Highly Efficient Target Power Control for Two-Receiver Wireless Power Transfer Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling of Two-Receiver WPT System
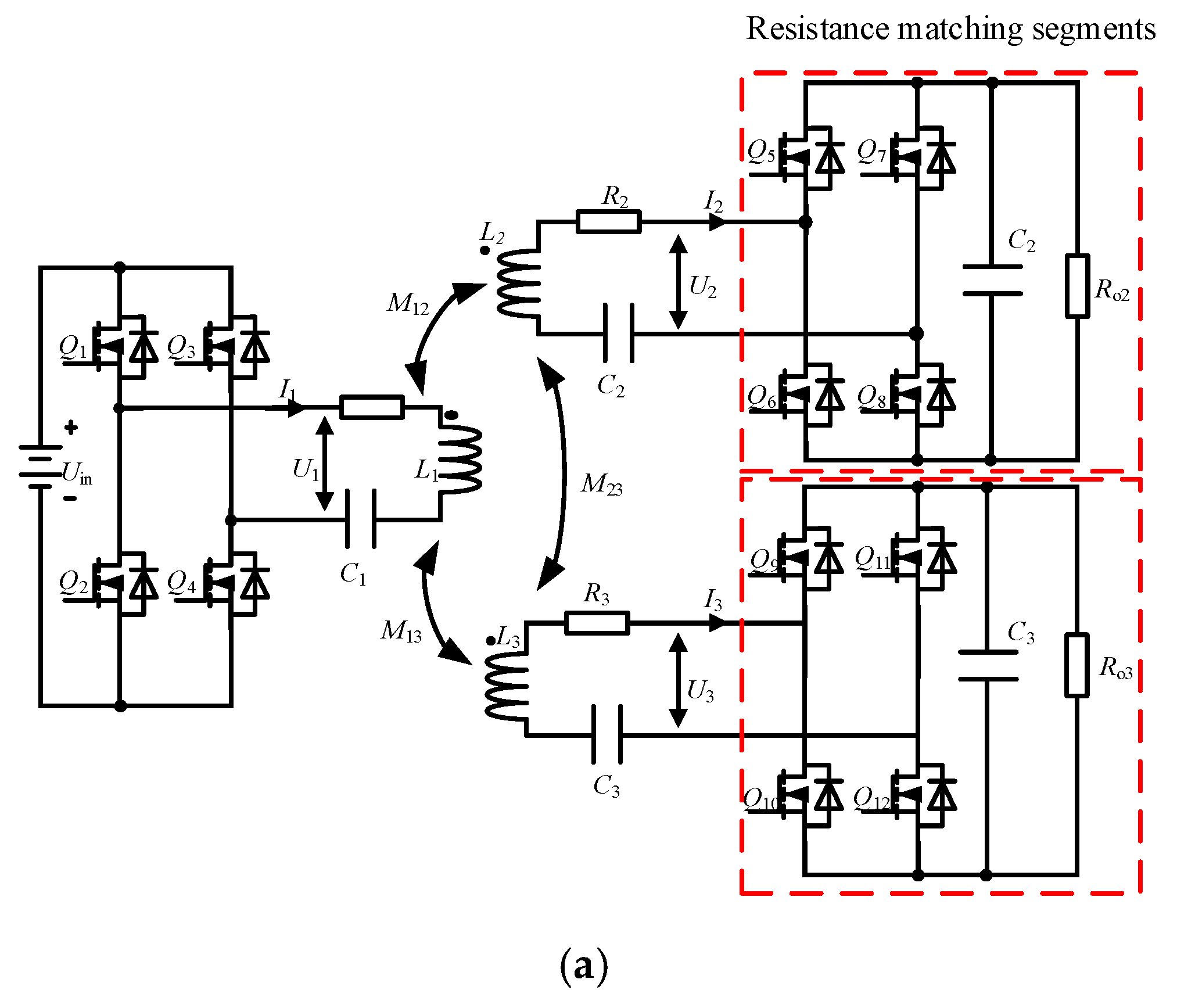
2.1. Circuit Model of Two-Receiver WPT System
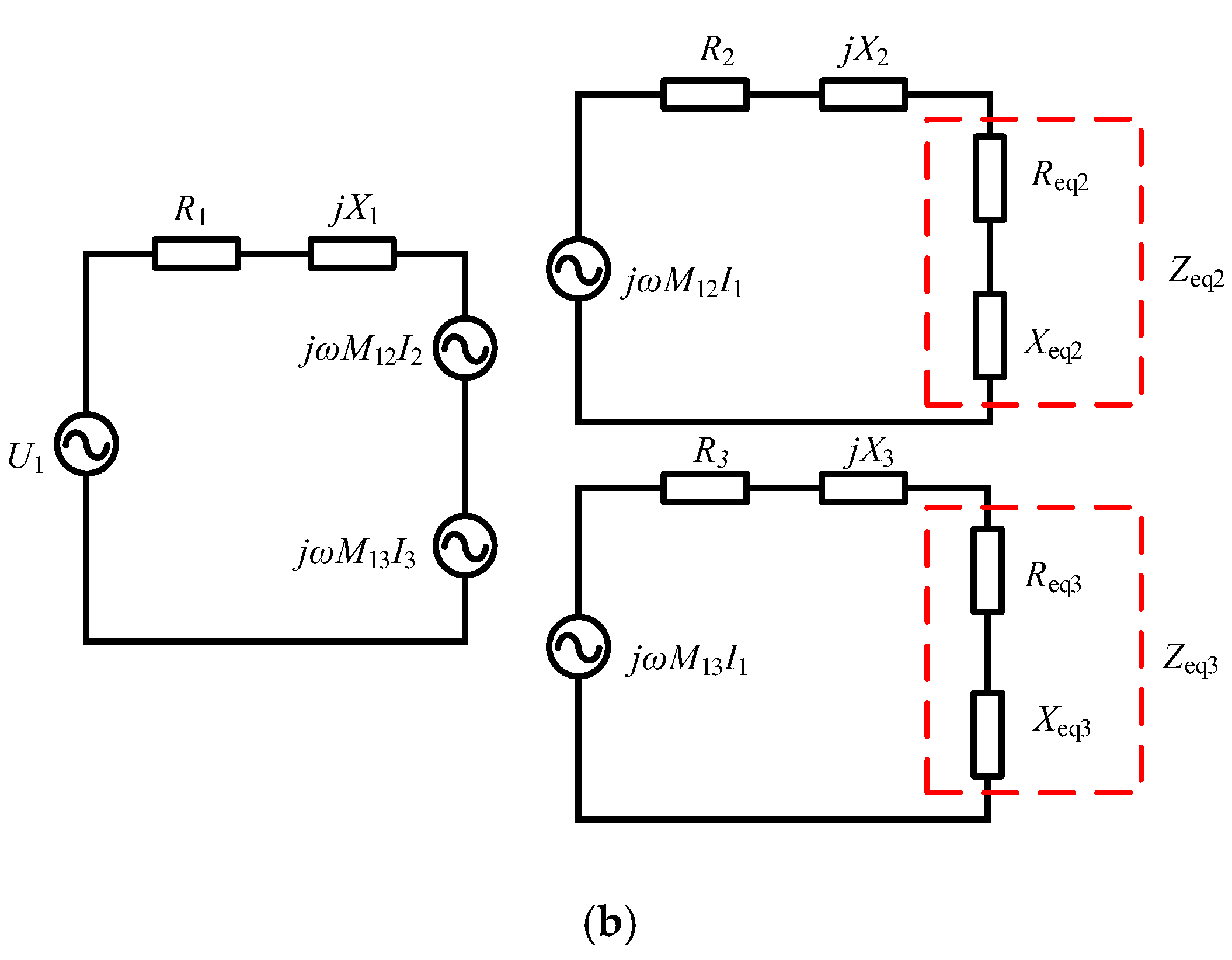
2.2. Impedance Matching Control
2.3. Optimal Mutual Inducatance Based on Impedance Matching Control
3. Target Power Control
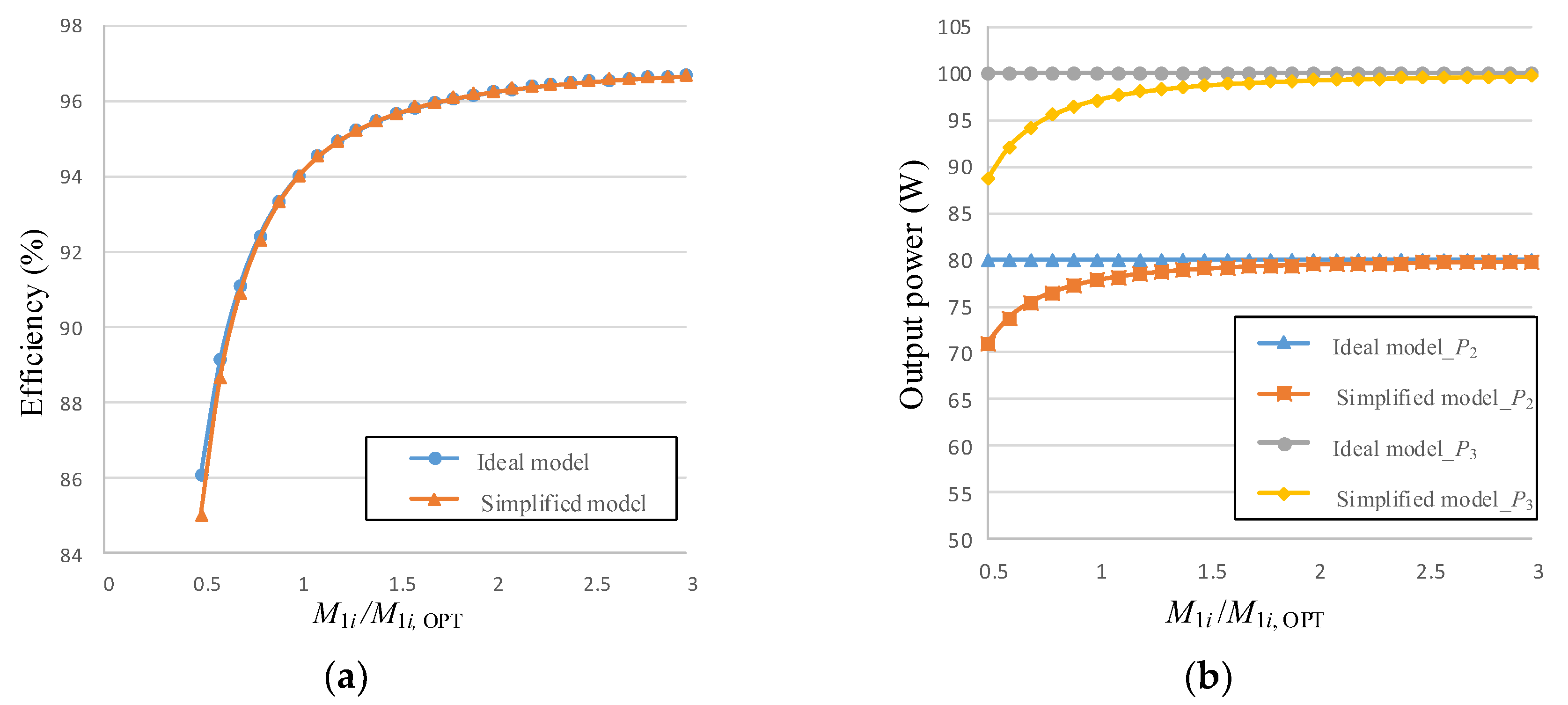
3.1. Simplified Model
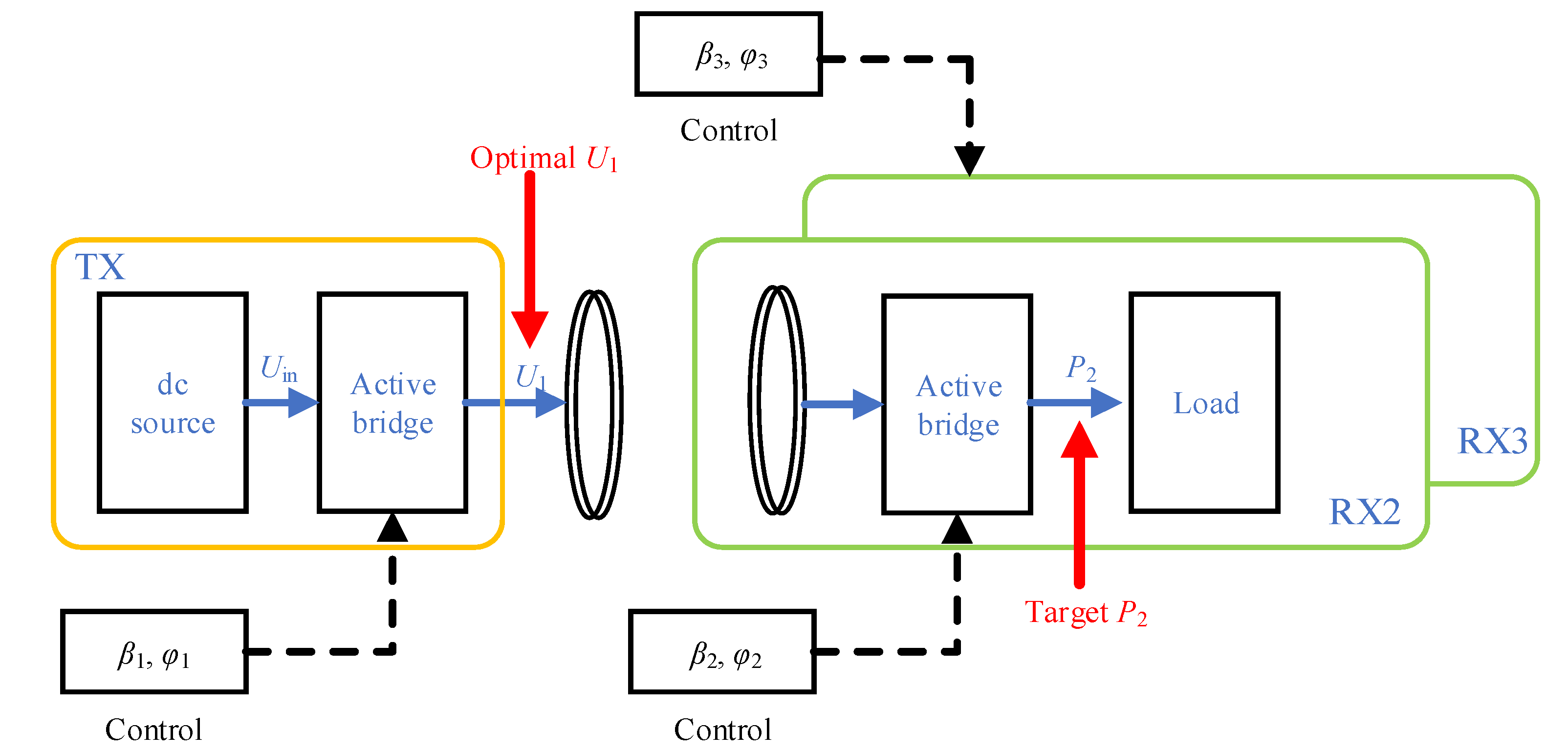
3.2. Target Power Control
4. Phase Manipulation and Flowchart
4.1. Phase Manipulation
4.2. Flowchart
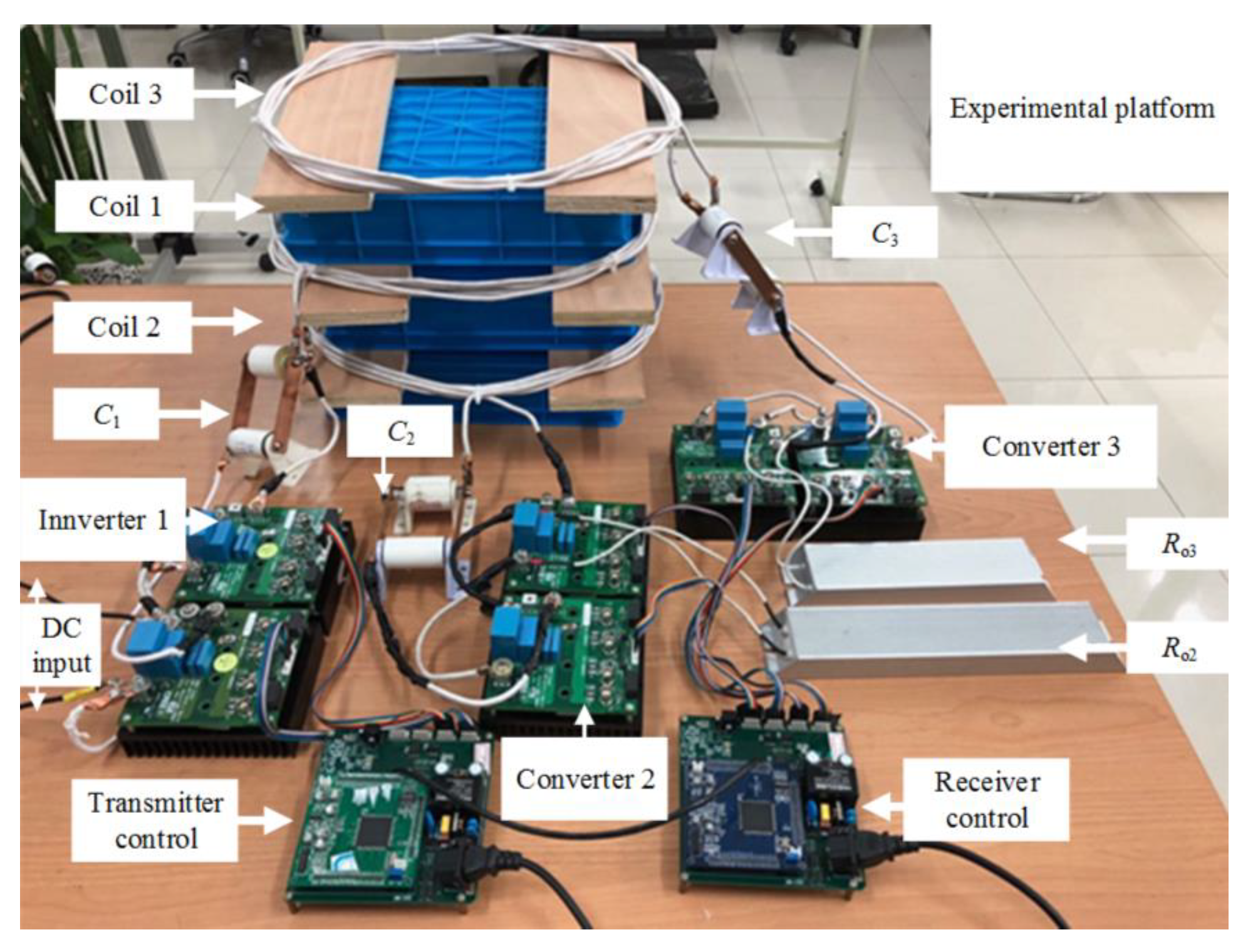
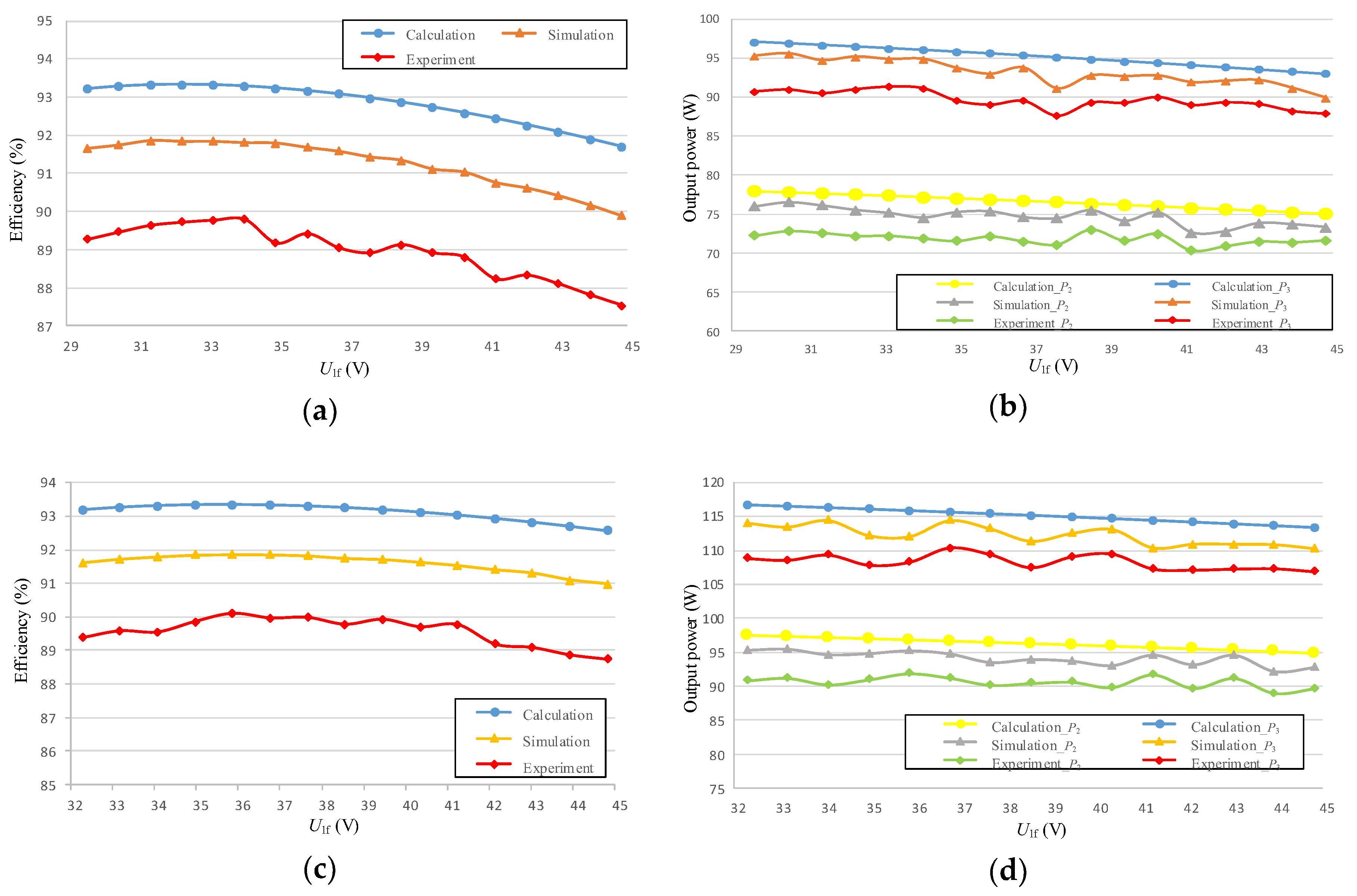
5. Results
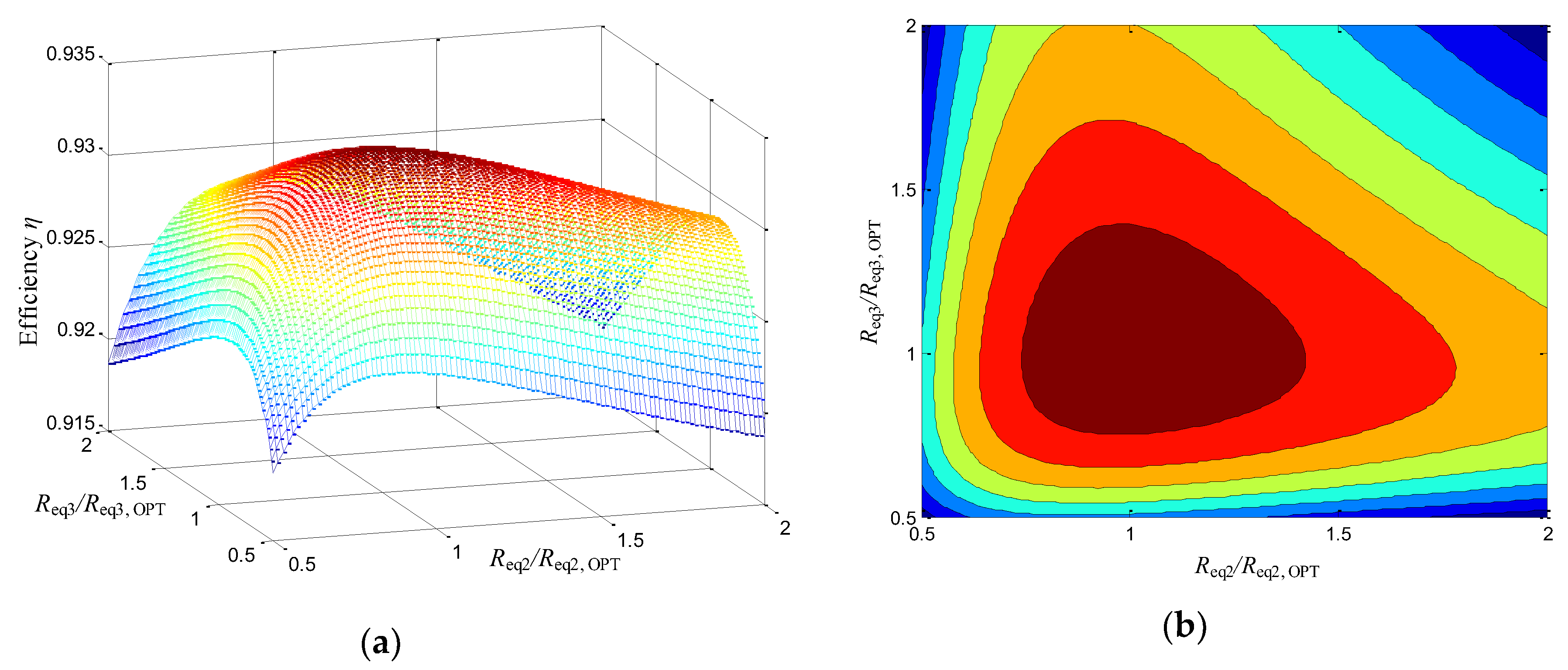
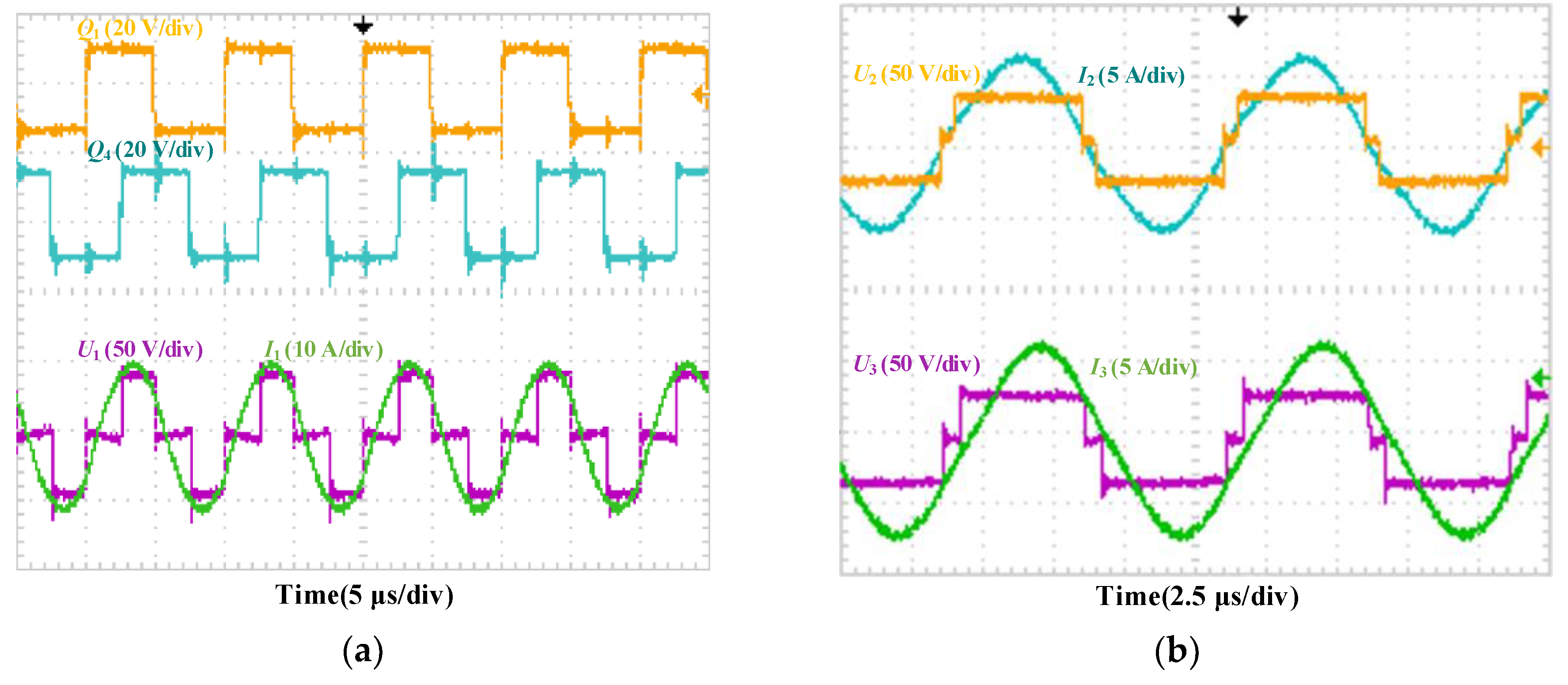
5.1. Result of Impedance Matching Control
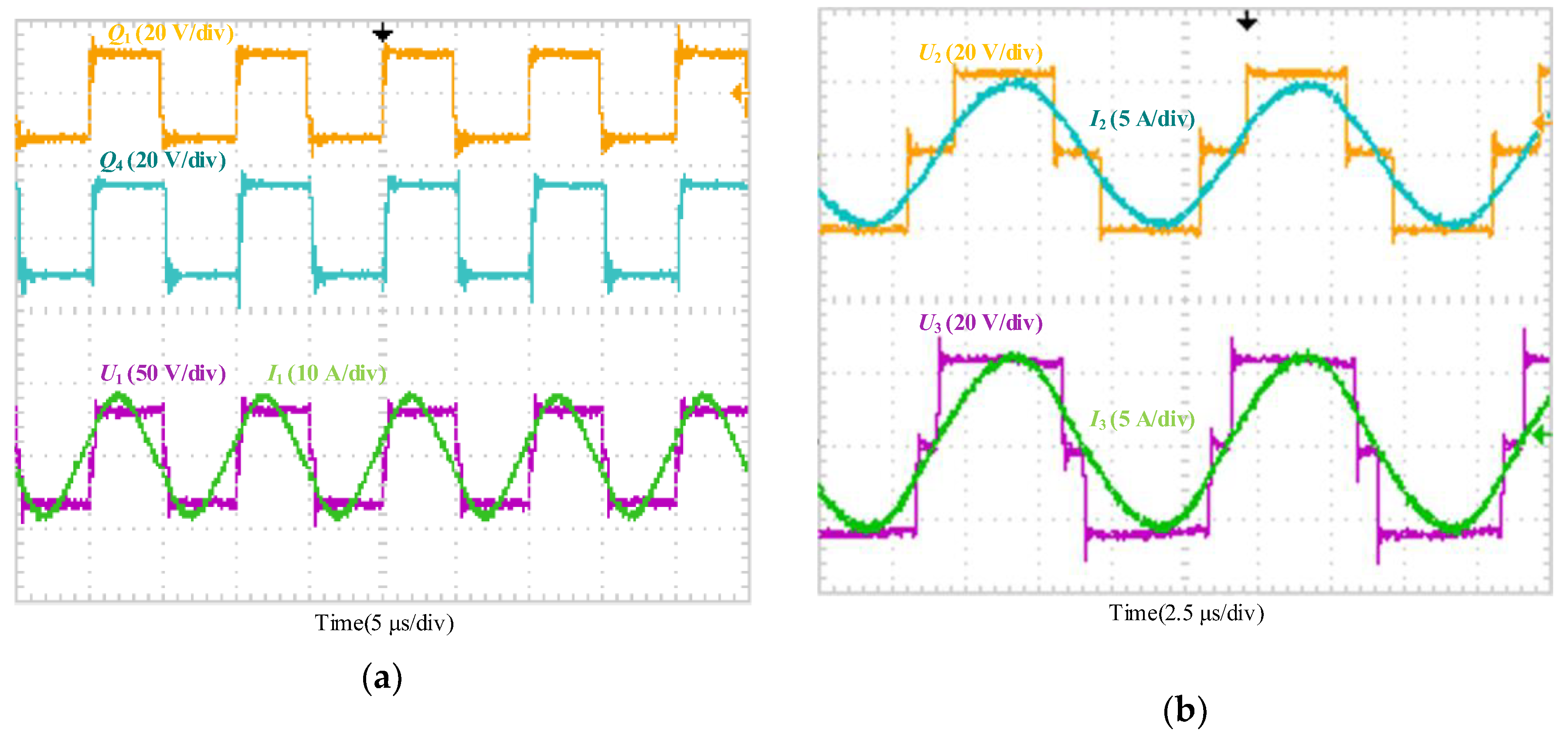
5.2. Result of Target Power Control
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Si, P.; Hu, A.P.; Malpas, S.; Budgett, D. A frequency control method for regulating wireless power to implantable devices. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2008, 2, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, R.F.; Cheng, K.W.; Je, M. High-Efficiency Wireless Power Transfer for Biomedical Implants by Optimal Resonant Load Transformation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Kiani, M. A Hybrid Inductive-Ultrasonic Link for Wireless Power Transmission to Millimeter-Sized Biomedical Implants. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2016, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramrakhyani, A.K.; Mirabbasi, S.; Mu, C. Design and optimization of resonance-based efficient wireless power delivery systems for biomedical implants. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2011, 5, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, J.; Bruning, H.; Bakker, S.; Rijnaarts, H. Near field resonant inductive coupling to power electronic devices dispersed in water. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 178, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Gu, W.; Chu, J.; Shen, A. Frequency splitting of underwater wireless power transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Electromagnetics: Applications and Student Innovation Competition, Nanjing, China, 16–18 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Klontz, K.W.; Divan, D.M.; Novotny, D.W.; Lorenz, R.D. Contactless power delivery system for mining applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Ding, E.J.; Xue, H. Multiple-Input Single-Output Wireless Power Transmission System for Coal Mine Application. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 462–463, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampubolon, M.; Pamungkas, L.; Chiu, H.J.; Liu, Y.C.; Hsieh, Y.C. Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer for Logistic Robots. Energies 2018, 11, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imura, T.; Hori, Y. Optimization using transmitting circuit of multiple receiving antennas for wireless power transfer via magnetic resonance coupling. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 33rd International Telecommunications Energy Conference (INTELEC), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 12 December 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Zhang, T.; Ma, C.; Zhu, X. Efficiency and Optimal Loads Analysis for Multiple-Receiver Wireless Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Yin, H.; Zhu, X.; Ma, C. Analysis and Tracking of Optimal Load in Wireless Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans Power Electron. 2015, 30, 3952–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Agostinelli, M.; Vesti, S.; Oliver, J.A.; Cobos, J.A.; Huemer, M. A Wireless Charging System Applying Phase-Shift and Amplitude Control to Maximize Efficiency and Extractable Power. IEEE Trans Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6338–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Chen, W. A Maximum Efficiency Point Tracking Control Scheme for Wireless Power Transfer Systems Using Magnetic Resonant Coupling. IEEE Trans Power Electron. 2015, 30, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Fu, M.; Ma, C.; Zhu, X. Optimal load analysis for a two-receiver wireless power transfer system. In Proceedings of the Wireless Power Transfer Conference, Jeju, South Korea, 8–9 May 2014; pp. 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Mai, R.; Liu, Y.; He, Z. Efficiency optimising strategy for dual-coupled transmitters based WPT systems. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 1877–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, X.; Jin, N.; Tang, H. Analysis and Design of a Wireless Power Transfer System with Dual Active Bridges. Energies 2017, 10, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Yin, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C. A 6.78 MHz Multiple-Receiver Wireless Power Transfer System with Constant Output Voltage and Optimum Efficiency. IEEE Trans Power Electron. 2017, 33, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Cho, D.H. Analysis of Wireless Power Transfer for Adjustable Power Distribution among Multiple Receivers. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Yin, H.; Ma, C. Megahertz Multiple-Receiver Wireless Power Transfer Systems with Power Flow Management and Maximum Efficiency Point Tracking. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, X.; Luk, C.K.; Ma, C. Compensation of Cross Coupling in Multiple-Receiver Wireless Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2016, 12, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Symbol | Quantity | Value |
|---|---|---|
| L1, L2, L3 C1, C2, C3 R1, R2, R3 f M12, M13 d φ1, φ2, φ3 | inductances of coils compensation capacitor parasitic resistances operating frequency mutual inductance distance between adjacent coils phase (see in Figure 4) | 22.78 µH, 22.97 µH, 22.97 µH 114 nF, 110 nF, 110 nF 0.01925 Ω, 0.01279 Ω, 0.01158 Ω 100 kHz 5 µH, 5 µH 12 cm 0, 0, 0 |
| Method | Math Model | Simulation | Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impedance matching method Target power control method | 93.4% 93.3% | 91.87% 91.85% | 90.1% 89.8% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, W.; Ma, D.; Tang, H.; Lai, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, L. Highly Efficient Target Power Control for Two-Receiver Wireless Power Transfer Systems. Energies 2018, 11, 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11102726
Cai W, Ma D, Tang H, Lai X, Liu X, Sun L. Highly Efficient Target Power Control for Two-Receiver Wireless Power Transfer Systems. Energies. 2018; 11(10):2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11102726
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Weikun, Dianguang Ma, Houjun Tang, Xiaoyang Lai, Xin Liu, and Longzhao Sun. 2018. "Highly Efficient Target Power Control for Two-Receiver Wireless Power Transfer Systems" Energies 11, no. 10: 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11102726
APA StyleCai, W., Ma, D., Tang, H., Lai, X., Liu, X., & Sun, L. (2018). Highly Efficient Target Power Control for Two-Receiver Wireless Power Transfer Systems. Energies, 11(10), 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11102726





