Chip Temperature-Based Workload Allocation for Holistic Power Minimization in Air-Cooled Data Center
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Strategy for Minimizing Holistic Power Consumption of Data Centers
3.1. Server Power Model
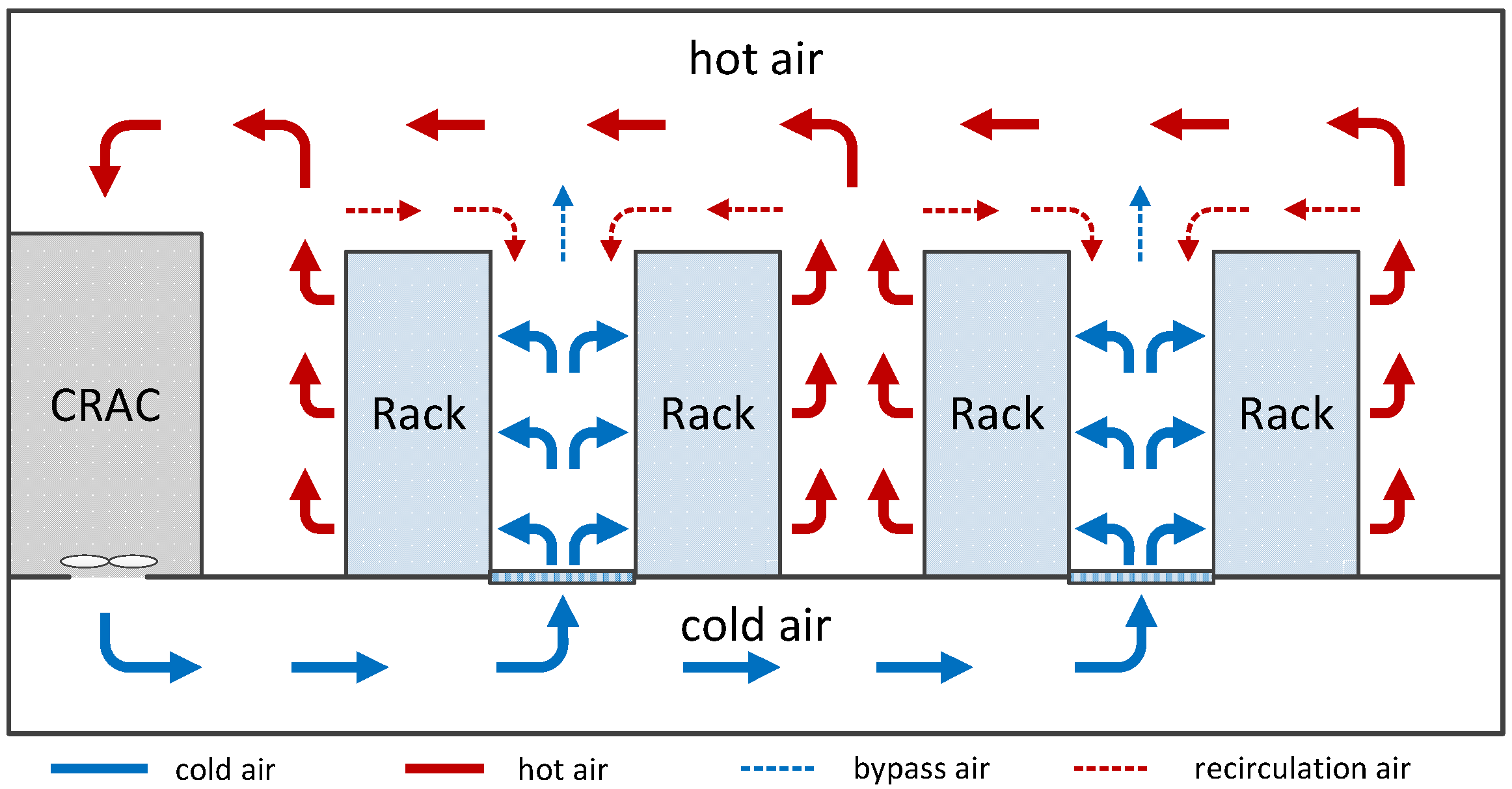
3.2. Abstract Heat-Flow Model
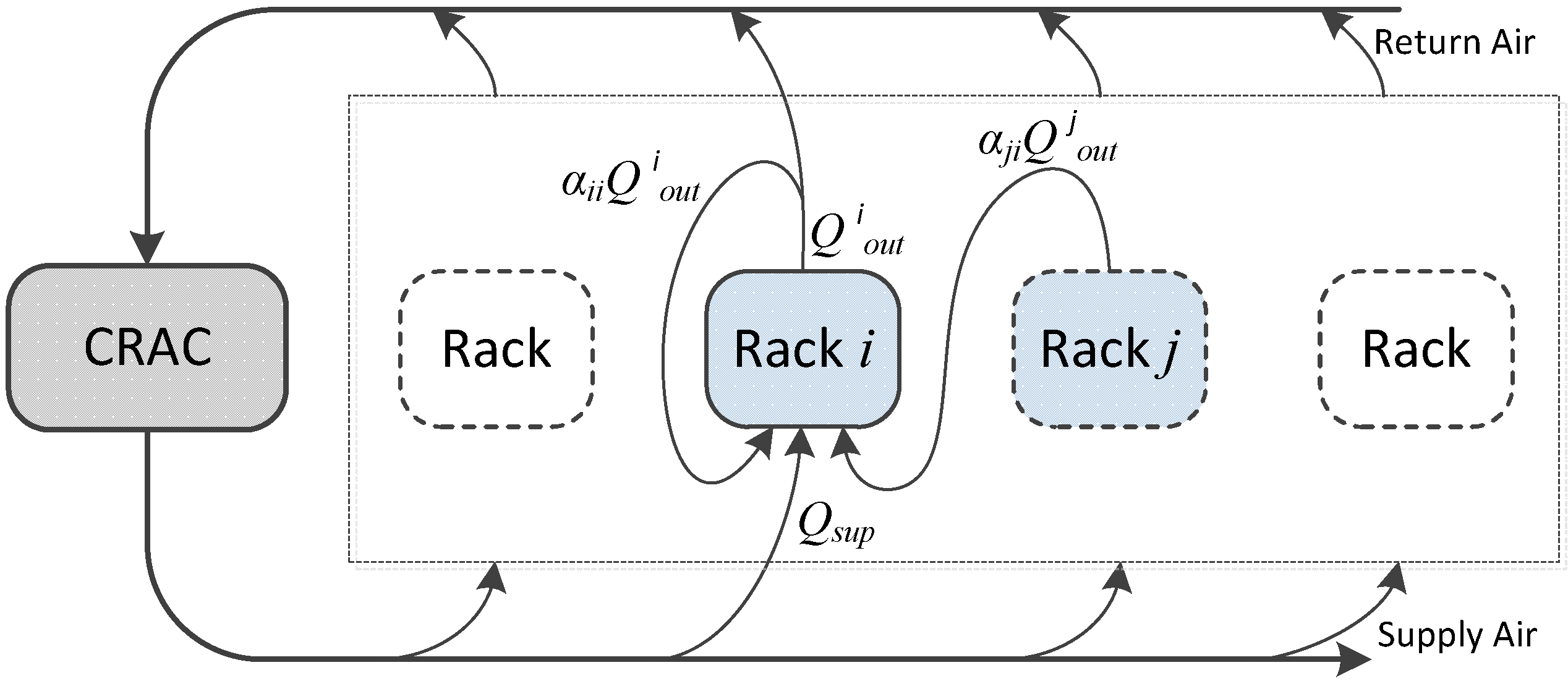
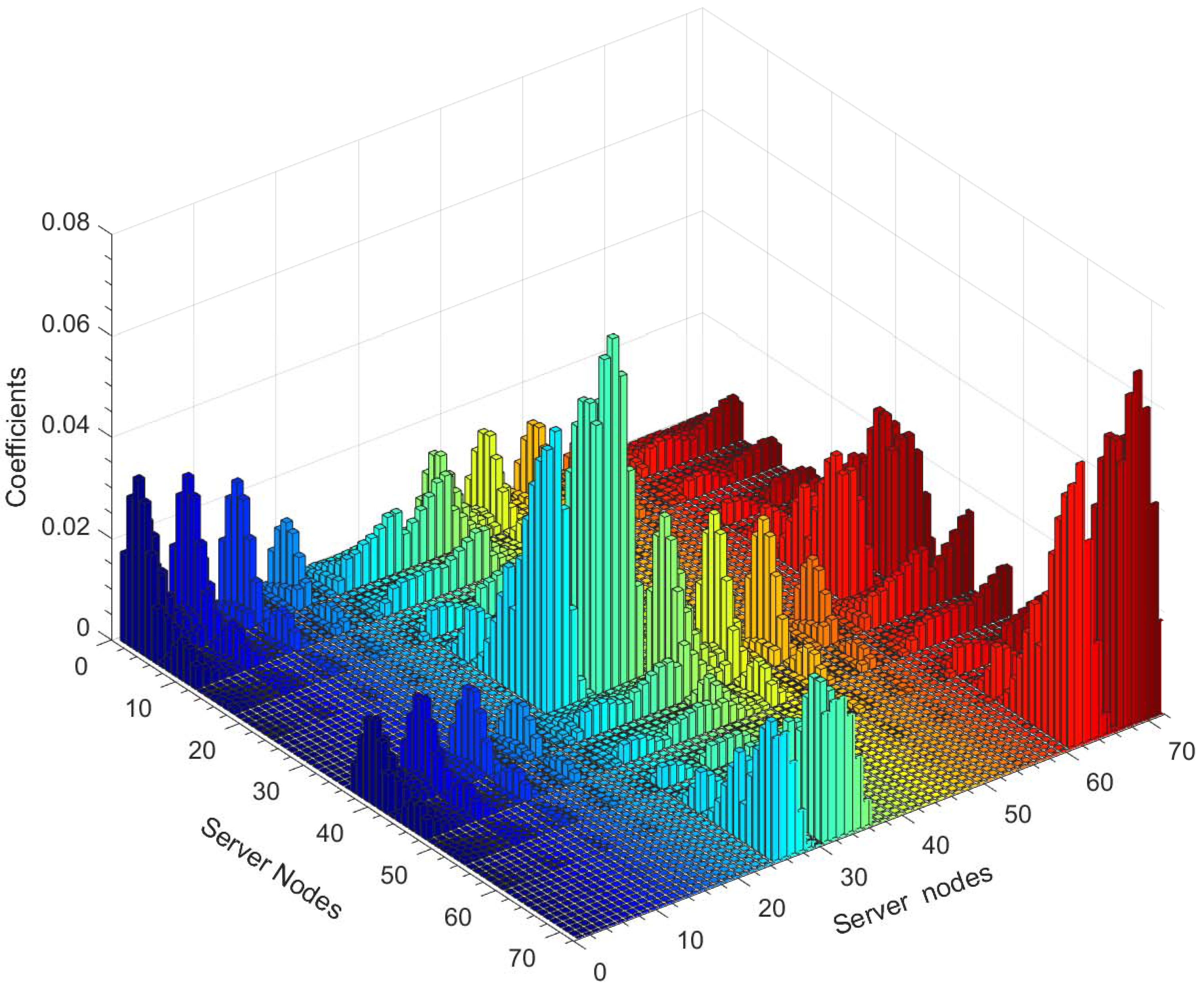
3.3. Equipment Thermal Resistance Model
3.4. Total Power Consumption of Data Center
3.5. Problem Statement and GA Optimization
| Algorithm 1: Minimizing the total power consumption using a genetic algorithm approach. |
 |
4. Case Study
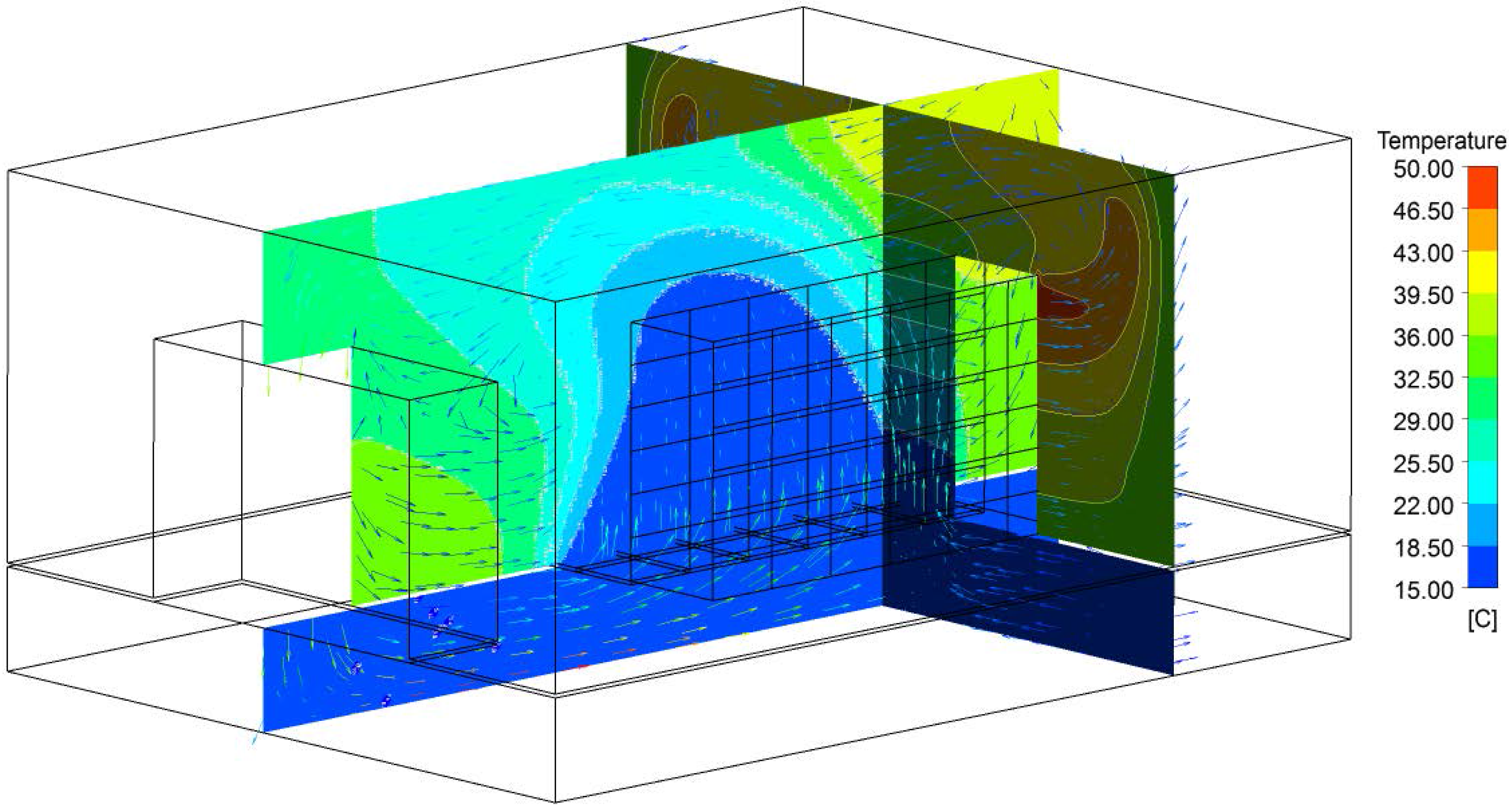
4.1. Simulation and Parameter Setup
- Modified Uniform Task (MUT): MUT assigns an equal amount of workload to each node. The goal of the MUT algorithm in this paper was to maximize the supply temperature while keeping the peak chip temperature below the threshold ().
- Minimizing the Peak Inlet Temperature through Task Assignment (MPIT-TA): This is a proactive scheduling algorithm that maximizes the supply temperature of teh cooling system through optimizing the workload allocation among servers with respect to the inlet temperature constraint, consequently achieving cooling energy saving. The threshold of the inlet temperature was set to according to the guidelines of ASHRAE [2].
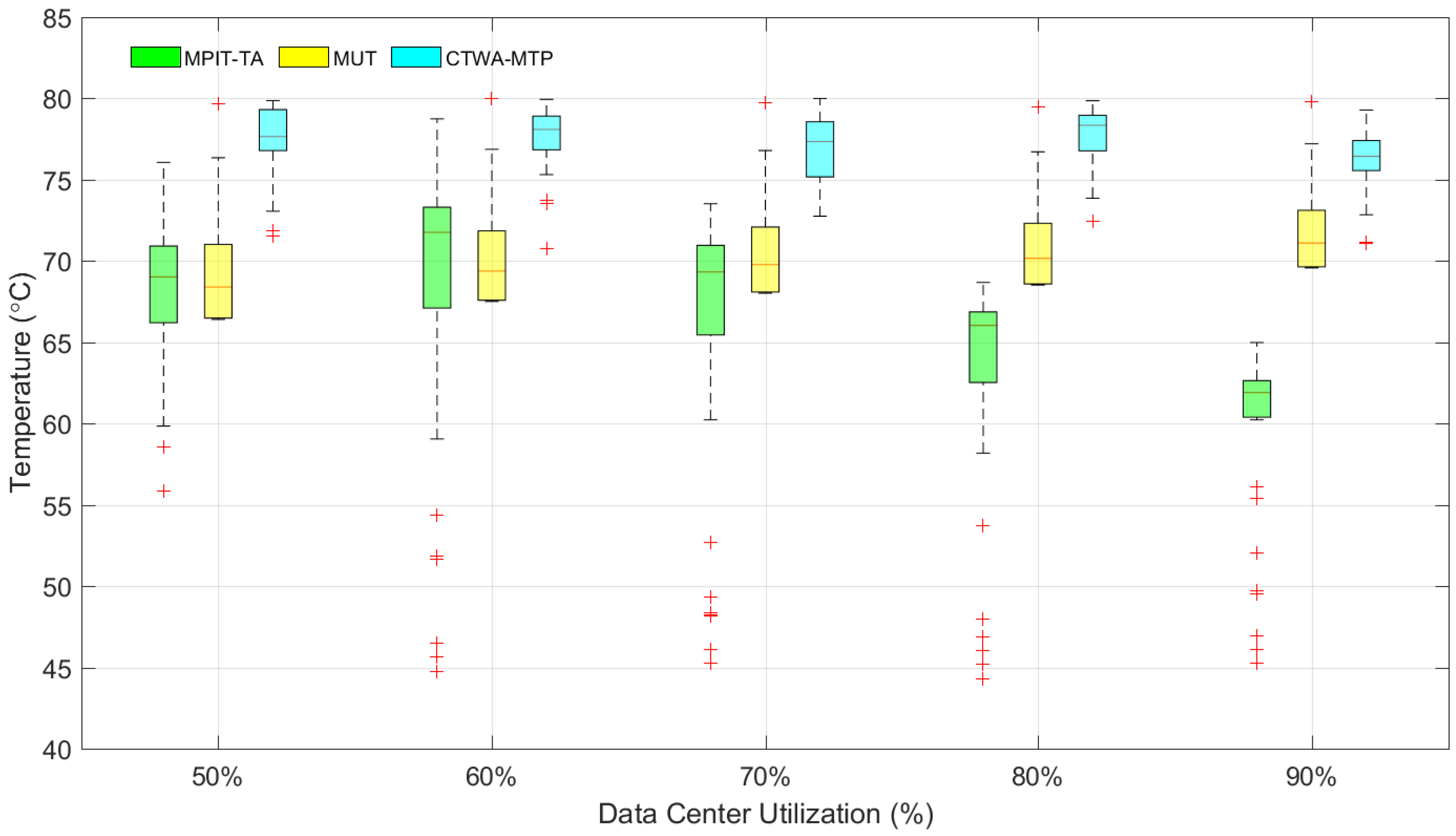
4.2. Evaluation of Total Power Consumption
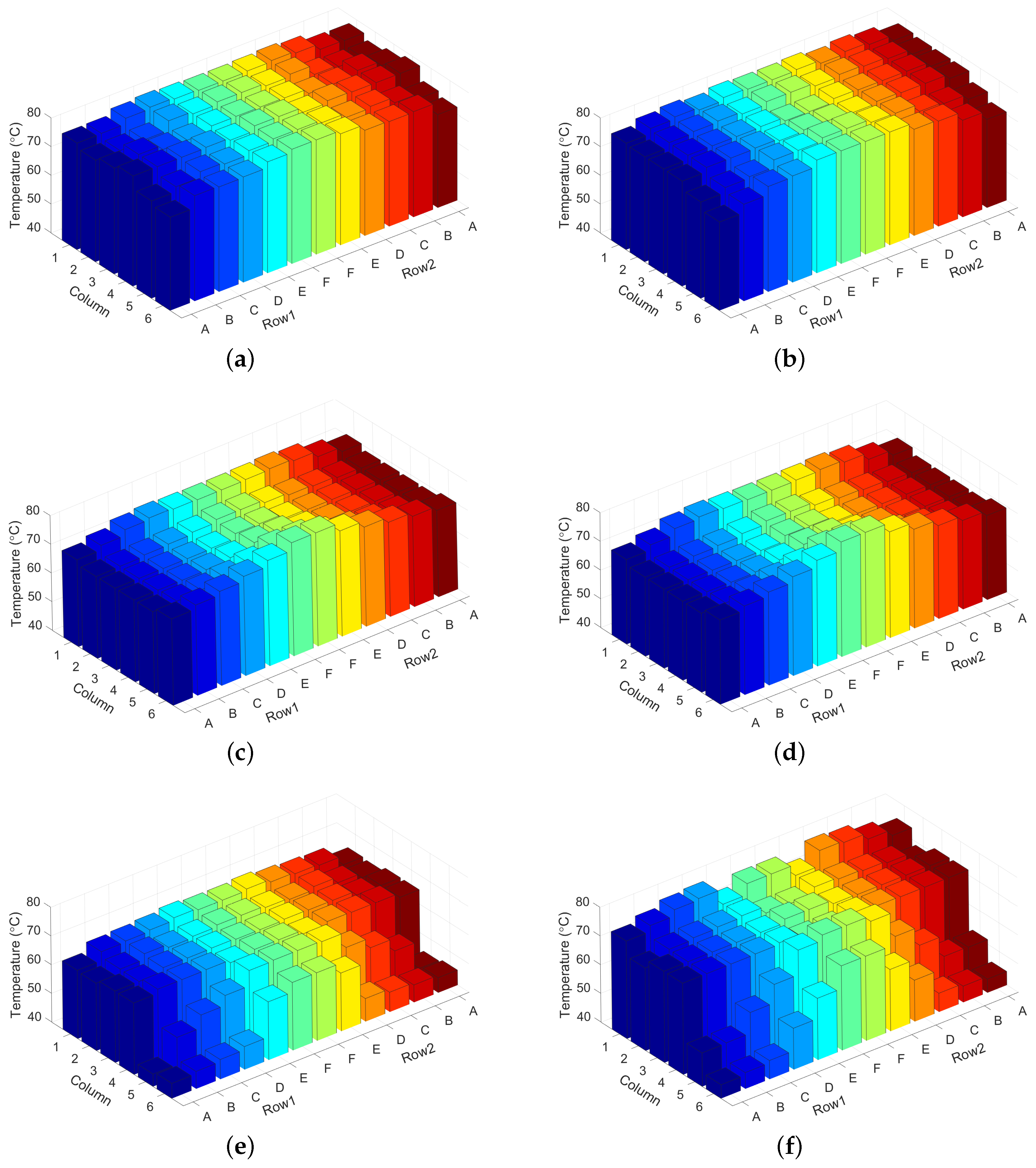
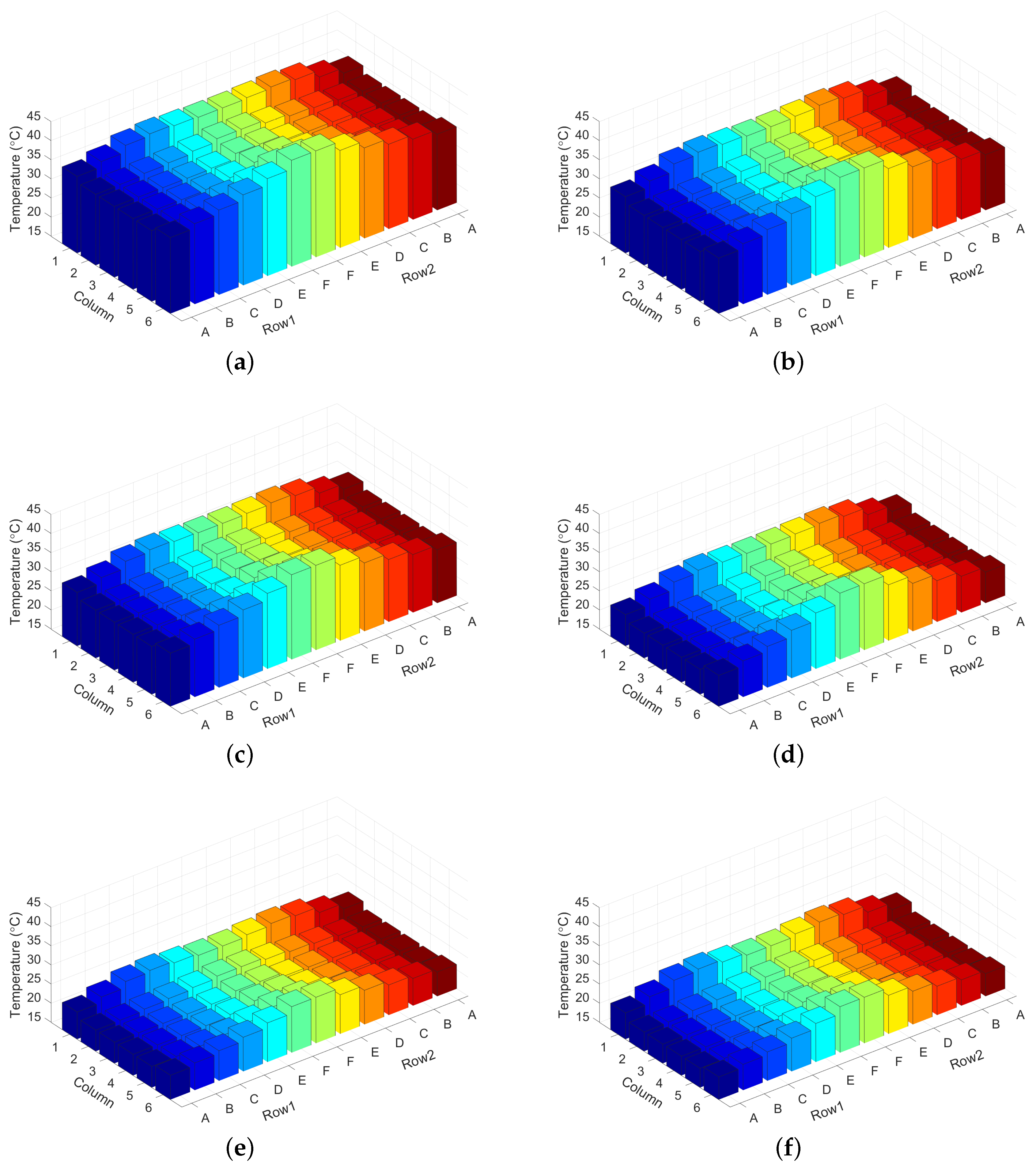
4.3. Evaluation of Chip Temperature and Inlet Temperature
4.4. Evaluation of Workload Allocation
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masanet, E.R.; Brown, R.E.; Shehabi, A.; Koomey, J.G.; Nordman, B. Estimating the energy use and efficiency potential of U.S. data centers. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE. Thermal Guidelines for Data Processing Environments-Expanded Data Center Classes and Usage Guidance; Whitepaper Prepared by ASHRAE Technical Committee (TC) 9.9; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Siriwardana, J.; Jayasekara, S.; Halgamuge, S.K. Potential of air-side economizers for data center cooling: A case study for key Australian cities. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.; Mills, E.; Tschudi, B.; Rumsey, P. Best practices for data centers: Lessons learned from benchmarking 22 data centers. In Proceedings of the ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Buildings, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 13–18 August 2006; pp. 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, G.I. Cooling energy-hungry data centers. Science 2010, 328, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nada, S.A.; Said, M.A.; Rady, M.A. Numerical investigation and parametric study for thermal and energy management enhancements in data centers’ buildings. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 98, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarathinam, S.; Fakhim, B.; Behnia, M.; Armfield, S. A comparison of parametric and multivariable optimization techniques in a raised-floor data center. J. Electron. Packag. 2013, 135, 030905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinarayana, N.; Fakhim, B. Thermal performance of an air-cooled data center with raised-floor and non-raised-floor configurations. Heat Transf. Eng. 2014, 35, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Gupta, S.K.S.; Stanzione, D.; Cayton, P. Thermal-Aware Task Scheduling to Minimize Energy Usage of Blade Server Based Datacenters. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 29 September–1 October 2006; pp. 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Gupta, S.K.S.; Varsamopoulos, G. Energy-efficient thermal-aware task scheduling for homogeneous high-performance computing data centers: A cyber-physical approach. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2008, 19, 1458–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Mukherjee, T.; Varsamopoulos, G.; Gupta, S.K.S. Integrating cooling awareness with thermal aware workload placement for HPC data centers. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2011, 1, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardana, J.; Halgamuge, S.K.; Scherer, T.; Schott, W. Minimizing the thermal impact of computing equipment upgrades in data centers. Energy Build. 2012, 50, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Mccauley, S.; Kaplan, F.; Leung, V.J.; Coskun, A.K. Simulation and optimization of hpc job allocation for jointly reducing communication and cooling costs. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2014, 6, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Wang, J.; Gong, Q.; Song, M. Thermal-aware energy management of hpc data center via two-time-scale control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2010, 13, 2260–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaj, A.H.; Scherer, T.; Siriwardana, J.; Halgamuge, S.K. Multi-objective efficiency enhancement using workload spreading in an operational data center. Appl. Energy 2015, 138, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, F.D.; Vömel, C. Neural network-based prediction and control of air flow in a data center. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2012, 4, 021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Murray, B.T.; Sammakia, B. Airflow and temperature distribution optimization in data centers using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 64, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadiani, E.; Joshi, Y. Proper orthogonal decomposition for reduced order thermal modeling of air cooled data centers. J. Heat Transf. 2010, 132, 271–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadiani, E.; Amur, H.; Krishnan, B.; Joshi, Y.; Schwan, K. Coordinated optimization of cooling and it power in data centers. J. Electron. Packag. 2010, 132, 031006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadiani, E.; Joshi, Y.; Allen, J.K.; Mistree, F. Adaptable robust design of multi-scale convective systems applied to energy efficient data centers. Numer. Heat Transf. A Appl. 2010, 57, 69–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Joshi, Y. Rapid temperature predictions in data centers using multi-parameter proper orthogonal decomposition. Numer. Heat Transf. A Appl. 2014, 66, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, Y. Reduced order thermal models of multi-Scale microsystems. J. Heat Transf. 2012, 134, 031008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, D.W.; Khalifa, H.E. Thermally aware, energy-based load placement in open-aisle, air-cooled data centers. J. Electron. Packag. 2013, 135, 030906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, D.W.; Khalifa, H.E. Expanded assessment of a practical thermally aware energy-optimized load placement strategy for open-aisle, air-cooled data centers. J. Electron. Packag. 2013, 135, 030907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi, K.; Wemhoff, A.P.; Silva-Llanca, L.; Abbasi, K.; Ortega, A. Optimization of data center cooling efficiency using reduced order flow modeling within a flow network modeling approach. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 124, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Gui, X.; Zhang, R.; Fu, L. Joint cooling and server control in data centers: A cross-layer framework for holistic energy minimization. IEEE Syst. J. 2017, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirokaw, T.; Hond, K.; Shibuy, T. Mercury and freon: Temperature emulation and management for server systems. ACM Sigplan Not. 2006, 41, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, P.; Leech, P.; Irwin, D.; Chase, J. Ensemble-level Power Management for Dense Blade Servers. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Boston, MA, USA, 17–21 June 2006; Volume 34, pp. 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dick, R.P.; Shang, L.; Yang, H. Accurate temperature-dependent integrated circuit leakage power estimation is easy. In Proceedings of the Conference on Design, Automation and Test in Europe, Nice, France, 16–20 April 2007; pp. 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapater, M.; Tuncer, O.; Ayala, J.L.; Moya, J.M.; Vaidyanathan, K.; Gross, K.; Coskun, A.K. Leakage-aware cooling management for improving server energy efficiency. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2015, 26, 2764–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroba, P.; Zapater, M.; Ayala, J.L.; Moya, J.M.; Olcoz, K.; Hermida, R. On the Leakage-Power modeling for optimal server operation. In Proceedings of the 24th Jornadas de Paralelismo, Madrid, Spain, 17–20 September 2013; pp. 240–244. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.; Chase, J.; Ranganathan, P.; Sharma, R. Making scheduling “Cool”: Temperature-aware workload placement in data centers. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on USENIX Annual Technical Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 10–15 April 2005; pp. 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, S.W.; Kim, M.H.; Choi, B.N.; Jeong, J.W. Simplified server model to simulate data center cooling energy consumption. Energy Build. 2015, 86, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konak, A.; Coit, D.W.; Smith, A.E. Multi-objective optimization using genetic algorithms: A tutorial. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2006, 91, 992–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, B.; Finlayson, E.U.; Sohn, M.D.; Thatcher, T.L.; Price, P.N.; Wood, E.E.; Sextro, R.G.; Gadgil, A.J. Tracer gas transport under mixed convection conditions in an experimental atrium: Comparison between experiments and cfd predictions. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5236–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bhagwat, H.; Singh, U.; Deodhar, A.; Singh, A.; Sivasubramaniam, A. Fast and accurate evaluation of cooling in data centers. J. Electron. Packag. 2014, 137, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schall, D.; Harder, T. Energy-proportional query execution using a cluster of wimpy nodes. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Workshop on Data Management on New Hardware, New York, NY, USA, 22–27 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | Value and Unit |
|---|---|
| Reference temperature | 25 C |
| Reference pressure | 101,325 Pa |
| Specific heat capacity | 1004.4 J/kg·K |
| Density | 1.225 kg/ |
| Data Center Utilization | Standard Deviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CTWA-MTP | MUT | MPIT-TA | |
| 90% | 2.28 | 3.31 | 5.05 |
| 80% | 1.94 | 3.12 | 9.52 |
| 70% | 2.14 | 2.92 | 9.01 |
| 60% | 1.70 | 2.73 | 7.30 |
| 50% | 2.01 | 2.54 | 5.58 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.; Gu, L. Chip Temperature-Based Workload Allocation for Holistic Power Minimization in Air-Cooled Data Center. Energies 2017, 10, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122123
Bai Y, Gu L. Chip Temperature-Based Workload Allocation for Holistic Power Minimization in Air-Cooled Data Center. Energies. 2017; 10(12):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122123
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yan, and Lijun Gu. 2017. "Chip Temperature-Based Workload Allocation for Holistic Power Minimization in Air-Cooled Data Center" Energies 10, no. 12: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122123
APA StyleBai, Y., & Gu, L. (2017). Chip Temperature-Based Workload Allocation for Holistic Power Minimization in Air-Cooled Data Center. Energies, 10(12), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122123





