Energy, CO2, and AQI Efficiency and Improvement of the Yangtze River Economic Belt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods
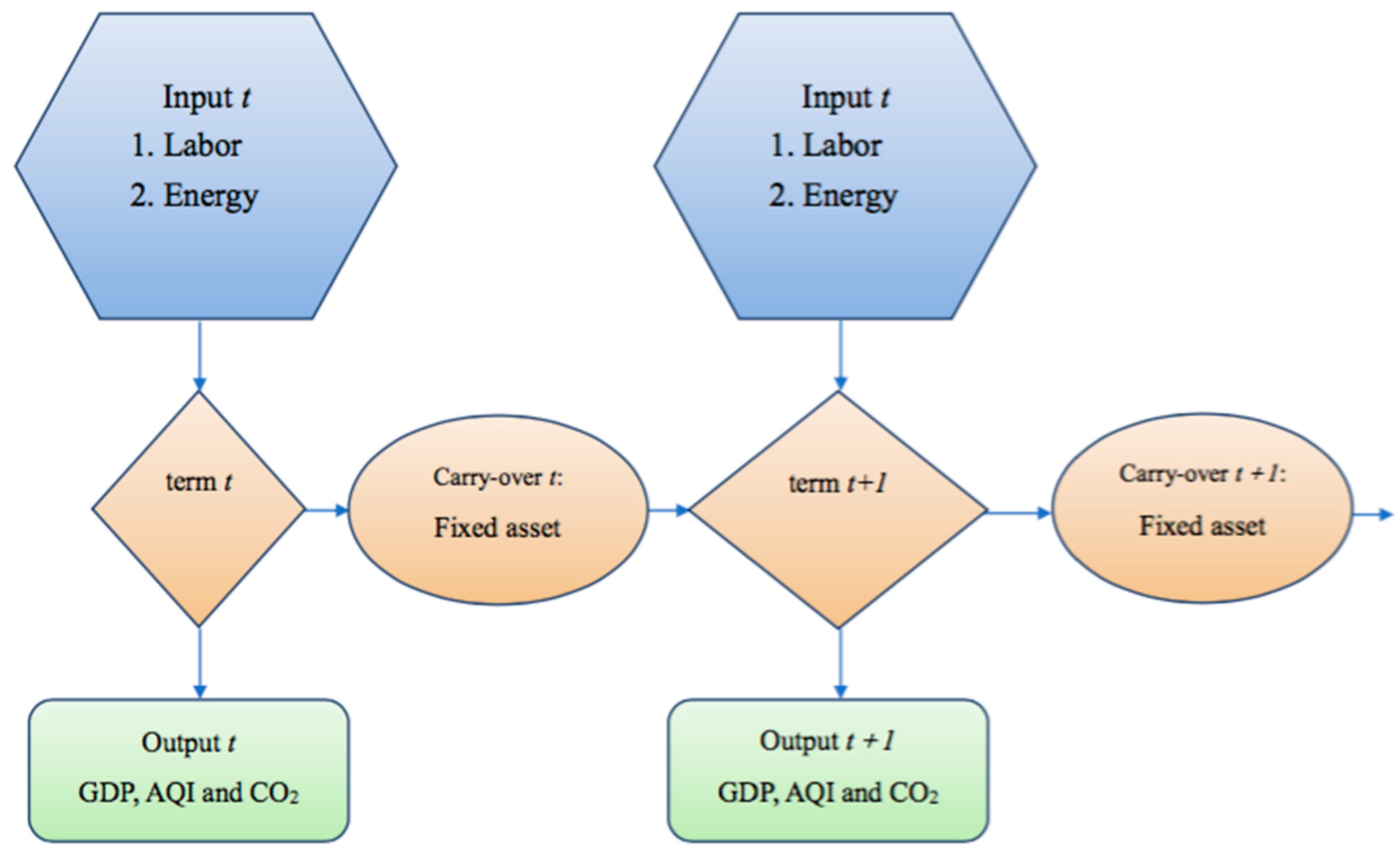
3.1. Dynamic DEA
3.2. The Modified Meta-frontier Dynamic Slack-Based Measures (SBM) Model
3.3. Energy, AQI, and CO2 Efficiencies
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Data and Variables
- Labor input (em): number of employees in each city at year-end. Unit: persons.
- Energy consumed (com): total energy consumed in each province. Unit: 100 million.
- Desired output (GDP): each province’s GDP is taken as its output. Unit: 100 million RMB.
- Undesired output:
- AQI: Air Pollution Index; the pollutants in the evaluation are SO2, NO2, PM10, PM2.5, O3, CO, and six other items. Unit: μg/m3.
- CO2: data on CO2 emissions for each city are estimated from the energy consumption breakdown by each fuel category.
- Fixed assets: capital stock of each city is calculated by fixed asset investment of each province. Unit: 100 million RMB.
4.2. Input-output Indicator Statistics
4.3. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Tang, Z. Evaluation on Chinese provincial resource input and environmental output efficiencies from 2000 to 2015. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.Q.; Meng, F.Y.; Bai, Y. Energy efficiency and congestion assessment with energy mix effect: The case of APEC countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Hong, X.; Fang, K. Chinese regional energy efficiency change and its determinants analysis: Malmquist index and Tobit model. Ann. Oper. Res. 2012, 228, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.-L.; Zhang, L.-L.; Liu, W.; Fisher, R. Bootstrap-DEA analysis of BRICS’ energy efficiency based on small sample data. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, D. Energy efficiency and production technology heterogeneity in China: A meta-frontier DEA approach. Econ. Model. 2013, 35, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.-H.; Cao, Y.-Y.; Liu, B. Energy efficiency evaluation for regions in China: an application of DEA and Malmquist indices. Energy Effic. 2013, 7, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lv, L.; Sun, J.; Ji, X. A comprehensive analysis of China’s regional energy saving and emission reduction efficiency: From production and treatment perspectives. Energy Policy 2015, 84, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lu, C.-C.; Lee, J.-H.; Chiu, Y.-H. Applying the dynamic DEA model to evaluate the energy efficiency of OECD countries and China. Energy 2017, 134, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baležentis, T.; Streimikiene, D.; Zhang, T.F.; Liobikiene, G. The role of bioenergy in greenhouse gas emission reduction in EU countries: An Environmental Kuznets Curve modelling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 142, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yu, S.; Zhang, W. China’s regional energy and environmental efficiency: A DEA window analysis based dynamic evaluation. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 58, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, C. A performance evaluation of the energy, environmental, and economic efficiency and productivity in China: An application of global data envelopment analysis. Appl. Energy 2015, 147, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhu, Q.; Lv, L.; Chu, J.; Wu, J. Efficiency evaluation of regional energy saving and emission reduction in China: A modified slacks-based measure approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, A.; Zhao, Q.; Song, M.; Baležentis, T.; Štreimikienė, D. Estimation and Factor Decomposition of Carbon Emissions in China’s Tourism Sector. Problemy Ekorozwoju 2018, 13, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.; Sheng, J.C.; Webber, M.; Baležentis, T.; Geng, Y.; Zhou, W.H. Measuring water use performance in the cities along China’s South-North Water Transfer Project. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 98, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.P.; Liu, R.Z. Study of the Energy and Environmental Efficiency of the Chinese economy based on a DEA Model. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, Z. Temporal-spatial Distribution Characteristics and Impact Factors of AQI in Fuzhou. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Heidarinejad, Z.; Kavosi, A.; Mousapour, H.; Daryabor, M.R.; Radfard, M.; Abdolshahi, A.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Saleh, H.N.; Yousefi, M. Data on evaluation of AQI for different season in Kerman, Iran, 2015. Data in Brief 2018, 20, 1917–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Jilin, G. The air quality analysis of Dalian based on the data of AQI. Fourth Semin. Nov. Optoelectron. Detect. Technol. Appl. 2018, 10697, 106973C. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Lu, L.C. Energy and AQI performance of 31 cities in China. Energy Policy 2018, 122, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, P. Efficiency and abatement costs of energy-related CO2 emissions in China: A slacks-based efficiency measure. Appl. Energy 2012, 98, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wei, Y.-M.; Zhang, X. Energy and emissions efficiency patterns of Chinese regions: A multi-directional efficiency analysis. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-P.; Cheng, X.-M.; Yuan, J.-H.; Gao, X.-J. Total-factor energy efficiency in developing countries. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-P.; Hu, J.-L. Total-factor energy productivity growth, technical progress, and efficiency change: An empirical study of China. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 3262–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Su, B.; Sun, J.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, D. Measurement and decomposition of energy-saving and emissions reduction performance in Chinese cities. Appl. Energy 2015, 151, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, A.; Li, A. Regional energy efficiency, carbon emission performance and technology gaps in China: A meta-frontier non-radial directional distance function analysis. Energy Policy 2015, 84, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Wang, X.; Baležentis, T.; Štreimikienė, D. Energy–economy–environmental (3E) performance of Chinese regions based on the data envelopment analysis model with mixed assumptions on disposability. Energy Environ. 2018, 29, 664–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Baležentis, T.; Tian, Z.; Shao, S.; Geng, Y.; Wu, R. Environmental Performance and Regulation Effect of China’s Atmospheric Pollutant Emissions: Evidence from “Three Regions and Ten Urban Agglomerations”. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lu, B.; Wei, Y.-M. China’s regional energy and environmental efficiency: A Range-Adjusted Measure based analysis. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Z.; Shen, N. Energy Efficiency and Energy Saving Potential in China: A Directional Meta-Frontier DEA Approach. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5476–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, C.; Zhang, B. An empirical analysis of China’s energy efficiency from both static and dynamic perspectives. Energy 2014, 74, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Aye, G.C.; Barros, C.P.; Gupta, R.; Wanke, P. Energy efficiency of selected OECD countries: A slacks based model with undesirable outputs. Energy Econ. 2015, 51, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-C. Energy intensity, target level of energy intensity, and room for improvement in energy intensity: An application to the study of regions in the EU. Energy Policy 2014, 67, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Kuang, H.-B.; Wu, C.-Y.; Li, Y. The changing trend and influencing factors of energy efficiency: The case of nine countries. Energy 2014, 64, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, S.; Hu, J.-L. A panel data parametric frontier technique for measuring total-factor energy efficiency: An application to Japanese regions. Energy 2014, 78, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ni, J.; Shen, M. Empirical Analysis of Provincial Energy Efficiency in China. China World Econ 2009, 17, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Zhou, J.; Zou, W.-J. Energy Efficiency Measures and Convergence in China, Taking into Account the Effects of Environmental and Random Factors. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. The improvement gap in energy intensity: Analysis of China’s thirty provincial regions using the improved DEA (data envelopment analysis) model. Energy 2015, 84, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.-J.; Cai, P.-H.; Shen, N.; Lu, C.-C. The technology gap of Chinese regions’ energy efficiency and spatial convergence—Based on the hybrid meta-frontier data envelopment analysis. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2015, 7, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, R.D.; Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W. Some Models for Estimating Technical and Scale Inefficiencies in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1984, 30, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S. Productivity and intermediate products: A frontier approach. Econ. Lett. 1996, 50, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogetoft, P.; Christensen, D.L.; Damgard, I.; Geisler, M.; Jakobsen, T.P.; Krøigaard, M.; Nielsen, J.D.; Nielsen, J.B.; Nielsen, K.; Pagter, J.; et al. Multiparty Computation Goes Live. In Proceedings of the Financial Cryptography and Data Security, Accra Beach, Barbados, 23–26 February 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 325–343. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-M. A network-DEA model with new efficiency measures to incorporate the dynamic effect in production networks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 194, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, J.; Goto, M. Dynamic data envelopment analysis: Modeling intertemporal behavior of a firm in the presence of productive inefficiencies. Econ. Lett. 1999, 64, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, J.; Goto, M. Measurement of Dynamic Efficiency in Production: An Application of Data Envelopment Analysis to Japanese Electric Utilities. J. Prod. Anal. 2003, 19, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Park, K. Measurement of multiperiod aggregative efficiency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 193, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. Dynamic DEA: A Slacks-based Measure Approach. Omega 2010, 38, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battese, G.E.; Rao, D.S.P. Technology gap, efficiency and a stochastic metafrontier function. Int. J. Bus. Econ. 2002, 1, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Battese, G.E.; Rao, D.S.P.; O’Donnell, C.J.; O’Donnell, C.J. A Metafrontier Production Function for Estimation of Technical Efficiencies and Technology Gaps for Firms Operating Under Different Technologies. J. Prod. Anal. 2004, 21, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, C.J.; Rao, D.S.P.; Battese, G.E. Metafrontier frameworks for the study of firm-level efficiencies and technology ratios. Empir. Econ. 2008, 34, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, S.C. Total-factor energy efficiency of regions in China. Energy Policy 2006, 34, 3206–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook. 2017. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/ (accessed on 8 April 2018).
- China Statistical Yearbooks Database. Demographics and the Employment Statistical Yearbook of China, and the Statistical Yearbooks of all Cities. China Academic Journals Electronic Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/ (accessed on 8 April 2018).
- China’s Environmental and Protection Bureau Reports. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2017. Available online: http://www.mep.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 March 2018).

| Statistical Presentation | Input Variables | Output Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labor | Fixed Assets | Energy | GDP | CO2 | AQI | |
| The Year of 2014 | ||||||
| Max | 1943.82 | 54,055.7 | 42,634.2 | 78,036.82 | 164,182.81 | 154 |
| Min | 61.88 | 3660.52 | 786.26 | 2575.8 | 2044.29 | 46.7500 |
| AVG | 627.3291 | 21,030.3434 | 14,577.9763 | 26,512.2156 | 41,211.3244 | 92.7624 |
| Std | 215.0595 | 16,211.0735 | 9062.1249 | 14,712.1203 | 23,561.5192 | 24.6898 |
| The Year of 2015 | ||||||
| Max | 1948.04 | 48,312.44 | 40,926.93 | 72,812.55 | 146,410.44 | 139.4167 |
| Min | 62.71 | 3210.63 | 1071.92 | 2417.05 | 2786.99 | 44.9167 |
| AVG | 600.9703 | 18,505.06 | 14,182.6044 | 24,058.0493 | 38,188.2830 | 92.3808 |
| Std | 216.4242 | 14,020.0395 | 8952.6012 | 14,051.5552 | 23,276.7673 | 25.3969 |
| The Year of 2016 | ||||||
| Max | 1943.82 | 54,055.7 | 42,634.2 | 78,036.82 | 164,182.81 | 154 |
| Min | 61.88 | 3660.52 | 786.26 | 2575.8 | 2044.29 | 46.75 |
| AVG | 627.3291 | 21,030.3434 | 14,577.9763 | 26,512.2156 | 41,211.3244 | 92.7624 |
| Std | 215.0595 | 16,211.0735 | 9062.1249 | 14,712.1203 | 23,561.5192 | 24.6898 |
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMU (Decision Making Unit) | Rank | Score | Rank | Score | Rank | Score |
| Anhui | 17 | 0.5405 | 17 | 0.5290 | 17 | 0.5161 |
| Beijing | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Chongqing | 16 | 0.5527 | 15 | 0.5805 | 15 | 0.5446 |
| Fujian | 10 | 0.7727 | 9 | 0.7786 | 9 | 0.8077 |
| Gansu | 27 | 0.2956 | 27 | 0.2648 | 28 | 0.2438 |
| Guangdong | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Guangxi | 12 | 0.6739 | 11 | 0.7372 | 12 | 0.7408 |
| Guizhou | 26 | 0.3321 | 26 | 0.3598 | 25 | 0.3704 |
| Hainan | 14 | 0.6165 | 16 | 0.5653 | 16 | 0.5355 |
| Hebei | 18 | 0.5391 | 19 | 0.4941 | 21 | 0.4655 |
| Heilongjiang | 23 | 0.4151 | 25 | 0.3718 | 24 | 0.3834 |
| Henan | 21 | 0.4499 | 22 | 0.4193 | 22 | 0.4314 |
| Hubei | 11 | 0.7275 | 12 | 0.6678 | 14 | 0.6943 |
| Hunan | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Jiangsu | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Jiangxi | 19 | 0.5351 | 18 | 0.4956 | 19 | 0.4868 |
| Jilin | 20 | 0.4948 | 20 | 0.4772 | 18 | 0.4952 |
| Liaoning | 15 | 0.6118 | 14 | 0.6055 | 11 | 0.7495 |
| Neimenggu | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ningxia | 29 | 0.2582 | 28 | 0.2537 | 27 | 0.2445 |
| Qinghai | 25 | 0.3723 | 23 | 0.3867 | 23 | 0.4110 |
| Shandong | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Shanghai | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Shanxi | 30 | 0.2491 | 30 | 0.2300 | 30 | 0.2101 |
| Shaanxi | 24 | 0.4021 | 24 | 0.3758 | 26 | 0.3563 |
| Sichuan | 13 | 0.6247 | 13 | 0.6624 | 10 | 0.7581 |
| Tianjin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Xinjiang | 28 | 0.2758 | 29 | 0.2388 | 29 | 0.2137 |
| Yunnan | 22 | 0.4355 | 21 | 0.4399 | 20 | 0.4782 |
| Zhejiang | 9 | 0.8072 | 10 | 0.7596 | 13 | 0.7349 |
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
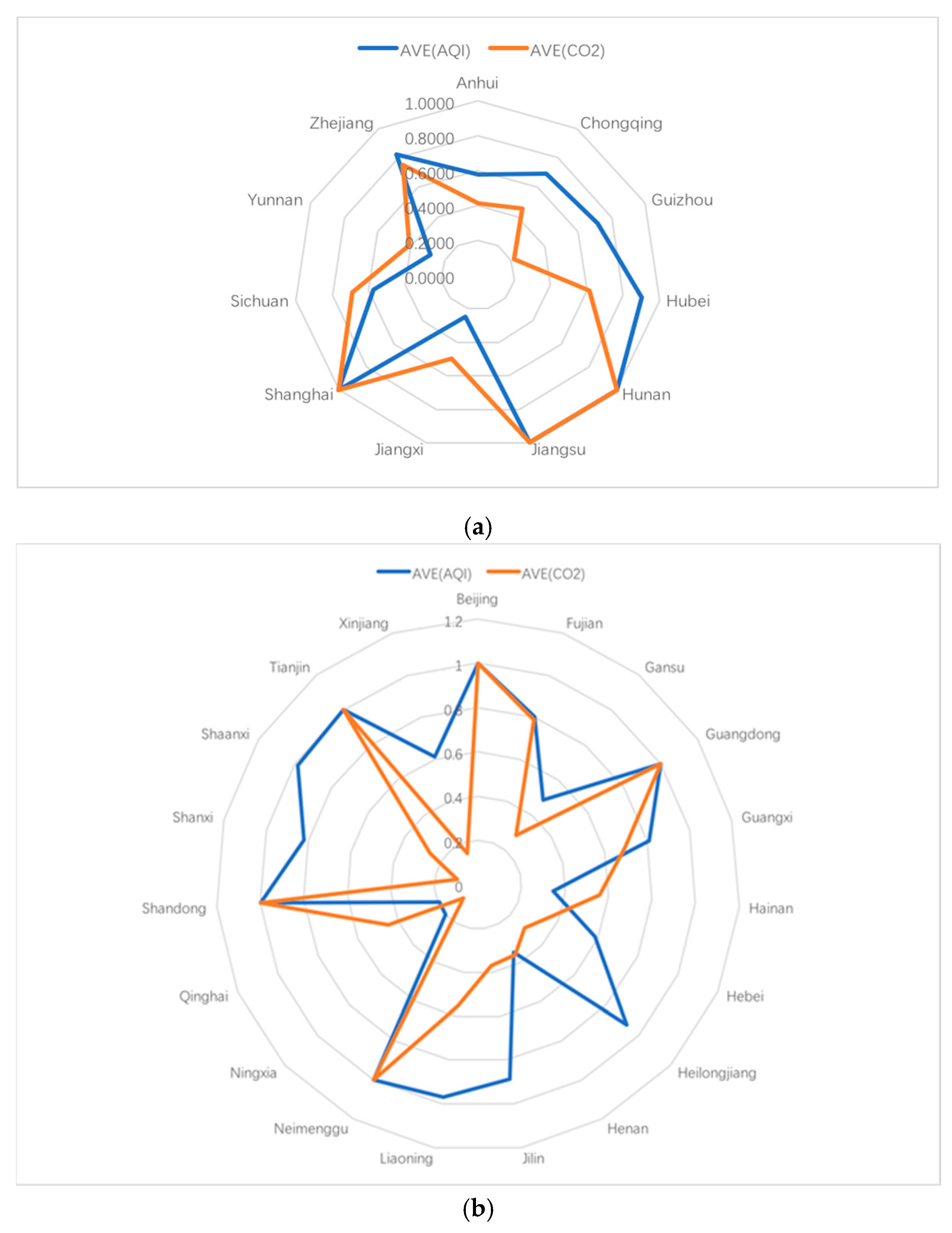
| DMU | Com | AQI | CO2 | Com | AQI | CO2 | Com | AQI | CO2 |
| Anhui | 0.4106 | 0.6751 | 0.4106 | 0.4146 | 0.5743 | 0.4146 | 0.4138 | 0.4767 | 0.4138 |
| Beijing | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Chongqing | 0.4991 | 0.5557 | 0.4991 | 0.4439 | 0.8268 | 0.4439 | 0.4134 | 0.6939 | 0.4134 |
| Fujian | 0.7657 | 0.8066 | 0.7657 | 0.7945 | 0.7484 | 0.7945 | 0.7998 | 0.8577 | 0.7998 |
| Gansu | 0.3119 | 0.5075 | 0.3119 | 0.2815 | 0.4720 | 0.2815 | 0.2559 | 0.4720 | 0.2559 |
| Guangdong | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Guangxi | 0.6233 | 0.7635 | 0.6233 | 0.6684 | 0.9106 | 0.6947 | 0.7216 | 0.7494 | 0.7645 |
| Guizhou | 0.2078 | 1 | 0.2078 | 0.2368 | 0.3398 | 0.2368 | 0.2120 | 0.8196 | 0.2120 |
| Hainan | 0.6335 | 0.3919 | 0.6335 | 0.5514 | 0.3320 | 0.5514 | 0.4953 | 0.3159 | 0.4953 |
| Hebei | 0.3288 | 0.9738 | 0.3288 | 0.3990 | 0.3541 | 0.3989 | 0.3529 | 0.4258 | 0.3529 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.3180 | 0.9652 | 0.3180 | 0.2867 | 0.8207 | 0.2867 | 0.2630 | 1 | 0.2630 |
| Henan | 0.3590 | 0.3941 | 0.3590 | 0.3554 | 0.2280 | 0.3554 | 0.3610 | 0.4161 | 0.3610 |
| Hubei | 0.6330 | 1 | 0.6330 | 0.6080 | 0.7801 | 0.6080 | 0.6041 | 0.9303 | 0.6041 |
| Hunan | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Jiangsu | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Jiangxi | 0.5249 | 0.2524 | 0.5249 | 0.4949 | 0.1884 | 0.4949 | 0.4752 | 0.3034 | 0.4752 |
| Jilin | 0.3891 | 0.8157 | 0.3891 | 0.3694 | 0.8443 | 0.3694 | 0.3532 | 1 | 0.3532 |
| Liaoning | 0.4611 | 0.9568 | 0.4611 | 0.4529 | 0.9477 | 0.4529 | 0.6289 | 1 | 0.7399 |
| Neimenggu | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ningxia | 0.0993 | 0.2230 | 0.0993 | 0.0894 | 0.1669 | 0.0894 | 0.0809 | 0.2102 | 0.0809 |
| Qinghai | 0.4043 | 0.1976 | 0.4043 | 0.4394 | 0.1878 | 0.4394 | 0.4972 | 0.1948 | 0.4972 |
| Shandong | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Shanghai | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Shanxi | 0.1055 | 0.9487 | 0.1055 | 0.0944 | 0.9192 | 0.0944 | 0.0936 | 0.5997 | 0.0936 |
| Shaanxi | 0.2887 | 1 | 0.2887 | 0.2604 | 0.9547 | 0.2604 | 0.2332 | 1 | 0.2332 |
| Sichuan | 0.6183 | 0.4958 | 0.6183 | 0.7107 | 0.4151 | 0.7107 | 0.7445 | 0.8036 | 0.7445 |
| Tianjin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Xinjiang | 0.1791 | 0.7415 | 0.1791 | 0.1470 | 0.6259 | 0.1470 | 0.1238 | 0.4701 | 0.1238 |
| Yunnan | 0.3687 | 0.3049 | 0.3687 | 0.4023 | 0.2293 | 0.4023 | 0.4594 | 0.3109 | 0.4594 |
| Zhejiang | 0.7637 | 0.9588 | 0.7637 | 0.7308 | 0.8512 | 0.7308 | 0.7565 | 0.6582 | 0.7565 |
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMU | Rank by div | Technology Gap | Rank by div | Technology Gap | Rank by div | Technology Gap |
| Anhui | 15 | 0.9977 | 24 | 0.9778 | 25 | 0.9733 |
| Beijing | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Chongqing | 19 | 0.9964 | 18 | 0.9953 | 16 | 0.9996 |
| Fujian | 13 | 0.9993 | 20 | 0.9937 | 23 | 0.9914 |
| Gansu | 24 | 0.9852 | 16 | 0.9961 | 1 | 1 |
| Guangdong | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Guangxi | 16 | 0.9975 | 17 | 0.9958 | 21 | 0.9927 |
| Guizhou | 26 | 0.9771 | 23 | 0.9838 | 1 | 1 |
| Hainan | 29 | 0.9436 | 1 | 1.0000 | 1 | 1 |
| Hebei | 28 | 0.9658 | 22 | 0.9839 | 24 | 0.9851 |
| Heilongjiang | 17 | 0.9973 | 21 | 0.9921 | 1 | 1 |
| Henan | 1 | 1 | 14 | 0.9977 | 18 | 0.9977 |
| Hubei | 22 | 0.9901 | 28 | 0.9192 | 28 | 0.9567 |
| Hunan | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Jiangsu | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Jiangxi | 1 | 1 | 26 | 0.9707 | 19 | 0.9975 |
| Jilin | 23 | 0.9863 | 19 | 0.9945 | 1 | 1 |
| Liaoning | 12 | 0.9999 | 25 | 0.9716 | 29 | 0.9158 |
| Neimenggu | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ningxia | 1 | 1 | 15 | 0.9976 | 17 | 0.9991 |
| Qinghai | 14 | 0.9990 | 13 | 0.9997 | 1 | 1 |
| Shandong | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Shanghai | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Shanxi | 21 | 0.9915 | 1 | 1 | 26 | 0.9716 |
| Shaanxi | 18 | 0.9969 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sichuan | 27 | 0.9751 | 29 | 0.9019 | 27 | 0.9700 |
| Tianjin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Xinjiang | 20 | 0.9922 | 1 | 1 | 20 | 0.9942 |
| Yunnan | 25 | 0.9820 | 27 | 0.9311 | 22 | 0.9917 |
| Zhejiang | 30 | 0.8653 | 30 | 0.8134 | 30 | 0.8080 |
| Average YREB | 0.9803 | 0.9539 | 0.9724 | |||
| STEDVP YREB | 0.9964 | 0.9953 | 0.9996 | |||
| Average non-YREB | 0.9923 | 0.9959 | 0.9920 | |||
| STEDVP non-YREB | 0.9993 | 0.9937 | 0.9914 | |||
| Year | Ave. Gap of YREB | Ave. Gap of Non-YREB | Wilcoxon Test Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.9803 | 0.9923 | 0.4592 |
| 2015 | 0.9539 | 0.9959 | 0.0241 ** |
| 2016 | 0.9724 | 0.9920 | 0.2080 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, F.-R.; Tian, Z.; Shen, Y.-T.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Lin, T.-Y. Energy, CO2, and AQI Efficiency and Improvement of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Energies 2019, 12, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040647
Ren F-R, Tian Z, Shen Y-T, Chiu Y-H, Lin T-Y. Energy, CO2, and AQI Efficiency and Improvement of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Energies. 2019; 12(4):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040647
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Fang-Rong, Ze Tian, Yu-Ting Shen, Yung-Ho Chiu, and Tai-Yu Lin. 2019. "Energy, CO2, and AQI Efficiency and Improvement of the Yangtze River Economic Belt" Energies 12, no. 4: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040647
APA StyleRen, F.-R., Tian, Z., Shen, Y.-T., Chiu, Y.-H., & Lin, T.-Y. (2019). Energy, CO2, and AQI Efficiency and Improvement of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Energies, 12(4), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040647





