The Role of Shearing Energy and Interfacial Gibbs Free Energy in the Emulsification Mechanism of Waxy Crude Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
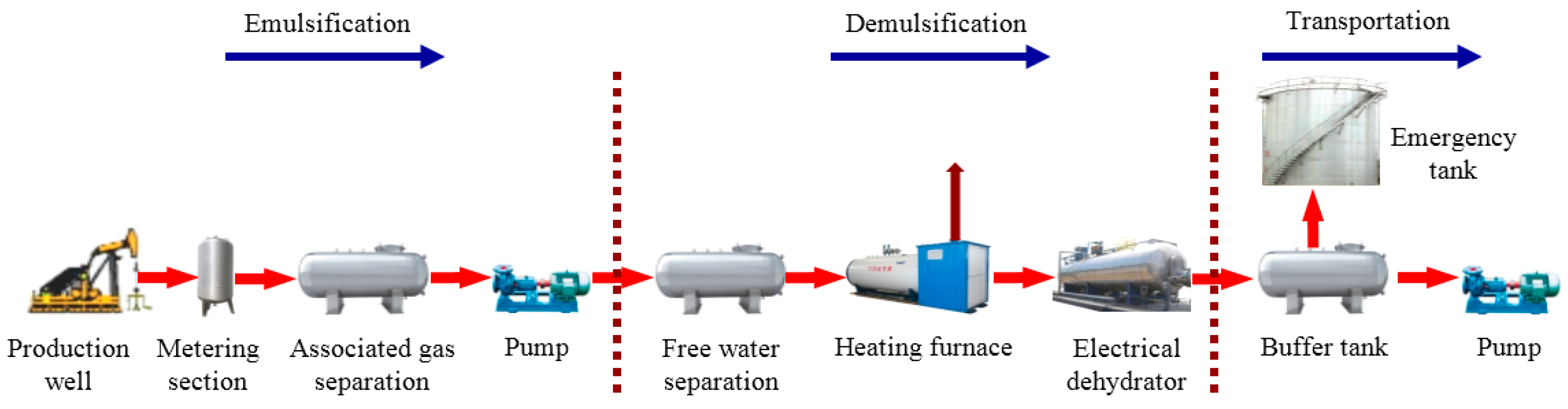
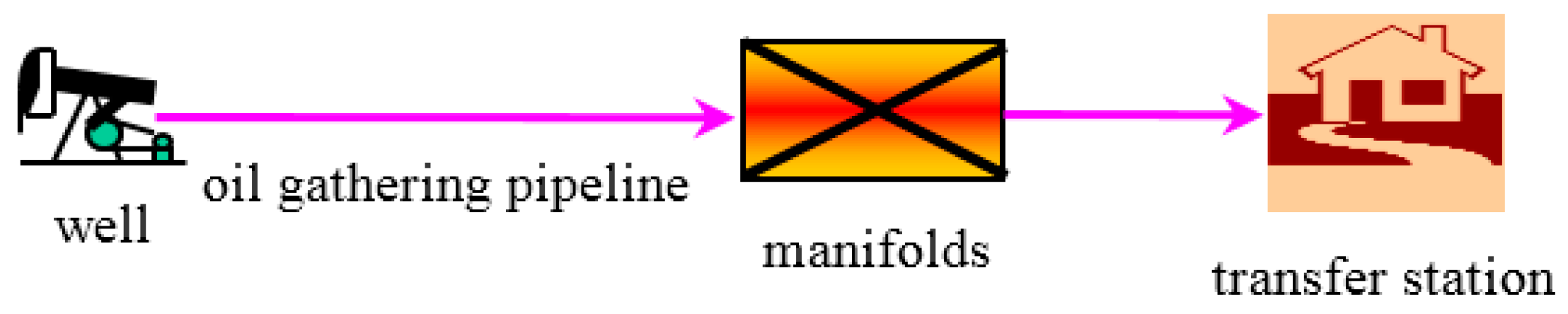
2. Experimental Material, Setup and Field Data
2.1. Materials and Emulsion Preparation
2.2. Emulsification Property Measurements
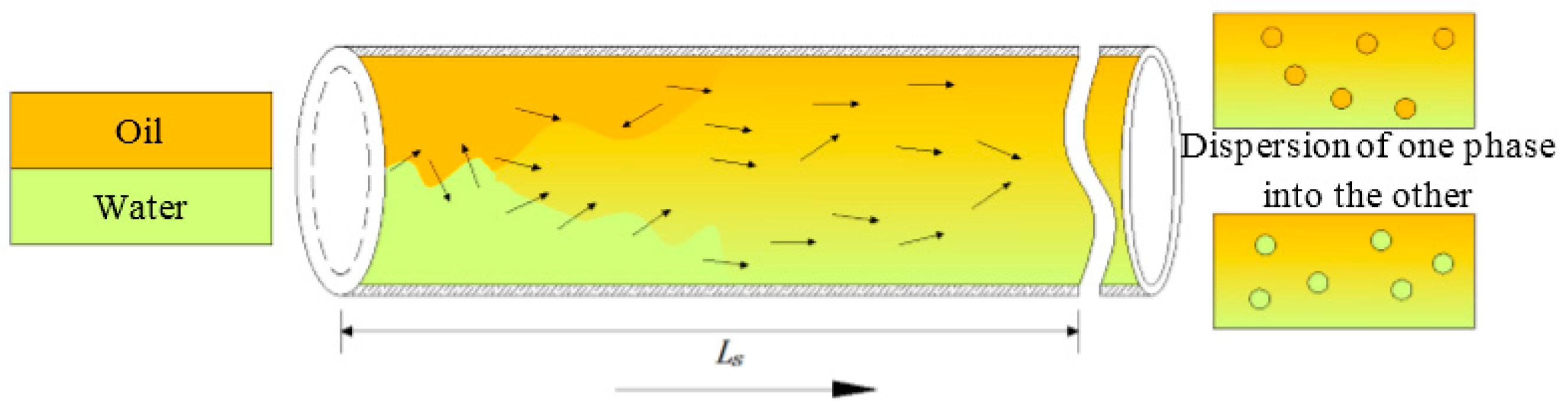
2.3. Characteristic Data of Flow Field
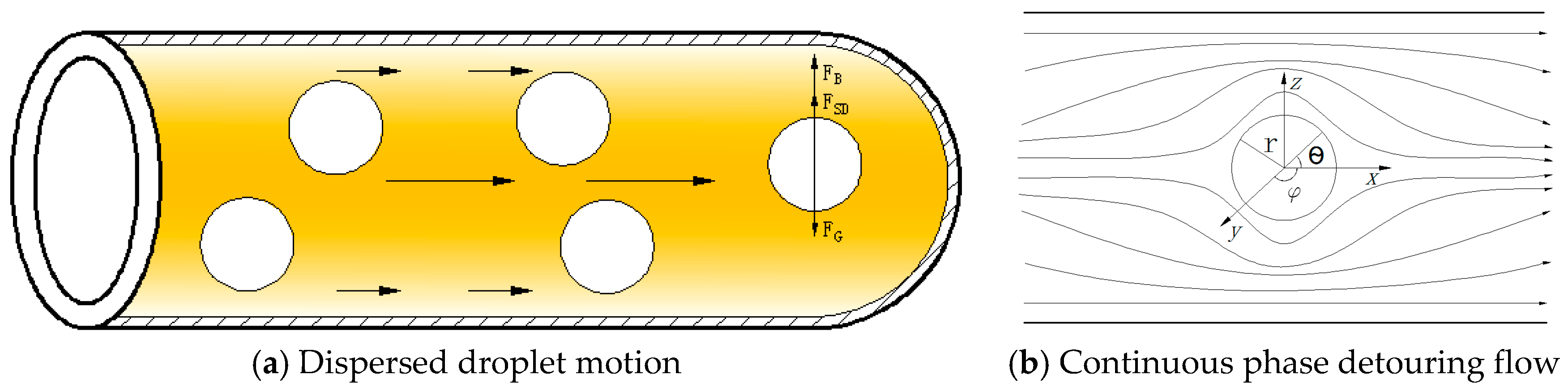
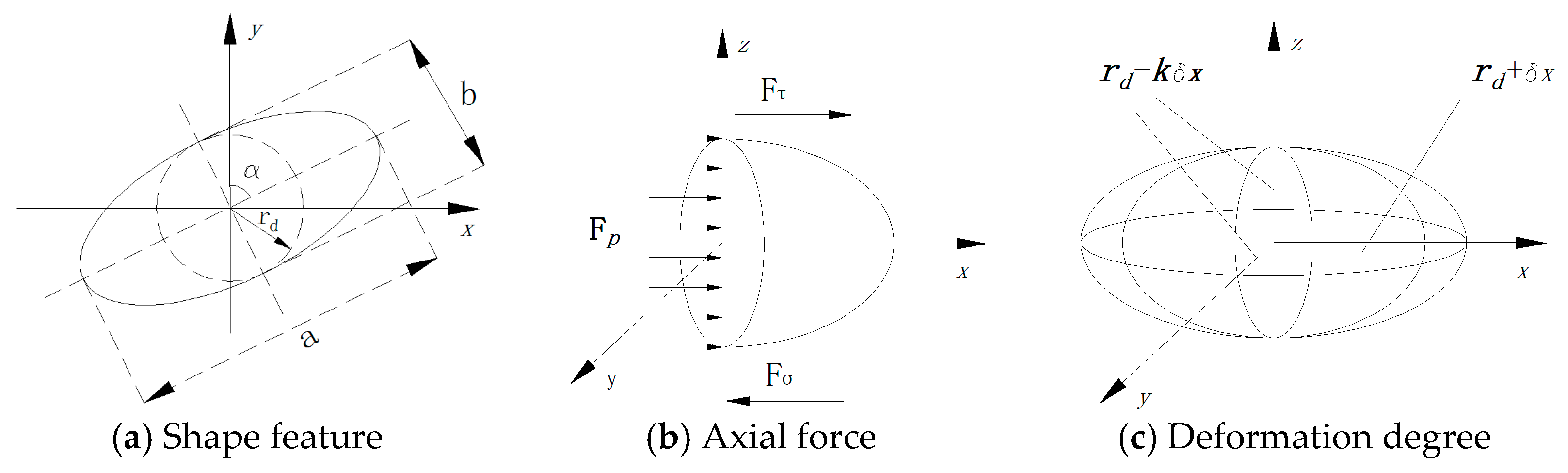
3. Mechanistic Model
4. Energy Model
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Properties of the Waxy Crude Oil
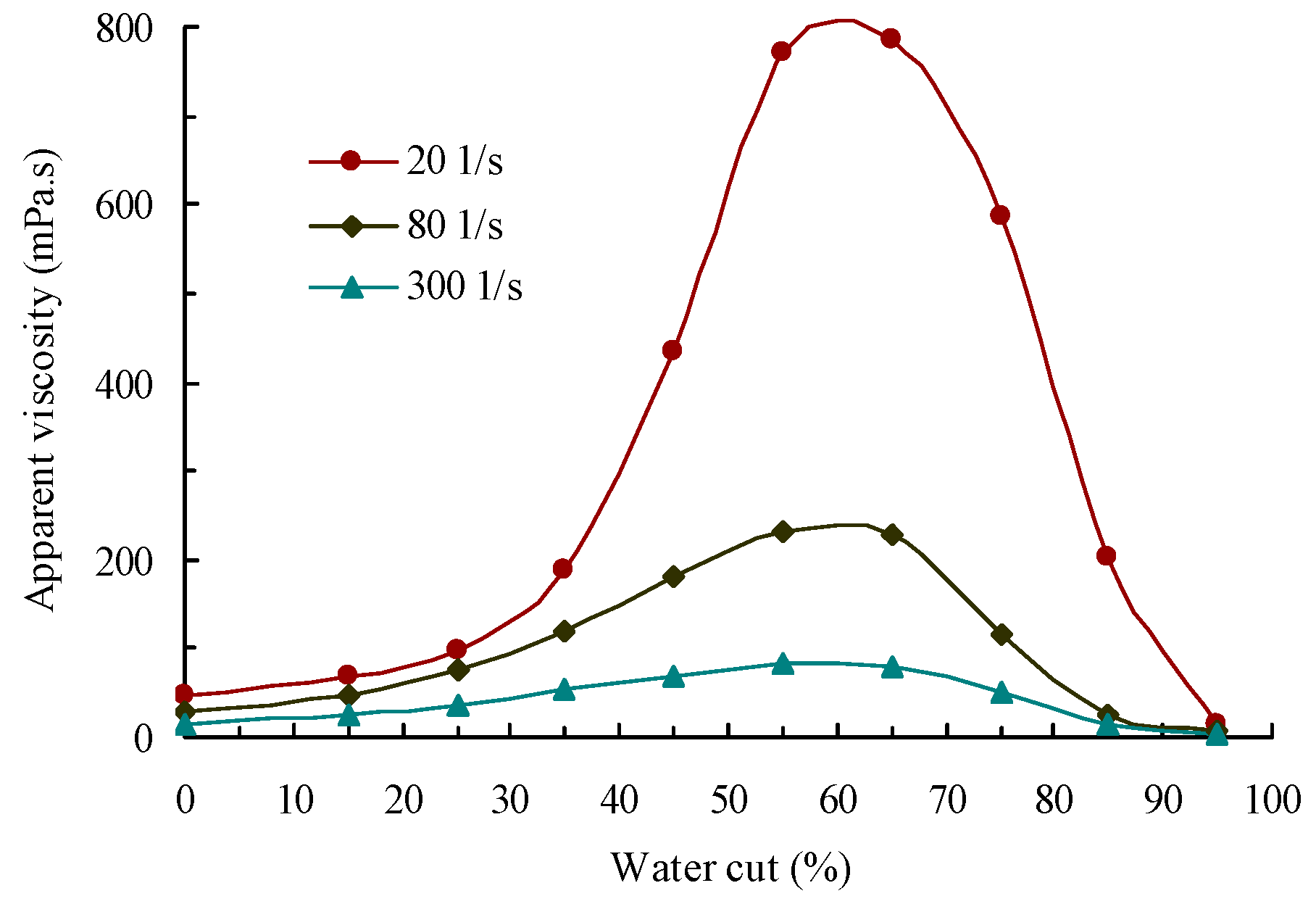
5.2. Phase Inversion and Emulsification Behavior of the Waxy Crude Oil Emulsions
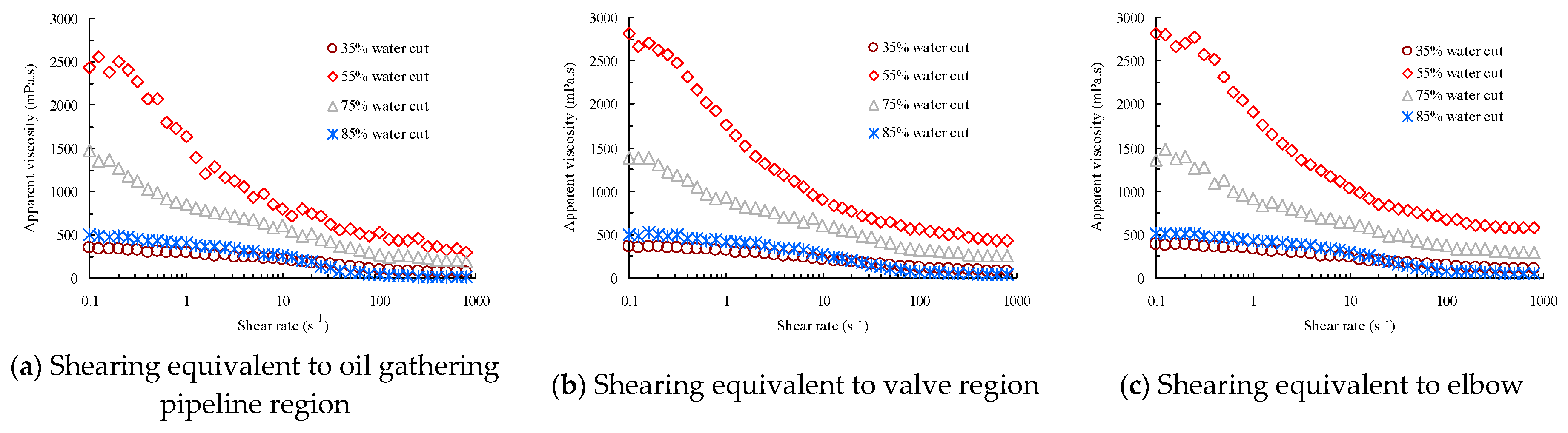
5.3. Interfacial and Rheological Properties of the Waxy Crude Oil Emulsions
5.4. Droplet Size and Droplet-Size Distribution of the Waxy Crude Oil Emulsions
5.5. Shearing Energy and Interfacial GIBBS Free Energy Change in the Actual Flow Field
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schubert, H.; Armbroster, H. Principles of formation and stability of emulsions. Chem. Ing. Tech. 1989, 61, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visintin, R.F.G.; Lockhart, T.P.; Lapasin, R.; D’Antona, P. Structure of waxy crude oil emulsion gels. J. Non Newton. Fluid Mech. 2008, 149, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Fogler, H.S. Fundamental investigation of wax diffusion characteristics in water-in-oil emulsion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4420–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, Q.; He, M.; Wang, W. Effect of water fraction on rheological properties of waxy crude oil emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2014, 35, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Z.; Metz, P.A.; Reynolds, D.B.; Chen, G.; Zhou, X. Regression models estimate pipeline construction costs. Oil Gas J. 2011, 109, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, F.; Zhu, Y.; Han, S. Full and partial emulsification of crude-systems as a function of shear intensity, water fraction, and temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9513–9520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, K.; Saito, H. The effect of temperature on the phase equilibria and the types of dispersions of the ternary system composed of water, cyclohexane, and nonionic surfactant. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, D.E.; Sharma, M.M. Factors controlling the stability of colloid-stabilized emulsions I. An experimental investigation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 157, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.A. A free energy model for curved surfaces and curved thin films in emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2002, 23, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kersten, S.R.A.; Schuur, B. Efficiency and mechanism of demulsification of oil-in-water emulsions using ionic liquids. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 7622–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli, M.; Chen, A.; Sung, C.; Kidder, K.M.; Lee, J.J.; Alhassan, S.M.; Vargas, F.M. Effect of emulsified water on asphaltene instability in crude oils. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 3676–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Fletcher, P.D.I.; Petsev, D.N.; Cho, W.G. Stability of oil-in-water emulsions in a low interfacial tension system. Langmuir 2000, 16, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angle, C.W.; Hamza, H.A.; Dabros, T. Size distributions and stability of toluene diluted heavy oil emulsions. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2006, 52, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Shear viscosity behavior of emulsions of two immiscible liquids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 225, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, P.D.; Hsu, C.; Arendell, J.P. Designing and selecting demulsifiers for optimum field performance on the basis of production fluid characteristics. SPE Prod. Eng. 1988, 3, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuhiro, K.; Paschalis, A. Effect of surfactant phase behavior on emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 466, 138–149. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Niu, Q.; Lan, Q.; Sun, D. Effect of dispersion pH on the formation and stability of Pickering emulsions stabilized by layered double hydroxides particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 306, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhuge, X.; Zhang, L. Study on two-phase oil-water gelling deposition behavior in low-temperature transportation. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 4570–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wei, M. Effective viscosity prediction of crude oil-water mixtures with high water fraction. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 147, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, V.; Wang, X.; Moradi, M. Stability proxies for water-in-oil emulsions and implications in aqueous-based enhanced oil recovery. Energies 2011, 4, 1058–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Su, Y.; Moghanloo, R.G.; Rui, Z.; Wang, W.; Shang, Y. A new analytical multi-linear solution for gas flow toward fractured horizontal well with different fracture intensity. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 23, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yin, X.; Winterfeld, P.H.; Wu, Y.S. A fully coupled thermal-hydrological-mechanical-chemical model for CO2 geological sequestration. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 28, 280–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yin, X.; Wu, Y.S.; Winterfeld, P.H. A fully coupled model of nonisothermal multiphase flow, solute transport and reactive chemistry in porous media. Proccedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, SPE 159380, San Antonio, TX, USA, 8–10 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.; Sadeghi, N.; Houston, C. Emulsion characteristics and novel demulsifiers for treating chemical EOR induced emulsions. Proccedings of the SPE Enhanced Oil Recovery Conference, SPE 143987, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–21 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.; Sadeghi, N. Stable emulsion and demulsification in chemical EOR flooding: Challenges and best practices. Proccedings of the SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, SPE 154044, Muscat, Oman, 16–18 April, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Correlations between emulsification behaviors of crude oil-water systems and crude oil compositions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Test Method for Plastics: Dynamic Mechanical Properties melt Rheology; ASTM D4440-2015; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Plastics: Determination of Dynamic Mechanical Properties Part 10: Complex Shear Viscosity Using a Parallel-Plate Oscillatory Rheometer; ISO 6721-10-1999; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- Taylor, G.I. The formation of emulsions in definable fields of flow. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1934, 146, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.G. The deformation of a drop in a general time-dependent fluid flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1969, 37, 601–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthès-Biesela, D.; Acrivosa, A. Deformation and burst of a liquid droplet freely suspended in a linear shear field. J. Fluid Mech. 1973, 61, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, B.J.; Leal, L.G. An experimental investigation of drop deformation and breakup in steady, two-dimensional linear flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 167, 241–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, L.; Macosko, C.W.; Pearson, S.D. Influence of normal stress difference on polymer drop deformation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokal, S. Crude-oil emulsions: A state-of-the-art review. SPE Prod. Facil. 2005, 20, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Le, X.; Feng, Y.; Hu, Z. Dehydration of aging oil by an electrochemical method. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2014, 50, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A. A review of technologies for transporting heavy crude oil and bitumen via pipelines. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2014, 4, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, R.; Fakhru’l-Razi, A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Elnashaie, S.S.E.H.; Pendashteh, A. Demulsification techniques of water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsions in petroleum industry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 377–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodenko, A.L.; Douglas, J.F. Generalized Stokes-Einstein equation for spherical particle suspensions. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 51, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. The viscosity of a fluid containing small drops of another fluid. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1932, 138, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausse, D.; Pezron, I.; Gauthier, A. Water transfer in mixed water-in-oil emulsions studied by differential scanning calorimetry. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1995, 110, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, V.; Giacchetta, G.; Leporini, M.; Marchetti, B.; Terenzi, A. Modelling blowdown of pressure vessels containing two-phase hydrocarbons mixtures with the partial phase equilibrium approach. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 126, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckenstein, E.; Ebert, G.; Platz, G. Phase behavior and stability of concentrated emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 133, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, L.; Das, K.P.; Chattoraj, D.K. Thermodynamics of adsorption of inorganic electrolytes at air/water and oil/water interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 121, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.T. Shear effects on thermoplastic foam nucleation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1993, 33, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opawale, A.; Osisanya, S.; Dulu, A.; Otakoro, S. An integrated approach to selecting and optimizing demulsifier chemical injection points using shearing energy analysis: A justification for downhole injection in high pressured well. Proccedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, OTC 21151, Houston, TX, USA, 2–5 May, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ersoy, G.; Sarica, C. Modeling of inversion point for heavy oil-water emulsion systems. SPE Proj. Facil. Constr. 2009, 4, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
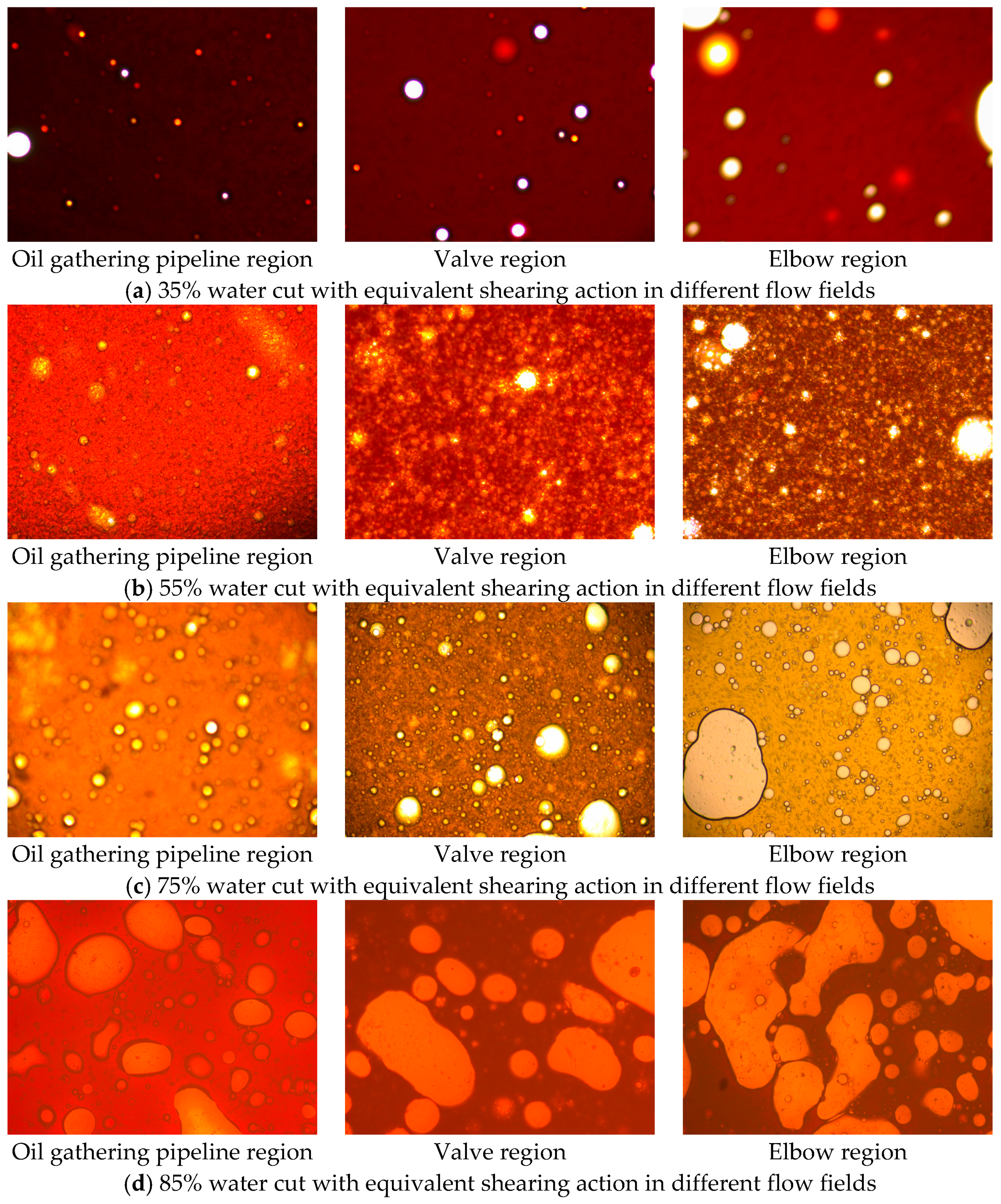
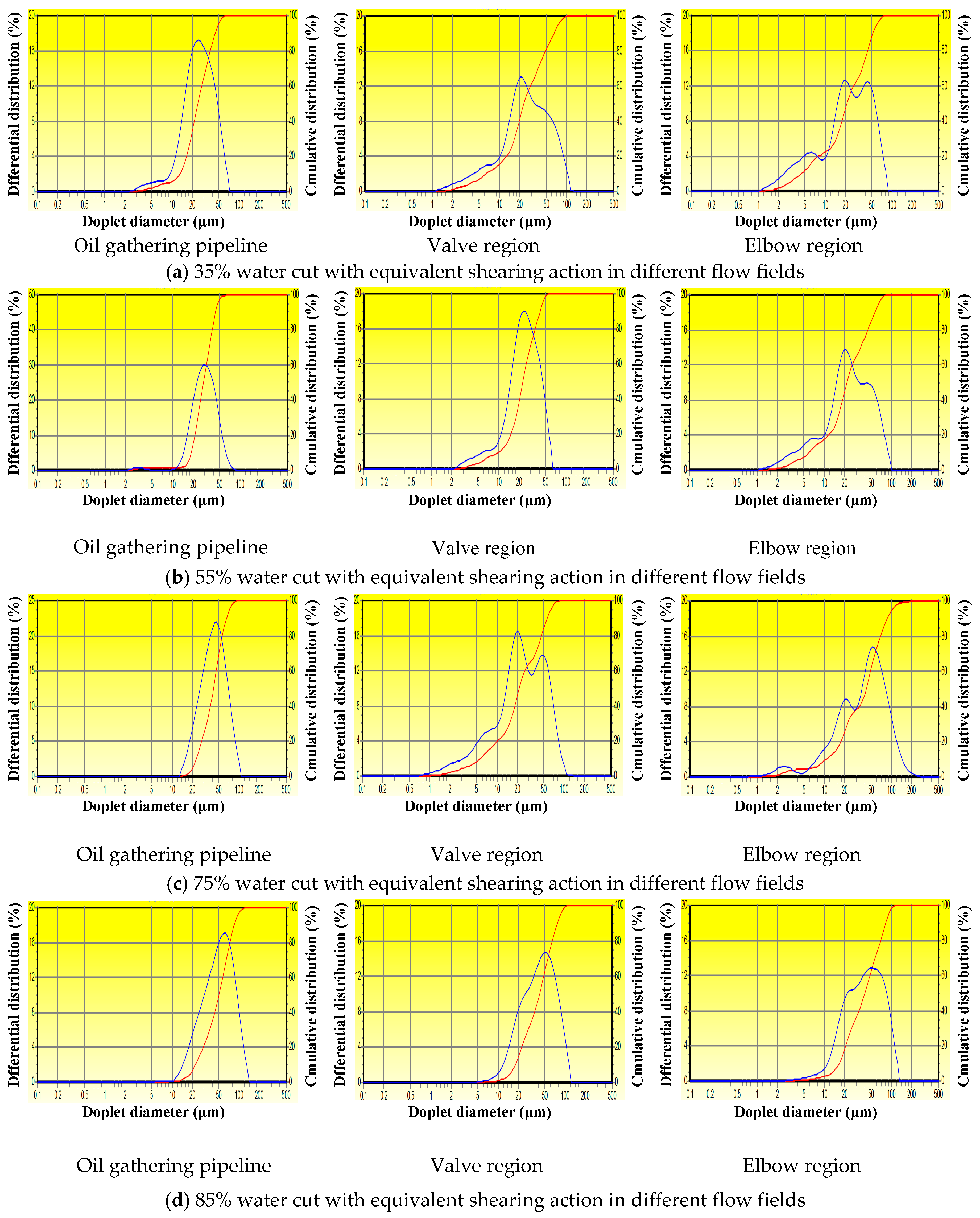
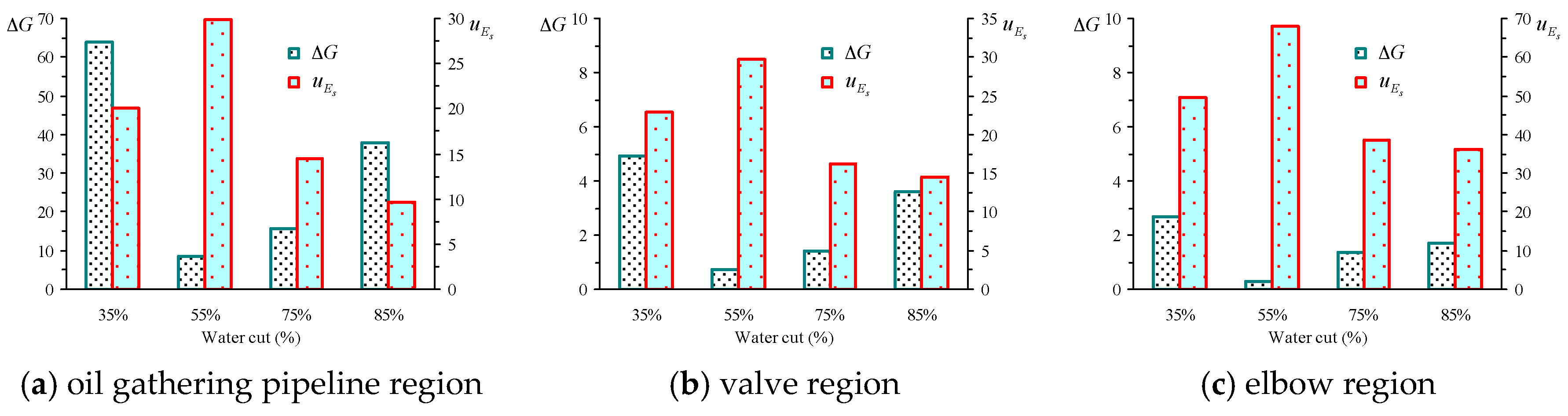
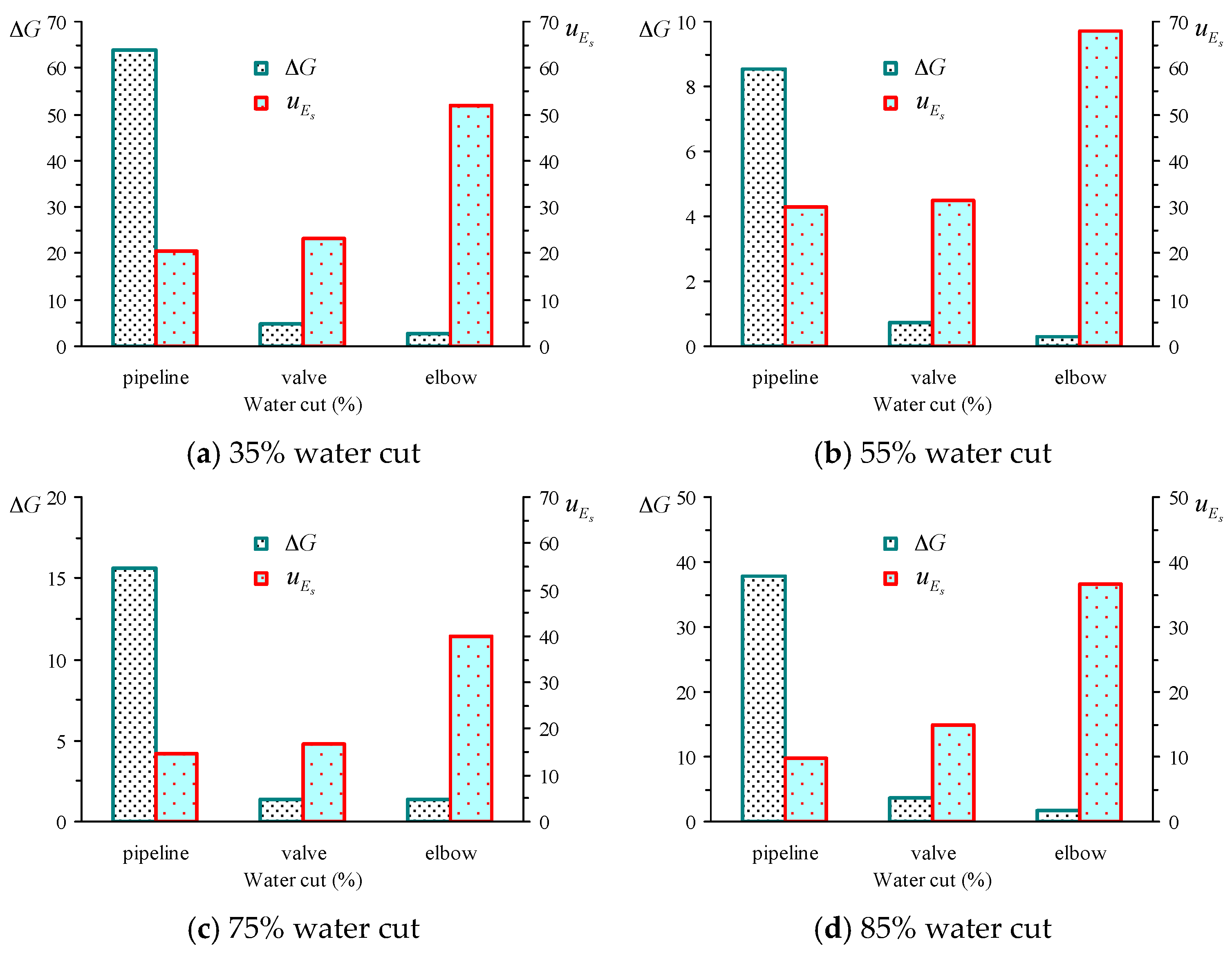
| Water Cut | Oil Gathering Pipeline Region | Valves Region | Elbow Region | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μm) | (rad) | (μm) | (rad) | (μm) | (rad) | |
| 35 | 1.442 | 0.2505 | 3.874 | 0.342 | 6.430 | 0.368 |
| 55 | 1.268 | 0.2536 | 3.512 | 0.406 | 5.346 | 0.459 |
| 75 | 2.287 | 0.2530 | 5.903 | 0.392 | 8.712 | 0.441 |
| 85 | 2.439 | 0.2508 | 6.510 | 0.345 | 10.488 | 0.394 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Rui, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhan, S. The Role of Shearing Energy and Interfacial Gibbs Free Energy in the Emulsification Mechanism of Waxy Crude Oil. Energies 2017, 10, 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10050721
Wang Z, Lin X, Rui Z, Xu M, Zhan S. The Role of Shearing Energy and Interfacial Gibbs Free Energy in the Emulsification Mechanism of Waxy Crude Oil. Energies. 2017; 10(5):721. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10050721
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhihua, Xinyu Lin, Zhenhua Rui, Mengmeng Xu, and Shuyi Zhan. 2017. "The Role of Shearing Energy and Interfacial Gibbs Free Energy in the Emulsification Mechanism of Waxy Crude Oil" Energies 10, no. 5: 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10050721
APA StyleWang, Z., Lin, X., Rui, Z., Xu, M., & Zhan, S. (2017). The Role of Shearing Energy and Interfacial Gibbs Free Energy in the Emulsification Mechanism of Waxy Crude Oil. Energies, 10(5), 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10050721







