Repair of Orbital Floor Fractures: Our Experience and New Technical Findings
Abstract
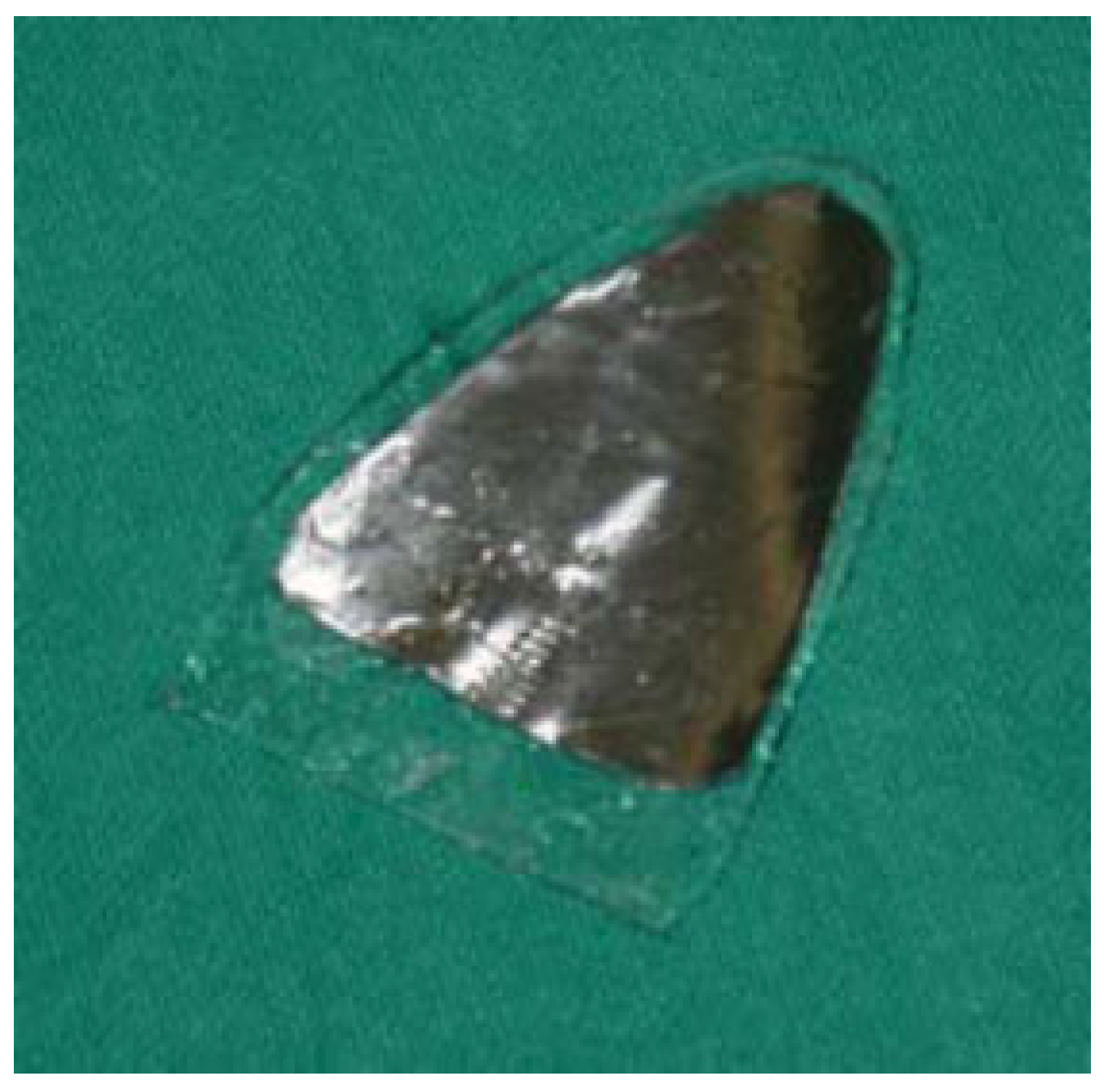
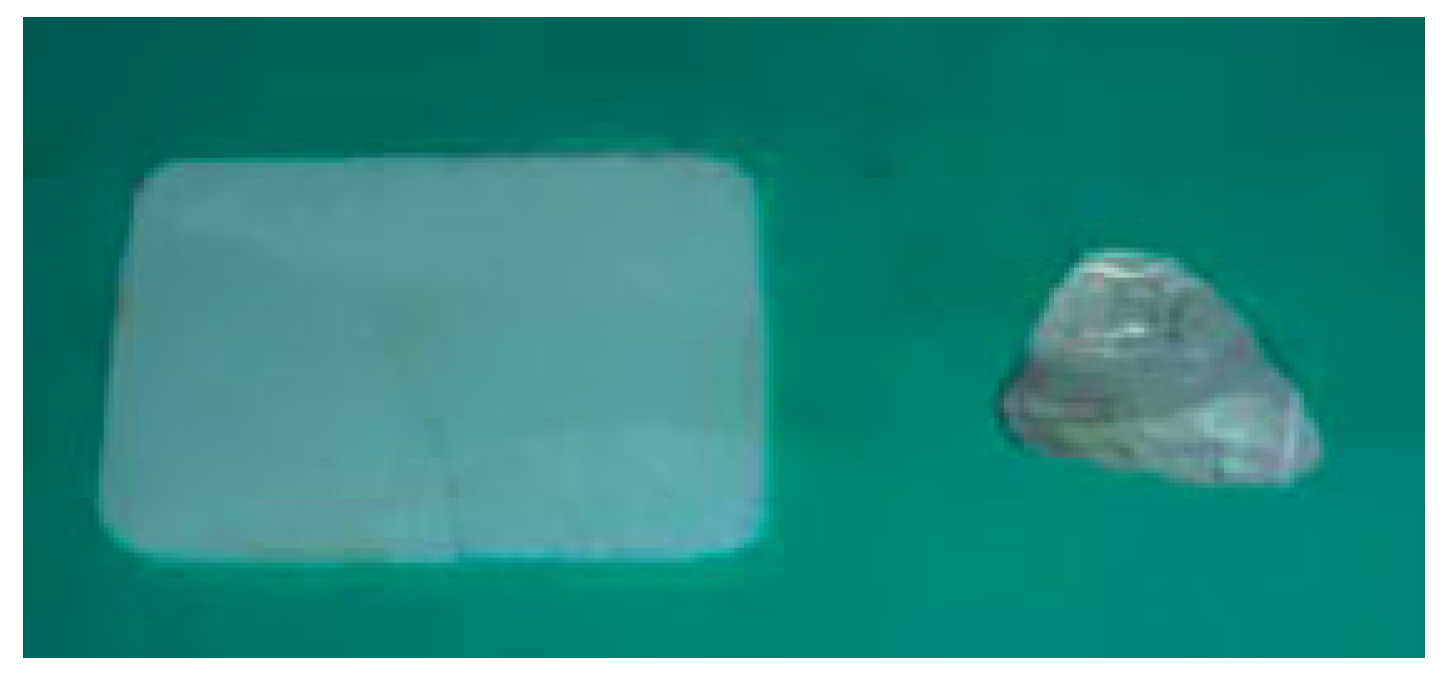
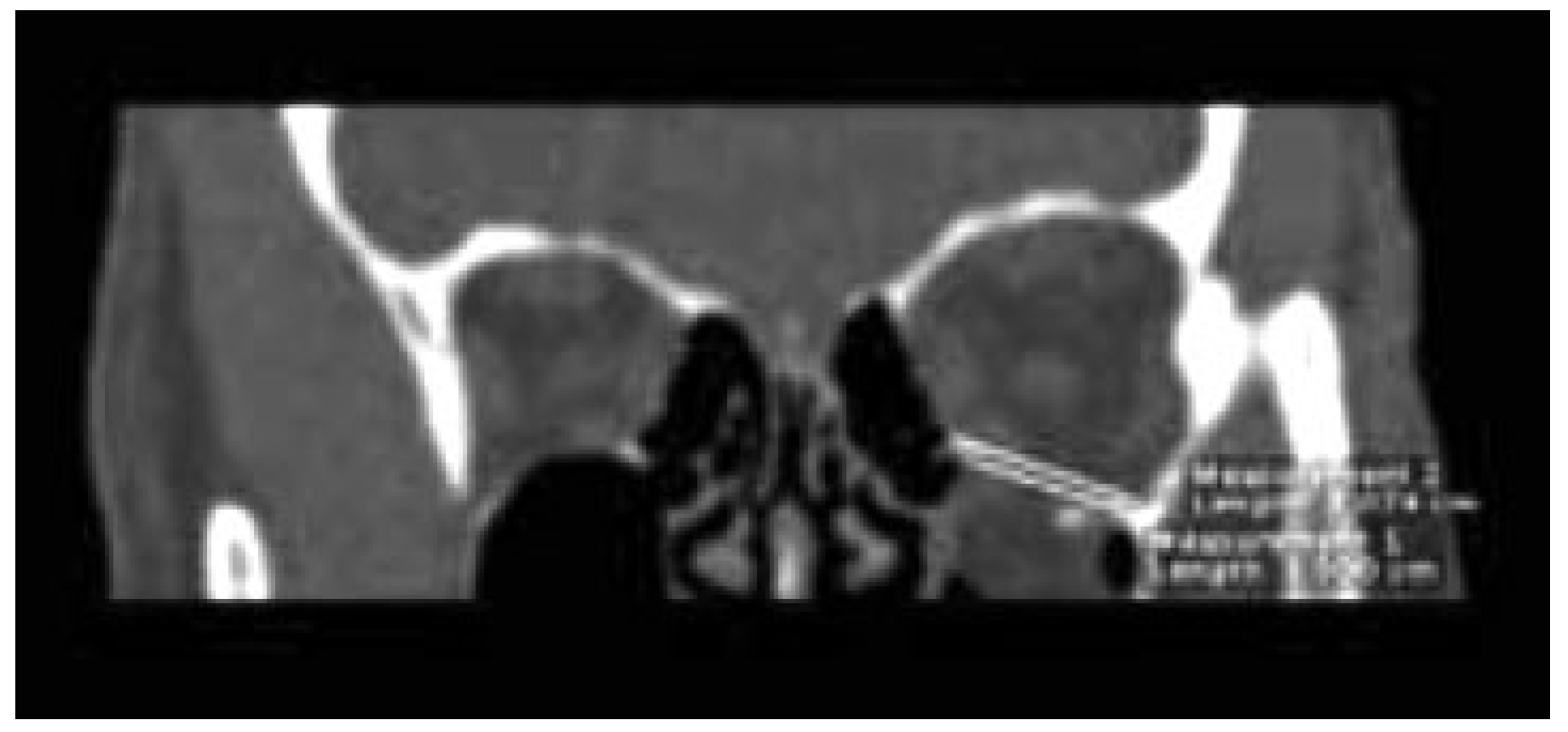
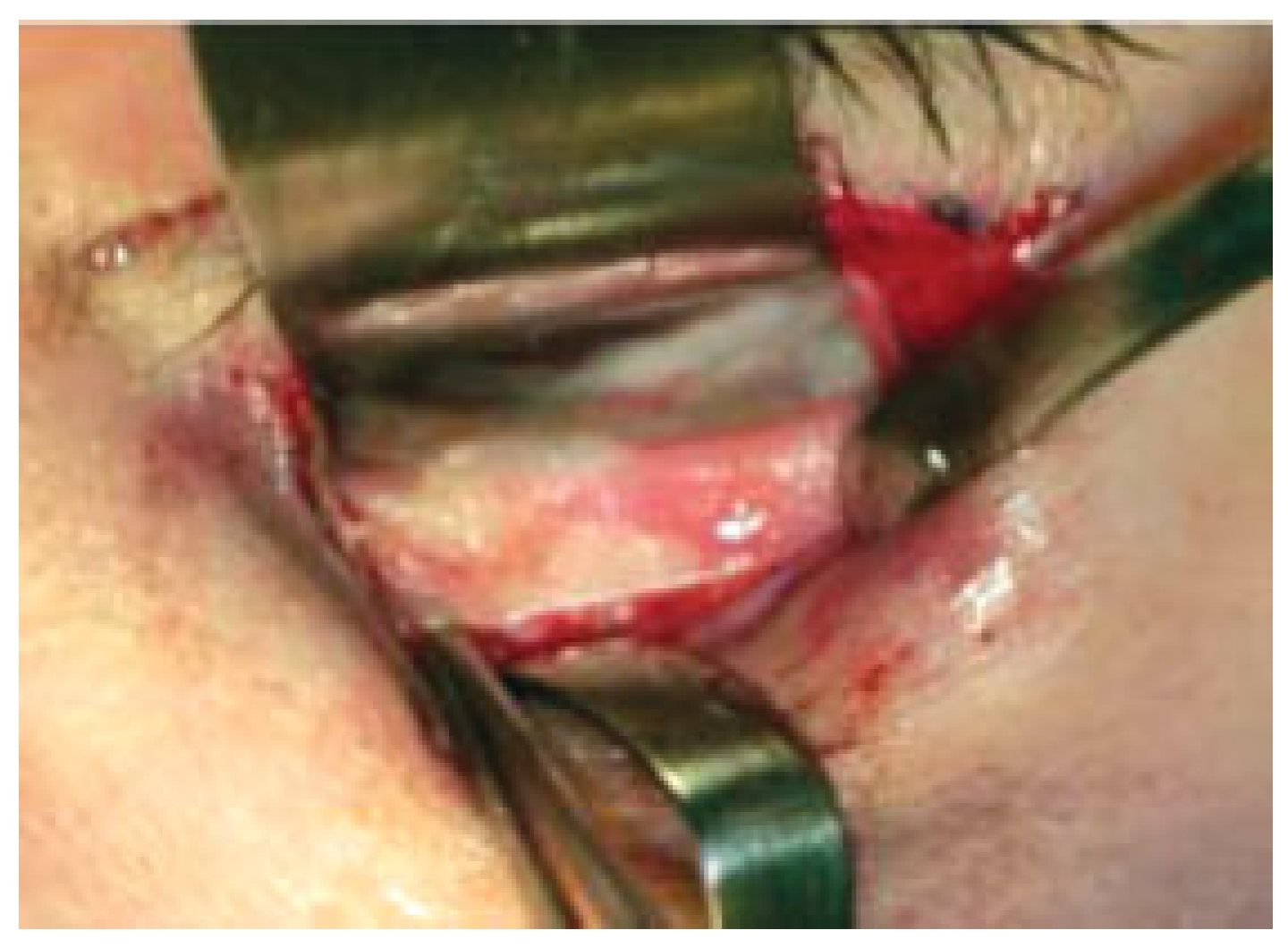
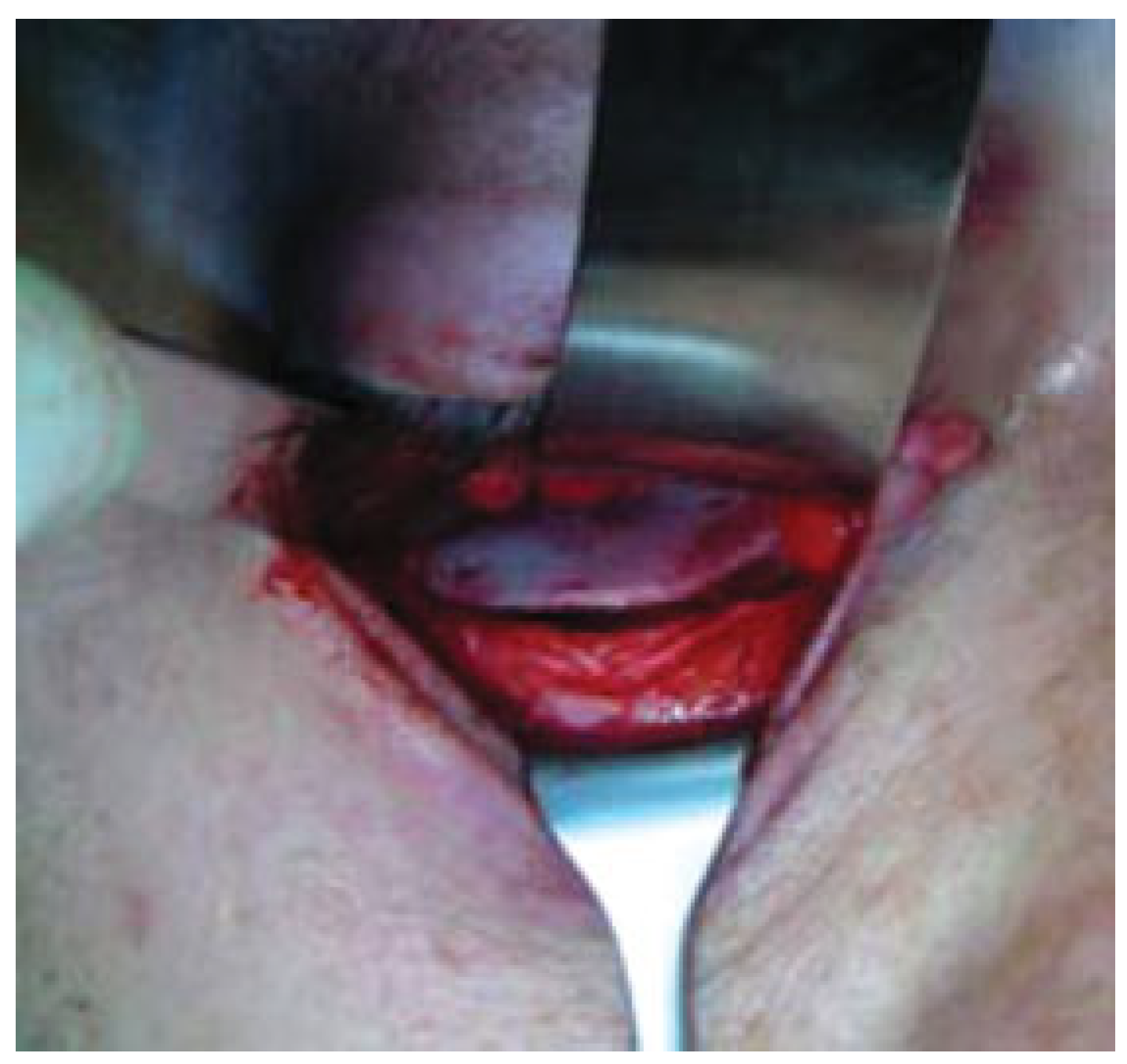
:Materials and Methods
Discussion
Conclusion
References
- Jank, S.; Schuchter, B.; Emshoff, R.; et al. Clinical signs of orbital wall fractures as a function of anatomic location. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2003, 96, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolidis, S.; Weeks, B.H.; Kirby, M.; Scarlett, M.; Hollier, L. Classification and surgical management of orbital fractures: experience with 111 orbital reconstructions. J Craniofac Surg 2002, 13, 726–737; discussion 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Bauer, R.J.; Buchman, S.R. A current 10-year retrospective survey of 199 surgically treated orbital floor fractures in a nonurban tertiary care center. Plast Reconstr Surg 2001, 108, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, F.; Kirkpatrick, N.A.; Lyne, J.; Urdang, M.; Waterhouse, N. Buckling and hydraulic mechanisms in orbital blowout fractures: fact or fiction? J Craniofac Surg 2006, 17, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punke, C.; Fritsche, A.; Martin, H.; Schmitz, K.P.; Pau, H.W.; Kramp, B. Investigation of the mechanisms involved in isolated orbital floor fracture. Simulation using a finite element model of the human skull. HNO 2007, 55, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burnstine, M.A. Clinical recommendations for repair of isolated orbital floor fractures: an evidence-based analysis. Ophthalmology 2002, 109, 1207–1210; discussion 1210–1211; quiz 1212–1213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dietz, A.; Ziegler, C.M.; Dacho, A.; et al. Effectiveness of a new perforated 0.15 mm poly-p-dioxanon-foil versus titaniumdynamic mesh in reconstruction of the orbital floor. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2001, 29, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Converse, J.M. Two plastic operations for repair of orbit following severe trauma and extensive comminuted fracture. Arch Ophthalmol 1944, 31, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, H.; Sugawara, Y.; Uda, H.; Kobayashi, N. The transconjunctival approach for orbital bony surgery: in which cases should it be used? J Craniofac Surg 2004, 15, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villarreal, P.M.; Monje, F.; Morillo, A.J.; Junquera, L.M.; Gonzalez, C.; Barbon, J.J. Porous polyethylene implants in orbital floor reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2002, 109, 877–885; discussion 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutaz, B.H. Biomaterials used on orbital floor fractures for reconstruction via the transconjunctival approach. Oper Tech Plastic Reconstr Surg 2003, 9, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrich, R.J.; Janis, J.E.; Adams, W.P.J.r. Subciliary versus subtarsal approaches to orbitozygomatic fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg 2003, 111, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, A.; Burggasser, G.; Gauss, N.; Ewers, R. Orbital floor reconstruction with an alloplastic resorbable polydioxanone sheet. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2002, 31, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchel, P.; Rahal, A.; Seto, I.; Iizuka, T. Reconstruction of orbital floor fracture with polyglactin 910/polydioxanon patch (ethisorb): a retrospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005, 63, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Ophthalmic Signs and Symptoms | Patients |
|---|---|
| Periorbital ecchymosis (%) | 75 |
| Subconjunctival hemorrhage (%) | 92 |
| Periorbital swelling and/or edema (%) | 33 |
| Diplopia, n (%)* | 18 (60) |
| Altered ocular motility, n (%)* | 8 (25) |
| Infraorbital nerve anesthesia, n (%)* | 22 (75) |
| Enophthalmos, n (%)* | 23 (76) |
| Hypoglobus, n (%)* | 7 (24) |
| Ophthalmic Signs and Symptoms* | Large Defect | Small Defect |
|---|---|---|
| Diplopia | 16 | 2 |
| Altered ocular motility | 6 | 2 |
| Infraorbital nerve anesthesia | 18 | 4 |
| Enophthalmos | 21 | 2 |
| Hypoglobus | 5 | 2 |
| Patient | Age | Cause | Type | Materials |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | Sports | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 2 | 83 | Vehicle accident | Small | Resorbable |
| 3 | 49 | Assault | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 4 | 45 | Vehicle accident | Small | Resorbable |
| 5 | 55 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 6 | 30 | Sports | Small | Resorbable |
| 7 | 39 | Fireworks | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 8 | 56 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 9 | 16 | Sports | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 10 | 32 | Assault | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 11 | 45 | Sports | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 12 | 36 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 13 | 23 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 14 | 63 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 15 | 39 | Assault | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 16 | 44 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 17 | 27 | Sports | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 18 | 86 | Fall | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 19 | 27 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 20 | 76 | Fall | Small | Resorbable |
| 21 | 65 | Assault | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 22 | 48 | Vehicle accident | Small | Resorbable |
| 23 | 67 | Assault | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 24 | 52 | Vehicle accident | Small | Resorbable |
| 25 | 45 | Sports | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 26 | 71 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 27 | 58 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 28 | 57 | Vehicle accident | Large | Nonresorbable |
| 29 | 61 | Assault | Small | Resorbable |
| 30 | 49 | Sports | Large | Nonresorbable |
| Ophthalmic Signs and Symptoms | Preoperative | Postoperative |
|---|---|---|
| Overall | ||
| Diplopia | 18 | 0 |
| Altered ocular motility | 8 | 0 |
| Infraorbital nerve anesthesia | 22 | 4 |
| Enophthalmos | 23 | 3 |
| Hypoglobus | 7 | 2 |
| Patients with large defects | ||
| Diplopia | 16 | 0 |
| Altered ocular motility | 6 | 0 |
| Infraorbital nerve anesthesia | 18 | 3 |
| Enophthalmos | 21 | 2 |
| Hypoglobus | 5 | 2 |
| Patients with small defects | ||
| Diplopia | 2 | 0 |
| Altered ocular motility | 2 | 0 |
| Infraorbital nerve anesthesia | 4 | 1 |
| Enophthalmos | 2 | 1 |
| Hypoglobus | 2 | 0 |
© 2010 by the author. The Author(s) 2010.
Share and Cite
Piombino, P.; Iaconetta, G.; Ciccarelli, R.; Romeo, A.; Spinzia, A.; Califano, L. Repair of Orbital Floor Fractures: Our Experience and New Technical Findings. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2010, 3, 217-221. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1268518
Piombino P, Iaconetta G, Ciccarelli R, Romeo A, Spinzia A, Califano L. Repair of Orbital Floor Fractures: Our Experience and New Technical Findings. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction. 2010; 3(4):217-221. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1268518
Chicago/Turabian StylePiombino, Pasquale, Giorgio Iaconetta, Roberto Ciccarelli, Antonio Romeo, Alessia Spinzia, and Luigi Califano. 2010. "Repair of Orbital Floor Fractures: Our Experience and New Technical Findings" Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction 3, no. 4: 217-221. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1268518
APA StylePiombino, P., Iaconetta, G., Ciccarelli, R., Romeo, A., Spinzia, A., & Califano, L. (2010). Repair of Orbital Floor Fractures: Our Experience and New Technical Findings. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction, 3(4), 217-221. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1268518



