Experimental Study of Mixed Gas Hydrates from Gas Feed Containing CH4, CO2 and N2: Phase Equilibrium in the Presence of Excess Water and Gas Exchange
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
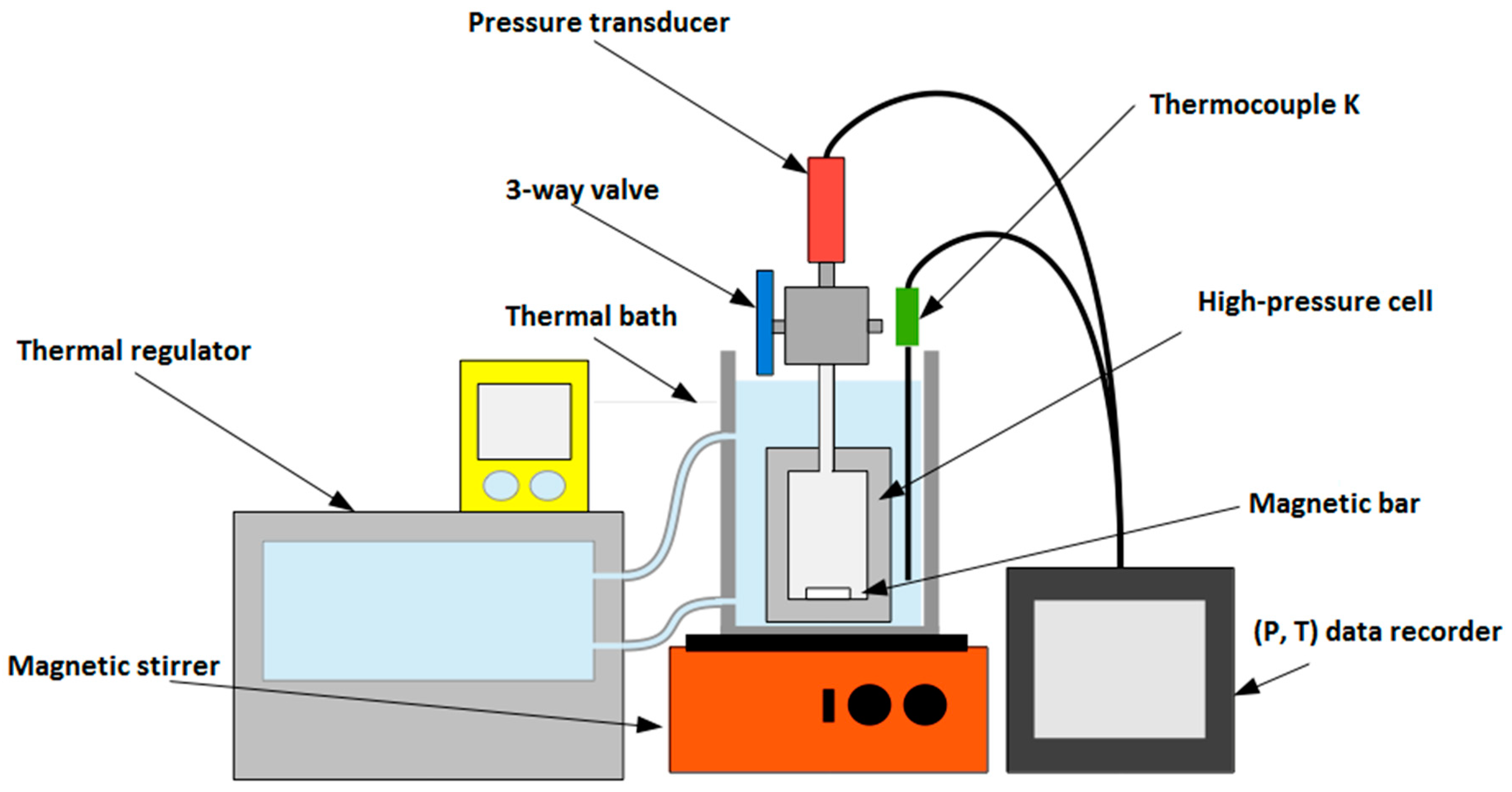
2.1. Experimental Setups
2.2. Materials
2.3. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
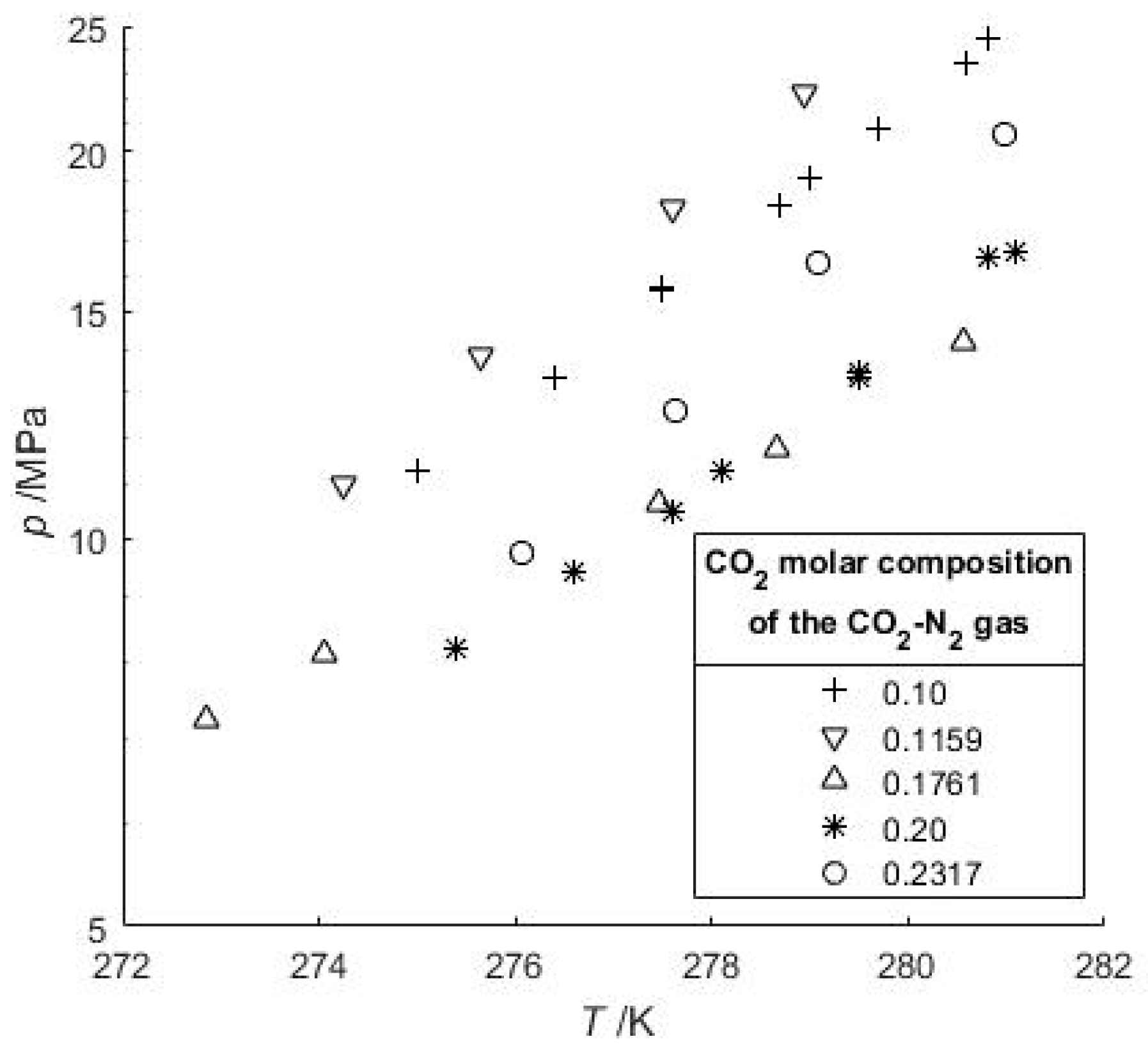
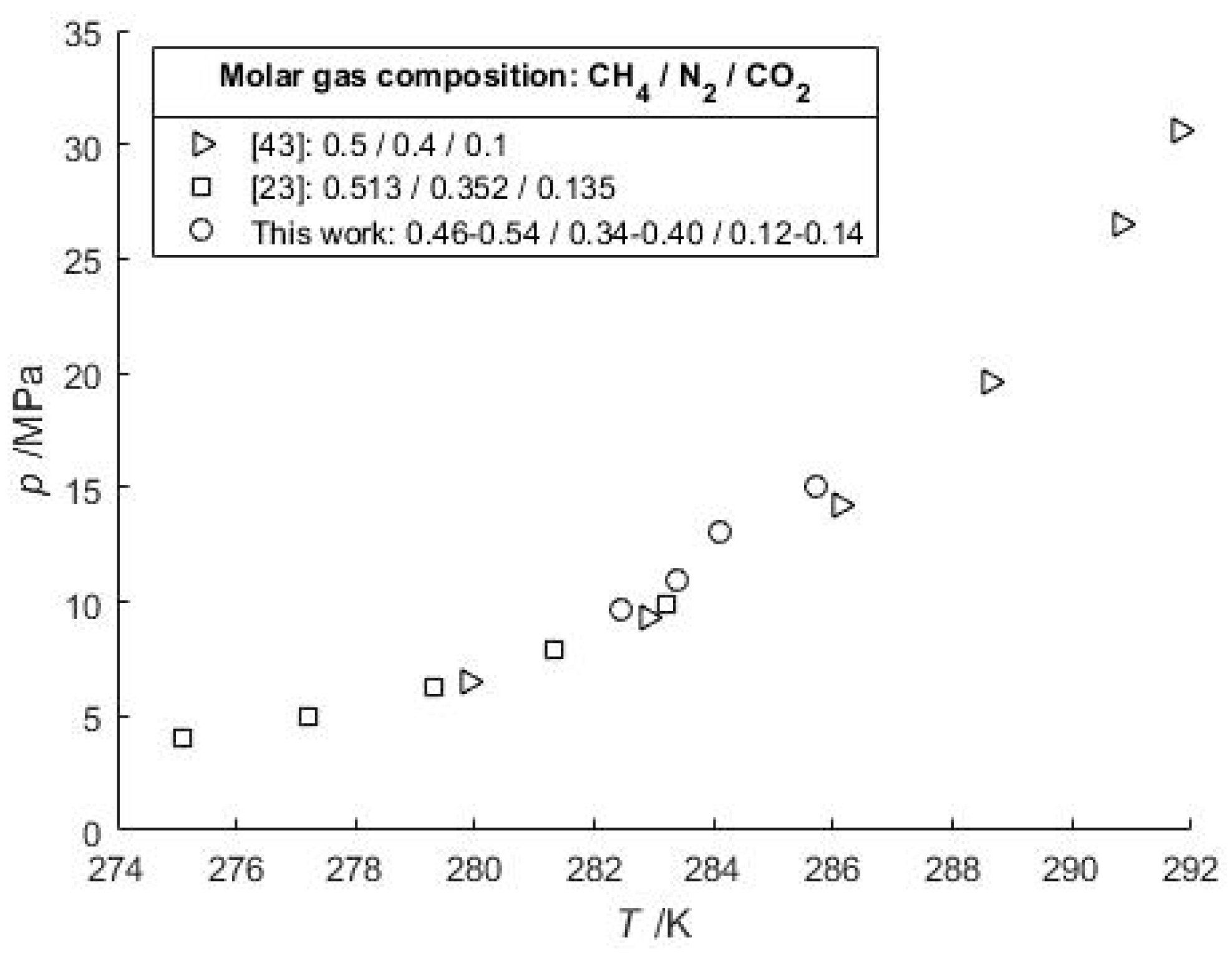
3.1. Phase Equilibrium of Mixed Gas Hydrates
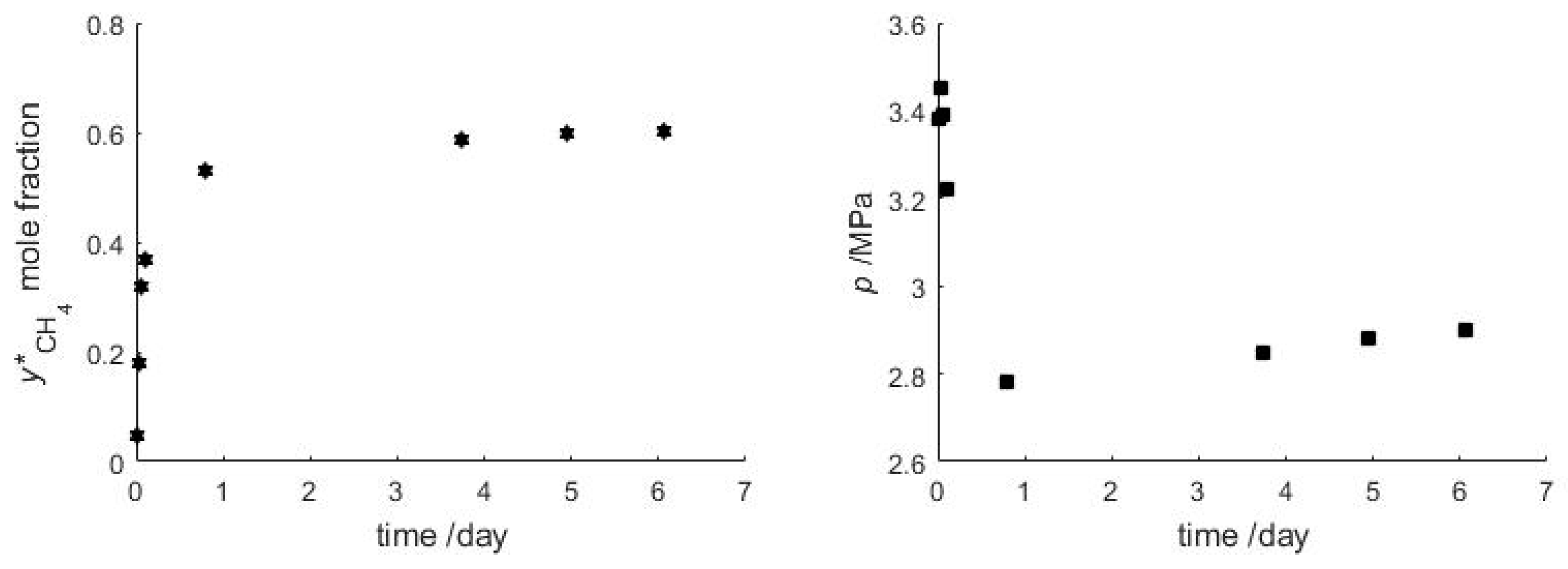
3.2. CH4-CO2 Exchange between a Vapor Phase and a Bulk Gas Hydrate Phase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Term | Symbol | Unit |
| Vapor phase composition of molecule i | yi | mole fraction |
| Vapor phase composition of molecule i without H2O | y*i | mole fraction |
| Gas hydrate composition of molecule i (i.e., hydration number for H2O) | hi | mole fraction |
| Gas hydrate composition of guest molecule i | h*i | mole fraction |
| Global composition of molecule i in the system | zi | mole fraction |
| Global composition of molecule i in the system without H2O | z*i | mole fraction |
Appendix A
| Time after Gas Replacement/h | T/K | p/MPa | y*CH4 Mole Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.53 | 277.0 | 3.38 | 0.049 |
| 0.97 | 277.8 | 3.45 | 0.178 |
| 1.47 | 277.8 | 3.39 | 0.318 |
| 2.65 | 277.8 | 3.22 | 0.368 |
| 18.90 | 277.7 | 2.78 | 0.530 |
| 89.73 | 277.7 | 2.85 | 0.586 |
| 118.90 | 277.8 | 2.88 | 0.597 |
| 145.73 | 277.7 | 2.90 | 0.603 |
References
- Sloan, E.D., Jr.; Koh, C.A. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Claypool, G.E.; Kvenvolden, K.A. Methane and other hydrocarbon gases in marine sediment. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1983, 11, 299–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvenvolden, K.A. Methane hydrate—A major reservoir of carbon in the shallow geosphere? Chem. Geol. 1988, 71, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinero, E.; Marquardt, M.; Hensen, C.; Haeckel, M.; Wallmann, K. Estimation of the global inventory of methane hydrates in marine sediments using transfer functions. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, M.; Khlystov, O.; Zemskaya, T.; Takahashi, N.; Minami, H.; Sakagami, H. Coexistence of structure I and II gas hydrates in Lake Baikal suggesting gas sources from microbial and thermogenic origin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L24603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Seo, Y.T.; Lee, J.W.; Moudrakovski, I.; Ripmeester, J.A.; Chapman, N.R.; Coffin, R.B.; Gardner, G.; Pohlman, J. Complex gas hydrate from the Cascadia margin. Nature 2007, 445, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourry, C.; Chazallon, B.; Charlou, J.L.; Donval, J.P.; Ruffine, L.; Henry, P.; Geli, L.; Cagatay, M.N.; Moreau, M. Free gas and gas hydrates from the Sea of Marmara, Turkey: Chemical and structural characterization. Chem. Geol. 2009, 264, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, J.S.; Parlaktuna, M.; Khokhar, A.A. Storing natural-gas a frozen hydrate. SPE Prod. Facil. 1994, 9, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, E.D. Fundamental principles and applications of natural gas hydrates. Nature 2003, 426, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslamimanesh, A.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Richon, D.; Naidoo, P.; Ramjugernath, D. Application of gas hydrate formation in separation processes: A review of experimental studies. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 46, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, K.S. A guide to CO2 sequestration. Science 2003, 300, 1677–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgaki, K.; Makihara, Y.; Takano, K. Formation of CO2 hydrate in pure and sea waters. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1993, 26, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, K.Z.; Schrag, D.P.; Harvey, C.F.; Lackner, K.S. Permanent carbon dioxide storage in deep-sea sediments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12291–12295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Huh, D.G.; Park, K.P.; Lee, J.; Lee, H. Sequestering carbon dioxide into complex structures of naturally occurring gas hydrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12690–12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoderbek, D.; Farrell, H.; Howard, J.; Raterman, K.; Silpngarmlert, S.; Martin, K.; Smith, B.; Klein, P. ConocoPhillips Gas Hydrate Production Test; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Boswell, R.; Schoderbek, D.; Collett, T.S.; Ohtsuki, S.; White, M.; Anderson, B.J. The Ignik Sikumi Field Experiment, Alaska North Slope: Design, Operations, and Implications for CO2–CH4 Exchange in Gas Hydrate Reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2016, 31, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Car, A.; Stropnik, C.; Yave, W.; Peinemann, K.V. Pebax®/polyethylene glycol blend thin film composite membranes for CO2 separation: Performance with mixed gases. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linga, P.; Adeyemo, A.; Englezos, P. Medium-pressure clathrate hydrate/membrane hybrid process for postcombustion capture of carbon dioxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Hu, J. A new cubic equation of state and its applications to the modeling of vapor-liquid equilibria and volumetric properties of natural fluids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 2997–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandino, O.; Trusler, J.M.; Vega-Maza, D. Phase behavior of (CO2 + H2) and (CO2 + N2) at temperatures between (218.15 and 303.15) K at pressures up to 15 MPa. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2015, 36, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westman, S.F.; Jacob Stang, H.G.; Lovseth, S.W.; Austegard, A.; Snustad, I.; Storset, S.O.; Ertesvag, I.S. Vapor-liquid equilibrium data for the carbon dioxide and nitrogen (CO2 + N2) system at the temperatures 223, 270, 298 and 303 K and pressures up to 18 MPa. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2016, 409, 207–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastanidis, P.; Romanos, G.E.; Stubos, A.K.; Economou, I.G.; Tsimpanogiannis, I.N. Two-and three-phase equilibrium experimental measurements for the ternary CH4 + CO2 + H2O mixture. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 451, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.H.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, G.B.; Guo, W.; Zhu, Y.H. Hydrate phase equilibrium of CH4 + N2 + CO2 gas mixtures and cage occupancy behaviors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 8133–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deusner, C.; Bigalke, N.; Kossel, E.; Haeckel, M. Methane Production from Gas Hydrate Deposits through Injection of Supercritical CO2. Energies 2012, 5, 2112–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, H.; Ota, M.; Smith, R.L., Jr.; Inomata, H. Review of CO2-CH4 clathrate hydrate replacement reaction laboratories studies-properties and kinetics. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 517–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.S.; Guo, T.M. Hydrate formation of CO2-rich binary and quaternary gas mixtures in aqueous sodium chloride solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1999, 44, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.B.; Majumdar, A.; Bishnoi, P.R. Experimental Studies on Hydrate Equilibrium-Carbon Dioxide and Its Systems. Int. J. Soc. Mater. Eng. Res. 1999, 7, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.T.; Kang, S.P.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.S.; Sung, W.M. Hydrate phase equilibria for gas mixtures containing carbon dioxide: A proof-of-concept to carbon dioxide recovery from multicomponent gas stream. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2000, 17, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.P.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.S.; Sung, W.M. Hydrate phase equilibria of the guest mixtures containing CO2, N2 and tetrahydrofuran. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2001, 185, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linga, P.; Kumar, R.; Englezos, P. Gas hydrate formation from hydrogen/carbon dioxide and nitrogen/carbon dioxide gas mixtures. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 4268–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruusgaard, H.; Beltrán, J.G.; Servio, P. Vapor− liquid water− hydrate equilibrium data for the system N2 + CO2 + H2O. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 2594–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herri, J.M.; Bouchemoua, A.; Kwaterski, M.; Fezoua, A.; Ouabbas, Y.; Cameirão, A. Gas hydrate equilibria for CO2–N2 and CO2–CH4 gas mixtures—Experimental studies and thermodynamic modelling. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2011, 301, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Do Seo, M.; Kang, J.W.; Lee, C.S. Hydrate-containing phase equilibria for mixed guests of carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2011, 306, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belandria, V.; Eslamimanesh, A.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Richon, D. Gas hydrate formation in carbon dioxide+ nitrogen+ water system: Compositional analysis of equilibrium phases. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 4722–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfaxi, I.B.A.; Belandria, V.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Lugo, R.; Richon, D. Phase equilibria of CO2 + N2 and CO2 + CH4 clathrate hydrates: Experimental measurements and thermodynamic modelling. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 84, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Seo, Y. Structure identification and dissociation enthalpy measurements of the CO2+N2 hydrates for their application to CO2 capture and storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 246, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.C.; Liu, C.L.; Meng, Q.G. Hydrate phase equilibrium of binary guest-mixtures containing CO2 and N2 in various systems. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2015, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeq, D.; Iglauer, S.; Lebedev, M.; Smith, C.; Barifcani, A. Experimental determination of hydrate phase equilibrium for different gas mixtures containing methane, carbon dioxide and nitrogen with motor current measurements. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 38, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazallon, B.; Pirim, C. Selectivity and CO2 capture efficiency in CO2-N2 clathrate hydrates investigated by in-situ Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixdorf, J.; Oellrich, L.R. Experimental determination of hydrate equilibrium conditions for pure gases, binary and ternary mixtures and natural gases. Fluid Phase Equilib. 1997, 139, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Nam, B.U.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, G.W.; Moon, D.; Shin, H.J.; Han, K.W.; Yoon, J.H. Thermodynamic stability, spectroscopic identification, and gas storage capacity of CO2–CH4–N2 mixture gas hydrates: implications for landfill gas hydrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4184–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakati, H.; Mandal, A.; Laik, S. Phase stability and kinetics of CH4 + CO2 + N2 hydrates in synthetic seawater and aqueous electrolyte solutions of NaCl and CaCl2. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Ro, H.; Seo, Y.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, H. Thermodynamic stability and guest distribution of CH4/N2/CO2 mixed hydrates for methane hydrate production using N2/CO2 injection. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2017, 106, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Liang, D. Phase Equilibrium Data for the Hydrates of Synthesized Ternary CH4/CO2/N2 Biogas Mixtures. J. Chem Eng. Data 2017, 63, 97–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffine, L.; Trusler, J. Phase behaviour of mixed-gas hydrate systems containing carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2010, 42, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga-Moreno, A.; Galicia-Luna, L.A. Densities of 1-Propanol and 2-Propanol via Vibrating Tube Densimeter from 313 to 363 K up to 25 MPa. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2002, 47, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffine, L.; Donval, J.P.; Charlou, J.L.; Cremière, A.; Zehnder, B.H. Experimental study of gas hydrate formation and destabilisation using a novel high-pressure apparatus. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2010, 27, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legoix, L.N.; Ruffine, L.; Donval, J.P.; Haeckel, M. Phase Equilibria of the CH4-CO2 Binary and the CH4-CO2-H2O Ternary Mixtures in the Presence of a CO2-Rich Liquid Phase. Energies 2017, 10, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi, B.; Burgass, R.W.; Danesh, A.; Østergaard, K.K.; Todd, A.C. Improving the accuracy of gas hydrate dissociation point measurements. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 912, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, H.O., Jr.; Campbell, J.M. Natural gas hydrates at pressures to 10,000 psia. J. Pet. Technol. 1961, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Adisasmito, S.; Frank, R.J.; Sloan, E.D., Jr. Hydrates of carbon dioxide and methane mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1991, 36, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.O.; Yang, I.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, C.S. Measurement and prediction of phase equilibria for water + CO2 in hydrate forming conditions. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2000, 175, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.H.; Anderson, R.; Tohidi, B. Carbon monoxide clathrate hydrates: Equilibrium data and thermodynamic modeling. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 2825–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somait, F.A.; Kidnay, A.J. Liquid-vapor equilibriums at 270.00 K for systems containing nitrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1978, 23, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, Q.; Sabil, K.M.; Lau, K.K. Measurement of isothermal (vapor+ liquid) equilibria, (VLE) for binary (CH4 + CO2) from T = (240.35 to 293.15) K and CO2 rich synthetic natural gas systems from T = (248.15 to 279.15) K. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, J.G.; Bruusgaard, H.; Servio, P. Gas hydrate phase equilibria measurement techniques and phase rule considerations. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 44, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falenty, A.; Qin, J.; Salamantin, A.N.; Yang, L.; Kuhs, W.F. Fluid composition and kinetics of the in situ replacement in CH4-CO2 hydrate system. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 27159–27172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference | T/K p/MPa | CO2 Mole Fraction | Number of Data Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| [26] | 273.1–280.2 1.22–3.09 | z*CO2= 0.9099–0.9652 | 9 |
| [27] | 273.4–281.9 1.986–9.550 | z*CO2 = 0.20–0.75 y*CO2 = 0.1620–0.7189 | 15 |
| [28,29] | 272.85–284.25 1.565–24.12 | z*CO2 = 0.0663–0.9659 | 28 |
| [30] | 273.7 7.7 | z*CO2 = 0.169 y*CO2 = 0.139 | 1 |
| [31] | 275.3–283.1 1.6–22.4 | z*CO2 = 0.21–0.80 y*CO2 = 0.162–0.787 | 24 |
| [32] | 273.4–281.1 5.30–6.60 | y*CO2 = 0.16–0.59 | 16 |
| [33] | 276.88–285.41 5.0–20.0 | z*CO2 = 0.841–0.906 | 16 |
| [34] | 273.6–281.7 2.032–17.628 | yCO2 = 0.127–0.747 | 35 |
| [35] | 278.1–285.3 3.24–29.92 | z*CO2 = 0.271–0.812 | 9 |
| [36] | 275.0–281.1 8.23–24.51 | z*CO2 = 0.1–0.2 | 17 |
| [37] | 273.4–278.4 5.28–17.53 | z*CO2 = 0.101–0.251 | 17 |
| [38] | 275.75–284.45 5–20 | z*CO2 = 0.26–0.36 | 10 |
| [39] | 270.5–278.3 | z*CO2= 0.01–0.47 | 9 |
| This work | 276.06–280.97 9.762–20.583 | z*CO2 = 0.2317 | 4 |
| Reference | T/K p/MPa | CH4 Mole Fraction | CO2 Mole Fraction | N2 Mole Fraction | Number of Data Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [40] | 276.85–293.41 3.454–23.979 | z*CH4 = 0.9497 | z*CO2 = 0.05 | z*N2 = 0.0003 | 6 |
| [41] | ca. 274–282 ca. 2–5 | z*CH4 = 0.41–0.55 | z*CO2 = 0.29–0.40 | z*N2 = 0.05–0.30 | 26 |
| [42] | 284.50–289.34 8.75–11.23 | z*CH4 = 0.8989 | z*CO2 = 0.05 | z*N2 = 0.0511 | 6 |
| [43] | 279.6–293.0 4.81–30.66 | z*CH4 = 0.5–0.9 | z*CO2 = 0.02–0.1 | z*N2 = 0.08–0.4 | 30 |
| [23] | 274.9–283.9 2.29–14.97 | y*CH4 = 0.203–0.826 | y*CO2 = 0.052–0.604 | y*N2 = 0.05–0.577 | 45 |
| [44] | 276.2–286.3 2.59–8.84 | z*CH4 = 0.4995–0.7005 | z*CO2 = 0.1998–0.4503 | z*N2 = 0.0490–0.1093 | 34 |
| This work | 282.46–288.62 9.679–15.645 | z*CH4 = 0.46–0.941 | z*CO2 = 0.015–0.14 | z*N2 = 0.044–0.379 | 5 |
| T/K | p /Mpa Experiment | p/MPa CSMGem (Deviation %) [1] | z*N2 | z*CO2 | z*CH4 | H2O:Gas Feed Molar Ratio | H2O Saturation vol.% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 276.06 | 9.762 | 11.165 (14.4) | 0.7683 | 0.2317 | 0 | 19.45 | 58.3 |
| 277.63 | 12.584 | 14.504 (15.3) | 0.7683 | 0.2317 | 0 | 21.52 | 66.8 |
| 279.09 | 16.373 | 18.539 (13.2) | 0.7683 | 0.2317 | 0 | 24.32 | 74.9 |
| 280.97 | 20.583 | 23.873 (16.0) | 0.7683 | 0.2317 | 0 | 24.25 | 78.2 |
| 280.92 | 3.410 | 3.5798 (5.0) | 0 | 0.8996 | 0.1004 | 44.66 | 83.2 |
| 282.61 | 4.291 | 4.3982 (2.5) | 0 | 0.8996 | 0.1004 | 37.46 | 83.2 |
| 284.97 | 6.206 | 6.3211 (1.9) | 0 | 0.8996 | 0.1004 | 42.47 | 91.9 |
| 282.46 | 9.679 | No convergence | 0.40 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 5.31 | 41.5 |
| 283.37 | 10.964 | 10.419 (−5.0) | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 6.32 | 39.4 |
| 284.11 | 13.102 | 10.901 (−16.8) | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.54 | 5.49 | 40.3 |
| 285.70 | 15.055 | 13.860 (−7.9) | 0.37 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 4.67 | 39.6 |
| 288.62 | 15.645 | 14.068 (−10.1) | 0.044 | 0.015 | 0.941 | 3.90 | 38.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Legoix, L.N.; Ruffine, L.; Deusner, C.; Haeckel, M. Experimental Study of Mixed Gas Hydrates from Gas Feed Containing CH4, CO2 and N2: Phase Equilibrium in the Presence of Excess Water and Gas Exchange. Energies 2018, 11, 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081984
Legoix LN, Ruffine L, Deusner C, Haeckel M. Experimental Study of Mixed Gas Hydrates from Gas Feed Containing CH4, CO2 and N2: Phase Equilibrium in the Presence of Excess Water and Gas Exchange. Energies. 2018; 11(8):1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081984
Chicago/Turabian StyleLegoix, Ludovic Nicolas, Livio Ruffine, Christian Deusner, and Matthias Haeckel. 2018. "Experimental Study of Mixed Gas Hydrates from Gas Feed Containing CH4, CO2 and N2: Phase Equilibrium in the Presence of Excess Water and Gas Exchange" Energies 11, no. 8: 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081984
APA StyleLegoix, L. N., Ruffine, L., Deusner, C., & Haeckel, M. (2018). Experimental Study of Mixed Gas Hydrates from Gas Feed Containing CH4, CO2 and N2: Phase Equilibrium in the Presence of Excess Water and Gas Exchange. Energies, 11(8), 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11081984





