Prediction of Wave Power Generation Using a Convolutional Neural Network with Multiple Inputs
Abstract
1. Introduction
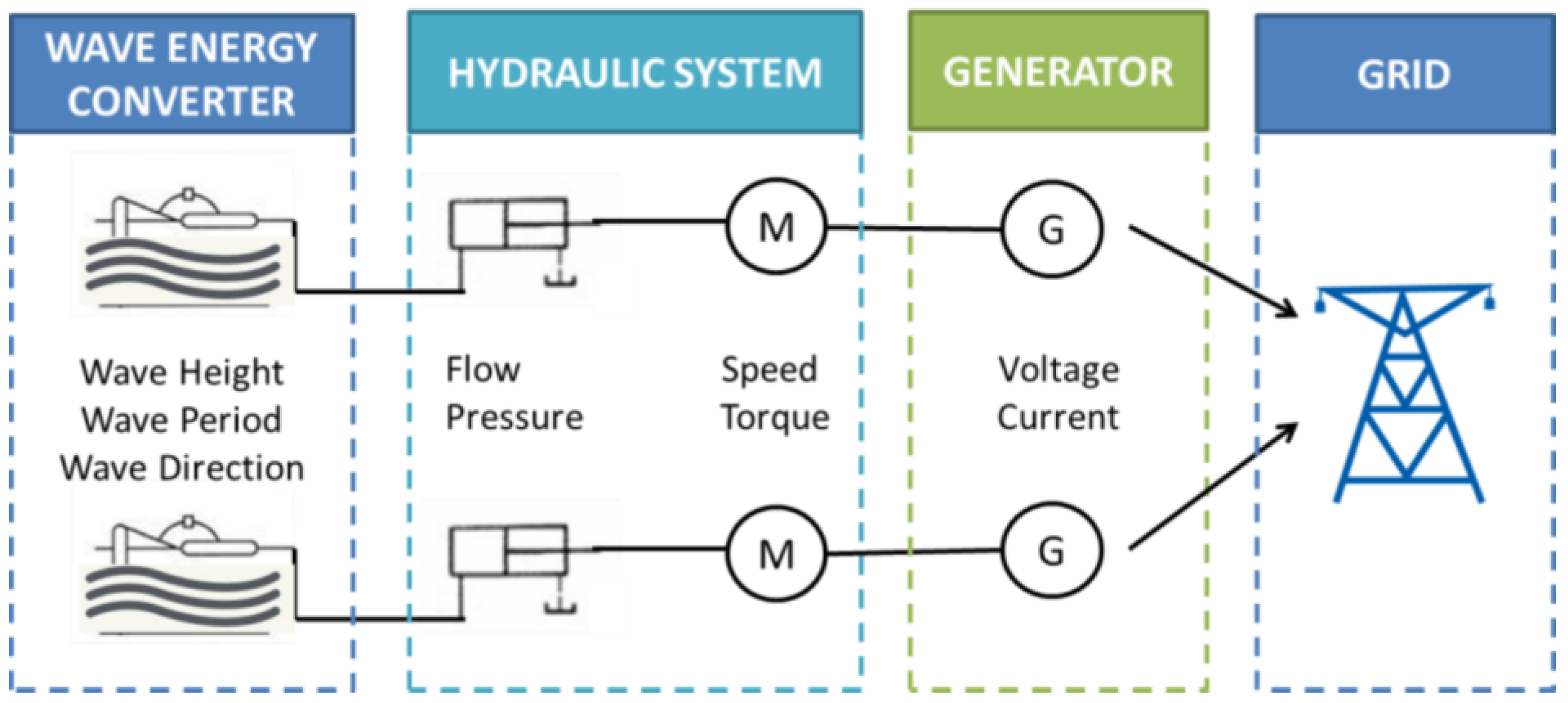
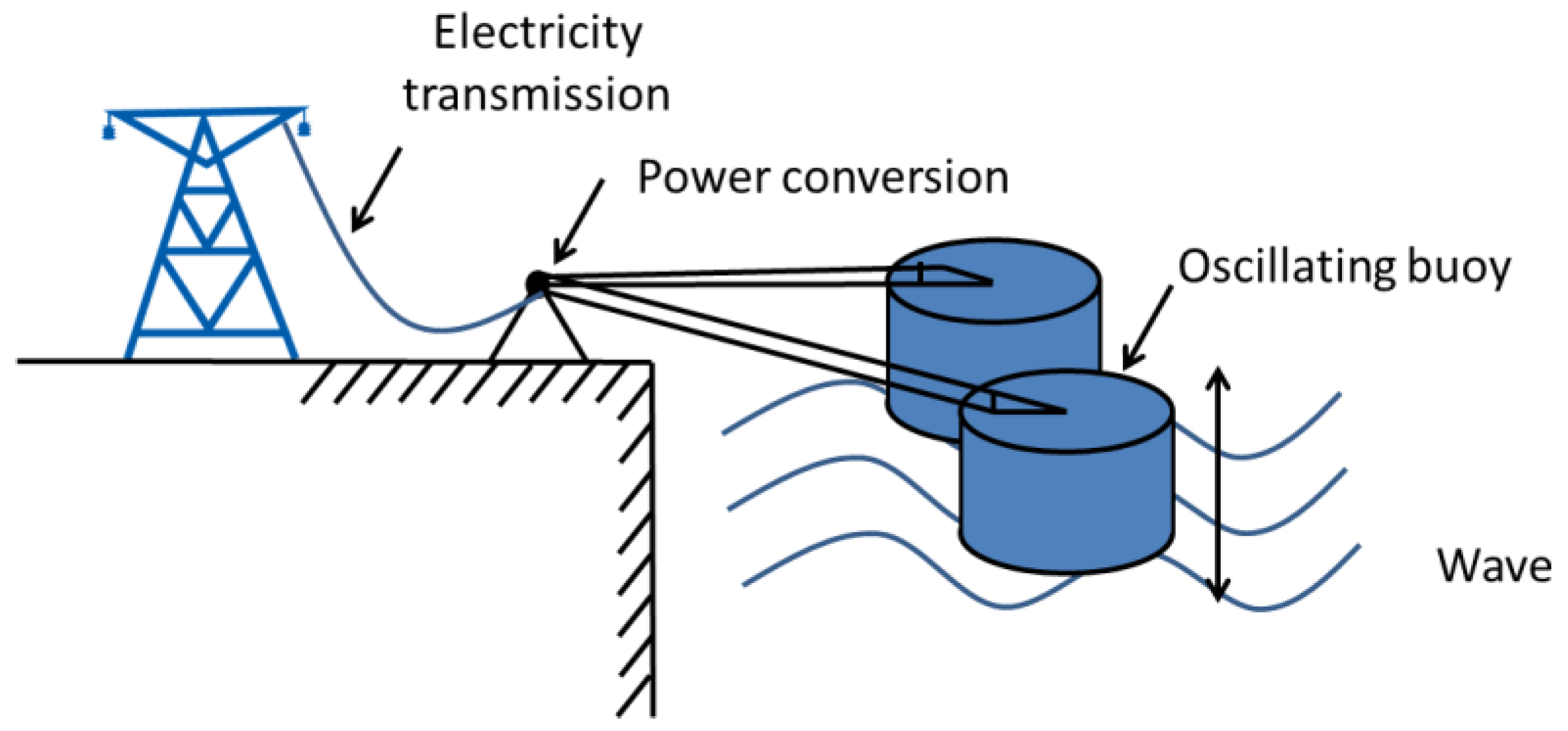
2. Operation and Performance Analysis
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Power Curves
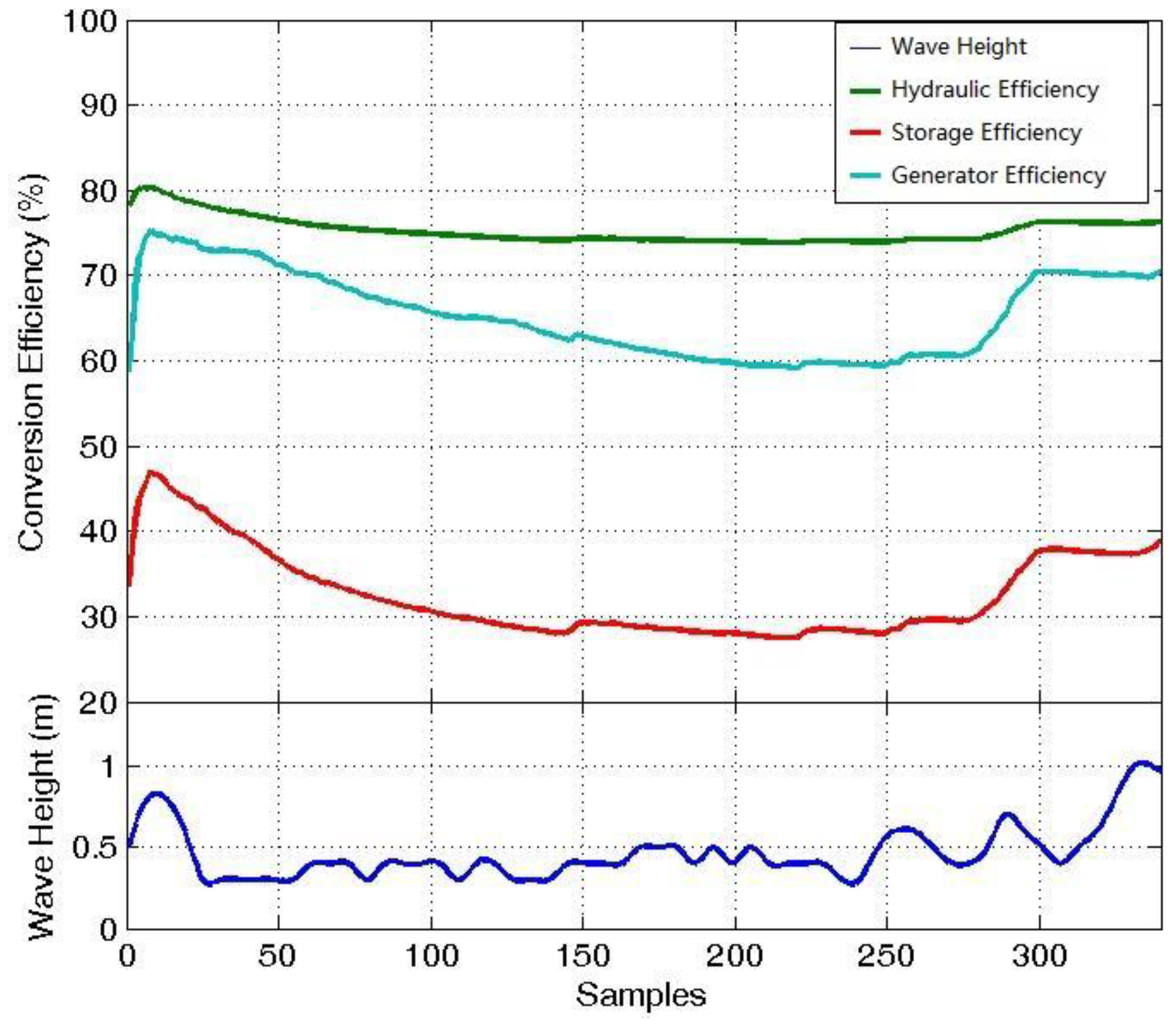
2.3. Energy Conversion Efficiency
3. Methodology
3.1. Convolutional Neural Networks
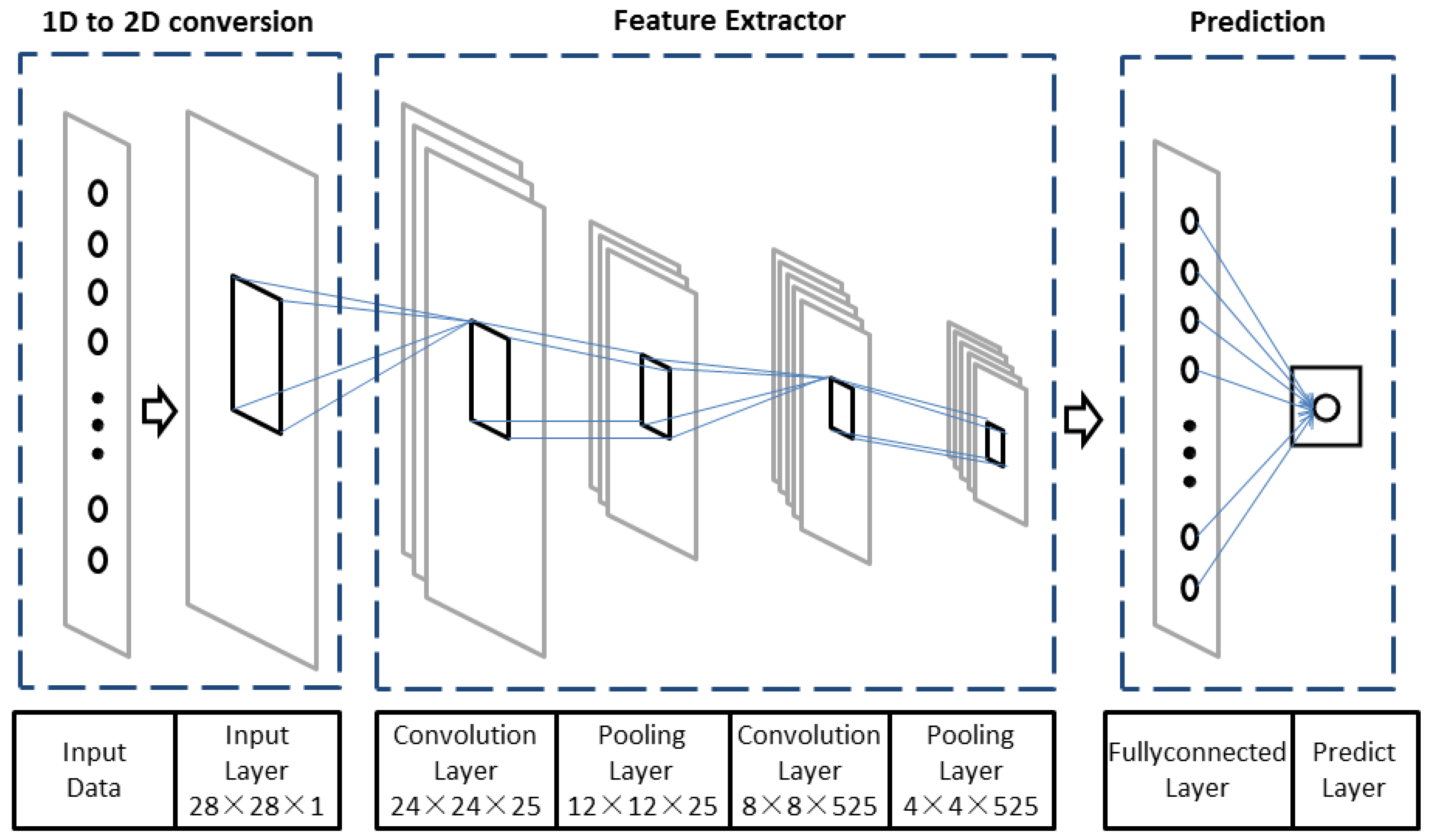
3.2. Network Architecture
3.3. Model Performance Metrics
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Results
4.3. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WEC | wave energy converter |
| OBD | oscillating body device |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| MCNN | Multi-input Convolutional Neural Network |
| TRL | technology readiness level |
| OWC | oscillating water column |
| PTO | power take-off |
| SCADA | supervisory control and data acquisition |
| ML | machine learning |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecast |
| GDAS | Global Data Assimilation Scheme |
| ANN | artificial neural network |
| PV | photovoltaic |
| LS | least-square |
| SVM | support vector machine |
| NN | neural network |
| LSTM | long short term memory |
| DBN | Deep Brief Net |
| RNN | recurrent neural network |
| 1D | 1-dimension |
| 2D | 2-dimension |
| AM | autoregressive models |
| LDS | Linear Dynamical Systems |
| HMM | Hidden Markov Model |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| BP | back propagation |
| SGD | stochastic gradient descent |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| MAE | mean absolute error |
| R2 | coefficient of determination |
| LR | Linear Regression |
| RT | regression tree |
| RLR | Robust Linear Regression |
| MT | medium tree |
| BT | boosted tree |
References
- Saadat, Y.; Fernandez, N.; Samimi, A.; Alam, M.R.; Shakeri, M.; Ghorbani, R. Investigating of helmholtz wave energy converter. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Abdelkhalik, O.; Robinett, R.; Bacelli, G.; Wilson, D. Optimal control of wave energy converters. Renew. Energy 2017, 103, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, N.; Baskaran, V.; Amarkarthik, A. A review on front end conversion in ocean wave energy Converters. Front. Energy 2015, 9, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magagna, D.; Monfardini, R.; Uihlein, A. JRC Ocean Energy Status Report 2016 Edition; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, M.-F.; Lin, I.-H.; Dorrell, D.; Hsieh, M.-J.; Lin, C.-C. Development of a wave energy converter using a two chamber oscillating water column. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2012, 3, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproul, A.; Weise, N. Analysis of a wave front parallel WEC prototype. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, P.; Iuppa, C.; Di Lauro, E.; Cavallaro, L.; Andersen, T.L.; Vicinanza, D. Wave loadings acting on innovative rubble mound breakwater for overtopping wave energy conversion. Coast. Eng. 2017, 122, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccino, M.; Vicinanza, D.; Salerno, D.; Banfi, D.; Calabrese, M. Nature and magnitude of wave loadings at seawave slot-cone generators. Ocean Eng. 2015, 95, 34–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, F.D.O. Wave energy utilization: A review of the technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 899–918. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, X. Simultaneous fault detection and sensor selection for condition monitoring of wind turbines. Energies 2016, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, F. Time domain prediction of power absorption from ocean waves with wave energy converter arrays. Renew. Energy 2016, 92, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reikard, G.; Pinson, P.; Bidlot, J.-R. Forecasting ocean wave energy: The ECMWF wave model and time series methods. Ocean Eng. 2011, 38, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reikard, G. Integrating wave energy into the power grid: Simulation and forecasting. Ocean Eng. 2013, 73, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uihlein, A.; Magagna, D. Wave and tidal current energy—A review of the current state of research beyond technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg, A.; Holst, U.; Holst, J. Forecasting near-surface ocean winds with Kalman filter techniques. Ocean Eng. 2005, 32, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izgi, E.; Oztopal, A.; Yerli, B.; Kaymak, M.K.; Şahin, A.D. Short–mid-term solar power prediction by using artificial neural networks. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Qiao, W. Short-term solar power prediction using a support vector machine. Renew. Energy 2013, 52, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, D.J.; Iuppa, C.; Cavallaro, L.; Cancelliere, A.; Foti, E. Significant wave height record extension by neural networks and reanalysis wind data. Ocean Model. 2015, 94, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.C.; Zhang, Y.; O'Donncha, F. A machine learning framework to forecast wave conditions. Coast. Eng. 2018, 137, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, L.; Paredes, G.; Bustos, G. Data mining techniques for very short term prediction of wind power. In Proceedings of the IREP Symposium-Bulk Power System Dynamics and Control-VIII, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–6 August 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Colak, I.; Sagiroglu, S.; Yesilbudak, M. Data mining and wind power prediction: A literature review. Renew. Energy 2012, 46, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarynskyy, O.; Makarynska, D.; Rusu, E.; Gavrilov, A. Filling gaps in wave records with artificial neural networks. Marit. Transp. Exploit. Ocean Coast. Resour. 2005, 2, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Ciortan, S.; Rusu, E. Prediction of the wave power in the Black Sea based on wind speed using artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Clean Energy Research (ICACER), Barcelona, Spain, 6–8 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, J.M.; Aguilar, R.M.; niga-Meneses, K.V.Z. Deep learning to predict the generation of a wind farm. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2018, 10, 013305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mi, X.; Li, Y. Wind speed forecasting method based on deep learning strategy using empirical wavelet transform, long short term memory neural network and elman neural network. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 156, 498–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, M.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, C. A whole system assessment of novel deep learning approach on short-term load forecasting. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Applied Energy (ICAE), Cardiff, UK, 21–24 August 2017; Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expected_value#cite_note-Ross-1 (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Yi, Z. Wind and Wave Analysis of QingShui Bay Based on WRF and SWAN Model. Available online: http://www.docin.com/p-1440602358.html (accessed on 26 April 2018).
- Contestabile, P.; Lauro, E.D.; Galli, P.; Corselli, C.; Vicinanza, D. Offshore wind and wave energy assessment around Malè and Magoodhoo island (Maldives). Sustainability 2017, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, P.; Ferrante, V.; Vicinanza, D. Wave energy resource along the coast of Santa Catarina (Brazil). Energies 2015, 8, 14219–14243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, R.X.; Wu, D. Deep learning for smart manufacturing: Methods and applications. J. Manuf. Syst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempener, R.; Neumann, F. Wave Energy Technology Brief. International Renewable Energy Agency, 2014. Available online: http://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2014/Wave-Energy_V4_web.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2018).
- Zang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, Y.; Fu, X. Hydrodynamic responses and efficiency analyses of a heaving-buoy wave energy converter with PTO damping in regular and irregular waves. Renew. Energy 2018, 116, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.W. Composable, Distributed-State Models for High-Dimensional Time Series. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Oerlemans, A.; Lao, S.; Wu, S.; Lew, M.S. Deep learning for visual understanding: A review. Neurocomputing 2016, 187, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A. Supervised Sequence Labelling; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012; pp. 5–13. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-642-24797-2_2 (accessed on 5 April 2018).
- Mozo, A.; Ordozgoiti, B.; GoÂmez-Canaval, S. Forecasting short-term data center network traffic load with convolutional neural networks. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimobaba, T.; Kakue, T.; Ito, T. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Regression for Depth Prediction in Digital Holography. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.00664 (accessed on 2 February 2018).
- Suryani, D.; Doetsch, P.; Ney, H. On the Benefits of Convolutional Neural Network Combinations in Offline Handwriting Recognition. Available online: https://www-i6.informatik.rwth-aachen.de/publications/download/1021/Suryani-ICFHR-2016.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2018).
- Wikipedia. Convolutional Neural Network. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convolutional_neural_network#Distinguishing_features (accessed on 29 June 2018).
- What are the Advantages of ReLU over Sigmoid Function in Deep Neural Networks. Stackexchange. Available online: https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/126238/what-are-the-advantages-of-relu-over-sigmoid-function-in-deep-neural-networks (accessed on 29 June 2018).
- Wang, H.Z.; Li, G.Q.; Wang, G.B. Deep learning based ensemble approach for probabilistic wind power forecasting. Appl. Energy 2017, 188, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, C. Sales Forecast in E-commerce using Convolutional Neural Network. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.07946 (accessed on 29 June 2018).
- Cross, P.; Ma, X. Nonlinear system identification for model-based condition monitoring of wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, D.R.; Hjort, N.L. Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S. Stephen Johnson on Digital Photography; O’Reilly: California, CA, USA, 2006; ISBN 0-596-52370-X. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.; Li, X.; Mo, Z.; Wu, H. Wind power prediction based on a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Circuits, Devices and Systems, Chengdu, China, 5–8 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fujieda, S.; Takayama, K.; Hachisuka, T. Wavelet Convolutional Neural Networks for Texture Classification; Cornel University Libruary: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Polikar, R. The Wavelet Tutorial Second Edition Part I. Available online: http://web.iitd.ac.in/~sumeet/WaveletTutorial.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2018).



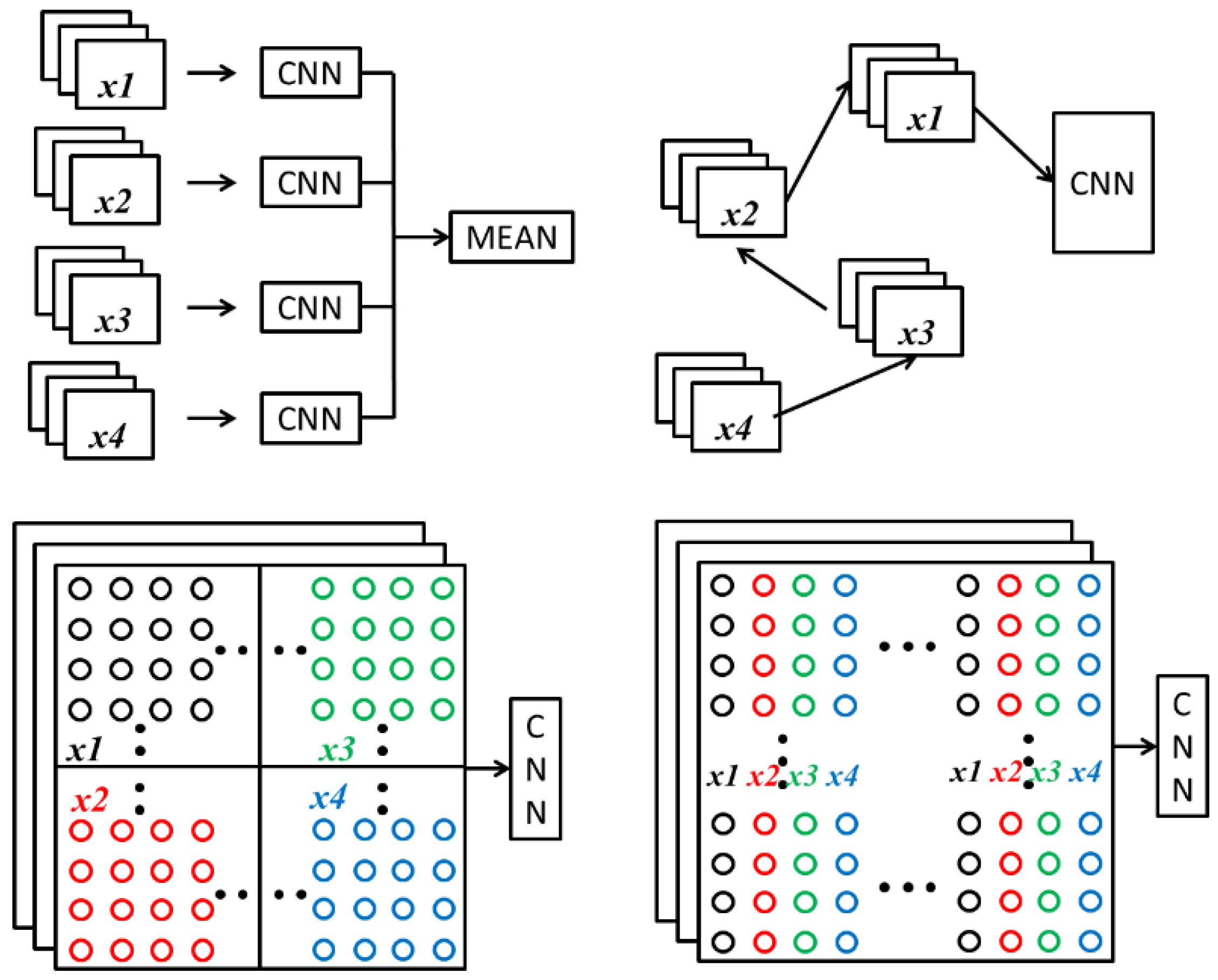
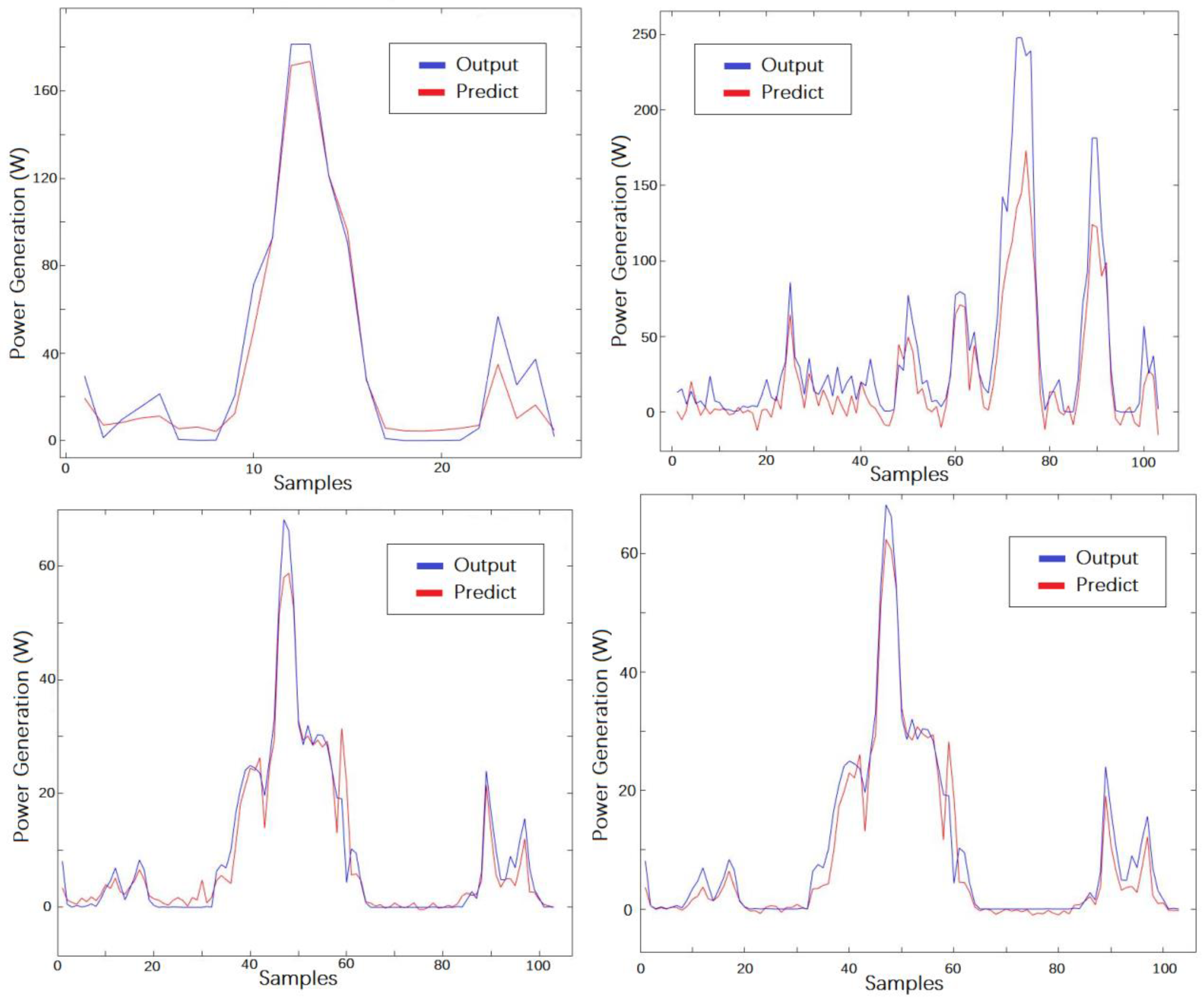
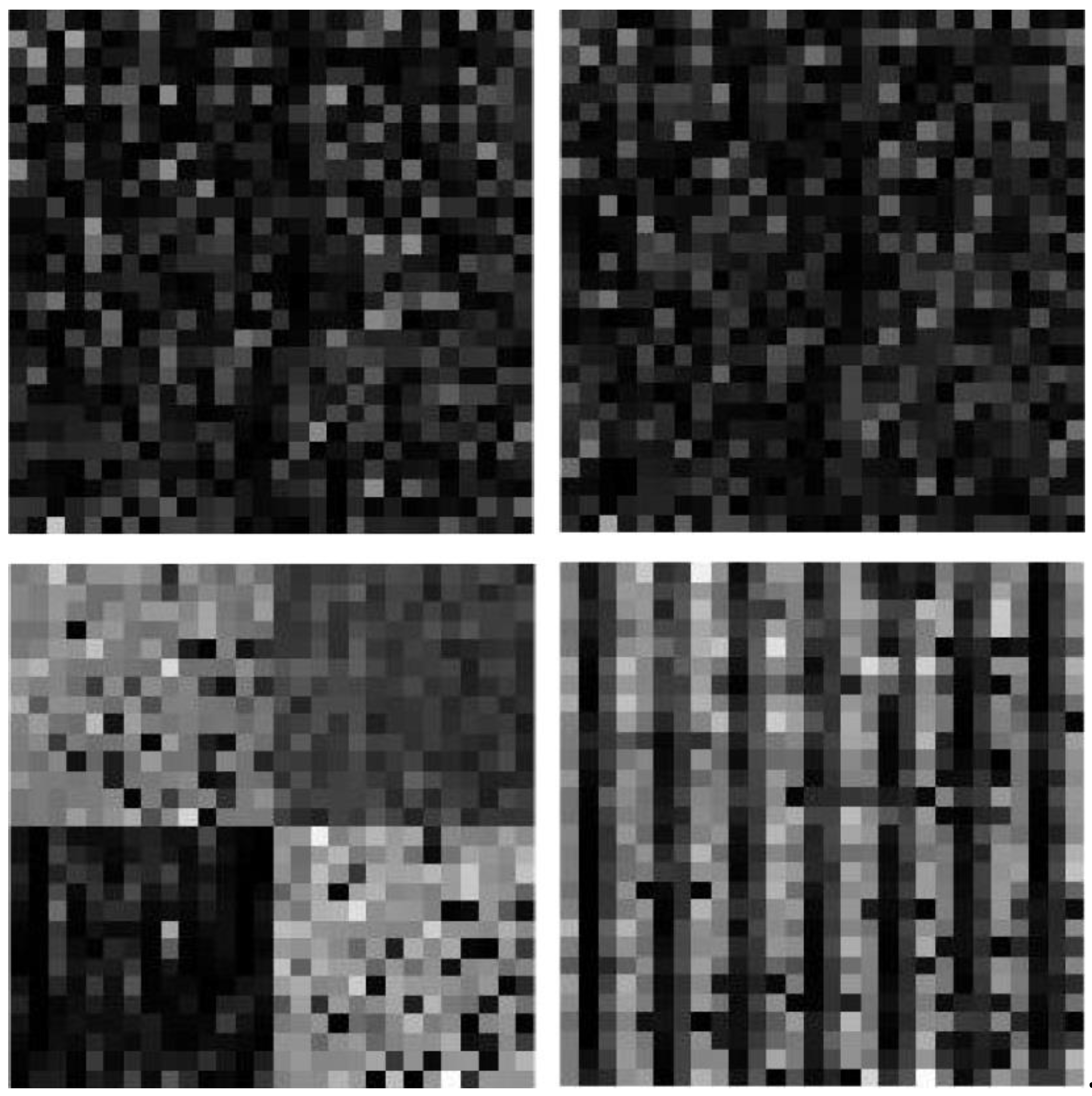
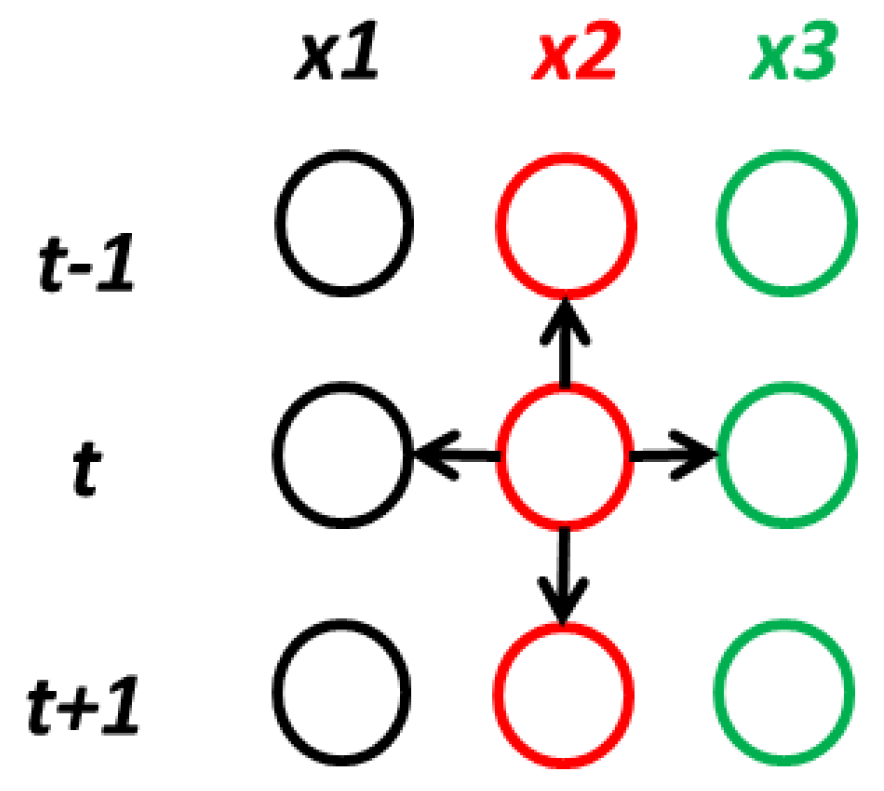
| Hyper-Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Input variables | 4 |
| CNN Layers | 25 |
| Fully Connected Layer | 40 |
| Predict Layer | 1 |
| Batch size | 20 |
| Number of Epochs | 100 |
| Image Size | 1st Conversion Method | 2nd Conversion Method | 3rd Conversion Method | 4th Conversion Method | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | |
| 28 × 28 | 10.02 | 8.05 | 0.95 | 23.48 | 21.19 | 0.85 | 3.37 | 2.23 | 0.94 | 3.11 | 1.92 | 0.96 |
| 20 × 20 | 16.43 | 8.64 | 0.91 | 29.46 | 23.67 | 0.77 | 3.63 | 1.84 | 0.94 | 3.76 | 2.14 | 0.93 |
| 12 × 12 | 20.48 | 9.63 | 0.87 | 25.21 | 19.82 | 0.83 | 4.45 | 2.81 | 0.91 | 4.25 | 2.45 | 0.92 |
| Approaches | RMSE | MAE | R2 | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANN | 2144.83 | 11.38 | 0.83 | 39.19 |
| SVM | 34.88 | 27.10 | 0.69 | 583 |
| RLR | 35.15 | 27.30 | 0.69 | 4.68 |
| MT | 23.36 | 12.92 | 0.86 | 7.21 |
| BT | 20.83 | 12.49 | 0.89 | 11.26 |
| CNN | 3.11 | 1.92 | 0.96 | 42.85 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, C.; Ma, X. Prediction of Wave Power Generation Using a Convolutional Neural Network with Multiple Inputs. Energies 2018, 11, 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082097
Ni C, Ma X. Prediction of Wave Power Generation Using a Convolutional Neural Network with Multiple Inputs. Energies. 2018; 11(8):2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082097
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Chenhua, and Xiandong Ma. 2018. "Prediction of Wave Power Generation Using a Convolutional Neural Network with Multiple Inputs" Energies 11, no. 8: 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082097
APA StyleNi, C., & Ma, X. (2018). Prediction of Wave Power Generation Using a Convolutional Neural Network with Multiple Inputs. Energies, 11(8), 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082097





