Computational Analysis of a Double-Nozzle Crossflow Hydroturbine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Double-Nozzle Design
3. Computational Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
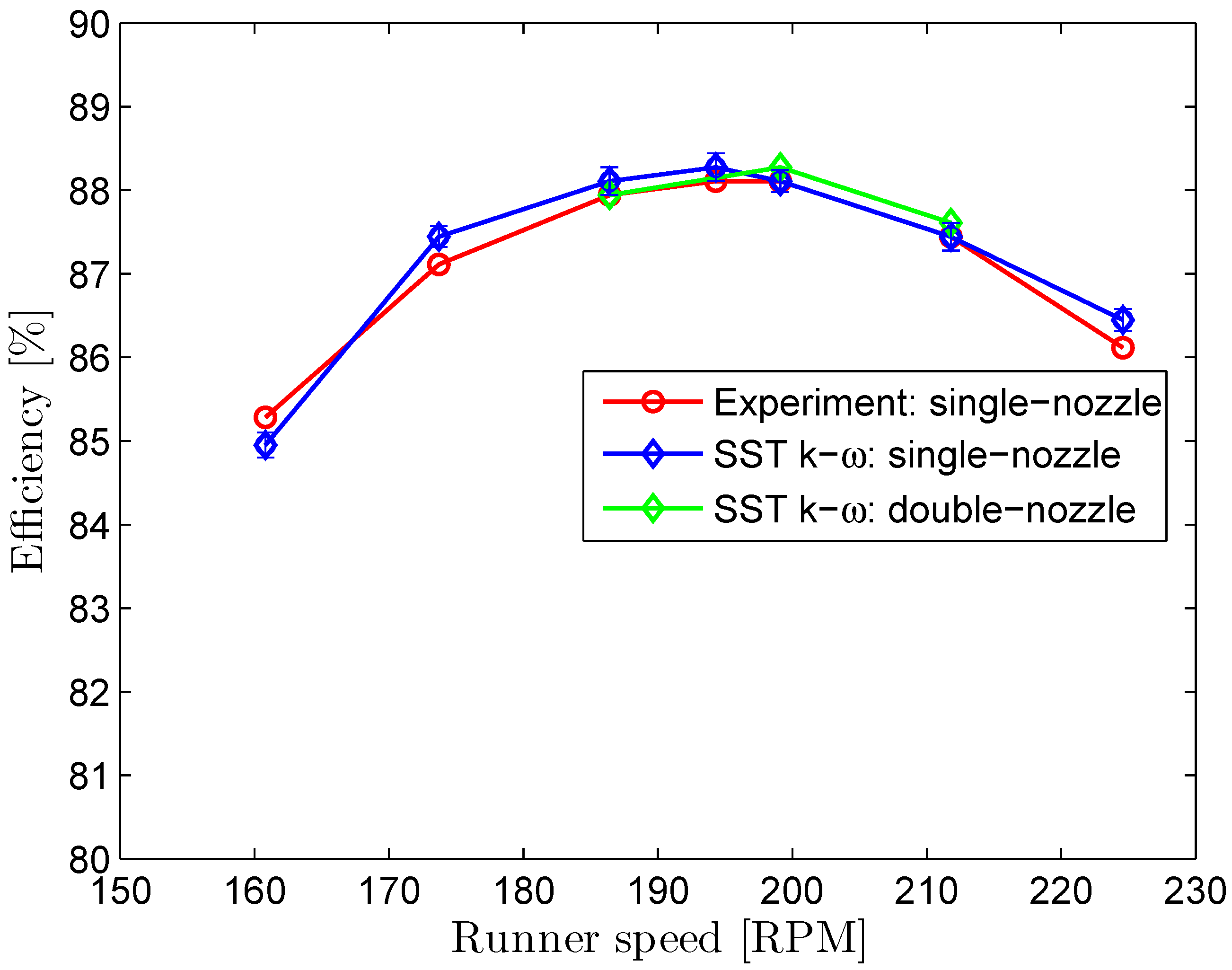
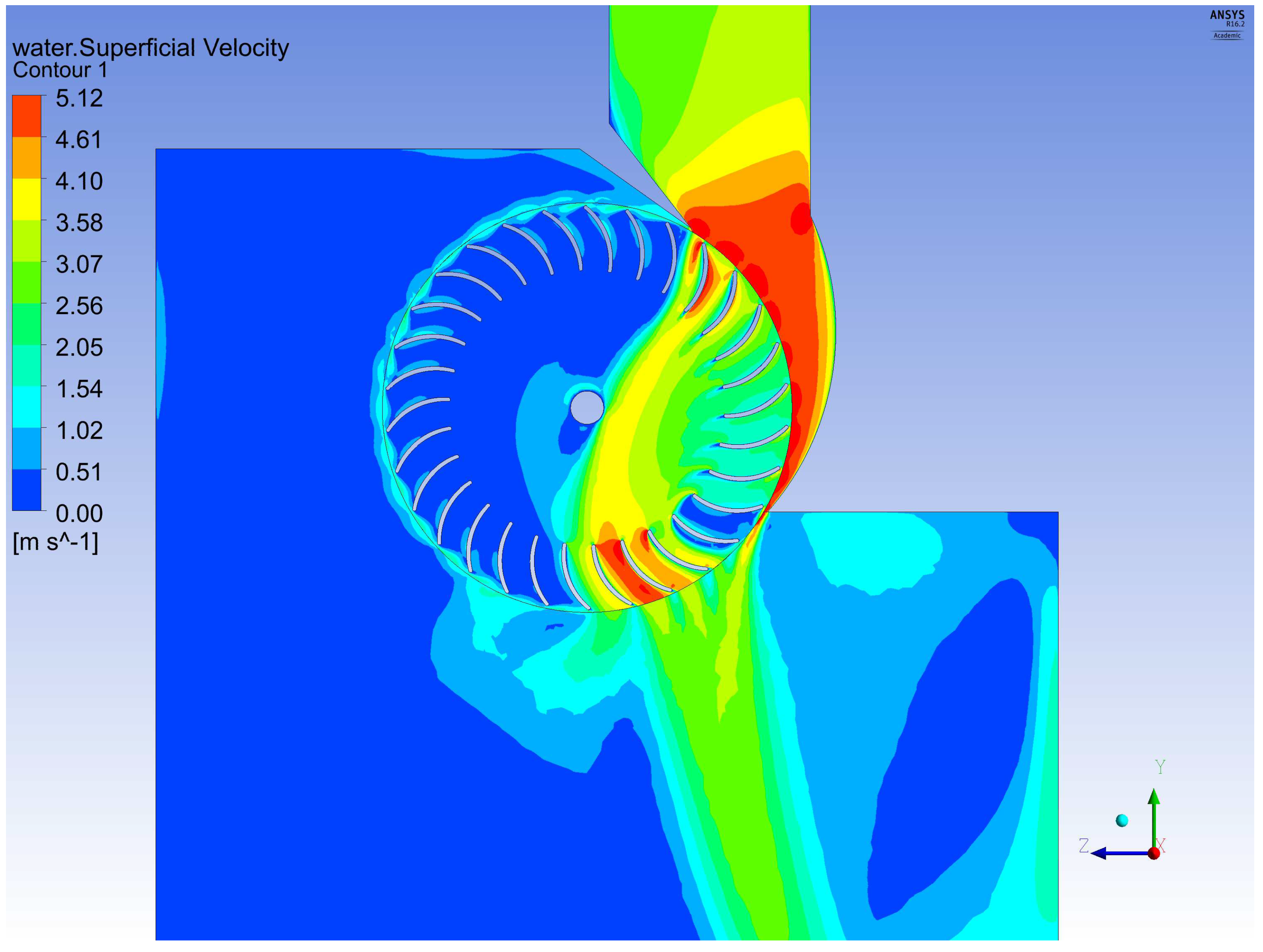
4.1. Flow and Performance of Single-Nozzle Turbine
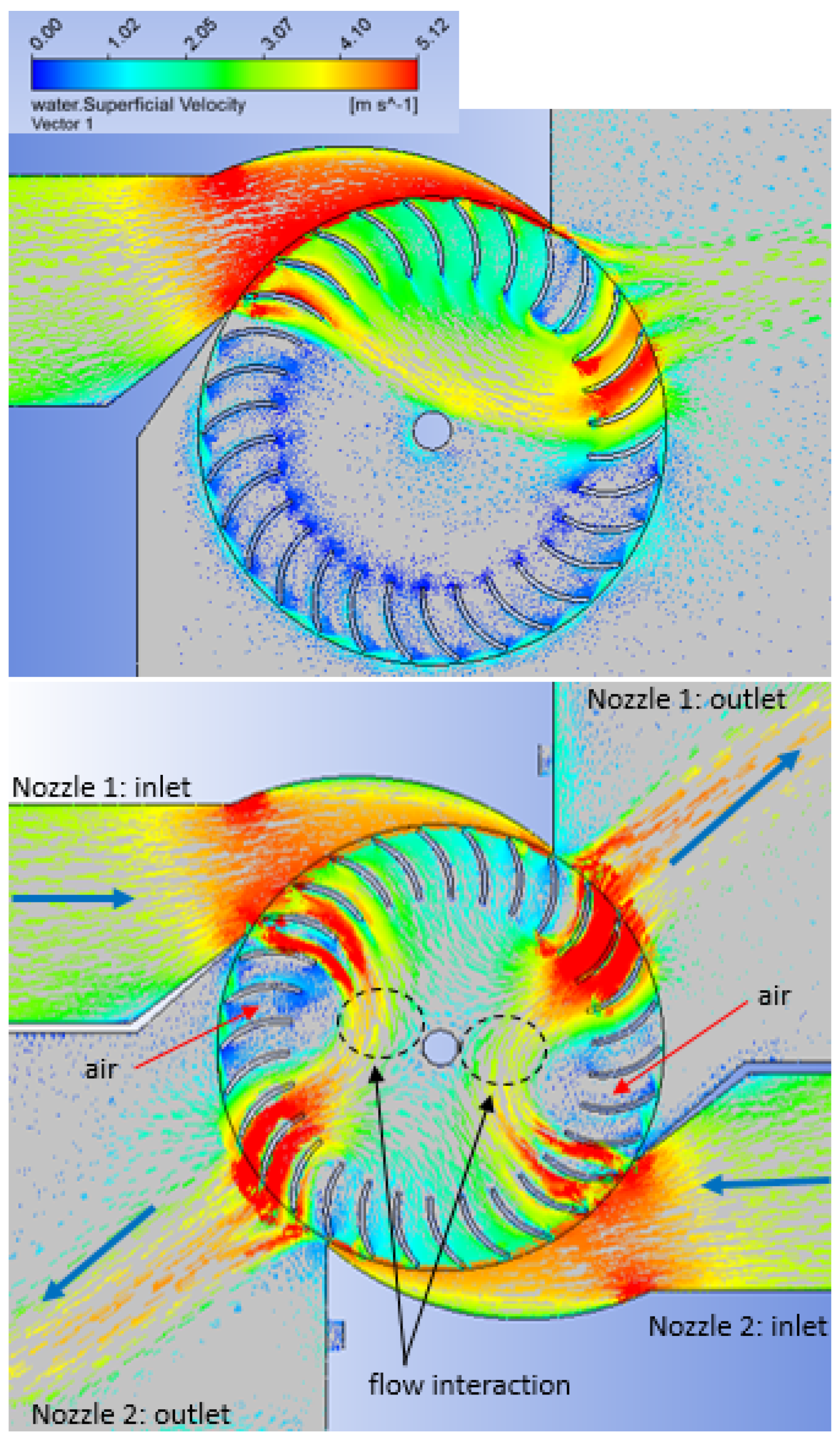
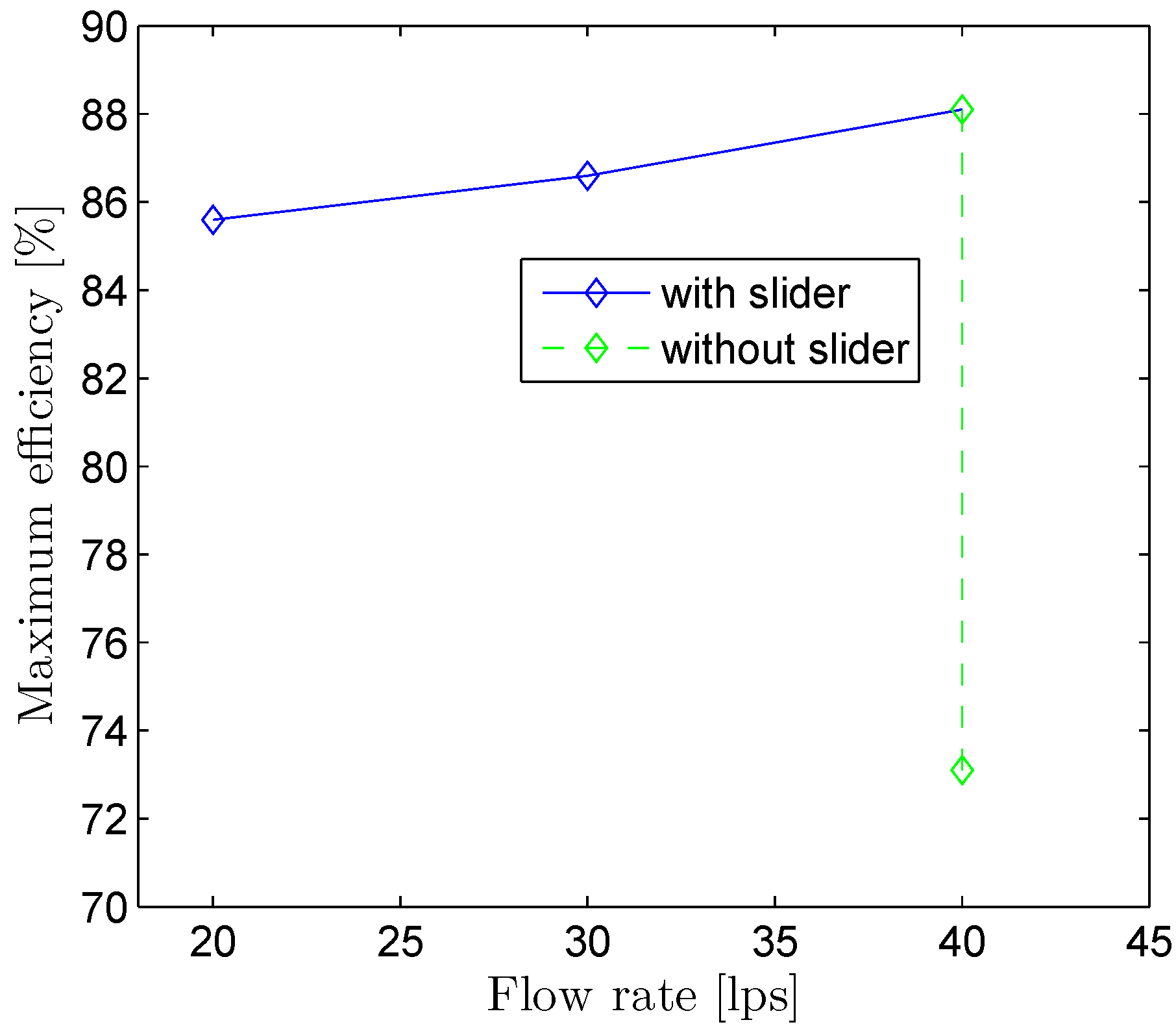
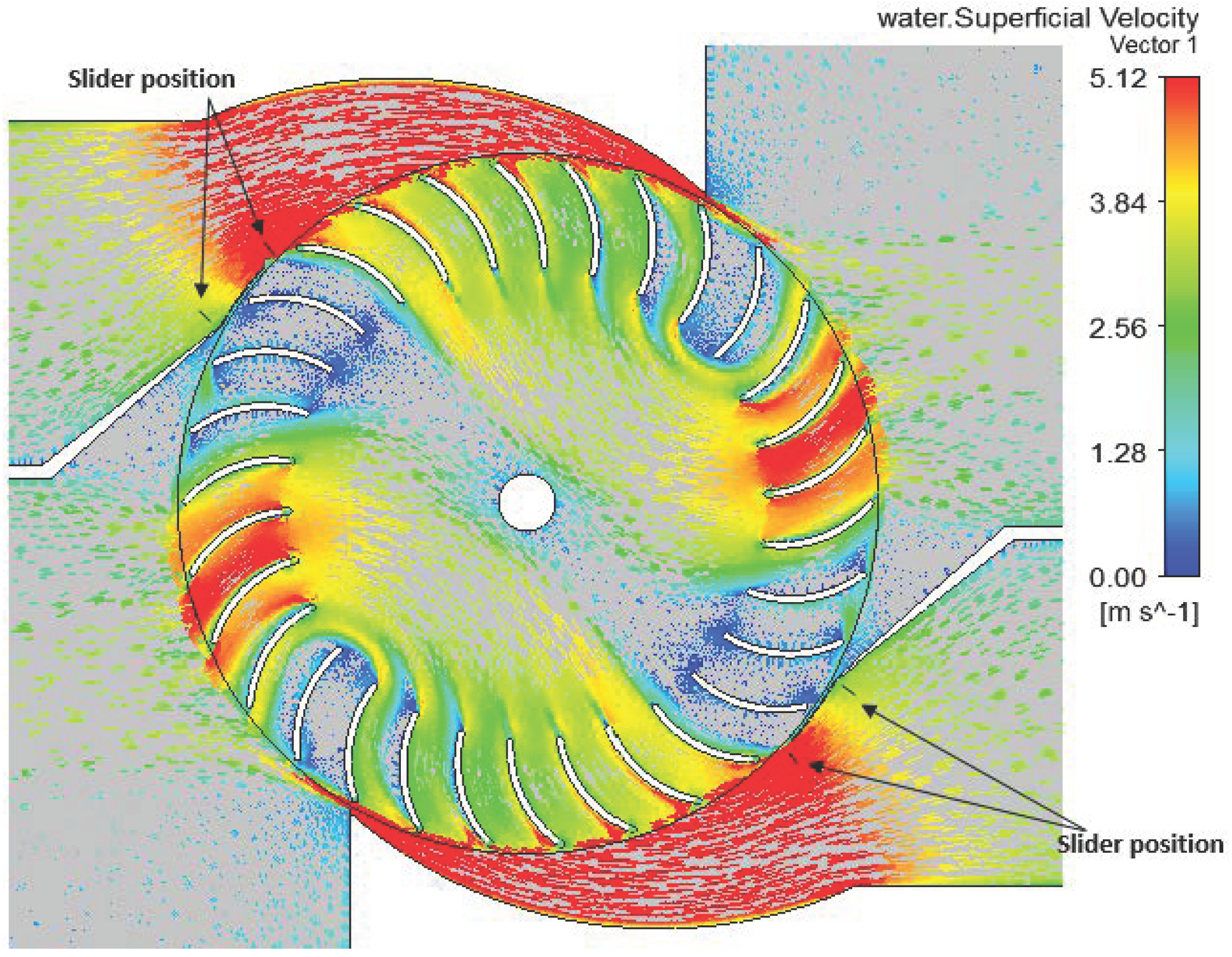
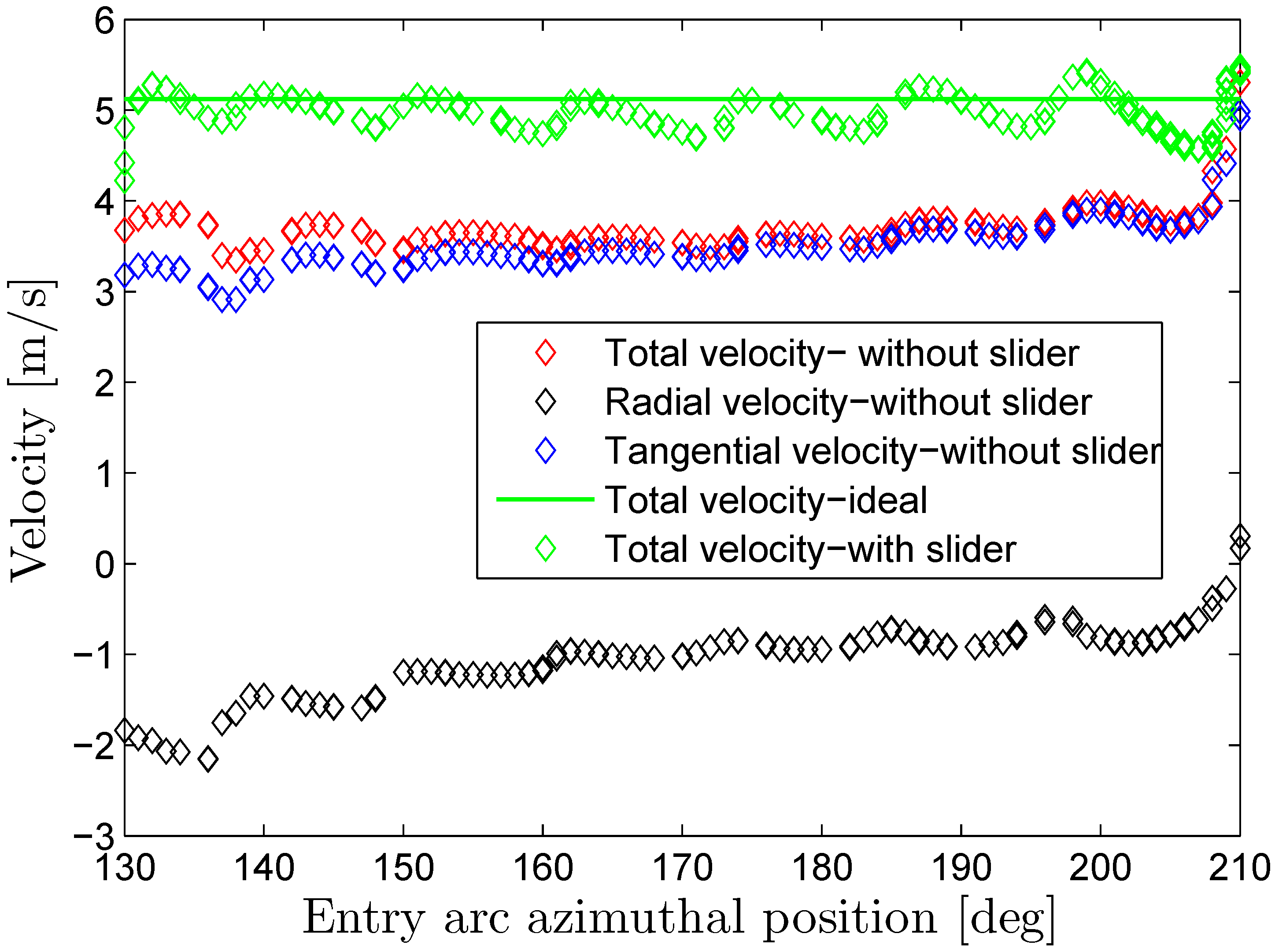
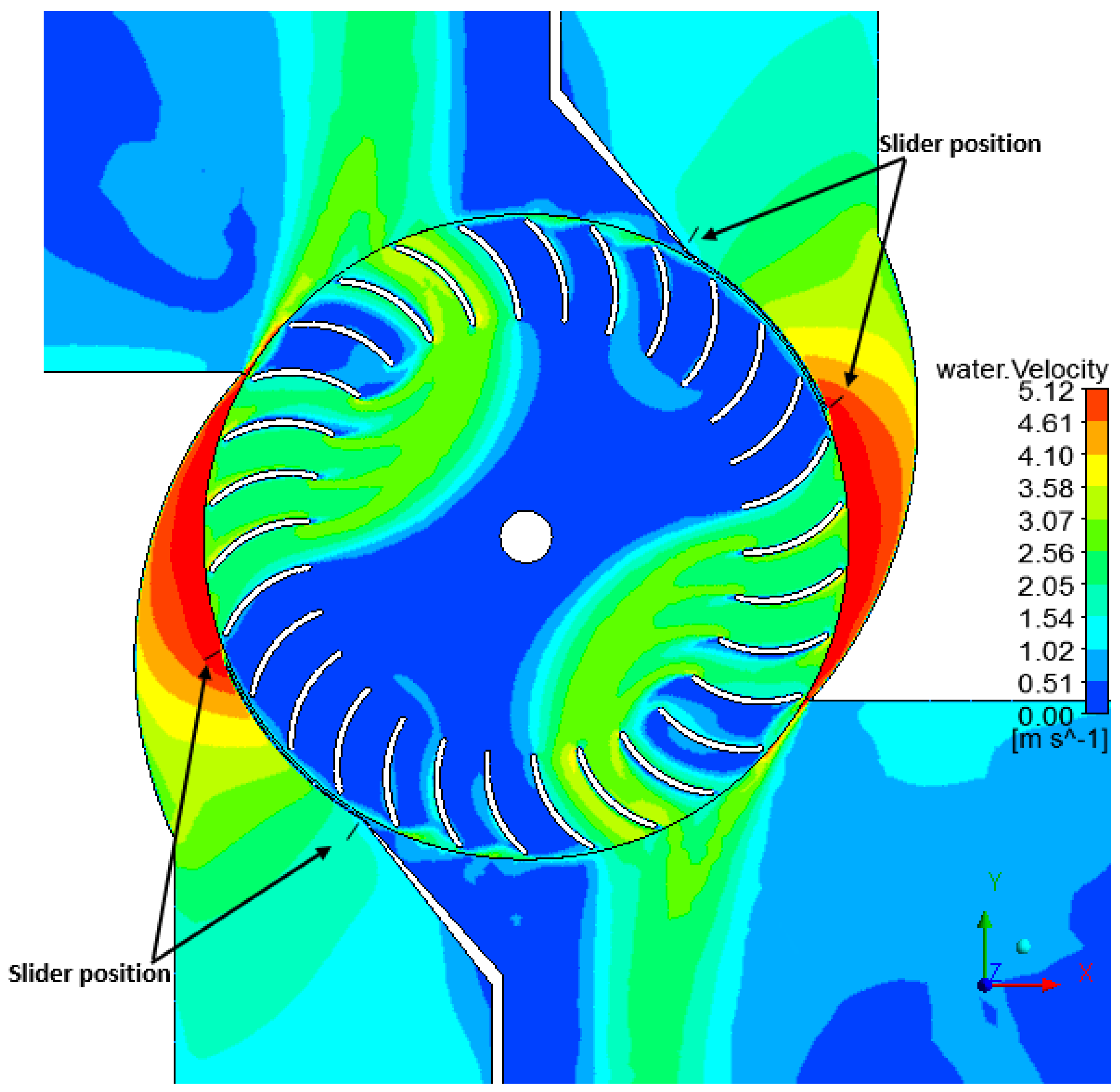
4.2. Flow and Performance of Double-Nozzle Turbine
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| RANS | Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
Appendix A. The Exit Arc of the Second Stage
References
- Macmore, C.; Merryfield, F. The Banki water turbine. Eng. Exp. Stn. 1949, 25, 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Khosrowpanah, S.; Fiuzat, A.; Albertson, M.L. Experimental study of crossflow turbine. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1988, 114, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade, J.; Curiel, C.; Kenyery, F.; Aguillón, O.; Vásquez, A.; Asuaje, M. Numerical investigation of the internal flow in a Banki turbine. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2011, 2011, 841214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, N.; Kim, C.G.; Thapa, B.; Lee, Y.H. Numerical analysis and performance enhancement of a cross-flow hydro turbine. Renew. Energy 2015, 80, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, V.R. A Parametric Study of the Cross-Flow Turbine Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, Clemson University, Clemson, SC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Totapally, H.G.; Aziz, N.M. Refinement of Cross-flow Turbine Design Parameters. J. Energy Eng. 1994, 120, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, R.; Wood, D. A new nozzle design methodology for high efficiency crossflow hydro turbines. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 41, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, R.; Wood, D. The Design of High Efficiency Crossflow Hydro Turbines: A Review and Extension. Energies 2018, 11, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Multi-jet Pelton Turbines. In Pelton Turbines; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, R. Design Improvement of Crossflow Hydro Turbine. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.D.; Lim, J.I.; Kim, Y.T.; Lee, Y.H. Performance and internal flow characteristics of a cross-flow hydro turbine by the shapes of nozzle and runner blade. J. Fluid Sci. Technol. 2008, 3, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinagra, M.; Sammartano, V.; Aricò, C.; Collura, A.; Tucciarelli, T. Cross-Flow turbine design for variable operating conditions. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS. ANSYS Academic Research; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brennen, C.E. Fundamentals of Multiphase Flow; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgin, W.; Fay, W. Some fluid flow characteristics of a cross-flow type hydraulic turbine. In Small Hydro Power Fluid Machinery; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, R.; Wood, D. Computational analysis of part-load flow control for crossflow hydro-turbines. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2018, 45, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
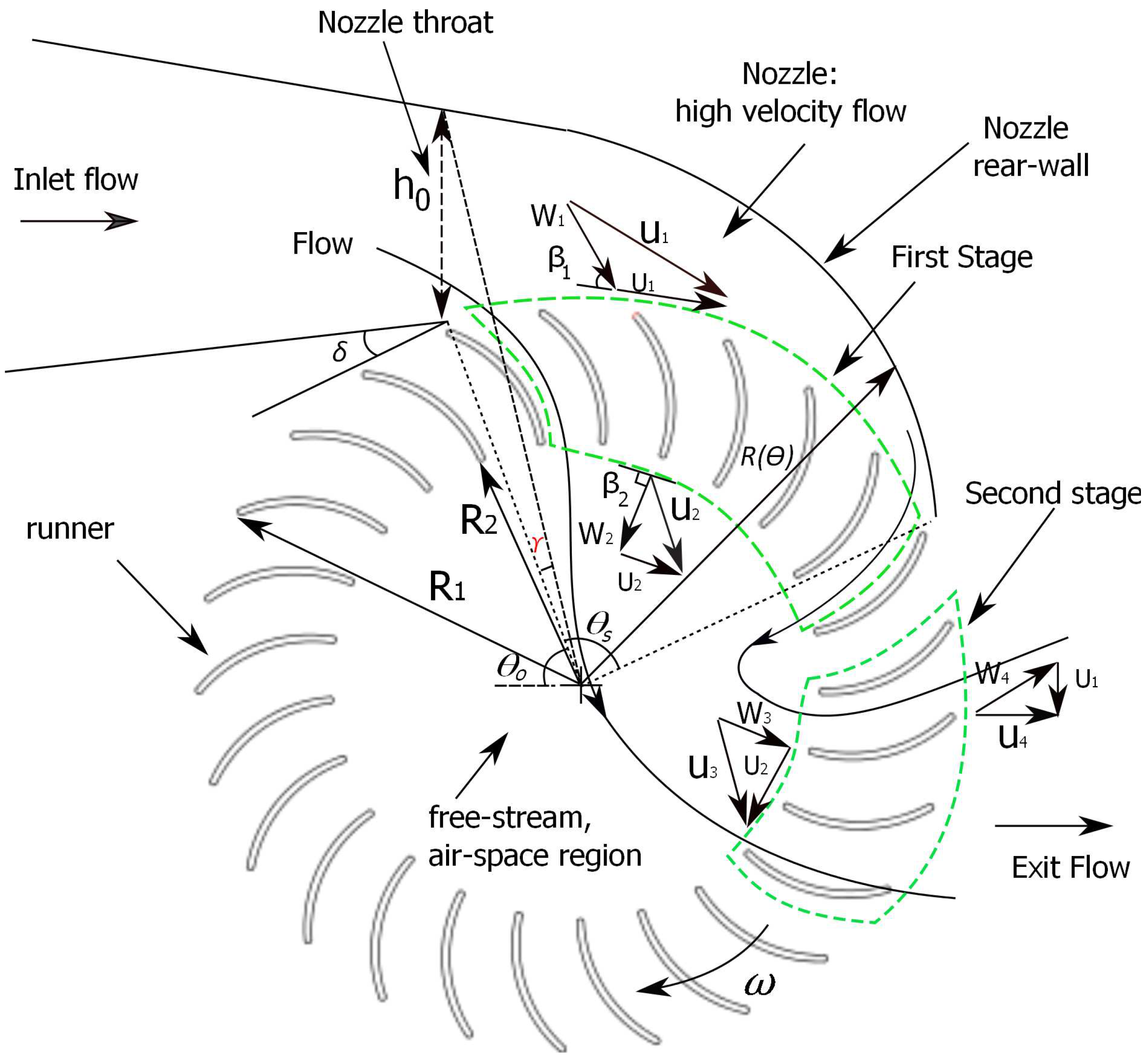
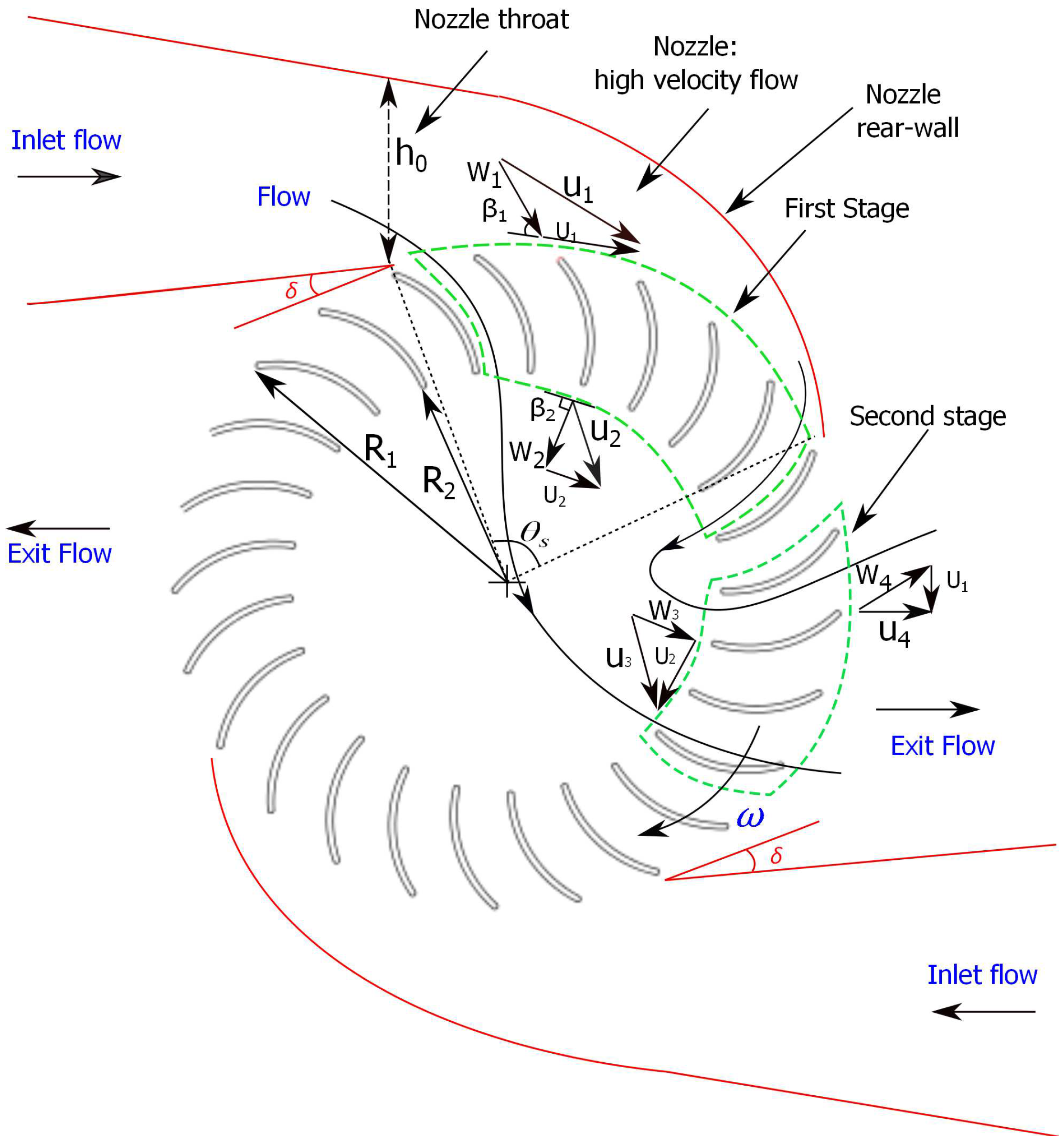
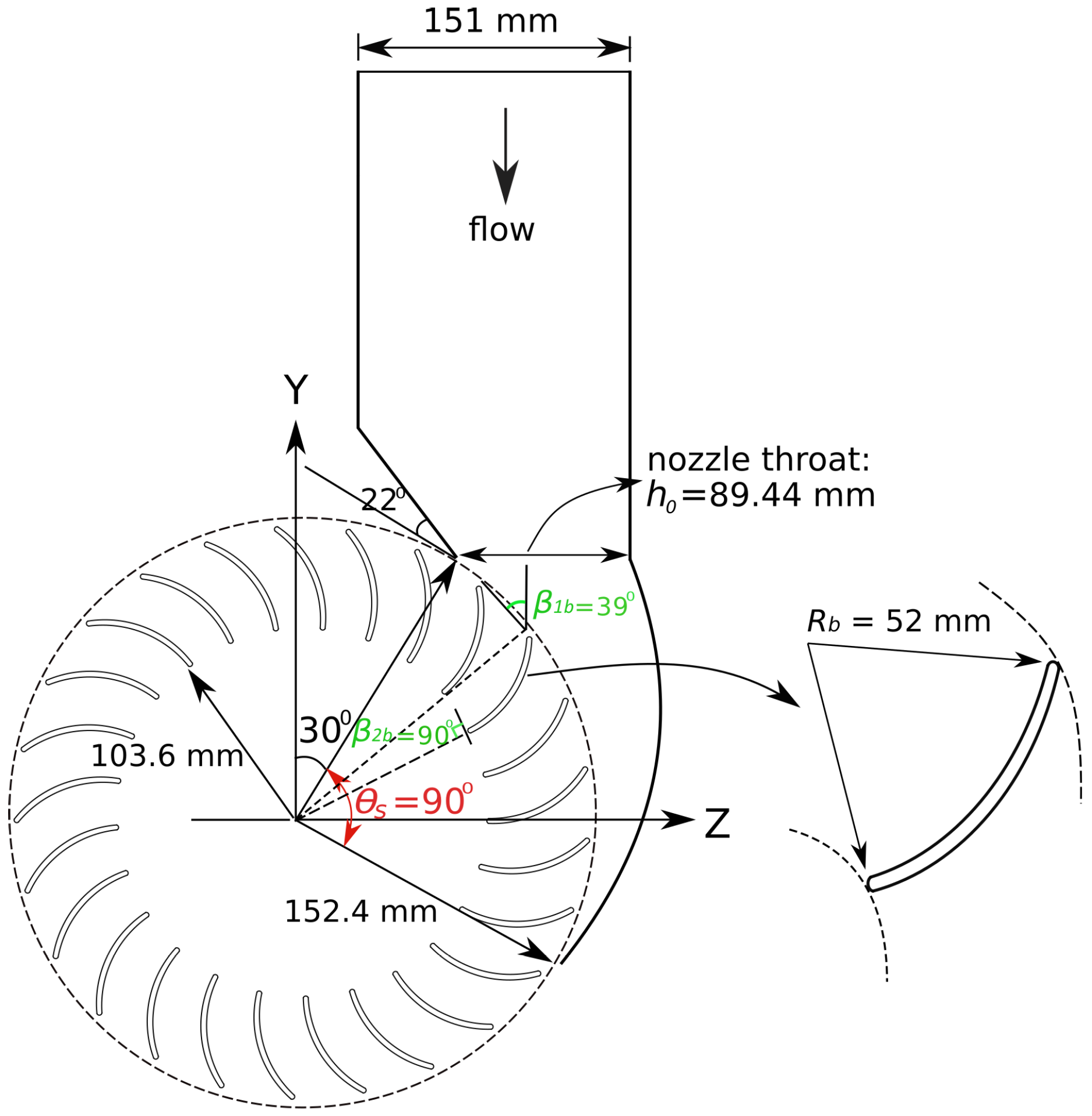
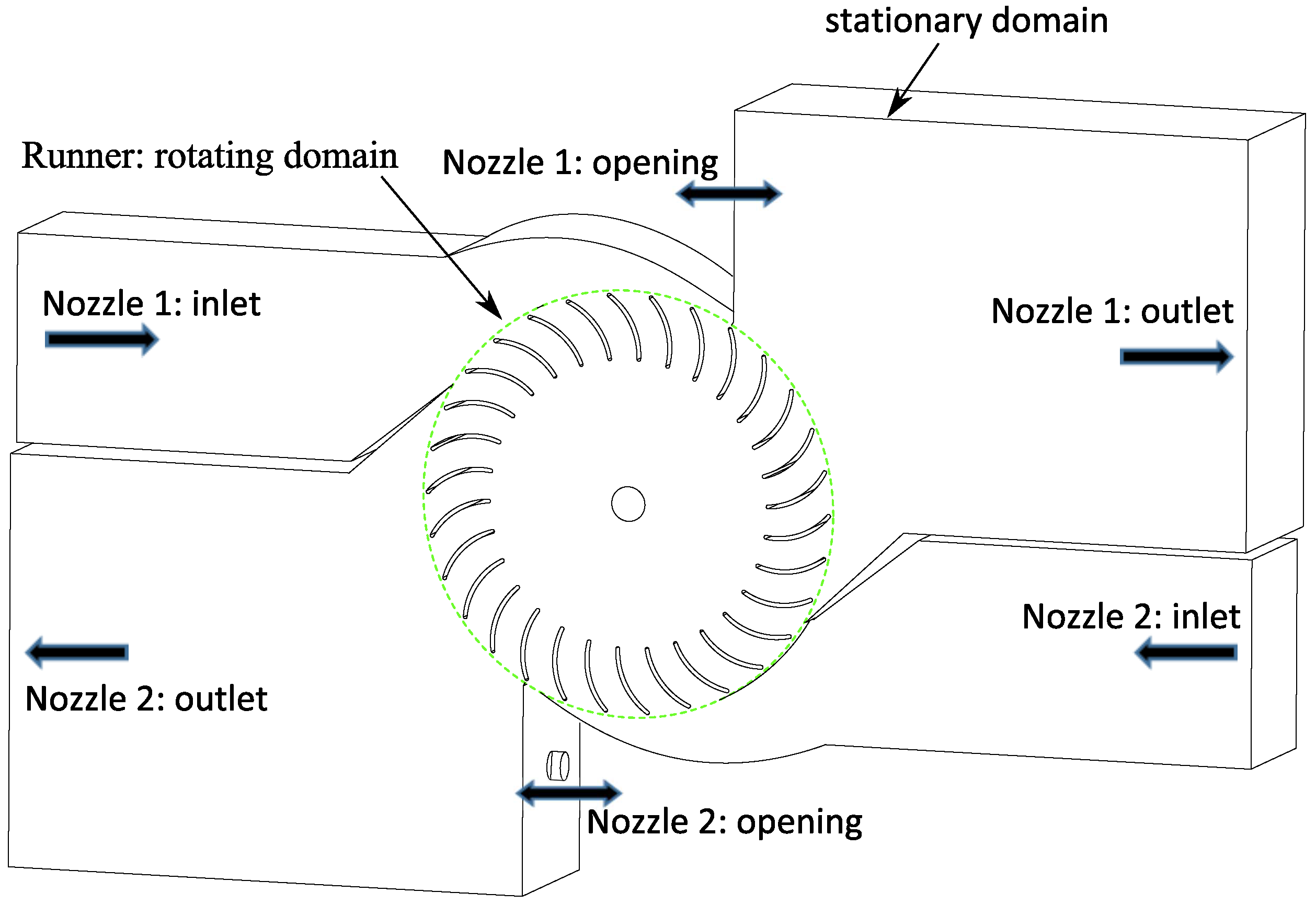


| Design Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Outer radius (), [mm] | 152.40 |
| Inner radius (), [mm] | 103.63 |
| Outer blade angle (), [] | 39 |
| Inner blade angle (), [] | 90 |
| Blade thickness (t), [mm] | 3.2 |
| Number of blades () | 30 |
| Runner and nozzle width (W), [mm] | 101.6 |
| Nozzle throat (), [mm] | 89.44 |
| Nozzle entry arc (), [] | 90 |
| Maximum flow rate (), [lps] | 46 |
| Operating head (H), [m] | 1.337 |
| No of Mesh Elements | Power Output, , kW | Numerical Uncertainty (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 8,132,567 | 1.041 | - |
| 8,356,212 | 1.046 | 0.47 |
| 8,736,545 | 1.053 | 0.66 |
| 9,516,906 | 1.057 | 0.37 |
| 10,716,017 | 1.065 | 0.75 |
| 11,012,531 | 1.068 | 0.28 |
| 13,122,371 | 1.070 | 0.18 |
| Flow Rate, lps | First-Stage Power (%) | Second-Stage Power (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 46 | 61.2 | 38.8 | 88.45 | |
| 40 | 78 | 37.7 | 75.3 | 24.7 | 88.31 |
| 30 | 58 | 27.9 | 78.9 | 20.1 | 87.47 |
| 20 | 39 | 18.8 | 87.3 | 12.7 | 85.68 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adhikari, R.; Wood, D. Computational Analysis of a Double-Nozzle Crossflow Hydroturbine. Energies 2018, 11, 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123380
Adhikari R, Wood D. Computational Analysis of a Double-Nozzle Crossflow Hydroturbine. Energies. 2018; 11(12):3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123380
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdhikari, Ram, and David Wood. 2018. "Computational Analysis of a Double-Nozzle Crossflow Hydroturbine" Energies 11, no. 12: 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123380
APA StyleAdhikari, R., & Wood, D. (2018). Computational Analysis of a Double-Nozzle Crossflow Hydroturbine. Energies, 11(12), 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123380






