Multi-Objective Optimal Cloud Model Design of Vehicle-to-Grid Connected Systems Based on the Multiple Performance Characteristic Index Method †
Abstract
1. Introduction
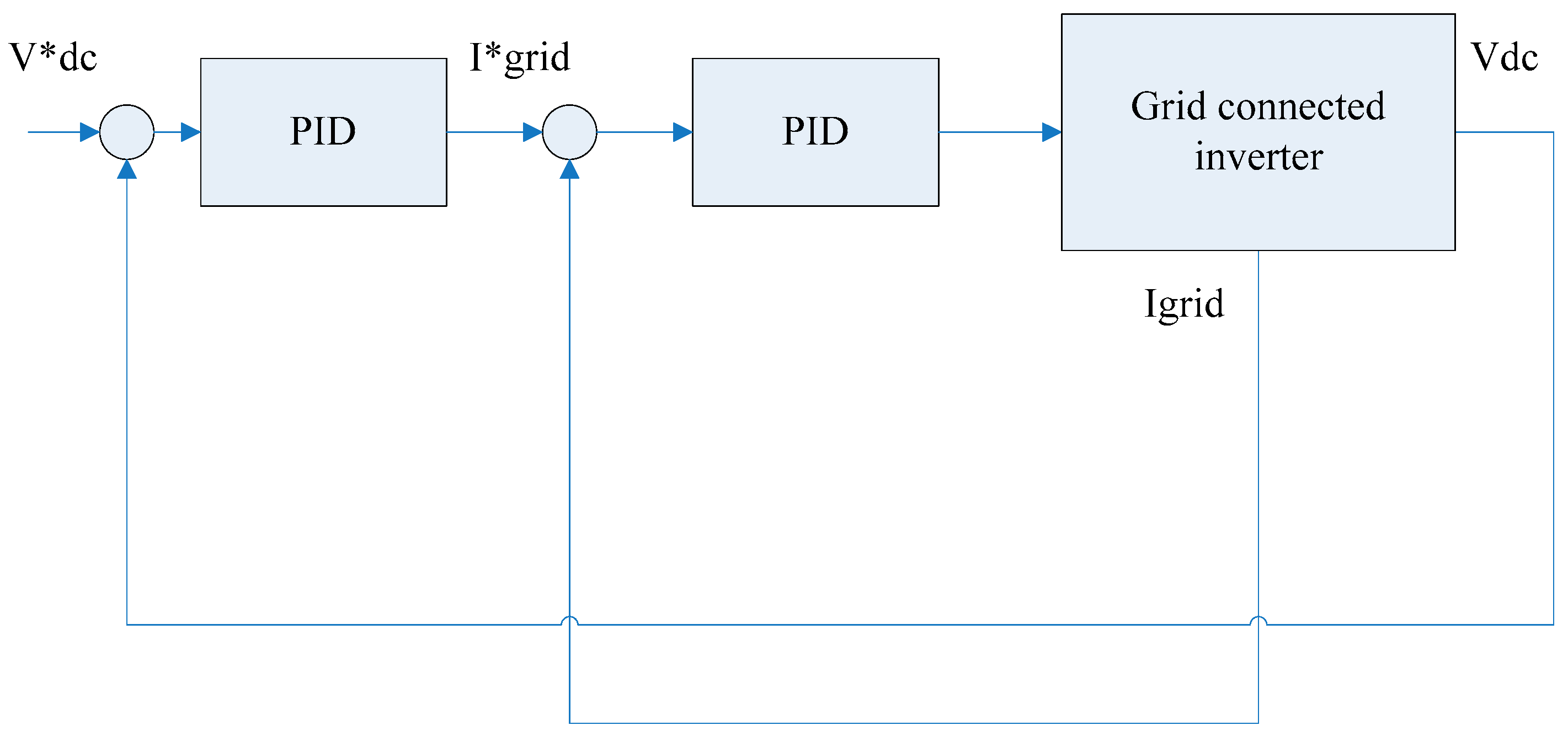
2. Principle of Vehicle-to-Grid Connected System Characteristics
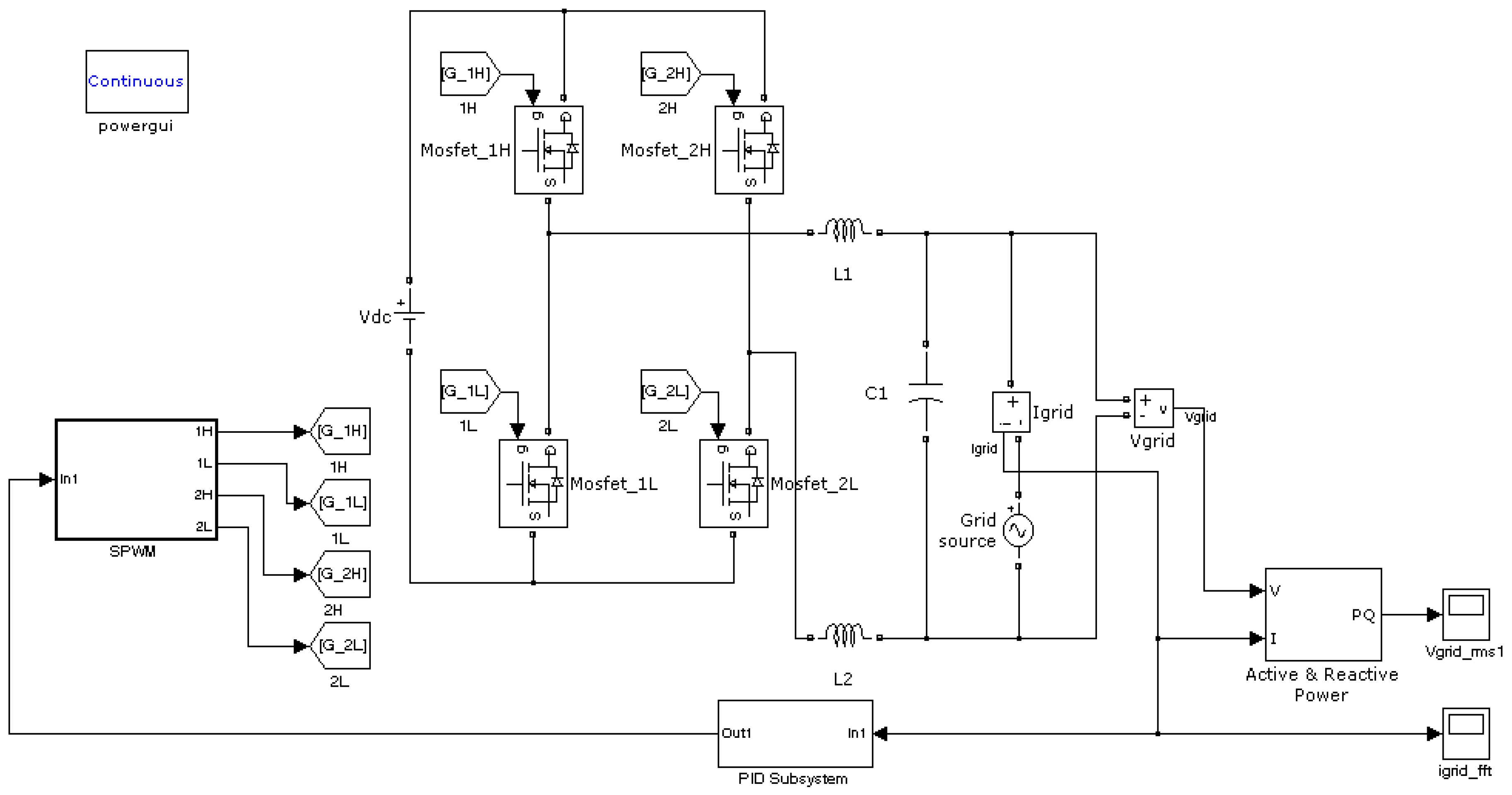
3. Initial Design of a Single-Phase Full-Bridge Vehicle-to-Grid Connected System
4. Cloud Model Formulation for Optimal Controller Design
4.1. Control Factors and Noise Factors for Selection of Cloud Data
4.2. Cloud Model Design by Using Combined Array Method
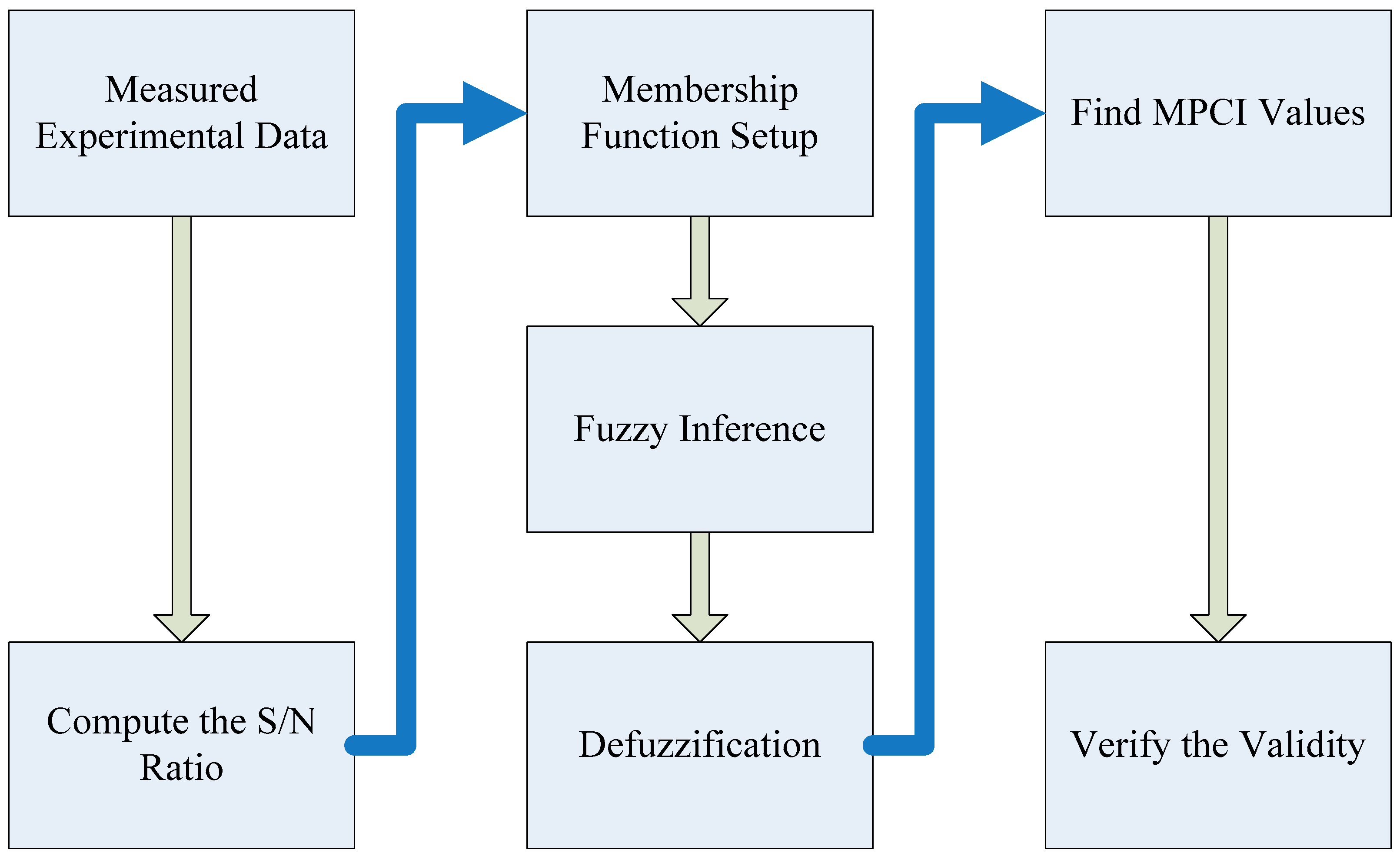
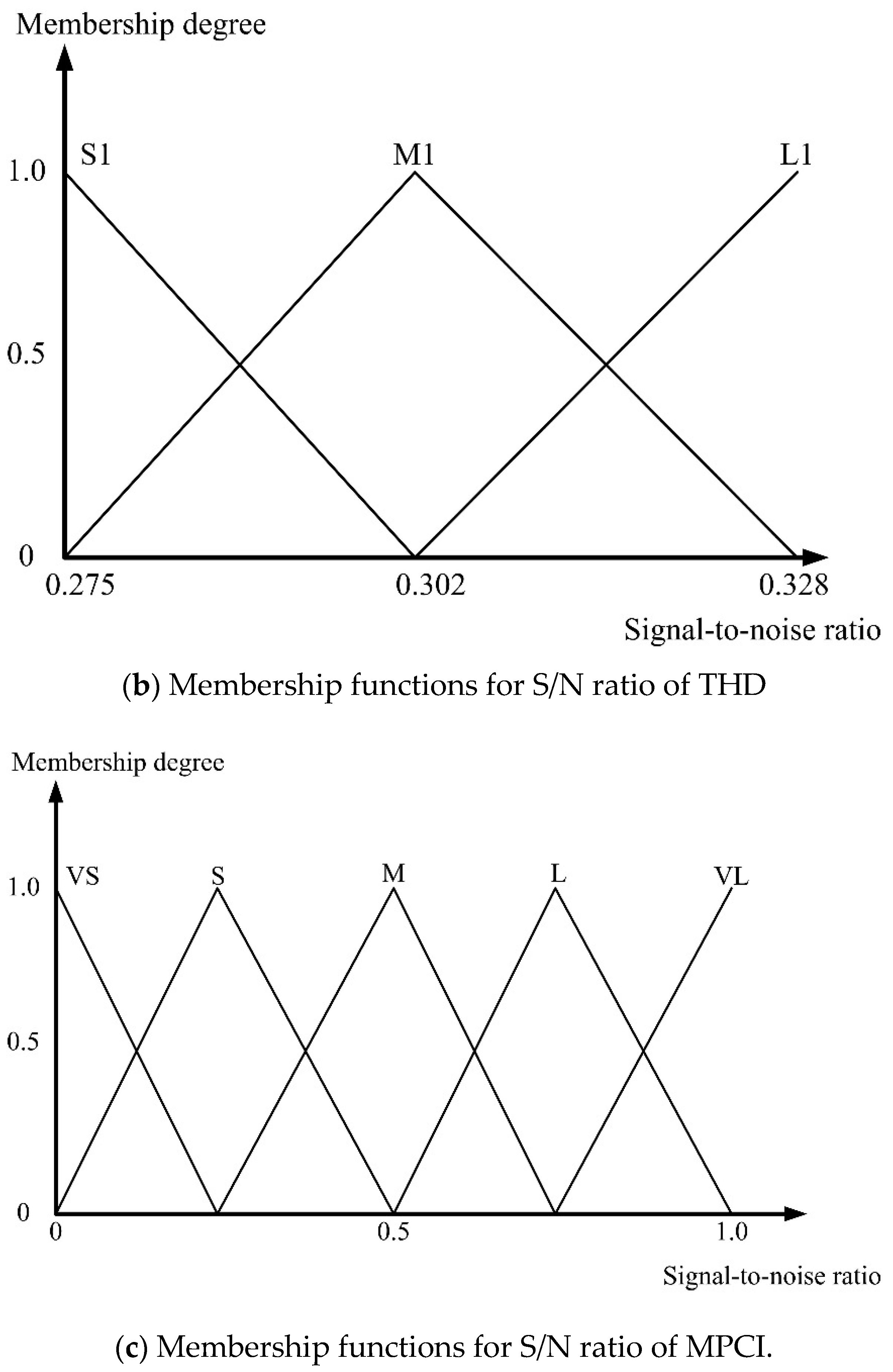
4.3. The Fuzzy Inference with MPCI in Cloud Model
4.4. Regressive Analysis and Response Surface Derivation
5. Optimization by Orthogonal Particle Swarm Method in Cloud Model
5.1. OPSO Modeling in Cloud Model
5.2. Orthogonal Array Algorithm in Cloud Model
5.3. Optimization Results of Cloud Model
5.4. Testing Results for the Cloud Model
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Araujo, S.V.; Zacharias, P.; Mallwitz, R. Highly Efficient Single-Phase Transformerless Inverters for Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 3118–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.M.; Lopes, B.M.; Filho, B.J.C.; Campana, R.P.; Bosventura, W.C. Performance evaluation of PLL algorithms for single-phase grid-connected systems. In Proceedings of the 39th IAS Annual Meeting, Conference Record of the 2004 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–7 October 2004; Volume 4, pp. 2259–2263. [Google Scholar]
- Furuhashi, T.; Okuma, S.; Uchikawa, Y. A Study on the Theory of Instantaneous Reactive Power. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1990, 37, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafaoui, A.; Wu, B.; Kouro, S. Improved active frequency drift anti-islanding method wit lower total harmonic distortion. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society Conference, Glendale, AZ, USA, 7–10 November 2010; pp. 3216–3221. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, S.; Neba, Y. Single-Phase Composite PWM Voltage Source Converter. In Proceedings of the IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 2–6 October 1994; Volume 2, pp. 761–768. [Google Scholar]
- Gaing, Z.L. A Particle Swarm Optimization Approach for Optimum Design of PID Controller in AVR System. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2004, 19, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, C.C.; Astrom, K.J.; Ho, W.K. Refinements of the Ziegler-Nichols tuning formula. IEE Proc. D 1991, 138, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Z.; Rashid, K. Comparison of optimization by response surface methodology withneurofuzzy methods. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2000, 36, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H.J. Fuzzy Set Theory and Its Applications; Kluwer Academic Publishers: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gaing, Z.L.; Chiang, J.A. Robust design of in-wheel PM motor by fuzzy-based Taguchi method. In Proceedings of the Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Providence, RI, USA, 25–29 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Eberhart, R. A modified Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–9 May 1998; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhart, R.C.; Shi, Y. Comparing inertia weights and constriction factors in particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the Congress on Evolutionary Computation, La Jolla, CA, USA, 16–19 July 2000; pp. 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, S.Y. Orthogonal Particle Swarm Optimization and Its Application to Task Assignment Problems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2008, 38, 288–298. [Google Scholar]



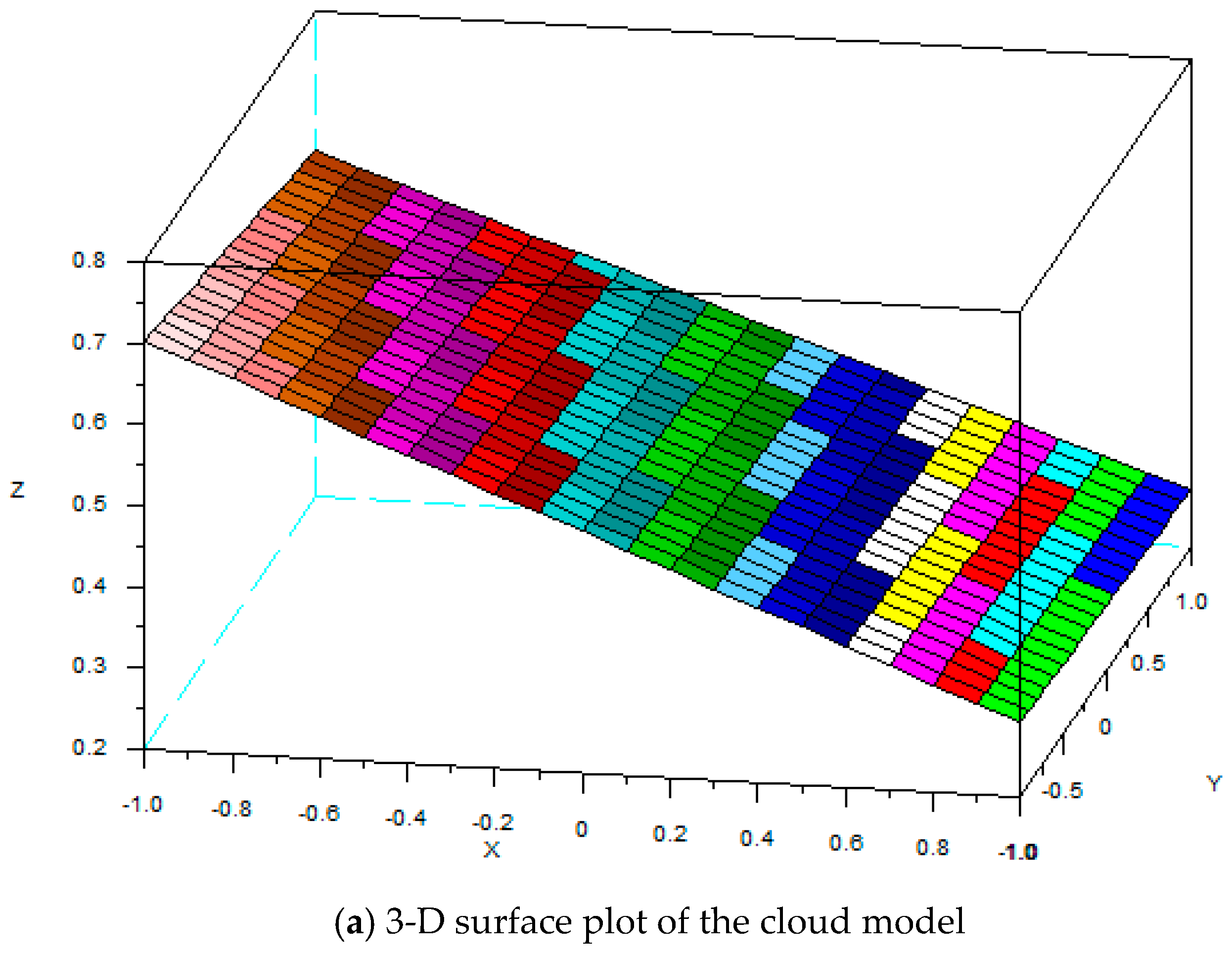
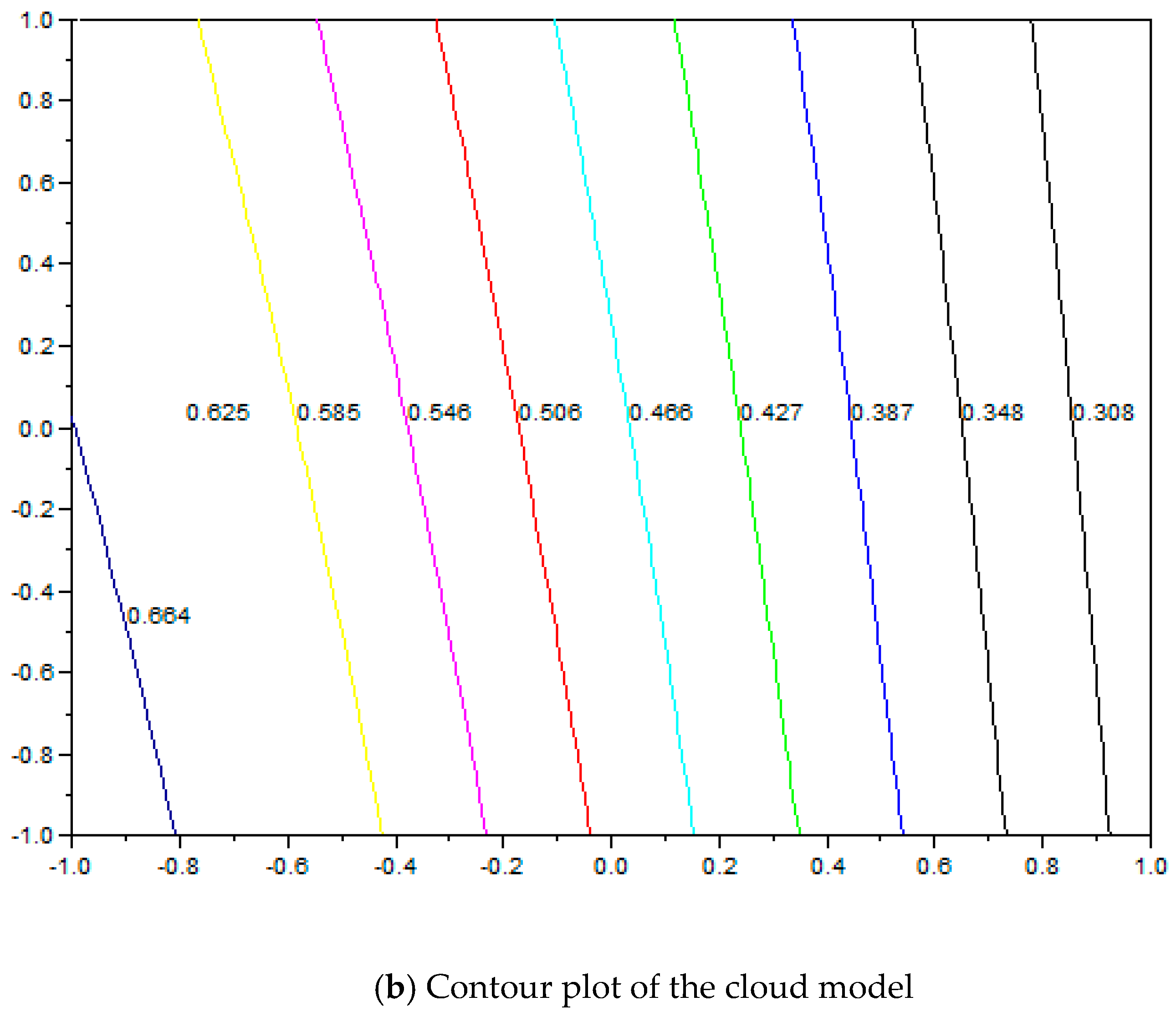

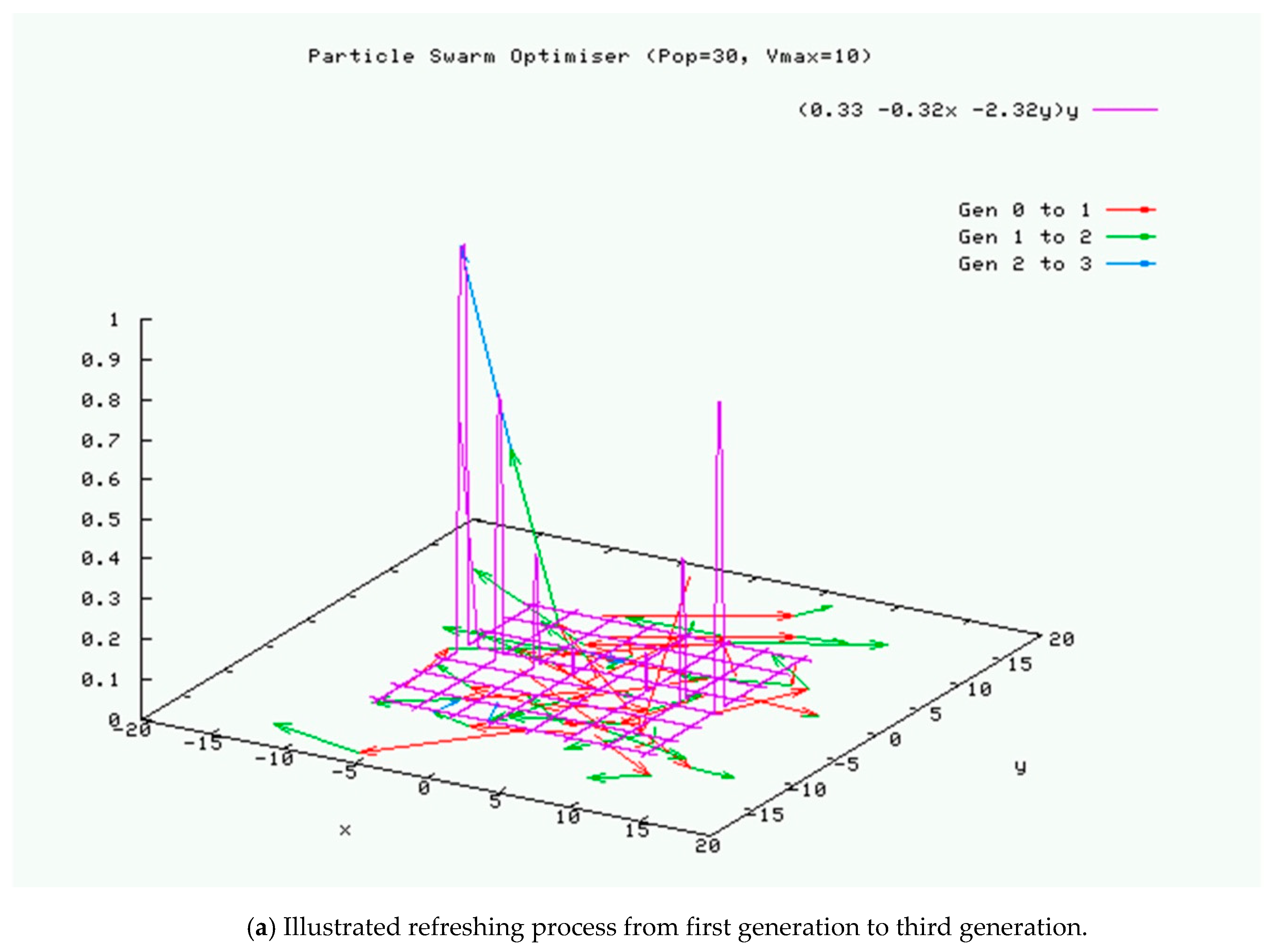

| Level | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | ||||
| Control factor A, Kp | 12,767 | 32,767 | 52,767 | |
| Control factor B, Ki | 367 | 567 | 767 | |
| Control factor C, Kd | 1 × 10−5 | 1 × 10−6 | 1 × 10−7 | |
| Noise factor 1, ESR (Ω) | 2 × 10−10 | 4 × 10−10 | 6 × 10−10 | |
| Noise factor 2, rL (Ω) | 1 × 10−6 | 3 × 10−6 | 5 × 10−6 | |
| Run | Kp | Ki | Kd | ESR (Ω) | rL (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 |
| 9 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 |
| 10 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 |
| 11 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 |
| 12 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 |
| 13 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 14 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 |
| 15 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 |
| 16 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Run | Kp | Ki | Kd | ESR (Ω) | rL (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Output MPCI, C | Input A | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | M | L | ||
| Input B | S | VS | S | M |
| M | S | M | L | |
| L | M | L | VL | |
| Reactive Power | Total Harmonic Distortion | MPCI |
|---|---|---|
| 0.14514 | 0.31646 | 0.69786 |
| 0.13587 | 0.27624 | 0.26379 |
| 0.12019 | 0.28329 | 0.21765 |
| 0.16835 | 0.29762 | 0.69497 |
| 0.1368 | 0.31746 | 0.59794 |
| 0.13587 | 0.27624 | 0.26379 |
| 0.14347 | 0.28329 | 0.41040 |
| 0.13947 | 0.29762 | 0.46805 |
| 0.15625 | 0.3268 | 0.83963 |
| 0.12285 | 0.30675 | 0.44023 |
| 0.1269 | 0.28818 | 0.27368 |
| 0.14409 | 0.30211 | 0.65908 |
| 0.12048 | 0.32787 | 0.56093 |
| 0.13123 | 0.30675 | 0.48839 |
| 0.11669 | 0.27473 | 0.25740 |
| 0.14599 | 0.30211 | 0.59001 |
| Reactive Power | Total Harmonic Distortion | MPCI |
|---|---|---|
| 0.13831 | 0.29762 | 0.44420 |
| 0.13699 | 0.29851 | 0.44330 |
| 0.13736 | 0.29674 | 0.42078 |
| 0.13717 | 0.29851 | 0.44466 |
| Item | Degree of Freedom | Sum of Squares, SS | Mean Square, MS | F-Statistics | Significance, p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regressive treatments | 14 | 0.4981 | 0.0356 | 3.1052 | 0.1086 |
| Error | 5 | 0.0573 | 0.0115 | - | - |
| Total | 19 | 0.5553 | - | - | - |
| Item | Coefficient | Standard Error | Statistic, t | Significance, p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.4738 | 0.0239 | 19.7976 | 0.000006 |
| x1 | 0.0008 | 0.0268 | 0.0299 | 0.9773 |
| x2 | −0.0363 | 0.0268 | −1.3578 | 0.2326 |
| x3 | −0.0281 | 0.0268 | −1.0510 | 0.3414 |
| z1 | 0.0309 | 0.0268 | 1.1559 | 0.3000 |
| z2 | 0.0087 | 0.0268 | 0.3269 | 0.7570 |
| x1x2 | 0.1558 | 0.0268 | 5.8231 | 0.0021 |
| x1x3 | −0.0029 | 0.0268 | −0.1067 | 0.9192 |
| x2x3 | 0.0132 | 0.0268 | 0.4927 | 0.6431 |
| x1z1 | 0.0300 | 0.0268 | 1.1195 | 0.3138 |
| x2z1 | −0.0323 | 0.0268 | −1.2068 | 0.2815 |
| x3z1 | −0.0114 | 0.0268 | −0.4246 | 0.6888 |
| x1z2 | 0.0050 | 0.0268 | 0.1855 | 0.8601 |
| x2z2 | 0.0371 | 0.0268 | 1.3870 | 0.2241 |
| x3z2 | −0.0071 | 0.0268 | −0.2645 | 0.8020 |
| Item | Reactive Power Experiment | THD Experiment | MPCI Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analysis method | Response surface method | Response surface method | MPCI fuzzy inference response surface method |
| Objective function | Smaller-the-better | Smaller-the-better | Smaller-the-better |
| Optimal combination | (1.0, 1.0, −1.0) | (−1.0, −1.0, −0.75) | (−1.0, −1.0, −0.99) |
| Optimal PID parameters | (52767, 767, 1 × 10−5) | (12767, 367, 1 × 10−5) | (12767, 367, 1 × 10−5) |
| Data in combined array | 5.94 (Var) 6.94 (Var) | 3.16 (%) 3.06 (%) | 6.89 (Var), 3.16 (%) 6.40 (Var), 3.06 (%) |
| OPSO solution | 6.52 (Var) | 3.10 (%) | 6.48 (Var), 3.08 (%) |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, J.-L. Multi-Objective Optimal Cloud Model Design of Vehicle-to-Grid Connected Systems Based on the Multiple Performance Characteristic Index Method. Energies 2019, 12, 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061041
Kuo J-L. Multi-Objective Optimal Cloud Model Design of Vehicle-to-Grid Connected Systems Based on the Multiple Performance Characteristic Index Method. Energies. 2019; 12(6):1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061041
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Jian-Long. 2019. "Multi-Objective Optimal Cloud Model Design of Vehicle-to-Grid Connected Systems Based on the Multiple Performance Characteristic Index Method" Energies 12, no. 6: 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061041
APA StyleKuo, J.-L. (2019). Multi-Objective Optimal Cloud Model Design of Vehicle-to-Grid Connected Systems Based on the Multiple Performance Characteristic Index Method. Energies, 12(6), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061041





