A Heuristic Diagnostic Method for a PV System: Triple-Layered Particle Swarm Optimization–Back-Propagation Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- We analyze the performance of PVs under various fault conditions, using open-circuit voltage (Voc), short-circuit current (Isc), maximum power (Pm) and voltage at maximum power point (Vm) to construct feature recognition criteria. The criteria reduce the running space and shorten the program execution time of the heuristic diagnostic method.
- (2)
- We evaluate the performance of a heuristic particle swarm optimization–back-propagation (PSO-BP) neural network method applied in PV fault diagnosis. The method has the merits of global search ability for particle swarm optimization (PSO) and local search ability for BP. The PSO-BP neural network ameliorates the convergence of the diagnostic method and improves the prediction accuracy of the photovoltaic diagnosis system effectively.
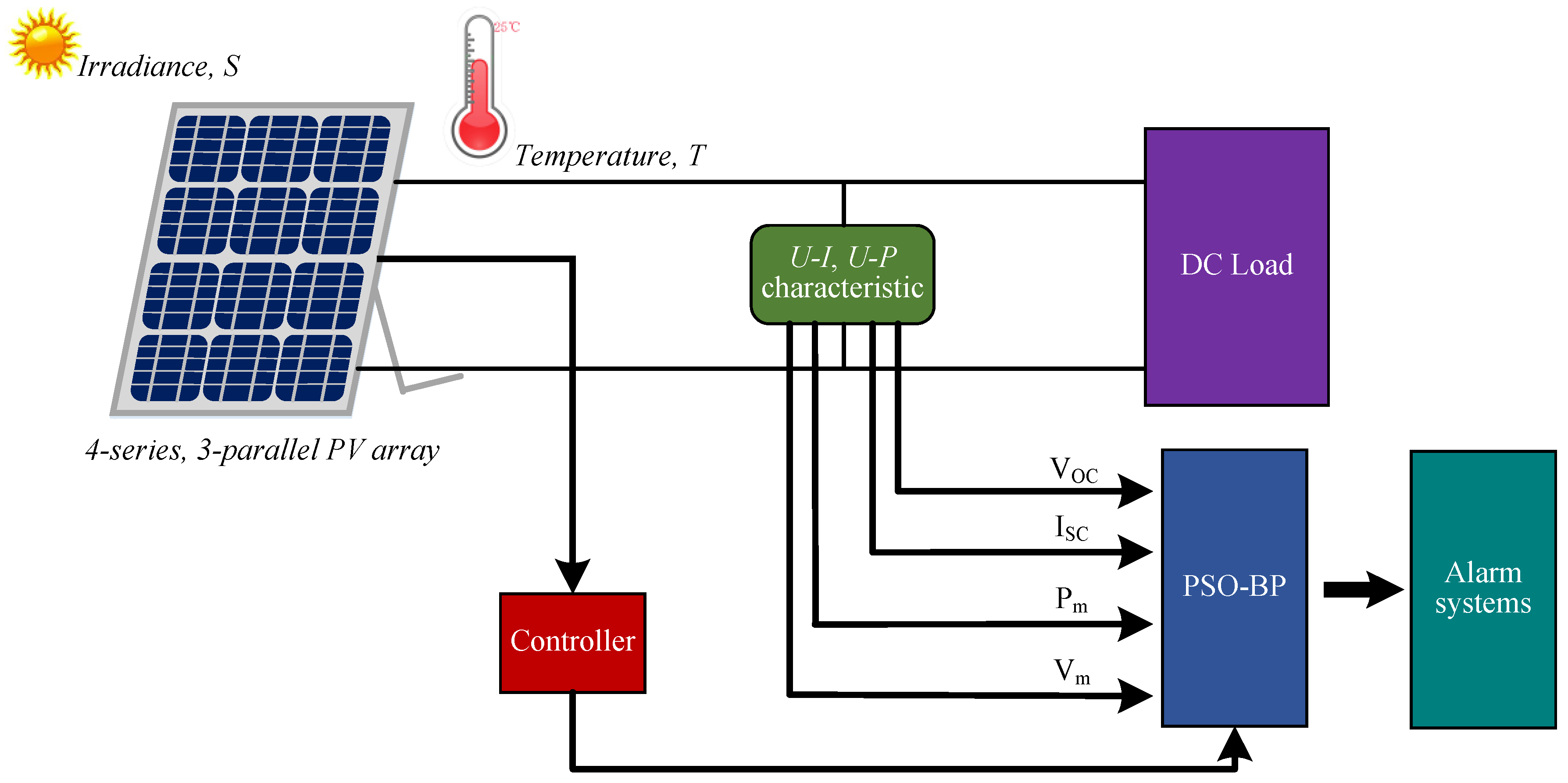
2. Configuration of Proposed System
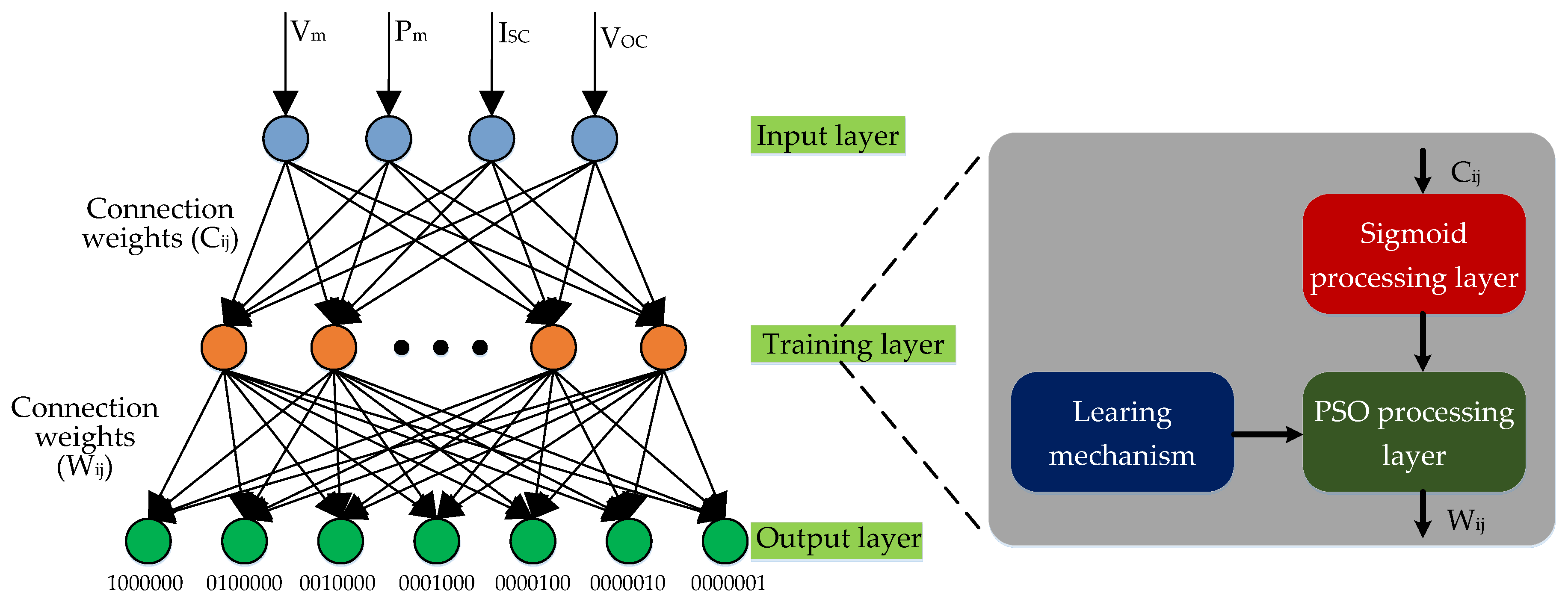
3. Proposed Fault Diagnosis Method
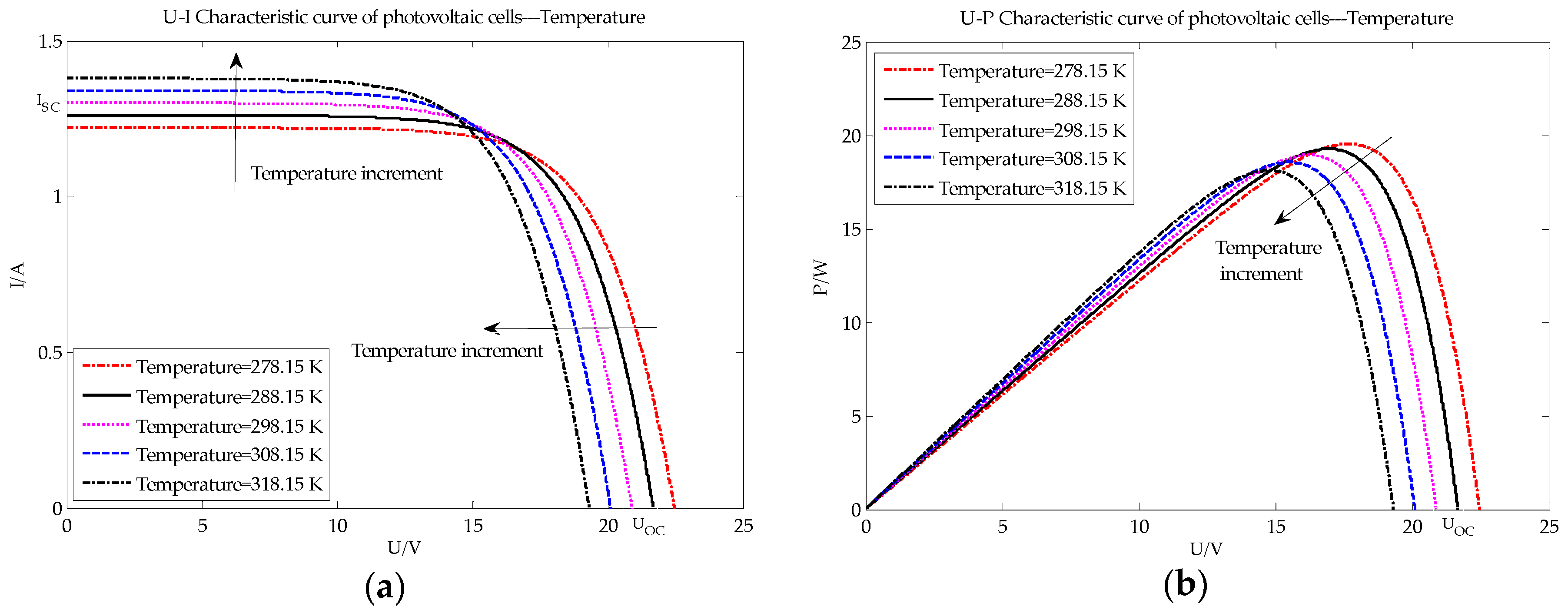
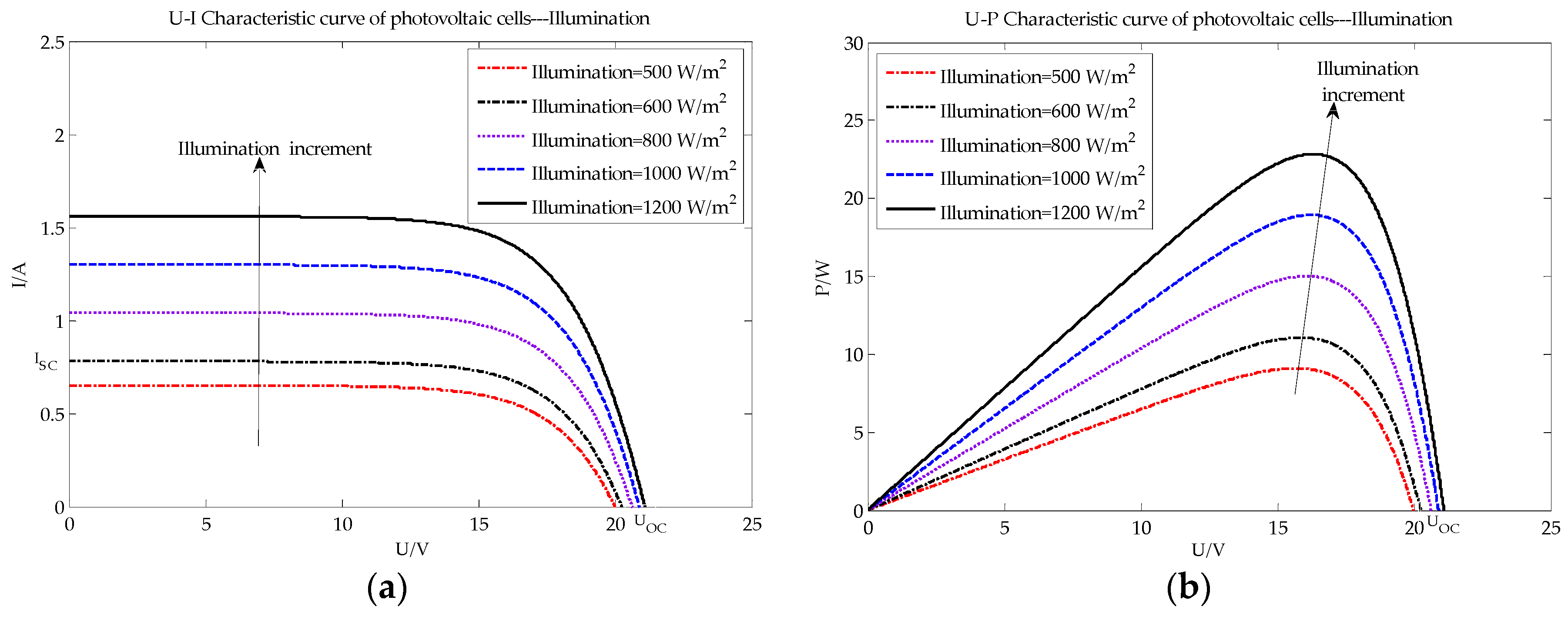
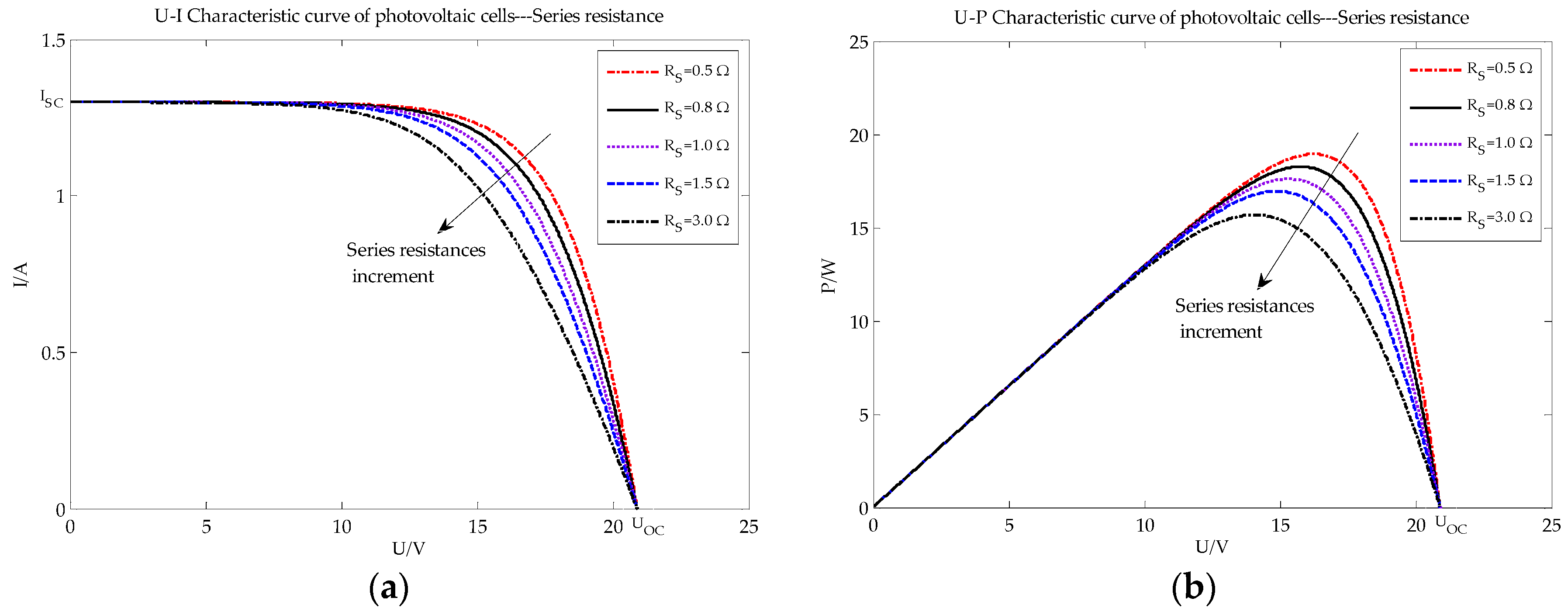
4. Data Collection
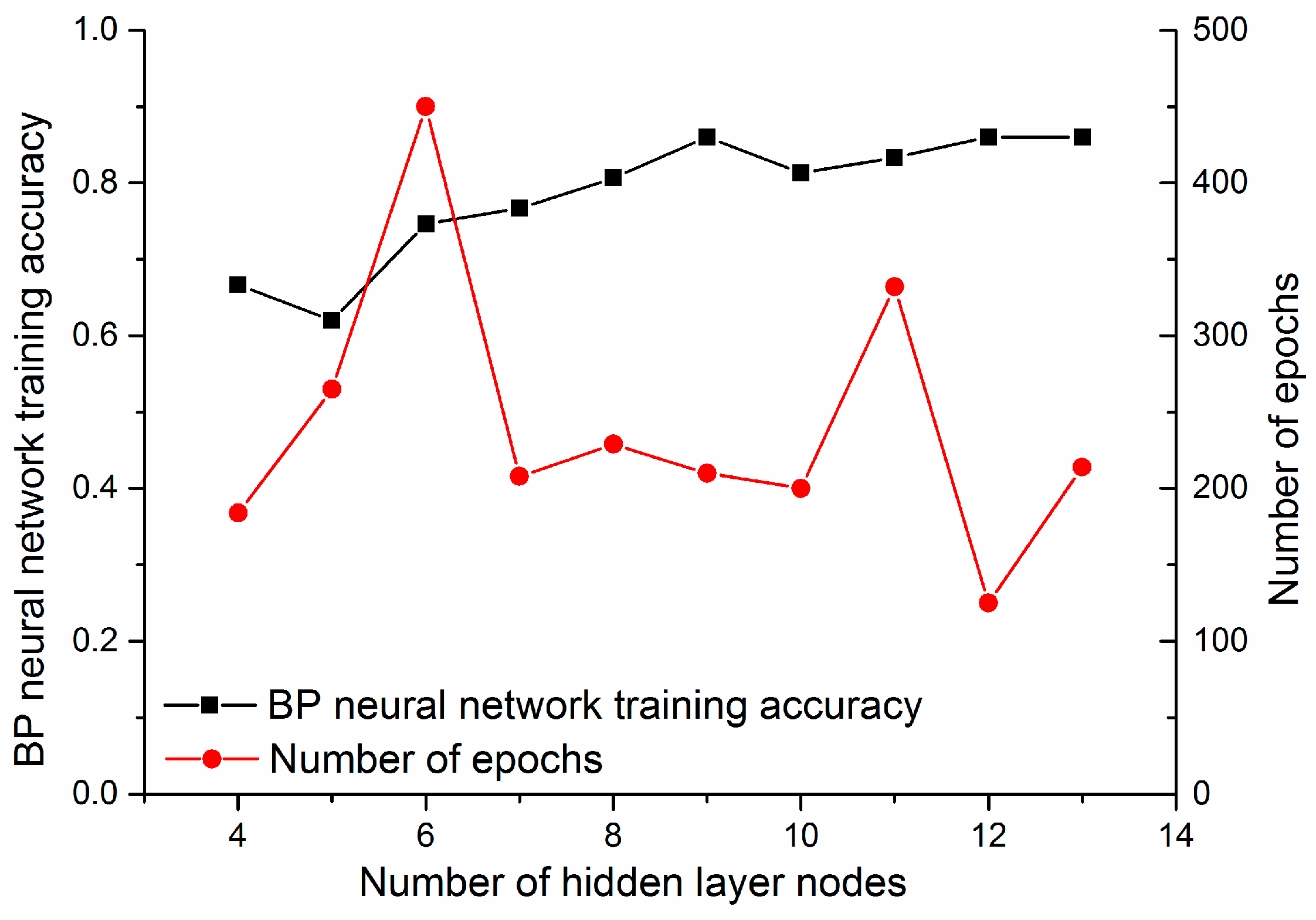
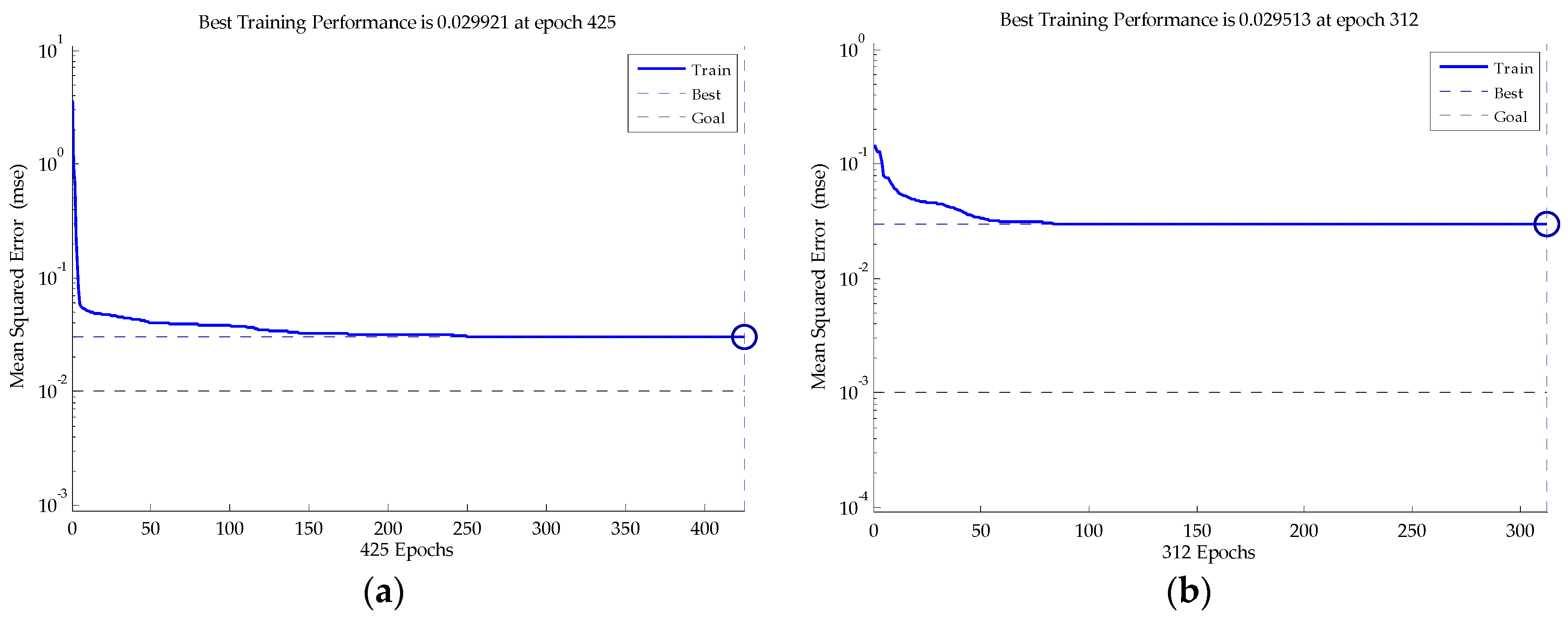
5. Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masson, G.; IEA PVPS Task 1. 2015 Snapshot of Global Photovoltaic Markets; IEA Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme: St. Ursen, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Ravindra, N.M. Temperature dependence of solar cell performance—An analysis. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 101, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.B.; Cao, Y.; Hao, Y.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Cao, F. Characteristic output of PV systems under partial shading or mismatch conditions. Sol. Energy 2015, 112, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushika, N.D.; Rai, A.K. An investigation of mismatch losses in solar photovoltaic cell networks. Energy 2007, 32, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; Otani, K.; Kato, K.; Ishida, M. Experimental studies of failure detection methods in PV module strings. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 7–12 May 2006; pp. 2227–2230.
- Takashima, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; Ishida, M. Disconnection detection using earth capacitance measurement in photovoltaic module string. Prog. Photovolt. 2008, 16, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, K.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Wang, M.H.; Chen, C.T. An intelligent fault detection method of a photovoltaic module array using wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.T.; Shiu, J. Study of intelligent photovoltaic system fault diagnostic scheme based on chaotic signal synchronization. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 816296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Li, Z.H.; Wu, C.H.; Zhou, D.Q.; Fu, L. A survey of fault diagnosis for PV array based on BP neural network. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2013, 41, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.C.; Lan, Q.L.; Sun, Y.Q. Application of BP neural network fault diagnosis in solar photovoltaic system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Changchun, China, 9–12 August 2009; pp. 2581–2585.
- Mellit, A.; Kalogirou, S.A. Artificial intelligence techniques for photovoltaic applications: A review. Prog. Energy Combust. 2008, 34, 574–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas’ud, A.A.; Albarracín, R.; Ardila-Rey, J.A.; Muhammad-Sukki, F.; Illias, H.A.; Bani, N.A.; Munir, A.B. Artificial Neural Network Application for Partial Discharge Recognition: Survey and Future Directions. Energies 2016, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning internal representations by error propagation. In Parallel Distributed Processing: Exploration in the Microstructure of Cognition, 1st ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 318–362. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Singh, S.N.; Lal, M.; Husain, M. Temperature dependence of I–V characteristics and performance parameters of silicon solar cell. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.; Dyk, E.E.V. Assessing the reliability and degradation of photovoltaic module performance parameters. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2004, 53, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Lok, T.M.; Lyu, M.R. A hybrid particle swarm optimization–back-propagation algorithm for feedforward neural network training. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 185, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadse, C.B.; Chaudhari, M.A.; Borghate, V.B. Conjugate gradient back-propagation based artificial neural network for real time power quality assessment. Int. J. Electr. Power 2016, 82, 197–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, B.; Schnitger, G. The power of approximating: A comparison of activation functions. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Giles, C.L., Hanson, S.J., Cowan, J.D., Eds.; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: Burlington, VT, USA, 1993; pp. 615–622. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.; Jeng, D.-S.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, J.-S. Predictions of bridge scour: Application of a feed-forward neural network with an adaptive activation function. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Y.; Xu, C.F. Optimization analysis of dynamic sample number and hidden layer node number based on BP neural network. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications, Hefei, China, 12–14 July 2013.
- Li, J.Y.; Shi, J.F.; Li, J.C. Exploring Reduction Potential of Carbon Intensity Based on Back Propagation Neural Network and Scenario Analysis: A Case of Beijing, China. Energies 2016, 9, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.H.; Abedini, M. A combination of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for optimal DG location and sizing in distribution systems. Int. J. Electr. Power 2012, 34, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Gandomi, A.H.; Yang, X.S.; Alavi, A.H. A novel improved accelerated particle swarm optimization algorithm for global numerical optimization. Eng. Comput. 2014, 31, 1198–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, A.; Rangnekar, S. A review of particle swarm optimization and its applications in Solar Photovoltaic system. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnaweera, A.; Halgamuge, S.K.; Watson, H.C. Self-organizing hierarchical particle swarm optimizer with time-varying acceleration coefficients. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 2004, 8, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Electrical Parameters | Value (Unit) |
|---|---|
| Maximum power | 21 (W) |
| Open-circuit voltage | 21.7 (V) |
| Short-circuit current | 1.3 (A) |
| Voltage at maximum power point | 17.6 (V) |
| Current at maximum power point | 1.17 (A) |
| Fault States | States Code | 0–1 Code |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1 | 1000000 |
| Temperature fault | 2 | 0100000 |
| Partial fading fault | 3 | 0010000 |
| Cells aging | 4 | 0001000 |
| Combination of temperature and partial shade faults | 5 | 0000100 |
| Combination of temperature fault and cells aging | 6 | 0000010 |
| Combination of partial shade fault and cells aging | 7 | 0000001 |
| Parameters (Symbol) | Value | Parameters (Symbol) | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population (M) | 40 | Cognitive factor () | 2 |
| Maximum iteration () | 200 | Social factor () | 3 |
| Maximum inertia weight () | 1.8 | Maximum particle velocity () | 0.05 |
| Minimum inertia weight () | 1.7 |
| Sample | Content | Actual Fault Code | Predict Result | Right or Wrong 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voc (V) | Isc (A) | Pm (W) | Vm (V) | BP | PSO-BP | BP | PSO-BP | ||
| 1 | 20.9756 | 1.2943 | 18.9784 | 16.3230 | 1000000 | 0000100 | 1000000 | × | √ |
| 2 | 21.0542 | 1.2903 | 19.0131 | 16.3905 | 1000000 | 1000000 | 1000000 | √ | √ |
| 3 | 16.4707 | 1.5209 | 16.1174 | 12.2254 | 0100000 | 0100000 | 0100000 | √ | √ |
| 4 | 18.8417 | 0.3103 | 4.0822 | 14.7464 | 0010000 | 0010000 | 0010000 | √ | √ |
| 5 | 20.8974 | 1.2976 | 14.3561 | 13.2862 | 0001000 | 0001000 | 0001000 | √ | √ |
| 6 | 20.2456 | 0.7783 | 11.0650 | 15.8445 | 0000100 | 0010000 | 0010000 | × | × |
| 7 | 21.0960 | 1.0863 | 16.1384 | 16.5977 | 0000100 | 0010000 | 0000100 | × | √ |
| 8 | 21.1328 | 1.2863 | 18.9137 | 16.3732 | 0000010 | 0000010 | 0000010 | √ | √ |
| 9 | 21.2950 | 1.9482 | 28.3066 | 16.2328 | 0000001 | 0010000 | 0000001 | × | √ |
| 10 | 20.8974 | 1.2981 | 17.3409 | 15.1531 | 0000001 | 0001000 | 0001000 | × | × |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Z.; Wang, D.; Tang, L.; Ren, J.; Liu, Z. A Heuristic Diagnostic Method for a PV System: Triple-Layered Particle Swarm Optimization–Back-Propagation Neural Network. Energies 2017, 10, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020226
Liao Z, Wang D, Tang L, Ren J, Liu Z. A Heuristic Diagnostic Method for a PV System: Triple-Layered Particle Swarm Optimization–Back-Propagation Neural Network. Energies. 2017; 10(2):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020226
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Zhenghai, Dazheng Wang, Liangliang Tang, Jinli Ren, and Zhuming Liu. 2017. "A Heuristic Diagnostic Method for a PV System: Triple-Layered Particle Swarm Optimization–Back-Propagation Neural Network" Energies 10, no. 2: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020226
APA StyleLiao, Z., Wang, D., Tang, L., Ren, J., & Liu, Z. (2017). A Heuristic Diagnostic Method for a PV System: Triple-Layered Particle Swarm Optimization–Back-Propagation Neural Network. Energies, 10(2), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020226





