Abstract
Most sun-tracking systems of solar concentrators are expensive, sensitive to operational costs, and complicated in optical design in which the receiver must be free to rotate about the axis. To overcome the aforementioned problems, this study presents a fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator (FFFSC) using polar-axis tracking which allows the Fresnel lens to concentrate sunlight to a fixed small heat-receiving area and the receiver remained fixed in location and rotation. Experimental research has been conducted to obtain the optical characteristics of the FFFSC for different solar times, tracking errors, and periodical adjustment errors. It has been found that maximum values of the relative optical efficiency loss (ηre-opt,loss) and minimum value of the optical efficiency (ηopt) of the FFFSC for different solar times are 1.87% and 71.61%, respectively. The mean value and maximum value of the local concentration ratio of the solar flux on the receiver are more than 86.64 and 1319.43, respectively. When the tracking error and periodical adjustment error are within 1°, the ηopt of the FFFSC can reach 70.38% and 68.94%, respectively. The optical characteristics of FFFSC is also verified numerically. Especially, according to the total year simulation of the FFFSC’s optical characteristics, maximum value of ηre-opt,loss is 0.116%, which means the proposed the FFFSC can achieve fixed-focus.
1. Introduction
Serious environmental problems which affect human health due to fossil fuel consumption have drawn worldwide awareness in recently years [1,2]. So far solar energy represents one of the best alternatives to reduce the burning of fossil fuels, which have drawn much attention worldwide [3]. With more and more research available, various types of solar concentrators are usually employed to collect solar energy [4].
Concentrating technologies are subdivided into line-focusing systems and point-focusing systems. The linear Fresnel solar collector is one of the most promising techniques of line-focusing systems, and many studies have been made and many ideas have been investigated. Zhu et al. [5] proposed a semi-parabolic linear Fresnel reflector solar concentrator, which has no shading and blocking shortcomings and can reduce the manufacturing cost. Huang et al. [6] proposed an azimuth tracking linear Fresnel solar concentrator, which can obtain annual mean total efficiency of 61% when the operational temperature of the receiver is 400 °C. Bellos et al. [7] investigated a linear Fresnel solar collector with a flat plate receiver, which can produce about 8.5 kW of useful heat in summer, 5.3 kW in spring, and 2.9 kW in winter. In order to enhance the thermal performance of the solar linear Fresnel reflector, Bellos et al. [8] also investigated the use of nanofluids. The final results show that the maximum thermal efficiency enhancement with the nanofluid is close to 0.8% at the expense of increasing the pumping work demand up to 50%. Boito et al. [9] presented the methods concerning the optical optimization of a linear Fresnel collector. Rungasamy et al. [10] proposed a compact linear Fresnel system which can create multiple receiver targets for the reflectors to reduce optical losses as adjacent mirrors have dissimilar angles. Since lower and smaller receivers may reduce the system cost, Benyakhlef et al. [11] investigated the effect of mirror curvature on optical performance of a linear Fresnel reflector solar field to find a trade-off between heliostat curvature and receiver height.
However, the point-focusing systems can produce a higher temperature compared with that of line-focusing systems because it enables higher concentration ratios to increase the energy density. In order to ensure that the point-focusing systems can receive maximum solar irradiation at all times, a two-axis sun-tracking system is always used in the solar system, especially azimuth-elevation tracking systems. Valmiki et al. [12] designed and experimentally tested a solar cooking stove with a Fresnel lens which can face the sunlight and concentrate it to a fixed heat-collecting area to maintain a stovetop surface at temperatures around as high as 300 °C. Zheng et al. [13] designed a centralized solar collection system based on the combination of a light funnel concentrator with a deflector, and the results show that the maximum energy density of the focal speckle on the receiver reaches 2500 W/m2. Schmitz et al. [14] designed a six-focus, high-concentration photovoltaic-thermal solar polygeneration system with a high geometric concentration ratio of 1733× at each of its six receivers. Chong et al. [15] reported a dense array concentrator photovoltaic system, which consists of a primary concentrator in the form of a non-imaging dish concentrator with a flux concentration ratio of more than 400 suns and a secondary concentrator.
Though the combination of a point-focus concentrator with an azimuth-elevation tracking system can obtain a high energy density, the solar concentrator must be free to rotate about the zenith-axis and the axis parallel to the surface of the Earth in the azimuth-elevation tracking. In other words, using an azimuth-elevation tracking system for a point-focus concentrator dramatically upsurges the system efficiency, but, in return, this results in an increase in the initial and operational costs. Compared with the azimuth-elevation tracking, the advantage of polar-axis tracking is that polar-axis tracking was the best one-axis tracker, delivering around 97% of the yearly energy of azimuth-elevation trackers, and its tracker cost is approximately half that of the azimuth-elevation one [16]. The tracking velocity of polar-axis tracking is almost constant at 15 degrees per hour and the sun declination angle may change weakly in several days [17].
Therefore, the control system of polar-axis tracking is easy to design. Yabe et al. [18] proposed a laser system that uses the Fresnel lens with a polar tracking system. Alexandru et al. [19] designed a polar dual-axis system for improving the energetic efficiency of a photovoltaic panel, it can reduce the angular field of the daily motion and the number of actuating operations, without significantly affecting the incoming solar energy. Lv et al. [20] investigated a concentrator photovoltaic (CPV) system with the polar tracking system which can satisfy to the maximum extent and the operating costs of the CPV system can be reduced. However, solar receivers must still be free to rotate with the solar concentrator which increases the energy consumption for tracking and cannot be separated or repaired conveniently. Thus, the key idea is to maximize the energy gained through orientation, and to minimize the energy consumption for tracking of the sun’s path. The energy reductions can be made by reducing the angular revolution field and the load of the solar concentrator, without significantly affecting the incident radiation.
In this paper, a fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator (FFFSC) is proposed as a new type of solar concentrator, which combines a Fresnel lens and a polar-axis tracking system. The FFFSC has the advantages of lower manufacturing cost than that of azimuth-elevation tracking systems and lower energy consumption by concentrating sunlight to a fixed small heat-receiving area (fixed-focus) in tracking the sun compared with that of the solar receiver needed to rotate with the solar concentrator. The optical performance of the FFFSC is tested experimentally and simulated numerically, considering the effects of different solar times, tracking errors, and periodical adjustment errors.
2. Working Principle of a Fixed-Focus Fresnel Lens Solar Concentrator
Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram of the FFFSC. The FFFSC uses a polar-axis tracking system in which the polar-axis of rotation is aligned parallel with the polar-axis of the Earth, and the declination axis is perpendicular to the polar axis. On the basis of guaranteeing the tracking accuracy, the tracking with the polar-axis biaxial linkage converts the sun’s elliptical moving trajectory to the solar azimuth spinning on the east–west single tilt axis and the declination angle pitching in the north–south direction. The sun declination angle of the FFFSC is changing due to the yearly change of the sun’s path [21]. Based on the rotation behavior of the Earth, the Fresnel lens rotates around the polar-axis from east to west every day by the earth rotation angular velocity. The focus of Fresnel lens is on the intersection of the two axes. Furthermore, the horizontal angle of the polar-axis depends on the local latitude angle (Φ), and the tracking angle of the declination axis is dependent on the sun declination angle (δ). In this study, coupling with the latitude angle of Guangzhou (latitude: 23°08′), the horizontal angle of the polar axis is 23°08′. Mechanical control is achieved through the use of a 12 V, DC gear motor and a manual lead screw adjustment device, the gear motor controls the rotation of the polar axis that holds the entire system. A manual lead screw adjustment device controls the sun declination angle of the arms that hold the Fresnel lens. The mechanical structure and installation resolve the conflict between tracking accuracy and operating cost. This kind of installation can greatly eliminate the impact of the Earth’s rotation by the rotating polar axis, avoiding power consumption owing to the frequent rotation in a relatively short period.
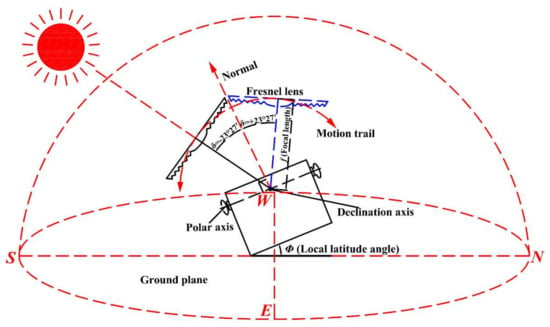
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of a fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator.
3. The Optical Experimental Analysis of a Fixed-Focus Fresnel Lens Solar Concentrator
To validate the fixed-focus performance of the FFFSC, an indirect measuring system was designed for performance testing in the real weather conditions. Figure 2a shows the schematic diagram of the indirect measuring system of FFFSC. The system mainly consists of a giant Fresnel lens, a polar-axis tracking unit, a solar pyranometer, an adjustable platform, a diffuse flat receiver, a CCD (charge-coupled device) camera, an absorptive-reflective neutral density filter (ND-filter), a data acquisition system, etc. Figure 2b shows the fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator using polar-axis tracking. The Fresnel lens was made of PMMA with an aperture diameter of 1100 mm, a thickness of 3 mm, with a groove pitch of 1 mm and a focal length of 1000 mm.
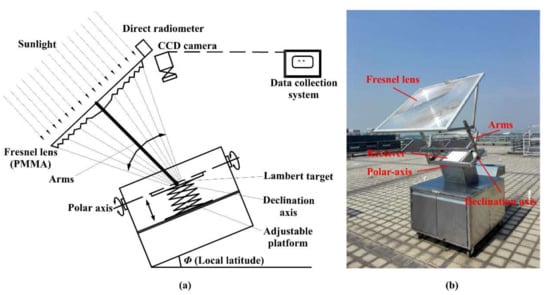
Figure 2.
(a) Schematic diagram of the experiment platform; and (b) a photo of the fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator using polar-axis tracking.
Sunlight passing through the Fresnel lens is finally directed to the diffuse flat receiver located at the focal point of the lens which is placed in parallel to the adjustable platform. The polar-axis tracking unit was used for sun tracking. On the basis of guaranteeing the tracking accuracy, the declination angle in the north–south direction was manually adjusted. The direct solar irradiance was measured by a solar pyranometer. The CCD camera was calibrated and used to shoot the image of the focal spot on the diffuse flat receiver. Both the camera and the lens were placed in the same plane, and the CCD camera was tilted to take the image of the receiver. In this particular situation, the problem of the angle between the CCD camera and the receiver is less significant [22]. Absorptive-reflective neutral density filters were placed in front of the camera lens to decrease the intensity of reflected concentrated radiation. After the test, the images taken by the CCD camera were recorded and processed by a data acquisition system in order to obtain the flux density distribution of the focal spot, including correcting the distortion of the image, transforming the coordinate unit, and converting the greyscale of the images to flux intensity. Although it is difficult to obtain an absolute irradiance value using the CCD camera as its sensitivity depends on the response wavelength, the relative irradiances under different experimental conditions for the same FFFSC are valid. The experiments were carried out in Guangzhou on 9 November 2017 (sun declination angle (δ): −16°48′). All the measuring instruments used in the tests has been calibrated and checked the conformance of the measuring instrument to the standards. The main parameters measured in this study were the solar radiation, tracking angle, and the flux density distribution on the diffuse flat receiver. The main errors were likely to be related to instrumentation issues (sensitivity and measurement inaccuracy), which can be calculated from Equation (1) [23]. Errors associated with the measuring instruments are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Accuracies and errors for measurement instruments.
3.1. Focal Spot Deviation
Figure 3 shows the flux density distributions on the diffuse flat receiver when the Fresnel lens and the receiver surface are adjusted to be parallel, which is in accordance with the situation of the rotating solar receiver. Generally, the aperture radius of the receiver is about 50 mm; therefore, a red circular area with a radius of 50 mm on the diffuse flat receiver is defined as the receiver area in experiment, which coincides with engineering actuality [24]. It is noted that irradiance on the diffuse flat receiver is basically distributed in the red circular area, and the optical characteristics of that is used as a reference group.
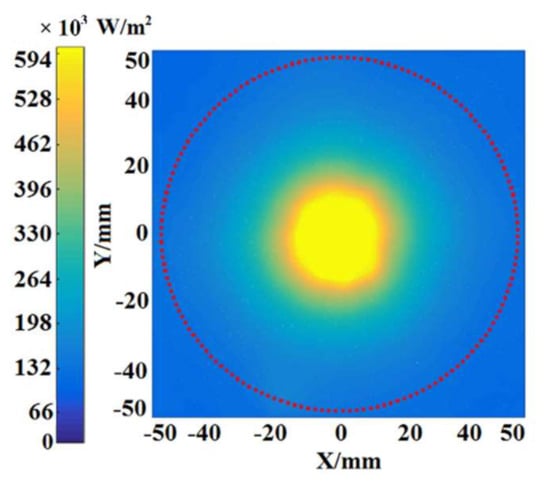
Figure 3.
The flux density distribution on the diffuse flat receiver when the Fresnel lens is parallel to the receiver surface.
In order to reduce the impact of irradiation fluctuation on measurement accuracy [25], the experiments were carried out between solar time 10:00 and 14:00. Figure 4 illustrates the flux density distributions on the diffuse flat receiver for apparent solar time at 10:00–14:00 with a one-hour interval. It can be seen that the focal spot is basically distributed in a red circular area and presents a different angle with the coordinate axis under different apparent solar time. Since the receiver is fixed, part of the light may not be received when the actual optical focus is offset. For the sake of describing the focal spot deviation, the optical efficiency of the FFFSC can be calculated by:
where Erec is the total energy received by the receiver with an aperture radius of 50 mm, R is the radius of Fresnel lens, and I is the direct solar irradiance for Fresnel lens. The mean value and maximum value of the local concentration ratio of the solar flux are simply obtained by applying Equation (3) and Equation (4), respectively:
where Gmean is the mean flux density on a receiver area, Gmax is the maximum flux density on a receiver area. To compare the optical characteristics of the FFFSC with the rotating solar receiver, the relative optical efficiency loss can be calculated by:
where Erec,ref is the total energy received by the receiver in the reference group. The threshold of the proposed FFFSC on the validity of fixed-focus performance that depends on the relative optical efficiency loss of FFFSC is 10%, which meets the general requirements of the solar concentrator [26].
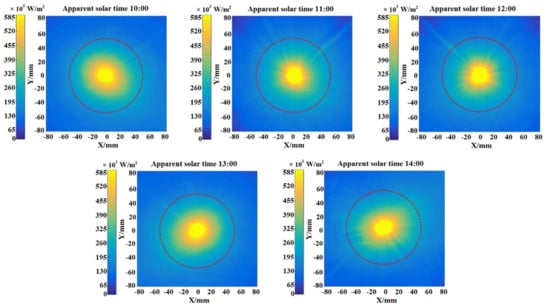
Figure 4.
The flux density distributions of focal spot under different apparent solar times.
Table 2 indicates experimental optical characteristics of the FFFSC under different apparent solar times measured in this work. As can be observed in the table, the relative optical efficiency loss between the experimental group and the reference is lower than 1.87%, which means the FFFSC can achieve a fixed-focus in the experiment. It is also remarkable the interdependence of Xmax, Xmean, and apparent solar time. This result was expected since, individually, there is an angle between the optical axis of the Fresnel lens and the receiver plane normal which is caused by changes of the solar hour angle, and that will lead to a change of the focal spot shape on the receiver. Moreover, the optical efficiency of the FFFSC is more than 71.61%, and the mean value and maximum value of the local concentration ratio of the solar flux on the receiver are more than 86.64 and 1319.43, respectively, as can be observed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Experimental optical characteristics of a fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator under different apparent solar times measured in this work.
3.2. Tracking Precision Requirement
Since the position of the sun in the sky changes all the time, the Fresnel lens usually needs to keep track of the sun. Generally, there exists a lag between the tracking position and the actual position of the sun, which leads to the tracking error and may cause the focal spot to move off the scope of the receiver. The requirement for tracking precision means the maximum acceptance angle that is allowed in tracking, and it is a main factor that influences the performance of the FFFSC. The acceptance angle is defined as the error angle at which the relative optical efficiency loss of the FFFSC is less than 10% [26]. In this experiment, the Fresnel lens was kept fixed for a period, while the change of the focal spot was recorded every minute using the CCD camera. Figure 5 shows flux density distribution shot by the CCD camera on the diffuse flat receiver for the tracking error angles from 0 to 2.5° with an interval angle of 0.5°.
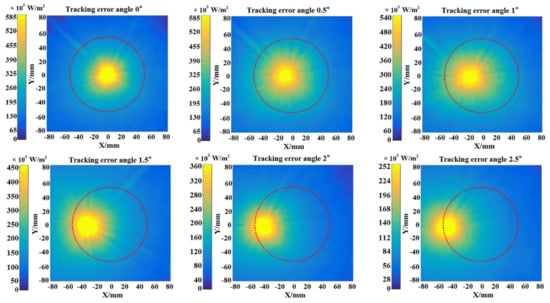
Figure 5.
The flux density distributions of focal spot under different tracking error angles.
It can be seen from Figure 5 that the focal spots are almost located in the red circular area when tracking is precise. With the increase of the tracking error angle, some of the focal spots tend to deviate from the red circular boundary. As a result, the focal spots are still located in the red circular area within the tracking error angle of 1.5°. Table 3 indicates the experimental optical characteristics of the FFFSC under different tracking error angles measured in this work. When the tracking error angle is within 1°, the FFFSC has lower relative optical efficiency loss of less than 3.55%; when the tracking error angle is bigger than 1.5°, the relative optical efficiency loss increases sharply, which is up to 17.42%. From this analysis, we can conclude that the tracking precision requirement should be about 1°. This accords with the requirement of a general solar concentrator for tracking accuracy [27].

Table 3.
Experimental optical characteristics of the fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator under different tracking error angles.
3.3. Effect of the Periodical Adjustment Error
For the FFFSC using polar-axis tracking, the focal spot and its position will change with the sun declination angle even when the tracking error angle is 0°. If the rotation angle of the declination axis is not suitable for the change of the sun declination angle when periodically adjusting the FFFSC, the focal spot would deviate from the red circular area.
An experiment was also conducted to evaluate this effect by changing the periodical adjustment error angle. During the experiment, the rotation angle of the declination axis was adjusted according to the sun declination angle, and the periodical adjustment error angle changed from 0 to 2.5° with an interval of 0.5°, too. The flux density distribution of focal spots under different periodical adjustment error angles are illustrated in Figure 6. It can be seen from the figure that the focal spot deviation rises with the increase of the periodical adjustment error angle, and the focal spots are still located in the red circular area within the periodical adjustment error angle of 1°. When the periodical adjustment error angle exceeded 1.5°, the focal spot began to depart from the red circular boundary.
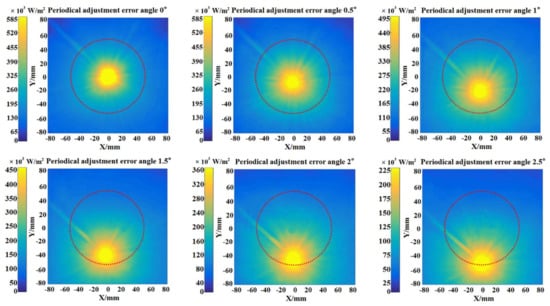
Figure 6.
The flux density distributions of focal spot under different periodical adjustment error angle.
Experimental optical characteristics of the FFFSC under different periodical adjustment error angle measured in this work are shown in Table 4. It is noticeable that the relative optical efficiency loss of FFFSC is 5.53% for the periodical adjustment error angle of 1°. As discussed before, this angle could be considered as the allowable periodical adjustment error angle. Because the maximum change of sun declination angle for one day does not exceed 0.5° [28], in other words, it may be appropriate to adjust the FFFSC’s declination axis with the period of two days when the sun declination angle is −16°48′.

Table 4.
Experimental optical characteristics of the fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator under different periodical adjustment error angle.
4. The Optical Simulation Analysis of the Fixed-Focus Fresnel Lens Solar Concentrator
In this section, the fixed-focus performance of the FFFSC is established by means of numerical methods. With these models, focal spot deviation of the FFFSC under different tracking conditions can be predicted. The optical simulation can also provide a method to evaluate the influence of independent parameters on the FFFSC’s performance, which are difficult to be obtained only by outdoor experiments. A raytracing program based on the Monte Carlo method for optical analysis of solid models named TracePro® (Lambda Research Corporation, Littleton, MA, USA) is then used to simulate the scattering and diffraction of light, and to sample of the distribution of rays emanating from certain light sources. TracePro® is a raytracing visual software where 3D modelling is allowed. It makes use of variance reduction techniques to reduce the number of rays required to obtain a reliable result [29]. TracePro® has been validated as a lighting design software, where it has been used in numerous research works as a part of the design process [29,30,31]. In Monte Carlo raytracing, scattering and diffraction are treated as random processes. Instead of propagating a distribution of light, discrete samples of the distribution, or rays, are propagated. The samples are randomly chosen, using the scattering distribution as a probability density. This allows the well-developed techniques of raytracing to be used to model scattering [32]. Solid models were created to obtain the light rays on the receiver.
According to the above reference discussions, the CAD model of the FFFSC was made and imported to the raytracing code Tracepro® V4.1.6 via an intermediate ACIS format, and the sizes were the same as the experimental FFFSC. The solar spectrum from 300 to 2500 nm is applied to the simulation with the solar half-angle of 0.27° [33]. Fresnel losses and absorption in dielectric materials are considered, but surface scattering and teeth rounded edges of the Fresnel lens are neglected. The corresponding refraction index of PMMA in Tracepro® can be calculated using Cauchy’s equation [34]:
where n is the refractive index, λ is the wavelength, and a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, etc., are the constant coefficients. , , , , , and the unit of λ is µm [35]. Different distributions of the Fresnel lens’ slope error and the FFFSC’s tracking error are proposed in literature which is based on the long-term performances of the solar system [36,37], but both of them are ignored in the simulation. The ray path passing through the FFFSC is illustrated in Figure 7.
Figure 7.
The ray path passing through fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator.
4.1. Focal Spot Deviation
Optical simulation is performed using the same condition as the experiment. The flux density distribution of the focal spots for various apparent solar times are presented in Figure 8. It can be seen that the flux density distribution of focal spots agreed well with the results of experiment that is shown in Figure 4. Similarly, simulation optical characteristics of the FFFSC have been measured in this work. The flux density distributions on the receiver when it is parallel to the Fresnel lens has been simulated, and the optical characteristics of that is also used as a reference group. The relative optical efficiency loss between the simulation group and the reference is lower than 0.062%, which means the FFFSC can realize a fixed-focus during the tracking process. Moreover, the optical efficiency of the FFFSC can reach about 74.80%, and the mean value and maximum value of the local concentration ratio of the solar flux on the receiver are more than 90.45 and 1371.12, respectively.
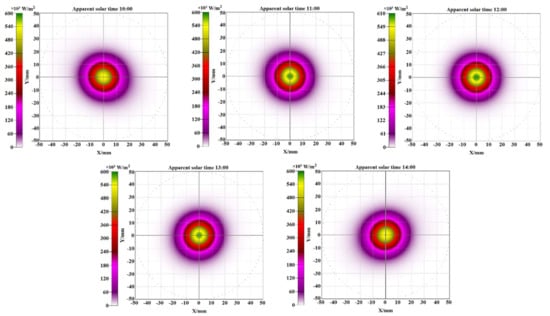
Figure 8.
The flux density distributions of the focal spots for various apparent solar times.
To verify the correctness of the simulation model, the simulation error of FFFSC can be calculated by:
where is the difference of the received energy between the simulation results and the measured data, and is the received energy in the corresponding experimental result. The threshold of the correctness between the results in the simulation and experiment that depends on the simulation error is 5%, which corresponds with the demand of engineering [38]. According to these equations, the optical efficiency and the simulation error of the FFFSC with different solar times for the receiver was estimated from the simulation results and the measured data, as shown in Figure 9.
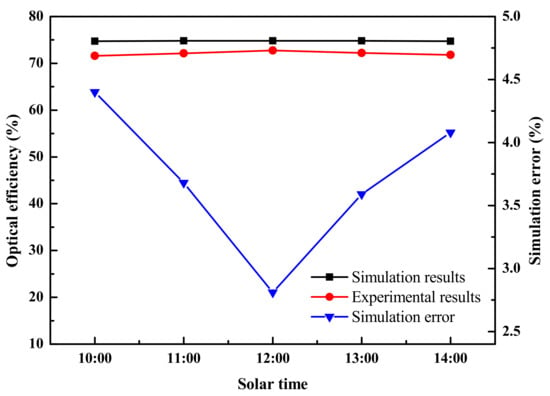
Figure 9.
The optical efficiency and the simulation error for various apparent solar times.
It can be seen from the figure that the trend of the experimental optical efficiency under various solar time is consistent with that of simulation but both had some variances. The simulation error has much variation with the changing solar hour angle of the FFFSC, due mainly to the influence of the non-Lambert property of the diffuse flat receiver [39]. Additionally, the experimental quantity is lower than that of the simulating results due to the difference between the response of the CCD camera and the solar spectrum, the manufacturing inaccuracy, surface scattering, the teeth rounded edges of the Fresnel lens, and so on. However, the maximum simulation error of the system is 4.40%, indicating that the simulation model is correct and the optical characteristics of the FFFSC can be verified by the optical simulation method.
4.2. Tracking Precision Requirement
The flux density distribution of the focal spots and the change of its position for various tracking errors are presented in Figure 10. It can be seen that the focal spot tends to deviate from the circular area with the increase of the tracking error angle, which is consistent with the experimental results in Figure 5. When the tracking error increases, some of the refracted or reflected rays tend to be deviated from the receiver.
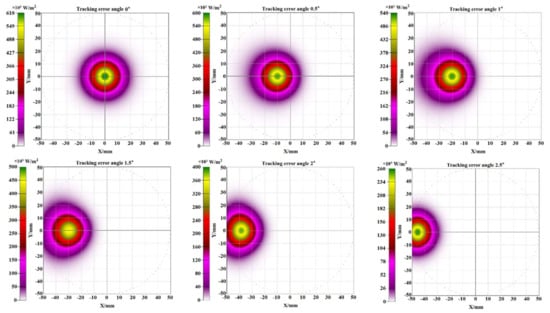
Figure 10.
The flux density distributions of the focal spots for various tracking error angle.
Figure 11 presents the comparison of optical efficiency between experiment and simulation. It is shown that similar trends in the experiment and simulation are obtained. It is also found that the simulation error of the FFFSC increases with increasing tracking error angle, but the maximum simulation error in the simulation results is 4.34%, implying that the simulation model is correct.
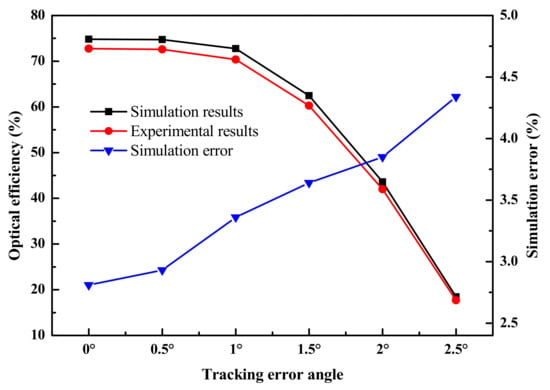
Figure 11.
The optical efficiency and the simulation error for various tracking error angle.
4.3. Effect of the Periodical Adjustment Error
A simulation was also conducted to evaluate the effect of periodical adjustment error by rotating the declination axis of the FFFSC. The flux density distribution of the focal spot is shown in Figure 12 for 0°, 0.5°, 1°, 1.5°, 2°, and 2.5° periodical adjustment error angles. It can be seen that the focal spot tends to deviate from the circular area as the rotation angle of the declination axis increases, which are also consistent with the experimental results in Figure 6. Especially, when the periodical adjustment error angle exceeded 1°, the focal spot began to depart from the circular boundary.
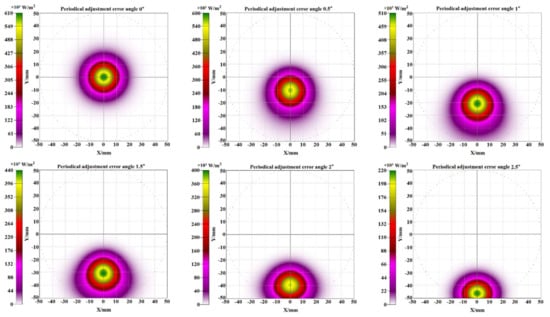
Figure 12.
The density distribution of the focal spot for various periodical adjustment error angles.
As can be observed from Figure 13, the optical efficiency of the experiment and simulation presented the same change trend under various periodical adjustment error angle. Obviously, the optical efficiency of FFFSC tends to decrease with the tracking error angle, quickly decrease when tracking error angle is more than 1.5°. The simulation error of the FFFSC also increases with the tracking error angle. Since the peak value of the simulation error is 4.24%, this means the simulation model is correct, too.
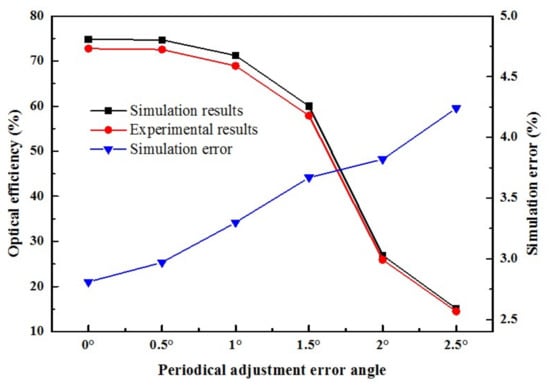
Figure 13.
The optical efficiency and the simulation error for various periodical adjustment error angles.
5. The Validity of the Fixed-Focus Fresnel Lens Solar Concentrator’s Fixed-Focus Performance under Different Incident Angles in Total Year
The objective of this work to the FFFSC is to make clear the important concern that whether the FFFSC can work properly in a convenient way, as expected, to track sunlight and achieve the fixed-focus performance under different incident angles in total year. Since the optical simulation model of FFFSC is correct, the validity of FFFSC’s fixed-focus performance under different incident angles in total year has been simulated and analyzed. To guarantee the correctness of the optical simulation model within limits, the simulations were carried out at intervals of 1 h between apparent solar time of 10:00 and 14:00 [40]. Since the declination angle of the sun that varies from −23°27′ to south +23°27′ during a year and the horizontal angle of the polar-axis equal to the local latitude angle [41], a sun declination angle of +23°27′, 0°, and −23°27′ has been chosen for comparison. Optical characteristics of FFFSC measured when the Fresnel lens and the receiver surface are adjusted to be parallel in the simulation are used as a reference group, which is in accordance with rotating solar receiver. Table 5 shows the simulation optical characteristics of FFFSC under different incident angles in total year.

Table 5.
Simulation optical characteristics of the fixed-focus Fresnel lens solar concentrator under different incident angles in total year.
According to Equation (5), the maximum value of ηre-opt,loss in Table 5 is 0.116%, corresponding to the sun declination angle of +23°27′ and −23°27′, and the apparent solar time are 10:00 and 14:00. The maximum value of ηre-opt,loss is so small that the focal spot will stay in the area of the receiver, which indicates that the FFFSC can realize fixed-focus under different incident angles in total year. Additionally, the optical efficiency of FFFSC is about 74.70%, mean value and maximum value of the local concentration ratio of the solar flux on the receiver are up to about 90.40 and 1346.70, respectively. It means that the FFFSC has high optical efficiency and can obtain high temperature in a practical application. The initial results are very promising and significant for broadening the application range of FFFSC with higher concentrations.
6. Conclusions
In this study, the FFFSC has been proposed and investigated. The experimental and optical simulation has been done to evaluate the validity of FFFSC’s fixed-focus performance. The results can be summarized as follows:
- -
- Maximum value of the relative optical efficiency loss of FFFSC in the experiment for one day is 1.87%. Mean value and maximum value of the local concentration ratio of the solar flux on the receiver are more than 86.64 and 1319.43, respectively.
- -
- The allowable angle of tracking error should be less than 1°. When the tracking error angle is bigger than 1.5°, the relative optical efficiency loss increases sharply which is up to 17.42%.
- -
- The allowable angle of periodical adjustment error should be less than 1°, too. It may be appropriate to adjust the FFFSC’s declination axis with the period of two days when the sun declination angle is −16°48′.
- -
- Experimental results are in coincidence with optical simulation results and the peak value of simulation errors are less than 5%, which indicates that the simulation model is correct and the optical characteristics of FFFSC can be verified by optical simulation method.
- -
- According to the total year simulation of FFFSC’s fixed-focus performance, the maximum relative optical efficiency loss of FFFSC is 0.116%, which indicates that the FFFSC can achieve the fixed-focus under different incident angles in total year.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 51476038); Guangzhou Science and Technology Program of Production and Research Collaborative Innovation Major Project (no. 2016201604030020); Guangdong Province Frontier and Key Technology Innovation Special Fund Project (no. 2016A050503042); Nansha District Science and Technology Program (no. 2016CX013); and Guangzhou Science and Technology Program Production and Research Collaborative Innovation Major Project (no. 201704030009).
Author Contributions
Hai Wang and Jin Huang conceived and designed the experiments; Hai Wang and Zijian Lu performed the experiments; Yanxin Hu analyzed the data; Mengjie Song and Yunfeng Wang contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; Hai Wang wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| Erec | The received energy (W) |
| G | The direct normal irradiance (W/m2) |
| Gmax | The maximum flux density on a receiver area (W/m2) |
| Gmean | The mean flux density on a receiver area (W/m2) |
| n | Refractive index of PMMA |
| Xmax | Maximum value of the local concentration ratio |
| Xmean | Mean value of the local concentration ratio |
| Greek Symbols | |
| δ | Sun declination angle (°) |
| ηopt | The optical efficiency of FFFSC (%) |
| ηre-opt,loss | The relative optical efficiency loss of FFFSC (%) |
| ηerror | The simulation error (%) |
| λ | The wavelength (µm) |
| Φ | Local latitude angle (°) |
| Abbreviations | |
| PMMA | Polymethyl methacrylate |
References
- Liu, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhai, X.; Qian, C.; Chen, X. Feasibility and performance study of the hybrid ground-source heat pump system for one office building in Chinese heating dominated areas. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cheng, K.; Li, H.; Cao, G.; Wu, D.; Shi, Y. Exploring the potential relationship between indoor air quality and the concentration of airborne culturable fungi: A combined experimental and neural network modeling study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 3510–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, D.; Yu, H.; Ma, W.; Jin, G. Field measurement and numerical simulation of combined solar heating operation modes for domestic buildings based on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau case. Energy Build. 2018, 167, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, K.; Yu, H.; Cheng, K. Design of high-performance water-in-glass evacuated tube solar water heaters by a high-throughput screening based on machine learning: A combined modeling and experimental study. Sol. Energy 2017, 142, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, H. Design and thermal performances of semi-parabolic linear fresnel reflector solar concentration collector. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 77, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Optical performance of an azimuth tracking linear Fresnel solar concentrator. Sol. Energy 2014, 108, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellos, E.; Mathioulakis, E.; Tzivanidis, C.; Belessiotis, V.; Antonopoulos, K.A. Experimental and numerical investigation of a linear Fresnel solar collector with flat plate receiver. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 130, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellos, E.; Tzivanidis, C. Multi-criteria evaluation of a nanofluid-based linear Fresnel solar collector. Sol. Energy 2018, 163, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boito, P.; Grena, R. Optimization of the geometry of Fresnel linear collectors. Sol. Energy 2016, 135, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungasamy, A.E.; Craig, K.J.; Meyer, J.P. 3-D CFD modeling of a slanted receiver in a compact linear Fresnel plant with etendue-matched mirror field. Energy Procedia 2015, 69, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyakhlef, S.; Al Mers, A.; Merroun, O.; Bouatem, A.; Boutammachte, N.; El Alj, S.; Ajdada, H.; Erregueraguia, Z.; Zemmouria, E. Impact of heliostat curvature on optical performance of Linear Fresnel solar concentrators. Renew. Energy 2016, 89, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valmiki, M.M.; Li, P.; Heyer, J.; Morgan, M.; Albinali, A.; Alhamidi, K.; Wagoner, J. A novel application of a Fresnel lens for a solar stove and solar heating. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, G.; Tao, T.; Su, Y.; Dai, J. Combination of a light funnel concentrator with a deflector for orientated sunlight transmission. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.; Wiik, N.; Ambrosetti, G.; Pedretti, A.; Paredes, S.; Ruch, P.; Steinfeld, A. A 6-focus high-concentration photovoltaic-thermal dish system. Sol. Energy 2017, 155, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.K.; Yew, T.K.; Wong, C.W.; Tan, M.H.; Tan, W.C.; Lim, B.H. Dense-array concentrator photovoltaic prototype using non-imaging dish concentrator and an array of cross compound parabolic concentrators. Appl. Energy 2017, 204, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousazadeh, H.; Keyhani, A.; Javadi, A.; Mobli, H.; Abrinia, K.; Sharifi, A. A review of principle and sun-tracking methods for maximizing solar systems output. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1800–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsengiyumva, W.; Chen, S.G.; Hu, L.; Chen, X. Recent advancements and challenges in Solar Tracking Systems (STS): A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 250–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Uchida, S.; Yoshida, K.; Nakatsuka, M.; Funatsu, T.; Daito, K. High-efficiency and economical solar-energy-pumped laser with Fresnel lens and chromium codoped laser medium. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, C.; Pozna, C. Simulation of a dual-axis solar tracker for improving the performance of a photovoltaic panel. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A 2010, 224, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Sheng, F.; Cheng, C.; Lv, Q. Tracking control and output power optimization of a concentrator photovoltaic system with polar axis. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron. Opt. 2016, 127, 3840–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Yao, N.; Song, L.F.; Wang, H.X. Design of the solar automatic tracker of polar axis type. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 455, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemisana, D.; Vossier, A.; Pujol, L.; Perona, A.; Dollet, A. Characterization of Fresnel lens optical performances using an opal diffuser. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekara, M.; Yadav, A. An experimental study of the effect of exfoliated graphite solar coating with a sensible heat storage and Scheffler dish for desalination. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 123, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.T.; Dai, Y.J.; Wang, R.Z. Numerical and experimental analysis of a point focus solar collector using high concentration imaging PMMA Fresnel lens. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ji, J.; Sun, W.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Jin, Z. Numerical simulation and experimental validation of a high concentration photovoltaic/thermal module based on point-focus Fresnel lens. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Feng, C.; Su, Y.; Dai, J.; Ma, X. Design and experimental analysis of a cylindrical compound Fresnel solar concentrator. Sol. Energy 2014, 107, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.W.; Kane, P.; Mokler, M. Modeling of solar tracking for giant Fresnel lens solar stoves. Sol. Energy 2013, 96, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodele, T.R.; Ogunjuyigbe, A.S.O. Prediction of monthly average global solar radiation based on statistical distribution of clearness index. Energy 2015, 90, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaly, I.A.; Nassar, K.; El-Haggar, S. Mathematical model for designing a light redirecting prismatic panel. Sol. Energy 2018, 159, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Meng, X.; Wei, X. Heat transfer and friction factor correlations for solar air collectors with hemispherical protrusion artificial roughness on the absorber plate. Sol. Energy 2015, 118, 460–468. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Jiang, C.; Yan, Q.; Lund, P.D. A novel 2-stage dish concentrator with improved optical performance for concentrating solar power plants. Renew. Energy 2017, 108, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zheng, H.; Ma, X.; Kutlu, C.; Su, Y. Experimental investigation of a multi-stage humidification-dehumidification desalination system heated directly by a cylindrical Fresnel lens solar concentrator. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 143, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.K.; Obianuju, O.N.; Yew, T.K.; Wong, C.W.; Tan, W.C. Design and construction of active daylighting system using two-stage non-imaging solar concentrator. Appl. Energy 2017, 207, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasarova, S.N.; Sultanova, N.G.; Ivanov, C.D.; Nikolov, I.D. Analysis of the dispersion of optical plastic materials. Opt. Mater. 2007, 29, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Yu, F. Optimization design of hybrid Fresnel-based concentrator for generating uniformity irradiance with the broad solar spectrum. Opt. Laser Technol. 2014, 60, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badescu, V. Theoretical derivation of heliostat tracking errors distribution. Sol. Energy 2008, 82, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badescu, V. Different tracking error distributions and their effects on the long-term performances of parabolic dish solar power systems. Int. J. Sol. Energy 1994, 14, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.M.; Choi, D.; Han, M.; Lee, J.S. Optical design of a static solar concentrator using Fresnel lenses. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, T. Development of flux density distribution measurement system based on CCD. J. Optoelectron. Laser 2008, 19, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Eldin, S.S.; Abd-Elhady, M.S.; Kandil, H.A. Feasibility of solar tracking systems for PV panels in hot and cold regions. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi Maleki, S.A.; Hizam, H.; Gomes, C. Estimation of hourly, daily and monthly global solar radiation on inclined surfaces: Models re-visited. Energies 2017, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).