Abstract
This paper presents a method for determining the sensitivity of the main air flow directions in ventilation subnetworks to changes in aerodynamic resistance and air density in mine workings. The authors have developed formulae for determining the sensitivity of the main subnetwork air flows by establishing the degree of dependency of the air volume stream in a given working on the variations in resistance or air density of other workings of the network. They have been implemented in the Ventgraph mine ventilation network simulator. This software, widely used in Polish collieries, provides an extended possibility to predict the process of ventilation, air distribution and, in the case of underground fire, the spread of combustion gasses. The new method facilitates an assessment by mine ventilation services of the stability of ventilation systems in exploitation areas and determines the sensitivity of the main subnetwork air flow directions to changes in aerodynamic resistance and air density. Recently in some Polish collieries new longwalls are developed in seams located deeper than the bottom of the intake shaft. Such a solution is called “exploitation below the level of access” or “sublevel”. The new approach may be applied to such developments to assess the potential of changes in direction and air flow rates. In addition, an interpretation of the developed sensitivity indicator is presented. While analyzing air distributions for sublevel exploitation, the application of current numerical models for calculations of the distribution results in tangible benefits, such as the evaluation of the safety or risk levels for such exploitation. Application of the Ventgraph computer program, and particularly the module POŻAR (fire) with the newly developed options, allows for an additional approach to the sensitivity indicator in evaluating air flow safety levels for the risks present during exploitation below the level of the intake shaft. The analyses performed and examples presented enabled useful conclusions for mining practice to be drawn.
1. Introduction
Ventilation systems of mines are often too complex to predict and control the flow without numerical modeling. A relatively simple but effective approach, based on the analogy to electrical networks and the application of both Kirhoff’s laws, was developed by H. Cross in the XIX century and customized to ventilation by Hinsley and Scott in the UK and locally by other researchers. The introduction of computers allowed for the development of several programs for designing and analysing mine ventilation networks like Ventsim, Vuma, VnetPC, 3D-CANVENT2000, and Mivena, compared in the paper [1]. In Poland, Ventgraph [2,3,4,5,6] is the most sophisticated tool for this purpose. It has been successfully implemented in a number of Polish coal mines, as well as in Australian, North American, Vietnamese, and Czech coal mines [7,8].
Nowadays, a systematic use of 2D and 3D dimensional flow modelling [9,10,11] resulting from the new development of Computational Fluid Dynamics provides insight, which is more detailed but limited to one or a few workings. In comparison to a one dimensional description 3D or even 2D approach, it is much more demanding in terms of time and computational resources at all stages, from the survey of objects, development of models, and actual computations to the analysis and interpretation of results. What is more, in many cases, the flow rate, average temperature, or gas concentration are considered. Then, a 1D approach is relevant. For those reasons, the modelling of large ventilation systems has so far been practically possible with only one dimensional flow approximation, used by programs like Ventgraph, which justifies their further development. The results thus obtained open new possibilities for study and analysis, particularly of phenomena caused by the methane inflow [4] to areas of mining longwalls and goaf.
It is obvious that a flow in a particular gallery is sensitive to changes in aerodynamic resistance and density in adjacent workings, but it is difficult to predict the degree of such sensitivity. The authors have developed a formal concept of sensitivity indices to both resistance and density changes.
The resistance sensitivity indicator provides ventilation services with information on the eventual possibility of changes in airflows in the network due to intentional regulations of flow or accidental roof falls. The density sensitivity indicator shows the potential of airflow changes caused by underground fires or the inflow of gases like methane or carbon dioxide [2,4]. According to the authors’ knowledge [1] such indices have not been introduced before Ventgraph. They both bring interesting elements to the evaluation of natural risks.
The subject of the stability of flows bringing air to the longwall is of utmost importance. In the event of a fire, weak and unstable air flows pose a risk of reversed flow. The stability of ventilation in exploitation areas is important not only for underground fires, but also for ventilating zones of methane hazards [4,11,12]. Changes in ventilation conditions in those zones may lead to a build-up of hazardous methane concentrations at the workplace. This not only results from the lack of a sufficient air volume needed to dilute the methane, but is also due to the gaseous dynamic processes present at the longwalls. The vital issue while ventilating mining areas is the variability in time for the output of the existing methane sources, which largely depends on the exploitation advance and ventilation conditions. Ventilation disturbances cause the air volumes migrating through the goaf to change and, consequently, result in changes in the methane quantities released from the goaf. The liberation of methane from the worked out area (goaf) is one of the most variable and difficult to control methane sources at the longwall, the activity of which mainly depends on the stability of air flow through the area. Therefore, the problem of possible flow irregularities apparent in the changed air output and its flow directions in specific branches of the ventilation network is of the utmost importance for the fire and methane safety of every mine.
A useful addition to the evaluation of air flow stability is a determination of the indices of the sensitivity of the main flows in ventilation subnetworks to the changes in the aerodynamic resistance of workings [13,14,15]. This parameter shows the degree of dependency of the air volume stream in a given working to the resistance of other workings forming the network. According to the experience of the employees of Polish mines, any kind of ventilation network should be checked for the potential of flow reversals in case of a fire. Recently, new longwalls in some Polish collieries have been developed in seams located deeper then the bottom of the intake shaft. Such a solution is called “exploitation below the level of access” or “sublevel” in short. In this solution, the air is supplied through descending currents, making them more prone to the flow direction reversal in case of a fire. For all cases, it is important to study the potential for changes in the stream volume and fire gasses when a fire develops. Therefore, a new approach is proposed for the subject of air flow assessment in workings below the level of access, and formulas are developed for a determination of the sensitivity of local air flows for the change (decrease) of air density.
For the formulae and equations presented, algorithms are proposed, based on which new procedures for the Ventgraph program have been developed [5]. Examples are presented to illustrate the performance of the new calculation capacities of the Ventgraph program. The results prove their usefulness for analyzing the changes of air flow direction and distribution in a ventilation system of an underground mine.
2. Calculation of Airflows in Workings of a Mine Ventilation Network with the Ventgraph Software
The mine ventilation system may be represented as a network, in which shafts, galleries, and longwalls are branches and places where they intersect are nodes. Then, the flow distribution may be calculated from the following system of matrix equations:
- Equation of the mass flow balance in the network nodes (Kirchhoff’s First Law)
- Equation of the pressure balance for independent loops (circuits) of the ventilation network (Kirchhoff’s Second Law)
- Equation linking the air mass streams in branches with loop streams
where
| a | — matrix of node-branch incidence of I × J dimension, |
| ai,j = 1 | — branch j is oriented towards node i, |
| ai,j = −1 | — branch j is oriented from node i, |
| ai,j = 0 | — node i is not a node of branch j, |
| b | — matrix of loop-branch incidence of K × J dimension, |
| bk,j = 1 | — loop k contains branch j, and the branch and loop orientations are consistent, |
| bk,j = −1 | — loop k contains branch j, and the branch and loop orientations are opposite, |
| bk,j = 0 | — loop k does not contain branch j, |
| I | — number of network nodes, |
| J | — number of branches in the network, |
| K | — number of independent loops in the network, K = J – I + 1, |
| q | — column matrix of air mass streams in branches qm j of dimension J, |
| p | — column matrix of branch pressure differences Δpj of dimension J, |
| Q | — column matrix of loop air mass streams Qk of dimension K, |
| 0 | — column zero matrix of dimension J. |
The difference in branch pressures Δpj for branch j is given by the Formula [16]:
where
| p0 j, pL j | — static pressures at the beginning and at the end of branch j, |
| q j | — air volume stream in branch j, |
| Rb j | — aerodynamic resistance of branch j, |
| Rl j | — local aerodynamic resistance in branch j (e.g., a ventilation door), |
| g | — acceleration of gravity, |
| ρav j | — average air density in branch j, |
| z0 j, zL j | — elevation of the beginning and of the end of branch j, |
| hw j | — pressure of a fan (if present) in branch j. |
The aerodynamic resistance of branch Rb and local aerodynamic resistance Rl for the air mass stream are given by the following formula:
where
| λ, ζ | — dimensionless coefficients of the branch resistance and of the local resistance, |
| ρav | — average air density in the branch, |
| A | — area of the branch cross-section, |
| P | — circumference of the branch cross-section, |
| L | — length of the branch. |
There is a relationship between the air mass stream q and volume stream qV
The average air density in the branch is given by the following formula:
where
| pav | — average atmospheric pressure in the branch , |
| p0, pL | — atmospheric pressures at the beginning and at the end of the branch, |
| Tav | — average air temperature (in K) in the branch |
| T0, TL | — air temperature at the beginning and at the end of the air split, |
| ℜ n | — gas constant of n-th air component, |
| CM n | — mass fraction of n-th air component. |
The Ventgraph software, developed at the Strata Mechanics Research Institute of the Polish Academy of Sciences [5], is a typical representation of computer software, in which a numerical method for airflow distribution is based on the Kirchhoff’s Second Law (2). The algorithm of the steady state computation is based on the one-dimensional mathematical model of air flow in the network, given above. This model is based on the equation describing the air flow in ventilation network branches. The software adopts a numerical algorithm for this system solution based on the modified Euler method, provided by Hardy Cross [14,17,18]. It is necessary to emphasize here, that the adopted mathematical model of flow takes into account changes in air density caused by the changes in atmospheric pressure and by the changes in air composition and temperature [3,5,7]. As a result, most phenomena, which could affect the airflows in the network, have been considered.
The software algorithm contains a number of possibilities related to the regulation of the ventilation network (calculations of the ventilation door resistance value or of the auxiliary fan pressure), including the control of the network condition and designing new workings, etc. The software contains an interactive graphical user interface. The results of the calculations are presented in an isometric diagram of a specific ventilation network.
3. Sensitivity of Local Area Air Flows
An important parameter for the evaluation and analysis of ventilation systems is the sensitivity of local area air flows. This parameter shows the degree of sensitivity of an air volume stream in a given working to disturbances in the workings forming the network. In the study, it is assumed that the disturbances can be resistance changes of ventilation branches and air density variations in those branches as a result of fire or methane inflow.
3.1. Indicator of Volume Stream Sensitivity in Branch i to Resistance Change in Branch j
The volume stream sensitivity in branch i to resistance changes in the ventilation network branches can be determined with the aid of the sensitivity indicator, defined as follows [15,19]:
where:
| qVi | — air volume stream in branch i; |
| Rj | — aerodynamic resistance in branch j. |
The resistance sensitivity indicator shows how the air stream in branch i changes due to the changed resistance of branch j. The higher the indicator’s absolute value, the higher the change in the air stream in branch i resulting from the change in the branch j resistance. The indicator’s sign shows the direction of change (decrease for negative).
A good approximation of this derivative value in the surroundings Rj is the following expression:
where a2,i,j and a1,i,j are factors of the parabola estimating the dependency :
The calculation of those factors requires the solution of the ventilation network for three resistance values Rj:
Now, the factors a0,i,j, a1,i,j, and a2,i,jj can be calculated by solving the system of equations, which takes the following form in matrix notation:
where
This system solution has the form:
where:
Determinant DR equals:
and K is the matrix of cofactors of the transpose of matrix, RT.
The factors a1,i,j and a2,i,j calculated from Equation (14) equal:
Co-factors in the Equations (17) and (18) equal:
Having calculated the factors a2,i,j and a1,i,j from the Equations (17) and (18), from Equations (8) and (9), the resistance sensitivity indicator showing the air volume stream sensitivity in branch i to the change in resistance in branch j can be calculated.
where qV i,1, qV i,2, and qV i,3—the air volume streams in branch i calculated for the resistance values Rj1, Rj2, and Rj3 of branch j, respectively.
Values of the factors AR j,1, AR j,2, and AR j,3 are determined by the Equation:
In the calculations, the following resistance for branch j is assumed:
Let ΔR be some fraction of the resistance value Rj so that:
where Rj—aerodynamic resistance in branch j.
The resistance sensitivity indicator equals:
The solution of a ventilation network for two resistance values Rj allows for the calculation of the sensitivity indicator [εi,j] for all sensitivity indicators located in column j of the sensitivity indicator matrix with dimensions J × J, where J is the number of branches in the ventilation network.
3.2. Interpretation of the Sensitivity Indicator in Terms of Resistance Change in the Brzanch
Having analyzed the indicators of air volume stream sensitivity to resistance changes in branches calculated for a ventilation network in terms of the value module and sign, it may be concluded that:
- A negative sign for the indicator corresponds to the basic dependency between the air volume stream and aerodynamic resistance, i.e., the volume stream decreases with an increase in the branch resistance.
- The module of indicator values enables the selection of branches in which the resistance change considerably affects the volume stream in a selected branch, i.e., parameters significant for the network regulation.
For example, when the indicator of air volume stream sensitivity in branch i to resistance change in branch j equals εi,j = −2, it means that an increase of resistance in branch j of 10% will cause the volume stream value in branch i to decrease by approximately 20%. The approximation results from the fact that the dependency between the air stream volume in branch i and the resistance in branch j is not linear.
3.3. Indicator of Volume Stream Sensitivity in Branch i to Air Density Change in Branch j
Similarly to the branch resistance, the density sensitivity indicator showing the volume stream sensitivity in a branch to air density changes in the ventilation network may be defined as:
where: qVi—the air volume stream in branch i; ρj—the air density in branch j.
The indicator of sensitivity to air density change is calculated in the same way as the indicator of sensitivity to branch resistance change, with the difference that in Equations (9)–(11), the resistance of the j-th branch Rj is replaced with the air density in this branch ρj, and Formula (12) takes the form:
where matrix G equals
For calculations, the following air density values may be assumed for branch j:
Let Δρ be some factor of air density value ρj so that:
where: ρj—the aerodynamic resistance in branch j.
The density sensitivity indicator equals:
The solution of a ventilation network for two air density values ρj enables a calculation of the density sensitivity indicator [κi,j] for all network branches in column j of the sensitivity factor matrices with dimensions J × J, where J is the number of branches in the ventilation network.
3.4. Interpretation of the Sensitivity Indicator in Terms of Air Density Changes
Having analyzed the indicators of air volume stream sensitivity to air density changes in the branches in terms of the value module and sign, it may be concluded that:
- A positive sign for the indicator means an increase in the air volume stream value in the branch, together with an increase in the air density in a different branch and a decrease in the stream value with decreasing air density in another branch.
- A decrease in air density in a working occurs in the case of a fire or methane inflow.
- The module of indicator values enables a selection of the branches in which the air density change considerably affects the volume stream in a selected branch. In combination with a positive sign for the indicator, this may indicate the possibility of reversing the air flow direction.
For example, when the sensitivity indicator of the air volume stream in branch i to air density change in branch j is κi,j > 2, this means that, in branch i, there is the probability of reversing the air flow direction. The limit value of the indicator κi,j = 2 results from the assumption that the air density value in the case of a fire in branch j could drop by as much as 50%, and would be accompanied by an air volume stream reduction in branch i of as much as 100%.
4. New Procedures with the Ventgraph Program
The above Equations, enabling the determination of the sensitivity of local area air flows, have enabled the development of a series of new procedures for the Ventgraph program.
In the GRAS module of the Ventgraph program, a new option—‘Indicators’—has been added. This includes a sub-option for the calculation of a sensitivity indicator for a selected branch. Functions of the new procedures of the program are shown in Figure 1, for example, in the area of longwall F-3 under liquidation, and the F-4 longwall in the reinforcement phase.
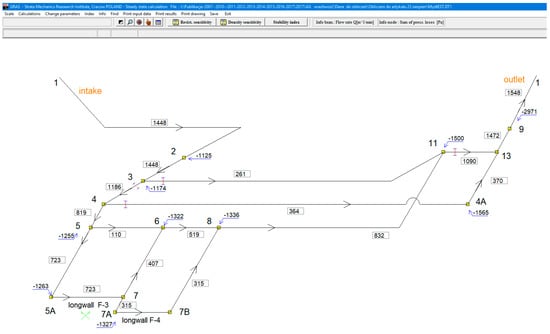
Figure 1.
Ventgraph program window, GRAS module. In rectangles—air flow volume stream (m3/min); In nodes—potential values (relative pressure, Pa); Arrows show the direction of flow; Numbers at junctions serve for are their identification.
Details of the network structures, workings of the area, and parameters describing the flow in the workings region are listed in Figure 2, which is a copy of a Ventgraph screen [5,6].
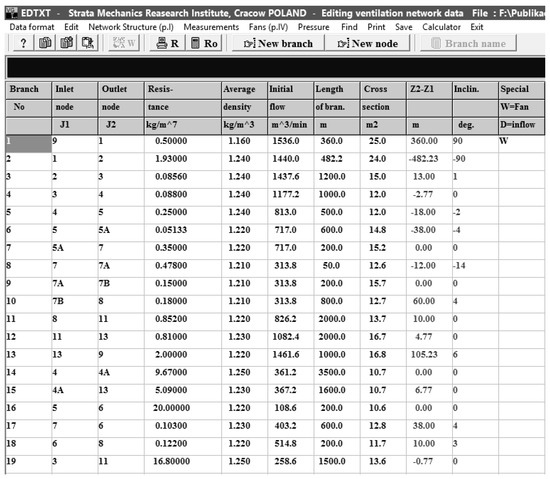
Figure 2.
Details of the network structures.
The mine working area (subnetwork), as shown in Figure 1, was selected to exemplify calculations of the sensitivity indicator εi,j. In the GRAS steady flow calculation module of the Ventgraph program, an additional ‘Indicators’ option is provided in the program menu. To make calculations after using this option, choose the ‘Sensitivity indicators for selected branch’ sub-option. When selected, and the ith branch is indicated, a program window is opened, as shown in Figure 3.
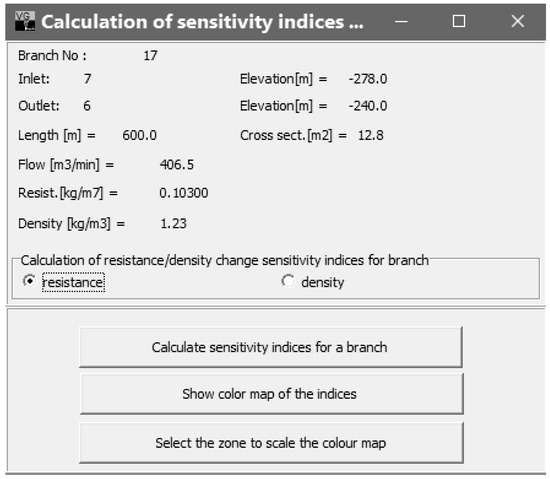
Figure 3.
Calculating sensitivity indicators for branch 17.
From the window shown in Figure 3, the sensitivity indicators may be calculated for branches of the selected area, due to the change in aerodynamic resistance of branch 17 or the change in density in that branch. Click on the active option button to make the selection.
With this function, sensitivity indicators shall be calculated for the network branches, due to the change in the chosen branch:
- Resistance—left-hand button of the window;
- Density—right-hand button of the window.
The matrix of sensitivity indicators created may be saved as a file with an extension ‘name.wrR’ or ‘name.wRo’, where the name is given by the user. This saving is enabled by the program option ‘Resist. Sensitivity’ and ‘Density Sensitivity’ available in the top bar (Figure 1) of the Ventgraph program.
The data are saved in a text file that can be read by MS Excel or Notepad. The sensitivity matrix εi,j determined for a sample working network is presented below in Table 1 (for resistance changes) and in Table 2 (for density changes). Row numbers in the tables correspond to the numbers of branches in which the air volume stream is changed as a result of resistance change (Table 1) or air density (Table 2) in the branch with the table column name.

Table 1.
Complete sensitivity matrix εi,j of a network of mine workings for aerodynamic resistance changes.

Table 2.
Complete sensitivity matrix κi,j of a network of mine workings for air density changes in branches.
For example, line 6 of Table 1 shows the sensitivity to ΔR—the change in the resistance of branch no 6. The position of column 1 of this line shows the values and sign of the flow change ΔQ in branch 1, column 2 refers to branch 2, and so on. A negative value of the sensitivity index in the branch different to branch no 6 means a possibility of the change of flow direction.
For Table 2, the interpretation is the same with respect to the response to the density changes Δρ. Line 6 describes the change of flow ΔQ in branches resulting from the variation of density Δρ in branch 6. A positive value of the sensitivity index shows the possibility of the change of flow direction. Changes of the density of air act in a twofold manner: by changing the value of resistance Equation (5) and through the natural ventilation pressure term of Equation (4), connected to the inclination of the branch.
An important part of working with a computer program is to adopt a ‘useful and friendly’ way of presenting the results of any determined sensitivity matrix, so that the information presented is useful in practice, particularly regarding air flow adjustment in a complex network of workings. Therefore, a graphic presentation of the results in an isometric diagram of the network of workings was proposed. The existing experience proves that, from a practical point of view, such a presentation of results provides useful data for a ventilation engineer.
Because of the size of the sensitivity matrix and the availability of only up to eight colors in the Ventgraph program, it was proposed that only the results for the given area of workings selected in the diagram should be shown. After choosing the option in the lower window shown in Figure 3, ‘Select network area to display indicators in color scale’, click the left mouse button and, keeping it pressed, drag the mouse to expand the white rectangular contours. Release the mouse button to finish the selection of the network area to display. Then, place the mouse cursor in the white rectangle area (cursor form changes) and click the mouse to display the sensitivity indicator in the selected color scale.
After their values are calculated by the program, the network branches shall be displayed in colors from the color scale presented in a separate panel. The borders of the color scale are calculated from the indicator module, starting from 0, to the maximum absolute value of the indicator (divided equally into eight colors). Branches for which the indicator value is positive are represented with dashed lines, and the negative ones with continuous lines. The branch for which the indicators are calculated is additionally marked with a double line in the relevant color.
Figure 4 shows, on the basis of a test example, the result of the calculation of sensitivity indicators
for the change in branch resistance of No. 17 (inlet-node 7–outlet-node 6); this branch is marked with bold lines and, in this case, in a violet color.
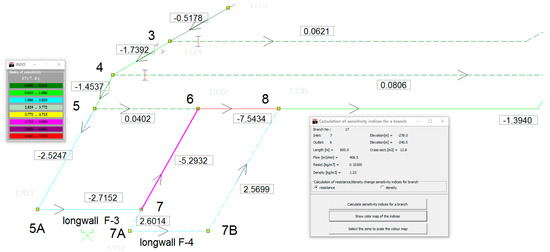
Figure 4.
Ventilation network area with the presentation of a sensitivity indicator for resistance changes of a branch in the adopted color scale. In rectangles—value of sensitivity; Arrows show the direction of flow; Numbers at junctions serve for are their identification.
Figure 5 shows the area of longwall N-15, for which the sensitivity indicators determined are presented graphically, for a density change in working no. 377, i.e., longwall N-15. The sample ventilation network of mine ‘K’ is created from 498 workings (branches). An interpretation of the sensitivity indicators is given in Section 3.2 and Section 3.4. Branch 377 is ascending and has a negative value of the density change sensitivity indicator. The decrease of density, for example, because of a fire in this branch, will cause the increase of flow.
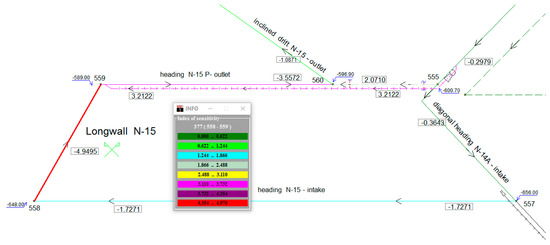
Figure 5.
Ventilation network area with the presentation of a sensitivity indicator for air density changes in the adopted color scale. In rectangles—value of sensitivity; In nodes—elevation (m); Arrows show the direction of flow; Numbers at junctions serve for are their identification.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents new options for determining the sensitivity of local subnetwork flows to the change in air flow directions. The method chosen to meet the objective involves an extended possibility to predict the process of ventilation, air distribution and, in the case of an underground fire, the spread of fire gasses. The widespread use of computer programs, including the Ventgraph system, facilitates the assessment by mine ventilation services of the stability of ventilation systems in exploitation areas and a determination of the sensitivity of local area flows to changes of air flow directions.
While analyzing air distributions for the exploitation below the level of access, the application of current numerical models for calculations of the distributions results in tangible benefits, such as an evaluation of the safety or risk levels for such exploitation. Application of the Ventgraph computer program, and particularly the module POŻAR (fire) [20], together with the newly developed options, enables a comprehensive analysis of the distribution for the real risks present in a specific case during exploitation below the level of access. The analyses performed and examples presented support the following statements:
- For the evaluation of air flow in workings below the level of access, a new approach to the problem has been proposed and Equations have been developed to determine the sensitivity of local area air flows due to the change (decrease) in air density. Determination of the sensitivity of the local area air flows presents the degree of dependency of the air volume stream in a given working on the changes of resistance or density in other workings included in the network. Interpretations of the sensitivity indicator are presented in Section 3.3 and Section 3.4.
- Since it is difficult to predict the distribution of fire gasses in the case of an underground fire, for newly designed working areas below the level of access, it is recommended that the possibility of changes in the volume (mass) of air flow (fire gasses) during a fire be investigated using the POŻAR (fire) module of the Ventgraph program. Currently, this is the only tool enabling the prediction of variation in the duration of a fire and its impact on the distribution pattern of air and fire gasses. The results obtained confirm the usefulness of the algorithms developed for the analysis and assessment of changes in the direction and the volume stream of air flowing in the ventilation system of an underground mine.
- The observations and opinions of the ventilation services have confirmed the applicability and usability of both indices. In any case, a dedicated in-situ experiment to confirm the values of estimated indices would be useful.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The National Centre for Research and Development, Poland, Research project entitled “Improving occupational safety in mines” (SP/K/2/143445/11, 2011–2013).
Author Contributions
Wacław Dziurzyński: analysis of calculation results and wrote the article; Andrzej Krach: calculation algorithm and wrote the article; Teresa Pałka: programming algorithms for Ventgraph;
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dziurzyński, W.; Krawczyk, J. Calculation possibilities of selected simulation programmes applied in the world mining industry describing the flow of air, fire gases and methane in the mine workings network. Prz. Gór. 2012, 5, 1–11. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Dziurzyński, W.; Krawczyk, J. Unsteady flow of gases in a mine ventilation network—A numerical simulation. Arch. Min. Sci. 2001, 46, 119–137. [Google Scholar]
- Dziurzyński, W.; Kruczkowski, J. Validation of the mathematical model used the Ventgraph program on the example of the introduction of new headings to the ventilation network of mine. Arch. Min. Sci. 2007, 52, 155–169. [Google Scholar]
- Dziurzyński, W.; Krawczyk, J.; Pałka, T. Computer simulation of air and methane flow following an outburst in transport gallery D-6, bed 409/4. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2008, 108, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Dziurzyński, W.; Pałka, T.; Krawczyk, J. Ventgraph for Windows—Ventilation Engineer’s Program System for Analyzing the Ventilation Network under Normal and Emergency Conditions—Simulation of Transient Flow of Air and Fire Gases—Manuals; Transaction of Strata Mechanics Research Institute: Krakow, Poland, 2013; pp. 1–100. [Google Scholar]
- Dziurzyński, W.; Pałka, T.; Krach, A. A reliable method of completing and compensating the results of measurements of flow parameters in a network of headings. Arch. Min. Sci. 2015, 60, 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gillies, A.D.S.; Wu, H.W.; Wala, A.M. Australian Mine Emergency Exercises Aided by Fire Simulation. Arch. Min. Sci. 2005, 50, 17–47. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, C.J. Validation of the Ventgraph program for use in metal/non-metal mines. In Proceedings of the 13th United States/North American Mine Ventilation Symposium, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 13–16 June 2010; pp. 455–462. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, J.; Janus, J. Modelling of the propagation of methane from the longwall goaf, performed by means of a two-dimensional description. Arch. Min. Sci. 2014, 59, 851–868. [Google Scholar]
- Kurnia, J.C.; Sasmito, A.P.; Mujumda, A. CFD simulation of methane dispersion and innovative methane management in underground mining faces. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 3467–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotniczny, P. Transient states in the flow of the air-methane mixture at the longwall outlet, induced by a sudden methane outflow. Arch. Min. Sci. 2014, 59, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystroń, H. An Approach to Mine Ventilation based on Aerodynamic Potential of Ventilating Air with Reference to Unit Mass of Dry Air. In Mine Environment and Ventilation, Abingdon, Oxon, UK; Panigrahi, D.C., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Kocsi, C.; Hardcastle, S. Sensitivity analysis on parameter changes in underground mine ventilation Systems. J. Coal Sci. Eng. 2011, 17, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, H.L.; Mutmansky, J.M.; Ramani, R.V.; Wang, Y.J. Mine Ventilation and Air Conditioning, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Jiang, S.; Dong, S. Selection and Application of Ventilation System’s Sensitive Branches Based on the Sensitivity. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1010–1012, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trutwin, W. On transients of airflow in mine workings. Min. Sci. Technol. 1988, 6, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, H. Analysis of Flow in Networks of Conduits or Conductors, Engineering Experiment Station; University of Illinois Bulletin: Urbana, IL, USA, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Volokh, K.Y. On foundations of the Hardy Cross method. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2002, 39, 4197–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarczyk, M. The Influence of the Structure of Mine Ventilation Networks on the Sensitivity of Air Currents to Changes in the Resistance of Side Branches; Zeszyty Naukowe Politechniki Śląskiej—Górnictwo 214; WPŚ: Gliwice, Poland, 1993; pp. 1–204. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Gillies, A.D.S.; Wala, A.M.; Wu, H.W. Simulation of the Effects of Inertisation of Fires on Mine Ventilation Systems. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Mine Ventilation Congress, Brisbane, Australia, 6–8 July 2005; pp. 317–324. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).