Disintegration of Wastewater Activated Sludge (WAS) for Improved Biogas Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
- In agriculture, for growing crops,
- For the reclamation of land, including land for agricultural purposes,
- For the adaptation of land to specific needs resulting from waste management plans, spatial development plans or decisions on building and land development conditions,
- For the production of compost,
- For the cultivation of flora not intended for consumption [2].
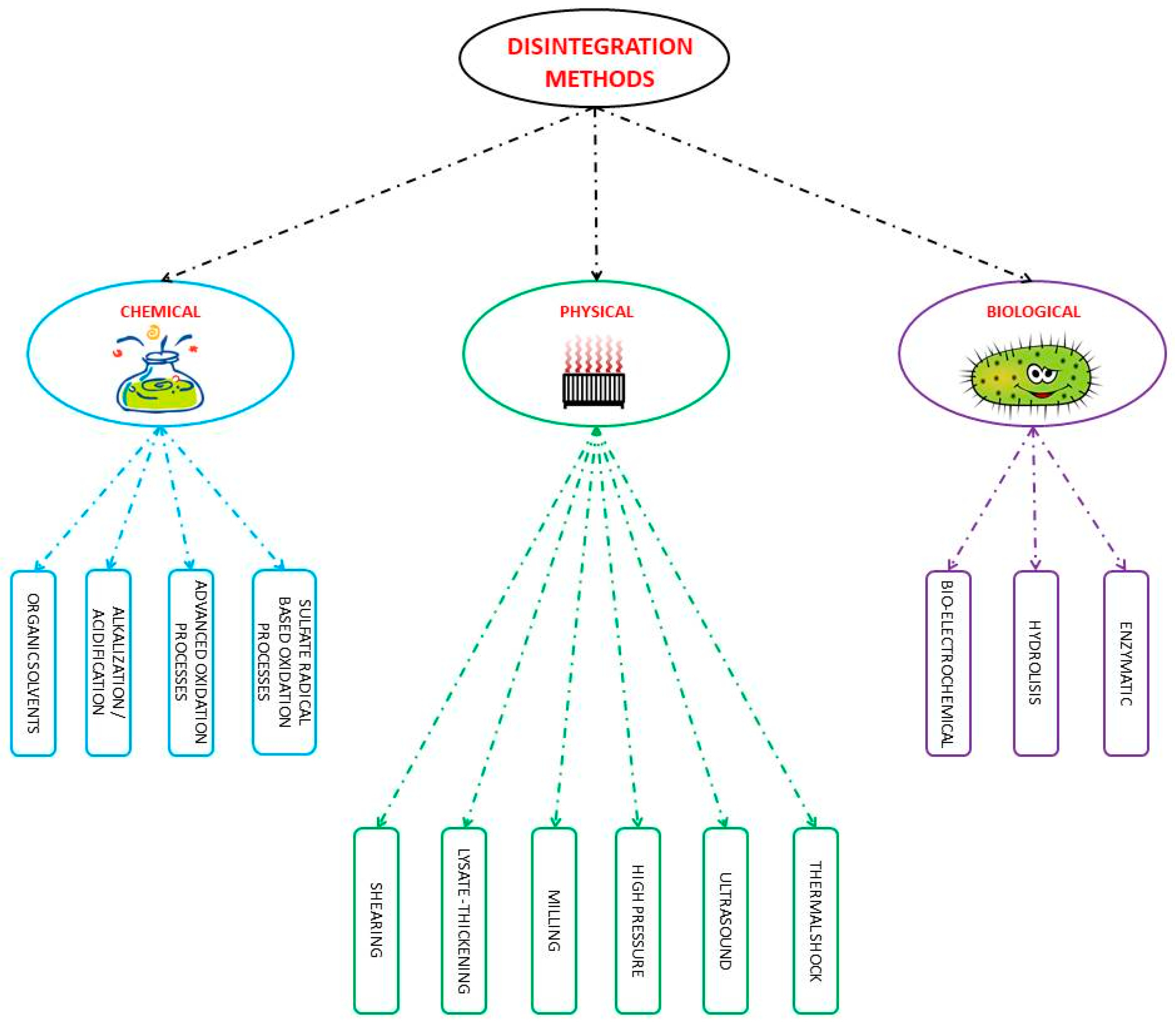
2. Pre-Treatment Methods
- Simple access to the organic substances that were trapped inside the biomass and their release into the supernatant/liquid phase, as well as to intracellular enzymes that cause direct decomposition of pollutants,
- Release of organic substrate (in the case of disintegration of surplus activated sludge; often represented as chemical oxygen demand (COD)) that can be an easily digestible organic carbon source for the denitrification process. The increase in COD solubilization can be often correlated with the increase in methane production [24],
- Removing activated sludge foam generated on the surface of bioreactors as well as elimination of foaming in digestion chambers and secondary settling tanks,
- Increase in the biogas production and biogas yield and hence energy production with faster digestion.
2.1. Biological
2.2. Chemical
2.3. Physical Methods
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Den, W.; Sharma, V.K.; Lee, M.; Nadadur, G.; Varma, R.S. Lignocellulosic Biomass Transformations via Greener Oxidative Pretreatment Processes: Access to Energy and Value-Added Chemicals. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lemos Chernicharo, C.A. Anaerobic Reactors; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007; ISBN 1843391643. [Google Scholar]
- Begum, L. Advanced Processes and Technologies for Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion; Green Nook Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2014; ISBN 0993904505. [Google Scholar]
- De Vrieze, J.; De Lathouwer, L.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. High-rate iron-rich activated sludge as stabilizing agent for the anaerobic digestion of kitchen waste. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3732–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. National Hazardous Waste Management Plan 2008–2012; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; ISBN 9781840952988.
- Fytili, D.; Zabaniotou, A. Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wzorek, M. Characterisation of the properties of alternative fuels containing sewage sludge. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 104, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiasson, A. Future of Biogas Europe. Available online: www.european-biogas.eu (accessed on 6 October 2018).
- Banu, J.R.; Kavitha, S. Various Sludge Pretreatments: Their Impact on Biogas Generation. In Waste Biomass Management—A Holistic Approach; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 39–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah Khan, I.; Hafiz Dzarfan Othman, M.; Hashim, H.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F.; Rezaei-DashtArzhandi, M.; Wan Azelee, I. Biogas as a renewable energy fuel—A review of biogas upgrading, utilisation and storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 150, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasi, S.; Veijanen, A.; Rintala, J. Trace compounds of biogas from different biogas production plants. Energy 2007, 32, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deublein, D.; Steinhauser, A. Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources: An Introduction; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; ISBN 9783527621705. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, T.; Edwards, E.A. Anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper mill wastewater and sludge. Water Res. 2014, 65, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, S.F.; Stuckey, D.C. Integrated model of the production of soluble microbial products (SMP) and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in anaerobic chemostats during transient conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 38, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.D.; Seon, J.; Lee, S.C.; Song, M.; Woo, H.-C. Maximization of volatile fatty acids production from alginate in acidogenesis. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, G.; Lu, X.; Kato, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.-Y. Overview of pretreatment strategies for enhancing sewage sludge disintegration and subsequent anaerobic digestion: Current advances, full-scale application and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujer, W.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Conversion processes in anaerobic digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 1983, 15, 127–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.A. Prospects and problems of sludge pre-treatment processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzynczyk, J. Enzymatic Treatment of Wastewater Sludge. Sludge Solubilisation, Improvement of Anaerobic Digestion and Extraction of Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Ph.D. Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Beijer, R. Enzymatic Treatement of Wastewater Sludge in Presence of a Cation Binding Agent: Improved Solubilisation and Increased Methane Production. Master’s Thesis, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, W.; Zhang, S.; Liang, S.; Song, J.; Xu, Q.; Ye, N.; He, S.; Yang, C.; et al. Synergetic conditioning of sewage sludge via Fe2+/persulfate and skeleton builder: Effect on sludge characteristics and dewaterability. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, S.F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrère, H.; Bougrier, C.; Castets, D.; Delgenès, J.P. Impact of initial biodegradability on sludge anaerobic digestion enhancement by thermal pretreatment. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2008, 43, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Jiang, J.-Q.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Lee, D.-J.; Wang, K.; Qiu, W. Conditioning of wastewater sludge using freezing and thawing: Role of curing. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5969–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka, E.; Machnicka, A.; Grübel, K. Improving of anaerobic digestion by dry ice disintegration of activated sludge. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2014, 21, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Kang, X. Effect of endogenous hydrolytic enzymes pretreatment on the anaerobic digestion of sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaze, W.H.; Kang, J.-W.; Chapin, D.H. The Chemistry of Water Treatment Processes Involving Ozone, Hydrogen Peroxide and Ultraviolet Radiation. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1987, 9, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, S.E.; Wukasch, R.F. A hydrolysis/thickening/filtration process for the treatment of waste activated sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 30, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grübel, K.; Suschka, J. Hybrid alkali-hydrodynamic disintegration of waste-activated sludge before two-stage anaerobic digestion process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 7258–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubel, K.; Machnicka, A.; Waclawek, S. Impact of alkalization of surplus activated sludge on biogas production. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2013, 20, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogate, P.R.; Shirgaonkar, I.Z.; Sivakumar, M.; Senthilkumar, P.; Vichare, N.P.; Pandit, A.B. Cavitation reactors: Efficiency assessment using a model reaction. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 2526–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machnicka, A.; Grubel, K.; Suschka, J. The use of hydrodynamic disintegration as a means to improve anaerobic digestion of activated sludge. Water SA 2009, 35, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J. Disintegration as a key-step in sewage sludge treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, A.; Poulios, I.; Nikolakaki, E.; Mantzavinos, D. Sonochemical disinfection of municipal wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W. Ultrasonic treatment of biological sludge: Floc disintegration, cell lysis and inactivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Zhang, J.; Raga, R.; Lavagnolo, M.C.; Pivato, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cossu, R.; Yue, D. Effectiveness of aerobic pretreatment of municipal solid waste for accelerating biogas generation during simulated landfilling. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrère, H.; Dumas, C.; Battimelli, A.; Batstone, D.J.; Delgenès, J.P.; Steyer, J.P.; Ferrer, I. Pretreatment methods to improve sludge anaerobic degradability: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrylin, J.; Kumar, S.A.; Kaliappan, S.; Yeom, I.-T.; Banu, J.R. Biological pretreatment of non-flocculated sludge augments the biogas production in the anaerobic digestion of the pretreated waste activated sludge. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreeyessus, G.D.; Jenicek, P. Thermophilic versus Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge: A Comparative Review. Bioengineering 2016, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; Vázquez, F.; Font, X. Long term operation of a thermophilic anaerobic reactor: Process stability and efficiency at decreasing sludge retention time. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsá, S.; Ferrer, I.; Vázquez, F.; Font, X. Optimization of the hydrolytic–acidogenic anaerobic digestion stage (55 °C) of sewage sludge: Influence of pH and solid content. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Jensen, P.D.; Batstone, D.J. Temperature phased anaerobic digestion increases apparent hydrolysis rate for waste activated sludge. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.M.; Park, S.K.; Ha, J.H.; Park, J.M. Microbial community structure in a thermophilic aerobic digester used as a sludge pretreatment process for the mesophilic anaerobic digestion and the enhancement of methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Vila, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Astals, S. The role of additives on anaerobic digestion: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzila, A. Mini review: Update on bioaugmentation in anaerobic processes for biogas production. Anaerobe 2017, 46, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapinagsorn, W.; Sittijunda, S.; Reungsang, A. Co-digestion of napier grass and its silage with cow dung for methane production. Energies 2017, 10, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Liu, H.; Wu, M.; Zeng, G.; Yang, C. Roles of acid-producing bacteria in anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.Y.; Chai, T.Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, Y.N.; Cao, Y.H.; Li, X.J.; Xie, Y.H.; Han, J.; Zhu, T. Review of Excess Sludge Disintegration Research. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 726–731, 2949–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi Kumar, S.; Merrylin, J.; Kaliappan, S.; Adish Kumar, S.; Tae Yeom, I.; Rajesh Banu, J. Effect of cation binding agents on sludge solubilization potential of bacteria. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2012, 17, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, M.E.; Le, M.S.; Ratcliff, R. A novel approach to pathogen reduction in biosolids: The enzymic hydrolyser. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayhew, M.; Le, M.S.; Brade, C.E.; Harrison, D. The united utitlities ‘enzymic hydrolysis process’—Validation of phased digestion at full scale to enhance pathogen removal. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2003, 2003, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, M.S.; Tada, C.; Sawayama, S. Enhancement of Biogas Production from Sewage Sludge with the Addition of Geobacillus sp. Strain AT1 Culture. Jpn. J. Water Treat. Biol. 2004, 40, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzynczyk, J.; Norrlöw, O.; Dey, E.; la Cour Jansen, J. Alternative Method for Sludge Reduction Using Commercial Enzymes. In Proceedings of the Aqua Enviro European Biosolids and Organic Residuals Conference, Wakefield, West Yorkshire, UK, 24–26 November 2003; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Davidsson, Å.; Wawrzynczyk, J.; Norrlöw, O.; la Cour Jansen, J. Strategies for enzyme dosing to enhance anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2007, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Recktenwald, M.; Wawrzynczyk, J.; Dey, E.S.; Norrlöw, O. Enhanced efficiency of industrial-scale anaerobic digestion by the addition of glycosidic enzymes. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 43, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Cho, H.U.; Park, S.K.; Ha, J.H.; Park, J.M. Influence of thermophilic aerobic digestion as a sludge pre-treatment and solids retention time of mesophilic anaerobic digestion on the methane production, sludge digestion and microbial communities in a sequential digestion process. Water Res. 2014, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayr, S.; Kaparaju, P.; Rintala, J. Screening pretreatment methods to enhance thermophilic anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper mill wastewater treatment secondary sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, S.; Jayashree, C.; Adish Kumar, S.; Yeom, I.T.; Rajesh Banu, J. The enhancement of anaerobic biodegradability of waste activated sludge by surfactant mediated biological pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.; Ferrer, I.; Baeza, M.; Artola, A.; Vázquez, F.; Font, X. Effects of thermal and mechanical pretreatments of secondary sludge on biogas production under thermophilic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 133, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjenbruch, M.; Kopplow, O. Enzymatic, mechanical and thermal pre-treatment of surplus sludge. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, S.; Shiota, N.; Katsura, K.; Akashi, A. Solubilization of organic sludge by thermophilic aerobic bacteria as a pretreatment for anaerobic digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, K.B.; Singh, R. Kinetic modelling of methane production during bio-electrolysis from anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, C.; Kim, T.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Eung-wook Kim, S.; Lee, J. Effects of Various Pretreatments for Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion with Waste Activated Sludge. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 95, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiba Karthikeyan, O.; Trably, E.; Mehariya, S.; Bernet, N.; Wong, J.W.C.; Carrere, H. Pretreatment of food waste for methane and hydrogen recovery: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, G.; Ye, L.; Yuan, Z. Enhancing methane production from waste activated sludge using combined free nitrous acid and heat pre-treatment. Water Res. 2014, 63, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, D.; Wacławek, S.; Gončuková, Z.; Padil, V.V.T.; Grübel, K.; Černík, M. A new method for assessment of the sludge disintegration degree with the use of differential centrifugal sedimentation. Environ. Technol. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Han, J.-I. The effects of waste-activated sludge pretreatment using hydrodynamic cavitation for methane production. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modenbach, A.A.; Nokes, S.E. The use of high-solids loadings in biomass pretreatment—A review. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 1430–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonglertarak, W.; Wichitsathian, B. Alkaline Pretreatment of Waste Activated Sludge in Anaerobic Digestion. J. Clean Energy Technol. 2014, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, K.; El-Din, M.G. Degradation of recalcitrant surfactants in wastewater by ozonation and advanced oxidation processes: A review. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2004, 26, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Smith, D.W.; El-Din, M.G. Application of advanced oxidation methods for landfill leachate treatment—A review. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2003, 2, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, M.; Ried, A.; Koll, R. Sludge treatment by ozonation Ð evaluation of full-scale results. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbajo, J.B.; Petre, A.L.; Rosal, R.; Berná, A.; Letón, P.; García-Calvo, E.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A. Ozonation as pre-treatment of activated sludge process of a wastewater containing benzalkonium chloride and NiO nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A. Combination of Advanced Oxidation Processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4141–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.; Lee, D.; Chang, B.-V.; You, C.; Tay, J. “Weak” ultrasonic pre-treatment on anaerobic digestion of flocculated activated biosolids. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2681–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.; Camacho, P.; Sperandio, M.; Ginestet, P. Technical and Economical Evaluation of a Thermal, and Two Oxidative Techniques for the Reduction of Excess Sludge Production. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2006, 84, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saktaywin, W.; Tsuno, H.; Nagare, H.; Soyama, T.; Weerapakkaroon, J. Advanced sewage treatment process with excess sludge reduction and phosphorus recovery. Water Res. 2005, 39, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, I.T.; Lee, K.R.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, S.H. Effects of ozone treatment on the biodegradability of sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrier, C.; Battimelli, A.; Delgenes, J.-P.; Carrere, H. Combined Ozone Pretreatment and Anaerobic Digestion for the Reduction of Biological Sludge Production in Wastewater Treatment. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2007, 29, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valo, A.; Carrère, H.; Delgenès, J.P. Thermal, chemical and thermo-chemical pre-treatment of waste activated sludge for anaerobic digestion. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, M.S.; Muz, M.; Komesli, O.T.; Gökçay, C.F. Enhancement of bio-gas production and xenobiotics degradation during anaerobic sludge digestion by ozone treated feed sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, G.; Ruiz, B.; Fiter, M.; Ferrer, C.; Berlanga, J.G.; Alonso, S.; Canut, A. Ozonation as a Pre-treatment for Anaerobic Digestion of Waste-Activated Sludge: Effect of the Ozone Doses. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2015, 37, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballa, M.; Manterola, G.; Larrea, L.; Ternes, T.; Omil, F.; Lema, J.M. Influence of ozone pre-treatment on sludge anaerobic digestion: Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougrier, C.; Delgenès, J.-P.; Carrère, H. Combination of Thermal Treatments and Anaerobic Digestion to Reduce Sewage Sludge Quantity and Improve Biogas Yield. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2006, 84, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battimelli, A.; Millet, C.; Delgenès, J.P.; Moletta, R. Anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge combined with ozone post-treatment and recycling. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbusinski, K. Fenton reaction—Controversy concerning the chemistry. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2009, 16, 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Dewil, R.; Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J. Peroxidation enhances the biogas production in the anaerobic digestion of biosolids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallaji, S.M.; Torabian, A.; Aminzadeh, B.; Zahedi, S.; Eshtiaghi, N. Improvement of anaerobic digestion of sewage mixed sludge using free nitrous acid and Fenton pre-treatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, S.; Vielma, S.; Borja, R.; Huiliñir, C.; Guerrero, L. Increase in biogas production in anaerobic sludge digestion by combining aerobic hydrolysis and addition of metallic wastes. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.; Al-Talhi, H.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; Kumar, R.; Barakat, M.A. Visible light photocatalytic disintegration of waste activated sludge for enhancing biogas production. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacławek, S.; Grübel, K.; Chłąd, Z.; Dudziak, M.; Chład, Z.; Dudziak, M.; Chłąd, Z.; Dudziak, M. Impact of peroxydisulphate on disintegration and sedimentation properties of municipal wastewater activated sludge. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.D.; Liang, H.M.; Ma, C. Enhancement of Sewage Sludge Anaerobic Digestibility by Sulfate Radical Pretreatment. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 518–523, 3358–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, B.; Chen, X. Sulfate radical-based oxidation for sludge treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by sludge-derived biochar for the degradation of triclosan in water and wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 356, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Xie, W.; Fan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Kong, D.; Lu, J. Degradation of trimethoprim by thermo-activated persulfate oxidation: Reaction kinetics and transformation mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Shin, W.S.; Hwang, I. Activation of Persulfate by Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron (NZVI): Mechanisms and Transformation Products of NZVI. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Sun, P.; Boyer, T.H.; Zhao, L.; Huang, C.-H. Degradation of Pharmaceuticals and Metabolite in Synthetic Human Urine by UV, UV/H2O2, and UV/PDS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3056–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, R.L.; Crimi, M.; Brown, R. In Situ Chemical Oxidation: Technology Description and Status; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4419-7825-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wacławek, S.; Lutze, H.V.; Grübel, K.; Padil, V.V.T.; Černík, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J. A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Niu, J.; Dai, J.; Li, N.; Zhou, P.; Niu, J.; Zhang, J.; Tao, H.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Z. New insights into the enhancement of biochemical degradation potential from waste activated sludge with low organic content by Potassium Monopersulfate treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godvin Sharmila, V.; Rajesh Banu, J.; Gunasekaran, M.; Angappane, S.; Yeom, I.T. Nano-layered TiO2 for effective bacterial disintegration of waste activated sludge and biogas production. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2701–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Hou, H. Studies on Effect of Peracetic Acid Pretreatment on Anaerobic Fermentation Biogas Production from Sludge. In Proceedings of the 2009 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, Wuhan, China, 27–31 March 2009; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zábranská, J.; Dohányos, M.; Jenícek, P.; Kutil, J. Disintegration of excess activated sludge—Evaluation and experience of full-scale applications. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, A.; Mahmood, T. Pretreatment technologies for advancing anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper biotreatment residues. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4273–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhart, M.; Krueger, M.; Kopp, J.; Dichtl, N. Effects of disintegration on anaerobic degradation of sewage excess sludge in downflow stationary fixed film digesters. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.S.; Pandit, A.B. Modeling Hydrodynamic Cavitation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 1999, 22, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grűbel, K.; Machnicka, A. Use of Hydrodynamic Disintegration to Accelerate Anaerobic Digestion of Surplus Activated Sludge. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 2420–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirota, K.; Grubel, K.; Machnicka, A. Design and assessment of cavitational device for enhancement of sewage sludge fermentation. Ochr. Śr. 2011, 33, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Siva Kumar, M.; Pandit, A. Experimental quantification of chemical effects of hydrodynamic cavitation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichare, N.P.; Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B. Optimization of Hydrodynamic Cavitation Using a Model Reaction. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2000, 23, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machnicka, A.; Grübel, K.; Mirota, K. Considerations of impact of Venturi effect on mesophilic digestion. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2015, 22, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiehm, A.; Nickel, K.; Zellhorn, M.; Neis, U. Ultrasonic waste activated sludge disintegration for improving anaerobic stabilization. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2003–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machnicka, A.; Grübel, K.; Suschka, J. The use of disintegrated foam to accelerate anaerobic digestion of activated sludge. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2009, 35, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Effects of ultrasound pretreatment on the characteristic evolutions of drinking water treatment sludge and its impact on coagulation property of sludge recycling process. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 27, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylin Alagöz, B.; Yenigün, O.; Erdinçler, A. Ultrasound assisted biogas production from co-digestion of wastewater sludges and agricultural wastes: Comparison with microwave pre-treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougrier, C.; Carrère, H.; Delgenès, J.P. Solubilisation of waste-activated sludge by ultrasonic treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 106, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsabil, M.R.; Prorot, A.; Casellas, M.; Dagot, C. Pre-treatment of activated sludge: Effect of sonication on aerobic and anaerobic digestibility. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 148, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Show, K.-Y. Influence of ultrasonication on anaerobic bioconversion of sludge. Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Show, K.Y. Performance of high-rate sludge digesters fed with sonicated sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizama, A.C.; Figueiras, C.C.; Pedreguera, A.Z.; Ruiz Espinoza, J.E. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on the semicontinuous anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge with increasing loading rates. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 130, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odnell, A.; Recktenwald, M.; Stensén, K.; Jonsson, B.H.; Karlsson, M. Activity, life time and effect of hydrolytic enzymes for enhanced biogas production from sludge anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2016, 103, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.H.; Chang, S.; Liu, Y. Biological hydrolysis pretreatment on secondary sludge: Enhancement of anaerobic digestion and mechanism study. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, H.; Du, L.; Liang, J.; Lu, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, K. Influence of NaOH and thermal pretreatment on dewatered activated sludge solubilisation and subsequent anaerobic digestion: Focused on high-solid state. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Hernando, M.; Martín-Díaz, J.; Labanda, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Llorens, J.; Lucena, F.; Astals, S. Effect of ultrasound, low-temperature thermal and alkali pre-treatments on waste activated sludge rheology, hygienization and methane potential. Water Res. 2014, 61, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqaralleh, R.M.; Kennedy, K.; Delatolla, R. Improving biogas production from anaerobic co-digestion of Thickened Waste Activated Sludge (TWAS) and fat, oil and grease (FOG) using a dual-stage hyper-thermophilic/thermophilic semi-continuous reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmasoumi, S.; Khoshbakhti Saray, R.; Ebrahimi, S. Evaluation of thermal pretreatment and digestion temperature rise in a biogas fueled combined cooling, heat, and power system using exergo-economic analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 163, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Du, M. Two-stage mesophilic anaerobic digestion from waste activated sludge enhanced by low-temperature thermal hydrolysis. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 7607–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, M.C.; Braguglia, C.M.; Gianico, A.; Mininni, G.; Nakamura, K.; Rossetti, S. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of thermal pretreated sludge: Role of microbial community structure and correlation with process performances. Water Res. 2015, 68, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenezer, A.V.; Arulazhagan, P.; Adish Kumar, S.; Yeom, I.-T.; Rajesh Banu, J. Effect of deflocculation on the efficiency of low-energy microwave pretreatment and anaerobic biodegradation of waste activated sludge. Appl. Energy 2015, 145, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtmeyers, S.; Degrève, J.; Willems, K.; Dewil, R.; Appels, L. Comparing the influence of low power ultrasonic and microwave pre-treatments on the solubilisation and semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, M.; Dębowski, M.; Krzemieniewski, M.; Rusanowska, P.; Zielińska, M.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Głowacka-Gil, A. Application of an Innovative Ultrasound Disintegrator for Sewage Sludge Conditioning Before Methane Fermentation. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.Á.; González, I.; Serrano, A.; Siles, J.Á. Evaluation of the improvement of sonication pre-treatment in the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Xiao, K.; Chen, Y.; Soh, Y.N.A.; Zhou, Y. Transformation of dissolved organic matters produced from alkaline-ultrasonic sludge pretreatment in anaerobic digestion: From macro to micro. Water Res. 2018, 142, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ni, B.-J.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; et al. Improved methane production from waste activated sludge by combining free ammonia with heat pretreatment: Performance, mechanisms and applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; Ponsá, S.; Vázquez, F.; Font, X. Increasing biogas production by thermal (70 °C) sludge pre-treatment prior to thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 42, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; Serrano, E.; Ponsa, S.; Vazquez, F.; Font, X. Enhancement of thermophilic anaerobic sludge digestion by 70 °C pre-treatment: Energy considerations. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks, A.T.W.M.; Zeeman, G. Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgenès, J.P.; Penaud, V.; Torrijos, M.; Moletta, R. Investigations on the changes in anaerobic biodegradability and biotoxicity of an industrial microbial biomass induced by a thermochemical pretreatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulfotoh, A.M.; EI Gohary, E.H.; EI Monayeri, O.D. Effect Of Thermal Pretreatment On The Solubilization Of Organic Matters In A Mixture Of Primary And Waste Activated Sludge. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2015, 9, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepp, U.; Machenbach, I.; Weisz, N.; Solheim, O.E. Enhanced stabilisation of sewage sludge through thermal hydrolysis—Three years of experience with full scale plant. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 42, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennouri, H.; Miladi, B.; Diaz, S.Z.; Güelfo, L.A.F.; Solera, R.; Hamdi, M.; Bouallagui, H. Effect of thermal pretreatment on the biogas production and microbial communities balance during anaerobic digestion of urban and industrial waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, J.; Starrenburg, D.; Tait, S.; Barr, K.; Batstone, D.J.; Lant, P. Decreasing activated sludge thermal hydrolysis temperature reduces product colour, without decreasing degradability. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4699–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batstone, D.J.; Balthes, C.; Barr, K. Model assisted startup of anaerobic digesters fed with thermally hydrolysed activated sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 1661–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohdziewicz, J.; Kuglarz, M.; Grubel, K. Influence of microwave pre-treatment on the digestion and higienisation of waste activated sludge. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2014, 21, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.G.; Lo, K.V.; Mavinic, D.S. Effects of microwave, ultrasonic and enzymatic treatment on chemical and physical properties of waste-activated sludge. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2014, 49, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.-J.; Ahn, J.-H. Effects of Microwave Pretreatment on Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion for Mixture of Primary and Secondary Sludges Compared with Thermal Pretreatment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2011, 16, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuglarz, M.; Karakashev, D.; Angelidaki, I. Microwave and thermal pretreatment as methods for increasing the biogas potential of secondary sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskicioglu, C.; Kennedy, K.J.; Droste, R.L. Enhanced disinfection and methane production from sewage sludge by microwave irradiation. Desalination 2009, 248, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Yu, L.; Huang, S.; Luo, J.; Zhuo, Y. Energy efficiency of pre-treating excess sewage sludge with microwave irradiation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5092–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montusiewicz, A.; Lebiocka, M.; Rożej, A.; Zacharska, E.; Pawłowski, L. Freezing/thawing effects on anaerobic digestion of mixed sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3466–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
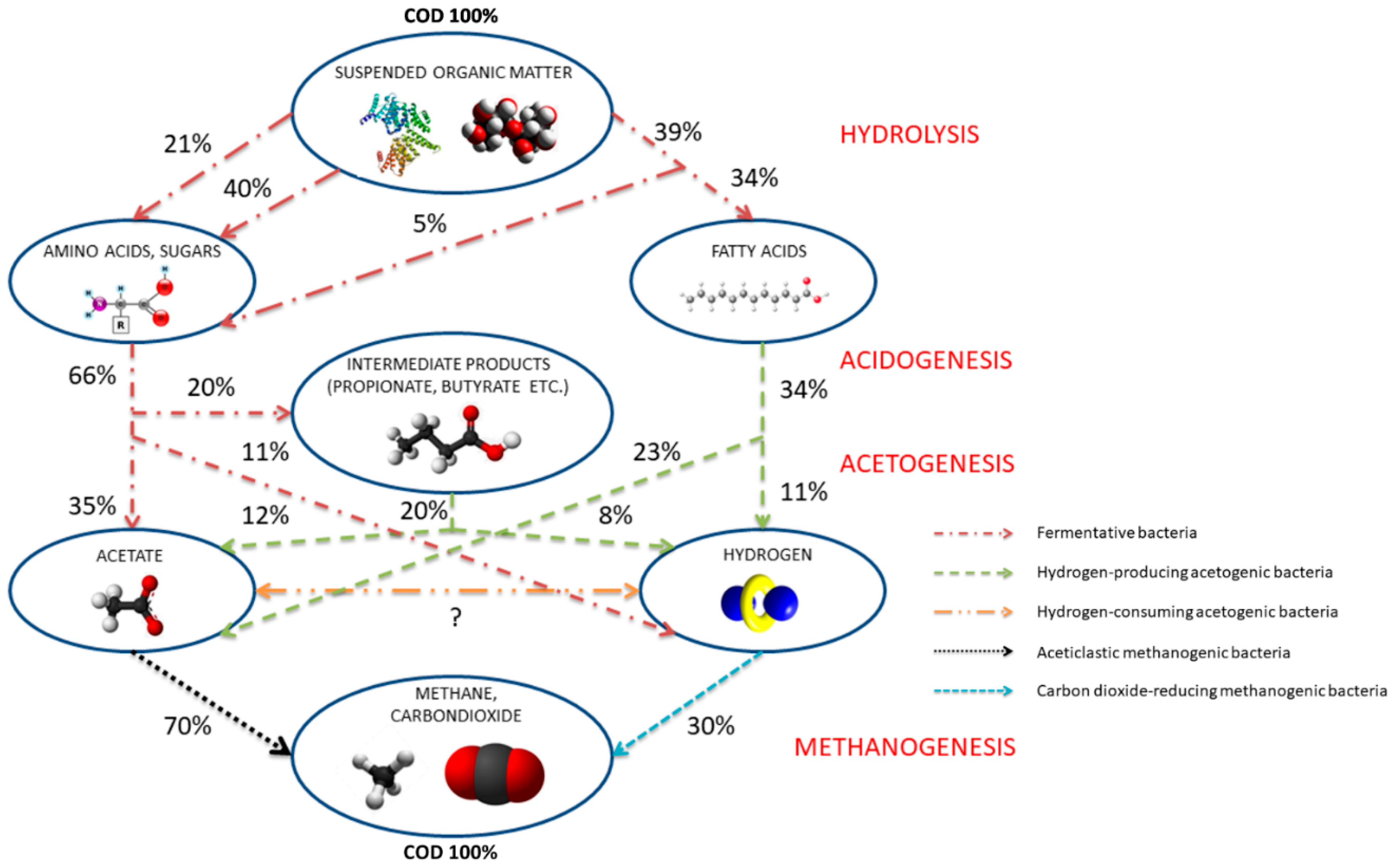
| Constituents | Energy (kW m−3) | Fuel Equivalent (L oil m−3 biogas) | Ignition Temperature (°C) | Critical Pressure (bar) | Critical Temperature (°C) | Normal Density (kg m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4: 55–70%, CO2: 30–45%, other gases | 6.0–6.5 | 0.6–0.65 | 650–750 | 75–89 | −82.5 | 1.2 |
| Disintegration Type | Treatment Type/Condition | Anaerobic Digestion Condition | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological | Amylase + protease | 37 °C | +23% biogas yield | [27] |
| Subtilisin | 38 °C | +37% biogas yield | [123] | |
| Biological hydrolysis | 35 °C | “significantly higher methane generation” | [124] | |
| Micro-aerobic hydrolysis | 35 °C | 38% methane yield | [90] | |
| Chemical | Acidification: 0.52–1.42 mg HNO2-N L−1 | 37 °C | +12–16% methane yield | [66] |
| Acidification: 2.5 mg L−1 HNO2 | 37 °C | +25% methane yield | [89] | |
| Alkalization: 20 mg NaOH g−1 TS | 37 °C | +35% methane yield | [125] | |
| Alkalization: 157 mg NaOH g−1 TS | 37 °C | +34% methane yield | [126] | |
| Oxidation: H2O2: 5 mg L−1 | 37 °C | +27% methane yield | [89] | |
| Oxidation: 0.1 g K2S2O8 g−1 SS | 35 °C | 180% methane yield | [93] | |
| Oxidation: ZnO-ZnS@polyaniline | 35 °C | 62% methane yield | [91] | |
| Hybrid: HNO2/H2O2 | 37 °C | +72% methane yield | [89] | |
| Physical and hybrid | Thermal:70 °C | 55 °C | +148% methane yield | [127] |
| Thermal: 90 °C | 55 °C | +161% methane yield | [128] | |
| Thermal: 100 °C | 33 °C | +343% biogas production | [129] | |
| Thermal: 120 °C | 33 °C | +345% biogas production | [129] | |
| Thermal: 134 °C | 55 °C | +47% biogas yield | [130] | |
| Microwaves: 14,000 kJ kg−1 TS | 35 °C | +570% biogas yield | [131] | |
| Ultrasounds: 96 kJ kg−1 Sludge | 37 °C | +27% biogas yield | [132] | |
| Ultrasounds: 750 kJ | 37 °C | +52% methane yield | [133] | |
| Ultrasounds: 1000 kJ kg−1 TS | 35 °C | +95% methane yield | [134] | |
| Ultrasounds: 25,000 kJ kg−1 TS | 36 °C | +560% biogas yield | [122] | |
| Hybrid: Alkalization + Ultrasounds | 35 °C | +33% biogas yield | [135] | |
| Hybrid: Free ammonia (135 mg L−1) + 70 °C | 35 °C | +25% biogas yield | [136] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wacławek, S.; Grübel, K.; Silvestri, D.; Padil, V.V.T.; Wacławek, M.; Černík, M.; Varma, R.S. Disintegration of Wastewater Activated Sludge (WAS) for Improved Biogas Production. Energies 2019, 12, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010021
Wacławek S, Grübel K, Silvestri D, Padil VVT, Wacławek M, Černík M, Varma RS. Disintegration of Wastewater Activated Sludge (WAS) for Improved Biogas Production. Energies. 2019; 12(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleWacławek, Stanisław, Klaudiusz Grübel, Daniele Silvestri, Vinod V. T. Padil, Maria Wacławek, Miroslav Černík, and Rajender S. Varma. 2019. "Disintegration of Wastewater Activated Sludge (WAS) for Improved Biogas Production" Energies 12, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010021
APA StyleWacławek, S., Grübel, K., Silvestri, D., Padil, V. V. T., Wacławek, M., Černík, M., & Varma, R. S. (2019). Disintegration of Wastewater Activated Sludge (WAS) for Improved Biogas Production. Energies, 12(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010021










