Analysis of the Effects of Blade Installation Angle and Blade Number on Radial-Inflow Turbine Stator Flow Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Analysis Model and Method
3. Results and Discussion
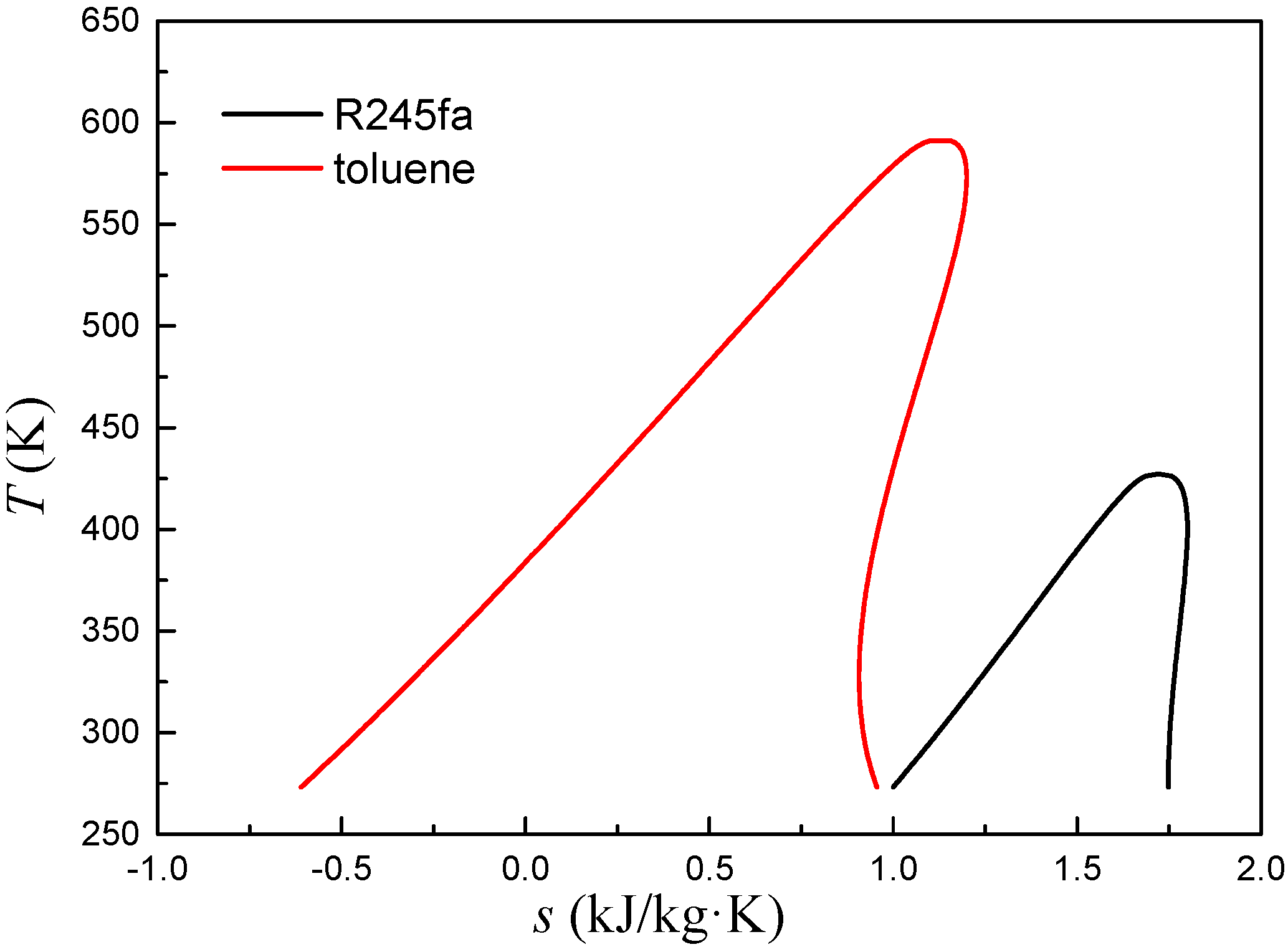
3.1. Low Temperature Working Fluid R245fa
3.2. High Temperature Working Fluid Toluene
3.3. Geometric Parameters Comparison of the Stator Blade between Low and High Temperature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| b | Chord length of blade (mm) |
| C0 | Imaginary expansion speed (m/s) |
| c | Absolute velocity (m·s−1) |
| cp | Specific heat capacity (kJ/kg·K) |
| cp0 | Zero pressure specific heat capacity (kJ/kg·K) |
| Ratio of wheel diameter | |
| F1 | Synthetic function of turbulence model coefficients |
| F2 | Blending functions |
| k | Specific turbulence kinetic energy (m2/s2); thermal conductivity (W/(m·K)) |
| keff | Effective thermal conductivity (W/(m·K)) |
| kt | Turbulent thermal conductivity (W/(m·K)) |
| P | Pressure (kPa) |
| Pk | Generation term of turbulence |
| Prt | Turbulent Prandtl number |
| R | Ideal gas constant, J/mol K |
| t | Time (s) |
| Relative pitch | |
| S | Modulus of the mean rate-of-strain tensor |
| T | Temperature (K) |
| u | Peripheral velocity (m/s) |
| Turbulence velocity (m/s) | |
| Vm | Molar volume, m3/mol |
| w | Relative velocity (m/s) |
| x | X coordinate value (mm) |
| Velocity ratio | |
| yB | Y coordinate value of suction surface (mm) |
| yH | Y coordinate value of pressure surface (mm) |
| Subscripts | |
| 1 | Rotor inlet |
| 2 | Rotor outlet |
| c | Critical point |
| k | Turbulent kinetic energy |
| ω | Specific dissipation rate |
| Greek Letters | |
| α | Absolute velocity angle (°) |
| α1,α* | Coefficients in SST k-ω model |
| β | Relative velocity angle (°) |
| βk, βω, γ | Turbulence model coefficient |
| δij | Kronecker symnol |
| Isentropic entropy drop (kJ/kg) | |
| ηu | Peripheral efficiency |
| μ | Physical dynamic viscosity (Pa·s) |
| μeff | Effective dynamic viscosity (Pa·s) |
| μt | Turbulent dynamic viscosity (Pa·s) |
| ρ | Density (kg/m3) |
| Turbulence model constant | |
| τij | Stress tensor |
| Stator blade velocity coefficient | |
| Rotor blade velocity coefficient | |
| ω | Specific turbulence dissipation rate (m2/s2) |
| ω0 | Acentric factor |
| Ω | Degree of reaction |
References
- Zhang, C.; Fu, J.L.; Kang, J.; Fu, W.C. Performance optimization of low-temperature geothermal organic Rankine cycles using axial turbine isentropic efficiency correlation. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, V. A comparative exergoeconomic analysis of different ORC configurations for binary geothermal power plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.H.; Li, P.; Han, X.; Mei, Z.K.; Wang, Z. Thermo-economic performance analysis of a regenerative superheating organic rankine cycle for waste heat recovery. Energies 2017, 10, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y. Comparison between regenerative organic Rankine cycle (RORC) and basic organic Rankine cycle (BORC) based on thermoeconomic multi-objective optimization considering exergy efficiency and levelized energy cost (LEC). Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 96, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gu, C.W.; Ren, X. Parametric design and off-design analysis of organic Rankine cycle (ORC) system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 112, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; An, Q.S. Multi-objective optimization and grey relational analysis on configurations of organic Rankine cycle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 114, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, Y.T. Preliminary design and performance analysis of a radial inflow turbine for ocean thermal energy conversion. Renew. Energy 2017, 106, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hu, D.; Cao, Y.; Dai, Y. Preliminary design and off-design performance analysis of an organic rankine cycle radial-inflow turbine based on mathematic method and CFD method. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 112, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Xu, G.; Luo, X.; Zhuang, L.; Quan, Y. Analysis of the supercritical organic Rankine cycle and the radial turbine design for high temperature applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 123, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lio, L.D.; Manente, G.; Lazzaretto, A. A mean-line model to predict the design efficiency of radial inflow turbines in organic Rankine cycle (ORC) systems. Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauret, E.; Gu, Y. Three-dimensional off-design numerical analysis of an organic rankine cycle radial-inflow turbine. Appl. Energy 2014, 135, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, K.; Mahmoud, S.; Al-Dadah, R.K.; Moazami, N. Parametric analysis and optimization of a small-scale radial turbine for Organic Rankine Cycle. Energy 2015, 83, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, P.; Rebay, S.; Harinck, J.; Guardone, A. Real-gas effects in ORC turbine flow simulations: Influence of thermodynamic models on flow fields and performance parameters. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics, Egmond aan Zee, The Netherlands, 5–8 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Colonna, P.; Harinck, J.; Rebay, S.; Guardone, A. Real-gas effects in organic Rankine cycle turbine nozzles. J. Propul. Power 2008, 24, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaschi, D.; Manfrida, G.; Maraschiello, F. Design and performance prediction of radial ORC turboexpanders. Appl. Energy 2015, 138, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Xu, G.; Li, T.; Luo, X.; Quan, Y. Parametric analysis of organic Rankine cycle based on a radial turbine for low-grade waste heat recovery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 126, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, X.D. Investigation of the organic Rankine cycle (ORC) system and the radial-inflow turbine design. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 96, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.S.; Ren, X. Aerodynamic optimization of a high-expansion ratio organic radial-inflow turbine. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 5485–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Sun, X.; Huang, D.A. Preliminary design and performance analysis of a centrifugal turbine for Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) applications. Energy 2017, 140, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadormanesh, N.; Rahat, S.; Yarali, M. Constrained multi-objective optimization of radial expanders in organic Rankine cycles by firefly algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 148, 1179–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Fan, W.; Zhao, R. Improved thermodynamic design of organic radial-inflow turbine and orc system thermal performance analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 150, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Xu, G.; Wen, J.; Quan, Y.; Fu, J.; Wu, H.; Li, T. An improved modeling for low-grade organic Rankine cycle coupled with optimization design of radial-inflow turbine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 153, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wang, H. Improved analysis of Organic Rankine Cycle based on radial flow turbine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 61, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gu, C.W.; Ren, X. Influence of the radial-inflow turbine efficiency prediction on the design and analysis of the Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 123, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; LU, G. Radial Inflow Turbine and Centrifugal Compressor; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Xu, G.; Li, T.; Quan, Y.; Zhai, L.; Wen, J. Numerical prediction of velocity coefficient for a radial-inflow turbine stator using R123 as working fluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 130, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinck, J.; Turunen-Saaresti, T.; Colonna, P.; Rebay, S.; Van, B. Computational study of a high-expansion ratio radial organic rankine cycle turbine stator. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2010, 132, 054501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, D.; Ghidoni, A.; Rebay, S. Shape optimization of an organic rankine cycle radial turbine nozzle. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2013, 135, 042308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusitalo, A.; Turunen-Saaresti, T.; Guardone, A.; Grönman, A. Design and flow analysis of a supersonic small scale ORC turbine stator with high molecular complexity working fluid. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2014, Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, Düsseldorf, Germany, 16–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.; Read, M.; Sayma, A. Using a cubic equation of state to identify optimal working fluids for an ORC operating with two-phase expansion using a twin-screw expander. In Proceedings of the 17th International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference, Purdue, IN, USA, 9–12 July 2018. [Google Scholar]

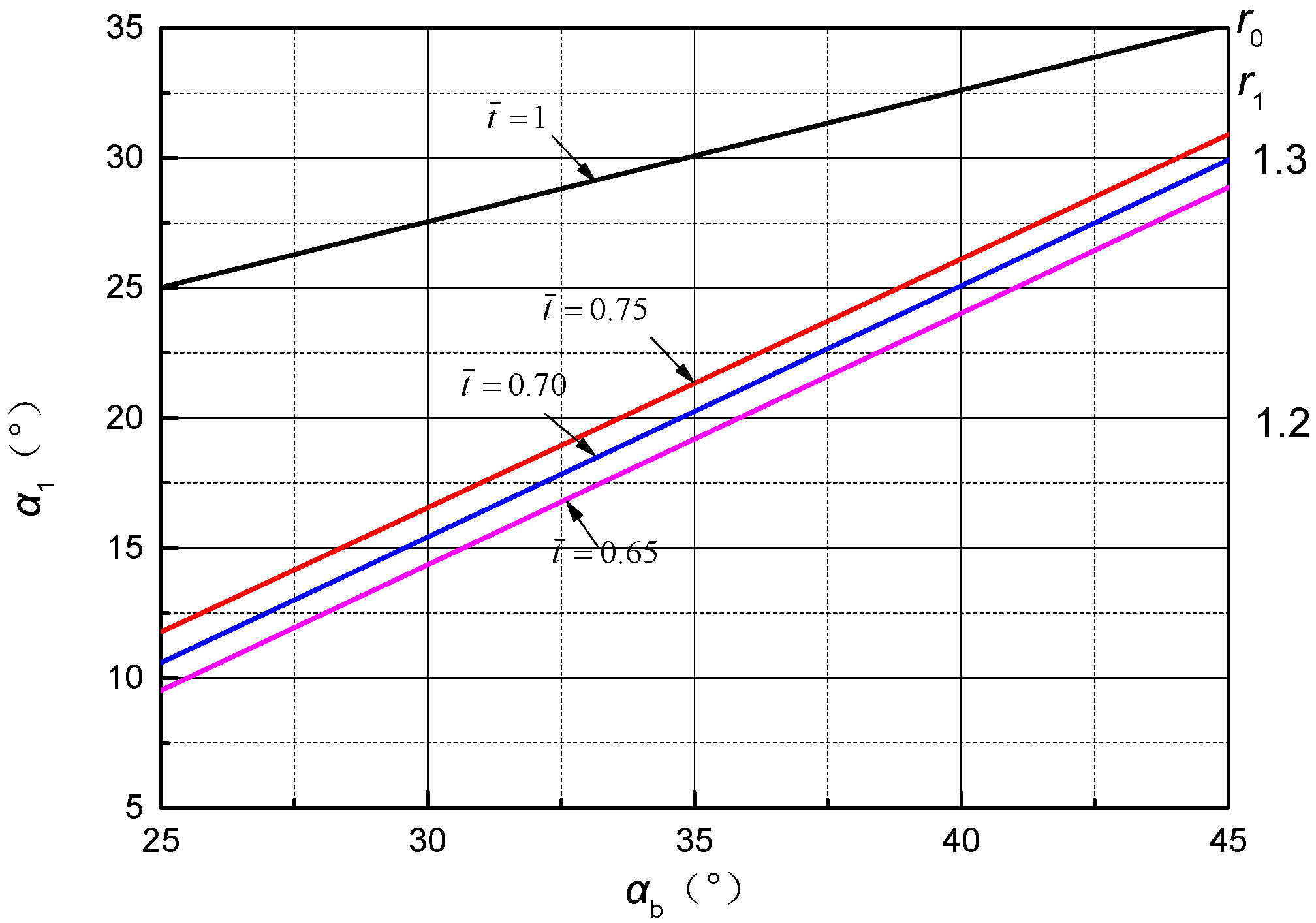

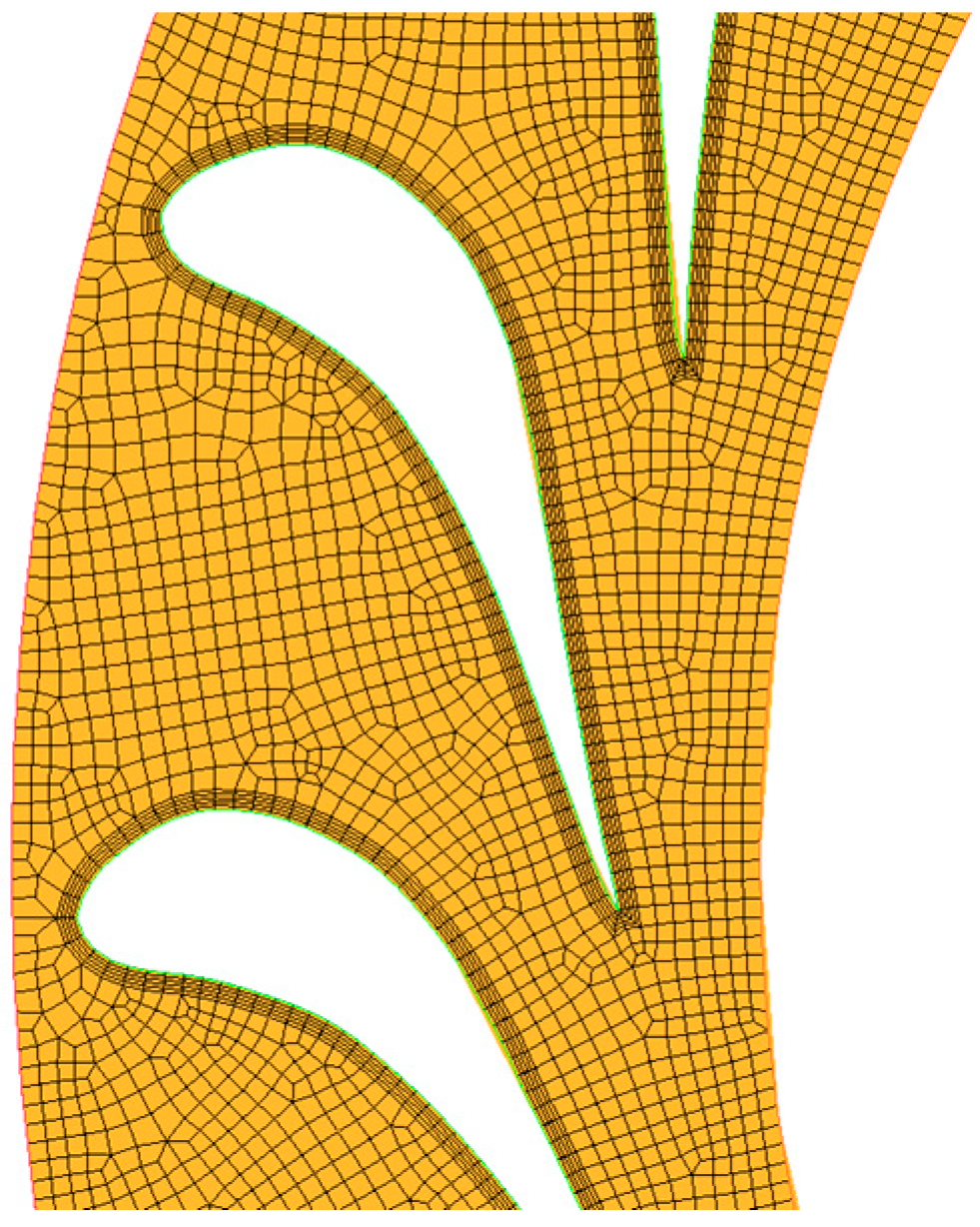

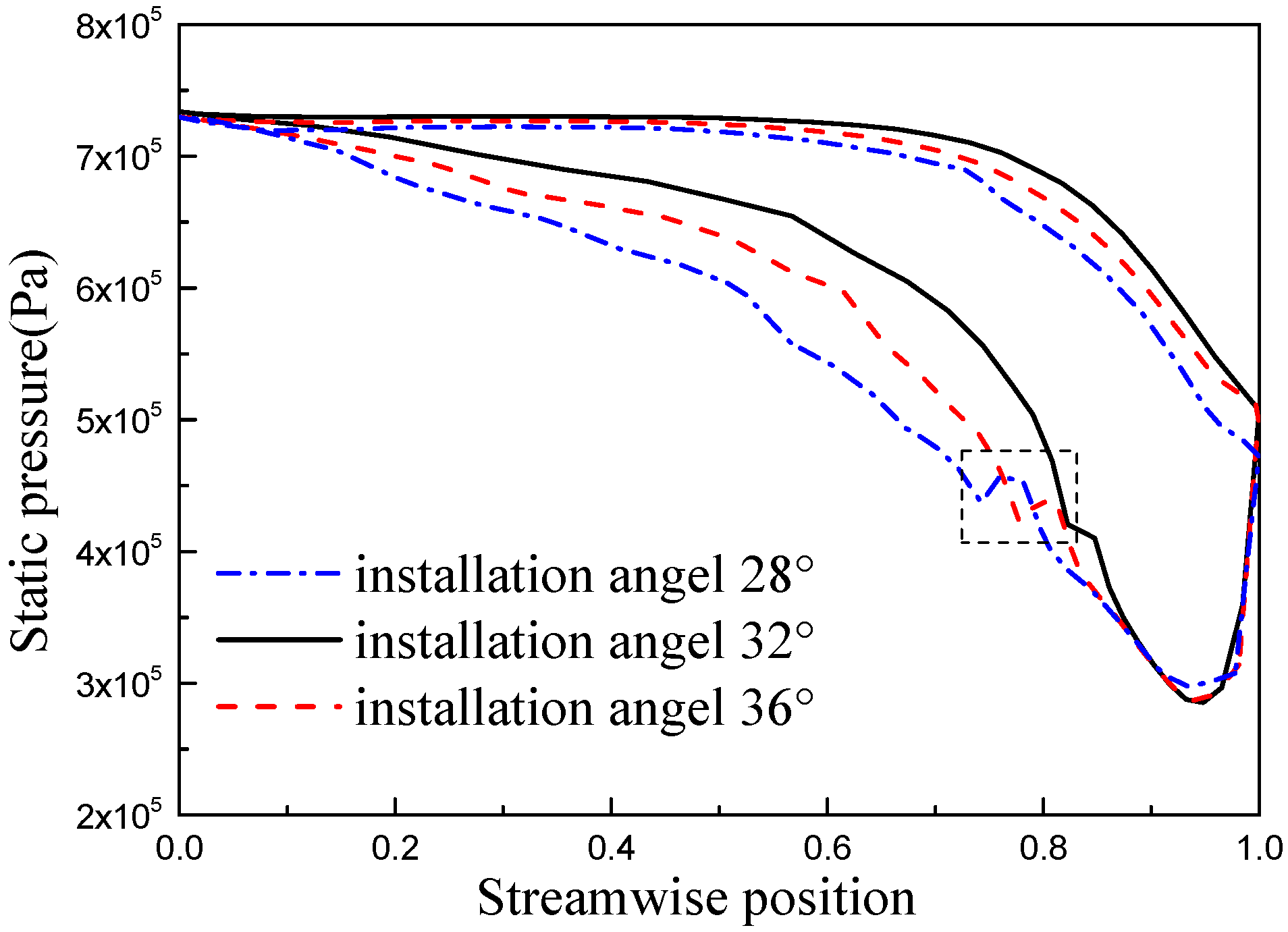
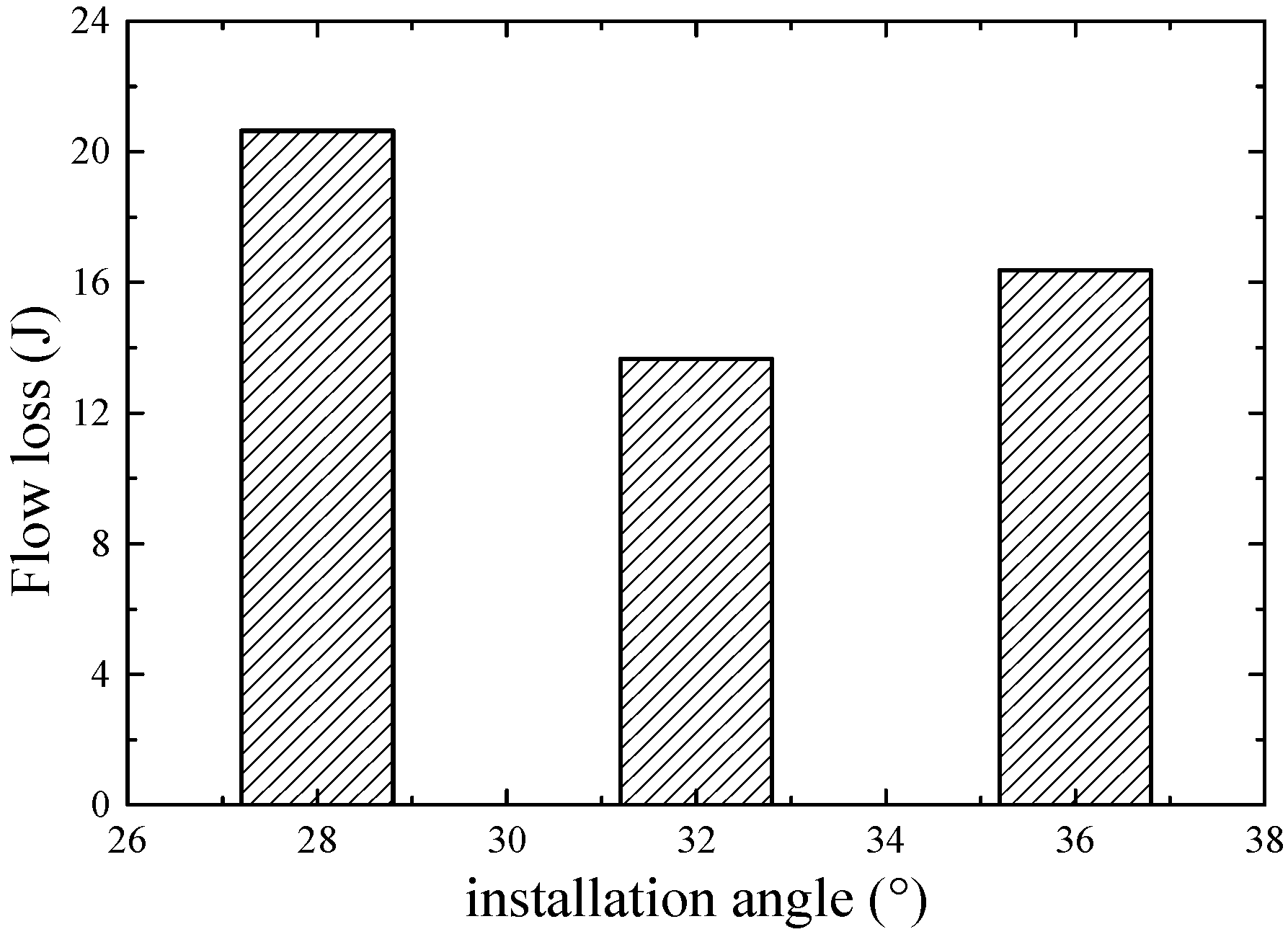
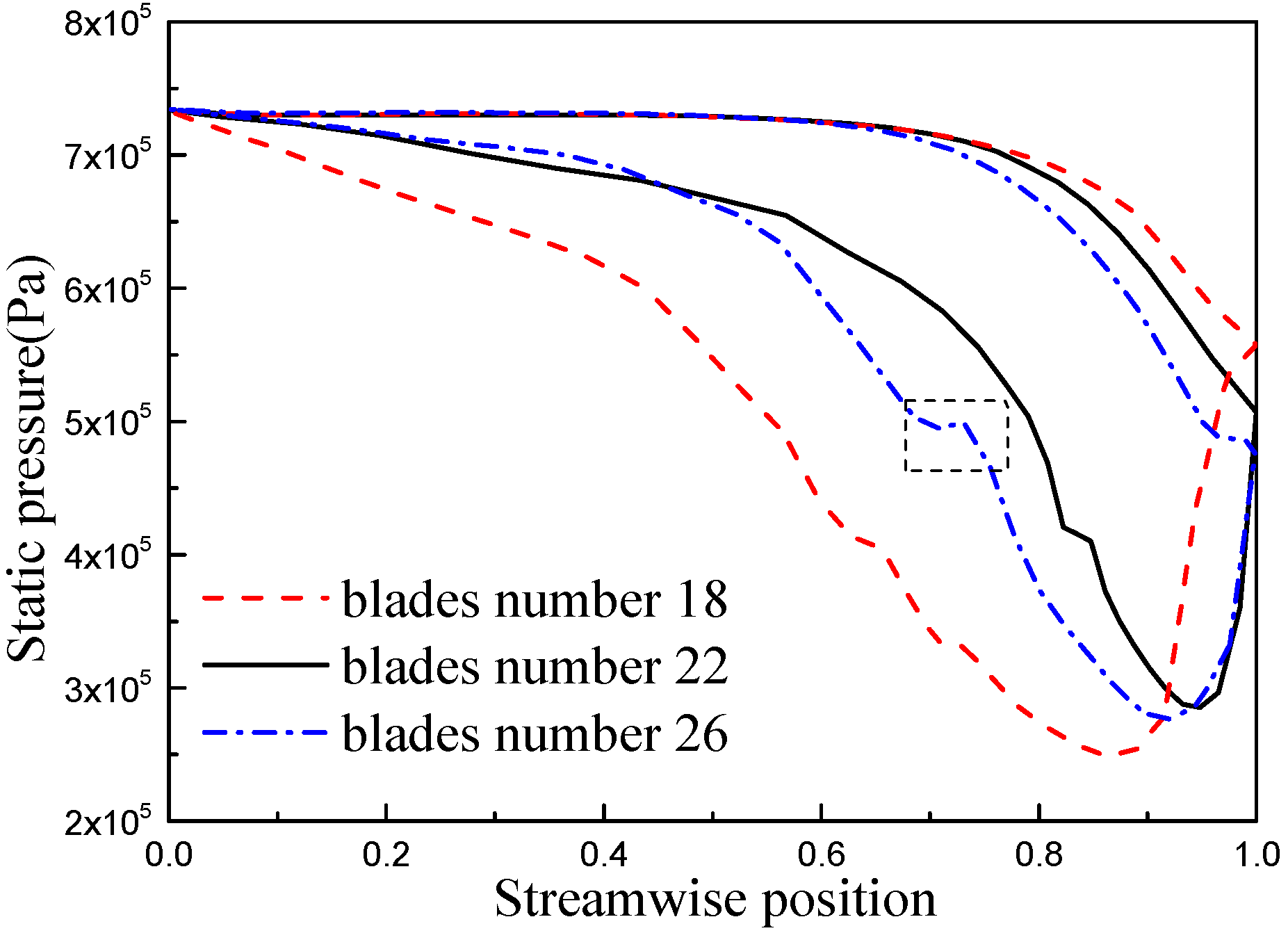
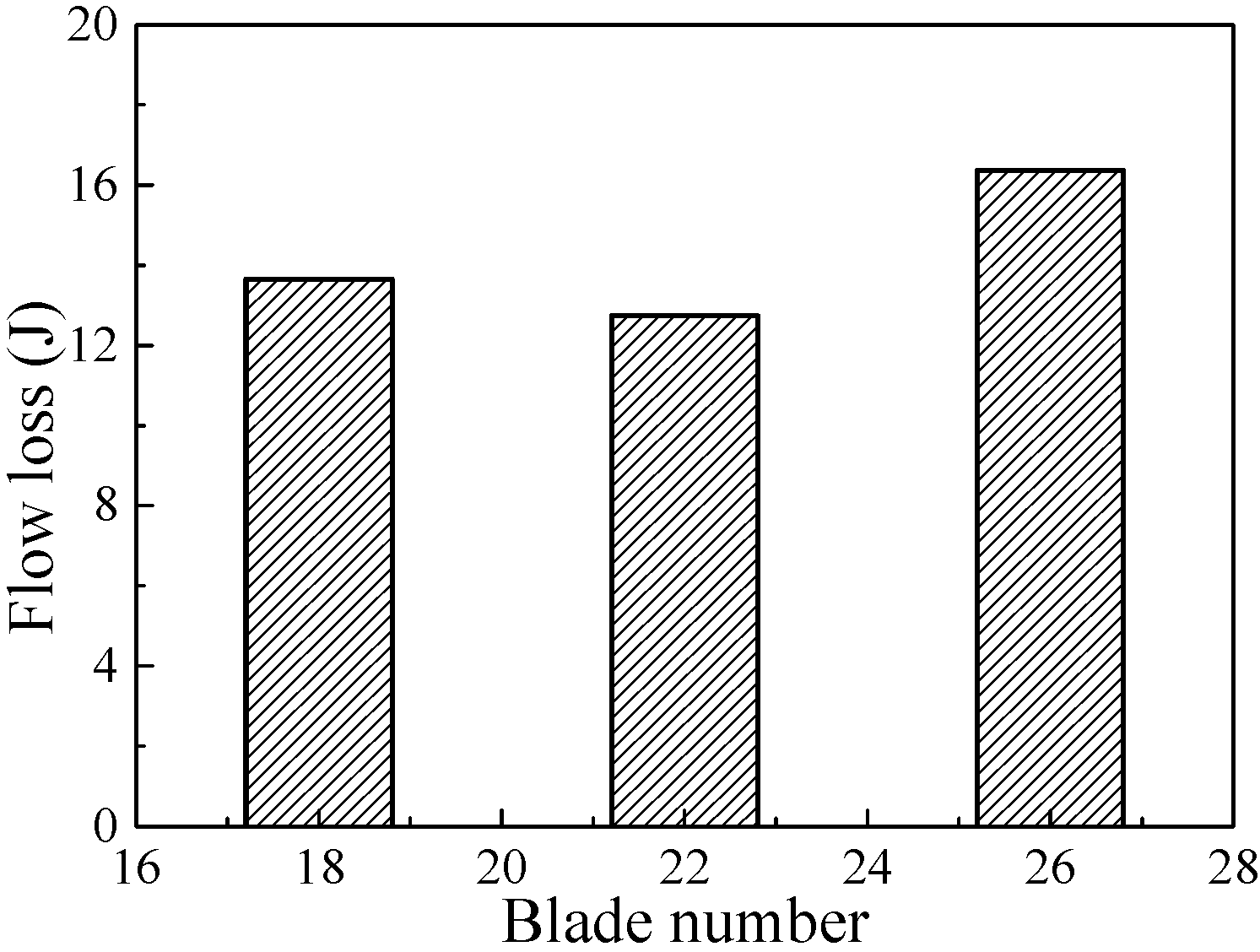
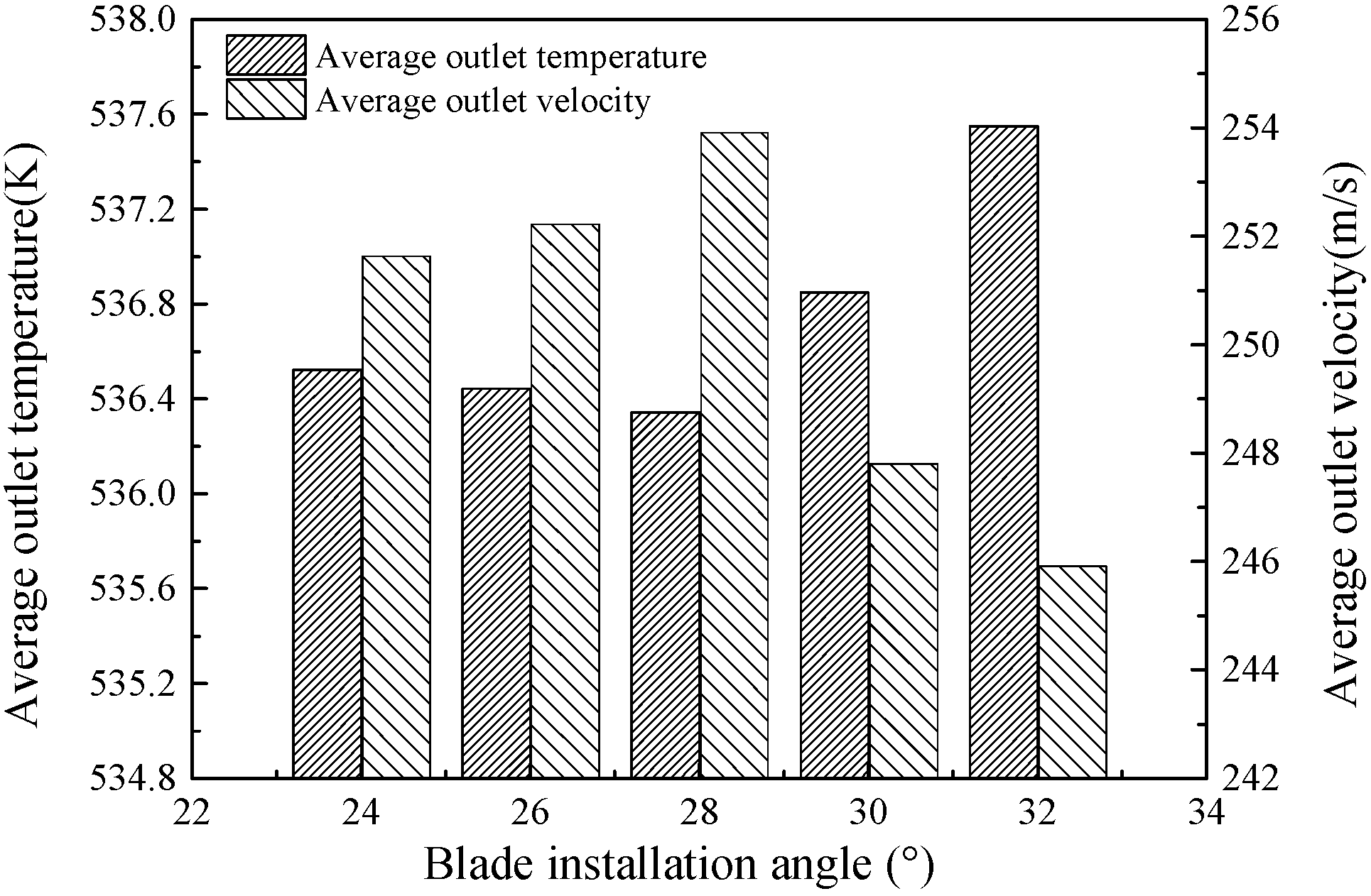
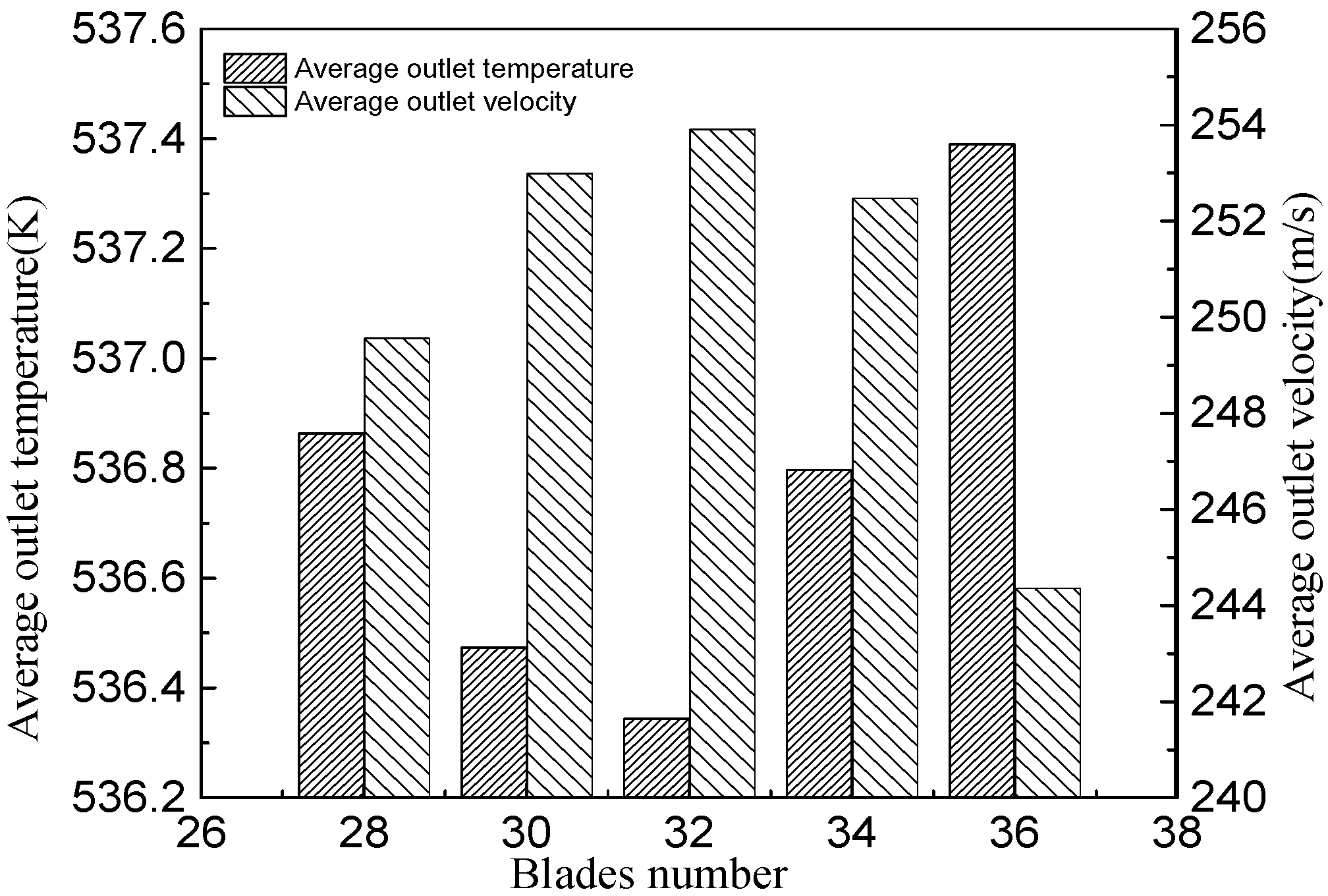

| x/b (%) | yB/b (%) | yH/b (%) | x/b (%) | yB/b (%) | yH/b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.453 | 0.453 | 55 | 24.40 | 11.70 |
| 0.25 | 1.57 | 0.280 | 60 | 26.35 | 12.96 |
| 5.0 | 2.545 | 0.815 | 65 | 27.7 | 11.8 |
| 7.5 | 3.445 | 1.45 | 70 | 28.6 | 10.9 |
| 10.0 | 4.46 | 2.10 | 75 | 29.0 | 2.24 |
| 12.5 | 5.45 | 2.72 | 80 | 28.4 | 7.15 |
| 15.0 | 6.52 | 3.39 | 82.5 | 27.9 | 5.9 |
| 17.5 | 7.59 | 4.005 | 85 | 27.2 | 4.44 |
| 20 | 8.66 | 4.65 | 87.5 | 26.3 | 2.72 |
| 25 | 10.84 | 5.94 | 90 | 25.0 | 0.127 |
| 30 | 13.06 | 7.20 | 92.5 | 23.4 | 0.362 |
| 35 | 15.35 | 8.47 | 95 | 21.2 | 0 |
| 40 | 17.69 | 9.46 | 97.5 | 17.4 | 0.905 |
| 45 | 4519.90 | 10.50 | 100 | 7.43 | 7.43 |
| 50 | 22.4 | 11.23 |
| Variables | 1D Thermal Design | CFD Numerical Results | Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet temperature (K) | 353.15 | 352.53 | −0.18 |
| Outlet temperature (K) | 328.66 | 328.54 | −0.037 |
| Inlet pressure (MPa) | 0.7355 | 0.7258 | −1.32 |
| Outlet pressure (MPa) | 0.3210 | 0.3209 | −0.031 |
| Velocity coefficient | 0.95 | 0.93 | −2.1 |
| Working Fluids | R245fa | Toluene |
|---|---|---|
| Chord length (mm) | 44.05 | 30.55 |
| Installation angle (°) | 32° | 28° |
| Blade number | 22 | 32 |
| Relative pitch | 0.67 | 0.65 |
| Cascade inlet diameter (mm) | 206 | 194 |
| Cascade outside diameter (mm) | 297 | 210 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Han, Z.; Jia, X.; Mei, Z.; Han, X. Analysis of the Effects of Blade Installation Angle and Blade Number on Radial-Inflow Turbine Stator Flow Performance. Energies 2018, 11, 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092258
Li P, Han Z, Jia X, Mei Z, Han X. Analysis of the Effects of Blade Installation Angle and Blade Number on Radial-Inflow Turbine Stator Flow Performance. Energies. 2018; 11(9):2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092258
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peng, Zhonghe Han, Xiaoqiang Jia, Zhongkai Mei, and Xu Han. 2018. "Analysis of the Effects of Blade Installation Angle and Blade Number on Radial-Inflow Turbine Stator Flow Performance" Energies 11, no. 9: 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092258
APA StyleLi, P., Han, Z., Jia, X., Mei, Z., & Han, X. (2018). Analysis of the Effects of Blade Installation Angle and Blade Number on Radial-Inflow Turbine Stator Flow Performance. Energies, 11(9), 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092258





