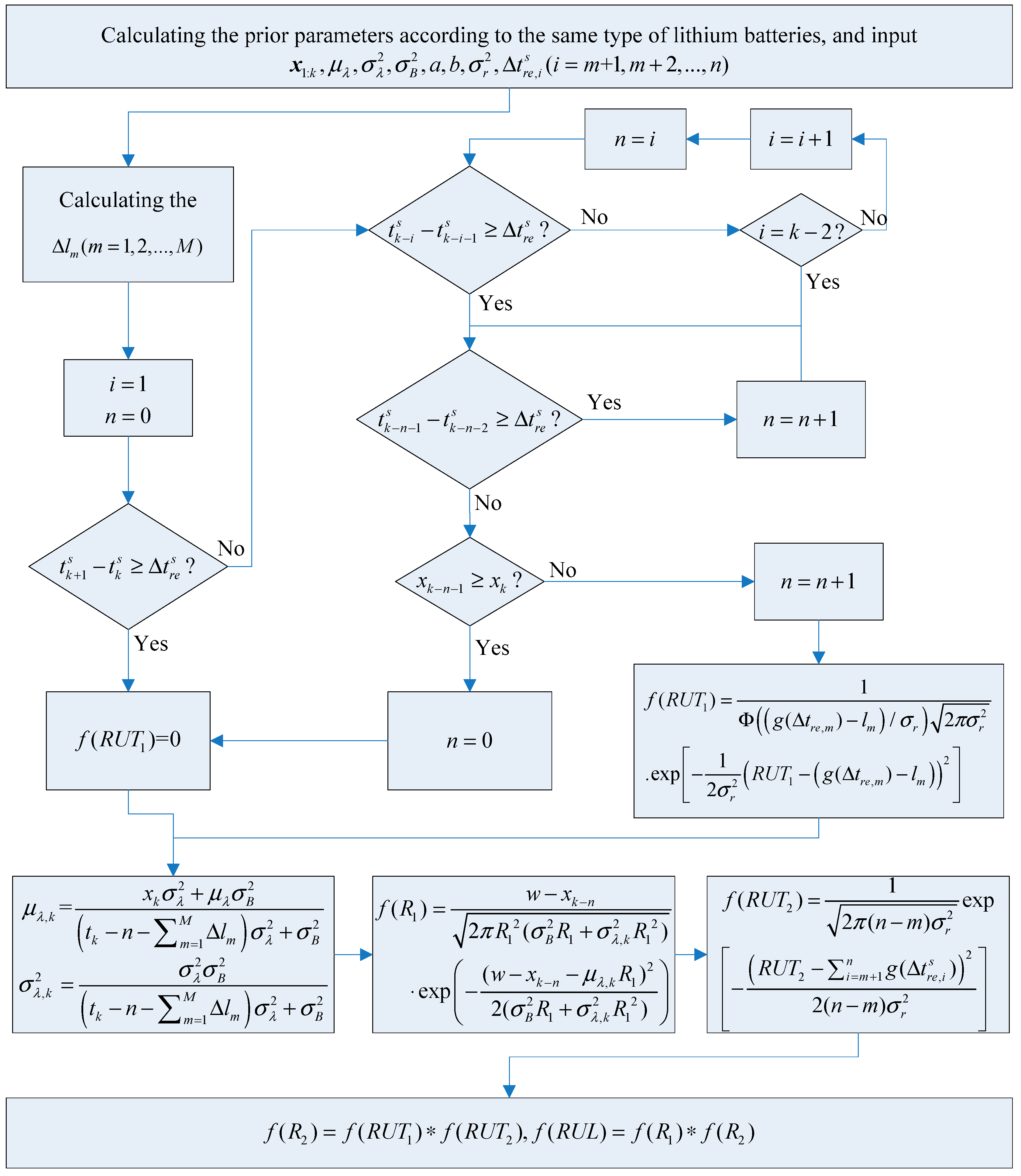
3.3. Prior Parameters Estimation
3.4. Online Parameter Updating and RUL Prediction
4. RUT Prediction for the Relaxation Effect
4.1. Modeling the RUT
4.2. Parameters Estimation
4.3. Predicting the RUT
5. The Global RUL Prediction for Lithium-Ion Batteries with Considering the Relaxation Effect
6. Experiment
6.1. Prior Parameters Estimation for the Data with Elimination of the Relaxation Effect
6.2. Parameters Estimation for the Model of RUT
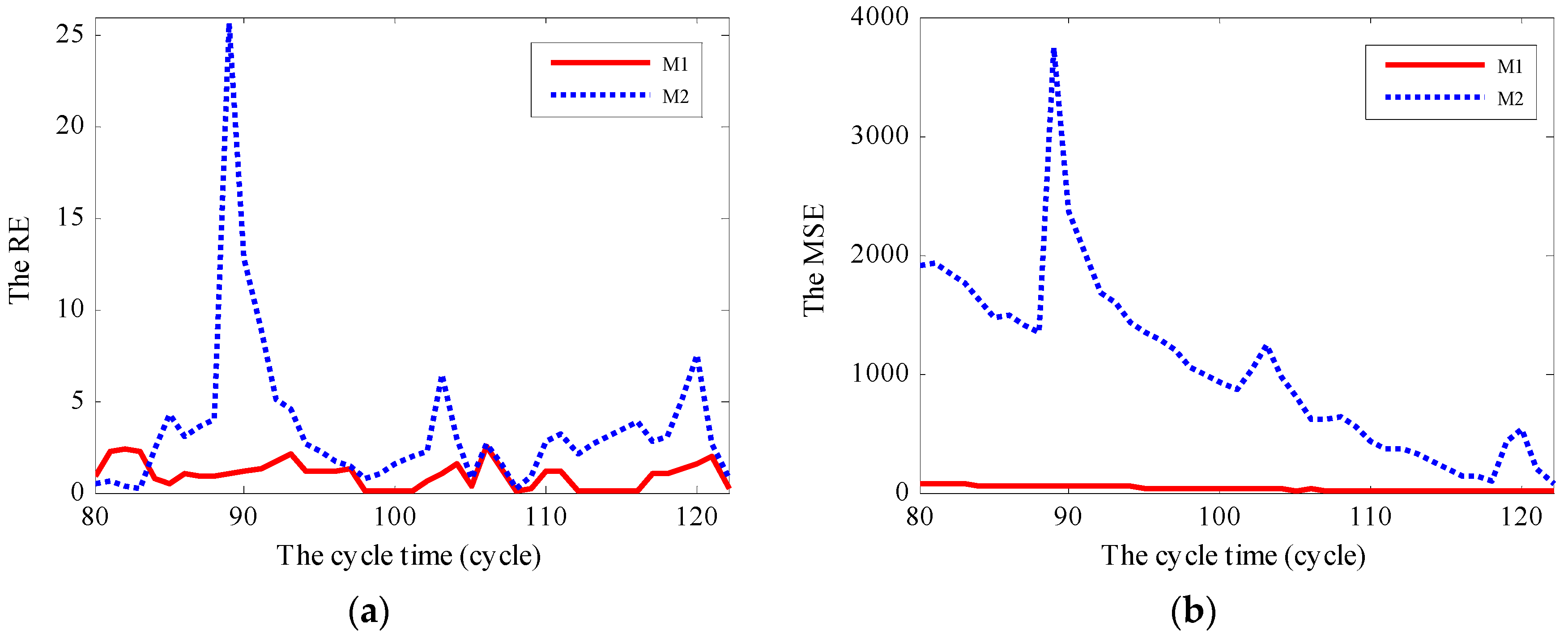
6.3. RUL Prediction
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. A Novel Battery State-of-Health Estimation Method for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhangu, B.S.; Bentley, P.; Stone, D.A.; Bingham, C.M. Nonlinear Observers for Predicting State-of-Charge and State-of-Health of Lead-Acid Batteries for Hybrid-Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2005, 54, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipu, M.S.H.; Hannan, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Hoque, M.M.; Ker, P.J.; Saad, M.H.M.; Ayob, A. A review of state of health and remaining useful life estimation methods for lithium-ion battery in electric vehicles: Challenges and recommendations. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucu, M.; Martinez-Laserna, E.; Gandiaga, I.; Camblong, H. A critical review on self-adaptive Li-ion battery ageing models. J. Power Sources 2018, 401, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tang, A.; Wang, W. A Review of SOH Estimation Methods in Lithium-ion Batteries for Electric Vehicle Applications. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 1920–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barré, A.; Deguilhem, B.; Grolleau, S.; Gérard, M.; Suard, F.; Riu, D. A review on lithium-ion battery ageing mechanisms and estimations for automotive applications. J. Power Sources 2013, 241, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecht, M. Prognostics and Health Management of Electronics. In Encyclopedia of Structural Health Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, R.; He, H.; Pecht, M.G. Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 5695–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tsui, K.-L.; Miao, Q. Prognostics and Health Management: A Review of Vibration Based Bearing and Gear Health Indicators. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Kottig, F. Review of Hybrid Prognostics Approaches for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Engineered Systems, and an Application to Battery Life Prediction. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2014, 63, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Matthews, D.E.; Zhou, Z. A Bayesian framework for on-line degradation assessment and residual life prediction of secondary batteries inspacecraft. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 113, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Goebel, K.; Poll, S.; Christophersen, J. Prognostics Methods for Battery Health Monitoring Using a Bayesian Framework. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 58, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Fu, X.; Guan, Y. Review of the Remaining Useful Life Prognostics of Vehicle Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Data-Driven Methodologies. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, P.L.T.; Raghavan, N. Heuristic Kalman optimized particle filter for remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 81, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepasi, S.; Ghorbani, R.; Liaw, B.Y. Inline state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries using state of charge calculation. J. Power Sources 2015, 299, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y. A new hybrid method for the prediction of the remaining useful life of a lithium-ion battery. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 1564–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Fang, H. An integrated unscented kalman filter and relevance vector regression approach for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life and short-term capacity prediction. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 144, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Köttig, F. A hybrid framework combining data-driven and model-based methods for system remaining useful life prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 44, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Chen, Z.; Wei, J.; Ling, Q. Battery Health Prognosis Using Brownian Motion Modeling and Particle Filtering. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 8646–8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Tsui, K.-L. Battery remaining useful life prediction at different discharge rates. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 78, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hao, X.; Pecht, M.; Zhou, Y. Remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries based on an integrated health indicator. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 88–90, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Z. Particle filter based on Particle Swarm Optimization resampling for vision tracking. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 8910–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, G.; Bu, S.; Han, J.; Tang, X.; Pecht, M. Particle Learning Framework for Estimating the Remaining Useful Life of Lithium-Ion Batteries. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. An improved unscented particle filter approach for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 81, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Miao, Q.; Liu, Z. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery using an improved UPF method based on MCMC. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 75, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuhic, A.; Terzimehic, T.; Soczka-Guth, T.; Buchholz, M.; Dietmayer, K. Health diagnosis and remaining useful life prognostics of lithium-ion batteries using data-driven methods. J. Power Sources 2013, 239, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-K.; Mamo, T. A hybrid model based on support vector regression and differential evolution for remaining useful lifetime prediction of lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2018, 401, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Qin, X.; Zhao, H.; Feng, W. A novel prediction method based on the support vector regression for the remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 85, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Jin, X.; Lou, Y.; Wang, C. Lithium-ion battery state of health monitoring and remaining useful life prediction based on support vector regression-particle filter. J. Power Sources 2014, 271, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, M.; Chen, Y.; Tao, Y. A novel health indicator for on-line lithium-ion batteries remaining useful life prediction. J. Power Sources 2016, 321, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, R.; He, H.; Pecht, M. Validation and verification of a hybrid method for remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, J.; Pan, D.; Peng, Y.; Peng, X. Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation with an optimized Relevance Vector Machine algorithm with incremental learning. Measurement 2015, 63, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L. Prediction of Bearing Remaining Useful Life with Deep Convolution Neural Network. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 13041–13049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z. An online method for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation using importance sampling and neural networks. Appl. Energy 2016, 173, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Dong, P. Remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries based on a hybrid model combining the long short-term memory and Elman neural networks. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Degradation model and cycle life prediction for lithium-ion battery used in hybrid energy storage system. Energy 2019, 166, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Zhao, S.; Chen, S.; Huang, D.; Liang, J. Adaptive and robust prediction for the remaining useful life of electrolytic capacitors. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 87, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Miao, Q.; Zheng, B.; Wu, S.; Pecht, M. Quantitative Analysis of Lithium-Ion Battery Capacity Prediction via Adaptive Bathtub-Shaped Function. Energies 2013, 6, 3082–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mi, C.C.; Fu, Y.; Xu, J.; Gong, X. Online battery state of health estimation based on Genetic Algorithm for electric and hybrid vehicle applications. J. Power Sources 2013, 240, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Zhao, L.; Hong, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L. Remaining Useful Life Prediction for Lithium-Ion Battery: A Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 50587–50598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.-S.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.-H.; Zhou, D.-H. Remaining useful life estimation—A review on the statistical data driven approaches. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 213, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Lei, Y. Degradation data analysis and remaining useful life estimation: A review on Wiener-process-based methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 271, 775–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Yu, C.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Si, X. Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on the Wiener Process with Measurement Error. Energies 2014, 7, 520–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, P.; Chao, K.H.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Y. Remaining Useful Life Prediction for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Gaussian Processes Mixture. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Q.; Ye, Z.-S. RUL Prediction of Deteriorating Products Using an Adaptive Wiener Process Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 2911–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.-S. An Adaptive Prognostic Approach via Nonlinear Degradation Modeling: Application to Battery Data. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5082–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X. Remaining Useful Life Prediction Using a Novel Two-Stage Wiener Process with Stage Correlation. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 65227–65238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Kvam, P.; Tang, Y. Remaining useful lifetime prediction based on the damage-marker bivariate degradation model: A case study on lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 70, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Goebel, K. Modeling Li-ion Battery Capacity Depletion in a Particle Filtering Framework. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 27 September–1 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, L.; Zhu, C.; Lu, R. Relaxation model of the open-circuit voltage for state-of-charge estimation in lithium-ion batteries. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2013, 3, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Zeng, S.; Guo, J.; Skaf, Z. State of Health Estimation of Li-ion Batteries with Regeneration Phenomena: A Similar Rest Time-Based Prognostic Framework. Symmetry 2016, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Zeng, S.; Guo, J.; Skaf, Z. A Rest Time-Based Prognostic Framework for State of Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries with Regeneration Phenomena. Energies 2016, 9, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-X.; Si, X.-S.; Hu, C.-H.; Pecht, M.G. A Prognostic Model for Stochastic Degrading Systems with State Recovery: Application to Li-Ion Batteries. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2017, 66, 1293–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, X.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Zhou, D. A Novel Multi-Phase Stochastic Model for Lithium-Ion Batteries’ Degradation with Regeneration Phenomena. Energies 2017, 10, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.-S.; Wang, W.; Chen, M.-Y.; Hu, C.-H.; Zhou, D.-H. A degradation path-dependent approach for remaining useful life estimation with an exact and closed-form solution. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 226, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Yu, C.; Tang, S.; Sun, X.; Si, X.; Wu, L. Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Wiener Processes with Considering the Relaxation Effect. Energies 2019, 12, 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091685
Xu X, Yu C, Tang S, Sun X, Si X, Wu L. Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Wiener Processes with Considering the Relaxation Effect. Energies. 2019; 12(9):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091685
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaodong, Chuanqiang Yu, Shengjin Tang, Xiaoyan Sun, Xiaosheng Si, and Lifeng Wu. 2019. "Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Wiener Processes with Considering the Relaxation Effect" Energies 12, no. 9: 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091685
APA StyleXu, X., Yu, C., Tang, S., Sun, X., Si, X., & Wu, L. (2019). Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Wiener Processes with Considering the Relaxation Effect. Energies, 12(9), 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091685






