Abstract
Substantial controversy exists regarding the timing of intervention and management of patients with orbital floor fractures. Recent advances in computer-aided technology, including the use of 3-dimensional printing, intraoperative navigational imaging, and the use of novel implants, have allowed for improvement in prospective management modalities. As such, this article aims to review the indications and timing of repair, surgical approaches, materials used for repair, and contemporary adjuncts to repair. Indications for orbital floor fracture repair remain controversial as many of these fractures heal without intervention or adverse sequelae. Intraoperative navigation and imaging, as well as endoscopic guidance, can improve visualization of defects mitigating implant positioning errors, thereby reducing the need for secondary corrective procedures. Patient-specific implants may be constructed to fit the individual patient’s anatomy using the preoperative CT dataset and mirroring the contralateral unaffected side and have been shown to improve pre-operative efficiency and minimize postoperative complications. With increased data, we can hope to form evidence-based indications for using particular biomaterials and the criteria for orbital defect characteristics, which may be best addressed by a specific surgical approach.
Introduction
Orbital floor fractures are a common outcome of trauma sustained to the midface. They are most commonly seen in the first 30 years of life.[1,2,3,4] The complex anatomy and proximity to vital structures present a reconstructive challenge to the surgeon. Furthermore, the approach to the management of these fractures is a source of continued controversy. Recent advances in computer-aided technology, including 3-dimensional printing, implementation of planning software, intraoperative navigational imaging, endoscopic guidance, and novel implants, have allowed for improvement in prospective management modalities. However, these innovations have also spurred further deliberation for the optimal approach and surgical correction of these complex injuries.[3,4]
Methods
A Pubmed and Cochrane search was performed with no date restrictions for literature on management of orbital floor fractures. The search terms used were “orbital floor fractures,” “management,” and various combinations of the terms. Articles not written in the English language were excluded.
Results
Indications and Timing of Repair
Indications for orbital floor fracture repair remain controversial as many of these fractures heal without intervention or adverse sequelae. Putterman et al. [2] recommended observation of all fractures for 4-6 months with late intervention if necessary for the development of enophthalmos or diplopia. On the contrary, other studies noted a significant increase in poor outcomes with the late repair of the fractures (>2 months).[3] In 2002, Burnstine[4] published recommendations for repair, which are widely employed by reconstructive surgeons but are primarily based on expert opinion. Despite these recommendations, there is still no consensus about which patients would benefit from surgical intervention, nor is there agreement about when the repair should be performed. Nevertheless, in all cases, a thorough history, clinical exam, and review of imaging are required to identify patients that may warrant urgent surgical exploration.
Urgent surgical repair is described as operative interventions in the first 24-48 hours after injury. Immediate intervention should be considered for early enophthalmos and hypoglobus, diplopia with evidence of muscle entrapment, hemorrhage, non-resolving oculocardiac reflex, and white-eyed blowout fractures in patients <18 years old (restriction of ocular mobility, entrapped soft tissue on imaging, and minimal periorbital ecchymosis or edema on the exam).[4] The oculocardiac reflex (OCR), though rare, results from pressure on the globe due to entrapped periorbital soft tissues and subsequent increase in efferent vagal tone causing syncope, bradycardia, potential heart block, nausea, and vomiting. The incidence of OCR varies widely in the literature depending on the clinical scenario, with a reported fatality risk of 1 in 3,500 cases.[5] Therefore, an immediate surgical exploration is indicated to prevent fatal cardiac arrhythmia.[5,6] Immediate repair has been shown to improve ocular motility in patients with signs of muscle entrapment due to the prevention of ischemic necrosis, resultant fibrosis, and strabismus. Delayed treatment of muscle entrapment has been shown to correlate with a higher incidence of persistent postoperative diplopia.[7,8,9] Several studies have shown that repair within 48 hours of injury significantly reduces this risk.[4,10,11,12,13]
Except for cases requiring urgent intervention, substantial controversy exists regarding the timing of treatment and identification of patients requiring surgical correction rather than observation. Bansagi and Meyer[10] evaluated 34 patients <18 years old with orbital floor fractures and found that early surgical intervention, defined as less than 2 weeks, resulted in a complete return of ocular motility compared with late intervention groups. Egbert et al.[11] observed a median time for improvement of preoperative duction deficits of 4 days for patients who underwent surgery within 7 days of the initial injury and 10.5 days for those who underwent repair after 14 days (P = 0.030). However, the timing of surgery did not affect the complete resolution of duction deficits or diplopia. Therefore, the authors concluded that early surgical repair resulted in more rapid improvement than a conservative delayed approach.[11]
Children tend to have greater bone elasticity allowing the orbital floor to bend and form a trapdoor (“white-eyed” fracture), where a bone fragment often hinged medially is transiently displaced inferiorly, allowing herniation of orbital contents into the maxillary sinus, thereby resulting in entrapment as the fragment returns to its prior position.[7,14,15] The blood flow to the entrapped tissue is compromised, resulting in muscle or fat ischemia, fibrosis, and diplopia. In contrast, adult patients have more brittle bones, which are more likely to break, resulting in tissue prolapse and an increase in orbital volume, which place the patient at risk for the development of enophthalmos hypoglobus, and diplopia.
In an attempt to better stratify patients, investigators have attempted to establish parameters to predict patients at high risk of late complications that may benefit from earlier intervention. These studies are largely based on CT findings evaluating the size (area) of the floor defect, the calculated change in orbital volume, or the degree of soft tissue herniation. Conventionally, defect size has been used as an indication for surgical repair, with fractures larger than 2 cm2 or defects greater than 50% of the orbital floor being the standard criteria for intervention.[3,16] Notably, studies have found that as little as a 5% increase in total orbital volume (~1.25 mL) is a predictor of clinically significant enophthalmos (>2 mm)[16,17,18,19] while others note that volume changes up to 1.5-2 mL or more can be observed.[16,20,21] Also, a linear association between an increase in orbital volume and enophthalmos has been demonstrated.[22]
Despite the criteria for early surgical intervention mentioned above, 7-10% of patients treated nonoperatively develop late enophthalmos.[3,23] Late correction of established enophthalmos has been associated with poor functional and cosmetic results due to fat atrophy and orbital fat scarring to the maxillary antrum.[3,24] However, in a study by Chen et al.,[25] authors conducted a study to evaluate the long-term enophthalmos outcomes following surgical management of different types of orbital fractures at various time intervals (<2 weeks, 2-4 weeks, and >4 weeks). The authors found no statistically significant differences in the enophthalmos improvement rates with surgical intervention at these various time intervals.
Diplopia secondary to muscle contusion or edema is also common after orbital injury and should continue to improve 2 weeks after injury. Patients with persistent diplopia associated with evidence of soft-tissue entrapment on computed tomographic (CT) imaging or positive forced duction test require surgical exploration and possible repair.[4] A study by Hawes and Dortzbach[3] showed a correlation between the time of repair and increased postoperative diplopia. Authors found 38% of patients undergoing surgery 2 months or longer after injury experienced persistent diplopia compared to only 7% who had surgery within 2 months. Similarly, Yu et al.[26] evaluated the impact of fracture type and timing of surgical intervention on diplopia outcomes and demonstrated that patients treated within 2 weeks of orbital injury exhibit a higher rate of diplopia resolution compared to those treated between 2-4 and more than 4 weeks.
Several studies have described rounding of the inferior rectus (IR) muscle as a relative indication for operative management. Matic and colleagues[27] found that a height-to-width ratio >1 in the inferior rectus muscle is predictive of late enophthalmos but not persistent diplopia (Figure 1). The authors postulate that the shape of the inferior rectus muscle may be a better predictor of post-traumatic enophthalmos than orbital floor defect size or orbital volume measurements as these values are only reflective of the status of osseous support while the former is representative of both bony and soft-tissue support.[27,28] A recent retrospective study by Gabrick et al.[29] correlated radiographic features of non-surgically managed orbital floor fractures with long-term patient-reported outcome measures (FACE-Q). They found a significant association between rounding the IR muscle and the appearancerelated psychosocial distress (P = 0.006). This factor should be considered when making decisions regarding the repair of orbital floor fractures.
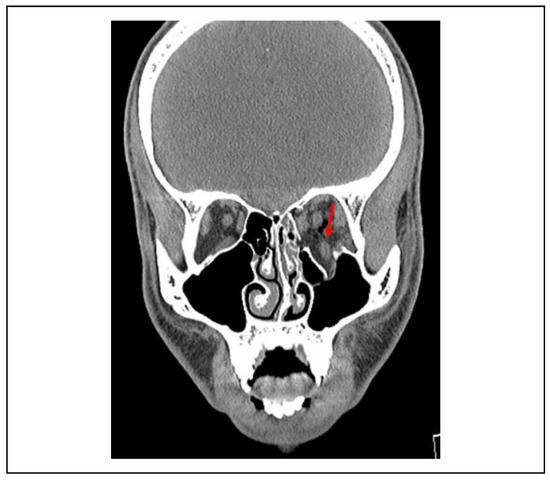
Figure 1.
Preoperative coronal soft tissue view of the orbital floor and medial wall fracture with inferior rectus (IR) muscle herniation. Shape of the inferior rectus muscle has been shown to be a better predictor of late enophthalmos.
Delayed Repair
Proponents of the delayed approach to the treatment of orbital fractures suggest that this allows for the resolution of traumatic edema before the repair allowing for proper identification of enophthalmos not initially appreciated on the exam and facilitating surgical exposure.[30] The goal of orbital fracture repair is not to achieve bone healing or prevent malunion like other fracture repairs but to reconstitute orbital volume allowing for the resolution of symptoms and intact vision. Patients that do not present with findings necessitating immediate intervention are routinely seen at a 2-week follow-up, at which time they are evaluated for unresolved or progressive symptoms such as infraorbital nerve hypoesthesia, diplopia, delayed enophthalmos, change in visual acuity, or hypoglobus. The development of these signs within the first 5-6 weeks after an injury should be considered a strong relative indication for surgery.[31] Progressive hypoesthesia of the V2 distribution of the infraorbital nerve has been demonstrated as a relative indication for surgical repair in patients with orbital floor fracture.[32,33]
Approach
The controversy surrounding the management of orbital floor fractures extends to the surgical approach as well. Unfortunately, there is still an insufficient level of evidence coupled with an inconsistency in outcome measures that has resulted in difficulty establishing a definitive evidence-based approach. Traditionally, external transorbital approaches have been used to repair orbital fractures, which provide exposure of the orbital floor and inferior orbital rim by one of several incisions: subciliary, subtarsal, transconjunctival, or transcaruncular.
The subciliary incision has been associated with a higher risk of cicatricial ectropion and may lead to significant scarring.[34] The subtarsal incision is generally considered the least technically demanding and provides the most direct access to the orbital rim and floor but has been noted to leave substantial visible scarring.[35,36,37] This remains a point of contention, as prior studies had shown that a subtarsal incision within a skin crease of the lower lid produced a superior aesthetic result compared to the options mentioned above.[38,39] The transconjunctival approach is the most extensively investigated method. This approach avoids scar formation and risk of ectropion; however, it is technically more advanced and does come with a risk of entropion. Complication rates in one meta-analysis were found to be the highest in the subciliary approach (19.1%) followed by the subtarsal approach (9.7%), and the lowest rate of complications was with transconjunctival access (2.1%).[40]
An alternative method to orbital floor management is a transantral approach under endoscopic guidance that is well-described in the literature.[41,42] This approach has been associated with minor complications such as transient infraorbital hypoesthesia or anesthesia; however, it allows successful reconstruction of orbital floor defects while minimizing manipulation of the globe and eliminating a lower eyelid incision. The transantral endoscopic approach has also shown efficacy in repairing complex orbital fractures beyond an isolated floor fracture.[42] Certainly, a surgeon’s familiarity with a particular technique and the patient’s distinct presentation are important factors in decision-making regarding the most appropriate approach.
Reconstruction of the Orbital Floor—Orbital Implants
Many materials have been described in the literature for orbital floor repair and may be divided into biological or alloplastic composition. The findings in the literature have been inconsistent and are largely retrospective case series with limited subjects without conclusive data.[43,44,45] Additionally, individual surgeon preferences vary on the type of orbital implant.[46] The choice of material is dependent on biocompatibility instead of the strength of graft material.[47] Biological materials offer several potential advantages, including improved biocompatibility but are limited by their donor site morbidity.[48,49] Synthetic, or alloplastic grafts, have been associated with higher rates of complications in the literature, including infection and extrusion of the material, but have the advantage of being readily obtainable, avoiding donor site complications.[50] Generally, rates of complications remain low and are attributed to the state of the orbital soft tissue at the time of repair. Regardless of the type of implant chosen, key factors to consider include assuring implants are placed on stable bony ledges, normal orbital volume is restored, soft-tissue contents are adequately reduced, and the normal orbital floor shape is restored. Rather than being a straight line and conical, the anatomic orbital floor is S-shaped (Figure 2).
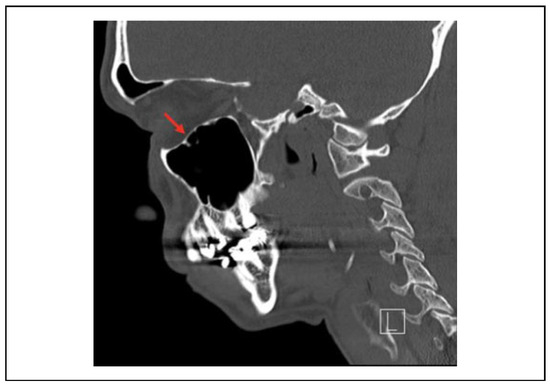
Figure 2.
Sagittal view of a normal orbital floor in an S-shape configuration.
Biological Materials
Autologous bone grafts have historically been considered the “gold standard” for orbital floor reconstruction as they offer both short and long-term viability by providing rigidity, molding capacity, minimal immune reactivity, vascularity, and biocompatibility.[45] Calvarial bone grafts can be used as full-thickness, split-thickness, bone chips, bone shavings, and dust.[44] The parietal bone has been described as being the most suitable, with regard to shape, for use in facial reconstruction.[50] Autologous cartilaginous grafts have also been shown to have utility in orbital reconstruction due to their ease of harvesting, malleability, reliable support without resorption, and fewer postoperative complications.[51,52] The primary sources for cartilaginous grafting are auricular concha, rib, and nasal septum.[53] Cartilage grafts are unique in that they have low anaerobic metabolism and are relatively avascular, which is thought to improve graft viability and reduce resorption rates compared to bone grafts.[51]
Allografts and Xenografts
Allografts used to reconstruct orbital floor fractures include lyophilized dura mater (LyoDura) and banked demineralized human bone (DHB). Lyodura is digested by macrophages and eventually replaced with endogenous collagenous connective tissue post-operatively.[54] Allogenic human or animal dura grafts undergo sterilization to decrease disease transmission; however, evidence in the literature has demonstrated that allografts are associated with increased donor-to-patient disease transmission risks.[55,56,57] DHB grafts are produced in biocompatible, resorbable sheets and are both osteoconductive and osteoinductive due to their ability to provide type 1 collagen; however, the utility of DHB implants in orbital floor reconstruction remains undetermined. Sallam Ahmed et al.[58] demonstrated that DHB sheets used in the setting of enophthalmos provided inadequate structural support and were an insufficient form of repair due to an elevated rate of resorption of DHB compared to the autologous bone.
Alloplastic Implants
Alloplasts can be subdivided into resorbable and non-resorbable plates. Resorbable alloplastic grafts include polymers composed of poly-L-lactic acid, polydioxanone, polyglycolic acid, or composite polymers.[55,59,60,61,62,63] These materials have been associated with delayed enophthalmos and severe inflammatory reactions resulting in ocular muscle adhesions and diplopia. Resorbable grafts provide temporary support and are replaced by fibrous granulation tissue as the material degrades, thereby providing resistance against herniation forces during the initial healing phase and maintaining orbital contents.[55,60,61]
Permanent, non-resorbable, alloplastic implants offer a longer-term rigid option for reconstruction and are commonly used in orbital floor fracture repair but have higher risks of implant-associated infections. Porous polyethylene is malleable while also allowing rigid fixation and vascular ingrowth due to open pore structure. However, if placed in close proximity to extraocular muscles, it may form adhesions.[64,65,66,67,68] Titanium mesh implants are easily contoured and biocompatible but may be difficult to position in deep orbital fractures and have also been shown to be associated with fibrosis, scar formation, and orbital adherence syndrome.[68,69,70] A systematic review by Avashia et al.[43] evaluated implant material for orbital reconstruction, concluding that the evidence supporting one material’s superiority over another is inadequate. Therefore, the surgeon must rely on his or her operative expertise in conjunction with the implant type’s unique characteristics to develop an individualized surgical approach that fits the patient’s specific needs.
Three-Dimensional Printing and Implant Contouring
Three-dimensional printing has increasingly gained popularity by surgeons for presurgical planning and intra-operative guidance. Computer-aided design and printing (CAD-CAM) are used to fabricate rapid prototypes using the following techniques: stereolithography using photocurable resin, selective laser sintering (fusion of polymers such as polystyrene or titanium), and fused deposition modeling employing the extrusion of thermoplastic materials. Stereolithographic (SLA) models have been shown, although anecdotally, to increase predictability in postoperative outcomes and decrease operating times compared to treatments without the use of these models.[79]
Three widely used implant contouring techniques include template contouring using an SLA model, preformed implants, and patient-specific implants. Template contouring can be significantly facilitated, as noted above, by the fabrication of 3-dimensional rapid prototype models using preoperative CT datasets and 3-D printing. Titanium mesh can then be shaped onto the model replicating the orbital contour (Figure 3). Park et al.[80] used this technique on 104 patients and demonstrated accurate volume reconstructions with an average of <1.5 ml discrepancy from the planned volume and minimal complication rates. Preformed implants have a standardized orbital contour based on a composite of several hundred standard CT datasets. Metzger et al.[81] evaluated the use of pre-bent titanium mesh implants in cadaveric orbits and found that these contoured implants provide accurate contours within 1 mm difference for both medial and orbital floor repair.
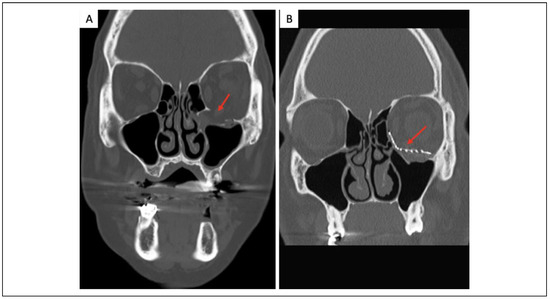
Figure 3.
A, Coronal view of isolated orbital floor fracture medial to the infraorbital nerve. B, Coronal view after reduction and placement of an anatomical 3-dimensional pre-bent titanium implant.
Patient-specific implants are constructed to fit the individual patient’s anatomy using the preoperative CT dataset and mirroring the contralateral unaffected side as detailed above. Gander et al.[82] implemented CT imaging to create a virtual implant using the mirrored contralateral unaffected orbit template in 12 patients. They reported an efficient preoperative planning time ranging from 30-36 minutes, with implant manufacturing taking approximately 4-6 days. The authors reported correction of enophthalmos and diplopia resolution with no need for reoperation to reposition implants or correct ocular bulb displacement in any of the patients. Select studies detailing contemporary management techniques are further presented in Online Supplemental Table 1.[76,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91]
Conclusion
Orbital floor fractures involve complex soft tissue and bony reconstruction. Although there has been considerable progress in the diagnosis, perioperative care, and technologically advanced approaches, insufficiency in the level of evidence still exists, preventing the development of a convincing general guideline or algorithmic approach to reconstruction. With increased data, we can hope to form evidence-based indications for the use of particular biomaterials or criteria for orbital defect characteristics, endoscopic guidance, or the use of preoperative planning and intraoperative imaging or navigation, which may be best addressed by a specific surgical approach.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental material for this article is available online.
Author Contributions
Drs Lighthall and Patel had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study concept and design: Patel, Shokri, and Lighthall. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Patel and Shokri. Drafting of the manuscript: All authors. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Lighthall. Administrative, technical, or material support: Patel and Ziai. Study supervision: Lighthall.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Publication Statement
The authors confirm that they have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
References
- Smith, B.; Regan, W.F., Jr. Blow-out fracture of the orbit: mechanism and correction of internal orbital fracture. Am J Ophthalmol. 1957, 44, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Putterman, A.M.; Stevens, T.; Urist, M.J. Nonsurgical management of blow-out fractures of the orbital floor. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974, 77, 232–239. [Google Scholar]
- Hawes, M.J.; Dortzbach, R.K. Surgery on orbital floor fractures. Influence of time of repair and fracture size. Ophthalmology. 1983, 90, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burnstine, M.A. Clinical recommendations for repair of isolated orbital floor fractures: an evidence-based analysis. Ophthalmology. 2002, 109, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sires, B.S.; Stanley, R.B., Jr.; Levine, L.M. Oculocardiac reflex caused by orbital floor trapdoor fracture: an indication for urgent repair. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998, 116, 955–956. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mendelblatt, F.I.; Kirsch, R.E.; Lemberg, L. A study comparing methods of preventing the oculocardiac reflex. Am J Ophthalmol. 1962, 53, 506–512. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, J.H., 3rd; Patrinely, J.R.; Weiss, A.H.; Kierney, P.C.; Gruss, J.S. Trapdoor fracture of the orbit in a pediatric population. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002, 109, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, R.D. Surgical management of persistent diplopia in blowout fractures of the orbit. Ann Ophthalmol. 1975, 7, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Kushner, B.J. Paresis and restriction of the inferior rectus muscle after orbital floor fracture. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982, 94, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bansagi, Z.C.; Meyer, D.R. Internal orbital fractures in the pediatric age group: characterization and management. Ophthalmology. 2000, 107, 829–836. [Google Scholar]
- Egbert, J.E.; May, K.; Kersten, R.C.; Kulwin, D.R. Pediatric orbital floor fracture: direct extraocular muscle involvement. Ophthalmology. 2000, 107, 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, D.R.; Allen, L.H.; White, J.; Harvey, J.; Pashby, R.; Esmaeli, B. Intervention within days for some orbital floor fractures: the white-eyed blowout. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998, 14, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachler, B.S.; Holds, J.B. The missing muscle syndrome in blowout fractures: an indication for urgent surgery. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998, 14, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, G.R.; Holt, J.E. Management of orbital trauma and foreign bodies. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1988, 21, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soll, D.B.; Poley, B.J. Trapdoor variety of blowout fracture of the orbital floor. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965, 60, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Manson, P.N.; Grivas, A.; Rosenbaum, A.; Vannier, M.; Zinreich, J.; Iliff, N. Studies on enophthalmos: II. The measurement of orbital injuries and their treatment by quantitative computed tomography. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986, 77, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bite, U.; Jackson, I.T.; Forbes, G.S.; Gehring, D.G. Orbital volume measurements in enophthalmos using three-dimensional CT imaging. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985, 75, 502–508. [Google Scholar]
- Manson, P.N.; Iliff, N. Management of blow-out fractures of the orbital floor. II. Early repair for selected injuries. Surv Ophthalmol. 1991, 35, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, G.S.; Mathog, R.H. Orbital wall and volume relationships. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1988, 114, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploder, O.; Klug, C.; Voracek, M.; Burggasser, G.; Czerny, C. Evaluation of computer-based area and volume measurement from coronal computed tomography scans in isolated blowout fractures of the orbital floor. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002, 60, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Yab, K.; Tajima, S.; Ohba, S. Displacements of eyeball in orbital blowout fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997, 100, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raskin, E.M.; Millman, A.L.; Lubkin, V.; della Rocca, R.C.; Lisman, R.D.; Maher, E.A. Prediction of late enophthalmos by volumetric analysis of orbital fractures. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998, 14, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Catone, G.A.; Morrissette, M.P.; Carlson, E.R. A retrospective study of untreated orbital blow-out fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1988, 46, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dulley, B.; Fells, P. Long-term follow-up of orbital blow-out fractures with and without surgery. Mod Probl Ophthalmol. 1975, 14, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-H.; Pan, C.-H.; Leow, A.-M.; Tsay, P.-K.; Chen, C.-T. Evolving concepts in the management of orbital fractures with enophthalmos: a retrospective comparative analysis. Formos J Surg. 2016, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Tsay, P.K.; Leow, A.M.; Pan, C.H.; Chen, C.T. Surgical timing and fracture type on the outcome of diplopia after orbital fracture repair. Ann Plast Surg. 2016, 76 (suppl 1), S91–S95. [Google Scholar]
- Matic, D.B.; Tse, R.; Banerjee, A.; Moore, C.C. Rounding of the inferior rectus muscle as a predictor of enophthalmos in orbital floor fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2007, 18, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Moore, C.C.; Tse, R.; Matic, D. Rounding of the inferior rectus muscle as an indication of orbital floor fracture with periorbital disruption. J Otolaryngol. 2007, 36, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrick, K.; Smetona, J.; Iyengar, R.; et al. Radiographic predictors of FACE-Q outcomes following non-operative orbital floor fracture management. J Craniofac Surg. 2020, 31, e388–e391. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, P.; Boyd, V.; Banerji, S.; Hollier, L.H., Jr. Comprehensive management of orbital fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007, 120 (7 suppl 2), 57S–63S. [Google Scholar]
- Rinna, C.; Ungari, C.; Saltarel, A.; Cassoni, A.; Reale, G. Orbital floor restoration. J Craniofac Surg. 2005, 16, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boush, G.A.; Lemke, B.N. Progressive infraorbital nerve hypesthesia as a primary indication for blow-out fracture repair. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994, 10, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Tengtrisorn, S.; McNab, A.A.; Elder, J.E. Persistent infra-orbital nerve hyperaesthesia after blunt orbital trauma. Aust NZJ Ophthalmol. 1998, 26, 259–260. [Google Scholar]
- De Riu, G.; Meloni, S.M.; Gobbi, R.; Soma, D.; Baj, A.; Tullio, A. Subciliary versus swinging eyelid approach to the orbital floor. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2008, 36, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kothari, N.A.; Avashia, Y.J.; Lemelman, B.T.; Mir, H.S.; Thaller, S.R. Incisions for orbital floor exploration. J Craniofac Surg. 2012, 23 (7 suppl 1), 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, B.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Suresh Kumar, P.; Saravanan, B.; Padhmanabhan, M. Comparison of various approaches for exposure of infraorbital rim fractures of zygoma. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2009, 8, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feldman, E.M.; Bruner, T.W.; Sharabi, S.E.; Koshy, J.C.; Hollier, L.H., Jr. The subtarsal incision: where should it be placed? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011, 69, 2419–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Holtmann, B.; Wray, R.C.; Little, A.G. A randomized comparison of four incisions for orbital fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981, 67, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, S.A. Treatment of post-traumatic orbital deformities. Clin Plast Surg. 1988, 15, 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, E.B.; Chen, C.; Colakoglu, S.; Gautam, S.; Lee, B.T. The incidence of lower eyelid malposition after facial fracture repair: a retrospective study and meta-analysis comparing subtarsal, subciliary, and transconjunctival incisions. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009, 124, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.T.; Chen, Y.R. Endoscopically assisted repair of orbital floor fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001, 108, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, E.C.; Chen, C.T.; Chen, Y.R. Broad application of the endoscope for orbital floor reconstruction: long-term followup results. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010, 125, 969–978. [Google Scholar]
- Avashia, Y.J.; Sastry, A.; Fan, K.L.; Mir, H.S.; Thaller, S.R. Materials used for reconstruction after orbital floor fracture. J Craniofac Surg. 2012, 23 (7 suppl 1), 1991–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilankovan, V.; Jackson, I.T. Experience in the use of calvarial bone grafts in orbital reconstruction. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992, 30, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, K.; Krause, G.E. Selection of materials for orbital floor reconstruction. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998, 124, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldekhayel, S.; Aljaaly, H.; Fouda-Neel, O.; Shararah, A.W.; Zaid, W.S.; Gilardino, M. Evolving trends in the management of orbital floor fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2014, 25, 258–261. [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen, A.C.; Ong, S.H.; Vissink, A.; Grijpma, D.W.; Bos, R.R. Reconstruction of orbital wall defects: recommendations based on a mathematical model. Exp Eye Res. 2012, 97, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zins, J.E.; Whitaker, L.A. Membranous versus endochondral bone: implications for craniofacial reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1983, 72, 778–785. [Google Scholar]
- Young, V.L.; Schuster, R.H.; Harris, L.W. Intracerebral hematoma complicating split calvarial bone-graft harvesting. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990, 86, 763–765. [Google Scholar]
- Tessier, P. Autogenous bone grafts taken from the calvarium for facial and cranial applications. Clin Plast Surg. 1982, 9, 531–538. [Google Scholar]
- Kruschewsky Lde, S.; Novais, T.; Daltro, C.; et al. Fractured orbital wall reconstruction with an auricular cartilage graft or absorbable polyacid copolymer. J Craniofac Surg. 2011, 22, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Castellani, A.; Negrini, S.; Zanetti, U. Treatment of orbital floor blowout fractures with conchal auricular cartilage graft: a report on 14 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002, 60, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kraus, M.; Gatot, A.; Fliss, D.M. Repair of traumatic inferior orbital wall defects with nasoseptal cartilage. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001, 59, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Stöss, H.; Pesch, H.J. Dura transplantation. Multi-sequential transplants of solvent dehydrated dura mater. Animal experiment studies on the question of sensitization. Fortschr Med. 1977, 95, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Jank, S.; Emshoff, R.; Schuchter, B.; Strobl, H.; Brandlmaier, I.; Norer, B. Orbital floor reconstruction with flexible Ethisorb patches: a retrospective long-term follow-up study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003, 95, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, D.G.; Li, P. Sterilization of HIV with irradiation: relevance to infected bone allografts. Aust N Z J Surg. 1999, 69, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E.; Carlson, E.R. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease from allogeneic dura: a review of risks and safety. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991, 49, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sallam Ahmed, M.; Hashem, H.; Shokier, H. Use of demineralized bone sheets in reconstruction of orbital floor trap door fracture. J Appl Sci Res. 2010, 6, 653–658. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sukhun, J.; Lindqvist, C. A comparative study of 2 implants used to repair inferior orbital wall bony defects: autogenous bone graft versus bioresorbable poly-L/DL-Lactide [P(L/ DL)LA 70/30] plate. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006, 64, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buchel, P.; Rahal, A.; Seto, I.; Iizuka, T. Reconstruction of orbital floor fracture with polyglactin 910/polydioxanon patch (Ethisorb): a retrospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005, 63, 646–650. [Google Scholar]
- Hollier, L.H.; Rogers, N.; Berzin, E.; Stal, S. Resorbable mesh in the treatment of orbital floor fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2001, 12, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, T.; Mikkonen, P.; Paukku, P.; Lindqvist, C. Reconstruction of orbital floor with polydioxanone plate. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991, 20, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kontio, R.; Suuronen, R.; Salonen, O.; Paukku, P.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Lindqvist, C. Effectiveness of operative treatment of internal orbital wall fracture with polydioxanone implant. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001, 30, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Tuncer, S.; Yavuzer, R.; Kandal, S.; et al. Reconstruction of traumatic orbital floor fractures with resorbable mesh plate. J Craniofac Surg. 2007, 18, 598–605. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, K.; Kim, D.H. Comparison of the supporting strength of a poly-L-lactic acid sheet and porous polyethylene (Medpor) for the reconstruction of orbital floor fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2010, 21, 847–853. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, J.J.; Iliff, N.T.; Manson, P.N. Use of Medpor porous polyethylene implants in 140 patients with facial fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 1993, 4, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, D.H.; Chi, M. Comparison of the outcomes of blowout fracture repair according to the orbital implant. J Craniofac Surg. 2011, 22, 1422–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, E., 3rd; Tan, Y. Assessment of internal orbital reconstructions for pure blowout fractures: cranial bone grafts versus titanium mesh. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003, 61, 442–453. [Google Scholar]
- Mischkowski, R.A.; Zinser, M.J.; Ritter, L.; Neugebauer, J.; Keeve, E.; Zöller, J.E. Intraoperative navigation in the maxillofacial area based on 3D imaging obtained by a cone-beam device. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007, 36, 687–694. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.C.; Kumta, S.M.; Antonio, G.E.; Tse, L.F. Image fusion for computer-assisted bone tumor surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008, 466, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar]
- Gellrich, N.C.; Schramm, A.; Hammer, B.; et al. Computerassisted secondary reconstruction of unilateral posttraumatic orbital deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002, 110, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Zizelmann, C.; Gellrich, N.C.; Metzger, M.C.; Schoen, R.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Schramm, A. Computer-assisted reconstruction of orbital floor based on cone beam tomography. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007, 45, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, A.; Suarez-Cunqueiro, M.M.; Rücker, M.; et al. Computer-assisted therapy in orbital and mid-facial reconstructions. Int J Med Robot. 2009, 5, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaye, D.A.; Tollefson, T.T.; Strong, E.B. Use of intraoperative computed tomography for maxillofacial reconstructive surgery. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2015, 17, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ewers, R.; Schicho, K.; Undt, G.; et al. Basic research and 12 years of clinical experience in computer-assisted navigation technology: a review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, E.Z.; Koh, Y.P.; Hing, E.C.; et al. Computer-assisted navigational surgery improves outcomes in orbital reconstructive surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2012, 23, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Essig, H.; Dressel, L.; Rana, M.; et al. Precision of posttraumatic primary orbital reconstruction using individually bent titanium mesh with and without navigation: a retrospective study. Head Face Med. 2013, 9, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Tel, A.; Sembronio, S.; Costa, F.; et al. Endoscopically assisted computer-guided repair of internal orbital floor fractures: an updated protocol for minimally invasive management. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019, 47, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, P.; Miner, J.; D’Innocenzo, R.; Nadershah, M. Use of 3-D stereolithographic models in oral and maxillofacial surgery. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2011, 10, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Choi, J.W.; Koh, K.S.; Oh, T.S. Mirror-imaged rapid prototype skull model and pre-molded synthetic scaffold to achieve optimal orbital cavity reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015, 73, 1540–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, M.C.; Schön, R.; Weyer, N.; et al. Anatomical 3-dimensional pre-bent titanium implant for orbital floor fractures. Ophthalmology. 2006, 113, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gander, T.; Essig, H.; Metzler, P.; et al. Patient specific implants (PSI) in reconstruction of orbital floor and wall fractures. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015, 43, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Novelli, G.; Tonellini, G.; Mazzoleni, F.; Bozzetti, A.; Sozzi, D. Virtual surgery simulation in orbital wall reconstruction: integration of surgical navigation and stereolithographic models. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014, 42, 2025–2034. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shyu, V.B.; Hsu, C.E.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, C.T. 3D-assisted quantitative assessment of orbital volume using an open-source software platform in a Taiwanese population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felding, U.A.; Bloch, S.L.; Buchwald, C. The dimensions of the orbital cavity based on high-resolution computed tomography of human cadavers. J Craniofac Surg. 2016, 27, 1090–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Strong, E.B.; Fuller, S.C.; Wiley, D.F.; Zumbansen, J.; Wilson, M.D.; Metzger, M.C. Preformed vs intraoperative bending of titanium mesh for orbital reconstruction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013, 149, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kozakiewicz, M.; Szymor, P. Comparison of pre-bent titanium mesh versus polyethylene implants in patient specific orbital reconstructions. Head Face Med. 2013, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakiewicz, M. Computer-aided orbital wall defects treatment by individual design ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene implants. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014, 42, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Stuck, B.A.; Hülse, R.; Barth, T.J. Intraoperative cone beam computed tomography in the management of facial fractures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012, 41, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.; Voineskos, S.H.; Avram, R.; Sommer, D.D. A systematic review of the endoscopic management of orbital floor fractures. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2013, 15, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gunarajah, D.R.; Samman, N. Biomaterials for repair of orbital floor blowout fractures: a systematic review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013, 71, 550–570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2021 by the author. The Author(s) 2021.