A New Control Method for Vibration and Noise Suppression in Switched Reluctance Machines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
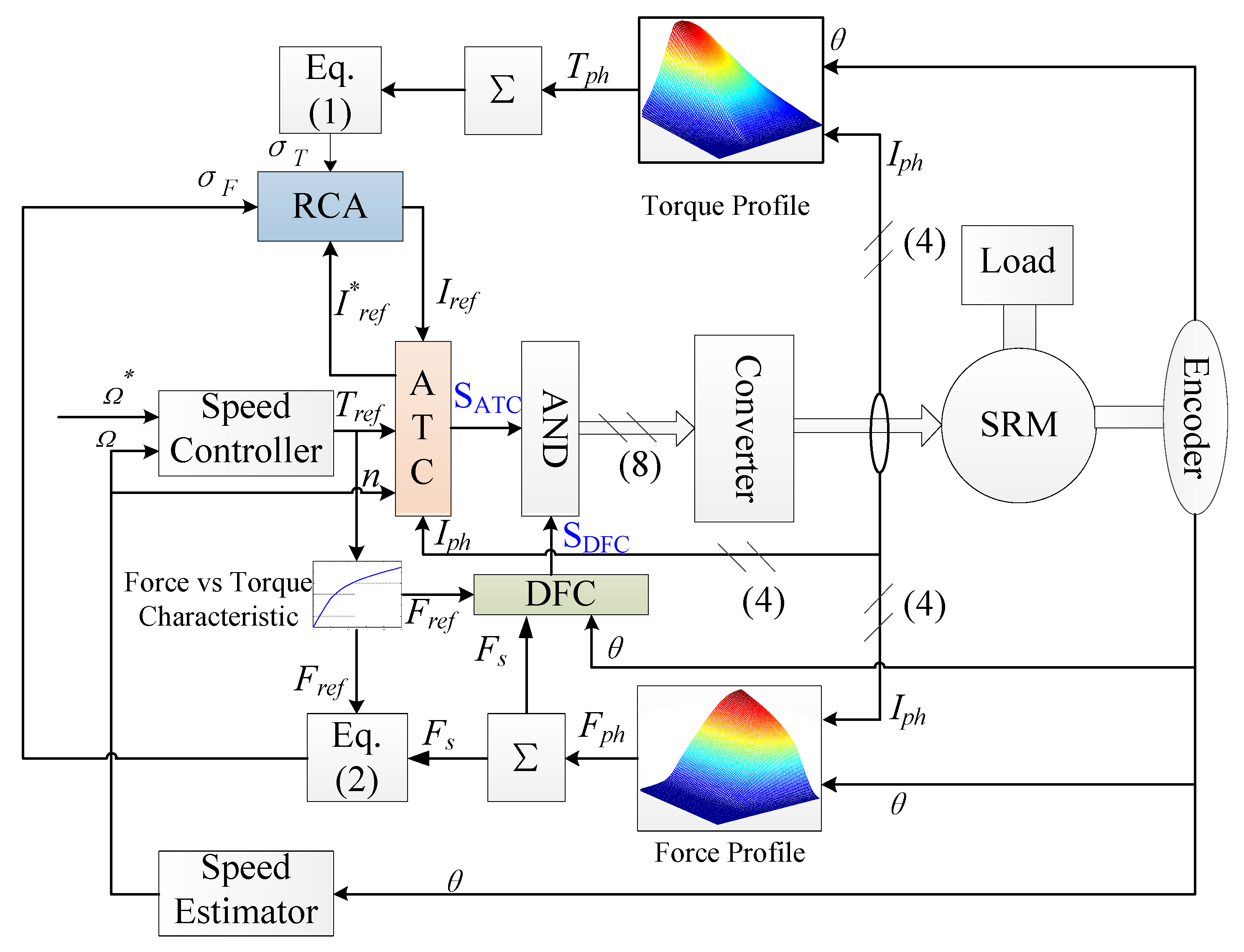
2. Materials and Methods
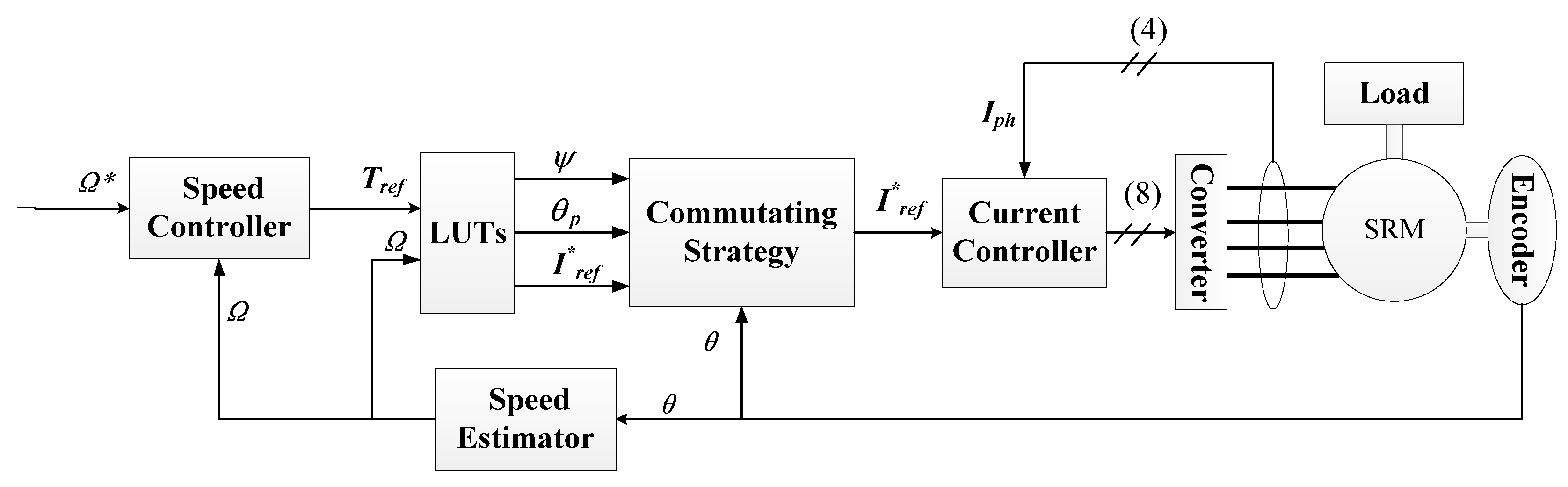
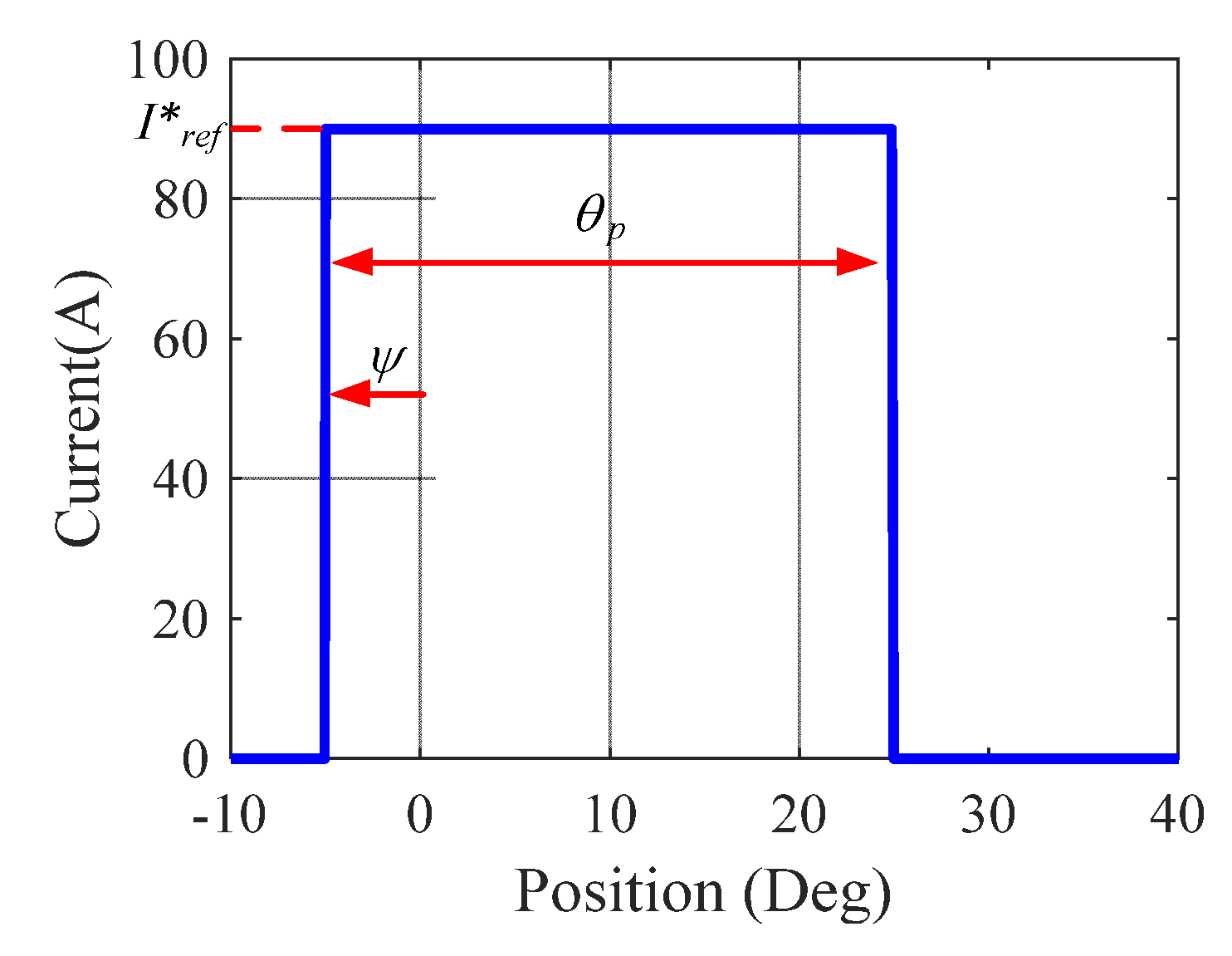
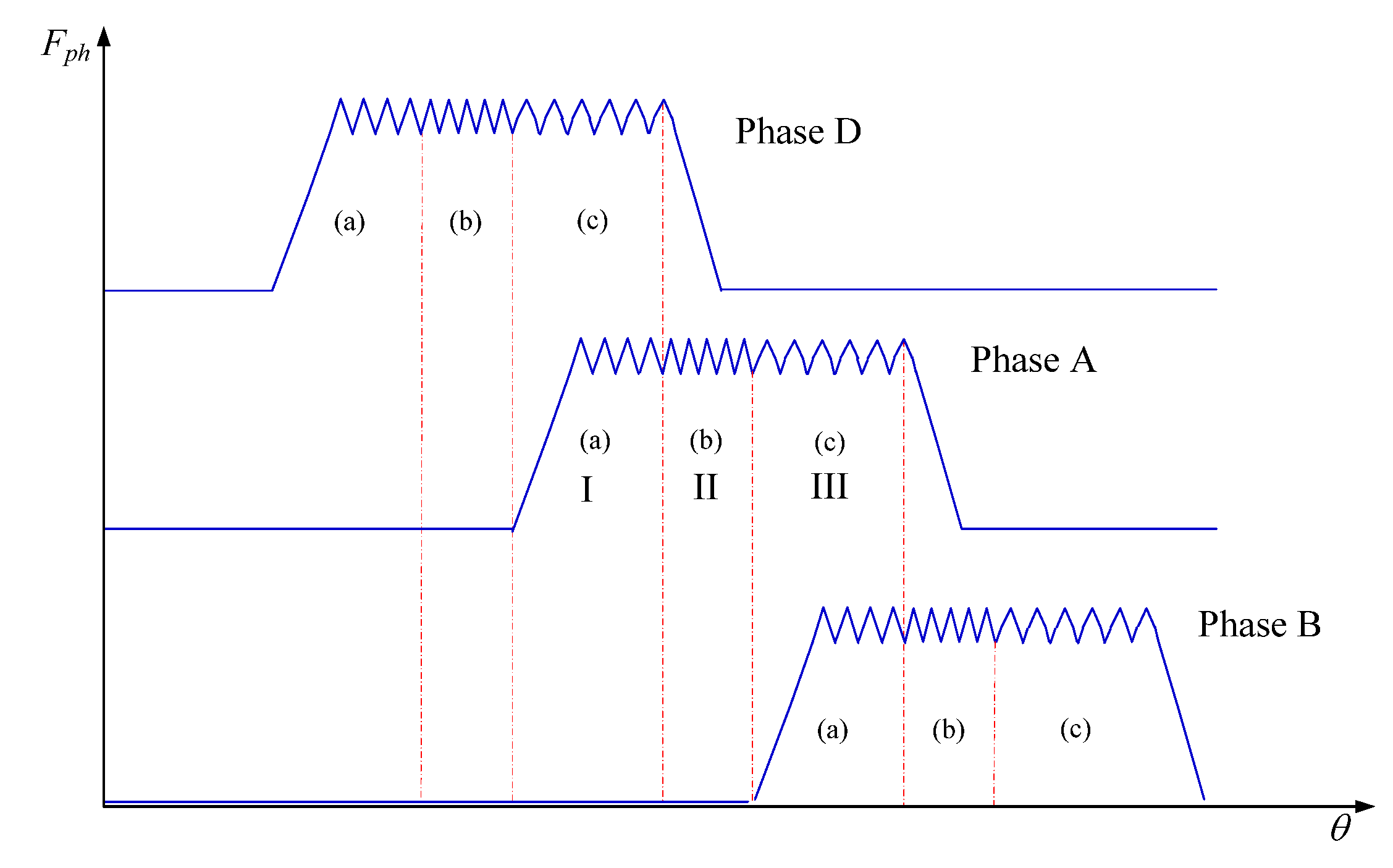
2.1. Conventional Control Strategy—ATC
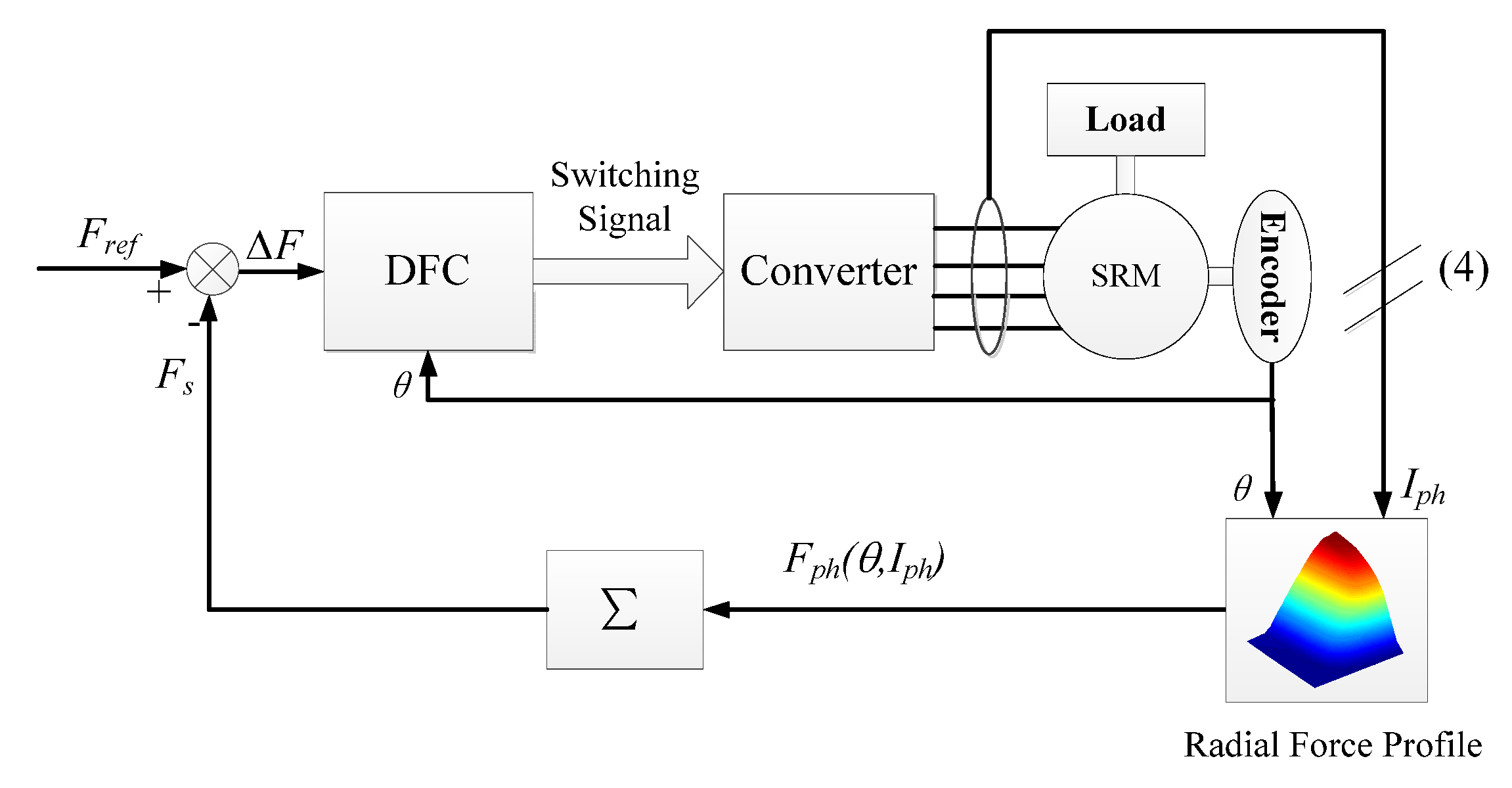
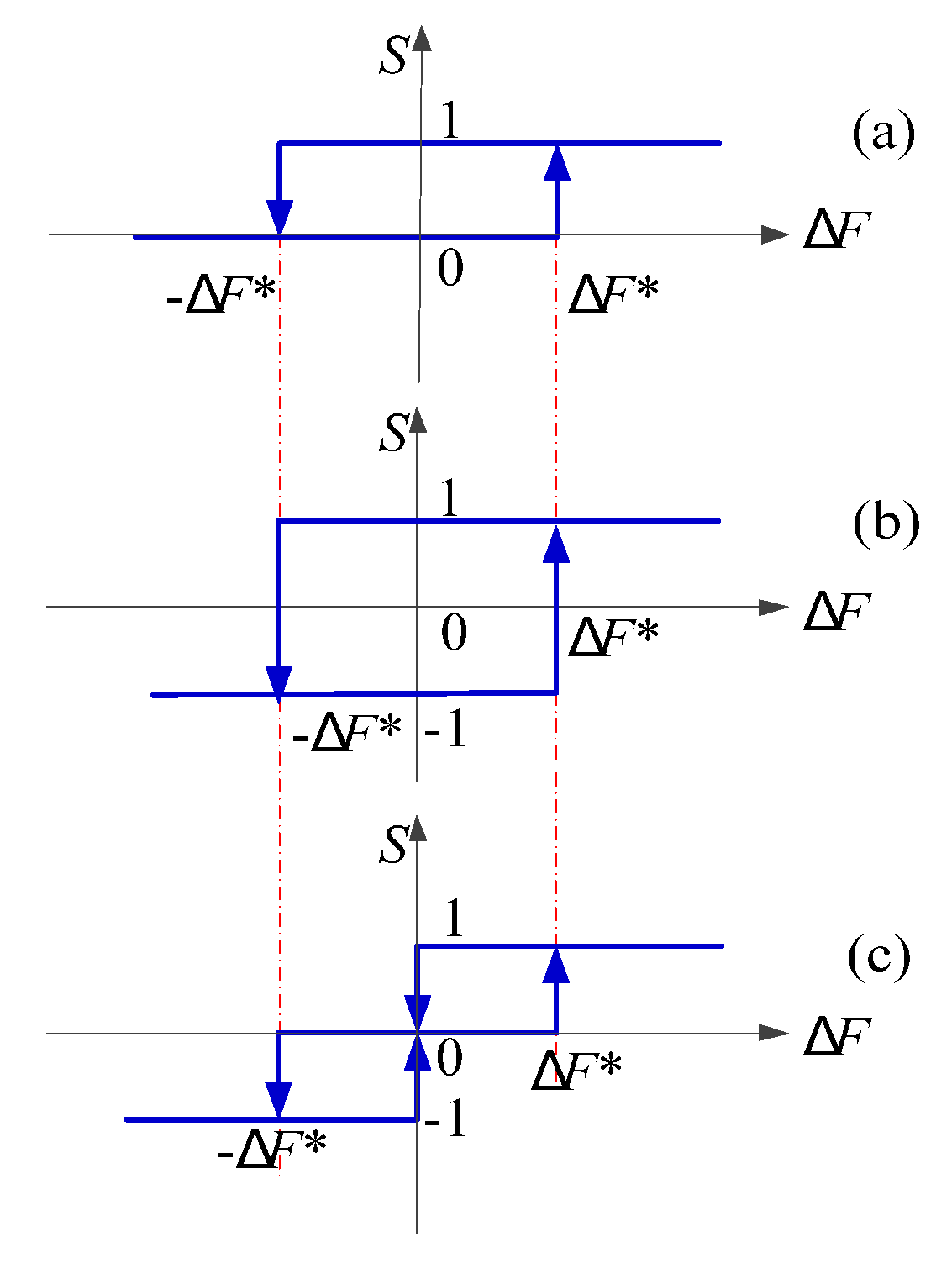
2.2. Vibraiton Reduction Block—DFC
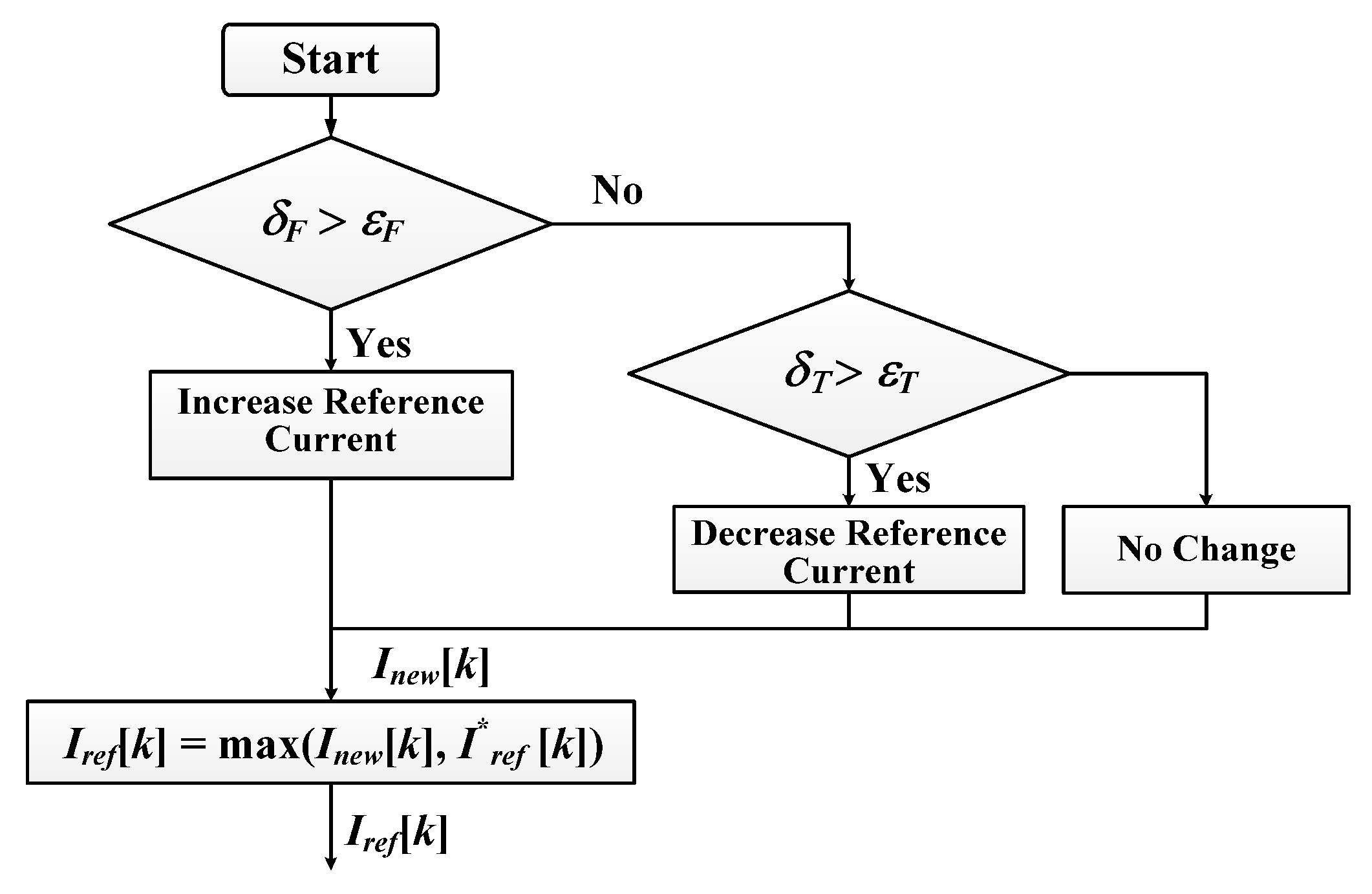
2.3. Blocks Ajustment—RCA
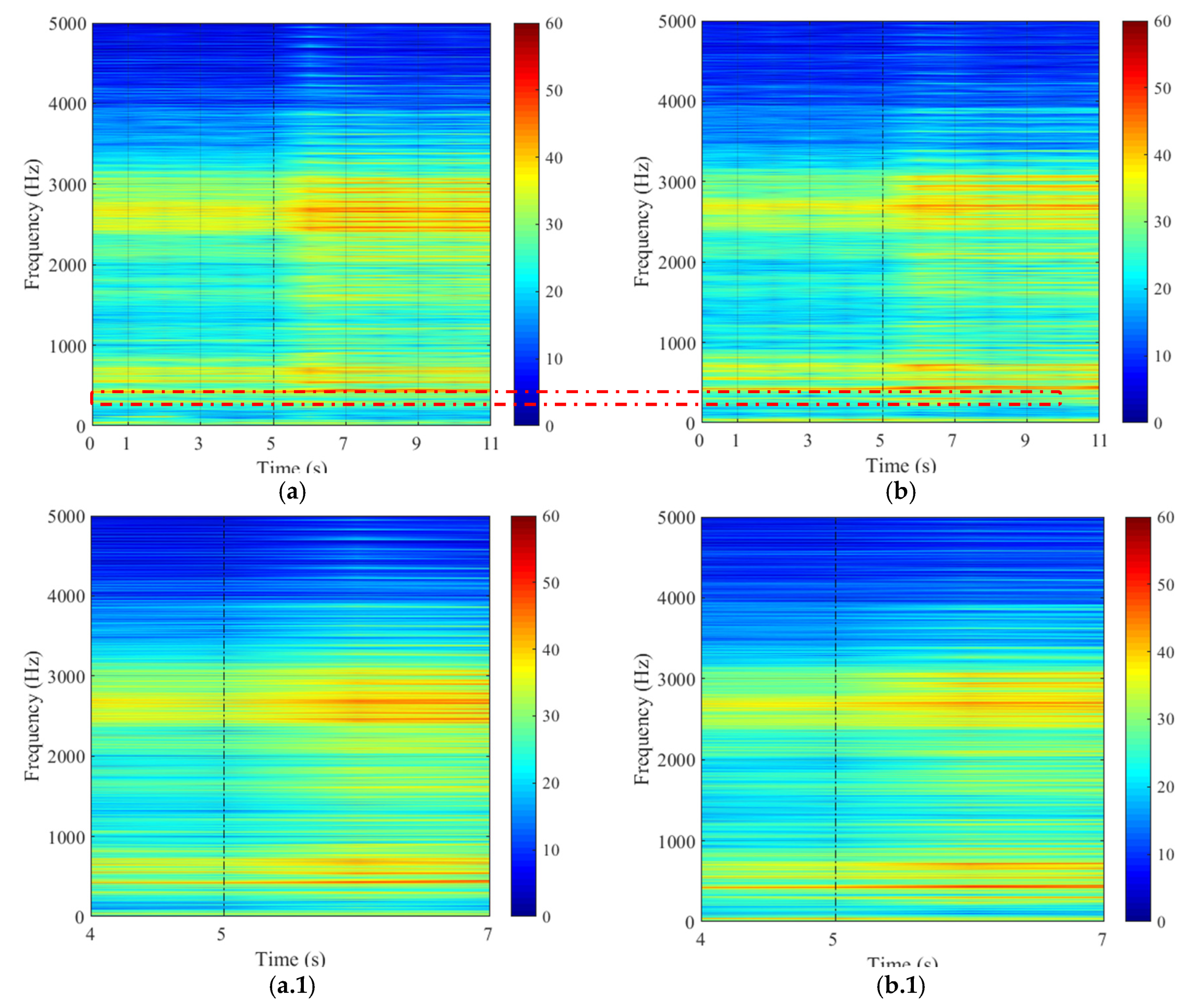
3. Experimental Results
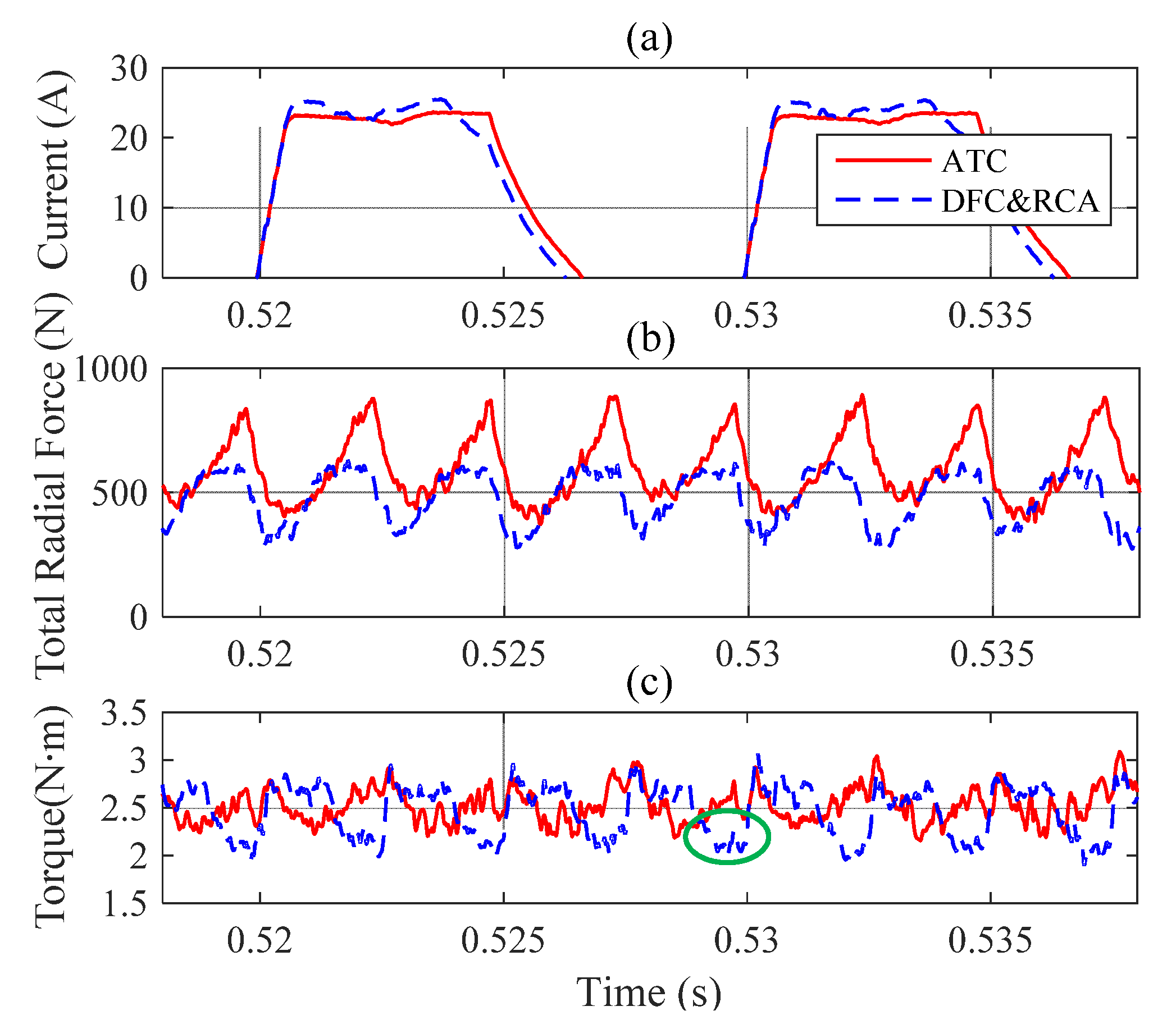
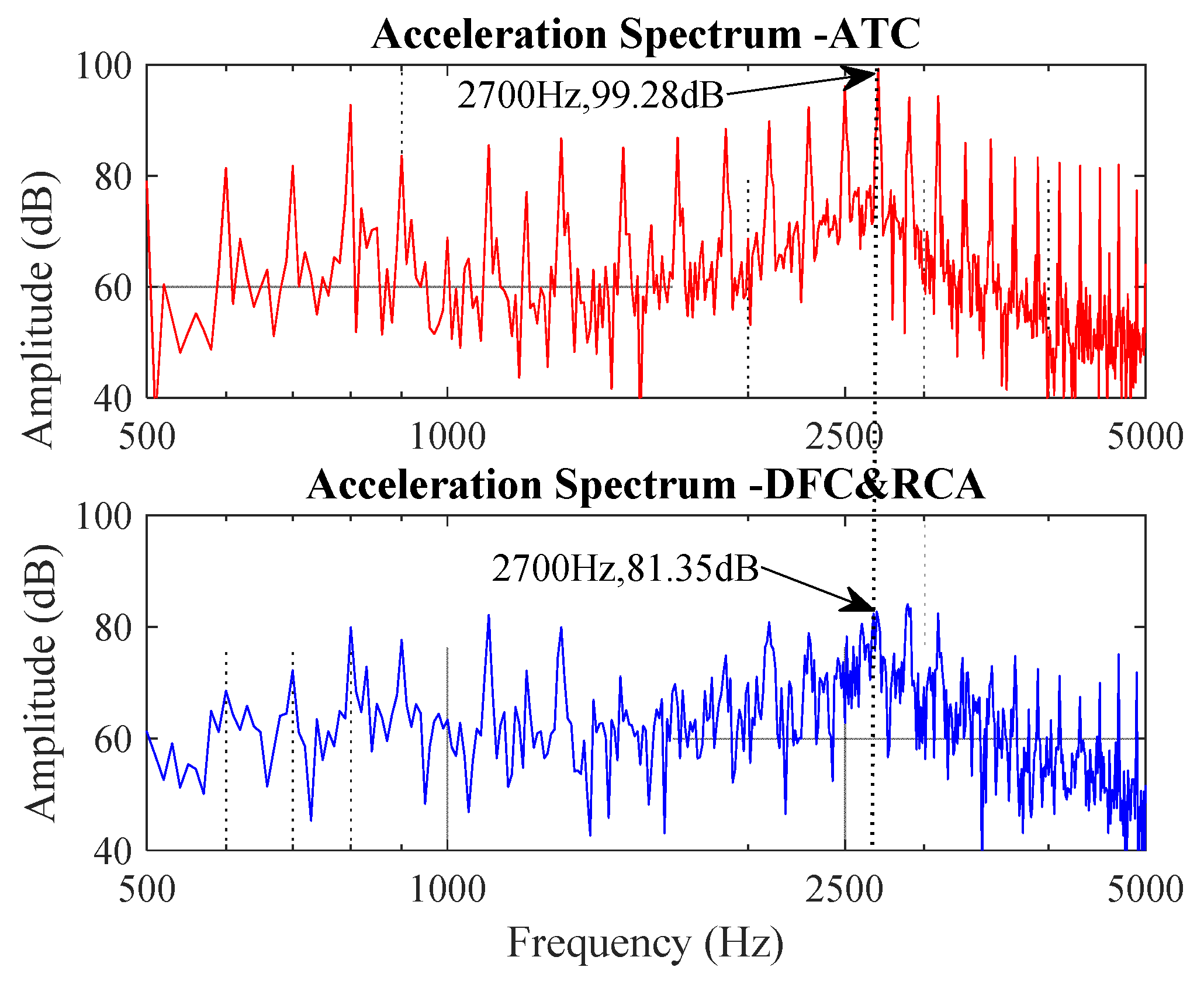
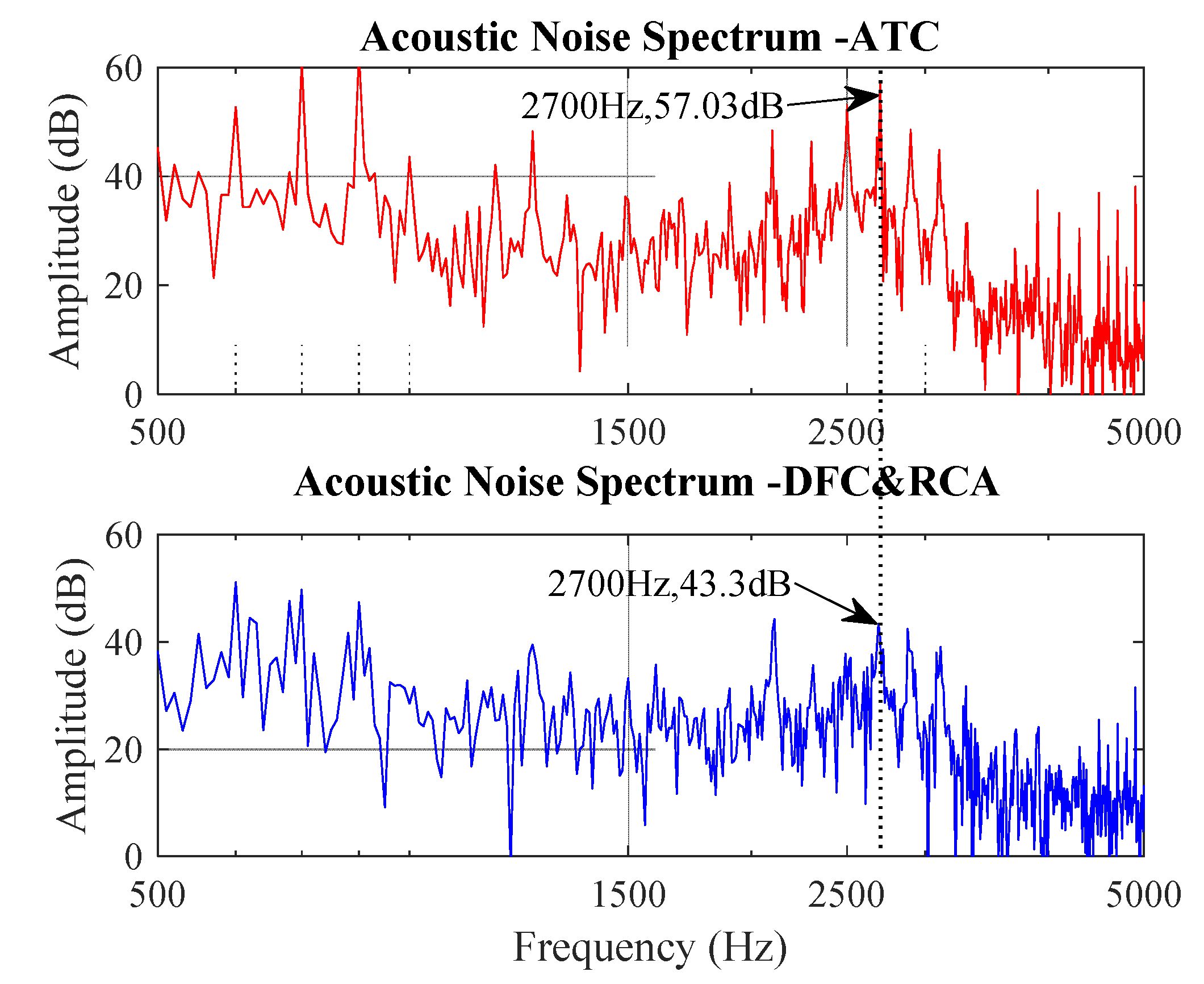
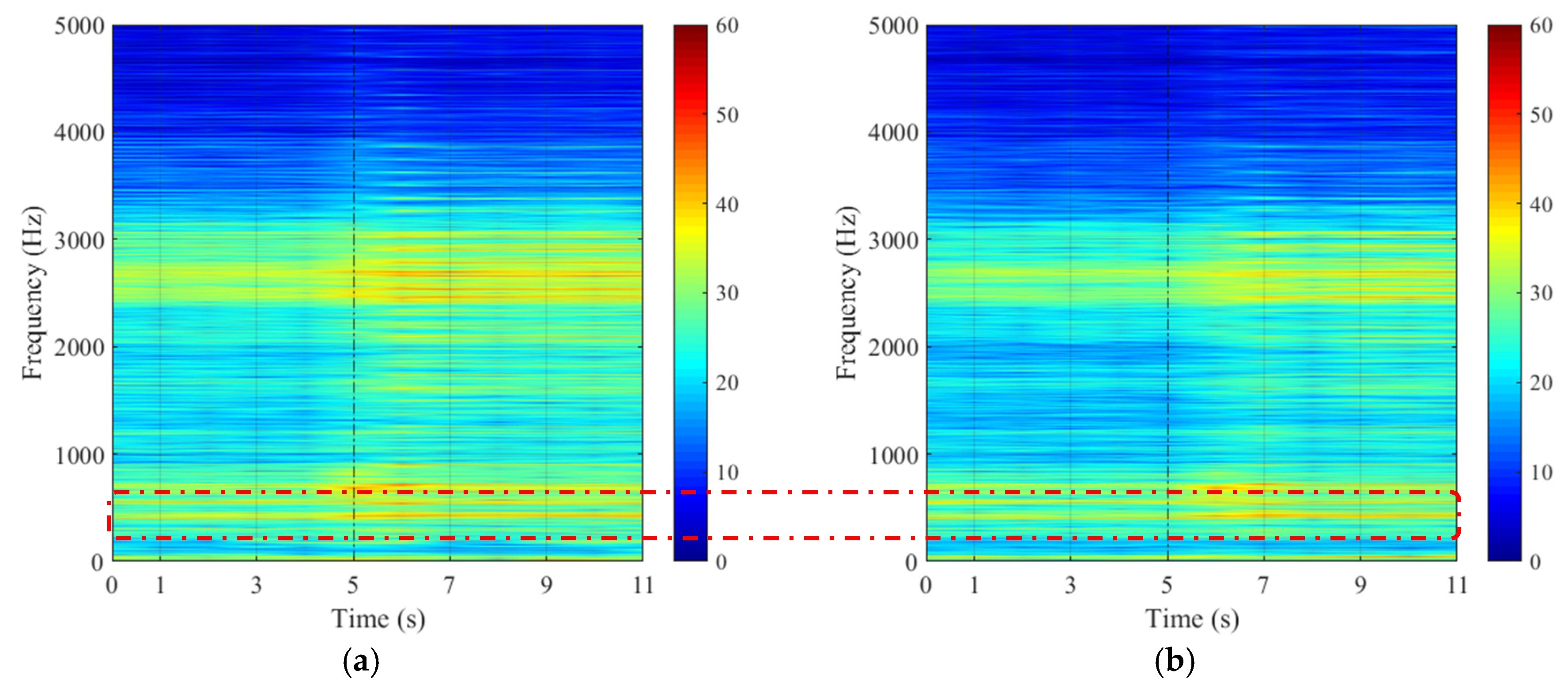
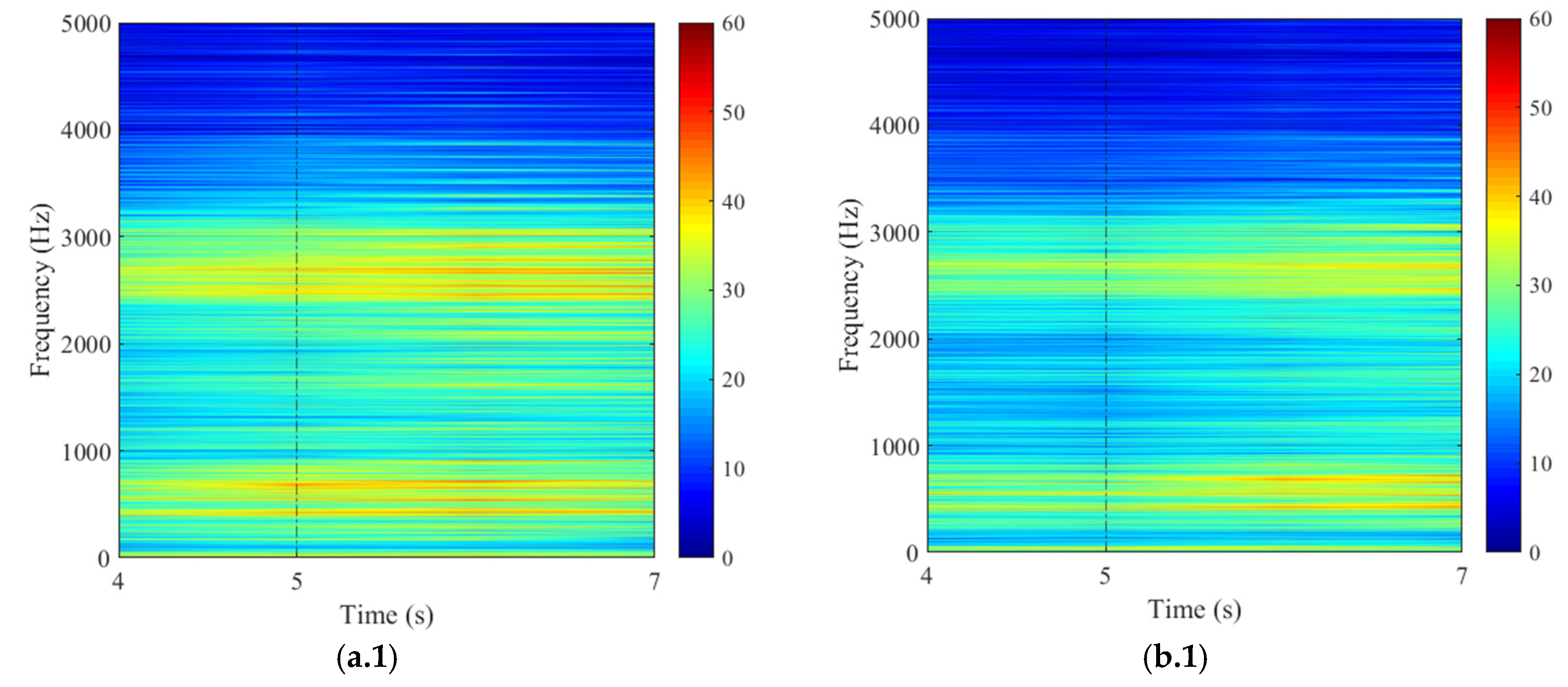
3.1. Steady Condition
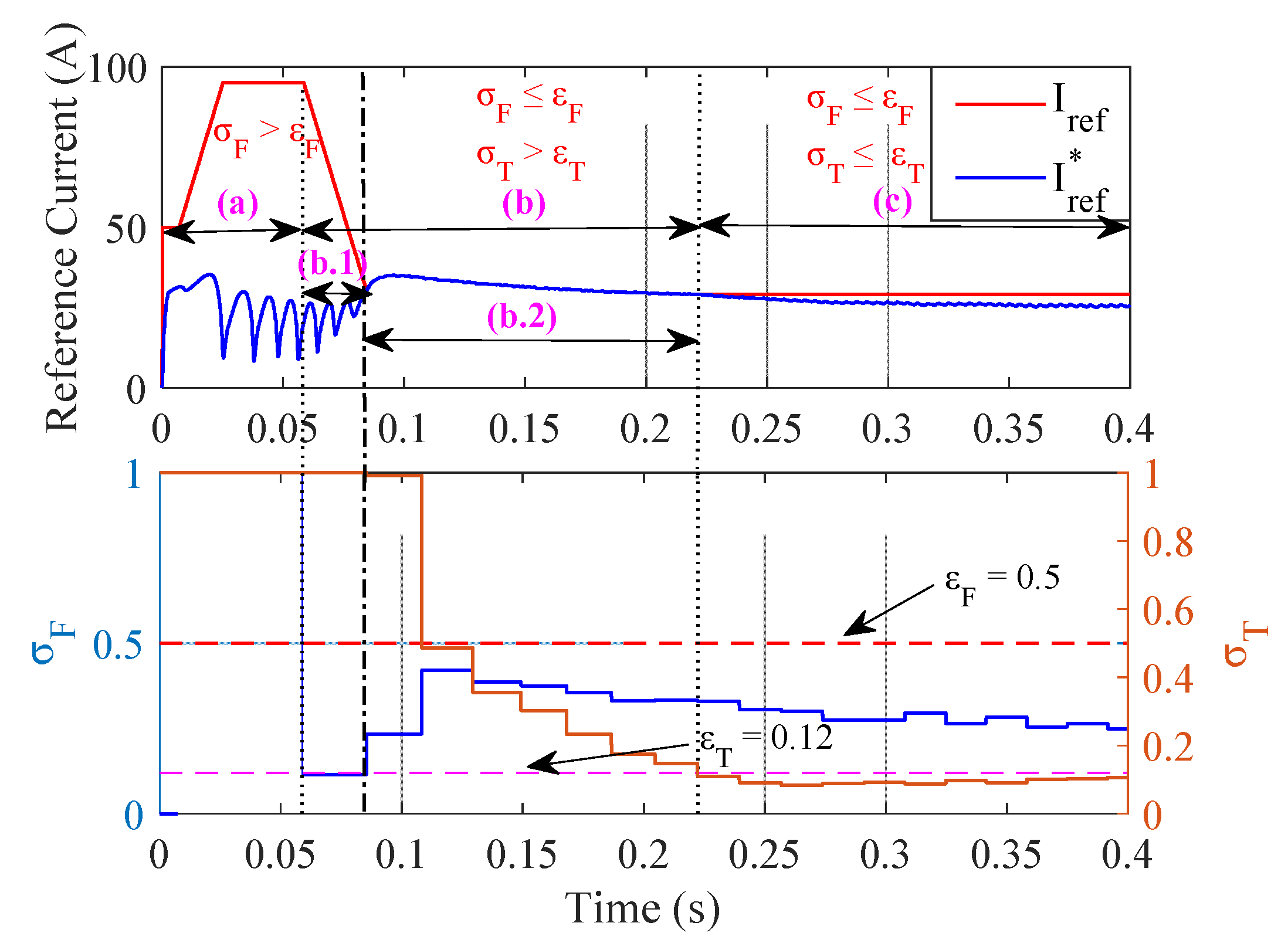
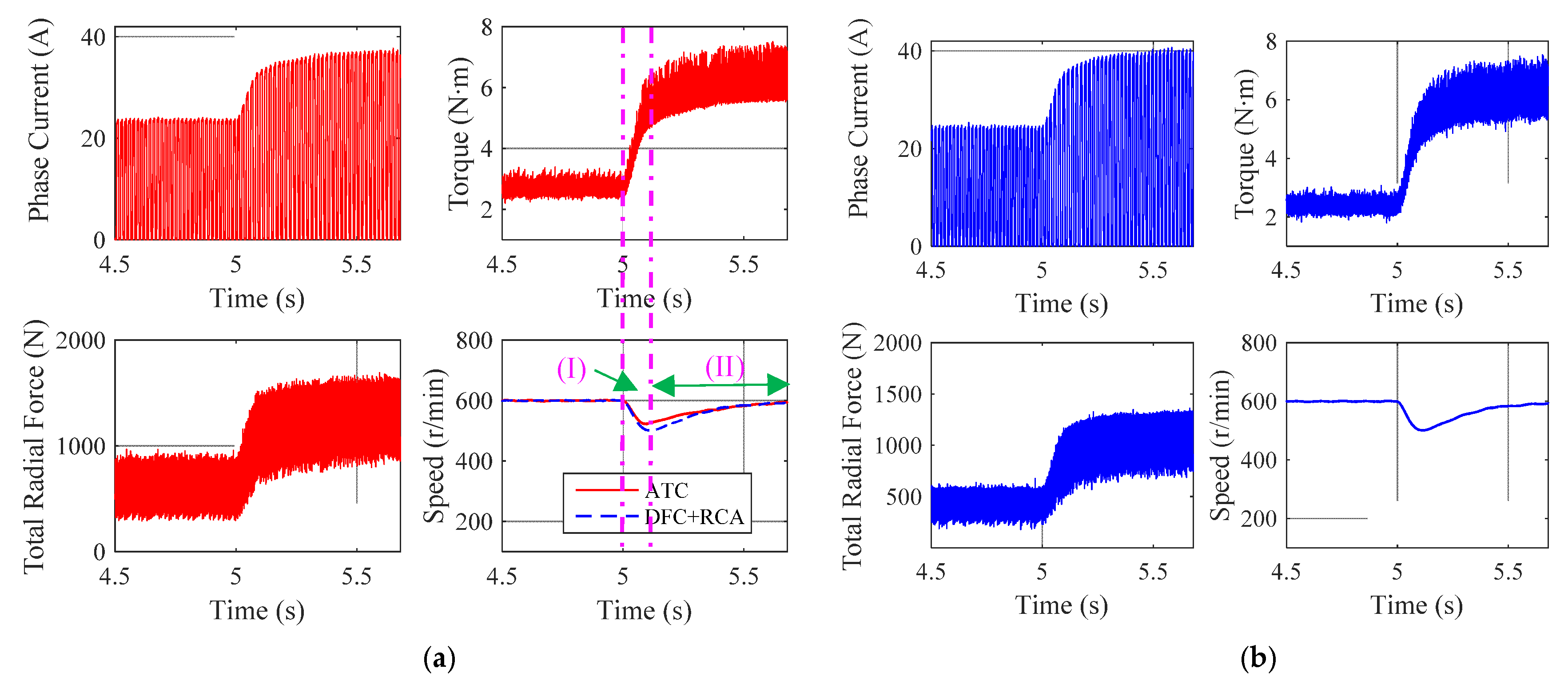
3.2. Transient Condition
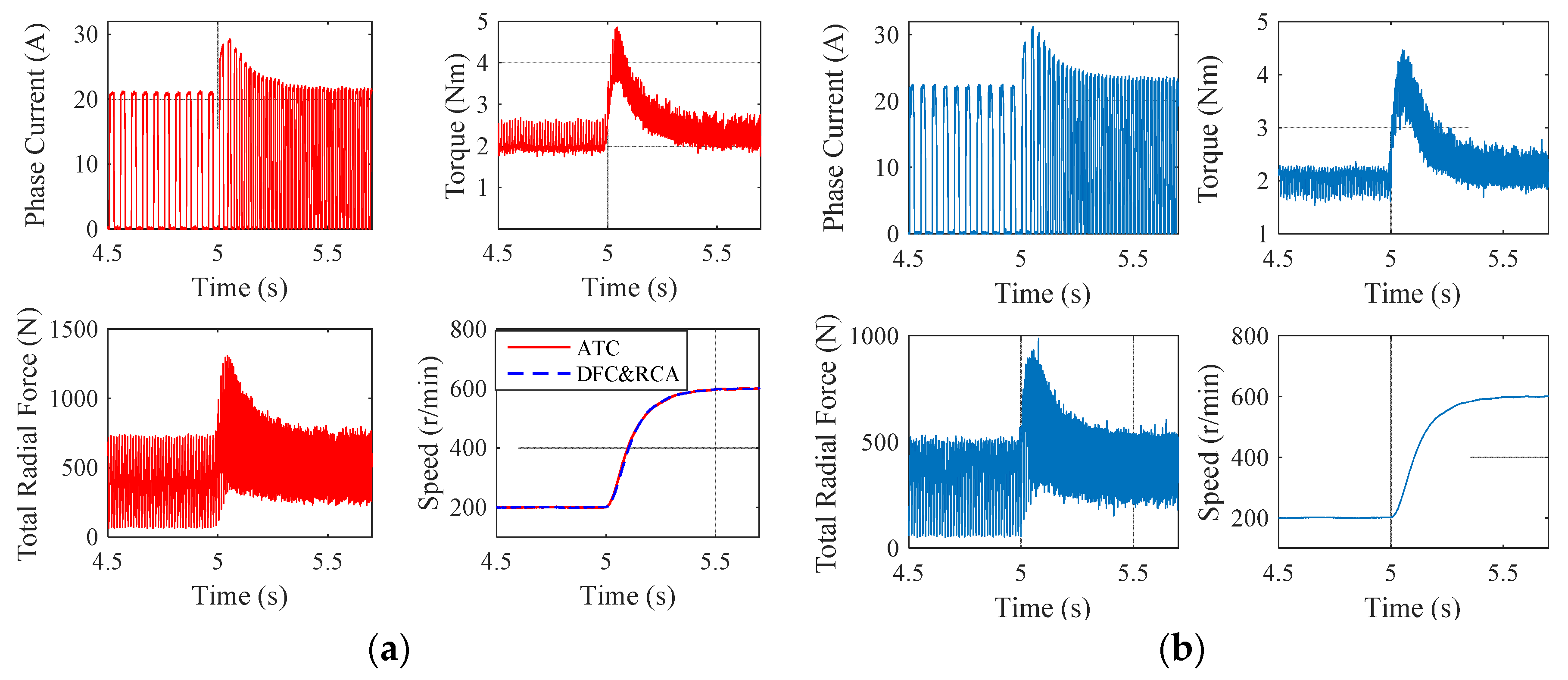
3.2.1. Reference Speed Variation
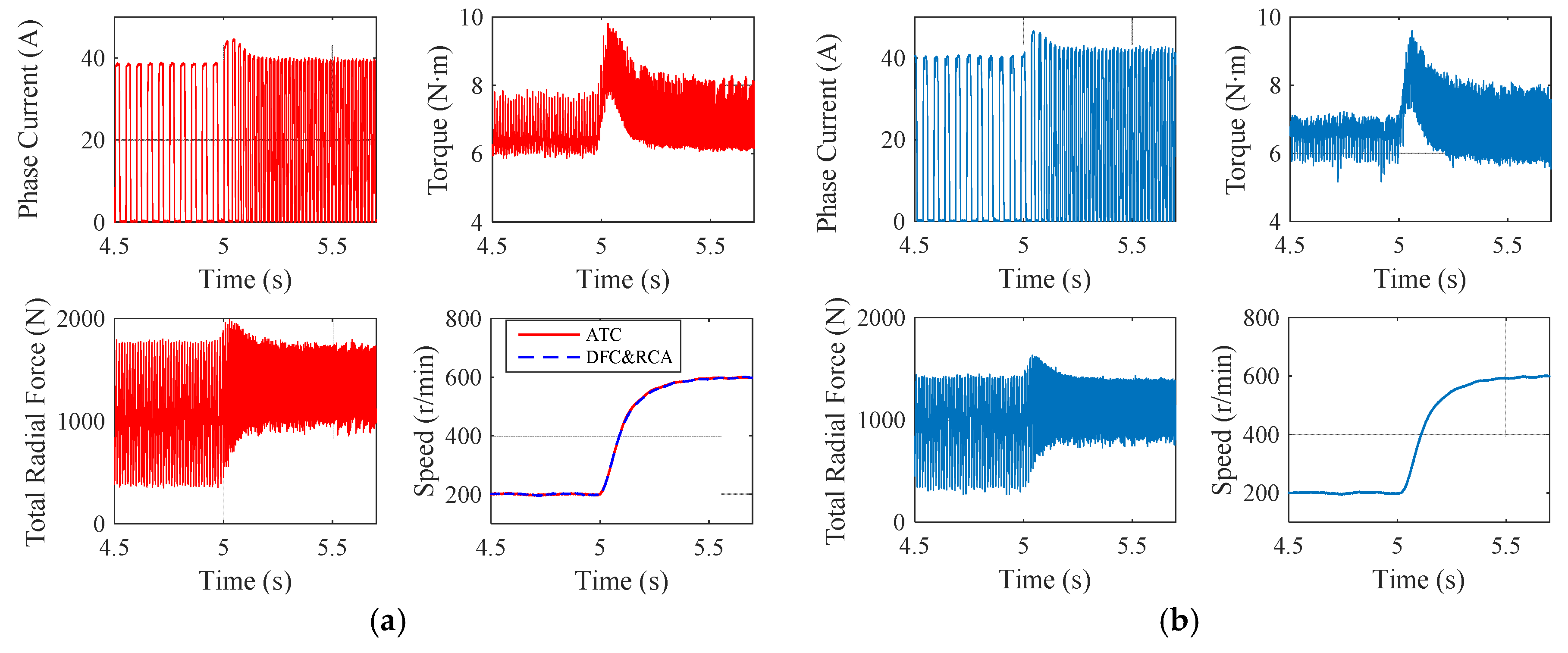
3.2.2. Torque Load Variation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiba, A.; Kiyota, K.; Hoshi, N.; Takemoto, M.; Ogasawara, S. Development of a Rare-Earth-Free SR Motor with High Torque Density for Hybrid Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Husain, I. Radial force calculation and acoustic noise prediction in switched reluctance machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, M.N.I.; Husain, M.S.; Sebastian, T. Evaluation of acoustic noise and mode frequencies with design variations of switched reluctance machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Wu, J.; Shen, M.; Yang, S.; Hu, Y.; Cao, W. Investigation of skewing effects on the vibration reduction of three-phase switched reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edamura, K.; Miki, I. Design of stator and rotor for noise reduction of SRM. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 1871–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Kakishima, T.; Kiyota, K.; Nakano, S.; Chiba, A. Pole selection and vibration reduction of Switched Reluctance Motor for hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing, China, 31 August–3 September 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Besbes, M.; Picod, C.; Camus, F.; Gabis, M. Influence of stator geometry upon vibratory behavior and electromagnetic performances of switched reluctance motors. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 1998, 145, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, S.M.; Bilgin, B.; Fairall, E.; Emadi, A. Acoustic noise analysis of a high-speed high-power switched reluctance machine: Frame effects. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasa, Y.; Tekgun, D.; Sozer, Y.; Kutz, J.; Tylenda, J. Effect of distributed airgap in the stator for acoustic noise reduction in switched reluctance motors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Tampa, FL, USA, 26–30 March 2017; pp. 633–639. [Google Scholar]
- Mademlis, C.; Kioskeridis, I. Performance optimization in switched reluctance motor drives with online commutation angle control. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2003, 18, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhobza, T.; Gabsi, M.; Grioni, B. Random variation of control angles, reduction of SRM vibrations. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (Cat. No.01EX485), Cambridge, MA, USA, 17–20 June 2001; pp. 640–643. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Pollock, C. Time domain analysis of vibration and acoustic noise in the switched reluctance drive. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Electrical Machines and Drives (Conf. Publ. No. 376), Oxford, UK, 8–10 September1993; pp. 558–563. [Google Scholar]
- Mininger, X.; Lefeuvre, E.; Gabsi, M.; Richard, C.; Guyomar, D. Semiactive and active piezoelectric vibration controls for switched reluctance machine. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, X.; Mininger, X.; Gabsi, M. An active piezoelectric absorber for vibration control of electrical machine. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Cape Town, South Africa, 25–28 February 2013; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, A.; Al-Dajani, A.; Bösing, M.; De Doncker, R.W. Direct instantaneous force control: A method to eliminate mode-0-borne noise in switched reluctance machines. In Proceedings of the International Electric Machines & Drives Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–15 May 2013; pp. 1009–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Annegret, K.H.; Hofmann, A.; De Doncker, R.W. Direct instantaneous torque and force control: A control approach for switched reluctance machines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 935–943. [Google Scholar]
- Takiguchi, M.; Sugimoto, H.; Kurihara, N.; Chiba, A. Acoustic noise and vibration reduction of SRM by elimination of third harmonic component in sum of radial forces. IEEE Trans. Energy. Convers. 2015, 30, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayless, J.; Kurihara, N.; Sugimoto, H.; Chiba, A. Acoustic noise reduction of switched reluctance motor with reduced RMS current and enhanced efficiency. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furqani, J.; Kawa, M.; Kiyota, K.; Chiba, A. Current Waveform for Noise Reduction of a Switched Reluctance Motor Under Magnetically Saturated Condition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, T.; Jiji, K.S. Comparison of Proportional-Integral (PI) and Integral-Proportional (IP) controllers for speed control in vector controlled induction motor drive. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Power, Control and Embedded Systems, Allahabad, India, 17–19 December 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Inderka, R.B.; De Doncker, R.W. DITC-direct instantaneous torque control of switched reluctance drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
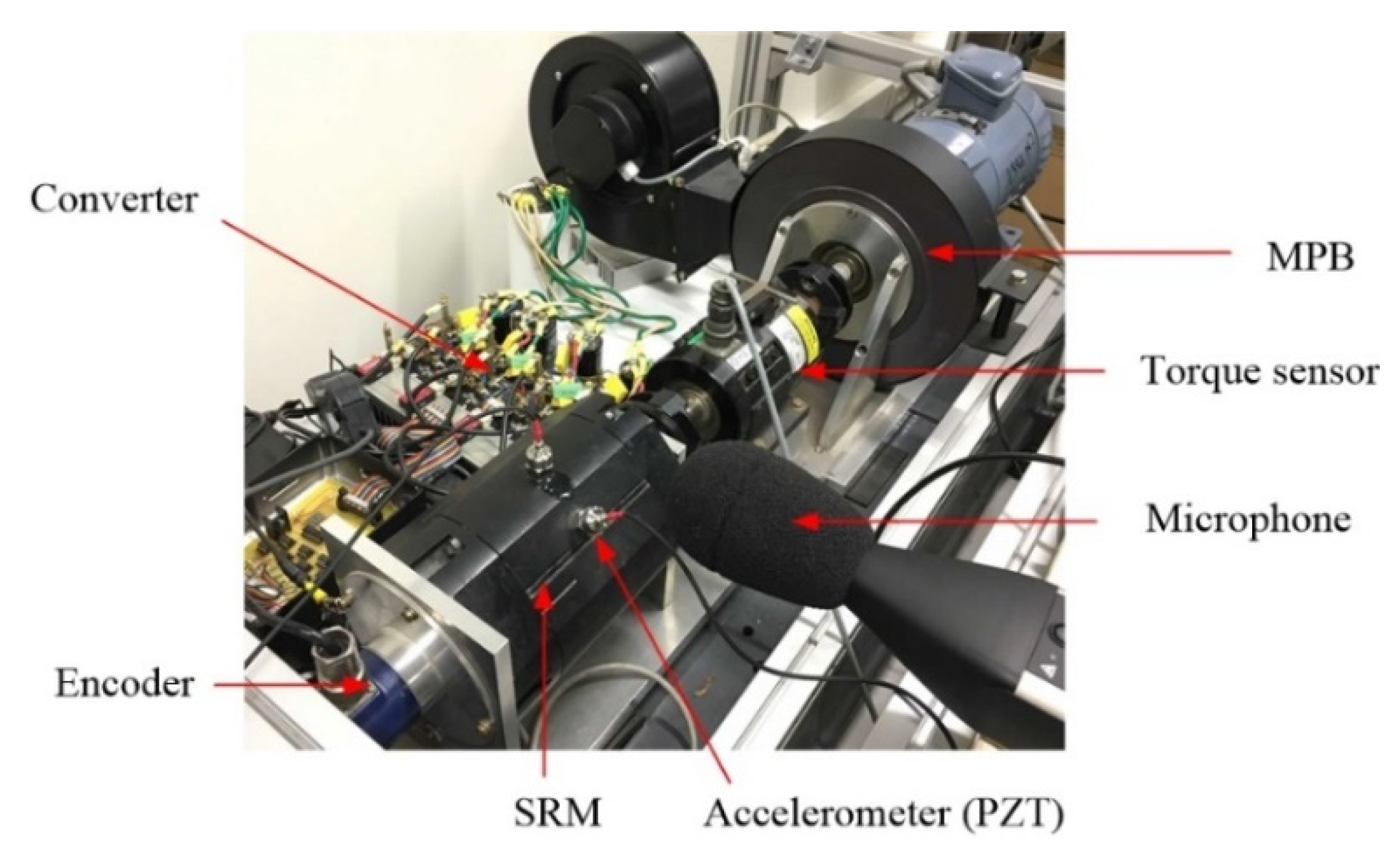

| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of phases | 4 |
| Nominal power | 1.2 kW |
| Nominal speed | 3000 r/min |
| Nominal voltage | 24 V |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Bahri, I.; Mininger, X.; Vlad, C.; Xie, H.; Berthelot, E. A New Control Method for Vibration and Noise Suppression in Switched Reluctance Machines. Energies 2019, 12, 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12081554
Zhang M, Bahri I, Mininger X, Vlad C, Xie H, Berthelot E. A New Control Method for Vibration and Noise Suppression in Switched Reluctance Machines. Energies. 2019; 12(8):1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12081554
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Man, Imen Bahri, Xavier Mininger, Cristina Vlad, Hongqin Xie, and Eric Berthelot. 2019. "A New Control Method for Vibration and Noise Suppression in Switched Reluctance Machines" Energies 12, no. 8: 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12081554
APA StyleZhang, M., Bahri, I., Mininger, X., Vlad, C., Xie, H., & Berthelot, E. (2019). A New Control Method for Vibration and Noise Suppression in Switched Reluctance Machines. Energies, 12(8), 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12081554




