A Preliminary Study of the Effect of Bioavailable Fe and Co on the Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feedstock and Inoculum
2.2. Trace Elements Dosing Strategy
2.3. BMP Tests
2.4. Sequential Extraction Protocol
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
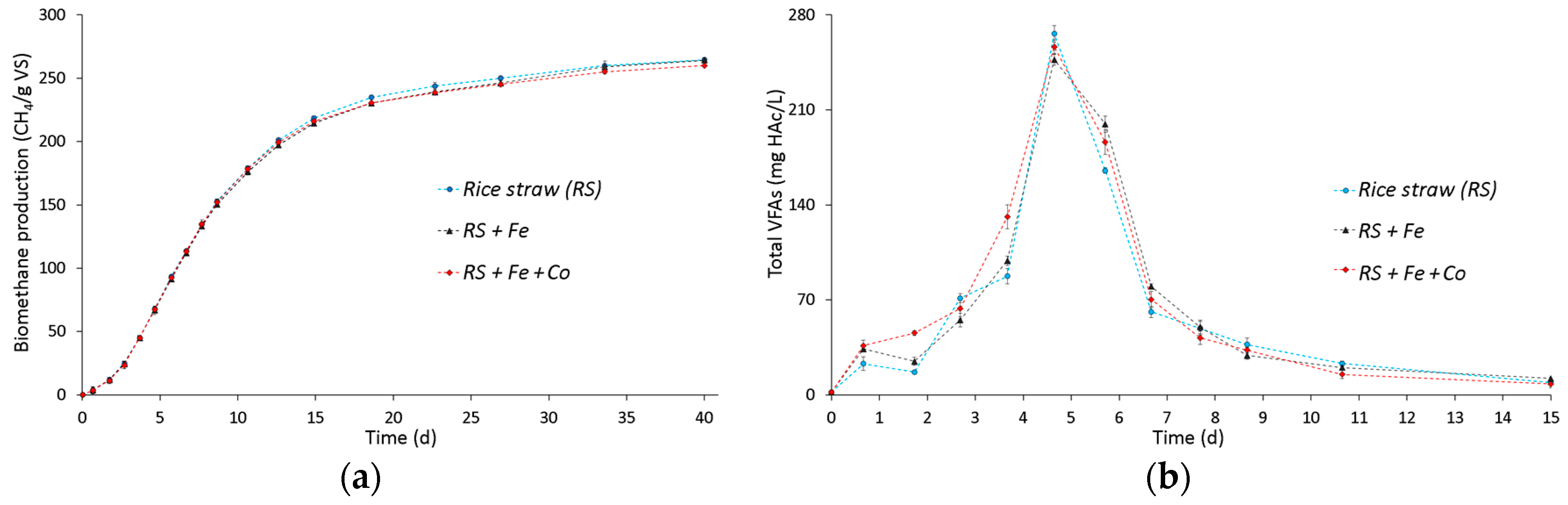
3.1. Effect of Fe and Co Addition on Biomethane Production and VFA Accumulation from Rice Straw
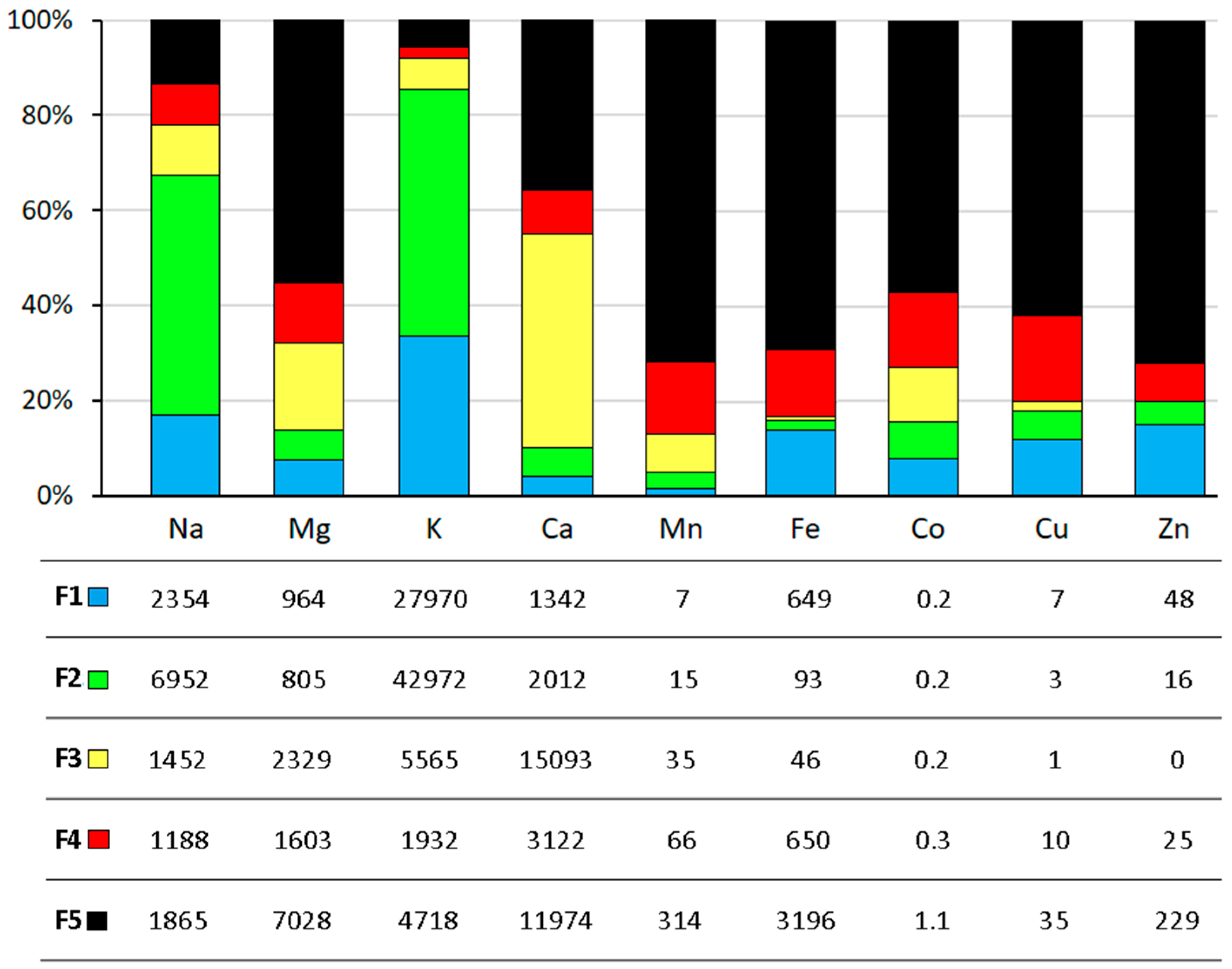
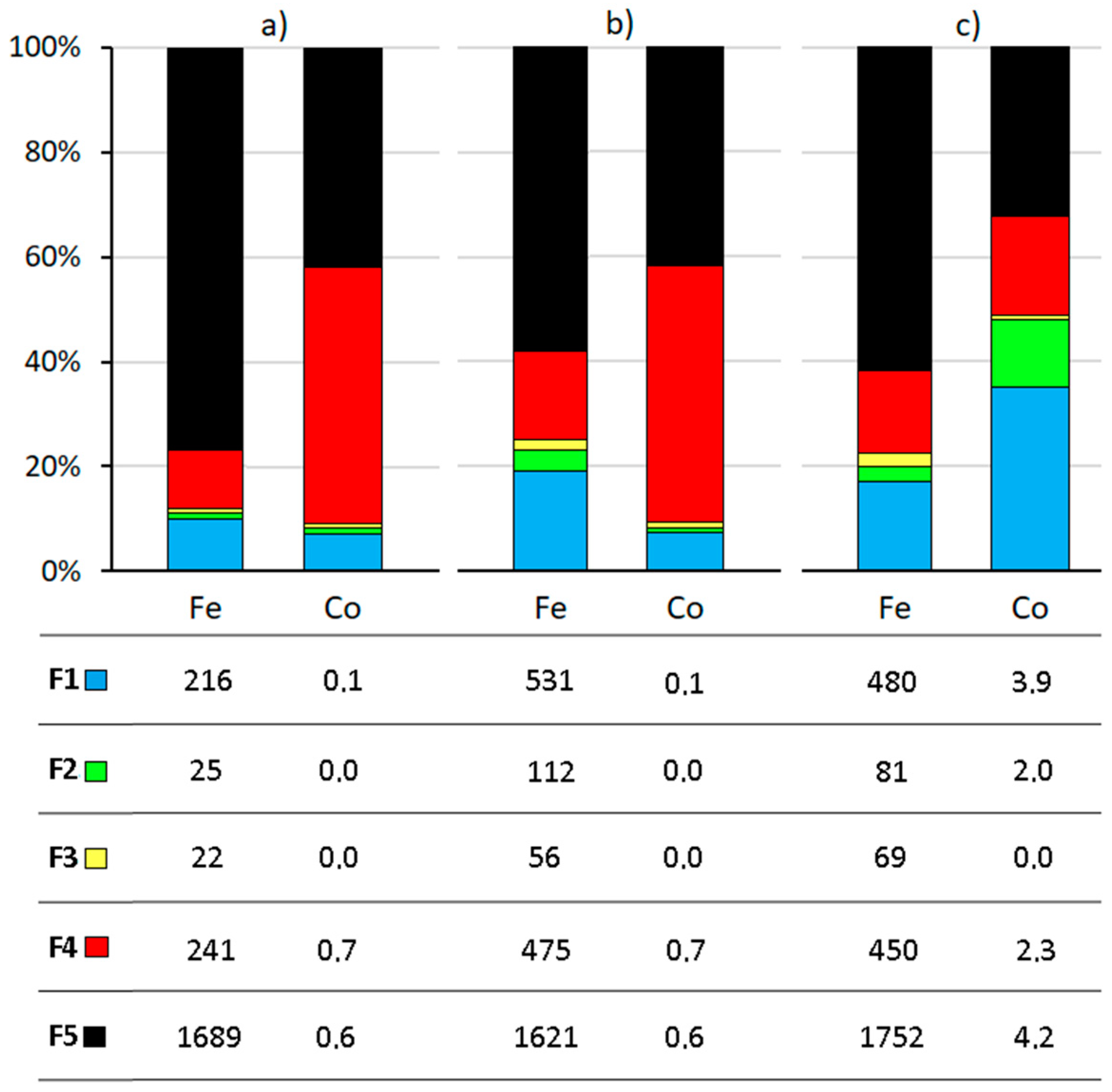
3.2. Sequential Extraction and Bioavailable Fractions of Fe and Co
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Bhowmick, G.; Sarmah, A.K.; Sen, R. Lignocellulosic biorefinery as a model for sustainable development of biofuels and value added products. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, S.; Singh, O.V. Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass: Biochemical and molecular perspectives. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, G.; Papirio, S.; Lens, P.N.L.; Esposito, G. Solvent pretreatments of lignocellulosic materials to enhance biogas production: A review. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 1892–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, W.; Sun, M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Y. Evaluation of biochemical methane potential and kinetics of the anaerobic digestion of vegetable crop residues. Energies 2019, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, J.K.; Nair, G.R.; Hussain, A.; Raghavan, G.V. Feedstocks, logistics and pre-treatment processes for sustainable lignocellulosic biorefineries: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussoline, W.; Esposito, G.; Giordano, A.; Lens, P.N.L. The anaerobic digestion of rice straw: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 895–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnklong, C.; Cone, J.W.; Pellikaan, W.; Hendriks, W.H. Utilization of rice straw and different treatments to improve its feed value for ruminants: A review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 23, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoliang, C.; Zhang, X.; Sunling, G.; Zheng, F. Investigation on emission factors of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from crop residue burning. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, R.; Takeuchi, H.; Hasegawa, T. Methane production from lignocellulosic agricultural crop wastes: A review in context to second generation of biofuel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1462–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, Y.Y.; Norli, I.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Yhaya, M.F. Impacts of trace element supplementation on the performance of anaerobic digestion process: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandvoort, M.H.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Fermoso, F.G.; Lens, P.N.L. Trace metals in anaerobic granular sludge reactors: Bioavailability and dosing strategies. Eng. Life Sci. 2006, 6, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobeheim, H.; Munk, B.; Johansson, J.; Guebitz, G.M. Influence of trace elements on methane formation from a synthetic model substrate for maize silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lee, Y.-W.; Jahng, D. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and piggery wastewater: Focusing on the role of trace elements. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5048–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, B.; Scherer, P. Trace element requirements of agricultural biogas digesters during biological conversion of renewable biomass to methane. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, G.; Papirio, S.; Riccardelli, G.; Lens, P.N.L.; Esposito, G. Trace elements dosing and alkaline pretreatment in the anaerobic digestion of rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fermoso, F.G.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Guibaud, G.; Collins, G.; Svensson, B.H.; Carliell-Marquet, C.; Vink, J.P.M.; Esposito, G.; Frunzo, L. Fate of trace metals in anaerobic digestion. In Biogas Science and Technology; Guebitz, G.M., Bauer, A., Bochmann, G., Gronauer, A., Weiss, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 171–195. [Google Scholar]
- Takashima, M.; Speece, R.E.; Parkin, G.F. Mineral requirements for methane fermentation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Contr. 1990, 19, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, J.B.; Orphan, V.J. Trace metal requirements for microbial enzymes involved in the production and consumption of methane and nitrous oxide. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortner, M.; Rameder, M.; Rachbauer, L.; Bochmann, G.; Fuchs, W. Bioavailability of essential trace elements and their impact on anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 99, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Vila, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Astals, S. The role of additives on anaerobic digestion: A review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hullebusch, E.D.; Guibaud, G.; Simon, S.; Lenz, M.; Yekta, S.S.; Fermoso, F.G.; Jain, R.; Duester, L.; Roussel, J.; Guillon, E.; et al. Methodological approaches for fractionation and speciation to estimate trace element bioavailability in engineered anaerobic digestion ecosystems: An overview. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 1324–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motte, J.-C.; Sambusiti, C.; Dumas, C.; Barakat, A. Combination of dry dark fermentation and mechanical pretreatment for lignocellulosic deconstruction: An innovative strategy for biofuels and volatile fatty acids recovery. Appl. Energy 2015, 147, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortner, M.; Rachbauer, L.; Somitsch, W.; Fuchs, W. Can bioavailability of trace nutrients be measured in anaerobic digestion? Appl. Energy 2014, 126, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcato, C.-E.; Pinelli, E.; Cecchi, M.; Winterton, P.; Guiresse, M. Bioavailability of Cu and Zn in raw and anaerobically digested pig slurry. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2009, 72, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osuna, M.; Iza, J.; Zandvoort, M.; Lens, P.N.L. Essential metal depletion in an anaerobic reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, B.; de la Luz Mora, M.; Bolan, N.; Naidu, R. Assessment of phosphorus bioavailability from organic wastes in soil. In Chemical Bioavailability in Terrestrial Environment (Series: Developments in Soil Science); Hartemink, A.E., McBratney, A.B., Naidu, R., Eds.; Elsevier Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 363–411. [Google Scholar]
- Preeti Rao, P.; Seenayya, G. Improvement of methanogenesis from cow dung and poultry litter waste digesters by addition of iron. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 10, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinken, L.; Urban, I.; Haun, E.; Weichgrebe, D.; Rosenwinkel, K.-H. The valuation of malnutrition in the mono-digestion of maize silage by anaerobic batch tests. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, G.; Papirio, S.; Lens, P.N.L.; Esposito, G. Effect of N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide pretreatment on biogas production from rice straw, cocoa shell, and hazelnut skin. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hullebusch, E.D.; Utomo, S.; Zandvoort, M.H.; Lens, P.N.L. Comparison of three sequential extraction procedures to describe metal fractionation in anaerobic granular sludges. Talanta 2005, 65, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Hyman, D.; Payne, C.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Wolfe, J. Determination of Total Solids in Biomass and Total Dissolved Solids in Liquid Process Samples; Technical Report NRELTP-510-42621; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Denver, CO, USA, 2008.
- Pansu, M.; Gautheyrou, J. Handbook of Soil Analysis: Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 497–547. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass; Technical Report NRELTP-510-42618; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Denver, CO, USA, 2008.
- Moestedt, J.; Nordell, E.; Shakeri Yekta, S.; Lundgren, J.; Martí, M.; Sundberg, C.; Ejlertsson, J.; Svensson, B.H.; Björn, A. Effects of trace element addition on process stability during anaerobic co-digestion of OFMSW and slaughterhouse waste. Waste Manag. 2016, 47, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.H.; Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B.K. Improving thermophilic anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Poquet, V.; Papirio, S.; Trably, E.; Rintala, J.; Escudié, R.; Esposito, G. Semi-continuous mono-digestion of OFMSW and co-digestion of OFMSW with beech sawdust: Assessment of the maximum operational total solid content. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, G.; Papirio, S.; Lens, P.N.L.; Esposito, G. Increased biogas production from wheat straw by chemical pretreatments. Renew. Energy 2018, 119, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, S.; Wu, S.; Kizito, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Dong, R. Synergistic effect of alkaline pretreatment and Fe dosing on batch anaerobic digestion of maize straw. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, T.; Rother, M. Selenoproteins in Archaea and Gram-positive bacteria. BBA Gen. 2009, 1790, 1520–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, C.J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Heaven, S. Trace element requirements for stable food waste digestion at elevated ammonia concentrations. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kabir, M.M.; Forgács, G.; Sárvári Horváth, I. Biogas from Lignocellulosic Materials. In Lignocellulose-Based Bioproducts; Karimi, K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 207–251. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, L.; Mi, X.; Chai, Y. Effect of ferrous chloride on biogas production and enzymatic activities during anaerobic fermentation of cow dung and Phragmites straw. Biodegradation 2016, 27, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chai, Y.; Wang, L.; Mi, X.; Zhang, L.; Ware, M.A. Biogas properties and enzymatic analysis during anaerobic fermentation of Phragmites australis straw and cow dung: Influence of nickel chloride supplement. Biodegradation 2017, 28, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, H.C.; Klein, A.; Thauer, R.K. Structure and function of the nickel porphinoid, coenzyme F430, and of its enzyme, methyl coenzyme M reductase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1990, 87, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, B.C.; Mattei, M.R.; Frunzo, L.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Esposito, G. ADM1 based mathematical model of trace element precipitation/dissolution in anaerobic digestion processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, B.C.; Mattei, M.R.; Frunzo, L.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Esposito, G. ADM1 based mathematical model of trace element complexation in anaerobic digestion processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Rice Straw | Inoculum |
|---|---|---|
| TS (%) | 94.2 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.2 |
| VS (%) | 80.0 ± 0.7 | 2.8 ± 0.1 |
| TKN (g N/kg TS) | 11.2 ± 0.2 | 27.1 ± 1.3 |
| Iron (Fe) (µg/g TS) | 477 ± 81 | 4634 ± 57 |
| Copper (Cu) (µg/g TS) | 17 ± 5 | 19 ± 0.2 |
| Zinc (Zn) (µg/g TS) | 62 ± 25 | 69 ± 2.0 |
| Cobalt (Co) (µg/g TS) | <1.0 | 2 ± 0.1 |
| Nickel (Ni) (µg/g TS) | 2 ± 0.0 | 10 ± 0.1 |
| Selenium (Se) (µg/g TS) | <1.0 | <1.0 |
| Sodium (Na) (mg/g TS) | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 13.8 ± 1.4 |
| Magnesium (Mg) (mg/g TS) | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 12.7 ± 0.4 |
| Potassium (K) (mg/g TS) | 14.5 ± 0.4 | 83.2 ± 7.1 |
| Calcium (Ca) (mg/g TS) | 9.1 ± 0.6 | 33.5 ± 1.6 |
| Cellulose (%) | 28.6 ± 0.2 | - |
| Hemicellulose (%) | 19.5 ± 1.2 | - |
| Lignin (%) | 17.3 ± 0.3 | - |
| Fraction | Extracting Agent | Extracting Conditions a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Temperature | Shaking Time | ||
| F1—water soluble fraction | - | - | - | - |
| F2—exchangeable fraction | 10 mL 1M NH4CH3COO | 7.0 | 25 °C | 60 min |
| F3—carbonate fraction | 10 mL 1M CH3COOH | 5.5 | 25 °C | 60 min |
| F4—organic matter and sulfide fraction | 10 mL H2O2 (30% w/w) | 2.0 | 35 °C | 180 min |
| F5—residual fraction b | 10 mL HNO3 | - | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mancini, G.; Papirio, S.; Lens, P.N.L.; Esposito, G. A Preliminary Study of the Effect of Bioavailable Fe and Co on the Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw. Energies 2019, 12, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040577
Mancini G, Papirio S, Lens PNL, Esposito G. A Preliminary Study of the Effect of Bioavailable Fe and Co on the Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw. Energies. 2019; 12(4):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040577
Chicago/Turabian StyleMancini, Gabriele, Stefano Papirio, Piet N. L. Lens, and Giovanni Esposito. 2019. "A Preliminary Study of the Effect of Bioavailable Fe and Co on the Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw" Energies 12, no. 4: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040577
APA StyleMancini, G., Papirio, S., Lens, P. N. L., & Esposito, G. (2019). A Preliminary Study of the Effect of Bioavailable Fe and Co on the Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw. Energies, 12(4), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12040577







