Combination of Compensations and Multi-Parameter Coil for Efficiency Optimization of Inductive Power Transfer System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
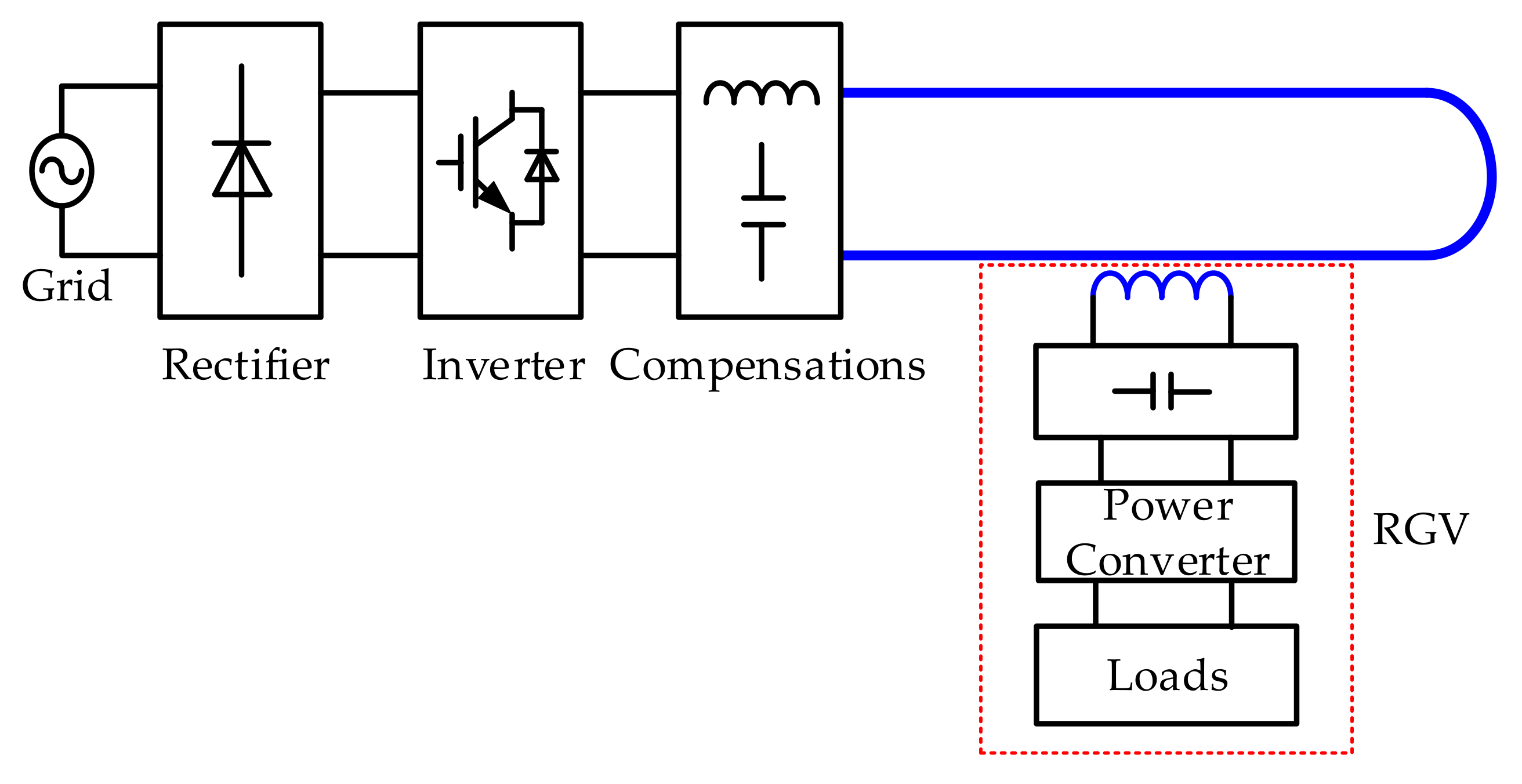
2. Efficiency Influencing Factors of IPT System
3. Accurate Computation of Coil Parameters
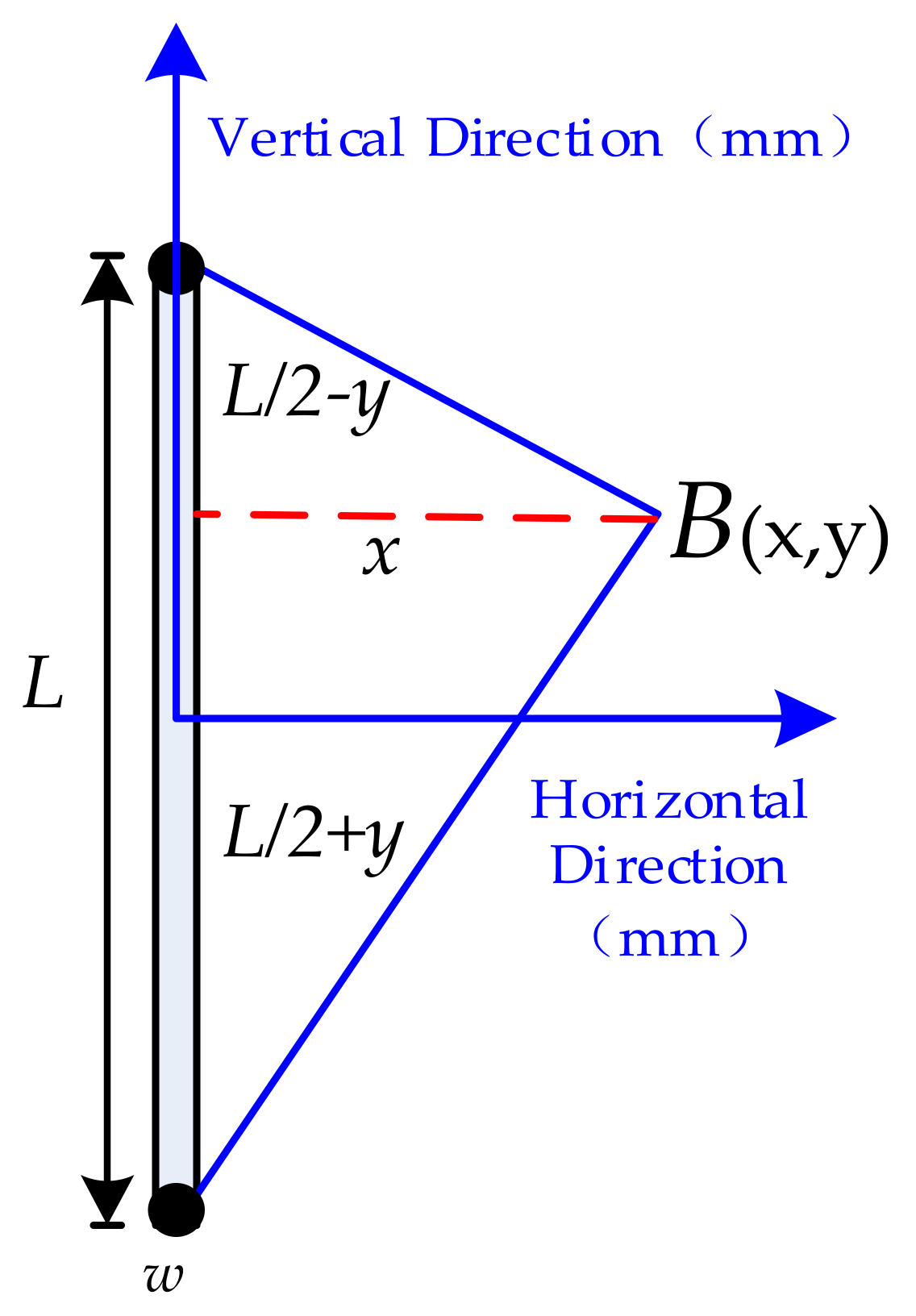
3.1. Calculation of Self-Inductance
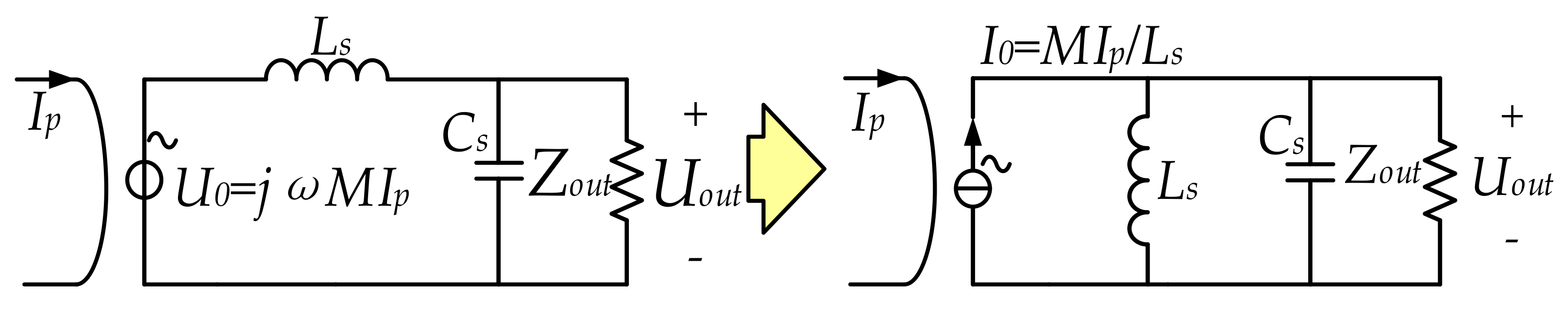
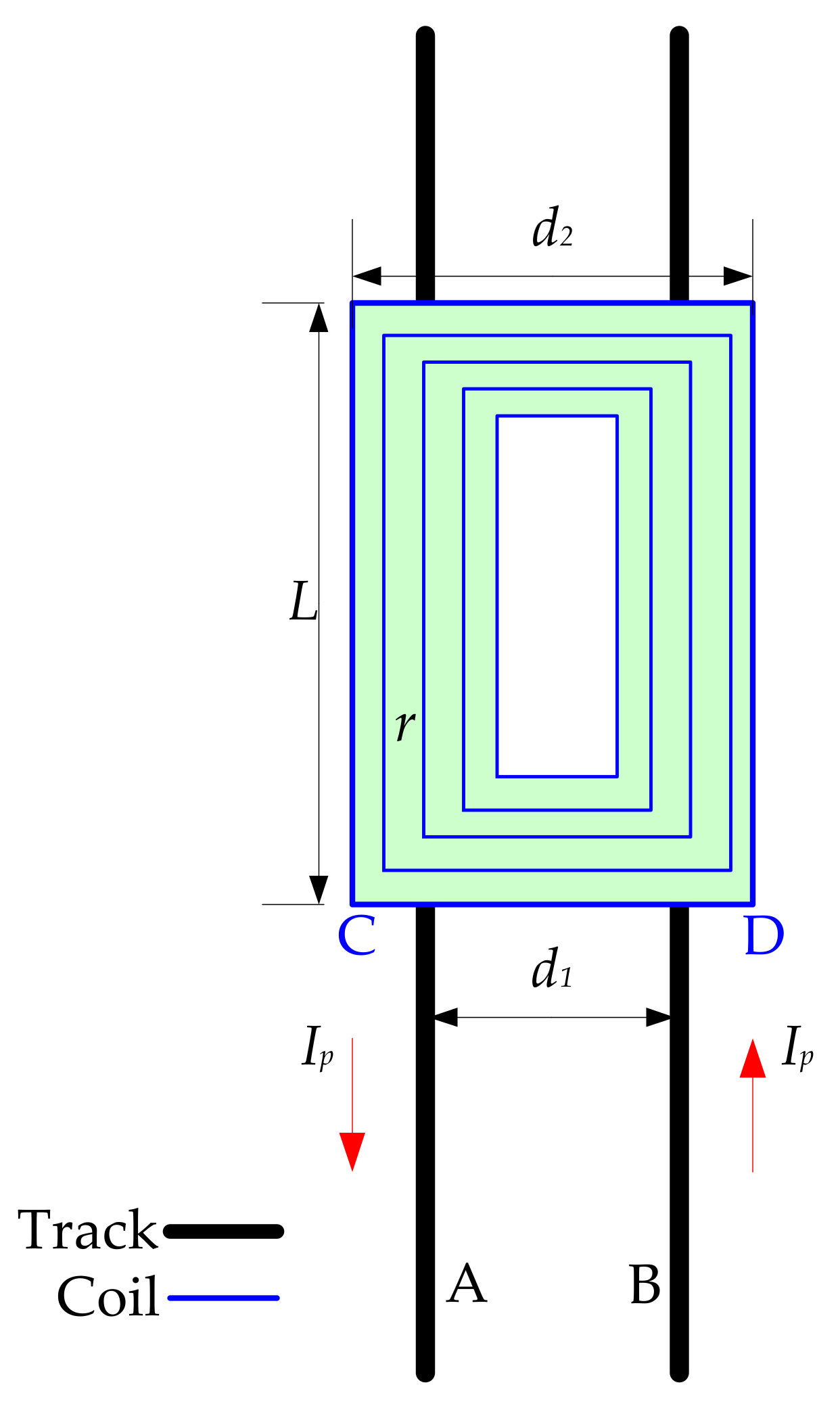
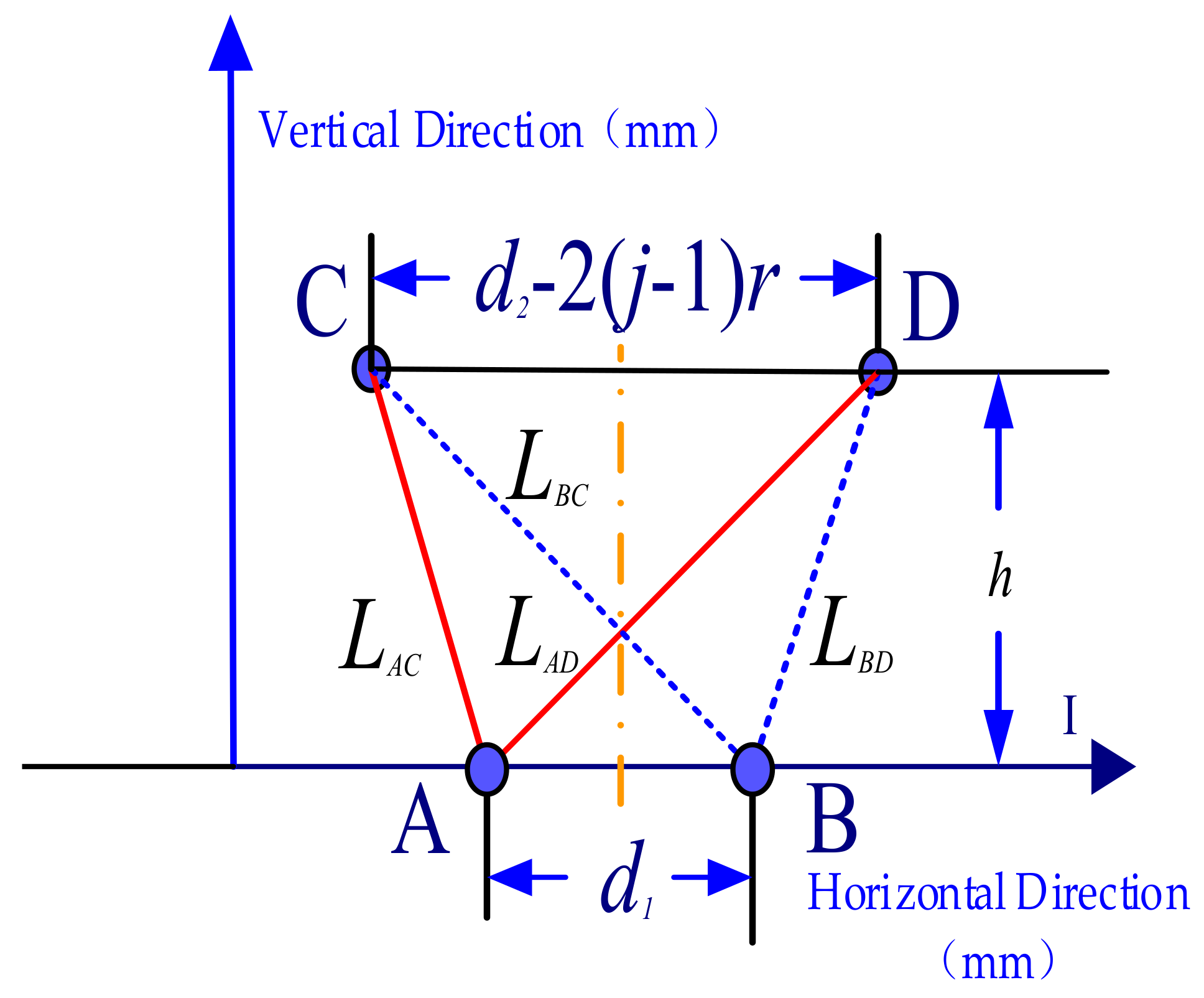
3.2. Accurate Computation of Mutual Inductance
3.3. Internal Resistance Calculation of Track and Coil
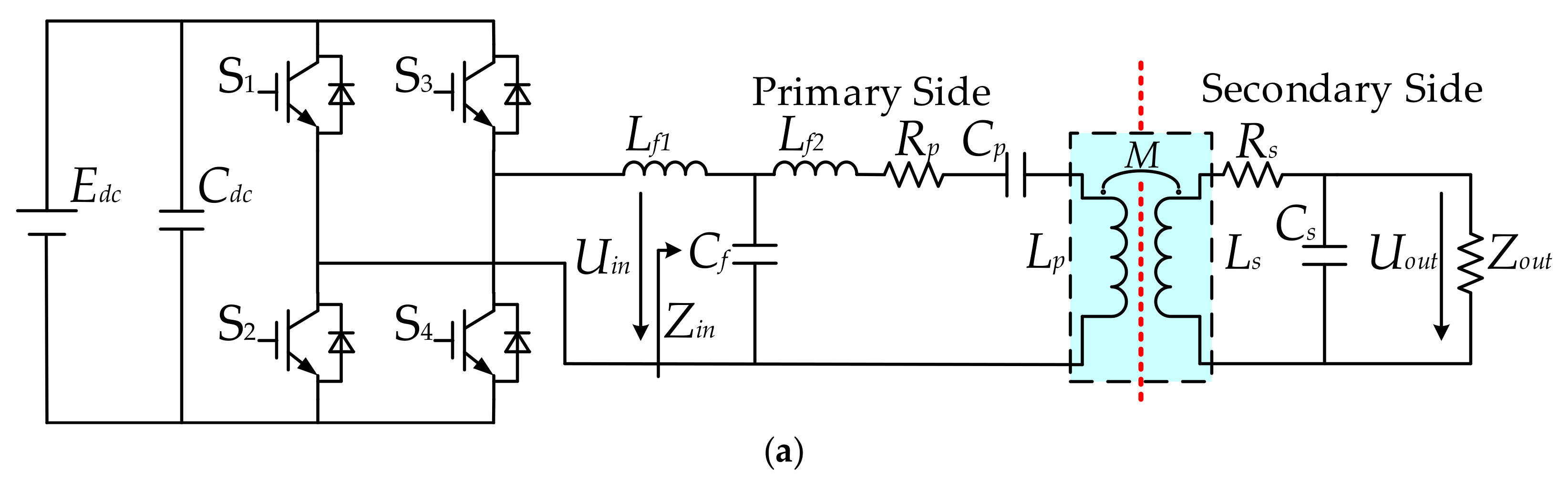
4. Efficiency Optimization Analysis of the IPT System
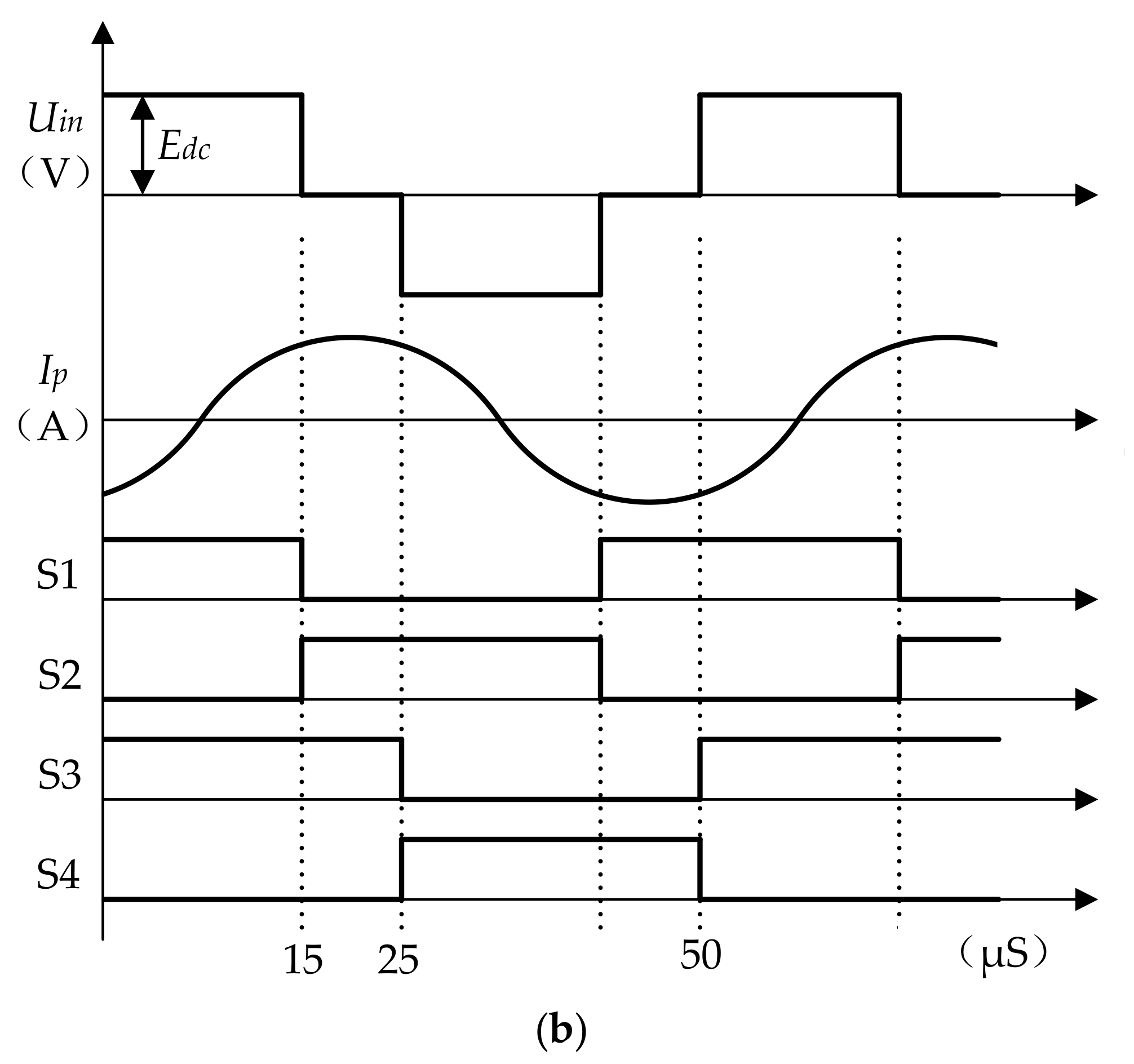
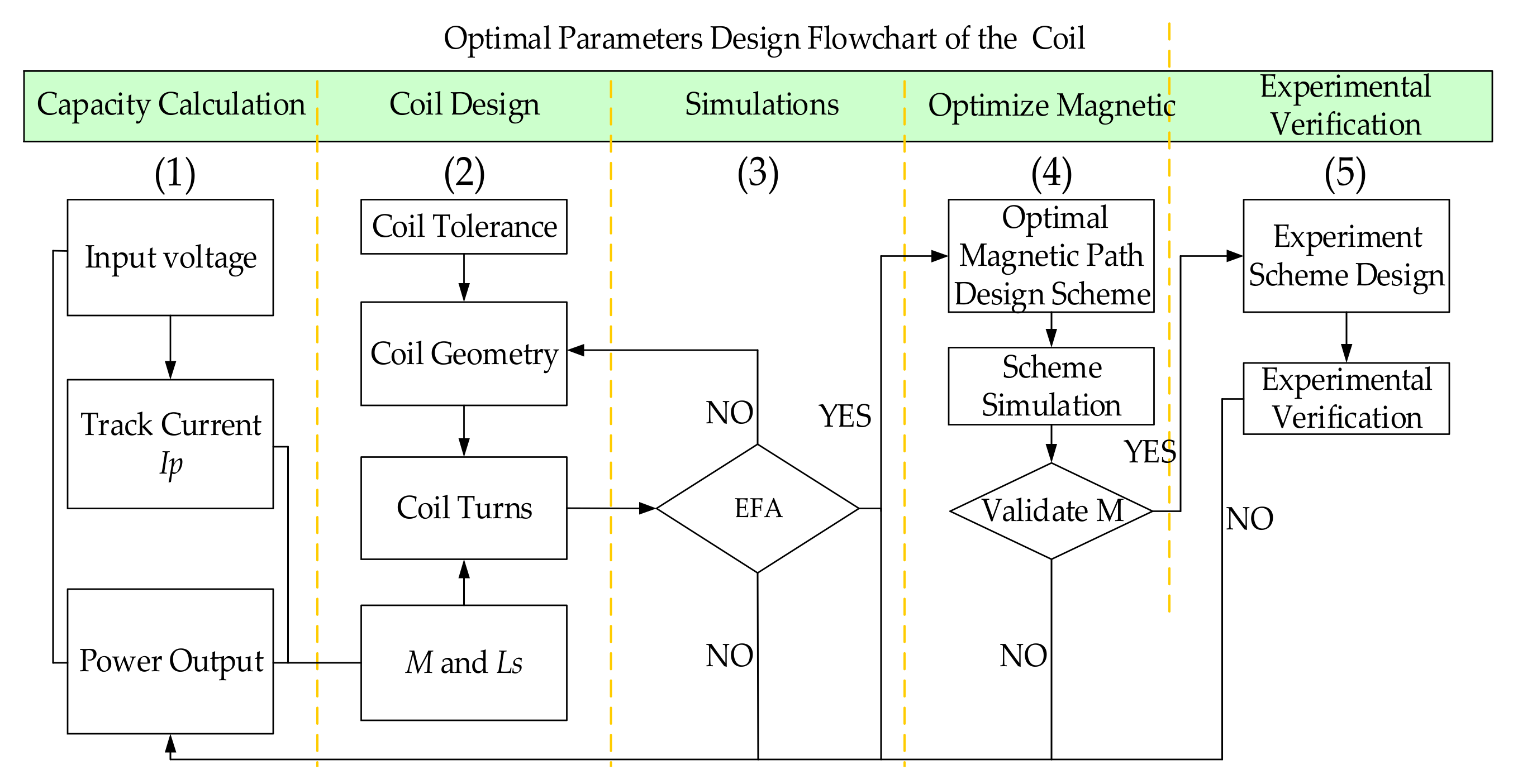
4.1. Optimization Design Process
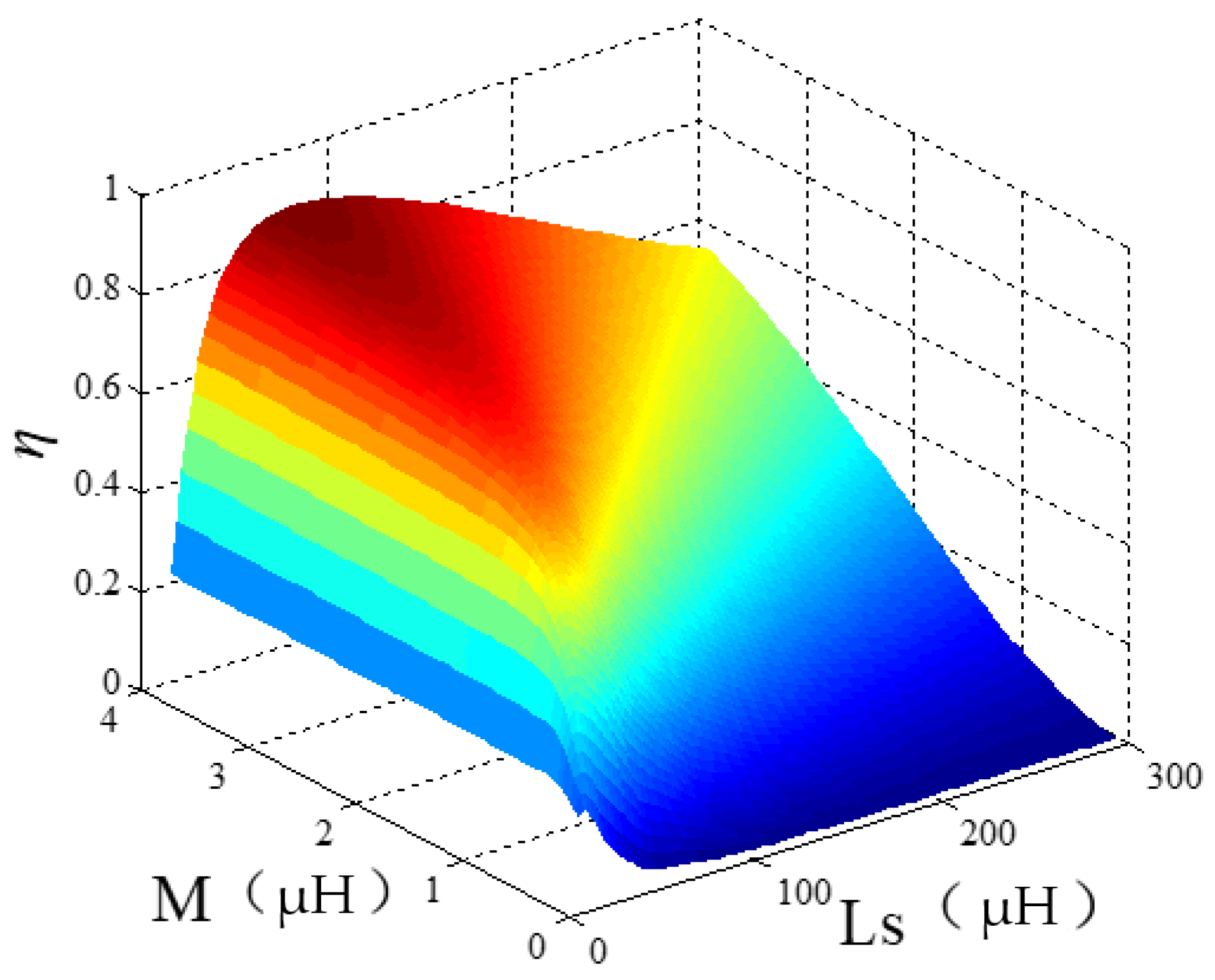
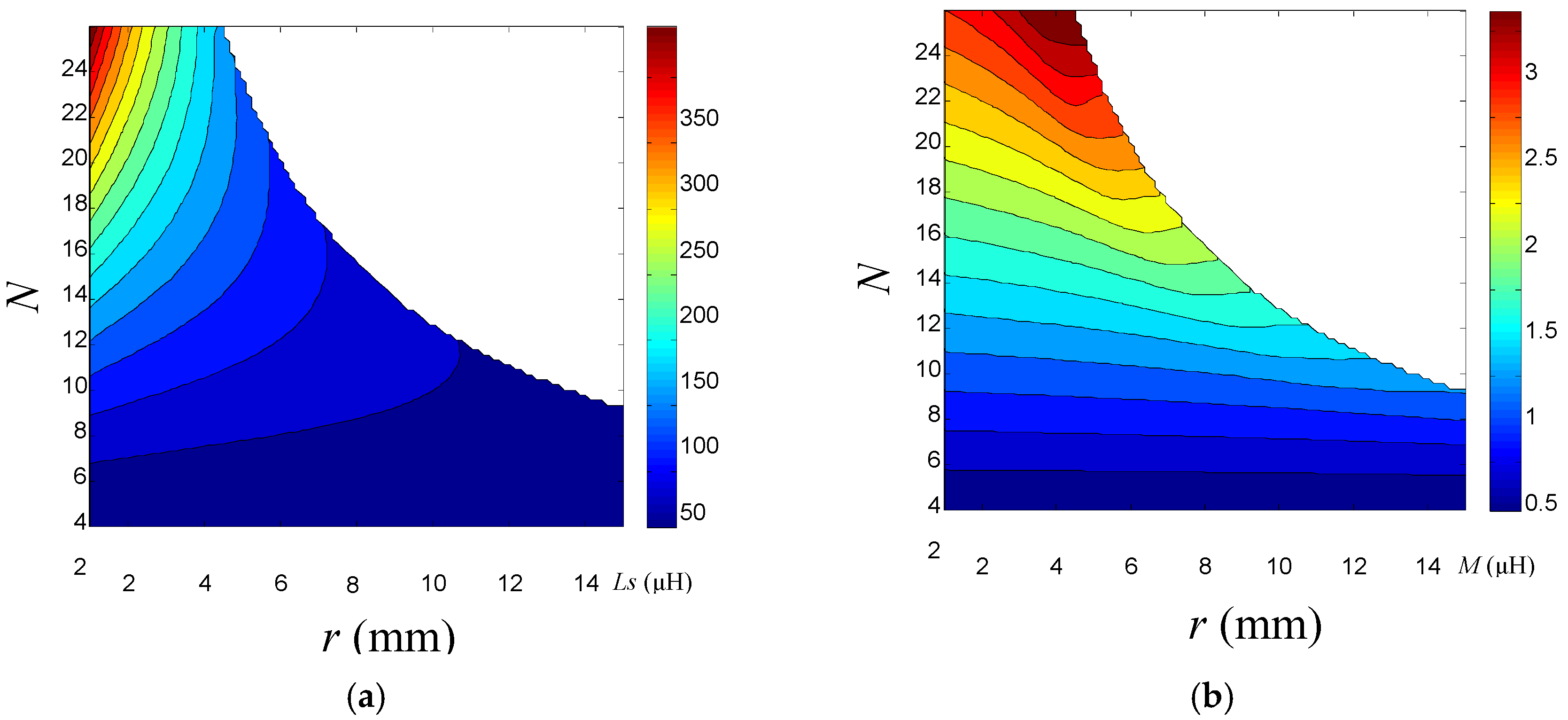
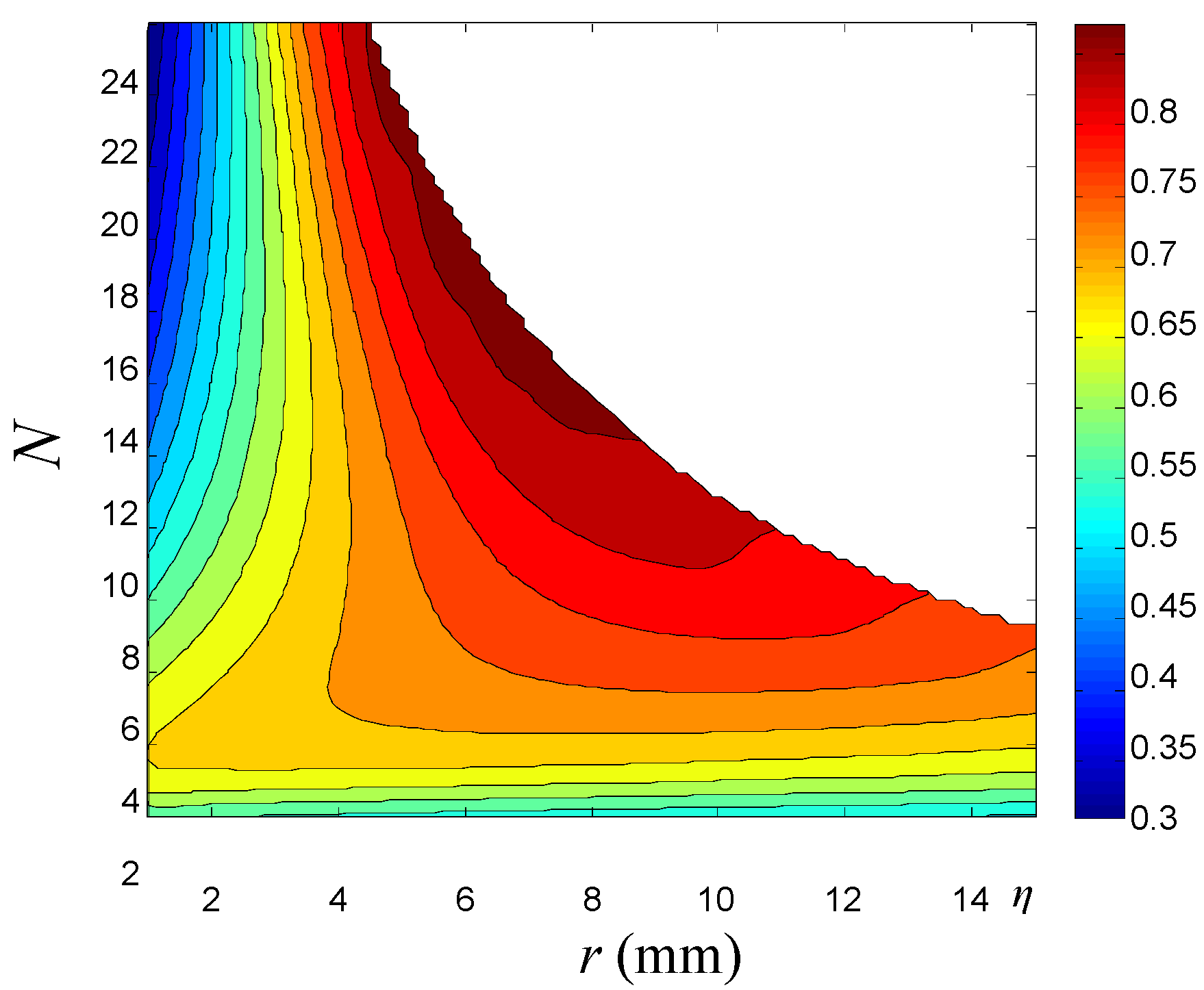
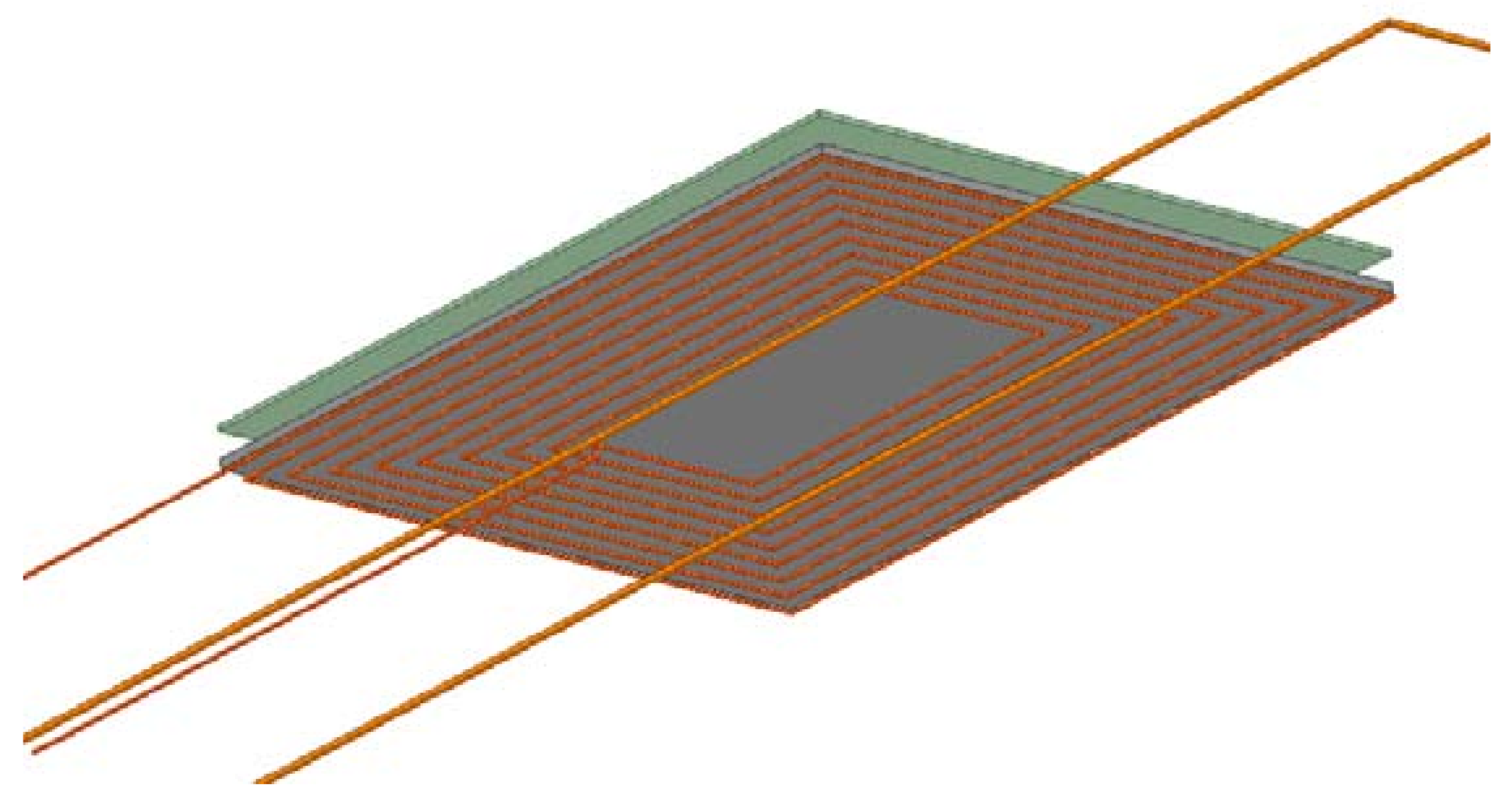
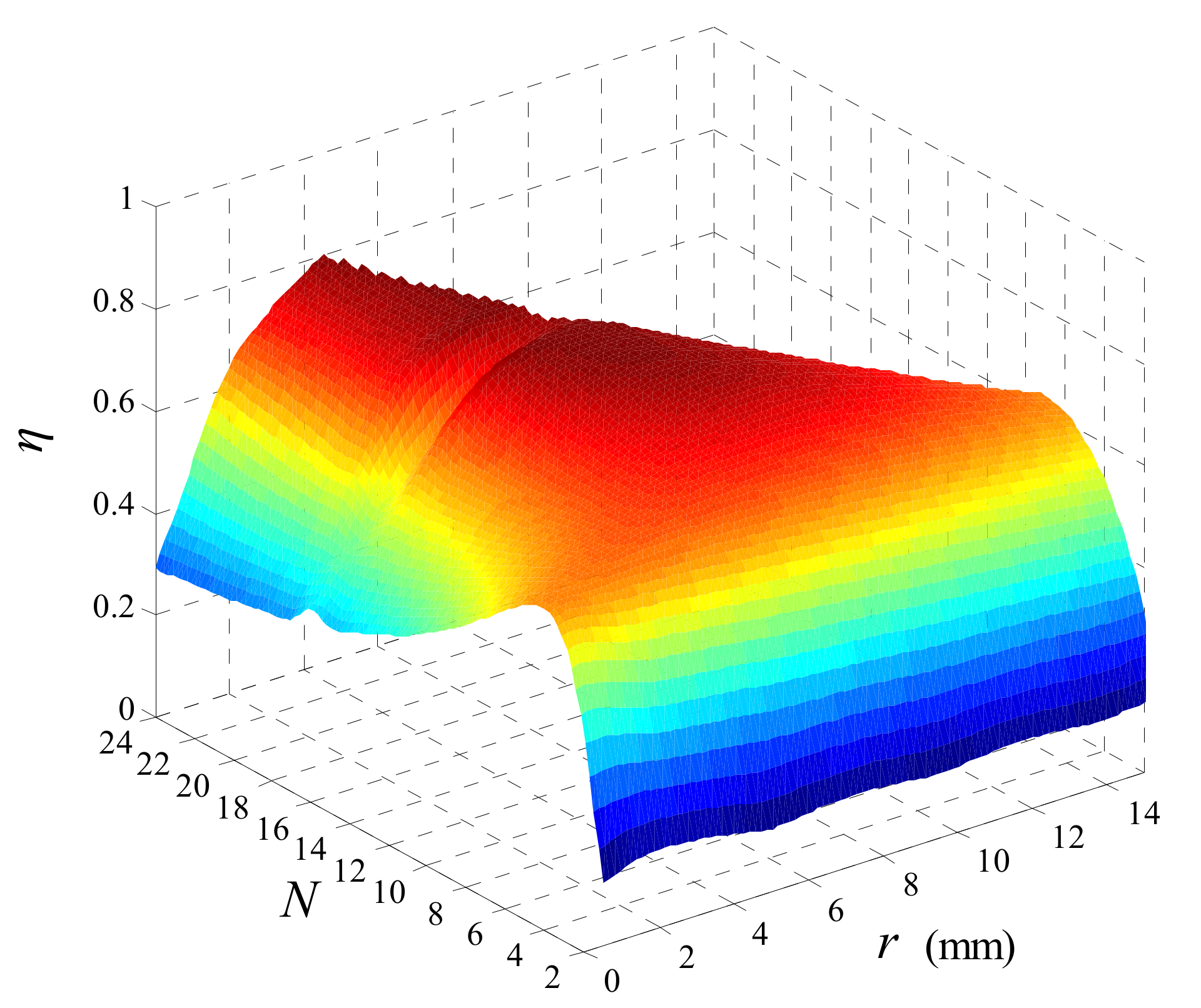
4.2. Optimization Analysis of Coil Parameters
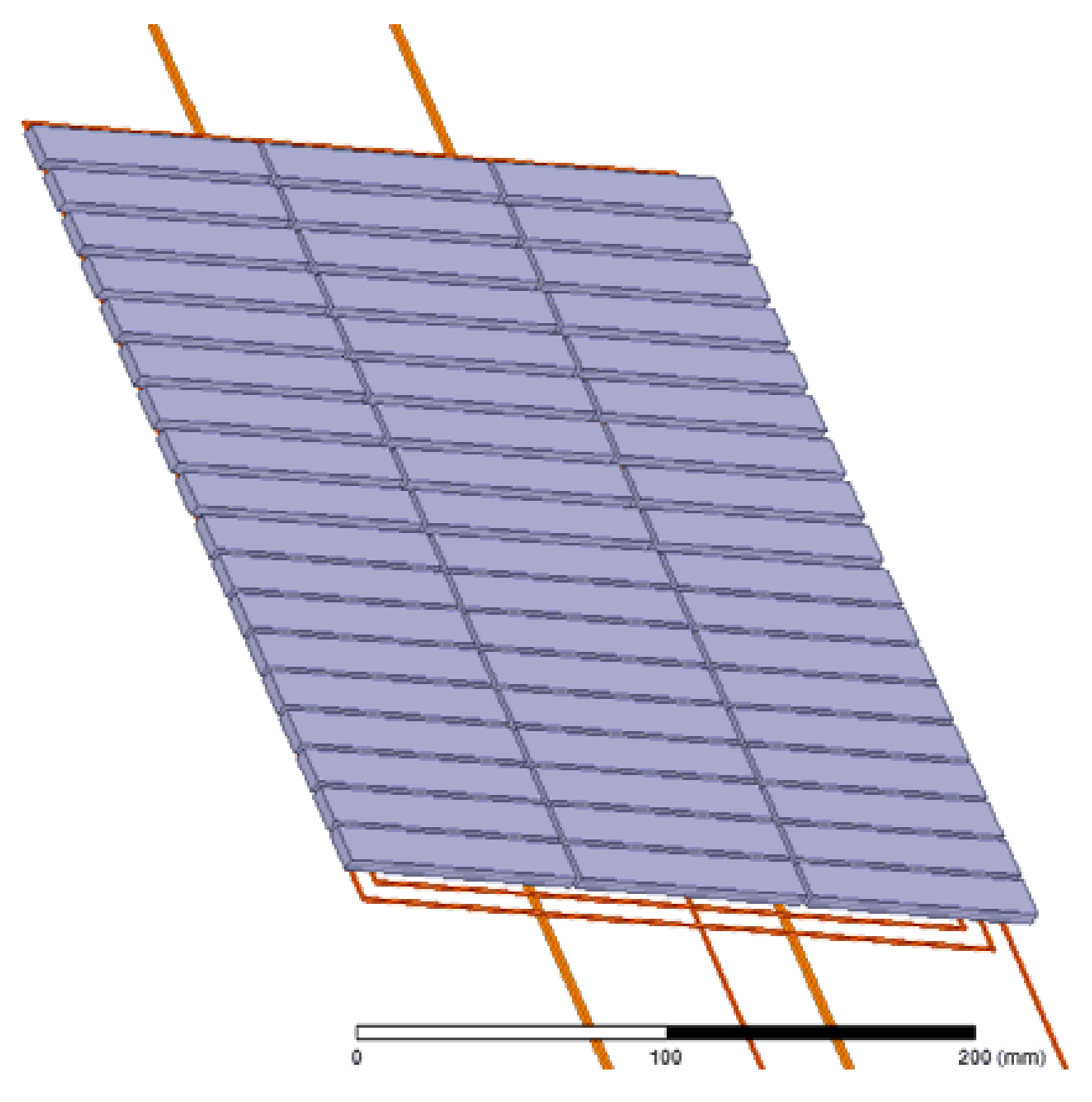
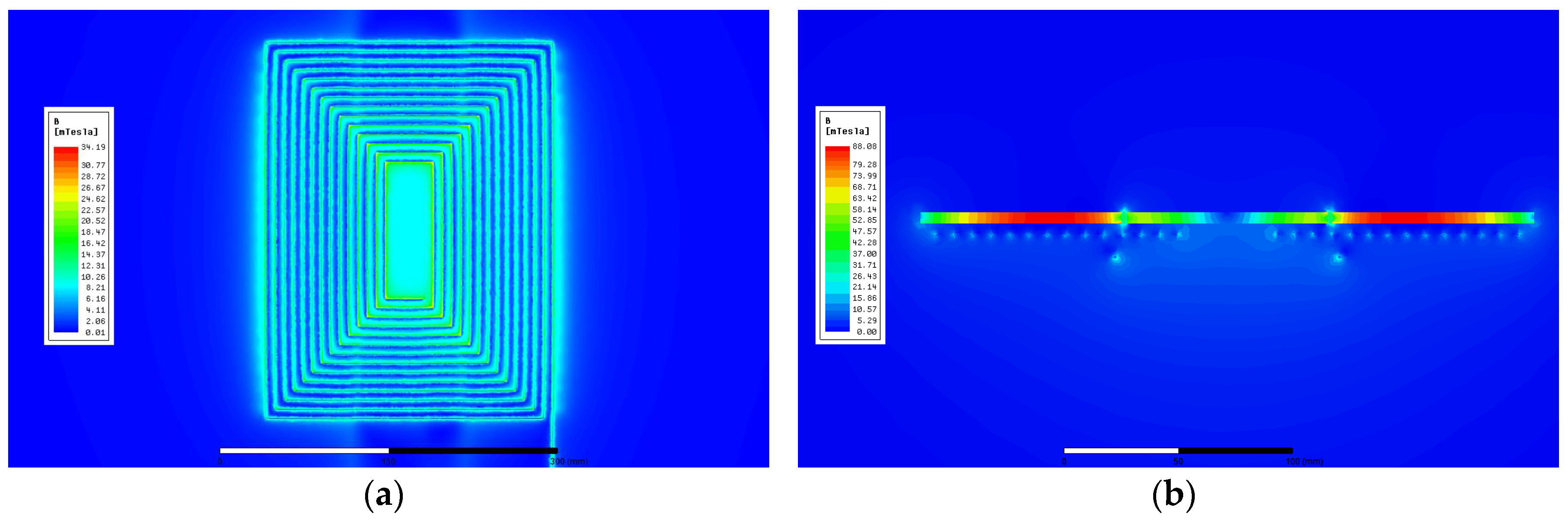
4.3. Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
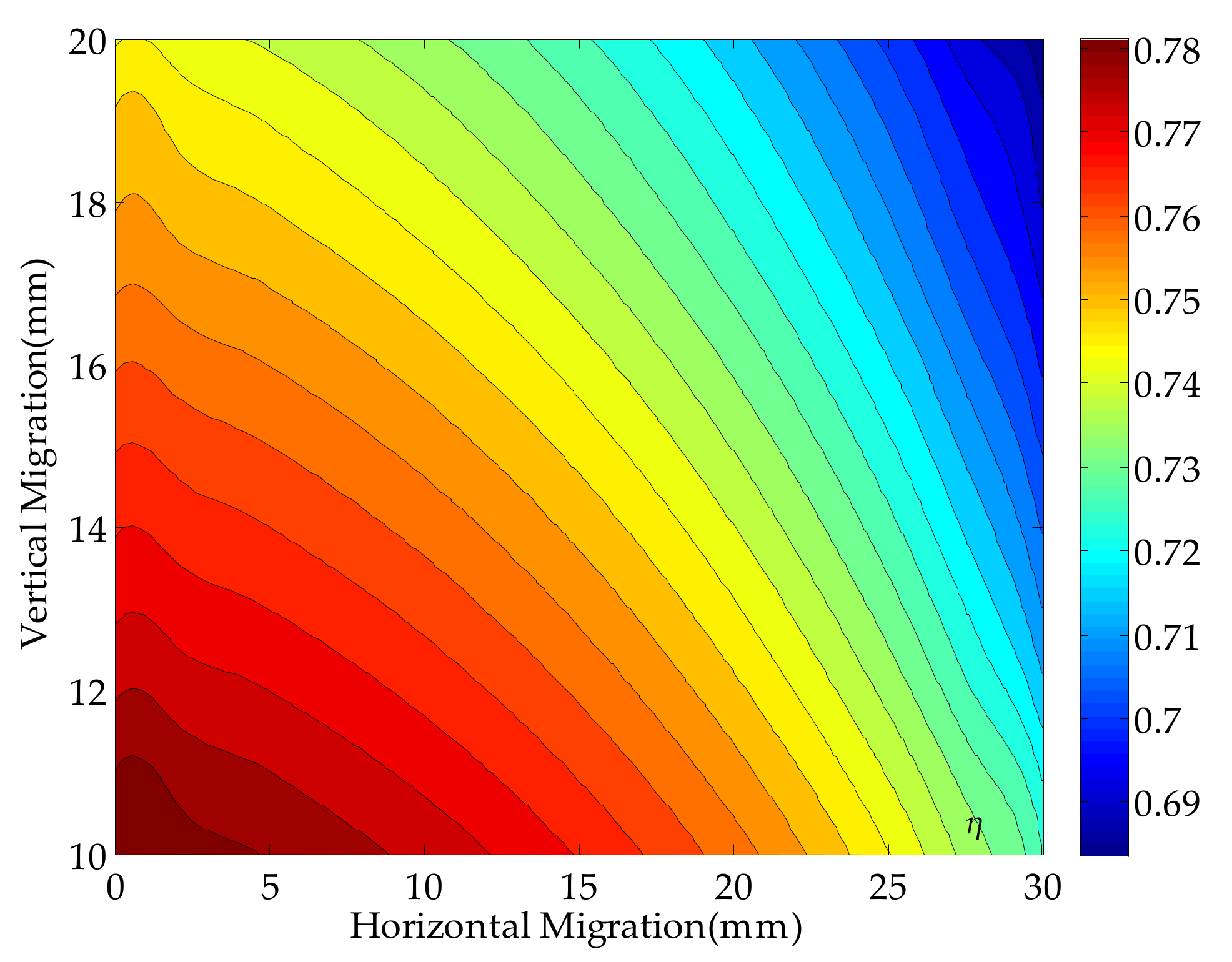
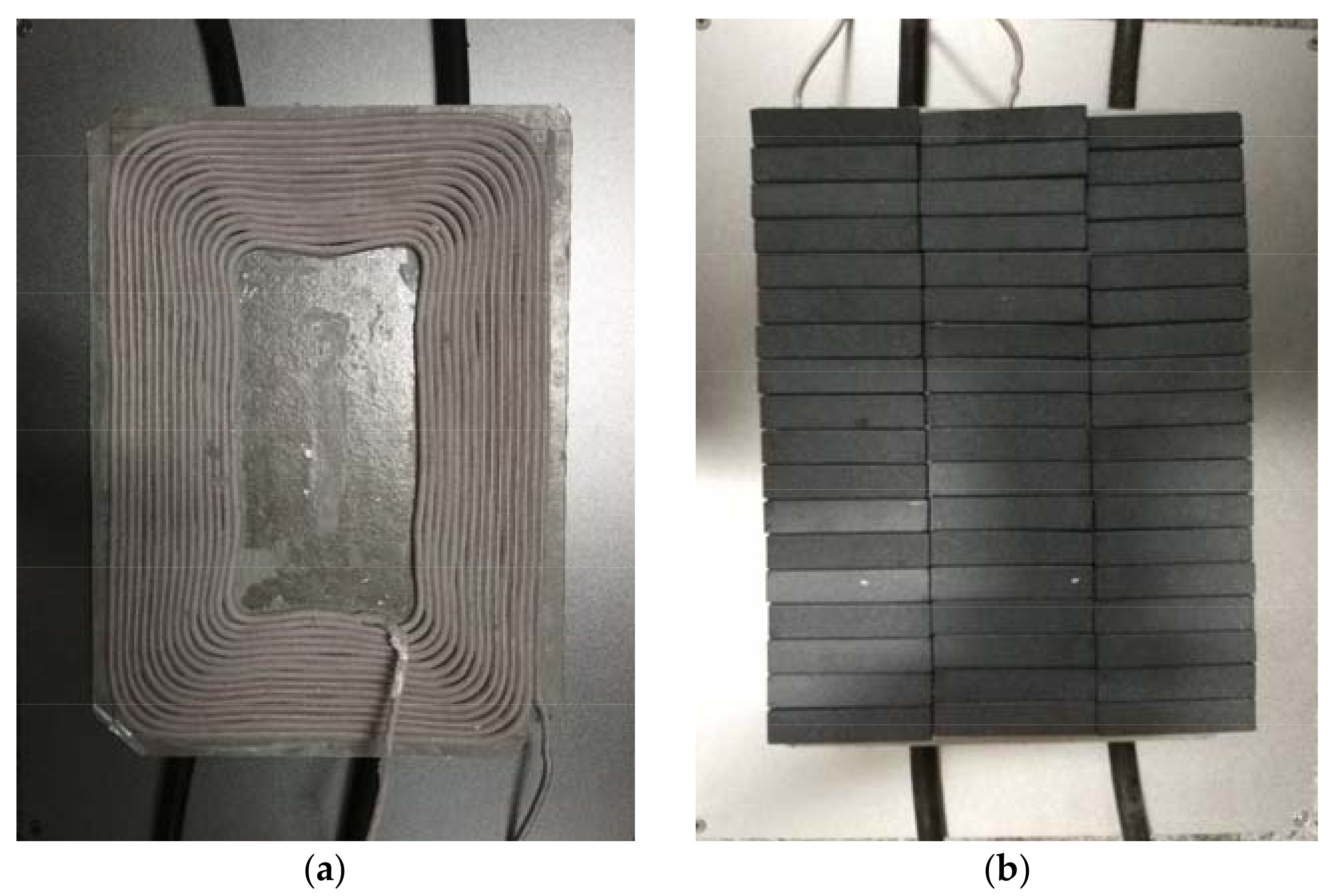
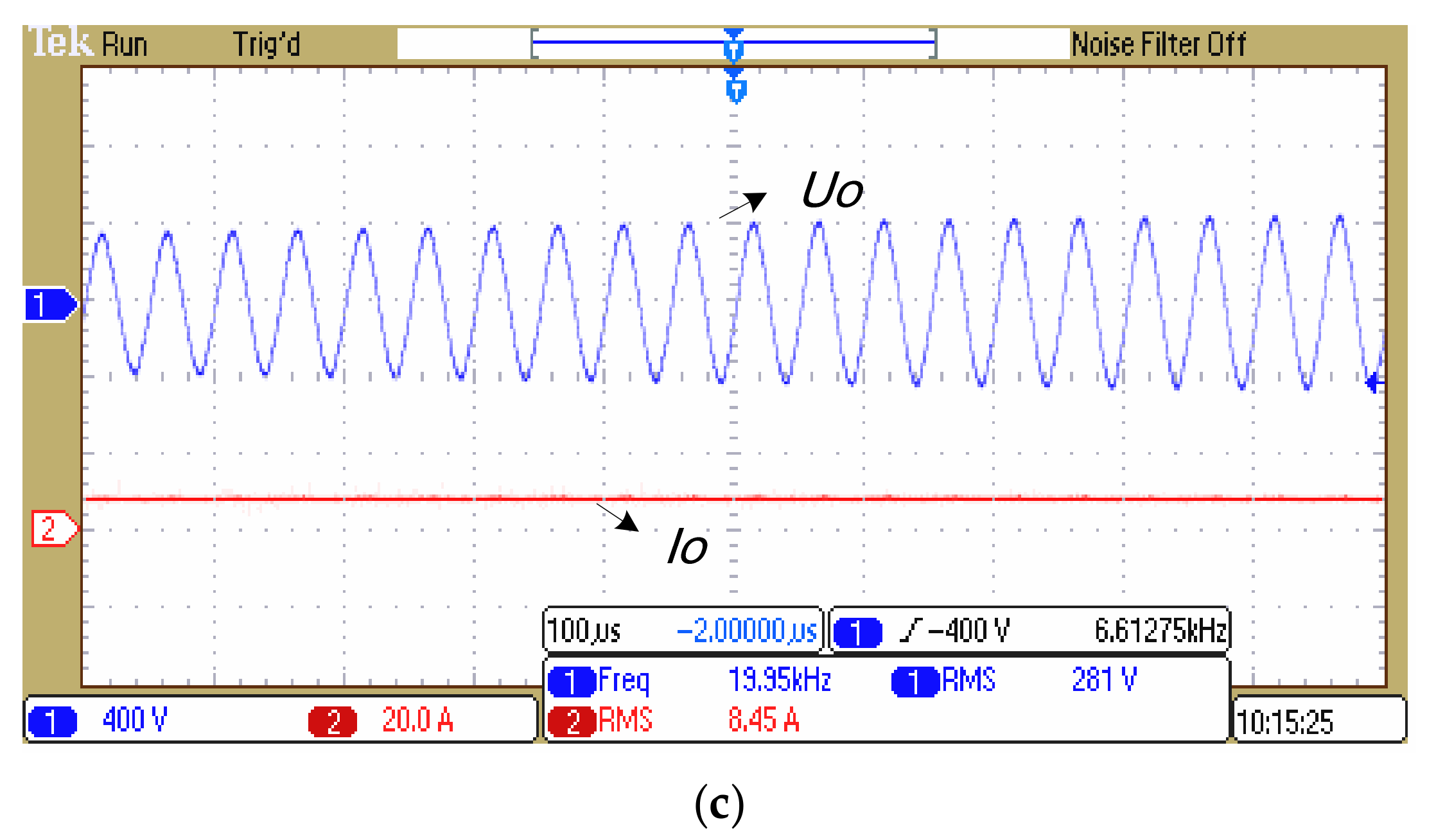
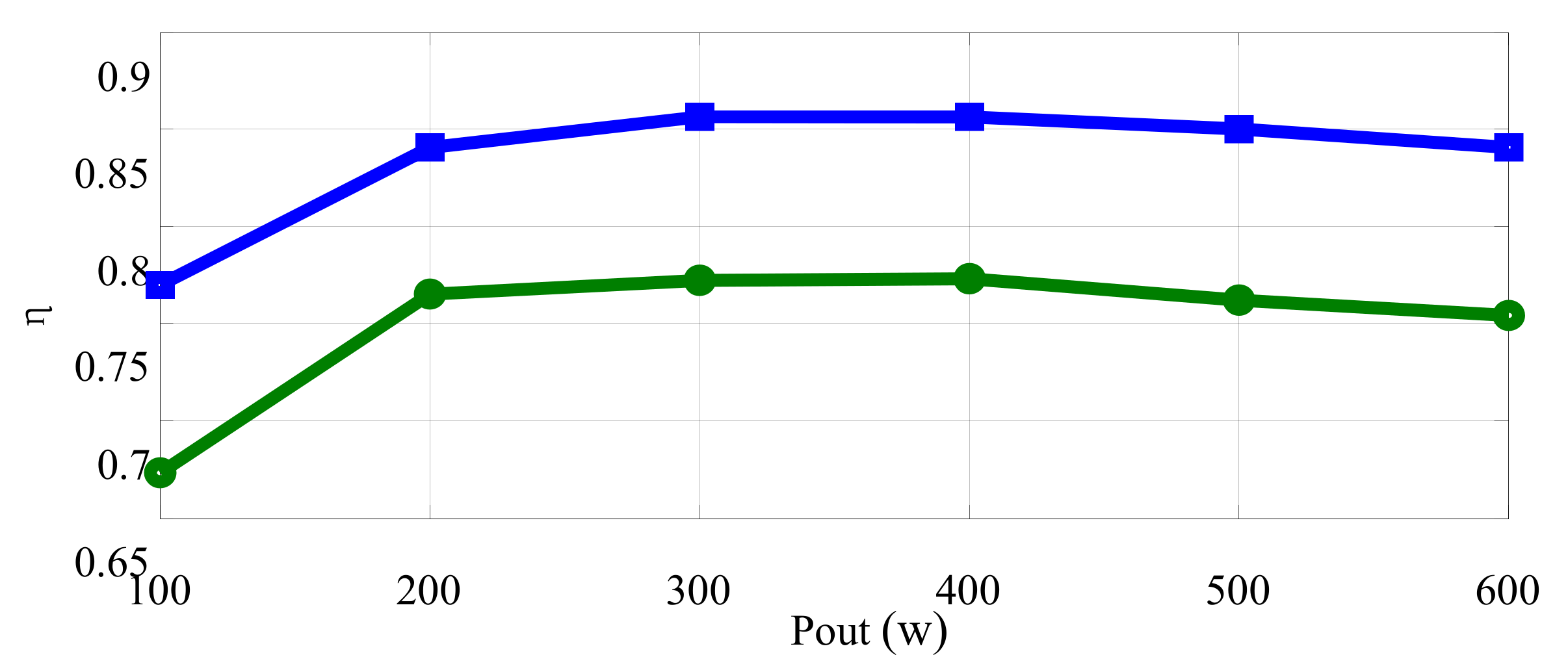
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kafeel, A.K.; Muhammad, A.; Saad, M. Inductively coupled power transfer for electric vehicle charging—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 462–475. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Zhang, H.; Hofmann, H.; Mi, C.C. A Dynamic Charging System with Reduced Output Power Pulsation for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6580–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K.; Chen, Q. Analysis and Comparison of Secondary Series- and Parallel-Compensated Inductive Power Transfer Systems Operating for Optimal Efficiency and Load-Independent Voltage-Transfer Ratio. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.E.; Robertson, D.J.; Covic, G.A. Improved AC Pickups for IPT Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 6361–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Hu, A.P.; Covic, G.A. A Direct AC–AC Converter for Inductive Power-Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, A.; Covic, A.G.; Kacprzak, D. A Bipolar Pad in a 10-kHz 300-W Distributed IPT System for AGV Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3288–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Shin, S.; Kim, Y.; Ahn, S.; Lee, S. Design and implementation of shaped magnetic-resonance-based wireless power transfer system for roadway-powered moving electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.C.; Beom, W.G.; Seog, Y.J.; Chun, T.R. Advances in Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Roadway-Powered Electric Vehicles. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 18–36. [Google Scholar]
- Budhia, M.; Boys, J.T.; Covic, G.A.; Huang, C.Y. Development of a single-sided flux magnetic coupler for electric vehicle IPT charging systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtchev, S.; Borges, B.; Brandisky, K.; Klaassens, J.B. Resonant contactless energy transfer with improved efficiency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, N.; Covic, A.G.; Hao, F.; George, L.; Boys, J.T. Variable Tuning in LCL Compensated Contactless Power Transfer Pickups. In Proceedings of the Energy Conversion Congress & Exposition, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–24 September 2009; pp. 1826–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. An Approximate Dynamic Model of LCL- T-Based Inductive Power Transfer Power Supplies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 5554–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Covic, G.A.; Stielau, O.H. Investigating an LCL load resonant inverter for inductive power transfer applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borage, M.; Tiwari, S.; Kotaiah, S. LCL-T Resonant Converter with Clamp Diodes: A Novel Constant-Current Power Supply with Inherent Constant-Voltage Limit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantic, Z.; Bai, S.; Lukic, M.S. ZCS LCC-Compensated Resonant Inverter forInductive-Power-Transfer Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 3500–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimen, S.G.; Pfannkuchen, A.; Schmuelling, B. Compensation Considerations for Bidirectional Inductive Charging Systems of Electric Vehicles with Coil Positioning Flexibility. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Cai, T.; Duan, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X. An LCC Compensated Resonant Converter Optimized for Robust Reaction to Large Coupling Variation in Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6591–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, G.; Suul, J.A. Minimizing Converter Requirements of Inductive Power Transfer Systems with Constant Voltage Load and Variable Coupling Conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6835–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, R.; Iruretagoyena, U.; Kolar, J.W. Comprehensive Evaluation of Rectangular and Double-D Coil Geometry for 50 kW/85 kHz IPT System. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2016, 4, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampos, A.S.; Zaspalis, V. Impact of ferrite shield properties on the low-power Inductive Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Boys, J.T.; Elliott, G.A.J.; Covic, G.A. An Appropriate Magnetic Coupling Co-Efficient for the Design and Comparison of ICPT Pickups. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhi, B.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Design and Optimization of Circular Magnetic Structures for Lumped Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3096–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, E.R.; Dalal, A.; Kumar, P. Accurate Computation of Mutual Inductance of Two Air Core Square Coils with Lateral and Angular Misalignments in a Flat Planar Surface. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulou, K.; Flynn, B.W. Wireless Power Transfer in Loosely Coupled Links: Coil Misalignment Model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, V.; Bauer, P. Distributed IPT Systems for Dynamic Powering: Misalignment Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6013–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Switching Frequency f | 20 kHz |
| Inductance Lf1 = Lf2 | 80 μH |
| Resonant Capacitance Cf | 0.5 μF |
| Self-inductance LP | 5 μH |
| Compensation Capacitance CP | 8 μF |
| Track Internal Resistance RP | 0.022 Ω |
| Inductive Coil Internal Resistance RS | 0.045 Ω |
| Output Power of Pickup | 400 W |
| Output Voltage of Pickup | 24 VDC |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Fang, Z.; Cai, C.; Lin, Z. Combination of Compensations and Multi-Parameter Coil for Efficiency Optimization of Inductive Power Transfer System. Energies 2017, 10, 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122088
Hu G, Zhang J, Wang J, Fang Z, Cai C, Lin Z. Combination of Compensations and Multi-Parameter Coil for Efficiency Optimization of Inductive Power Transfer System. Energies. 2017; 10(12):2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122088
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Guozhen, Junkun Zhang, Junhua Wang, Zhijian Fang, Changsong Cai, and Zhongzheng Lin. 2017. "Combination of Compensations and Multi-Parameter Coil for Efficiency Optimization of Inductive Power Transfer System" Energies 10, no. 12: 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122088
APA StyleHu, G., Zhang, J., Wang, J., Fang, Z., Cai, C., & Lin, Z. (2017). Combination of Compensations and Multi-Parameter Coil for Efficiency Optimization of Inductive Power Transfer System. Energies, 10(12), 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122088





