Design and Experiment Analysis of a Direct-Drive Wave Energy Converter with a Linear Generator
Abstract
1. Introduction
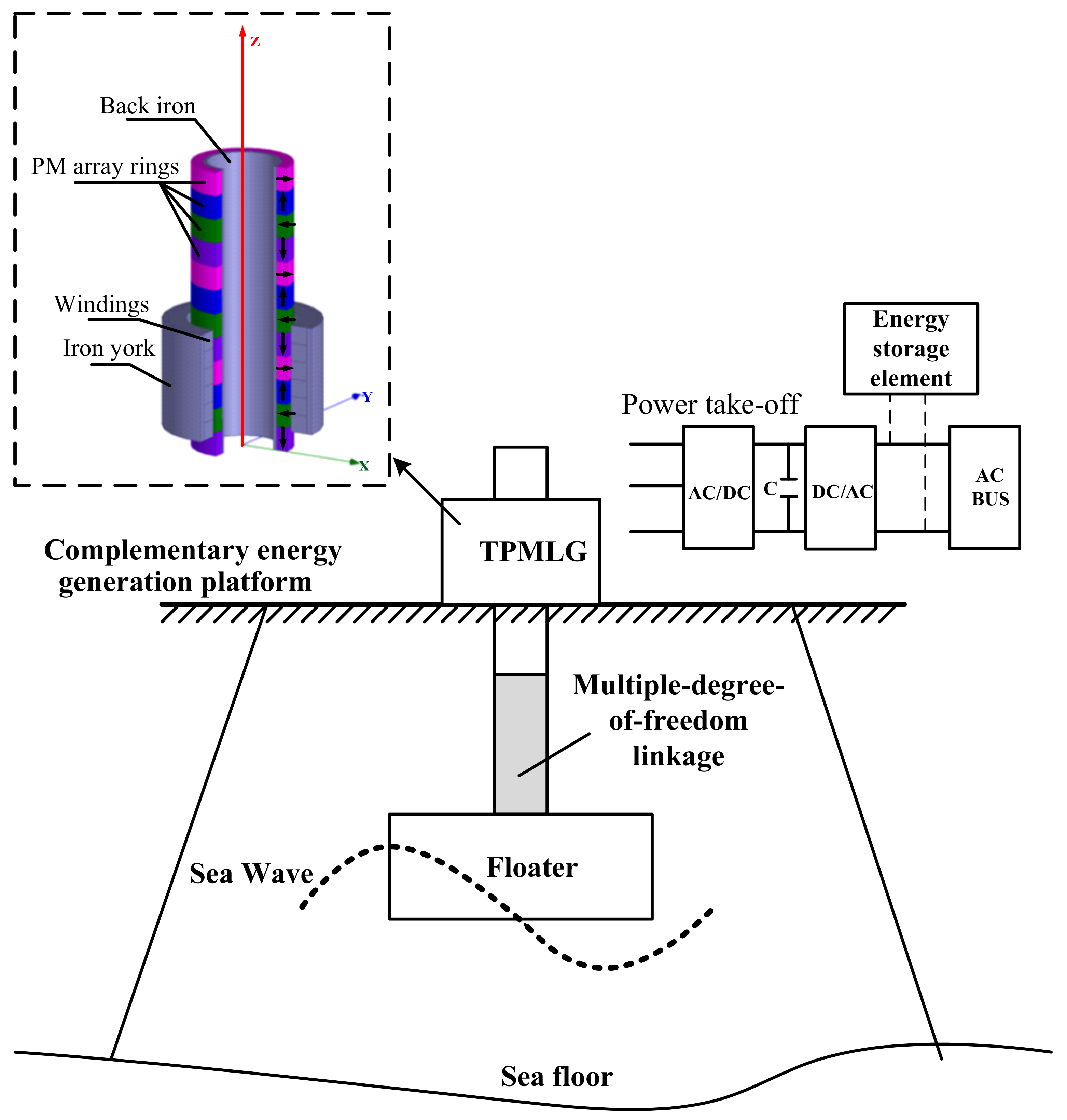
2. System Configuration and Operation Principle
2.1. Configuration of the D-DWEC System
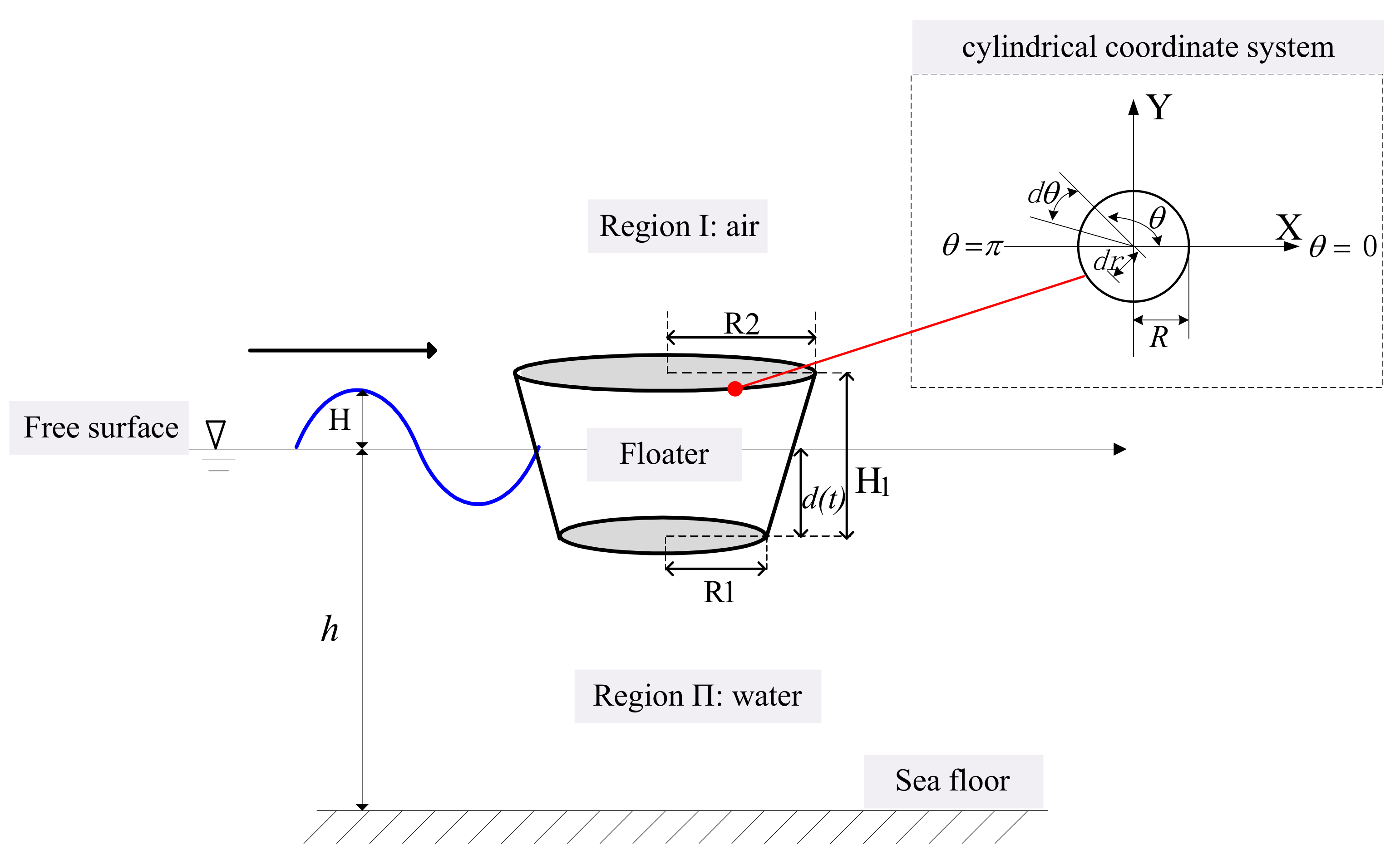
2.2. Configuration of the Floater
2.3. Forces Analysis of Floater
- ➢
- The K-epsilon turbulence model is used in the CFD analysis.
- ➢
- The pressure-implicit with splitting of operators algorithm is applied in the solver.
- ➢
- A model for the two-phase flow (gas and water) is built and analyzed. The upper portion of the floater is gas, and the bottom is water.
- ➢
- In wave propagation, static buoyancy and dynamic lift act on the floater in the vertical orientation, and their sum equals that of the floater affected by gravity.
3. Analysis of TPMLG in D-DWEC
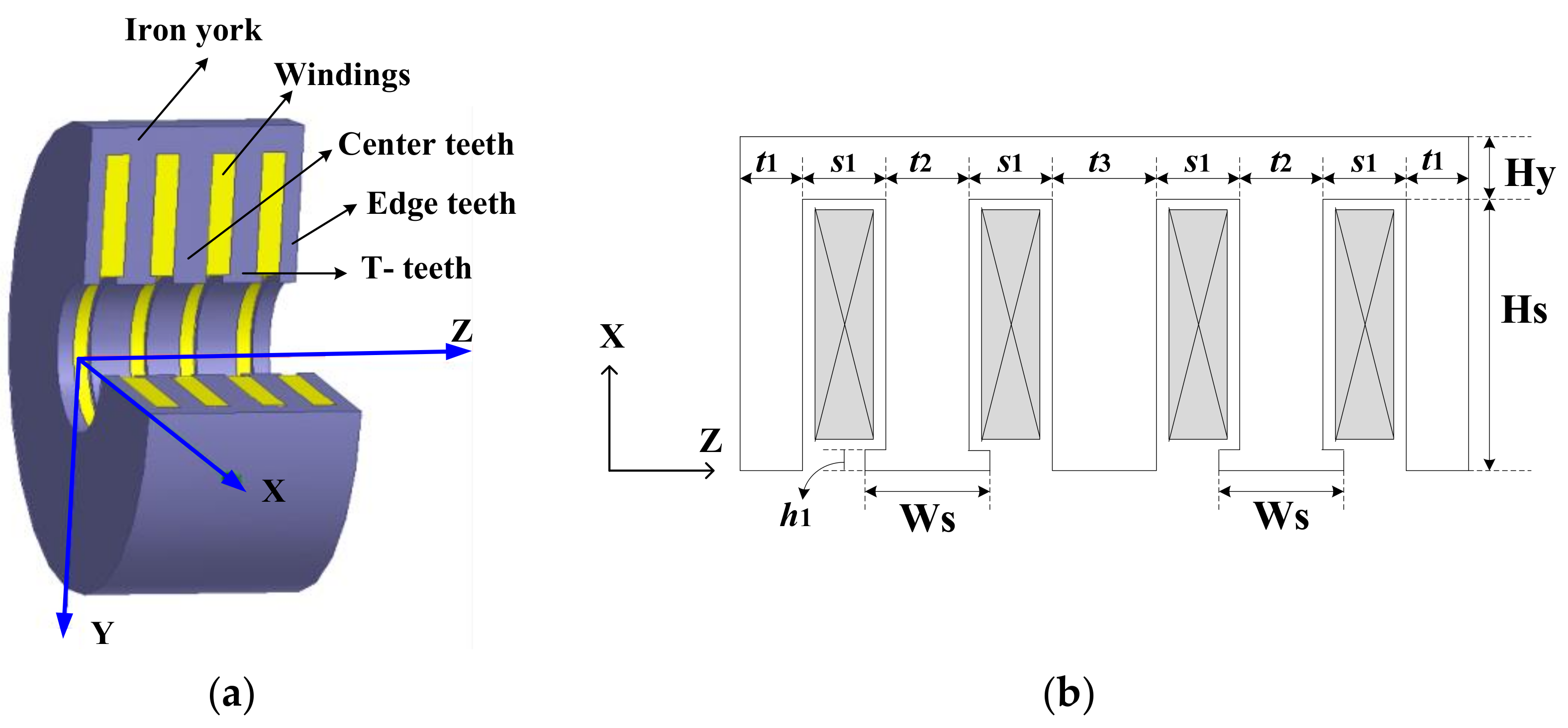
3.1. Configuration of TPMLG
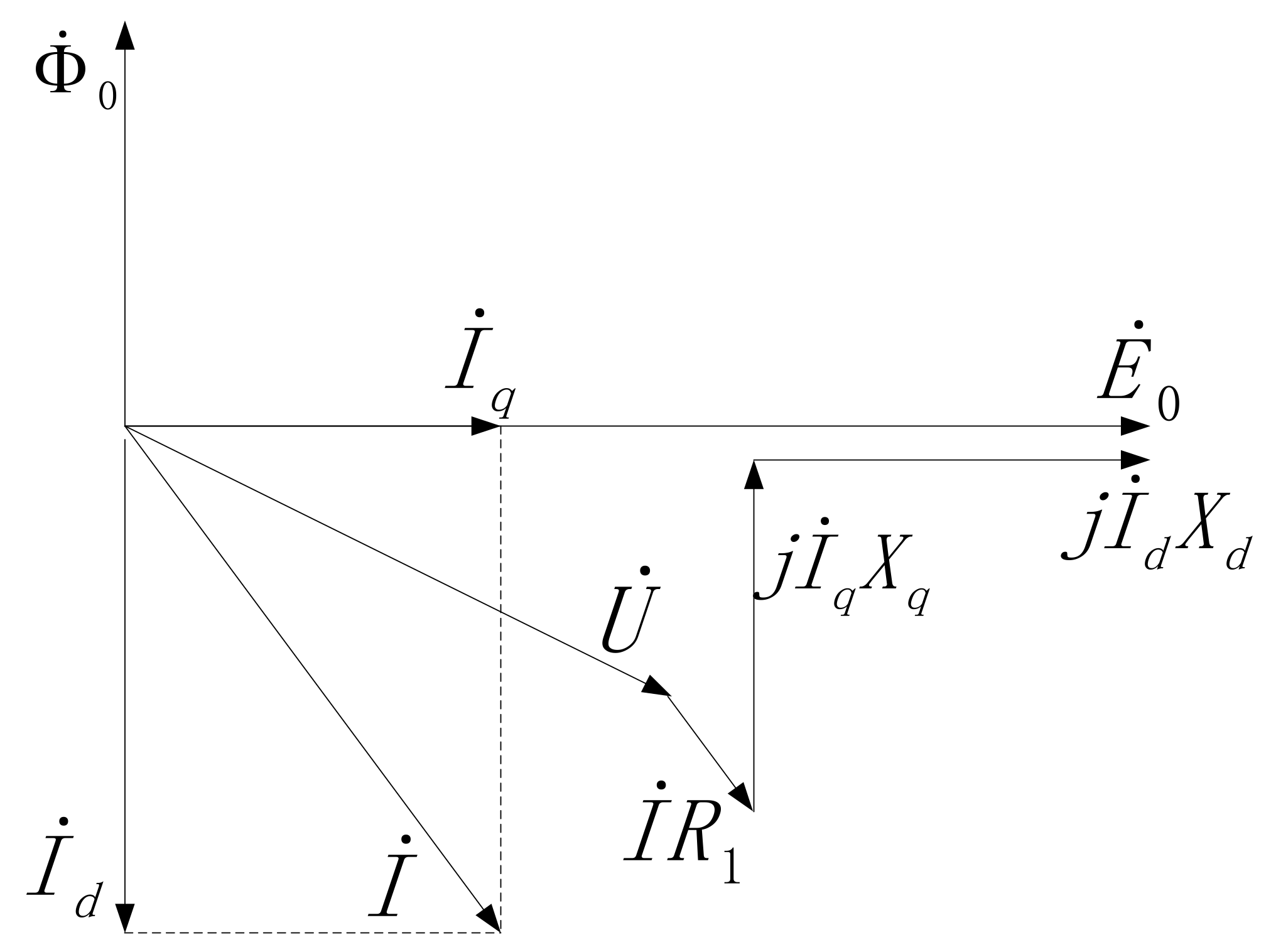
3.2. Equation and Vector Diagram of TPMLG
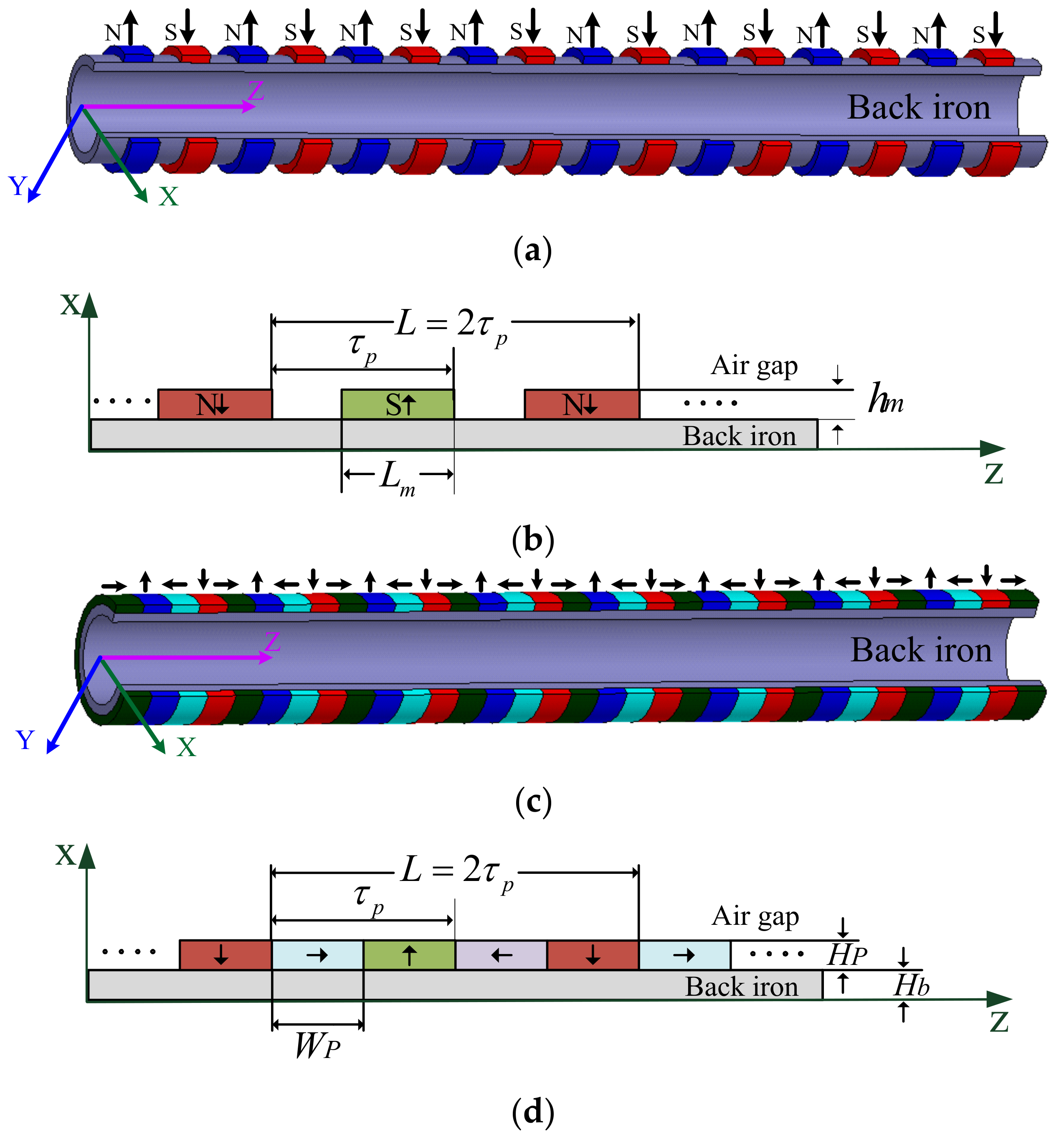
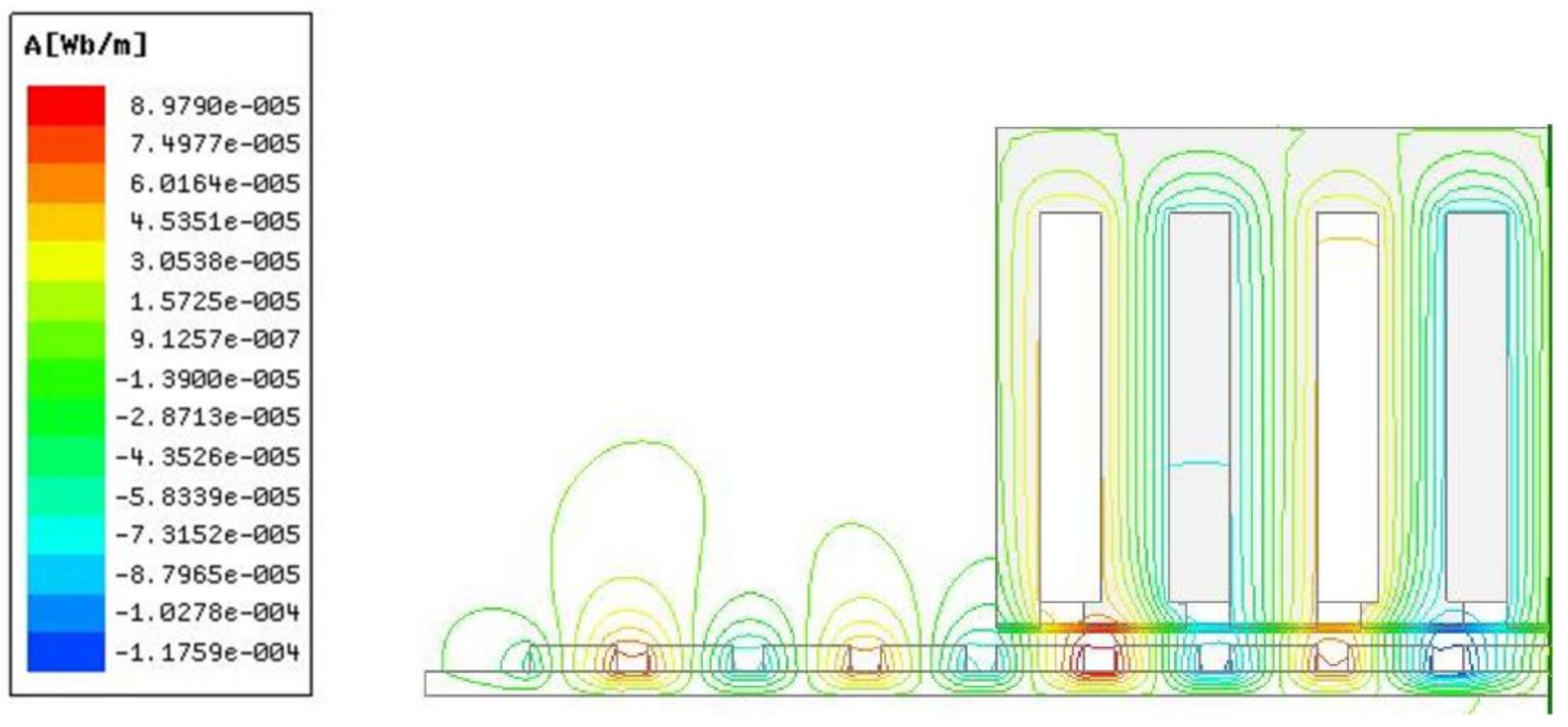
3.3. Magnetic Field Distribution
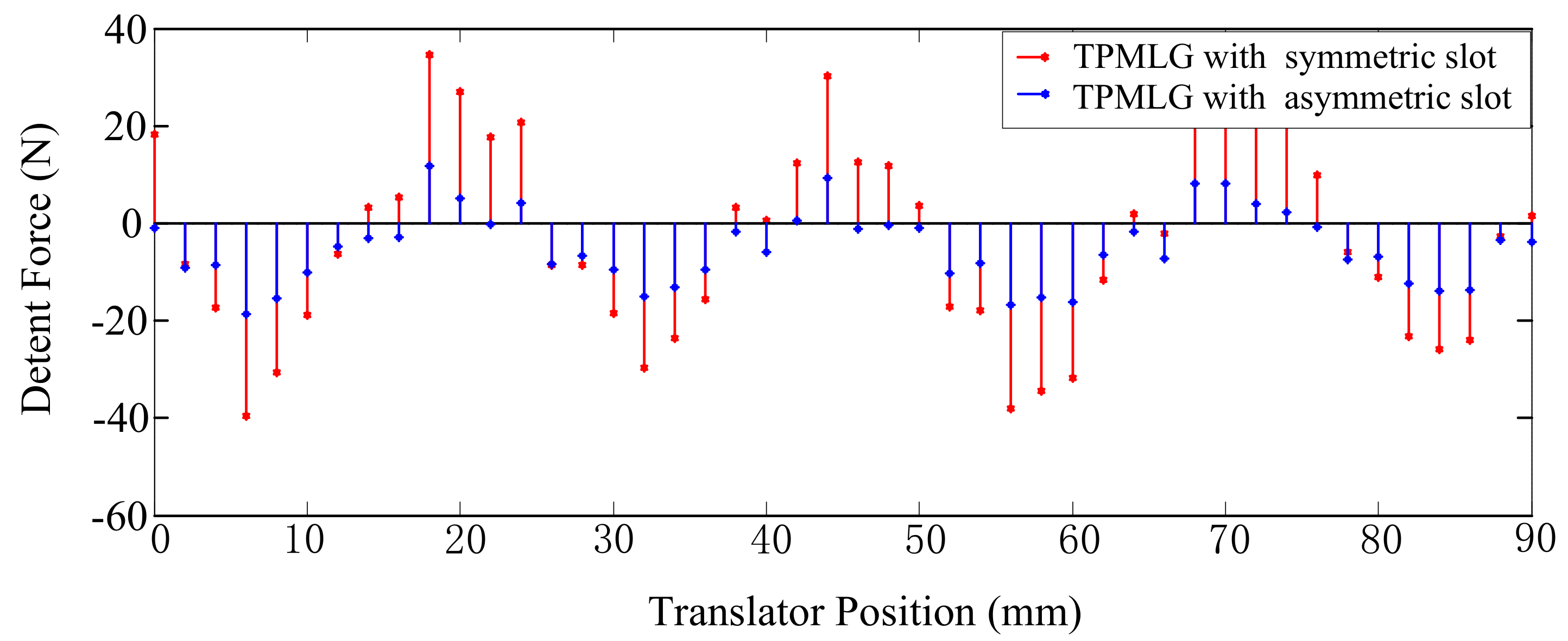
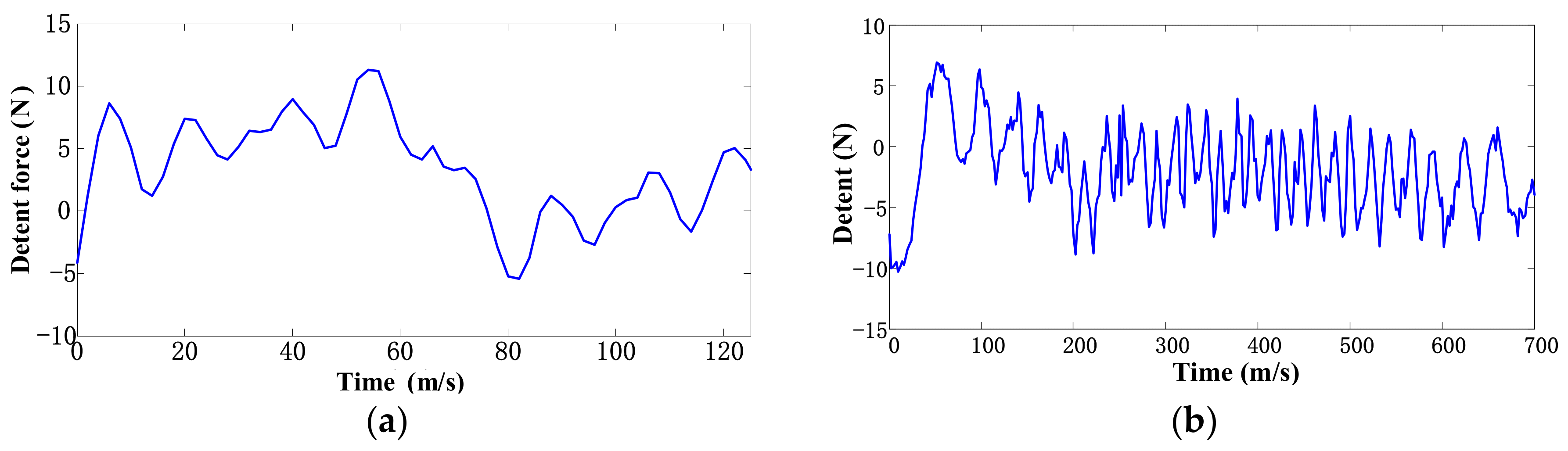
3.4. Analysis of Detent Force
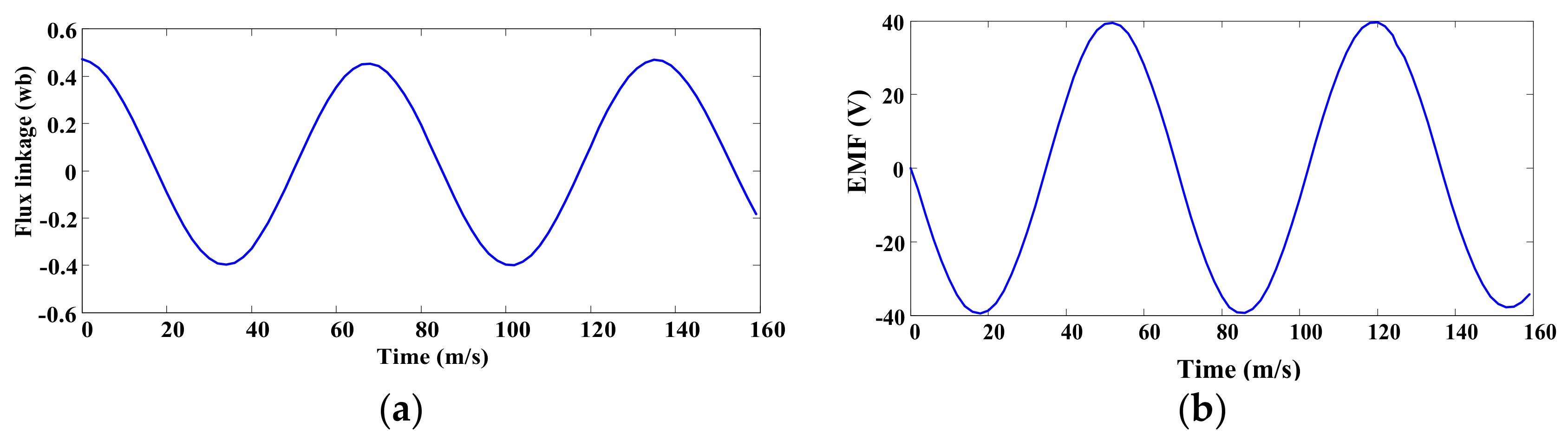
3.5. Power and Efficiency Analysis of TPMLG
4. Conversion Efficiency of D-DWEC
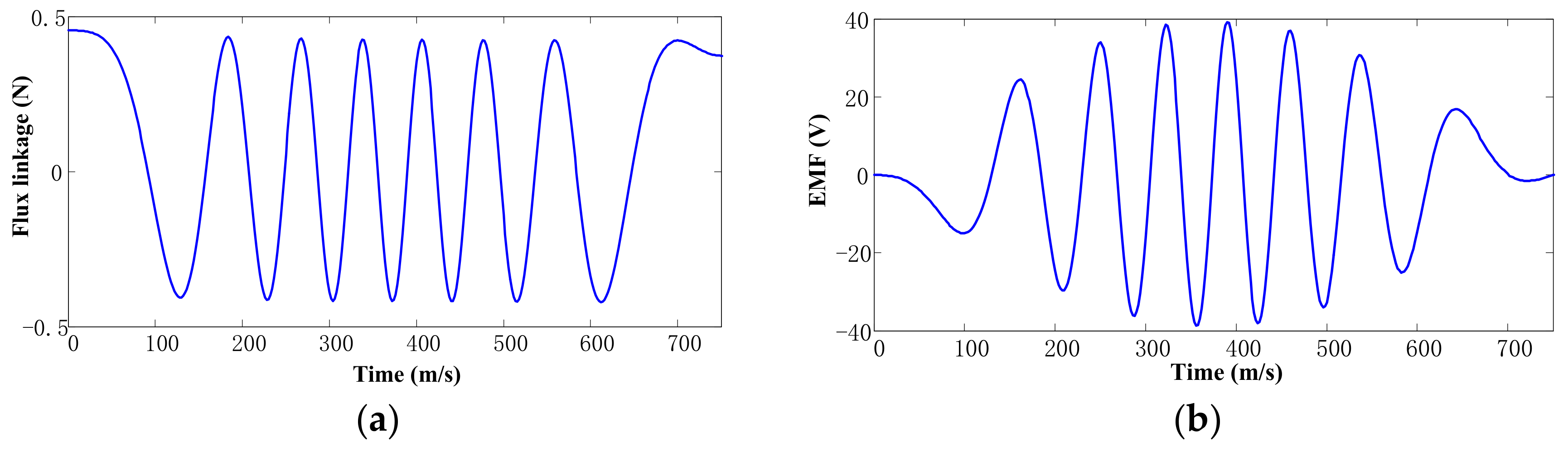
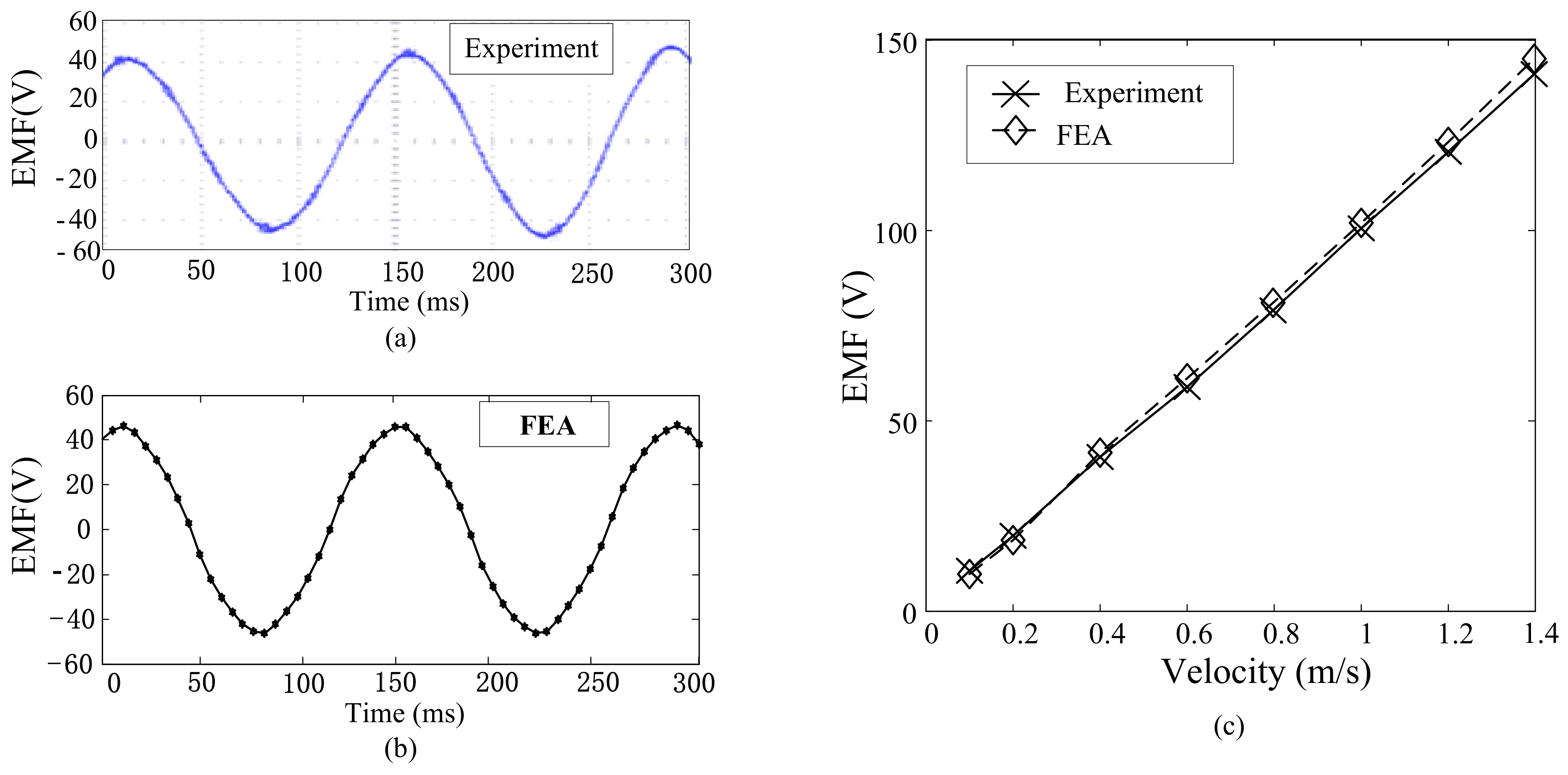
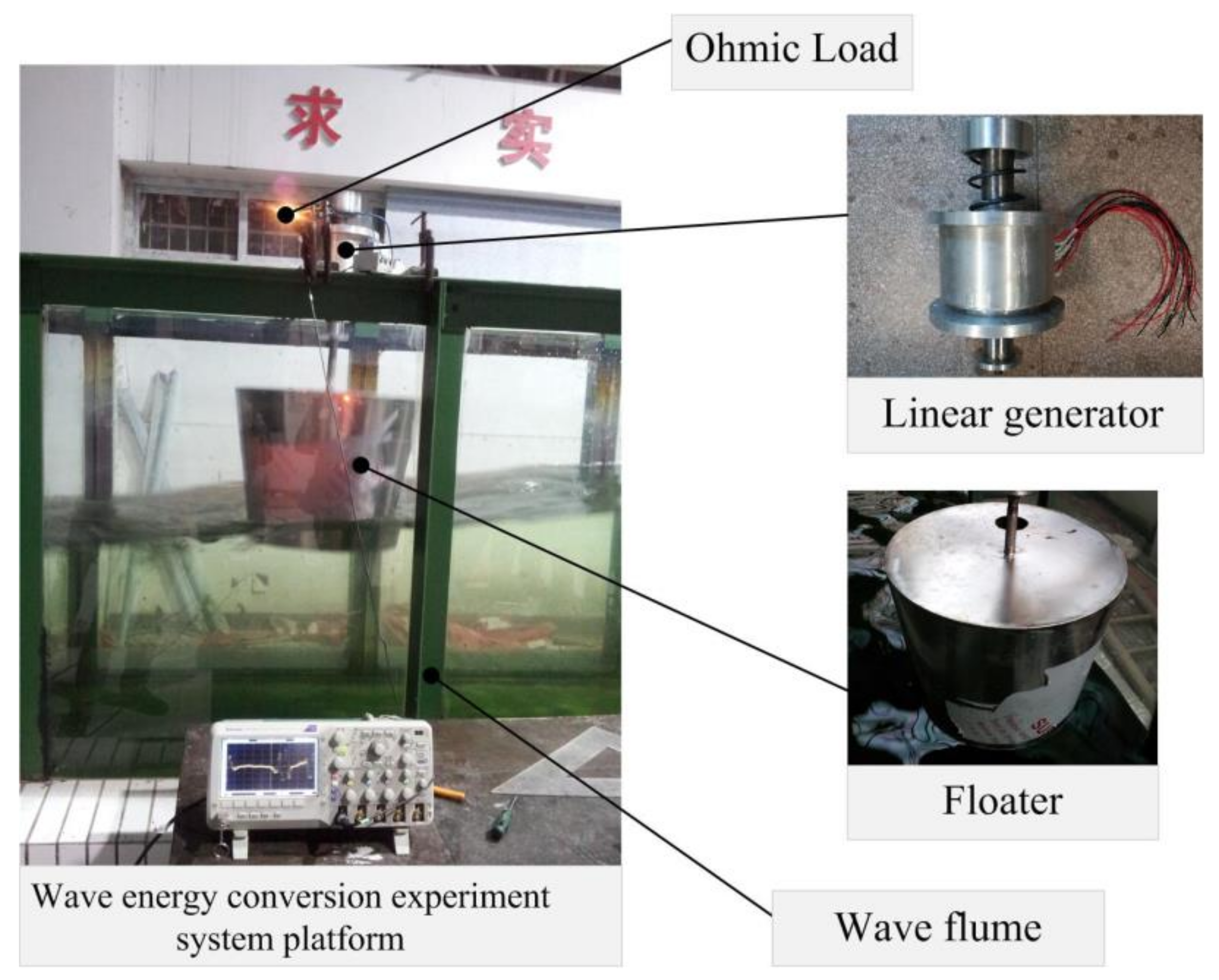
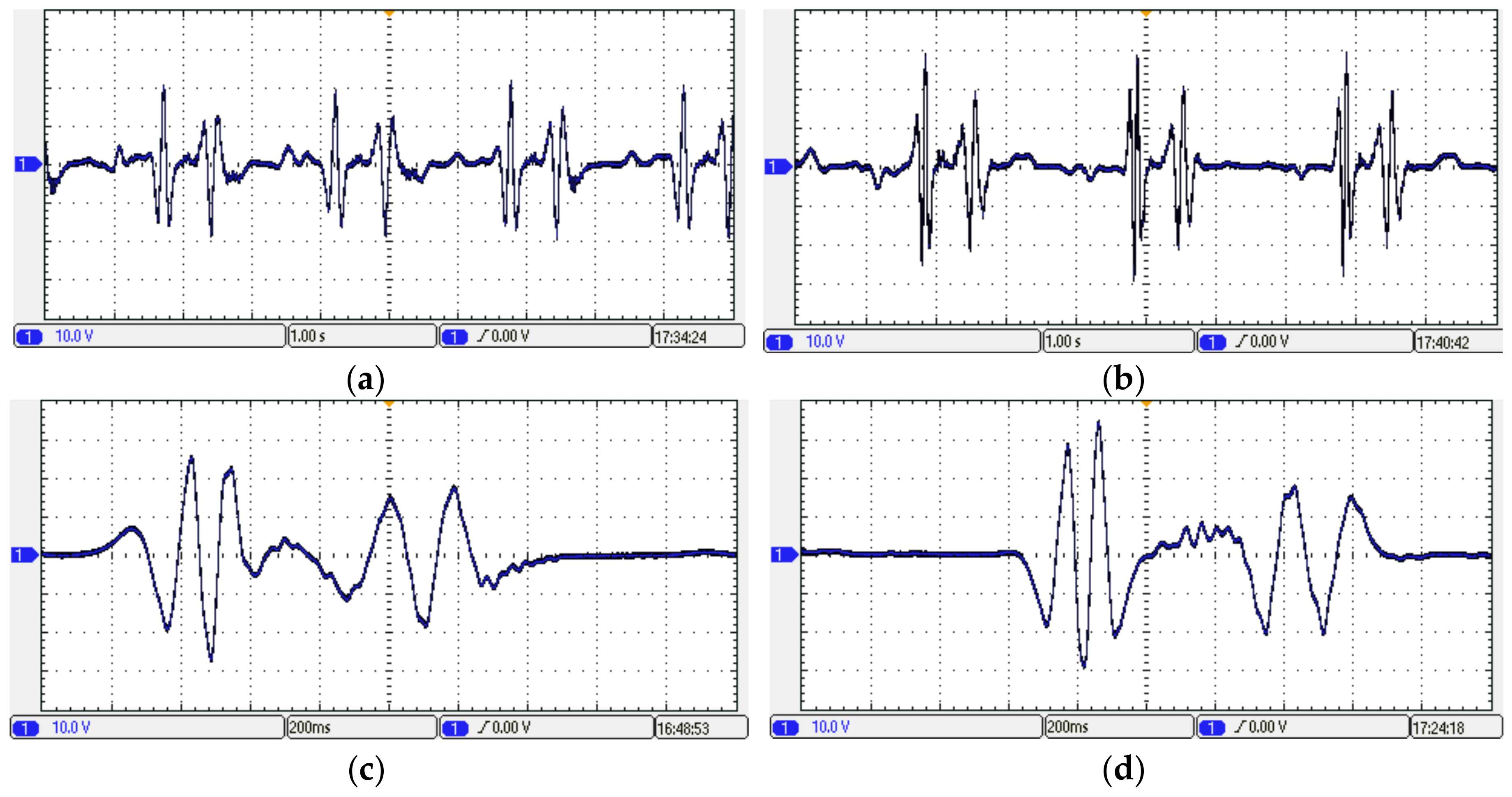
5. Experiment Analysis
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WEC | wave energy converter |
| D-DWEC | direct-drive wave energy conversion |
| TPMLG | tubular permanent magnet linear generator |
| CFD | computational fluid dynamics |
| FEA | finite element analysis |
| OWC | oscillating water column |
| AWS | Archimedes wave swing |
| RANS | Reynolds Averaged Navier Stokes |
| PM | permanent magnet |
| PTO | power take-off |
| EMF | electromotive force |
| THD | total harmonic distortion |
| NdFeB | neodymium iron boron |
| VOF | volume of fluid method |
| MMF | magnetic motive force |
References
- Melikoglu, M. Current status and future of ocean energy sources: A global review. Ocean Eng. 2018, 148, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, B.; Plummer, A.R.; Sahinkaya, M.N. A review of wave energy converter technology. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2009, 223, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinder, H.; Mattia, S. Wave energy converters and their impact on power systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Future Power Systems, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 18 November 2005; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkop, E.; Altas, I.H. Control, power and electrical components in wave energy conversion systems: A review of the technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.K.; Truong, D.Q.; Tien, H.H.; Yoon, J., II. An innovative design of wave energy converter. Renew. Energy 2012, 42, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shao, S.; Zou, H.; Tang, M.; Xu, H.; Tian, C. A fully floating system for a wave energy converter with direct-driven linear generator. Energy 2016, 95, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekken, T.K.A.; von Jouanne, A.; Han, H.Y. Ocean wave energy overview and research at Oregon State University. In Proceedings of the Power Electronics and Machines in Wind Applications, Lincoln, NE, USA, 24–26 June 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Ekström, R.; Ekergård, B.; Leijon, M. Electrical damping of linear generators for wave energy converters—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinder, H.; Mecrow, B.C.; Jack, A.G.; Dickinson, P.G.; Mueller, M.A. Conventional and TFPM Linear Generators for Direct-Drive Wave Energy Conversion. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.A. Electrical generators for direct drive wave energyconverters. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2002, 149, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudell, J.; Stoddard, M.; Amon, E.; Brekken, T.K.A.; Jouanne, A. A permanent-Magnet Tubular Linear Generator for Ocean Wave Energy Conversion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 46, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Isberg, J.; Leijon, M. Hydrodynamic modelling of a direct drive wave energy converter. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2004, 43, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serena, A.; Molinas, M.; Cobo, I. Design of a Direct Drive Wave Energy Conversion System for the Seaquest Concept. Energy Procedia 2012, 20, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feng, N.; Yu, H.; Hu, M.; Huang, L.; Shi, Z. A Study on a Linear Magnetic-Geared Interior Permanent Magnet Generator for Direct-Drive Wave Energy Conversion. Energies 2016, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoho, S.; Arkkio, A. Mixed-grade pole design for permanent magnet synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics, Bodrum, Turkey, 10–12 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Leijon, J.; Sjölund, J.; Ekergård, B.; Boström, C.; Eriksson, S.; Temiz, I.; Leijon, M. Study of an Altered Magnetic Circuit of a Permanent Magnet Linear Generator for Wave Power. Energies 2018, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q. Analysis of Electromagnetic Performance of Halbach PM Brushless Machines Having Mixed Grade and Unequal height of Magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | Symbol | Value | Item | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Floater height (m) | H1 | 0.45 | Wave velocity (m/s) | c | 1.00 |
| Underwater depth (m) | d(t) | 0.25 | Wave length (m) | λ | 2.00 |
| Bottom radius (m) | R1 | 0.225 | Wave height (m) | H | 0.20 |
| Top radius (m) | R2 | 0.30 | Water depth (m) | h | 5.00 |
| Wave Period (s) | T | 2.00 | Lift force (N) | FL | 1074.48 |
| Water density (kg/m3) | ρ | 1.25 | Viscous force (N) | FV | 12.04 |
| Kinetic viscosity (pa.s) | μ | 1.7894 | Total force (N) | FT | 1086.52 |
| TPMLG with an Asymmetric Slot | TPMLG with a Symmetric Slot | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of PMs (mm) | Hp | 3 | Length of PMs (mm) | Hp | 3 |
| Width of PMs (mm) | Wp | 10 | Width of PMs (mm) | Wp | 10 |
| Length of air gap (mm) | Hg | 2 | Length of air gap (mm) | Hg | 2 |
| Pole pitch (mm) | τp | 20 | Pole pitch (mm) | τp | 20 |
| Length of back iron (mm) | Hb | 3 | Length of back iron (mm) | Hb | 3 |
| Height of slot (mm) | Hs | 48 | Height of slot (mm) | Hs | 48 |
| York height of stator (mm) | Hy | 10 | York height of stator (mm) | Hy | 10 |
| Height of T-teeth edge (mm) | h1 | 3 | Width of teeth (mm) | Wp | 8.5 |
| Width of slot (mm) | s1 | 7 | Width of slot (mm) | s2 | 6 |
| Width of edge teeth (mm) | t1 | 5 | Length of stator (mm) | LS | 64 |
| Width of center teeth (mm) | t3 | 10 | Stator winding turns per coil | N | 60 |
| Width of T-teeth (mm) | t2 | 8 | Number of slots | NS | 4 |
| Wave Period T (s) | Wave Height H (m) | Input Power of Wave PW (W) | Output Power of Generator PG (W) | Efficiency of System Conversion ηS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 0.15 | 36.75 | 12.45 | 33.87 |
| 1.5 | 0.18 | 52.92 | 17.4 | 32.87 |
| 1.5 | 0.20 | 65.33 | 19.44 | 29.75 |
| 1.7 | 0.20 | 57.64 | 25.6 | 44.41 |
| 2.0 | 0.20 | 49 | 28.8 | 58.77 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Shi, Z. Design and Experiment Analysis of a Direct-Drive Wave Energy Converter with a Linear Generator. Energies 2018, 11, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040735
Zhang J, Yu H, Shi Z. Design and Experiment Analysis of a Direct-Drive Wave Energy Converter with a Linear Generator. Energies. 2018; 11(4):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040735
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jing, Haitao Yu, and Zhenchuan Shi. 2018. "Design and Experiment Analysis of a Direct-Drive Wave Energy Converter with a Linear Generator" Energies 11, no. 4: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040735
APA StyleZhang, J., Yu, H., & Shi, Z. (2018). Design and Experiment Analysis of a Direct-Drive Wave Energy Converter with a Linear Generator. Energies, 11(4), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040735




