Modeling and Control of Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology with Semi-Bridgeless Active Rectifier for Inductive Power Transfer System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
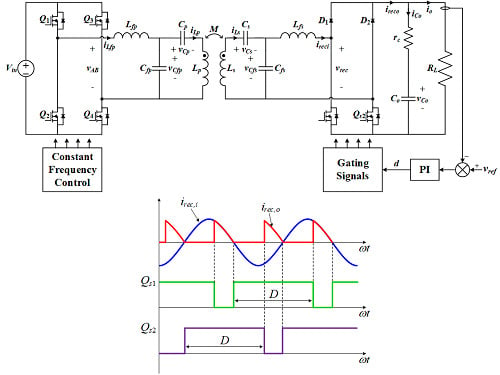
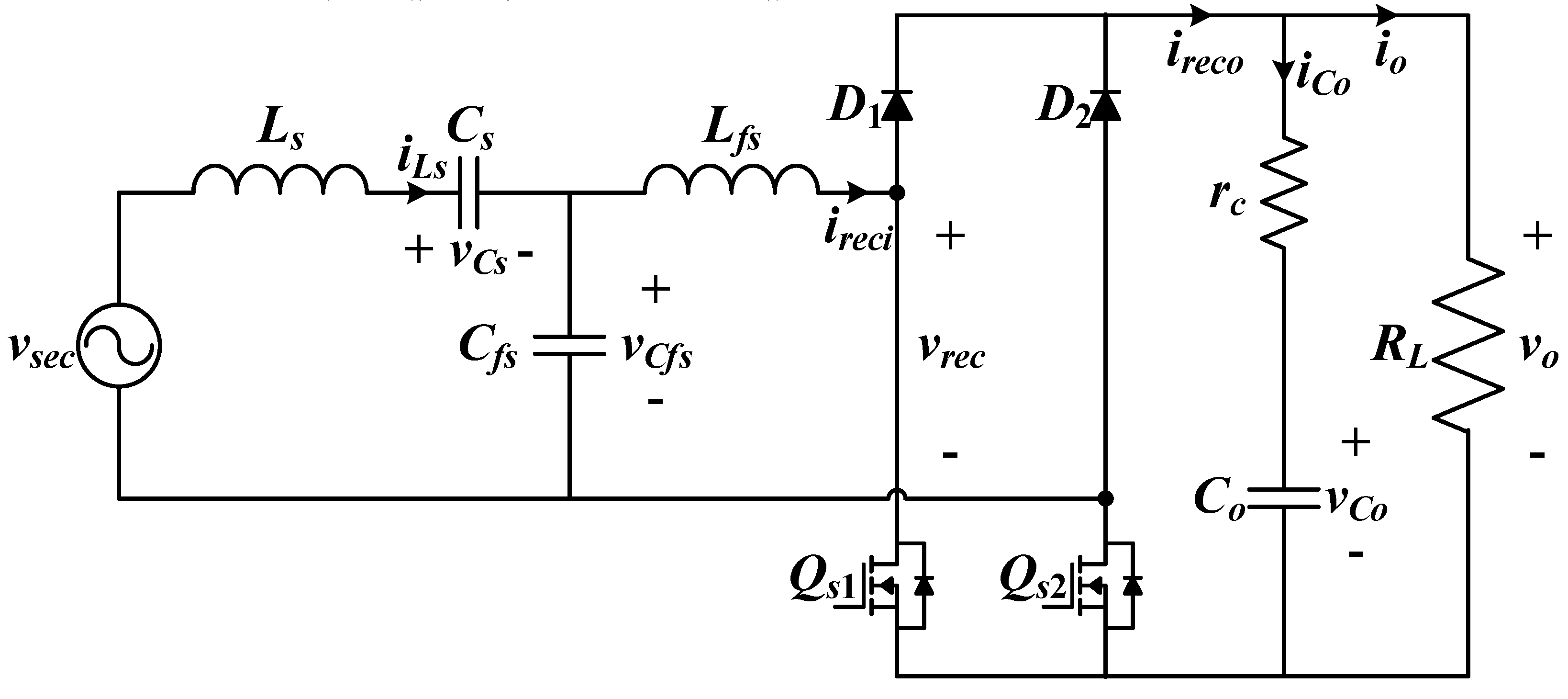
2. IPT System with S-BAR
2.1. System Description
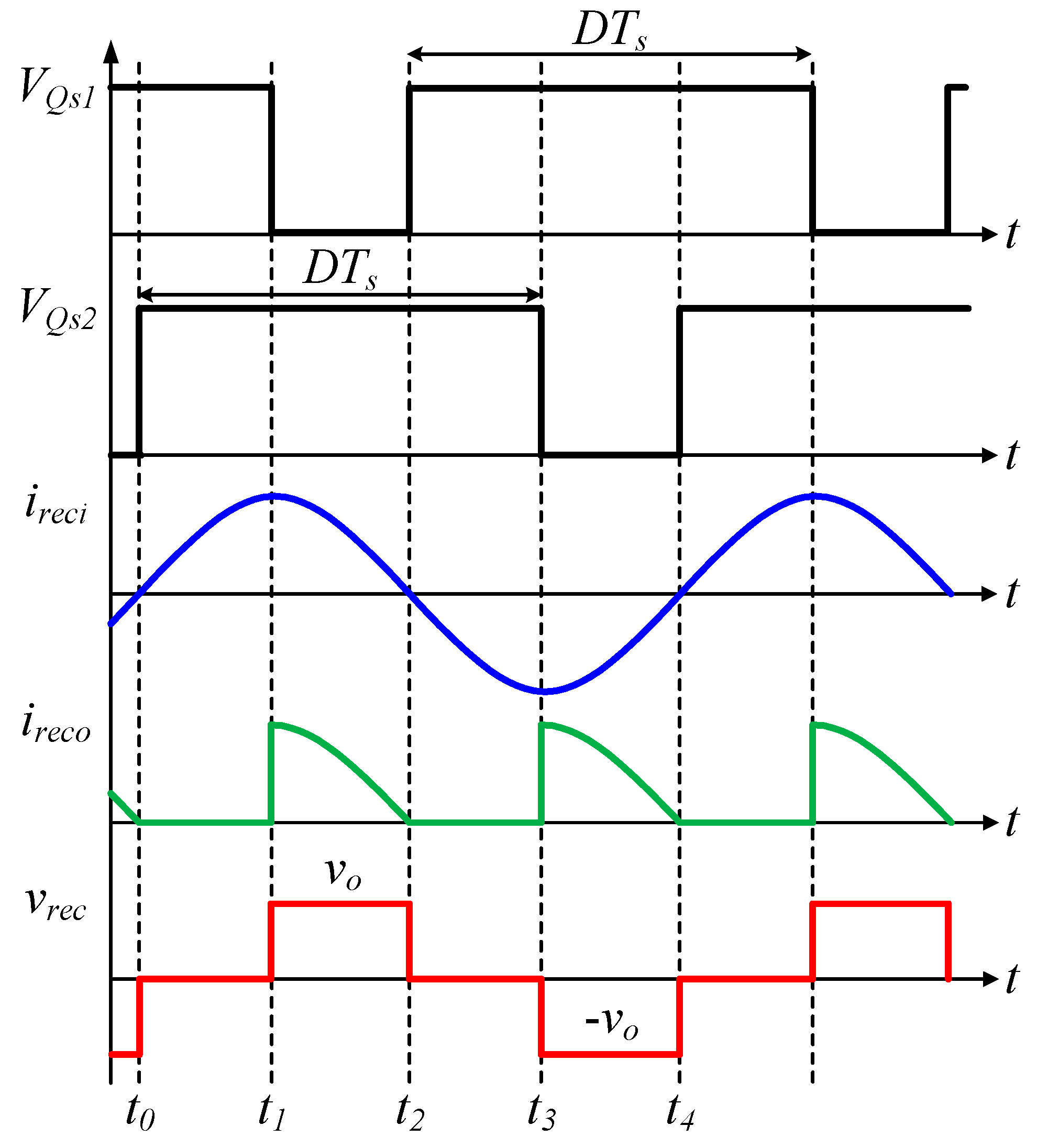
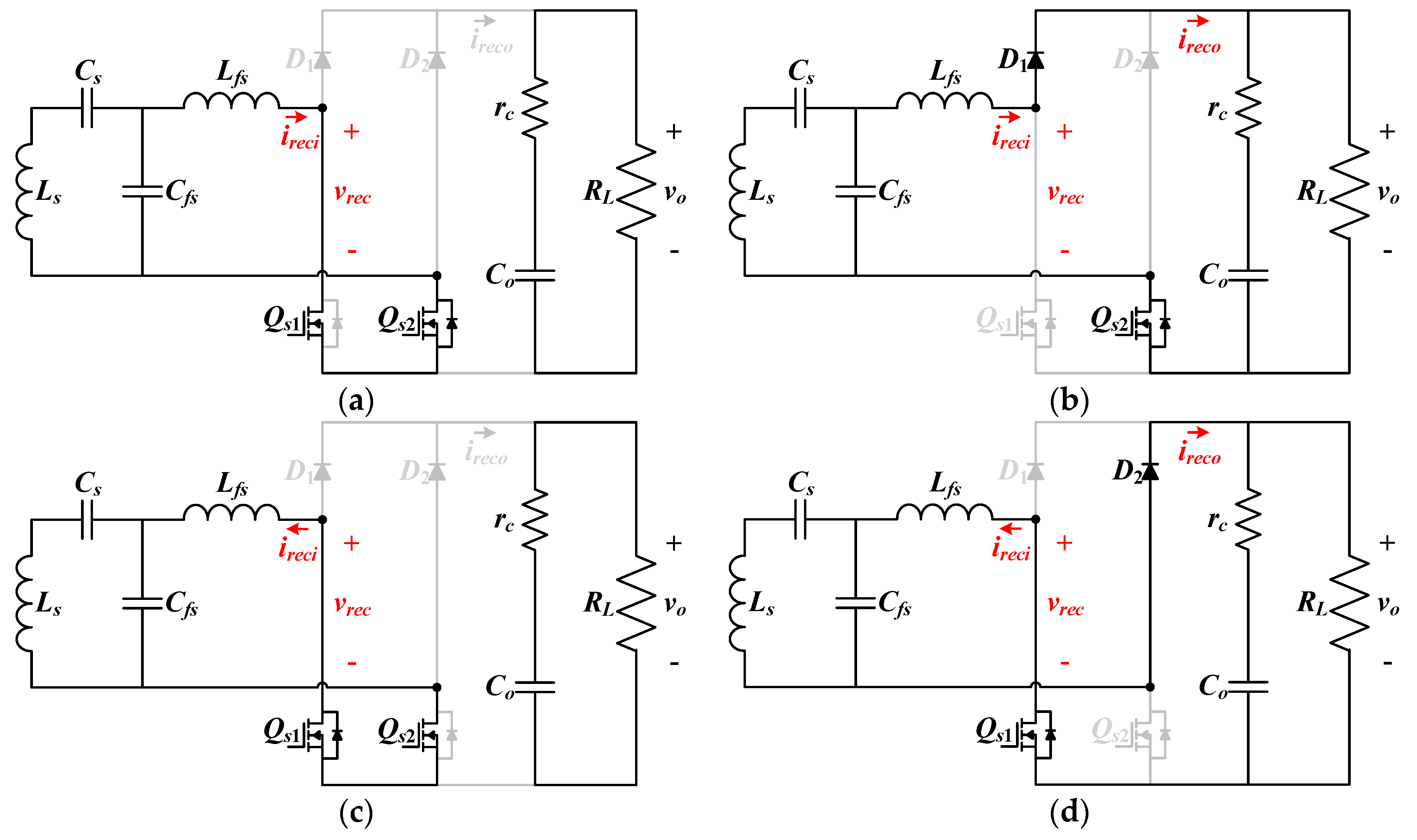
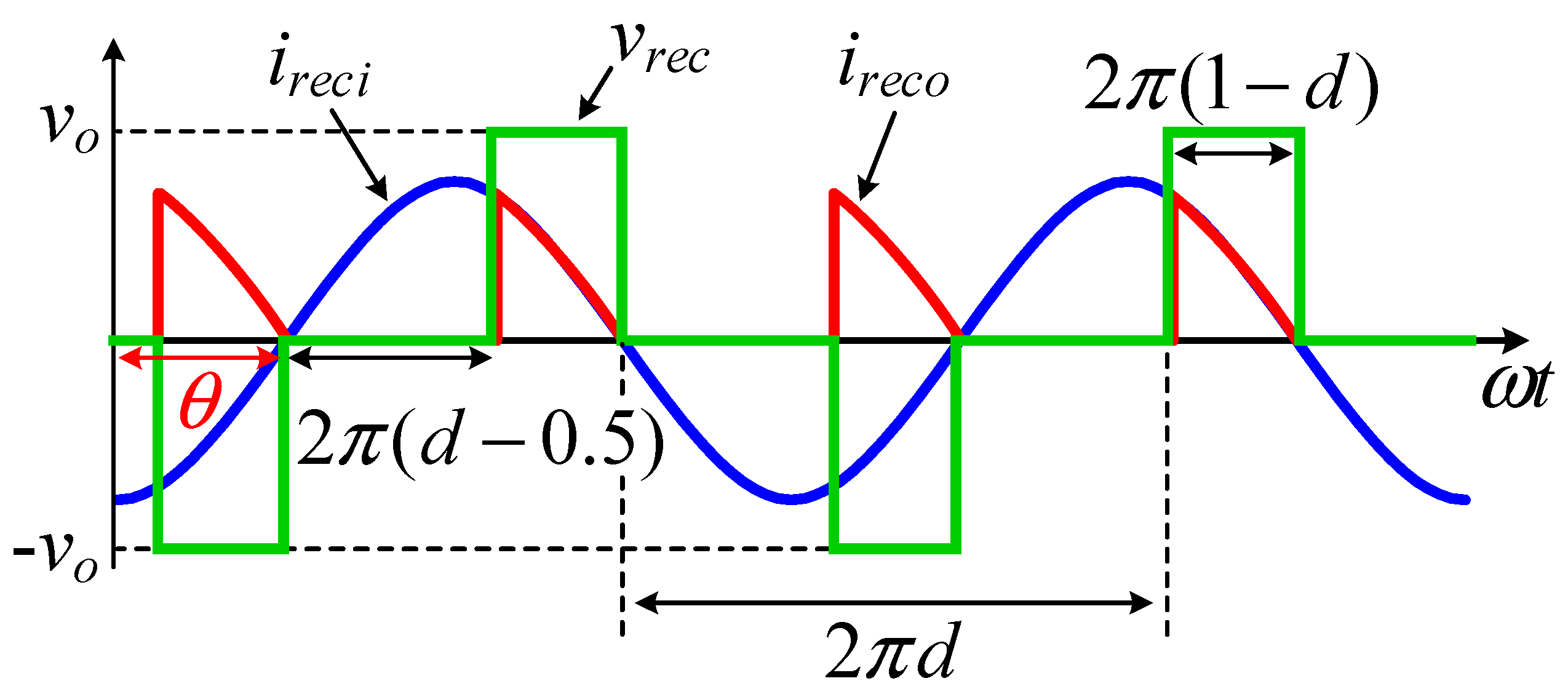
2.2. Operation Principle
3. Proposed Modeling
3.1. Nonlinear State Equations
3.2. Harmonic Approximation
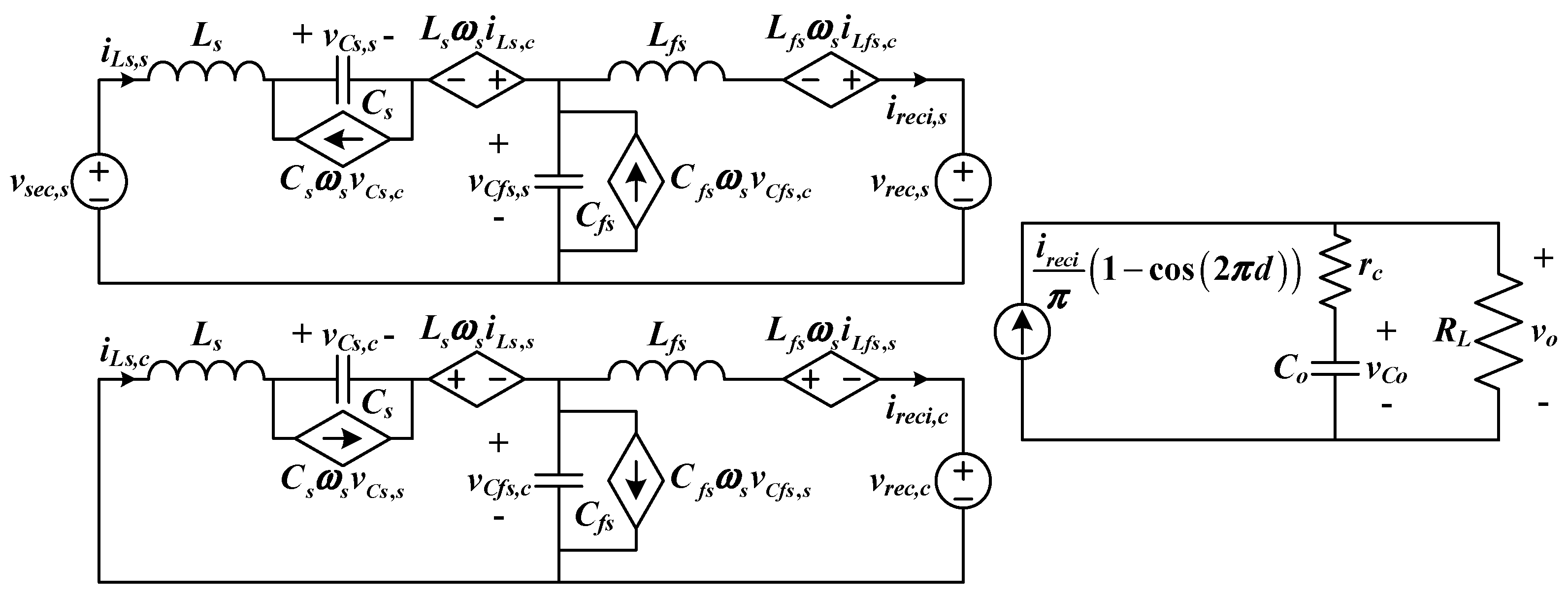
3.3. Extended Describing Functions
3.4. Harmonic Balance
3.5. Steady-State Solution
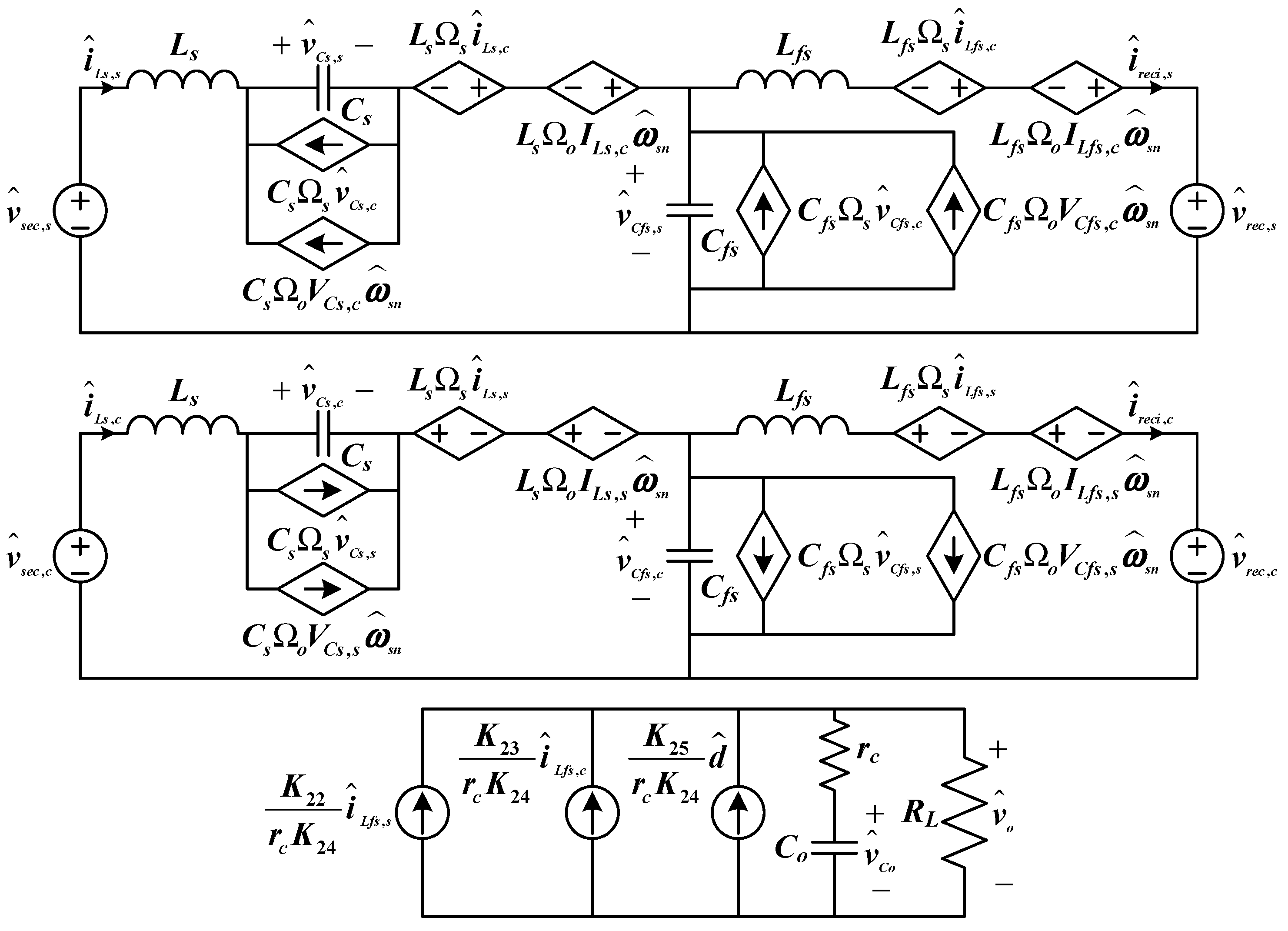
3.6. Perturbation and Linearization of Large-Signal Model
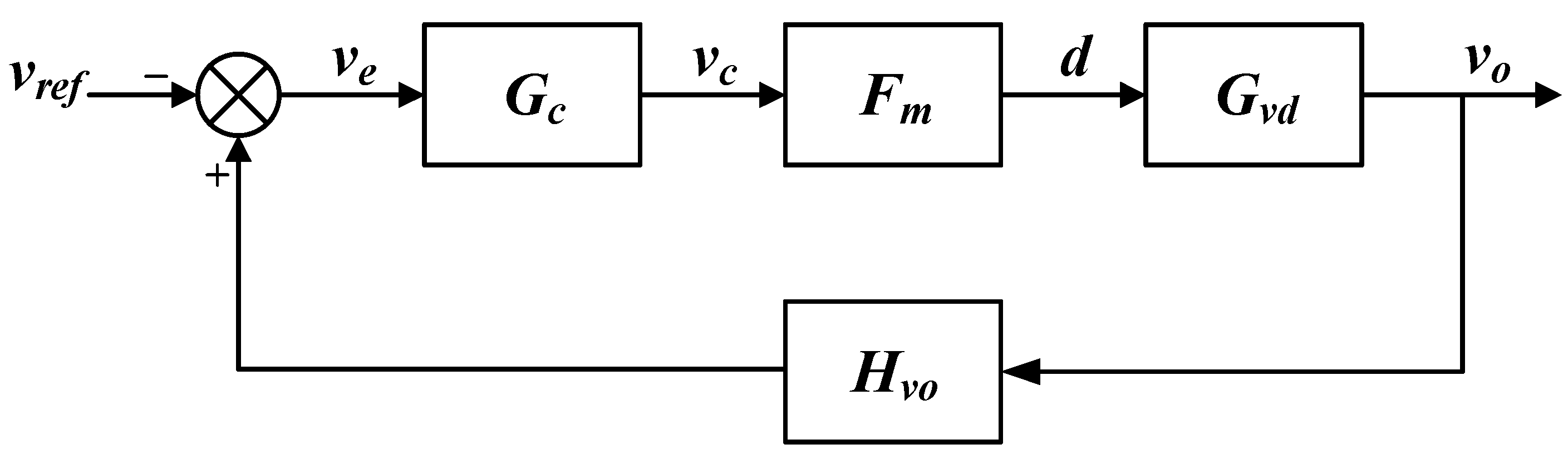
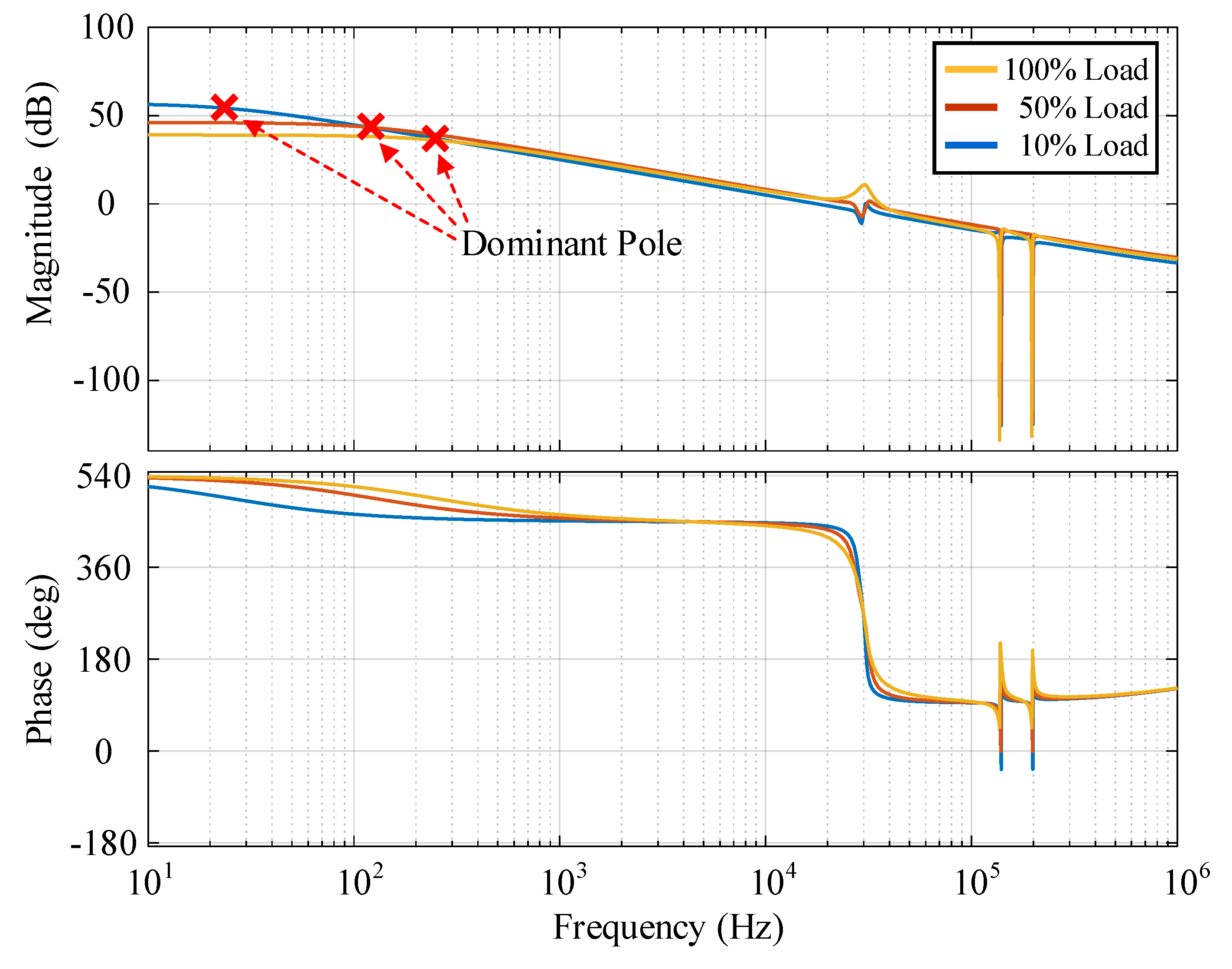
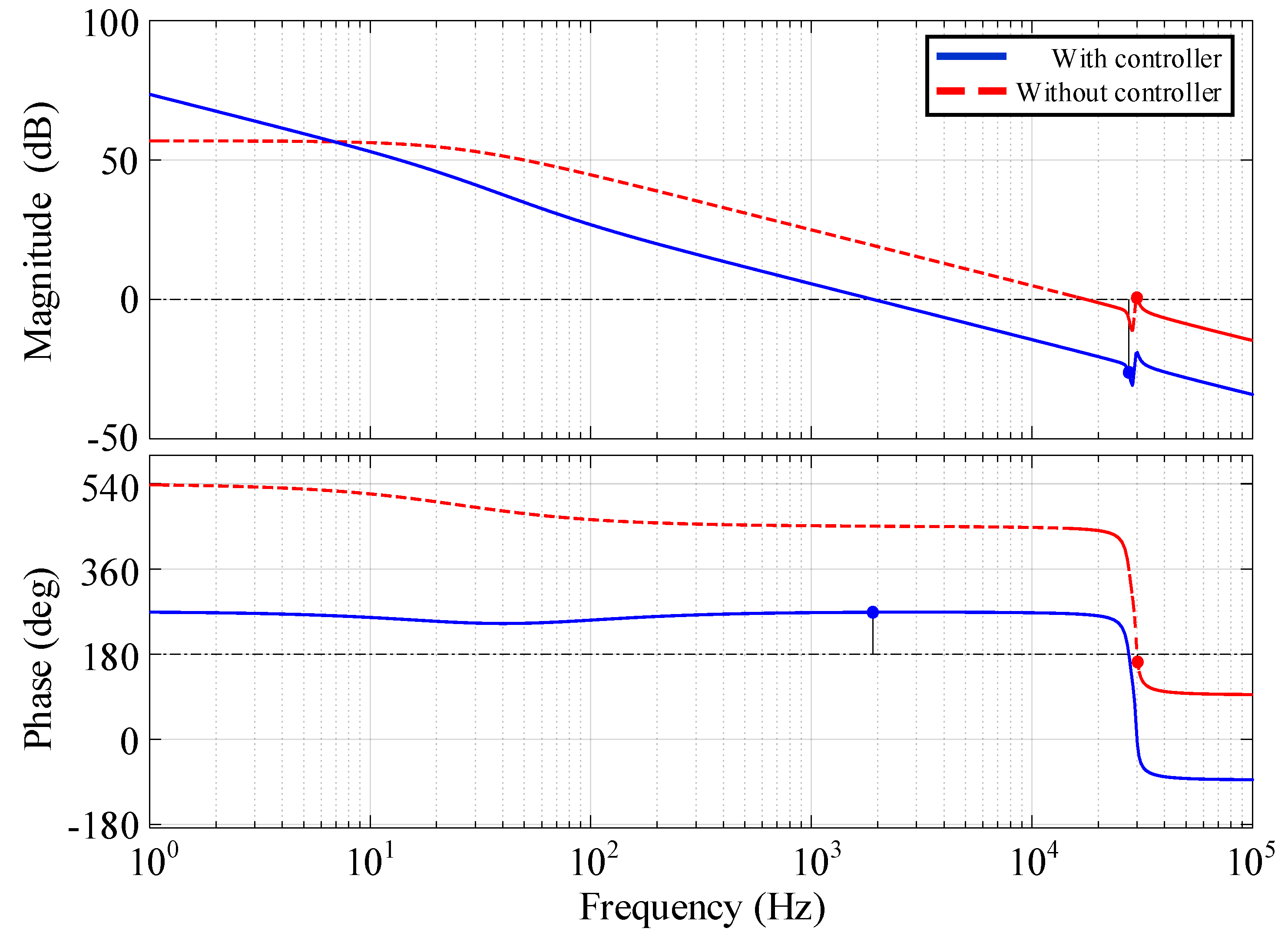
4. Controller Design
5. Experimental Results
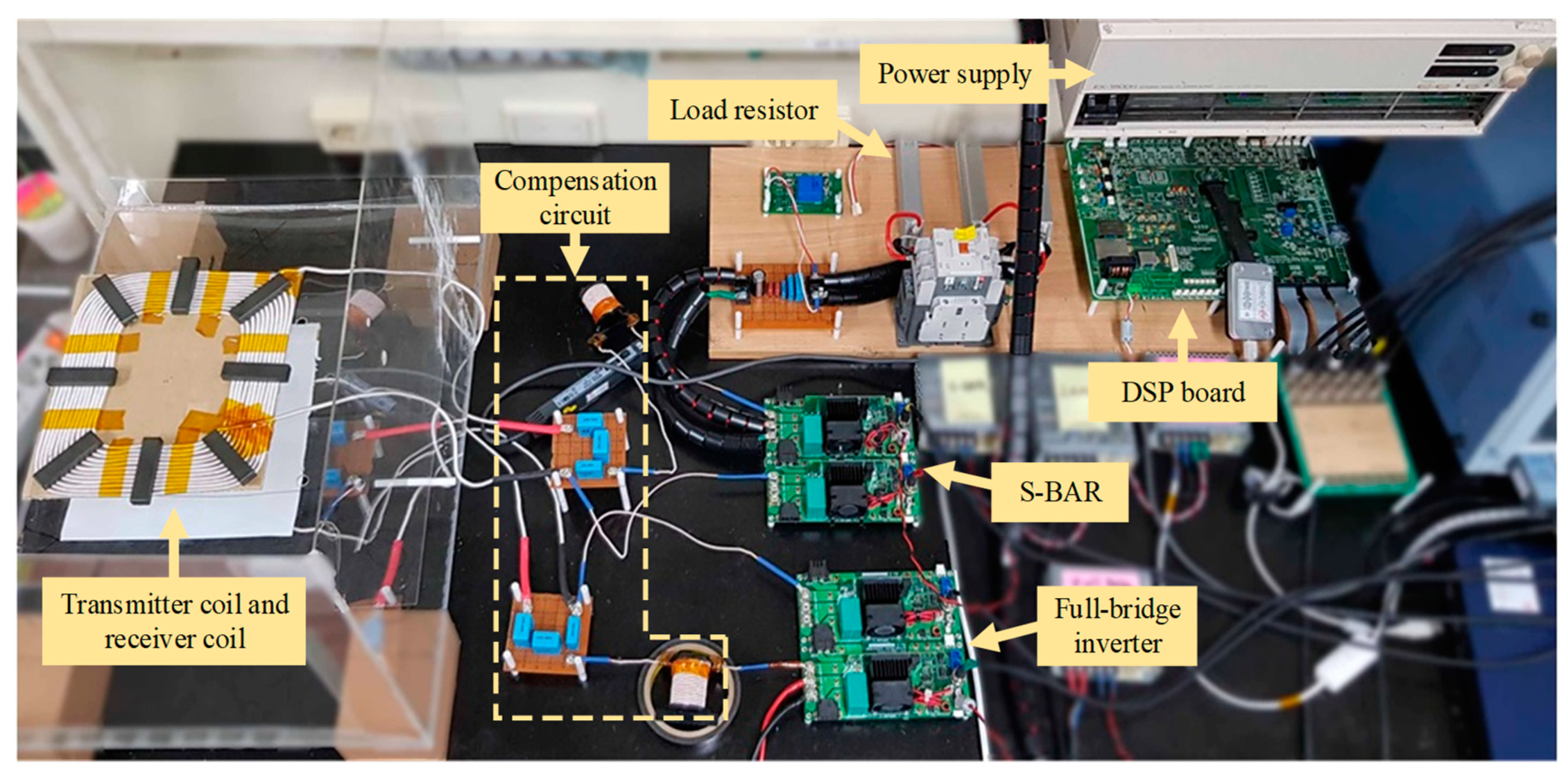
5.1. Test Setup
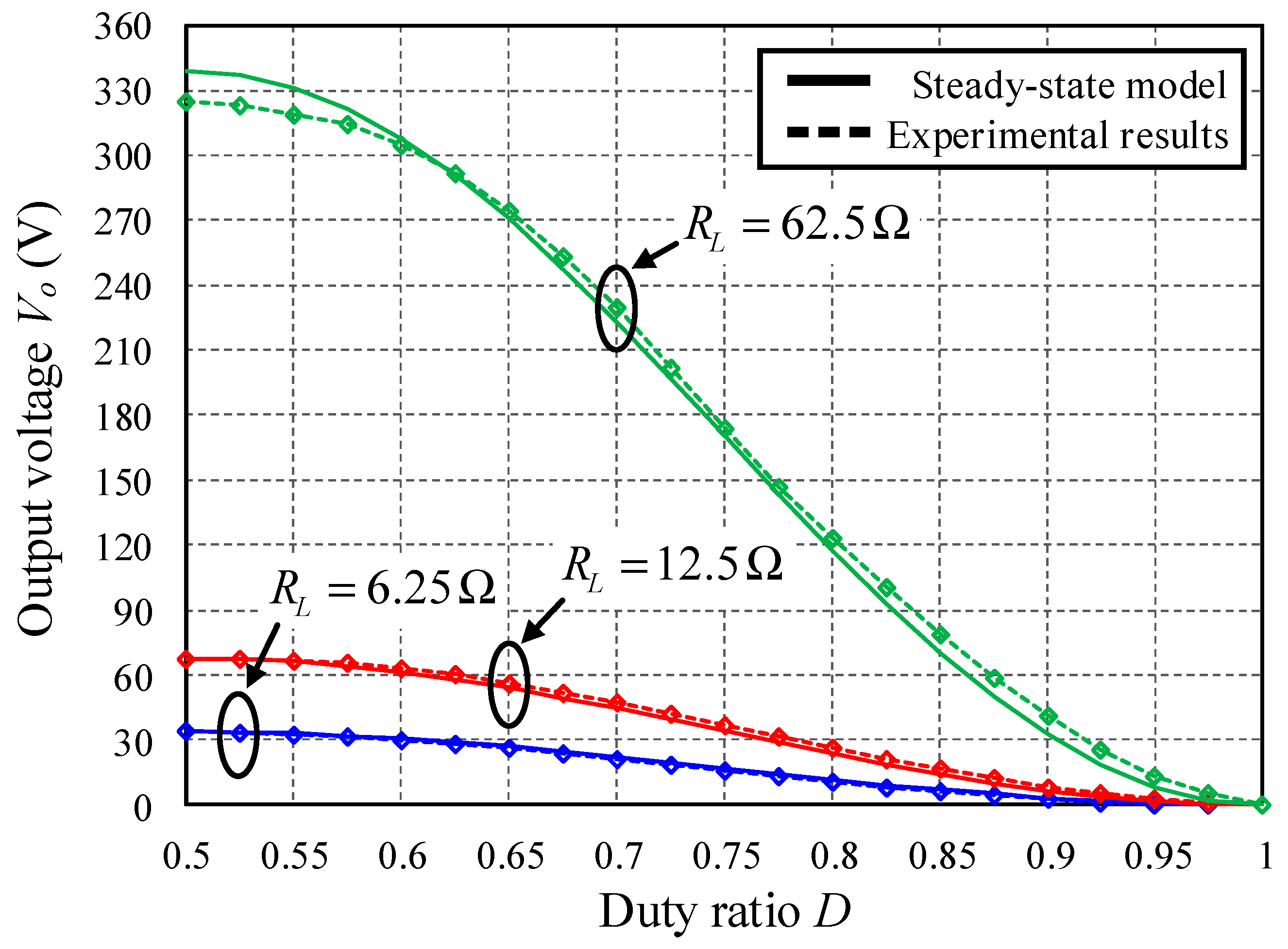
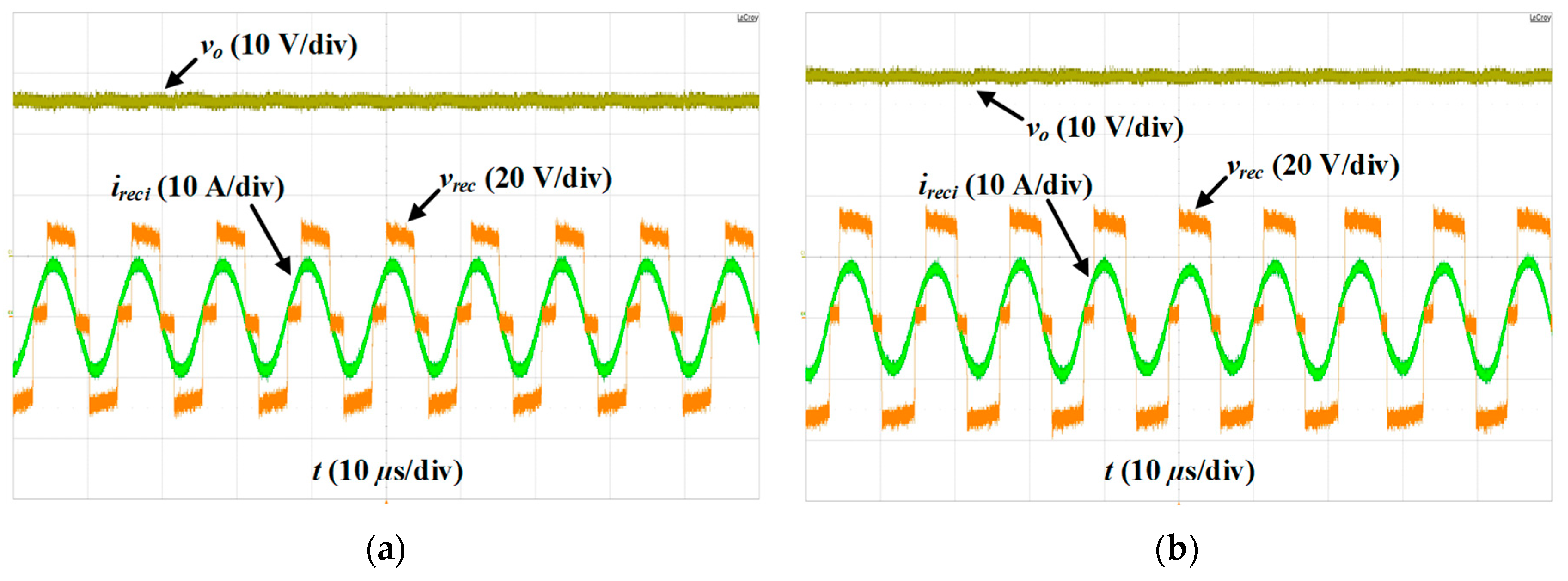
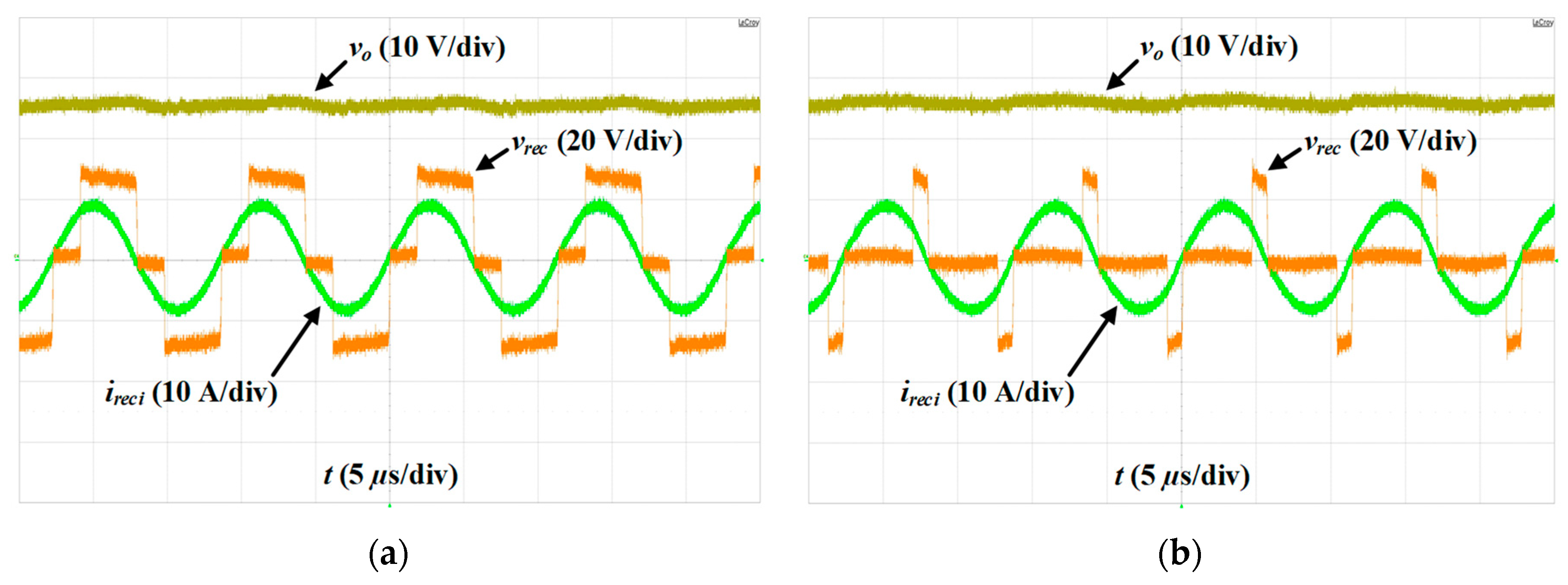
5.2. Verification of Steady-State Performance
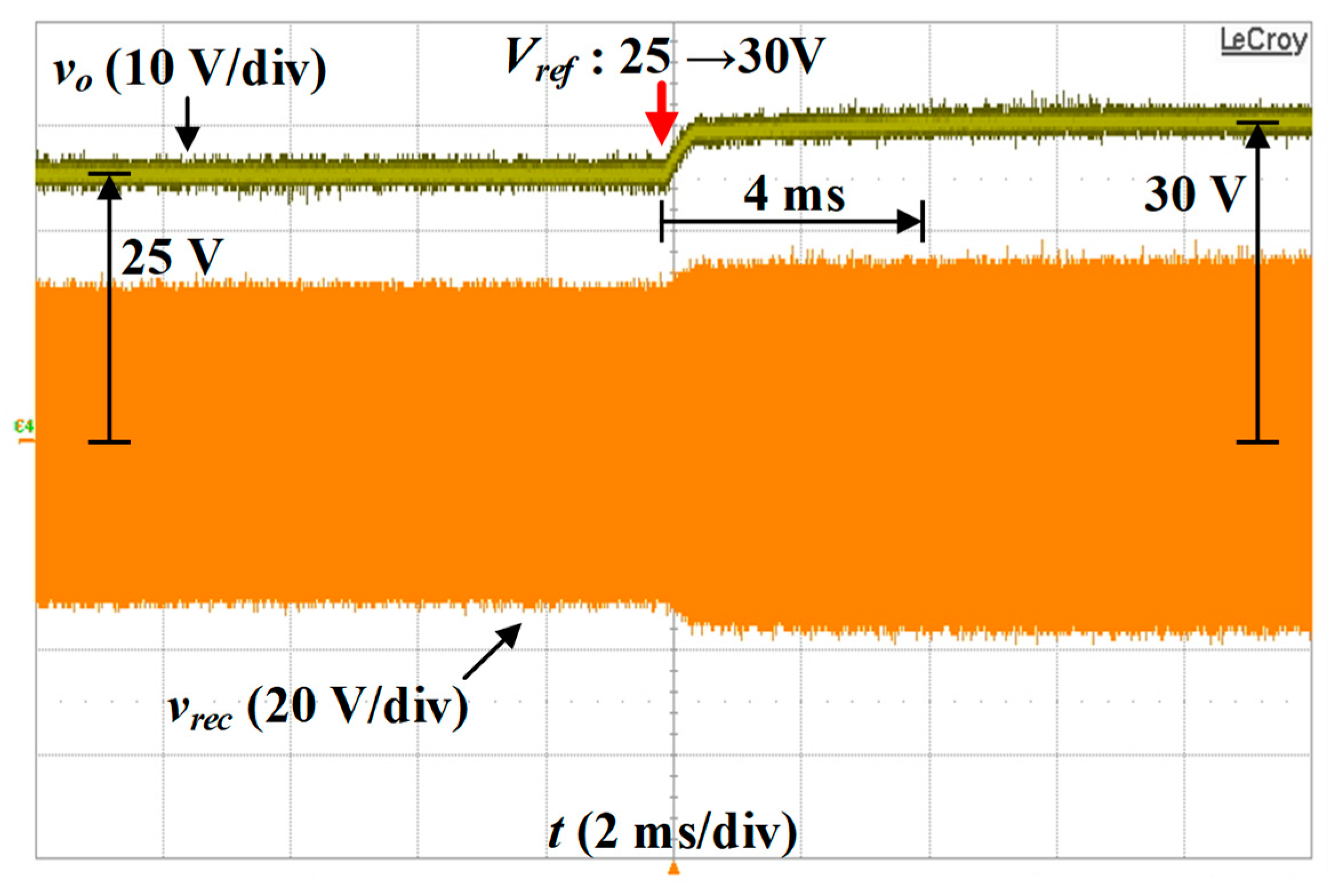
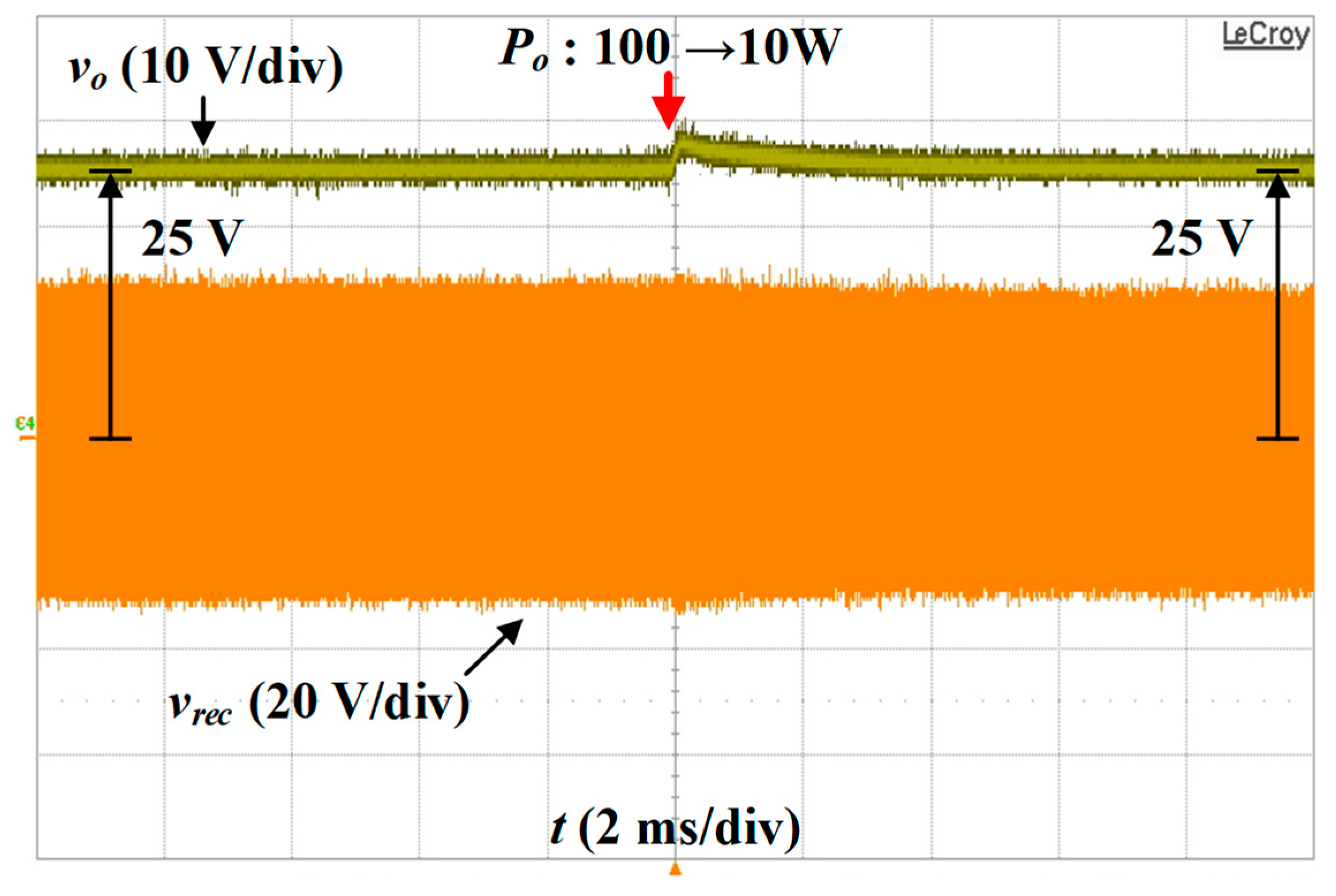
5.3. Transient Response Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Li, S.; Mi, C.C. Wireless power transfer for electric vehicle applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 4–17. [Google Scholar]
- Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Inductive power transfer. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Ludois, D.C. A survey of wireless power transfer and a critical comparison of inductive and capacitive coupling for small gap applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6017–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, N.A.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. A unity-power-factor IPT pickup for high-power applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wong, S.C.; Chi, K.T.; Chen, Q. Design for efficiency optimization and voltage controllability of series–series compensated inductive power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wong, S.C.; Chi, K.T.; Chen, Q. Analysis and comparison of secondary series-and parallel-compensated inductive power transfer systems operating for optimal efficiency and load-independent voltage-transfer ratio. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.H.; Choi, B.H.; Lee, E.S.; Lim, G.C.; Cho, G.-H.; Rim, C.T. General unified analyses of two-capacitor inductive power transfer systems: Equivalence of current-source SS and SP compensations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6030–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mi, C.C. Compensation topologies of high-power wireless power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 4768–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-S.; Stielau, O.H.; Covic, G. Design considerations for a contactless electric vehicle battery charger. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, W.; Deng, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Mi, C.C. A double-sided LCC compensation network and its tuning method for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Deng, J.; Li, S.; Mi, C.C. Comparison study on SS and double-sided LCC compensation topologies for EV/PHEV wireless chargers. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 4429–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Clare, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, J. A Design Method for Making an LCC Compensation Two-Coil Wireless Power Transfer System More Energy Efficient Than an SS Counterpart. Energies 2017, 10, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Deng, X.; Shu, W.; Wei, X.; Li, S. A New ZVS Tuning Method for Double-Sided LCC Compensated Wireless Power Transfer System. Energies 2018, 11, 307. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Li, W.; Nguyen, T.D.; Li, S.; Mi, C.C. Compact and efficient bipolar coupler for wireless power chargers: Design and analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6130–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Chu, H.; Wong, S.-C.; Chi, K.T. An IPT Battery Charger With Near Unity Power Factor and Load-Independent Constant Output Combating Design Constraints of Input Voltage and Transformer Parameters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 7719–7727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.-B.; Tran, D.-H.; Choi, W. Implementation of the constant current and constant voltage charge of inductive power transfer systems with the double-sided LCC compensation topology for electric vehicle battery charge applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 7398–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilian, M.; Guglielmi, P. Primary-Side Control of a Wireless Power Transfer System with Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology for Electric Vehicle Battery Charging. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Telecommunications Energy Conference (INTELEC), Turin, Italy, 7–11 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, A.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. The Load Estimation and Power Tracking Integrated Control Strategy for Dual-Sides Controlled LCC Compensated Wireless Charging System. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 75749–75761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.-B.; Phan, V.-T.; Dahidah, M.; Pickert, V. Multiple Output Inductive Charger for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 7350–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, J.-H.; Li, W.-J.; Zhu, G.-R. Realization of CC and CV Mode in IPT System Based on the Switching of Doublesided LCC and LCC-S Compensation Network. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Industrial Informatics-Computing Technology, Intelligent Technology, Industrial Information Integration (ICIICII), Wuhan, China, 3–4 December 2016; pp. 364–367. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, B.; Deng, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z. Secondary-side power control method for double-side LCC compensation topology in wireless EV charger application. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017–43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 7860–7865. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Boys, J.T.; Covic, G.A. LCL pickup circulating current controller for inductive power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 2081–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekhans, T.; De Doncker, R.W. A dual-side controlled inductive power transfer system optimized for large coupling factor variations and partial load. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6320–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Joo, D.-M.; Lee, B.K. High efficient power conversion circuit for inductive power transfer charger in electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 3rd International Future Energy Electronics Conference and ECCE Asia (IFEEC 2017-ECCE Asia), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 3–7 June 2017; pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Onar, O.C.; Galigekere, V.; Pries, J.; Su, G.-J.; Khaligh, A. Secondary Active Rectifier Control Scheme for a Wireless Power Transfer System with Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018–44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; pp. 2145–2150. [Google Scholar]
- Mishima, T.; Morita, E. High-frequency bridgeless rectifier based ZVS multiresonant converter for inductive power transfer featuring high-voltage GaN-HFET. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 9155–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Shi, L.; Yin, Z.; Li, Y. A novel pulse density modulation with semi-bridgeless active rectifier in inductive power transfer system for rail vehicle. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2017, 1, 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; Shi, L.; Yin, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, F. Improved Pulse Density Modulation for Semi-bridgeless Active Rectifier in Inductive Power Transfer System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 5893–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, K.; Asa, E.; Bojarski, M.; Czarkowski, D.; Onar, O.C. A novel phase-shift control of semibridgeless active rectifier for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6288–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, S.; Son, W.-J.; Byun, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, B.K. Switch Design for a High-Speed Switching Semi-Bridgeless Active Rectifier of Inductive Power Transfer Systems Considering Reverse Recovery Phenomenon. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia (ICPE 2019–ECCE Asia), Busan, Korea, 27–30 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Zhu, C.; Lu, R.; Song, K.; Wei, G. Modeling and design of control loop with semi-bridgeless rectifier in wireless charging system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia–Pacific), Harbin, China, 7–10 August 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, H.-R.; Park, K.-H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, R.-Y. Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology with Semi-Bridgeless Rectifier for Wireless Power Transfer System. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia (ICPE 2019–ECCE Asia), Busan, Korea, 27–30 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Cha, H.-R.; Jung, S.-M.; Kim, R.-Y. An Integrated Current-Voltage Compensator Design Method for Stable Constant Voltage and Current Source Operation of LLC Resonant Converters. Energies 2018, 11, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value (Unit) |
|---|---|
| Nominal input voltage (Vin) | 150 (V) |
| Output power (Po) | 100 (W) |
| Output voltage (Vin) | 25 (V) |
| Self-inductance of transmitter coil (Lp) | 48 (μH) |
| Self-inductance of receiver coil (Ls) | 48 (μH) |
| Primary side series compensation inductor (Lfp) | 18.2 (μH) |
| Secondary side series compensation inductor (Lfs) | 18.2 (μH) |
| Primary side series compensation capacitor (Cp) | 110 (nF) |
| Secondary side series compensation capacitor (Cs) | 110 (nF) |
| Primary side parallel compensation capacitor (Cfp) | 180 (nF) |
| Secondary side parallel compensation capacitor (Cfs) | 180 (nF) |
| Coupling coefficient (k) | 0.175 |
| Resonant frequency (fo) | 88 (kHz) |
| Output capacitor (Co) | 100 (μF) |
| ESR of output capacitor (rc) | 1 (mΩ) |
| Load resistance (RL) | 6.25–62.5 (Ω) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cha, H.-R.; Kim, R.-Y.; Park, K.-H.; Choi, Y.-J. Modeling and Control of Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology with Semi-Bridgeless Active Rectifier for Inductive Power Transfer System. Energies 2019, 12, 3921. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12203921
Cha H-R, Kim R-Y, Park K-H, Choi Y-J. Modeling and Control of Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology with Semi-Bridgeless Active Rectifier for Inductive Power Transfer System. Energies. 2019; 12(20):3921. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12203921
Chicago/Turabian StyleCha, Hwa-Rang, Rae-Young Kim, Kyung-Ho Park, and Yeong-Jun Choi. 2019. "Modeling and Control of Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology with Semi-Bridgeless Active Rectifier for Inductive Power Transfer System" Energies 12, no. 20: 3921. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12203921
APA StyleCha, H.-R., Kim, R.-Y., Park, K.-H., & Choi, Y.-J. (2019). Modeling and Control of Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology with Semi-Bridgeless Active Rectifier for Inductive Power Transfer System. Energies, 12(20), 3921. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12203921