Modelling Load Profiles of Heat Pumps
Abstract
:1. Introduction
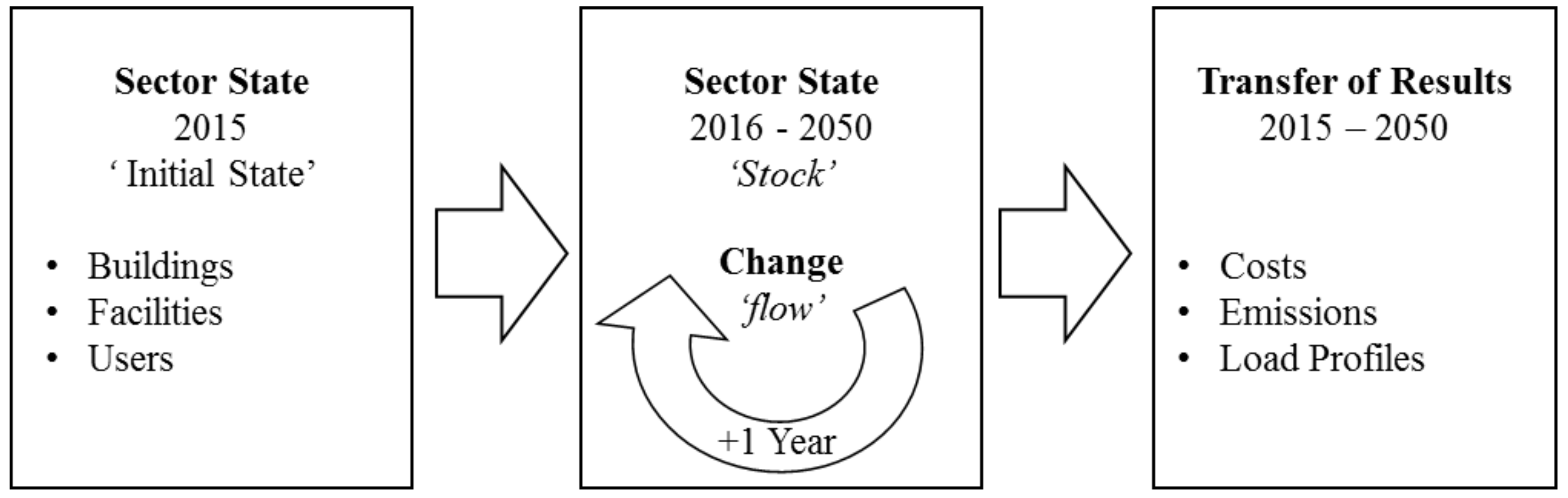
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
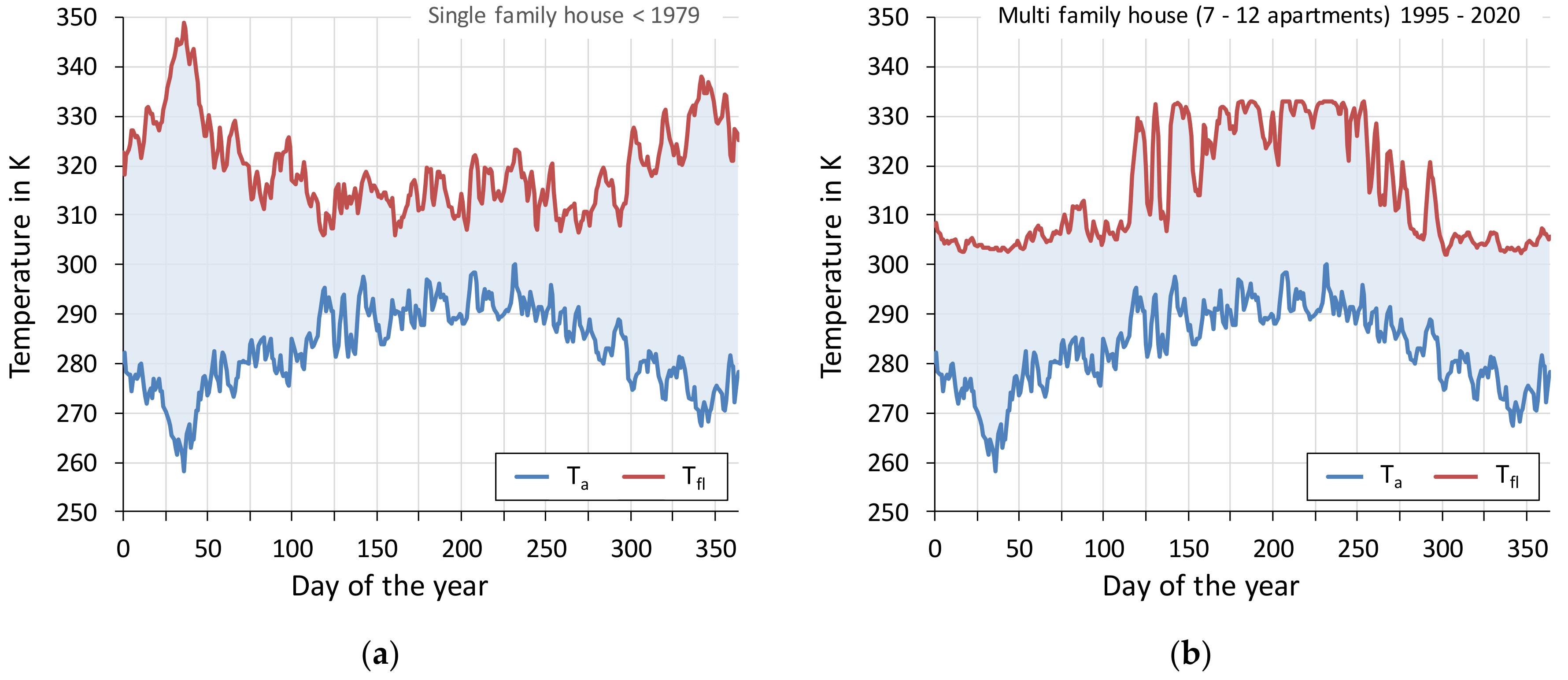
3.1. Temperature Spread—Air Source Heat Pump
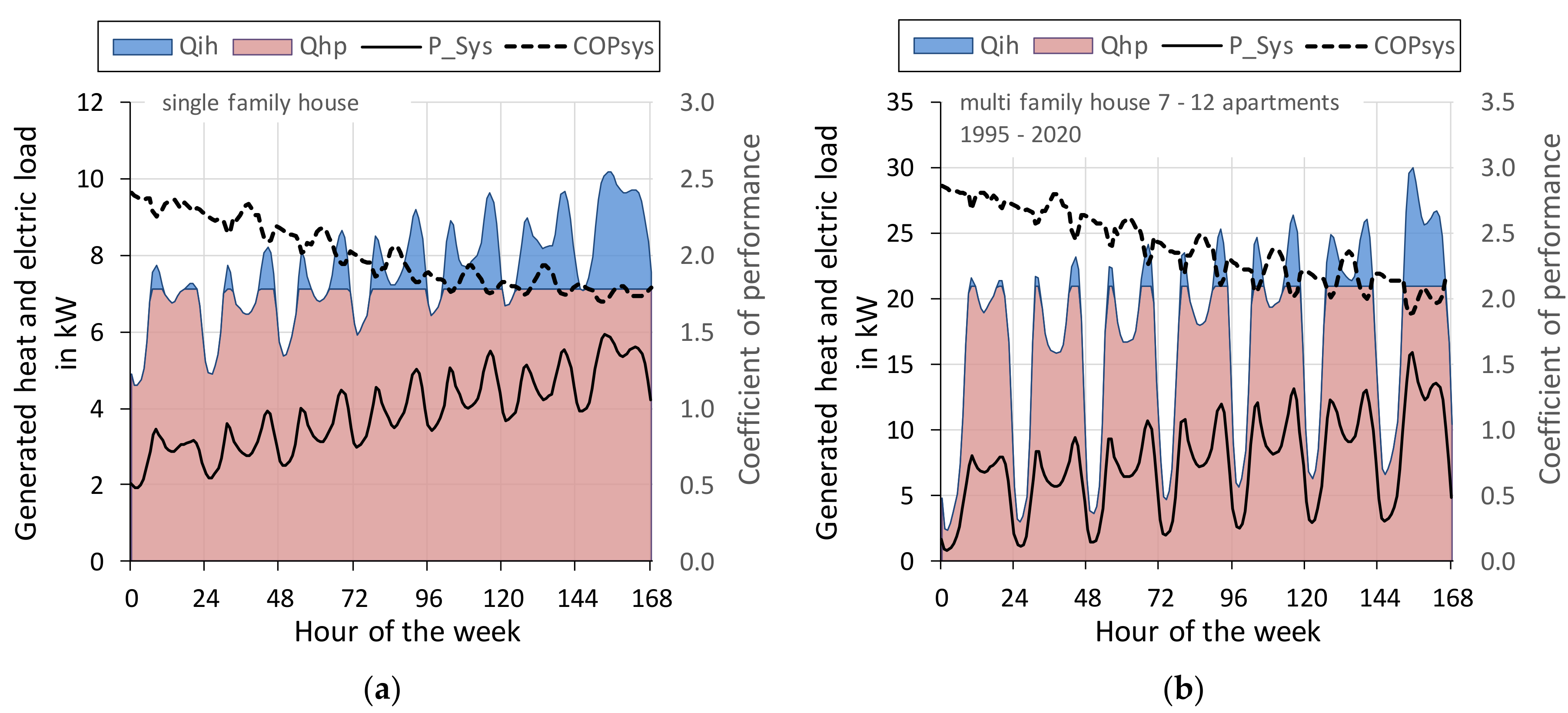
3.2. Coefficient of Performance–Air and Ground Source Heat Pump
3.3. Thermal and Electrical Load Profile—Air Source Heat Pump
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Building | Building Age Class | Renovation Level | Qsh in kWh/a | Qhw in kWh/a | Living Space in m² | COP ASHP (Sih) | COP GSHP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single family house | <1979 | - | 19,041 | 2160 | 139 | 2.9 (5.6%) | 3.3 |
| partial | 18,631 | 2160 | 139 | 3.0 (4.8%) | 3.4 | ||
| full | 9775 | 2160 | 139 | 3.3 (4.7%) | 3.8 | ||
| 1979–1994 | - | 15,017 | 2438 | 139 | 3.1 (4.6%) | 3.5 | |
| partial | 14,315 | 2438 | 139 | 3.1 (4.8%) | 3.6 | ||
| full | 9,901 | 2438 | 139 | 3.3 (4.7%) | 3.8 | ||
| 1995–2020 | - | 10,615 | 2470 | 139 | 3.3 (4.8%) | 3.8 | |
| 2021–2050 | - | 2286 | 2470 | 139 | 3.8 (4.1%) | 4.4 | |
| Multi-family house <7 apartments | <1979 | - | 37,025 | 5597 | 310 | 3.1 (4.5%) | 3.5 |
| partial | 33,457 | 5597 | 310 | 3.1 (4.9%) | 3.6 | ||
| full | 19,499 | 5597 | 310 | 3.4 (4.7%) | 3.9 | ||
| 1979–1994 | - | 29,345 | 6023 | 310 | 3.2 (4.2%) | 3.7 | |
| partial | 25,293 | 6023 | 310 | 3.3 (5.0%) | 3.8 | ||
| full | 19,466 | 6023 | 310 | 3.4 (4.9%) | 3.9 | ||
| 1995–2020 | - | 21,521 | 6251 | 310 | 3.3 (4.5%) | 3.8 | |
| 2021–2050 | - | 4915 | 6251 | 310 | 3.8 (3.3%) | 4.4 | |
| Multi-family house 7–12 apartments | <1979 | - | 65,866 | 11,627 | 589 | 3.1 (4.8%) | 3.6 |
| partial | 48,866 | 11,627 | 589 | 3.3 (5.0%) | 3.8 | ||
| full | 30,121 | 11,627 | 589 | 3.5 (4.7%) | 4.0 | ||
| 1979–1994 | - | 52,388 | 12,920 | 589 | 3.2 (4.7%) | 3.7 | |
| partial | 36,472 | 12,920 | 589 | 3.4 (4.6%) | 4.0 | ||
| full | 30,843 | 12,920 | 589 | 3.5 (4.3%) | 4.0 | ||
| 1995–2020 | - | 37,082 | 12,517 | 589 | 3.4 (3.8%) | 3.9 | |
| 2021–2050 | - | 9573 | 12,517 | 589 | 3.8 (3.7%) | 4.4 | |
| Multi-family house >12 apartments | <1979 | - | 143,088 | 27,874 | 1398 | 3.2 (4.7%) | 3.6 |
| partial | 102,564 | 27,874 | 1398 | 3.4 (4.9%) | 3.9 | ||
| full | 66,463 | 27,874 | 1398 | 3.5 (4.0%) | 4.1 | ||
| 1979–1994 | - | 117,793 | 28,615 | 1398 | 3.3 (3.8%) | 3.8 | |
| partial | 84,349 | 28,615 | 1398 | 3.4 (4.2%) | 4.0 | ||
| full | 66,877 | 28,615 | 1398 | 3.5 (4.3%) | 4.1 | ||
| 1995–2020 | - | 79,113 | 22,845 | 1398 | 3.4 (3.3%) | 4.0 | |
| 2021–2050 | - | 18,467 | 22,845 | 1398 | 3.8 (3.1%) | 4.5 |
References
- Ein neuer Aufbruch für Europa Eine neue Dynamik für Deutschland Ein neuer Zusammenhalt für unser Land—Koalitionsvertrag zwischen CDU, CSU und SPD 19; Legislaturperiode: Berlin, Germany, 2018.
- Climate Action Plan 2050—Principles and Goals of the German Government’s Climate Policy; Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety: Berlin, Germany, 2016.
- Zeitreihen zur Entwicklung der Erneuerbaren Energien in Deutschland unter Verwendung von Daten der Arbeitsgruppe Erneuerbare Energien-Statistik (AGEE-Stat); Umweltbundesamt, Fachgebiet I 2.5—Energieversorgung und -daten: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2018.
- Rasch, M.; Regett, A.; Pichlmaier, S.; Conrad, J.; Greif, S.; Guminski, A.; Rouyrre, E.; Orthofer, C.; Zipperle, T. Eine Anwendungsorientierte Emissionsbilanz—Kosteneffiziente und Sektorenübergreifende Dekarbonisierung des Energiesystems in BWK; Verein Deutscher Ingenieure (VDI): Düsseldorf, Germany, 2017; Volume 03/2017, pp. 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kosten und Potenziale der Vermeidung von Treibhausgasemissionen in Deutschland—Eine Studie von McKinsey & Company, Inc., Erstellt im Auftrag von “BDI Initiativ—Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz”; BDI Bundesverband der Deutschen Industrie e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2007.
- Gerhardt, N.; Sandau, F.; Scholz, A.; Hahn, H.; Schumacher, P.; Sager, C.; Bergk, F.; Kämper, C.; Knörr, W.; Kräck, J.; Lambrecht, U.; et al. Interaktion EE-Strom, Wärme und Verkehr—Analyse der Interaktion zwischen den Sektoren Strom, Wärme/Kälte und Verkehr in Deutschland in Hinblick auf steigende Anteile fluktuierender Erneuerbarer Energien im Strombereich unter Berücksichtigung der Europäischen Entwicklung; Fraunhofer-Institut für Windenergie und Energiesystemtechnik: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kruse, J.; Hennes, O.; Wildgrube, T.; Lencz, D.; Hintermayer, M.; Gierkink, M.; Peter, J.; Lorenczik, S. Dena-Leitstudie Integrierte Energiewende—Teil B; ewi Energy Research & Scenarios gGmbH: Köln, Germany, 2018; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, J.; Fattler, S.; Regett, A. Ongoing Project: Dynamis—Dynamic and Intersectoral Evaluation of Measures for the Cost-Efficient Decarbonisation of the Energy System; Research Center for Energy Economics: Munich, Germany, 2016; Available online: https://www.ffe.de/en/783 (accessed on 9 January 2017).
- Langenheld, A.; Mellwig, P.; Pehnt, M.; von Oehsen, A.; Blömer, S.; Lempik, J.; Werle, M.; Ganal, I.; Gerhardt, N.; Becker, S.; et al. Wert der Effizienz im Gebäudesektor in Zeiten der Sektorenkopplung; Agora Energiewende: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Verhelst, C.; Logist, F.; Van Impe, J.; Helsen, L. Study of the optimal control problem formulation for modulating air-to-water heat pumps connected to a residential floor heating system. Energy Build. 2012, 45, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, J.; Greif, S. Modelling the private households sector and the impact on the energy system. In Proceedings of the 41st IAEE Conference, Groningen, The Netherlands, 10–13 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger, M.; Lindenberger, D.; Lutz, C. Development of Energy Markets—Energy Reference Forecast—Projekt Nr. 57/12; Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stratou, E. Auswirkung der Energetischen Gebäudequalität auf den Wärmelastgang von Wohngebäuden—Abbildung Mittels Repräsentativer Typologien und Baualtersklassen. Master’s Thesis, Technische Universität München and Forschungsstelle für Energiewirtschaft e.V., Munich, Germany, 2018; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Greif, S.; Conrad, J.; Schmid, T. Methoden zur Erstellung Synthetischer Wärmelastgänge. et—Energiewirtschaftliche Tagesfragen—Zeitschrift für Energiewirtschaft, Recht, Technik und Umwelt; EW Medien und Kongresse GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 10, pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Energy Data: Complete Edition; Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy: Berlin, Germany, 2016.
- Recknagel, H.; Sprenger, E.; Schramek, E.R. Recknagel—Taschenbuch für Heizung + Klimatechnik; Karl-Joseph Albers: Munich, Germany, 2016; Volume 78. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, D.; Miara, M.; Langner, R.; Helmling, S.; Wapler, J. WP Monitor—Feldmessung von Wärmepumpenanlagen; Fraunhofer-Institut für Solare Energiesysteme (ISE): Freiburg, Germany, 2014; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Weather Data of the DWD; Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD): Offenbach, Germany, 2014; Available online: https://webservice.dwd.de/cgi-bin/spp1167/webservice.cgi (accessed on 6 December 2018).
- Arbeitsblatt W 551—Trinkwassererwärmungs- und Trinkwasserleitungsanlagen; Technische Maßnahmen zur Verminderung des Legionellenwachstums; Planung, Errichtung, Betrieb und Sanierung von Trinkwasser-Installationen; DVGW Deutsche Vereinigung des Gas- und Wasserfaches e.V.: Bonn, Germany, 2004.
- Tischer, L. Installation Rules and Guidelines; Robur S.p.A.: Verdellino, Italy, 2014. Available online: https://slideplayer.com/slide/10888512/ (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- Kleinertz, B.; Dufter, C.; Greif, S.; Conrad, J. Energieeinsparpotenziale Durch die Optimierung Bestehender Trinkwassersysteme—Betrachtung von Mietwohnungen und Einfamilienhäusern mit Zentralem und dezentralem System; Forschungsstelle für Energiewirtschaft e.V.: Munich, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, J.; von Roon, S. Beitrag Elektrischer Heizsysteme zur Jahreshöchstlast im Deutschen Übertragungsnetz in: Energiewirtschaftliche Tagesfragen; etv Energieverlag GmbH: Essen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]

| Building Type | Parameter | Min | Max | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single family house <1979 | ta in K | 256 | 308 | 283 |
| tfl in K | 297 | 352 | 320 | |
| COPSYS | 1.7 | 14 | 2.9 | |
| SIH_el | 0% | 52% | 6% | |
| PSYS in kW | 0.0 | 6.1 | 1.0 | |
| Multi family house 7–12 apartments 2021–2050 | tfl in K | 256 | 308 | 283 |
| COPSYS | 2.1 | 6.9 | 3.8 | |
| SIH_el | 0% | 66% | 4% | |
| PSYS in kW | 0.0 | 8.8 | 0.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conrad, J.; Greif, S. Modelling Load Profiles of Heat Pumps. Energies 2019, 12, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040766
Conrad J, Greif S. Modelling Load Profiles of Heat Pumps. Energies. 2019; 12(4):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040766
Chicago/Turabian StyleConrad, Jochen, and Simon Greif. 2019. "Modelling Load Profiles of Heat Pumps" Energies 12, no. 4: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040766
APA StyleConrad, J., & Greif, S. (2019). Modelling Load Profiles of Heat Pumps. Energies, 12(4), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040766





