Torque Ripple Reduction for Switched Reluctance Motor with Optimized PWM Control Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model and Principles of SRM Operation
3. Proposed Control Method Based on the TSF Using Predictive Current Control
3.1. Block Diagram of Proposed Control Method
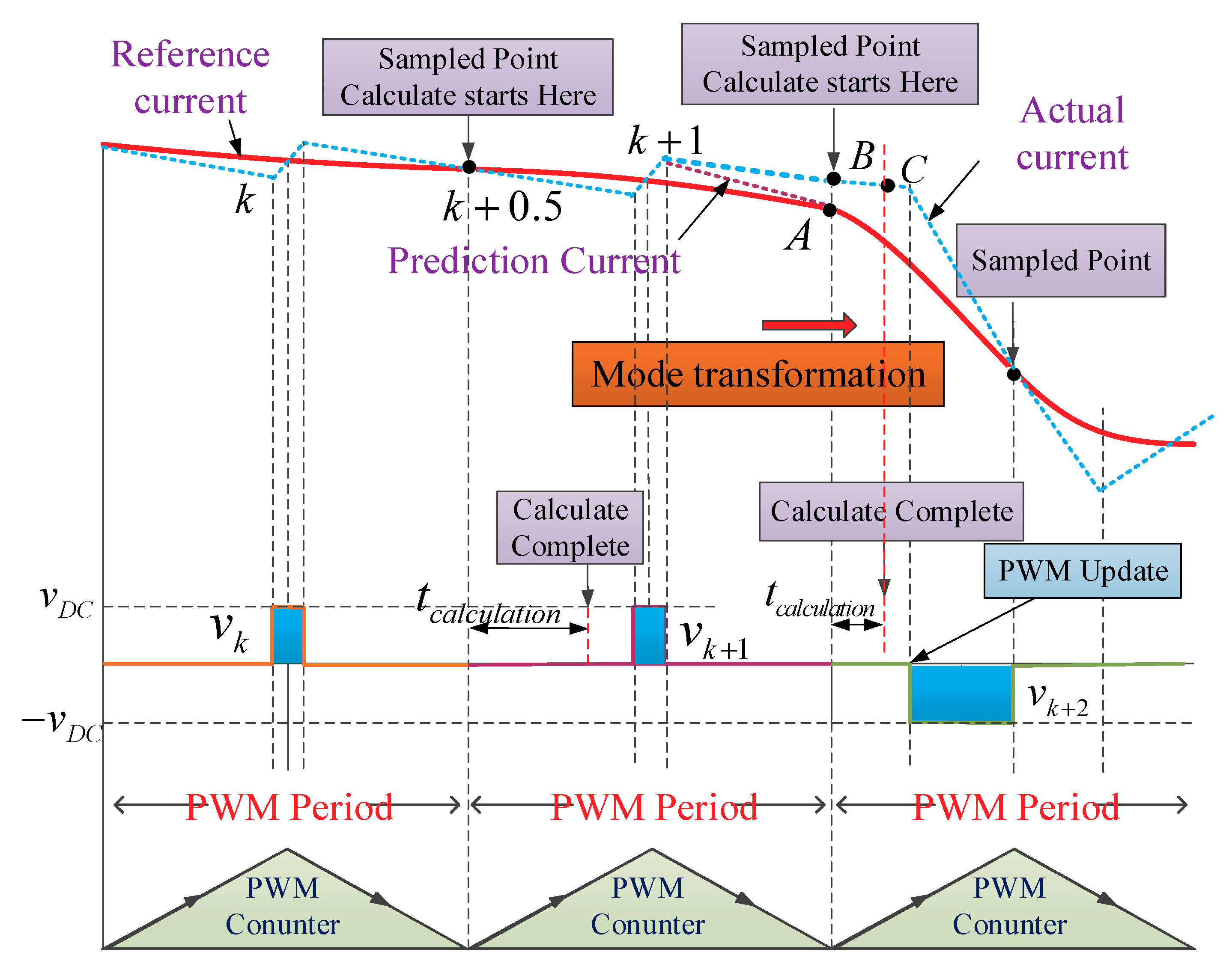
3.2. Peration of an Asymmetric Converter
3.3. Current Build-Up and Flat Flowing Region
3.4. Region of Descending Current
3.5. Operation of the Asymmetric Converter
3.6. Communication Region
4. Analysis of the Simulation and Experimental Results
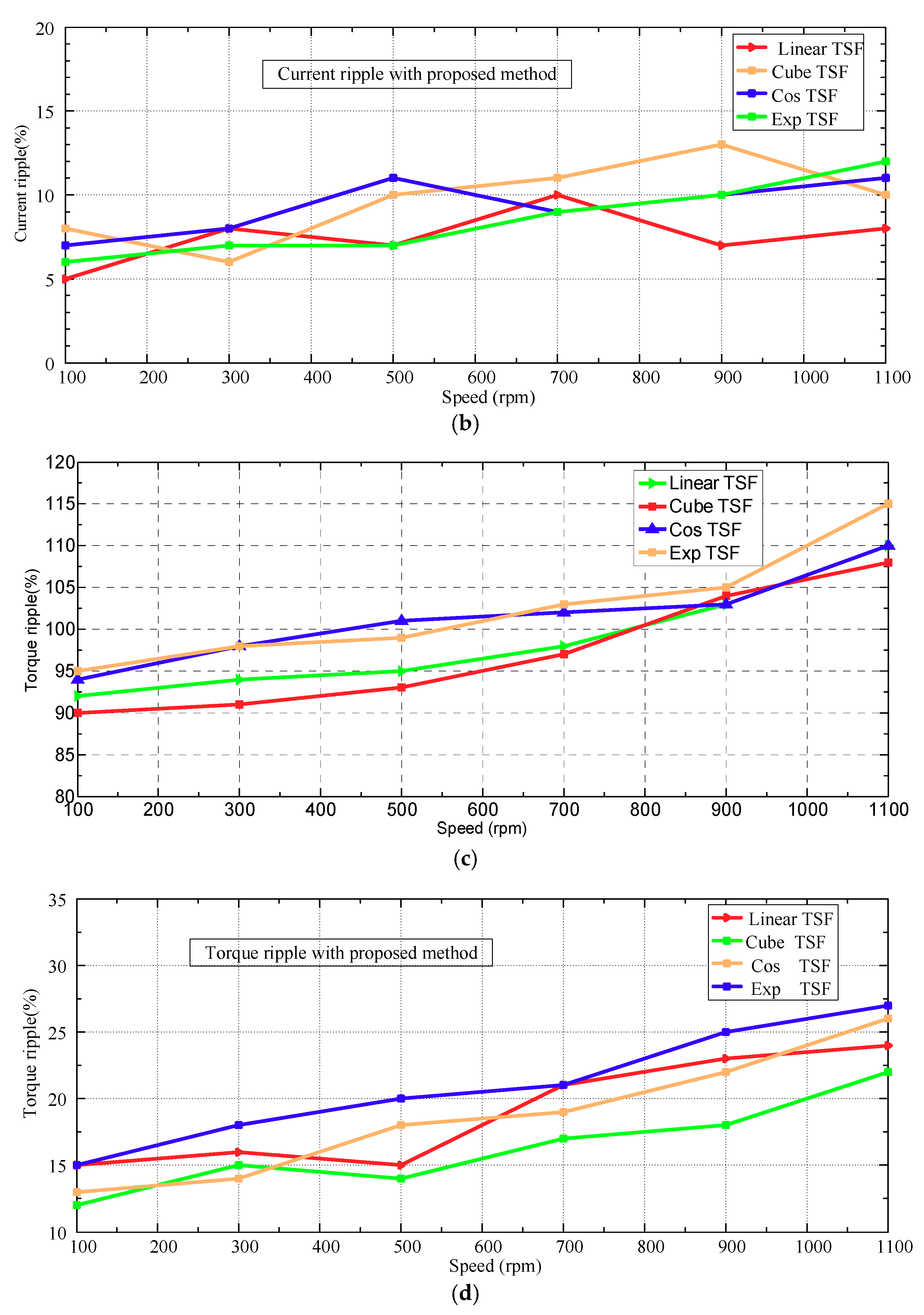
4.1. Simulation Results and Analysis
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Suggested Improvements and Future Direction of this Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Parameters c1, c2, c, kr[0.1,0.25], kf[0,1.0], k, xb[1/9.0,1/3.0], xe[7/9.0,1.0], x1[7/18.0,11.0/18.0];
- Variable x, y, z;
- ConstStr fs = 1 − kf × ((x − x1)2);
- ConstStr fr = kr × ((x/xb)(3/2));
- ConstStr ff = 1 − x25;
- ConstStr ff1 = (((1 − x)/(1 − xe))25)/(1 + (((1 − x)/(1 − xe))25));
- ConstStr L0p = k × (((x/xb)13) × fs + fr) × ff1/(1 + ((x/xb)13));
- ConstStr f = c1/(1 + c × ((x − xb)2)) + c2/(1 + c × ((x − xe)2));
- ConstStr f1 = f × ((x/xb)13)/(1 + ((x/xb)13));
- Function z = (0.5 × L0p × (y2))/((1 + f × (y3))(1/3));
- c1: 1.54202819947362 × 10−5
- c2: 0.000442753170130073
- c: 301.641864196729
- kr: 0.248303583528203
- kf: 0.999999999999997
References
- Jiang, J.W.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. Three-Phase 24/16 Switched Reluctance Machine for a Hybrid Electric Powertrain. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electr. 2017, 3, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieller, D.; Nguyen, N.K.; Wira, P.; Sturtzer, G.; Abdeslam, D.O.; Merckle, J. A Self-Learning Solution for Torque Ripple Reduction for Nonsinusoidal Permanent-Magnet Motor Drives Based on Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayless, J.; Kurihara, N.; Sugimoto, H.; Chiba, A. Acoustic Noise Reduction of Switched Reluctance Motor with Reduced RMS Current and Enhanced Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, W. A Torque Impulse Balance Control for Multi-Tooth Fault Tolerant Switched-Flux Machines under Open-Circuit Fault. Energies 2018, 11, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, W.; Husain, T.; Sozer, Y.; Husain, I. Design Methodology of a Switched Reluctance Machine for Off-Road Vehicle Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, M.; Chuchon, M.; Adriano, R.; Samaniego, J. Design and implementation of a low-cost prototype system for continuous monitoring of electric fields generated by mobile base stations in the 850 MHz and 1900 MHz frequency bands. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezamabadi, M.M.; Afjei, E.; Torkaman, H. Design, Dynamic Electromagnetic Analysis, FEM, and Fabrication of a New Switched-Reluctance Motor with Hybrid Motion. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, A.; Kiyota, K.; Hoshi, N.; Takemoto, M.; Ogasawara, S. Development of a Rare-Earth-Free SR Motor with High Torque Density for Hybrid Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.-S. Rapid Optimization of Double-Stators Switched Reluctance Motor with Equivalent Magnetic Circuit. Energies 2017, 10, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, E.; Yuan, J.; Qiu, L.; Wu, X. Complimentary Force Allocation Control for a Dual-Mover Linear Switched Reluctance Machine. Energies 2017, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, E.S.; Santisteban, J.A. Mutual Inductances Effect on the Torque of an Axial Magnetic Flux Switched Reluctance Motor. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2015, 13, 2239–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikail, R.; Husain, I.; Islam, M.S.; Sozer, Y.; Sebastian, T. Four-Quadrant Torque Ripple Minimization of Switched Reluctance Machine Through Current Profiling with Mitigation of Rotor Eccentricity Problem and Sensor Errors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermanipour, M.J.; Ganji, B. Modification in Geometric Structure of Double-Sided Axial Flux Switched Reluctance Motor for Mitigating Torque Ripple. Can. J. Elect. Comput. Eng. 2015, 38, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaked, N.T.; Rabinovici, R. New procedures for minimizing the torque ripple in switched reluctance motors by optimizing the phase-current profile. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labiod, C.; Srairi, K.; Mahdad, B.; Benbouzid, M.E.H. A novel control technique for torque ripple minimization in switched reluctance motor through destructive interference. Electr. Eng. 2017, 100, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin Woo, L.; Hong Seok, K.; Byung Il, K.; Byung Taek, K. New rotor shape design for minimum torque ripple of SRM using FEM. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 754–757. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, N.K.; Rajagopal, K.R. Torque profiles of a switched reluctance motor having special pole face shapes and asymmetric stator poles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 2035–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi, B.; Emadi, A.; Sepe, R.B. A switched reluctance machine-based starter/alternator for more electric cars. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2004, 19, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, Z.G.; Liang, J.; Ahn, J.W. Single-Phase SRM Drive with Torque Ripple Reduction and Power Factor Correction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2007, 43, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. An Improved Torque Sharing Function for Torque Ripple Reduction in Switched Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 1. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8357897 (accessed on 11 May 2018). [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.K.; Yoon, H.S.; Koh, C.S. Pole-Shape Optimization of a Switched-Reluctance Motor for Torque Ripple Reduction. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 1797–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.D.; Cheng, K.W.E.; Ho, S.L. Optimization and Evaluation of Torque-Sharing Functions for Torque Ripple Minimization in Switched Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2076–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Liang, J.; Lee, Z.G.; Ahn, J.W. A Simple Nonlinear Logical Torque Sharing Function for Low-Torque Ripple SR Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 3021–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-U.; Park, K.; Lee, K.-B. A Non-Unity Torque Sharing Function for Torque Ripple Minimization of Switched Reluctance Generators in Wind Power Systems. Energies 2015, 8, 11685–11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, J.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. An Offline Torque Sharing Function for Torque Ripple Reduction in Switched Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuengwarodsakul, N.H.; Menne, M.; Inderka, R.B.; Doncker, R.W.D. High-dynamic four-quadrant switched reluctance drive based on DITC. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. An Extended-Speed Low-Ripple Torque Control of Switched Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujičić, V.P. Minimization of Torque Ripple and Copper Losses in Switched Reluctance Drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Chen, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y. Phase current reconstruction strategy for switched reluctance machines with fault-tolerant capability. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Hu, Y.; Cao, W.; Yang, S. Independent Current Control of Dual Parallel SRM Drive Using a Public Current Sensor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dúbravka, P.; Rafajdus, P.; Makyš, P.; Szabó, L. Control of switched reluctance motor by current profiling under normal and open phase operating condition. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, T.; Hara, T.; Umetani, K.; Hiraki, E. Simple control technique to eliminate source current ripple and torque ripple of switched reluctance motors for electric vehicle propulsion. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016—42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016; pp. 1876–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.S.; Narayanan, G. Linearized Modeling of Switched Reluctance Motor for Closed-Loop Current Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 3146–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong-Hee, L.; JongHeon, L.; Jin-Woo, A. Current control of a high speed SRM with an advanced 4-level converter. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 8th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia (ICPE & ECCE), Jeju, Korea, 30 May–3 June 2011; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, F.; Ye, J.; Emadi, A. A Digital PWM Current Controller for Switched Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 7087–7098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Wu, J.; Sun, Q.; Yang, S.; Hu, Y.; Jin, L. Low-cost direct instantaneous torque control for switched reluctance motors with bus current detection under soft-chopping mode. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Malysz, P.; Emadi, A. A Fixed-Switching-Frequency Integral Sliding Mode Current Controller for Switched Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 381–394. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J.Y.; Liaw, C.M. Reduction of speed ripple and vibration for switched reluctance motor drive via intelligent current profiling. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2010, 4, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shamsi, P. Model Predictive Current Control of Switched Reluctance Motors with Inductance Auto-Calibration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3934–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shamsi, P. Inductance Surface Learning for Model Predictive Current Control of Switched Reluctance Motors. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrification 2015, 1, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikail, R.; Husain, I.; Sozer, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Sebastian, T. A Fixed Switching Frequency Predictive Current Control Method for Switched Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3717–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-K.; Yu, J.-T.; Huang, H.-Q.; Wang, J.-T.; Yu, H.-C.; Lai, Y.-S. A Dual-Voltage-Vector Model-Free Predictive Current Controller for Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drive Systems. Energies 2018, 11, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.; Li, M.; Hui, W.; Shen, S.Q.; Wang, W. Torque ripple minimization for switched reluctance motor with predictive current control method. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sydney, Australia, 11–14 August 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, S.; Martínez, A.; Millán, W.; Montaño, C.E.; Pérez-Cebolla, F. Design, Characterization, and Validation of a 1-kW AC Self-Excited Switched Reluctance Generator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















| Number of stator/rotor poles | 12/8 |
| Rated speed | 1190 r/min |
| Rated power | 5.5 kW |
| Rated voltage | 200 V |
| Phase resistance | 200 V |
| Type of silicon steel sheet | 50 w270 |
| DSP | TMS320F28335 |
| Torque transducer | JN338 |
| Magnetic power brake | FZ-J |
| DC power supply | KD-200A |
| Converter | Asymmetric half-bridge |
| Current sensor | ETCR035AD |
| Rotary transformer | TS2660N141E64 |
| Poles | 12/8 |
| Aligned inductance | 0.5 × 10−3 H |
| Unaligned inductance | 0.14 × 10−3 H |
| Saturated aligned inductance | 400 A |
| Maximum current | 0.14 × 10−3 H |
| Maximum flux linkage | 0.472 V·s |
| Stator resistance | 0.01 Ohm |
| Inertia | 0.022 kg·m2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, H.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Shen, S.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, J. Torque Ripple Reduction for Switched Reluctance Motor with Optimized PWM Control Strategy. Energies 2018, 11, 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113215
Cai H, Wang H, Li M, Shen S, Feng Y, Zheng J. Torque Ripple Reduction for Switched Reluctance Motor with Optimized PWM Control Strategy. Energies. 2018; 11(11):3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113215
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Hui, Hui Wang, Mengqiu Li, Shiqi Shen, Yaojing Feng, and Jian Zheng. 2018. "Torque Ripple Reduction for Switched Reluctance Motor with Optimized PWM Control Strategy" Energies 11, no. 11: 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113215
APA StyleCai, H., Wang, H., Li, M., Shen, S., Feng, Y., & Zheng, J. (2018). Torque Ripple Reduction for Switched Reluctance Motor with Optimized PWM Control Strategy. Energies, 11(11), 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113215





