Results
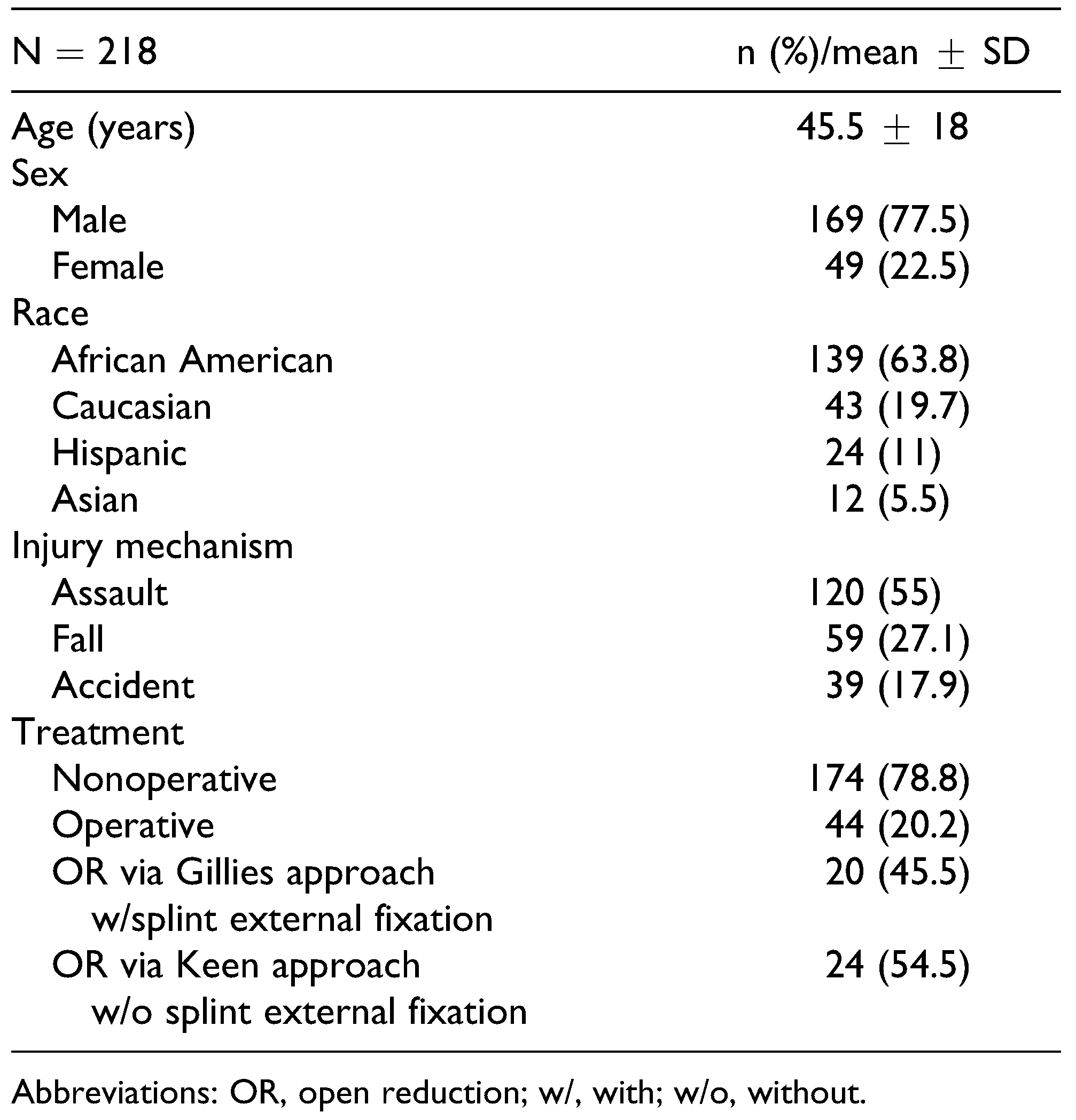
Two hundred eighteen (N = 218) patients met the inclusion parameters for this study. The average age of this cohort was 45.5 ± 18 years, with 77.5% being male. The majority of these patients were African American (63.4%), while Asian was the least commonly captured race (5.5%). Injury mechanisms included assault, accidents, and falls. Of these, assault (55%) was most the frequent, with accidents being the least common (17.9%). Management course also varied, with only 20.2% of patients undergoing operative treatment, and the remaining (78.8%) undergoing nonoperative management (
Table 1).
We aimed to identify preoperative characteristics that were more likely to be associated with operative or nonoperative management. Forty-four (n = 44) patients received operative treatment compared to 174 who were managed nonoperatively. The mean age between the groups were similar (43.3 years, operative vs 46.1 years, nonoperative) as well as the sex distribution (77% vs 79.5% males). Race distribution was also similar across operative and nonoperative groups. Further, the mechanism of injury was not found to be associated with any particular treatment course (
Table 2).
Patients in the operative cohort, when compared to their nonoperative counterparts, were more likely to clinically present with zygomatic deformity (97.7% vs 18.4%), paresthesia (29.5% vs 2.9%), and trismus (29.5% vs 6.9%), respectively. On multivariate analysis, zygomatic deformity, paresthesia, and trismus were all independently associated with an operative course of treatment (
p < .001 for all). Finally, all management teams utilized a nonoperative approach more frequently than operative, with otolaryngology-led management having the greatest nonoperative rates (86% vs 14%, respectively) and oral and maxillofacial surgery-led (OMFS) having the least (63.6% vs 36.4%;
Table 2).
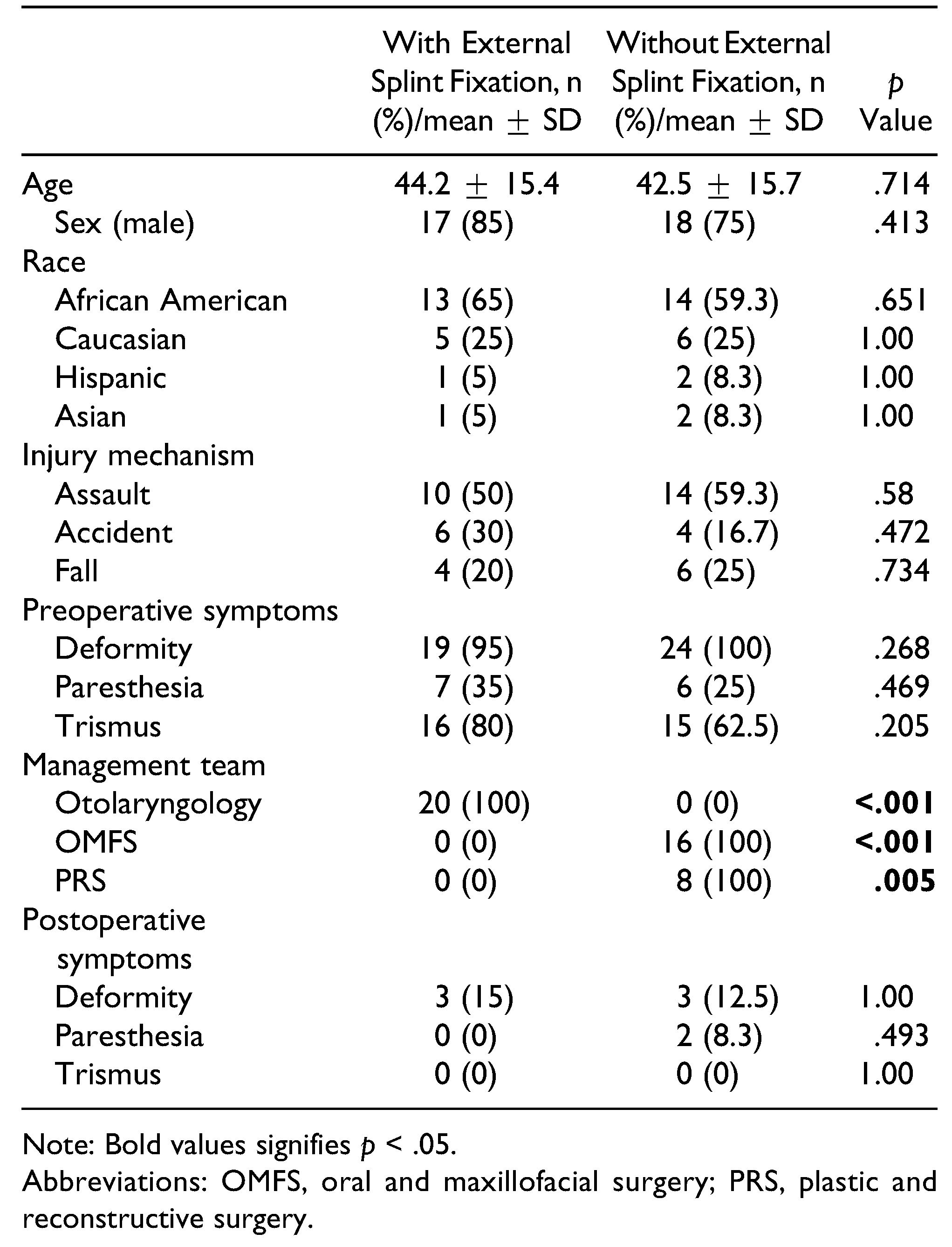
Patients undergoing operative management were compared based upon the utilization of external fixation. Of the 44 operatively managed patients, 20 underwent external fixation with a splint, whereas 24 did not. Patient demographics, including age, sex, and race, did not significantly differ between those who did and did not undergo external fixation. Injury mechanism was also similar, with or without an external fixation. Furthermore, there were no significant differences in the presence of zygomatic deformity, paresthesia, and trismus. Management team, however, was found to have significant associations. Otolaryngology had greater rates of splint usage (100% vs 0%,
p < .001). Conversely, OMFS and plastic and reconstructive surgery (PRS) were found to have no significant external splint usage (both 0%;
p < .001 for OMFS and .005 for PRS). Postoperative symptoms, including deformity, paresthesia, and trismus, all occurred at similar rates between the groups (
Table 3).
Discussion
The zygomatic arch is a bony arch formed by the zygoma and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone. Medially, the zygoma articulates with the maxilla, where the zygomaticomaxillary complex contributes to the contour of the cheek. The masseter muscle attaches directly to the zygomatic arch, and the temporalis muscle runs under the arch to reach the coronoid process of the mandible, both of which contribute to jaw movement.[
7] The prominence of the zygoma causes the zygoma to be susceptible to traumatic injury and accounts for its frequency in injury.[
2]
The zygomaticomaxillary region is the third most commonly fractured area in the face. The majority of zygomatic arch fractures occur in men 30 to 40 years of age, as a result of traffic accidents.[
5] However, other studies have reported assault to be the most common mechanism.[
1,
4] Zygomatic arch fractures occur in isolation in 5% of all patients with facial fractures and in 10% of patients with any zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture.[
7] Zygomatic arch fractures often occur as part of a tripod fracture of the zygoma and Le Fort III-type maxillary fractures.[
8]
Zygomatic arch fractures may produce a visible depression of the malar eminence leading to cosmetic asymmetry, enophthalmos, dystopia as well as trismus if the arch impinges upon the coronoid process.[
2,
9] If the zygomatic arch fracture is not properly treated, serious functional consequences including impaired mouth opening, temporomandibular joint ankylosis, and facial nerve palsy may occur.[
1] Although contour restoration can be performed with bone grafting, the use of implants can correct mild-to-moderate deformities safely, with minimal morbidity.[
2] Others have also employed fat grafting or reosteotomy with plate fixation.[
1]
Zygomatic fractures that are asymptomatic and with no or minimal displacement are often treated with observation. However, fractures with displacement or with functional or cosmetic impairments, including diplopia, extraocular muscle entrapment, malocclusion, and/or trismus, often require surgical intervention.[
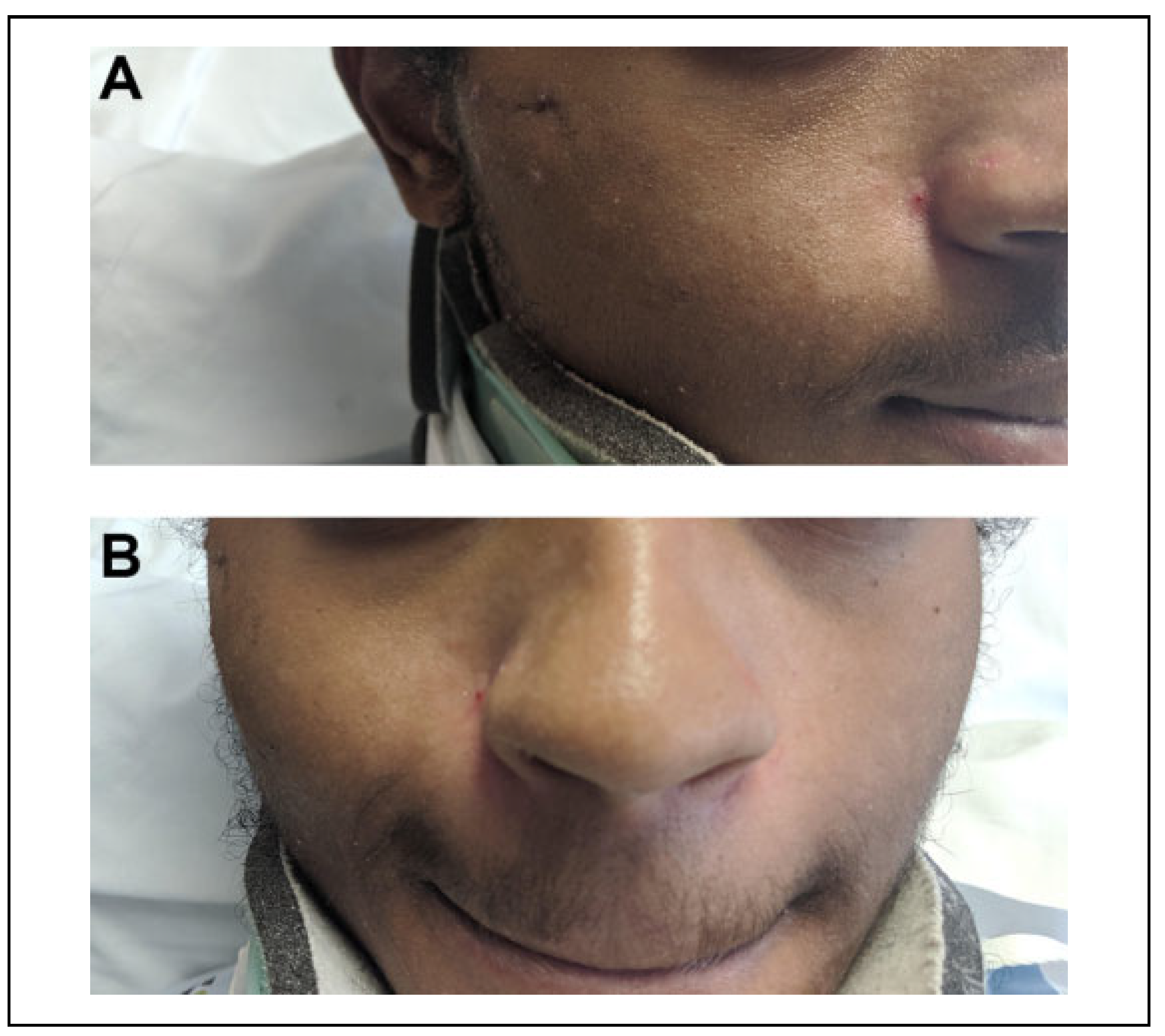
10] In our series, patients undergoing surgical repair frequently had cosmetic deformity, paresthesia in the V2 distribution, and/or trismus. These findings markedly improved after surgical intervention regardless of approach and surgical team.
Different techniques have been described to reduce zygomatic arch fractures. Of these, the Gillies approach is used most often. The Gillies approach involves a temporal hairline incision, placing an elevator superficial to the surface of the temporalis muscle under the deep temporal fascia and sliding the elevator under the arch to lift it into reduction.[
7] The Gillies approach is often favored because it is easy to perform, results in no obvious scar, and involves a low possibility of facial nerve damage or direct trauma to the globe.[
5] The Keen approach has also been described; it is an older technique that involves an intraoral approach to the zygomatic arch.[
11] In one study surveying members of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons and the American Society of Maxillofacial Surgeons, the preferred method of repair was via the Gillies approach (40%), followed by the Keen approach (33%), coronal incision (18%), and direct overlying incision (1%). Sixty-eight percent of respondents did not use any means of fixation following reduction. Of the 27% of surgeons who performed fixation, 12% used plate fixation, 12% used external splinting, and 3% used Kirschner-wire fixation.[
1]
For the most part, surgical repair results in favorable outcomes.[
4] Patient-reported functional, aesthetic, and overall satisfaction after zygomatic arch repair has been reported to be 87% to 96%.[
1] Bezuhly et al demonstrated that a Gillies approach combined with percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation provides restoration of facial contour that is not significantly different from that of open reduction and internal fixation, with less soft-tissue morbidity. Therefore, this technique should be considered in isolated zygomatic fractures. In this series, only 1 patient noticed slight malar asymmetry. Two patients reported slightly decreased but insignificant infraorbital sensation following surgery/injury.[
4] However, in another series, 37% of patients had contour irregularities following treatment.[
1] In our series, patients were successfully managed by the Gillies approach with external fixation and showed improvements in zygomatic deformity, paresthesias, and trismus. However, this improvement was not significantly different from that from the Keen approach without external fixation employed by our PRS and OMFS colleagues.
After reduction of the zygomatic arch, more than 90% of the fractures are stable enough to not require fixation measure. This is in part due to the splinting effect provided by the masseter muscle and the temporalis fascia.[
12] However, stabilization of the fracture by means of fixation is sometimes required. Various methods of internal and external fixation methods have been described in the literature. The internal fixation and stabilization methods are often more invasive and include direct wiring with a Kirschner wire, stabilization with a Foley catheter, Penrose drain or silicone nasogastric tube, and mini-plate fixation.[
4,
8,
10] Various methods of external fixation have also been documented in the literature. The majority of these methods include some form of external stabilizing material, via an orthopedic aluminum finger splint,[
9,
13,
14] steel eye shield,[
1] aquasplint,[
8] acrylic bow,[
15] polyurethane foam,[
12] or plastic endotracheal tubing.[
16]
In 1980, Zaworski was the first to introduce external fixation using an aluminum orthopedic splint.[
13] Shortly after, Ash and Mercuri further described this technique using a tapered needle with an attached steel wire suture which is passed transcutaneously around the fractured segment. Fixation is then obtained by ligation of the wire to a 1 × 5-cm
2 orthopedic finger splint that rests above the stable malar eminence anteriorly and above the stable por-tion of the zygomatic arch posteriorly. The splint was left in place for 3 weeks.[
14]
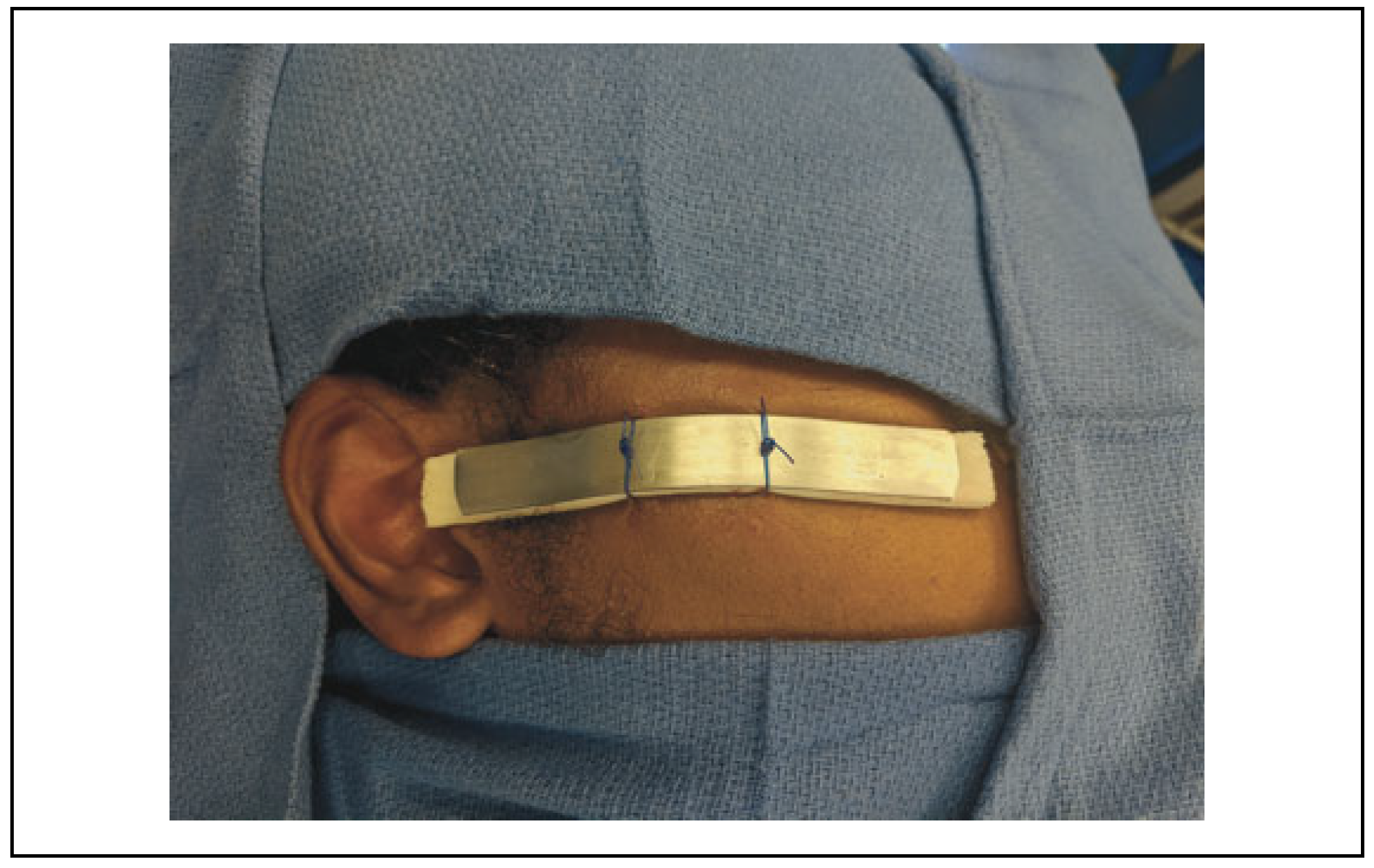
Goldsmith and Fry also described an external fixation technique using an aluminum finger splint.[
9] In this technique, two 2-0 nylon sutures are passed through the skin around the fracture zygomatic arch with a large, heavy curved needle. A finger is placed intraorally to facilitate accurate direction of the needle under the arch. The aluminum finger splint is then cut and molded to conform to the zygomatic arch, from just anterior to the tragus to the zygomaticomaxillary suture line. V-shaped notches are then cut in the splint to prevent slippage of the suture. The suture is then tied over the splint to achieve external fixation. The splint is kept in place for 1 to 2 weeks.
In our series, we have employed a similar but modified technique. Although it did not produce superior results, we feel it provides additional stabilization of the fracture site. External fixation with the orthopedic splint has shown to have several advantages including (a) that stabilization can be achieved without an added extraoral incision; (b) it provides rigidity without excessive bulk; (c) it is readily available material that is easily modified to a length that will enable it to rest over stable proximal and distal bone; (c) it can be easily contoured to follow the curvature of the lateral aspect of the patient’s face; (d) it has a cushion that, when applied to the skin surface, will reduce the possibility of postoperative necrosis; and(e) it will allow for adequate visualization of the skin so that infection or necrosis can be recognized.[
14]
Guven described an external fixation technique using an acrylic bow.[
15] In this technique, first a plaster model is prepared from the contralateral zygomatic arch to ensure symmetric reduction. A self-curing acrylic bow is then constructed on the model. Wires are then passed around the zygomatic arch and placed on retention sites twisted around the bow. Vaseline gauze is placed between the skin and the acrylic bow to prevent skin necrosis, and the bow is removed 3 weeks later.
Kim et al described a contouring technique using an aquasplint after fracture reduction. Suture points are marked, and 3-0 polydioxanone sutures are placed under the fractured zygomatic arch with a round-tip needle to avoid facial nerve injury. The sutures are then tied to the aquasplint, and the splint is removed after 2 weeks. In this series, external fixation was shown to significantly improve the cosmetic and functional result compared to no fixation.[
8]
Rodriguez-Vegas described an external fixation technique using a polyurethane foam dressing. In this technique, one or two 0-1 monofilament nonabsorbable sutures are passed around the fractured zygomatic arch with a 40-mm round-tip needle. A low-adherent dressing made from polyurethane is then applied between the punctured sites along the arch. A 1- to 1.5-cm-wide wet plaster cast is then placed over the foam dressing, and the sutures are tied down over the plaster and secured fixed once the plaster has dried. The device is kept in place for 1 to 2 weeks.[
12]
Hindin et al described an external fixation technique using a steel eye shield. In this technique, number 7 cardiac steel wires are passed through the skin around each of the zygomatic arch fracture segments with a large needle. The wires were then passed through a steel eye shield and secured down. The shield was removed 2 to 3 weeks later. In this series, external fixation was shown to significantly improve postoperative interincisor opening distance and malar symmetry compared to other techniques. External fixation was also found to have the highest patient and physician-rated aesthetic score.[
1]
Jones described a technique using an endotracheal tube. In this technique, 2 stainless steel wires on large curved needles were passed under the zygomatic arch and secured over a short piece of 8.0 plastic endotracheal tubing. This was subsequently removed 2 weeks later with a favorable result.[
16]
There are possible complications related to external fixation of zygomatic arch fractures. External splints can cause facial nerve palsy by pressure or injury associated with passing a large curved needle and suture around the arch.[
8] A false aneurysm of the facial artery can also occur from passing the needle.[
16] For those reasons, rounded-tip needles may be preferred. Suture abscess and hematoma have also been reported as complications of external fixation.[
1] Skin necrosis due to excessive pressure and infection are also theoretical complications.[
14,
15]