Same-Admission Microvascular Maxillofacial Ballistic Trauma Reconstruction Using Virtual Surgical Planning: A Case Series and Systematic Review
Abstract
:Introduction
Materials and Methods
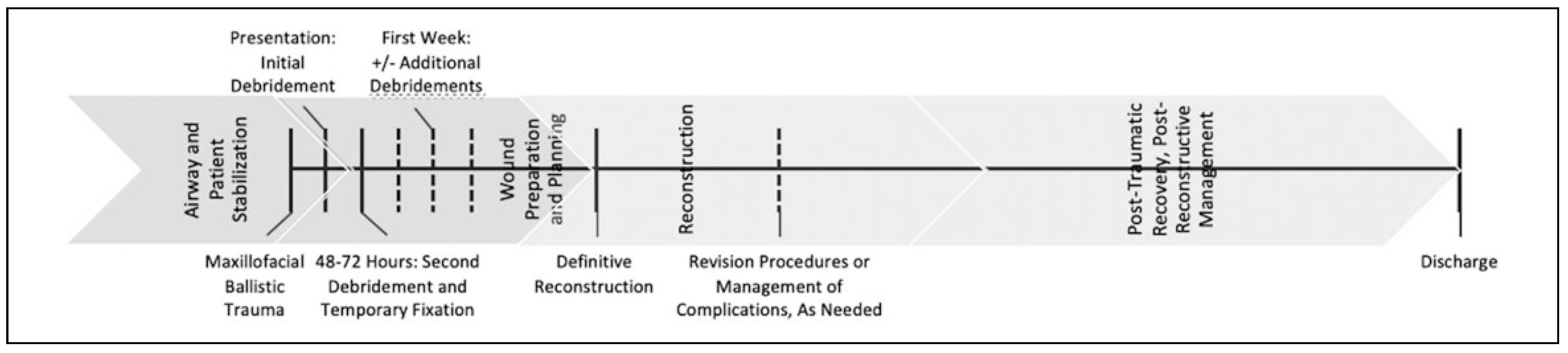
Case Series
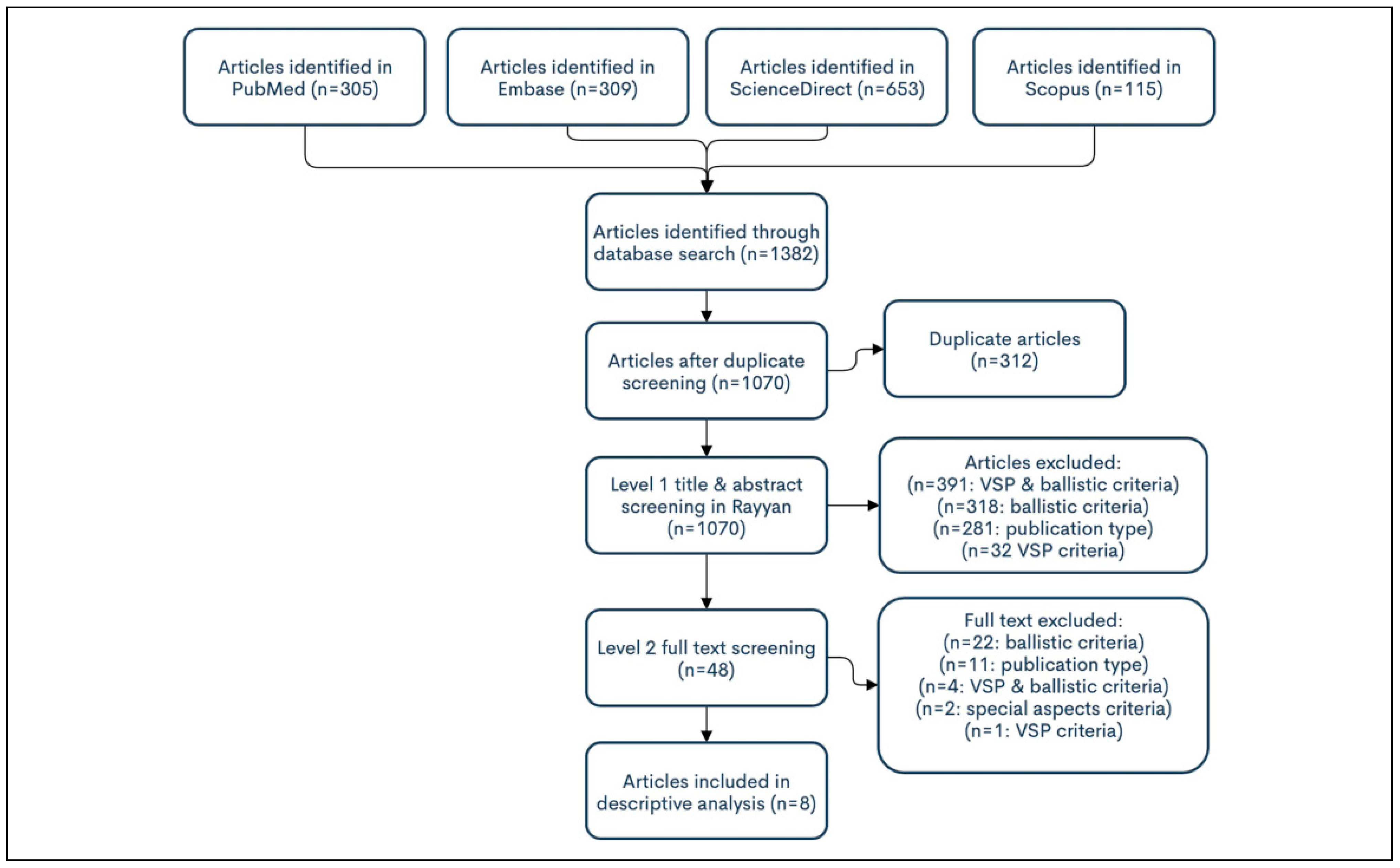
Systematic Review
Results
Case Series
Case Presentations
Systematic Review
Discussion
Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Considerations
References
- Fowler, K.A.; Dahlberg, L.L.; Haileyesus, T.; Annest, J.L. Firearm injuries in the United States. Prev Med. 2015, 79, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconez, H.C.; Shockley, M.E.; Luce, E.A. High-energy gunshot wounds to the face. Ann Plast Surg. 1996, 36, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breeze, J.; Gibbons, A.J.; Hunt, N.C.; et al. Mandibular fractures in British military personnel secondary to blast trauma sustained in Iraq and Afghanistan. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011, 49, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeze, J.; Tong, D.; Gibbons, A. Contemporary management of maxillofacial ballistic trauma. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017, 55, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravvanis, A.; Iconomou, T.; Tsoutsos, D.; Katsikeris, N. Aesthetic and anatomic subunit reconstruction of composite mandibular gunshot wound. J Craniofac Surg. 2012, 23, e95–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, O.; Ozgentas, H.E.; Dikici, M.B. Simultaneous reconstruction of large maxillary and mandibular defects with a fibular osteocutaneous flap combined with an anterolateral thigh flap. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2004, 20, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleier, P.; Hyckel, P.; Fried, W.; et al. Vertical distraction of fibula transplant in a case of mandibular defect caused by shotgun injury. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006, 35, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.A.; McWilliams, S.R.; Lee, M.; Warburton, G. Management of self-inflicted gunshot wounds to the face: retrospective review from a single tertiary care trauma centre. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018, 56, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachar, M.R.; Labella, C.; Kittle, C.P.; Baer, P.B.; Hale, R.G.; Chan, R.K. Characterization of mandibular fractures incurred from battle injuries in Iraq and Afghanistan from 2001-2010. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013, 71, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaca, E.E.; Bellamy, J.L.; Sinno, S.; Rodriguez, E.D. Management of high-energy avulsive ballistic facial injury: a review of the literature and algorithmic approach. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018, 6, e1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, M.; Leiser, Y.; Emodi, O.; Krausz, A. Treatment protocol for high velocity/high energy gunshot injuries to the face. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2012, 5, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, C.S. Clinical update: gunshot wound ballistics. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003, 408, 28–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, C.S.; Helfet, D.L.; Hausman, M.R.; Strauss, E. Ballistics and gunshot wounds: effects on musculoskeletal tissues. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000, 8, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Sawatari, Y.; Peleg, M. High-energy traumatic maxillofacial injury. J Craniofac Surg. 2015, 26, 1487–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, N.R.; McKinney, S.M.; Wax, M.K.; Louis, P.J.; Rosenthal, E.L. Free flap reconstruction of self-inflicted submental gunshot wounds. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2011, 4, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, A.; Arya, S.; Nagori, S. High-velocity ballistic injuries inflicted to the maxillofacial region. J Craniofac Surg. 2019, 30, e511–e514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, Y.; Cole, P.; Hollier, L. Contemporary issues in facial gunshot wound management. J Craniofac Surg. 2008, 19, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, A.S.; Shokri, T.; Sokoya, M.; Ducic, Y.; Hollier, L.H., Jr. Facial gunshot wounds. Facial Plast Surg. 2019, 35, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, M.H. Primary treatment of penetrating injuries to the face. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007, 65, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.R.; Brennan, J. Management and reconstruction of blast wounds of the head and neck. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016, 24, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.; Cole, P.; Hollier, L.H., Jr. Facial gunshot wounds: trends in management. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2009, 2, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breeze, J.; Gibbons, A.J.; Opie, N.J.; Monaghan, A. Maxillofacial injuries in military personnel treated at the Royal Centre for Defense Medicine June 2001 to December 2007. Br J Maxillofac Surg. 2010, 48, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majors, J.S.; Brennan, J.; Holt, G.R. Management of high-velocity injuries of the head and neck. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2017, 25, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, J.N.; Moore, C.E.; Yellin, S.A. Gunshot wounds to the face—acute management. Facial Plast Surg. 2005, 21, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVeigh, K.; Breeze, J.; Jeynes, P.; Martin, T.; Parmar, S.; Monaghan, A.M. Clinical strategies in the management of complex maxillofacial injuries sustained by British military personnel. J R Army Med Corps. 2010, 156, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, M.H. Primary management of maxillofacial hard and soft tissue gunshot and shrapnel injuries. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003, 61, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, M.H.; Behnia, H. Experience with regional flaps in the comprehensive treatment of maxillofacial soft-tissue injuries in war victims. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1999, 27, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.H.; Sabino, J.M.; Nanos, G.P., III; Valerio, I.L. Ballistic trauma: lessons learned from Iraq and Afghanistan. Semin Plast Surg. 2015, 29, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollier, L.; Grantcharova, E.P.; Kattash, M. Facial gunshot wounds: a 4-year experience. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001, 59, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayvada, H.; Menderes, A.; Yilmaz, M.; Mola, F.; Kzlkaya, A.; Atabey, A. Management of close-range, high-energy shotgun and rifle wounds to the face. J Craniofac Surg. 2005, 16, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser, C.; Gencel, E.; Kesiktas¸, E.; Yavuz, M. Outcomes of anatomic reconstruction of gunshot-inflicted lower face defects by free osteoseptocutaneous fibula flap and expanded or nonexpanded temporal scalp flap combination in males. J Craniofac Surg. 2016, 27, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.C.; Celik, N.; Chen, H.C.; Cheng, M.H.; Huang, W.C. Combined anterolateral thigh flap and vascularized fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap in reconstruction of extensive composite mandibular defects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002, 109, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghazal, S.K.; Sully, L.; Fallowfield, L.; Blamey, R.W. The psychological impact of immediate rather than delayed breast reconstruction. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2000, 26, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godina, M. Early microsurgical reconstruction of complex trauma of the extremities. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986, 78, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benateau, H.; Chatellier, A.; Caillot, A.; Labbe, D.; Veyssiere, A. Computer-assisted planning of distraction osteogenesis for lower face reconstruction in gunshot traumas. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016, 44, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, B.; Gelesko, S.; Amundson, M.; et al. Updates in management of craniomaxillofacial gunshot wounds and reconstruction of the mandible. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2017, 25, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokosis, G.; Davidson, E.H.; Pedreira, R.; Macmillan, A.; Dorafshar, A.H. The use of computer-aided design and manufacturing in acute mandibular trauma reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018, 76, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troulis, M.J.; Everett, P.; Seldin, E.B.; Kikinis, R.; Kaban, L.B. Development of a three-dimensional treatment planning system based on computed tomographic data. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002, 31, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.J.; Gateno, J.; Teichgraeber, J.F. Three-dimensional computer-aided surgical simulation for maxillofacial surgery. Atlas of Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2005, 13, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuehmer, C.; Essig, H.; Schramm, A.; Rücker, M.; Eckardt, A.; Gellrich, N.C. Intraoperative navigation assisted reconstruction of a maxillo-facial gunshot wound. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008, 12, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M.; Laughlin, R. Reconstruction of hard and soft tissue maxillofacial defects. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2013, 21, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupfer, P.; Cheng, A.; Patel, A.; Amundson, M.; Dierks, E.J.; Bell, R.B. Virtual surgical planning and intraoperative imaging in management of ballistic facial and mandibular condylar injuries. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2017, 25, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, B.; Cuddy, K.; Cheng, A.; et al. Functional anatomic computer engineered surgery protocol for the management of self-inflicted gunshot wounds to the maxillofacial skeleton. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018, 76, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breeze, J.; Powers, D.B. Current opinion in the assessment and management of ballistic trauma to the craniomaxillofacial region. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020, 28, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunluoglu, R.; Glasgow, M.; Williams, S.A.; Gurunluoglu, A.; Antrobus, J.; Eusterman, V. Functional reconstruction of total lower lip defects using innervated gracilis flap in the setting of high-energy ballistic injury to the lower face: preliminary report. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012, 65, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

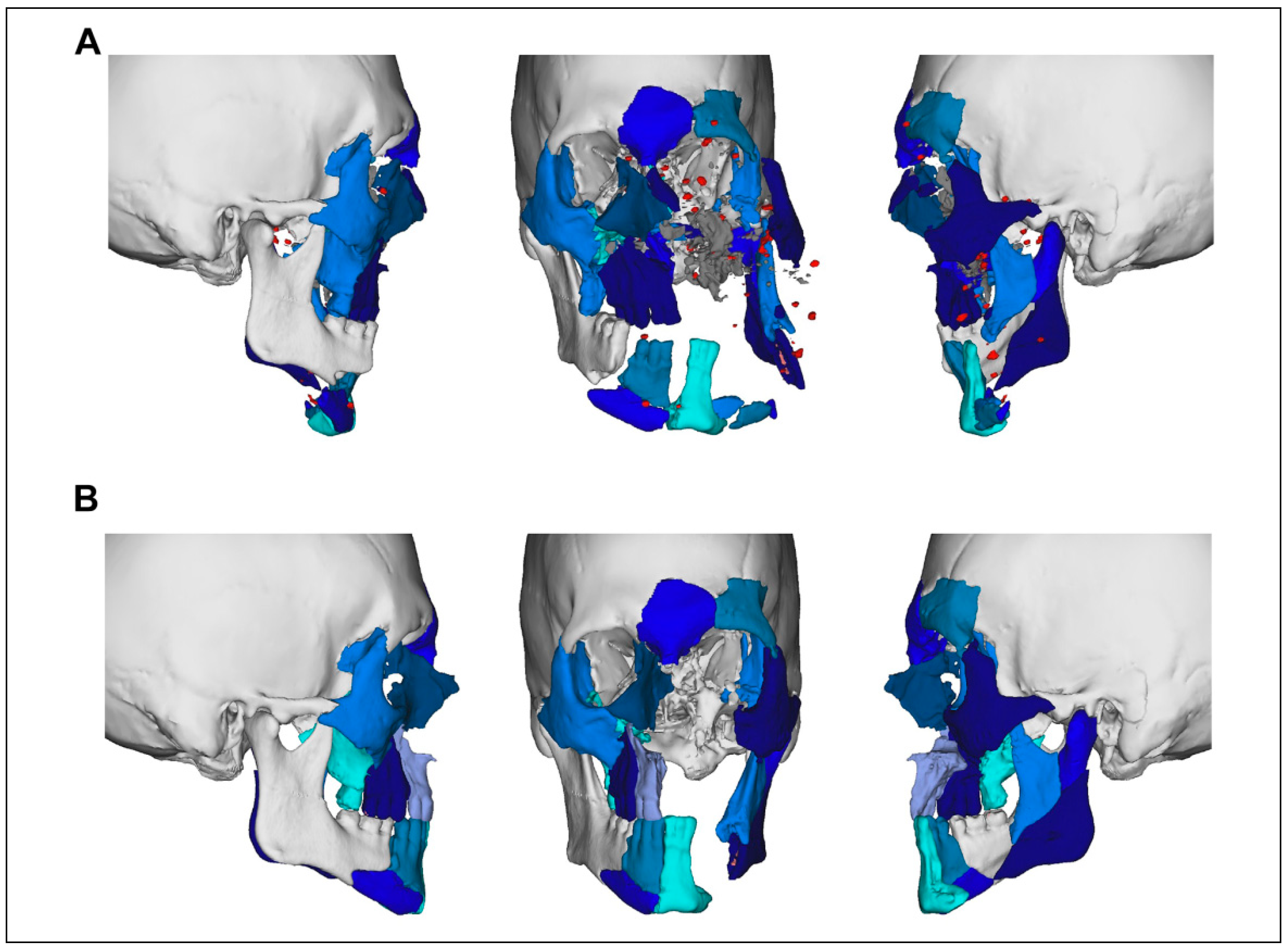
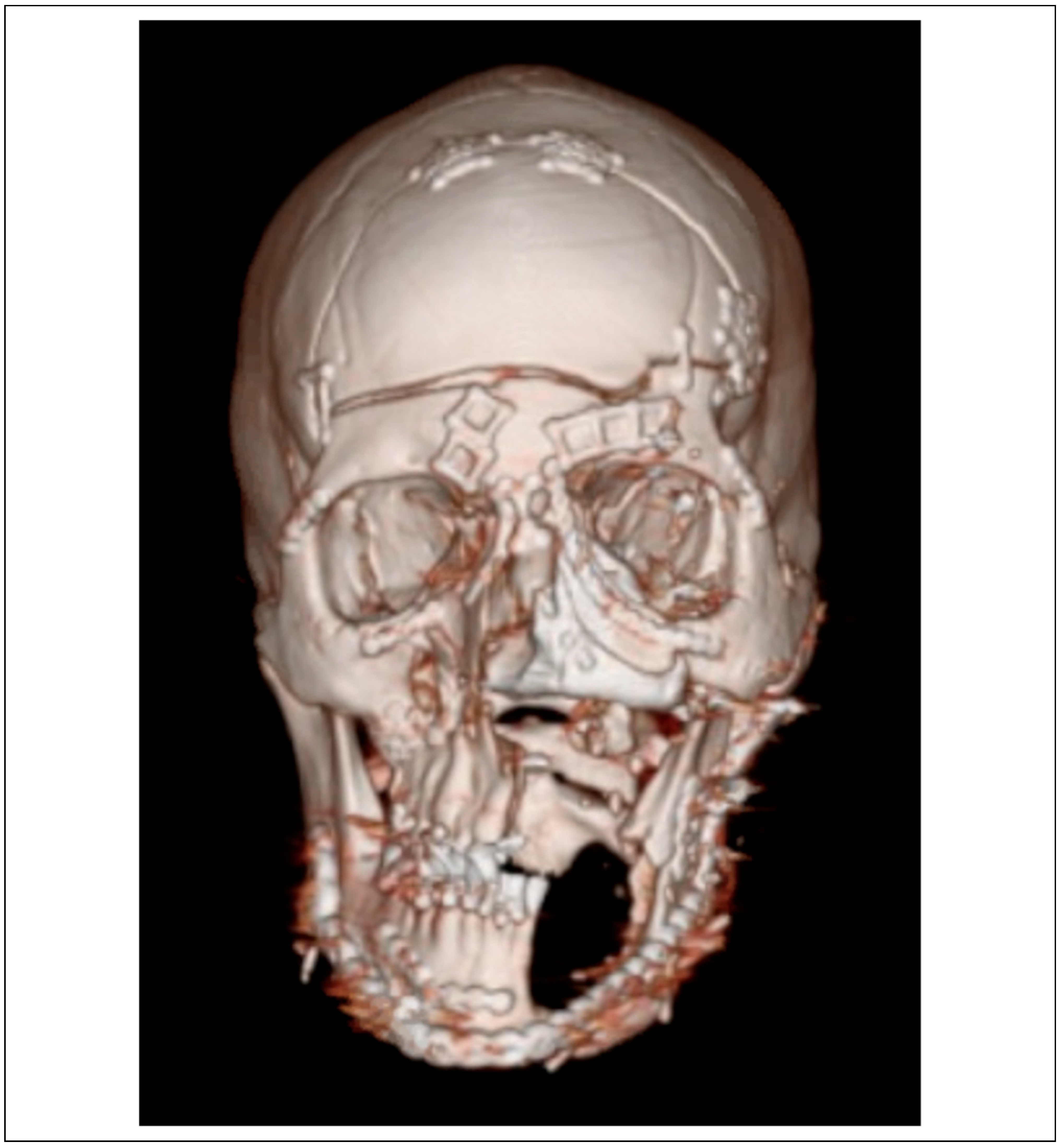
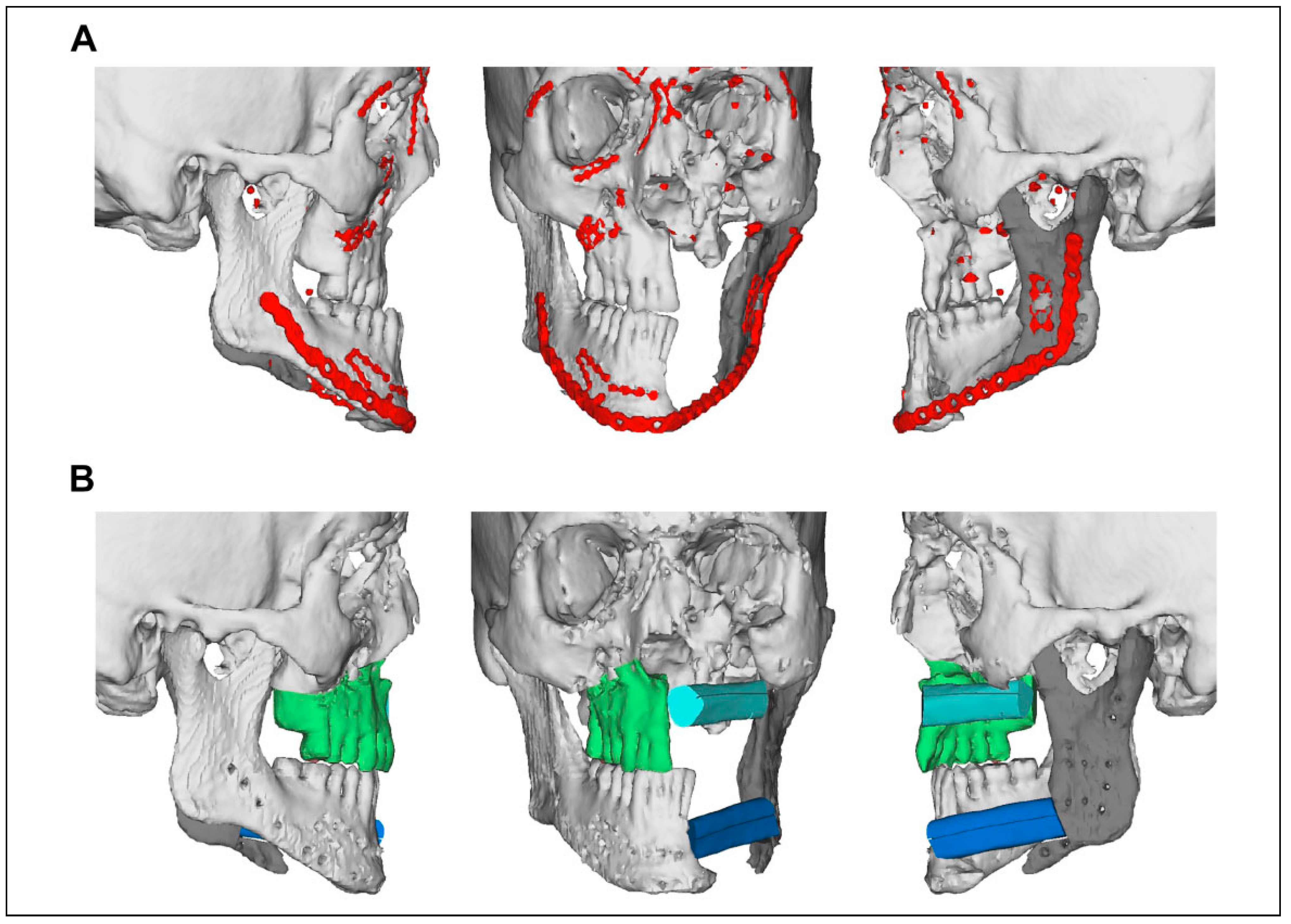
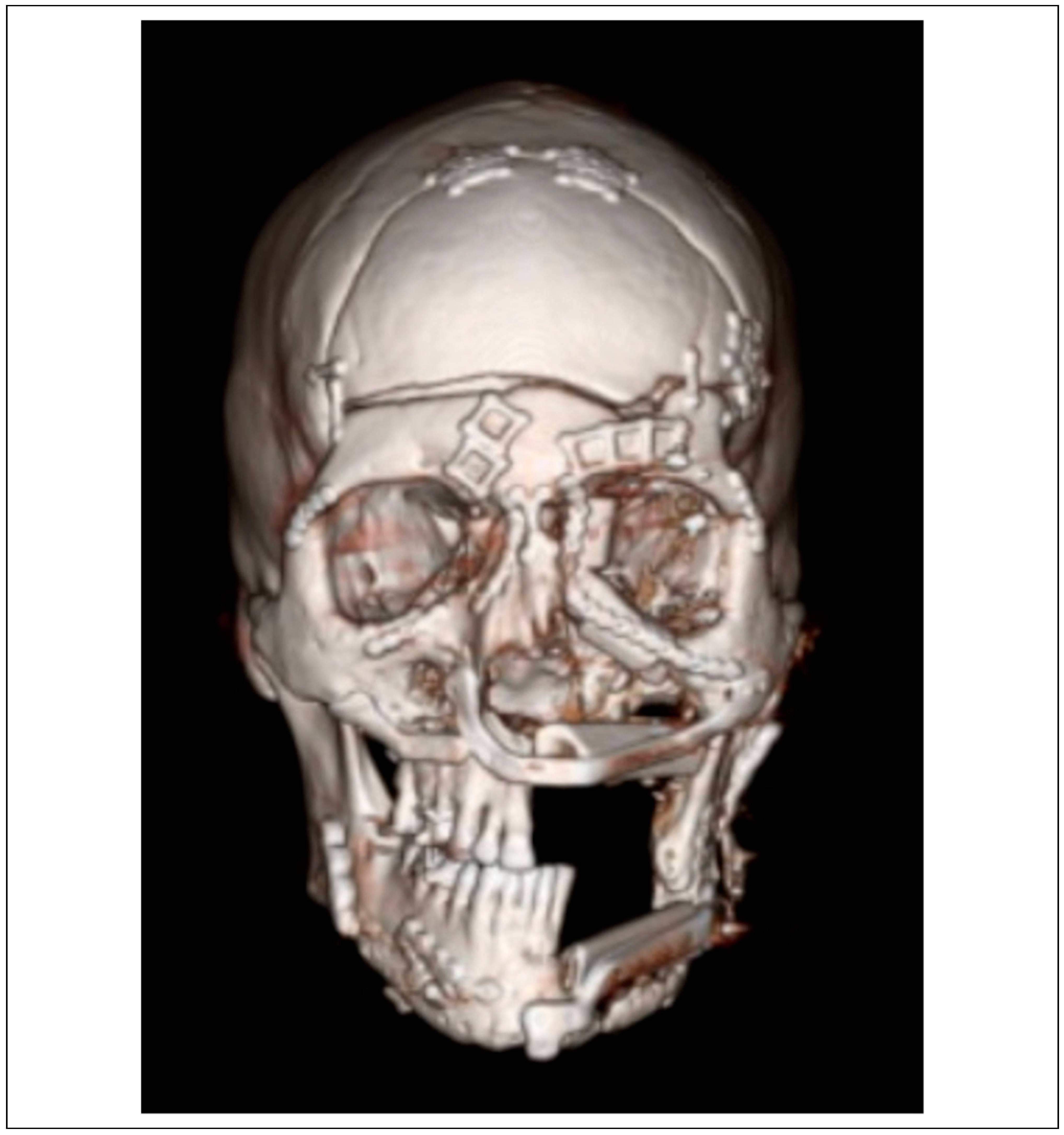
| Patient | Age | Gender | Days to Flap | Number of Flaps (Inpatient) | Operations (Inpatient) | Days Inpatient | Complications (Inpatient) | Weeks Follow-Up | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minor | Major | ||||||||
| 1 | 25 | M | 16 | 1 | 4 | 50 | 4 | 0 | 49 |
| 2 | 18 | M | 6 | 1 | 6 | 48 | 5 | 0 | 307 |
| 3 | 26 | M | 24 | 3 | 10 | 54 | 1 | 0 | 138 |
| 4 | 42 | M | 27 | 2 | 8 | 78 | 4 | 0 | 449 |
| 5 | 31 | M | 9 | 1 | 3 | 28 | 1 | 0 | 11 |
| Mean | 28.4 | M: 100% | 16.4 | 1.6 | 6.2 | 51.6 | 3.0 | 0.0 | 191.0 |
| Standard Deviation | 8.9 | — | 9.1 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 17.8 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 183.9 |
| Flap | Overall Usage | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Anterior lateral thigh | 3 | 3/8 (37.5%) |
| Osteocutaneous free fibula | 2 | 2/8 (25.0%) |
| Radial forearm | 2 | 2/8 (25.0.2%) |
| Free rectus | 1 | 1/8 (12.5%) |
| Total | 8 | 8/8 (100.0%) |
| Study | Type | Perspective | LOE | n | Population | Mandible | Microsurgery | Same Admission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stuehmer et al. 2008[40] | Case Report | Retrospective | V | 1 | Civilian | Yes | Yes | No |
| Harris and Laughlin 2013[41] | Review | Expert Opinion | V | N/a | N/a | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Benateau et al. 2016[35] | Case Series | Retrospective | IV | 2 | Civilian | Yes | No | No |
| Khatib et al. 2017[36] | Review | Expert Opinion | V | N/a | N/a | Yes | Yes | No |
| Kupfer et al. 2017[42] | Review | Expert Opinion | V | N/a | N/a | Yes | Yes | No |
| Khatib et al. 2018[43] | Case Series | Retrospective | IV | 10 | Civilian | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Volk et al. 2019[18] | Review | Expert Opinion | V | N/a | N/a | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Breeze and Powers 2020[44] | Review | Expert Opinion | V | N/a | N/a | Yes | No | Yes |
| Totals | — | — | — | 13 | — | 100% | 75% | 50% |
| Knudson et al. (Current study) | Case Series | Retrospective | IV | 5 | Civilian | Yes | Yes | Yes |
© 2021 by the author. The Author(s) 2021.
Share and Cite
Knudson, S.A.; Day, K.M.; Kelley, P.; Padilla, P.; Collier, I.X.; Henry, S.; Harshbarger, R.; Combs, P. Same-Admission Microvascular Maxillofacial Ballistic Trauma Reconstruction Using Virtual Surgical Planning: A Case Series and Systematic Review. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2022, 15, 206-218. https://doi.org/10.1177/19433875211026432
Knudson SA, Day KM, Kelley P, Padilla P, Collier IX, Henry S, Harshbarger R, Combs P. Same-Admission Microvascular Maxillofacial Ballistic Trauma Reconstruction Using Virtual Surgical Planning: A Case Series and Systematic Review. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction. 2022; 15(3):206-218. https://doi.org/10.1177/19433875211026432
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnudson, Sean A., Kristopher M. Day, Patrick Kelley, Pablo Padilla, Ian X. Collier, Steven Henry, Raymond Harshbarger, and Patrick Combs. 2022. "Same-Admission Microvascular Maxillofacial Ballistic Trauma Reconstruction Using Virtual Surgical Planning: A Case Series and Systematic Review" Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction 15, no. 3: 206-218. https://doi.org/10.1177/19433875211026432
APA StyleKnudson, S. A., Day, K. M., Kelley, P., Padilla, P., Collier, I. X., Henry, S., Harshbarger, R., & Combs, P. (2022). Same-Admission Microvascular Maxillofacial Ballistic Trauma Reconstruction Using Virtual Surgical Planning: A Case Series and Systematic Review. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction, 15(3), 206-218. https://doi.org/10.1177/19433875211026432



